Malaysian Virgin Soil Extracts as Natural Growth Enhancer for Targeted Green Microalgae Species
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
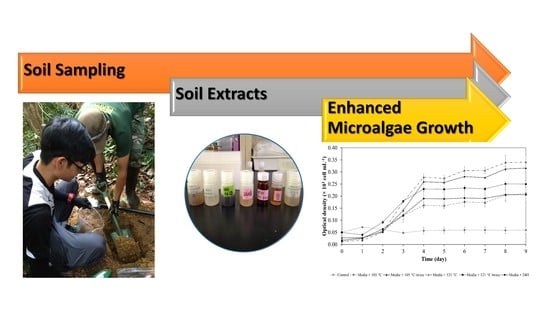
2.1. Collection of Sample and Preparation
2.2. Soil Extraction and Analyses
2.3. Microalgae
- (a)
- the mineral solution—100 g of NaNO3, 45 g of disodium EDTA (C6H16N2O8), 33.6 g of H3BO3, 20 g of NaH2PO4·4H2O, 1.3 g of FeCl3·6H2O, 0.36 g of MnCl2·4H2O, and 1 mL trace metal solution in 1 L of ultrapure water;
- (b)
- the trace metal solution—0.21 g of ZnCl2, 0.2 g of CoCl3·6H2O, 0.09 g of (NH4)6MO7O2·4H2O, and 0.2 g of CuSO4·5H2O in 0.1 L of ultrapure water;
- (c)
- the vitamin solution—0.2 g of thiamine (B1) and cyanocobalamin (B12) in 0.1 L of ultrapure water;
- (d)
- the silicate solution—2 g of Na2SiO3 in 0.1 L of ultrapure water;
- (e)
- the nitrate solution—2 g of KNO in 0.1 L of ultrapure water.
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nutrient Recovery from Different Extraction Methods
3.2. Effects of Soil Extracts on the Growth of Microalgae
3.3. Evaluation of Specific Growth Rate (SGR, µ) and Division Rate (k) for Selected Microalgae in Modified Soil Extract Medium
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrera, A.; D’Imporzano, G.; Fernandez, F.G.A.; Adani, F. Sustainable production of microalgae in raceways: Nutrients and water management as key factors influencing environmental impacts. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 287, 125005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cezare-Gomes, E.A.; del Carmen Mejia-da-Silva, L.; Pérez-Mora, L.S.; Matsudo, M.C.; Ferreira-Camargo, L.S.; Singh, A.K.; de Carvalho, J.C.M. Potential of microalgae carotenoids for industrial application. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 188, 602–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benemann, J.R.; Woertz, I.; Lundquist, T. Autotrophic microalgae biomass production: From niche markets to commodities. Ind. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, F.; Macedo, A.; Malcata, F. Potential industrial applications and commercialization of microalgae in the functional food and feed industries: A short review. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Mar Morales-Amaral, M.; Gómez-Serrano, C.; Acién, F.G.; Fernández-Sevilla, J.M.; Molina-Grima, E. Production of microalgae using centrate from anaerobic digestion as the nutrient source. Algal Res. 2015, 9, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Mujtaba, G.; Memon, S.A.; Lee, K.; Rashid, N. Exploring the potential of microalgae for new biotechnology applications and beyond: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 92, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Kujawska, N.; Talbierz, S. Microalgae cultivation technologies as an opportunity for bioenergetic system development—Advantages and limitations. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenpour, S.F.; Hennige, S.; Willoughby, N.; Adeloye, A.; Gutierrez, T. Integrating micro-algae into wastewater treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorupskaite, V.; Makareviciene, V.; Levisauskas, D. Optimization of mixotrophic cultivation of microalgae Chlorella sp. for biofuel production using response surface methodology. Algal Res. 2015, 7, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M.; Kisielewska, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Dudek, M.; Świca, I.; Rudnicka, A. The cultivation of lipid-rich microalgae biomass as anaerobic digestate valorization technology—A pilot-scale study. Processes 2020, 8, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Malik, S.; Zhu, H.; Xu, J.; Nawaz, M.Z.; Nawaz, S.; Alam, M.A.; Mehmood, M.A. Cultivating microalgae in wastewater for biomass production, pollutant removal, and atmospheric carbon mitigation; a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debowski, M.; Kisielewska, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Rudnicka, A. The effects of Microalgae Biomass Co-Substrate on Biogas Production from the Common Agricultural Biogas Plants Feedstock. Energies 2020, 13, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Abdullah, N.; Koji, I.; Yuzir, A.; Mohamad, S.E. Potential of Microalgae in Bioremediation of Wastewater. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2021, 16, 413–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premaratne, M.; Nishshanka, G.K.S.H.; Liyanaarachchi, V.C.; Nimarshana, P.H.V.; Ariyadasa, T.U. Bioremediation of textile dye wastewater using microalgae: Current trends and future perspectives. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 3249–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.S.; Tan, W.G.; Munawaroh, H.S.H.; Gupta, V.K.; Ho, S.H.; Show, P.L. Multifaceted roles of microalgae in the application of wastewater biotreatment: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page-Dumroese, D.S. A Guide to Soil Sampling and Analysis on the National Forests of the Inland Northwest United States; (No. 326); US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Intermountain Research Station: Ogden, UT, USA, 1995.
- Anderson, B.H.; Magdoff, F.R. Autoclaving soil samples affects algal-available phosphorus. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 1958–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khatoon, H.; Banerjee, S.; Syakir Syahiran, M.; Mat Noordin, N.B.; Munafi Ambok Bolong, A.; Endut, A. Re-use of aquaculture wastewater in cultivating microalgae as live feed for aquaculture organisms. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 29295–29302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacob, N.S.; Ahmad, M.F.; Kawasaki, N.; Maniyam, M.N.; Abdullah, H.; Hashim, E.F.; Sjahrir, F.; Wan Mohd Zamri, W.M.I.; Komatsu, K.; Kuwahara, V.S. Kinetics Growth and Recovery of Valuable Nutrients from Selangor Peat Swamp and Pristine Forest Soils Using Different Extraction Methods as Potential Microalgae Growth Enhancers. Molecules 2021, 26, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sahoo, P.K.; Singhal, S.; Patel, A. Impact of various media and organic carbon sources on biofuel production potential from Chlorella spp. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohutskyi, P.; Liu, K.; Nasr, L.K.; Byers, N.; Rosenberg, J.N.; Oyler, G.A.; Betenbaugh, M.J.; Bouwer, E.J. Bioprospecting of microalgae for integrated biomass production and phytoremediation of unsterilized wastewater and anaerobic digestion centrate. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6139–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, A.; Michel, C.; Joulian, C.; Touzé, S.; Amalric, L.; Bataillard, P.; Morlay, C.; Battaglia-Brunet, F. Decrease of the level of extractable polychlorinated biphenyls in soil microcosms: Influence of granular activated carbon and inoculation by natural microbial consortia. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 105, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Feng, Y.L.; Chen, Y.J.; Tian, Y.H. Soil microbes alleviate allelopathy of invasive plants. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, P.; Xu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Tu, X.; Song, G.; Zuo, Y.; Bi, Y. Addition of humic acid accelerates the growth of Euglena pisciformis AEW501 and the accumulation of lipids. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, D.; Luo, Y.; Lai, C.; Huang, B.; Pan, X. Double-dose responses of Scenedesmus capricornus microalgae exposed to humic acid. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Gruau, G.; Dupas, R.; Petitjean, P.; Li, Q.; Pinay, G. Respective roles of Fe-oxyhydroxide dissolution, pH changes and sediment inputs in dissolved phosphorus release from wetland soils under anoxic conditions. Geoderma 2019, 338, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, M.; Fehmi, J.S.; Rasmussen, C.; Gallery, R.E. Soil amendments alter plant biomass and soil microbial activity in a semi-desert grassland. Plant Soil 2017, 419, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan Mohd Zamri, W.M.I.; Sjahrir, F.; Yaacob, N.S.; Dzulkafli, N.F.; Ahmad, M.F.; Abdullah, H.; Maniyam, M.N.; Hashim, E.F.; Kawasaki, N.; Komatsu, K.; et al. Assessment of Aqueous Extraction Methods on Extractable Organic Matter and Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic Fractions of Virgin Forest Soils. Molecules 2021, 26, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinweg, J.M.; Jagadamma, S.; Frerichs, J.; Mayes, M.A. Activation energy of extracellular enzymes in soils from different biomes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59943. [Google Scholar]
- Kamaruddin, M.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Ibrahim, N.; Zawawi, M.H. Resource recovery from municipal solid waste by mechanical heat treatment: An opportunity. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1835, 020031. [Google Scholar]
- Arumugam, K.; Ahmad, M.F.; Yaacob, N.S.; Ikram, W.M.; Maniyam, M.N.; Abdullah, H.; Katayama, T.; Komatsu, K.; Kuwahara, V.S. Enhancement of targeted microalgae species growth using aquaculture sludge extracts. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.; Atta, M.; Bukhari, A. Effect of soil extracts concentration on specific growth rate and lipid content of Chlorella vulgaris in bolds basal medium. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2014, 10, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglisi, I.; Barone, V.; Sidella, S.; Coppa, M.; Broccanello, C.; Gennari, M.; Baglieri, A. Biostimulant activity of humic-like substances from agro-industrial waste on Chlorella vulgaris and Scenedesmus quadricauda. Eur. J. Phycol. 2018, 53, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaguvatova, R.; Myasina, Y.; Zakharenko, V.; Gaysina, L. A simple method for the cultivation of algae Chlorella vulgaris Bejerinck. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 390, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Nan, F.; Feng, J.; Lv, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Xie, S. Effects of different environmental factors on the growth and bioactive substance accumulation of Porphyridium purpureum. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latiffi, N.A.A.; Mohamed, R.M.S.R.; Apandi, N.M.; Tajuddin, R.M. Preliminary assessment of growth rates on different concentration of microalgae Scenedesmus sp. in industrial meat food processing wastewater. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 103, 06010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teo, C.L.; Idris, A.; Akhtar, J. Effect of Soil Extract in Different Culture Medium for Marine Microalgae’s Biomass and Lipid Production in Biodiesel Production. J. Life Sci. Technol. 2016, 4, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammoud, N.; Mayhoub, H.; Allaan, T. The influence of illumination and soil extract concentration on growth rate and protein content of Cosmarium subtumidum microalgae. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2015, 3, 27–31. [Google Scholar]




| Microalgae | Wastewater Source | Biomass Production Productivity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microalgae | Dairy wastewater | 160 mgdm/L/d | [10] |
| Chlorella sorokiniana | Cooking cocoon | 85.7 mg/L/d | [11] |
| Chlorella pyrenoidosa | Olive-oil mill | 1.25 mg/L/d | [11] |
| Scenedesmus sp. | Meat market | 98.5 mg/L/d | [11] |
| Chlorella vulgaris | Textile wastewater | 3.08 × 10−3 g per cathode electrode area | [14] |
| Chlamydomonas sp. TRC-1 | Textile wastewater | 2.49 g/L on day 7 | [14] |
| Auxenochlorella protothecoides | Concentrated municipal wastewater | 0.193 g/L/d | [15] |
| Chlamydomonas mexicana | Piggery wastewater (filter sterilized) | 0.028 g/L/d | [15] |
| Extraction/Treatment Methods | Protocol | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Approach | Temperature | Extraction Time | |
| Natural extraction (24 h) | Natural extraction | Room temperature | 24 h |
| Autoclave 105 °C once | Autoclave | 105 °C | 1 h |
| Autoclave 121 °C once | Autoclave | 121 °C | 1 h |
| Autoclave 105 °C twice | Autoclave | 105 °C | 1 h autoclave followed by 30 min cooling period and another cycle of 1 h autoclave |
| Autoclave 121 °C twice | Autoclave | 121 °C | 1 h autoclave followed by 30 min cooling period and another cycle of 1 h autoclave |
| Treatment Methods | DOC (mg/L) | TDN (mg/L) | TDP (mg/L) | C:N:P Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural extraction (24 h) | 58.67 | 5.07 | 0.08 | 73.3:6.3:0.1 |
| Autoclave 105 °C once | 135.30 | 10.30 | 0.12 | 123.0:10.8:0.1 |
| Autoclave 105 °C twice | 161.80 | 10.60 | 0.12 | 161.8:10.6:0.1 |
| Autoclave 121 °C once | 229.60 | 13.40 | 0.14 | 164.0:9.6:0.1 |
| Autoclave 121 °C twice | 336.56 | 13.40 | 0.14 | 240.4:9.5:0.1 |
| Modified Soil Extract Medium | Specific Growth Rate (SGR), μ (d−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nannochloropsis ocenica | Nannochloropsis oculata | Chlorella sorokiniana | |
| Control medium | 0.032 c ± 0.001 | 0.020 e ± 0.001 | 0.038 e ± 0.001 |
| Medium + 105 °C once | 0.038 c ± 0.005 | 0.071 d ± 0.001 | 0.067 c ± 0.002 |
| Medium + 105 °C twice | 0.059 b ± 0.003 | 0.105 b ± 0.001 | 0.073 b ± 0.002 |
| Medium + 121 °C once | 0.069 a ± 0.003 | 0.069 d ± 0.003 | 0.080 a ± 0.001 |
| Medium + 121 °C twice | 0.032 c ± 0.005 | 0.087 c ± 0.007 | 0.076 b ± 0.004 |
| Medium + 24 h | 0.037 c ± 0.003 | 0.114 a ± 0.007 | 0.048 d ± 0.005 |
| Modified Soil Extract Medium | The Division Rate (k) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nannochloropsis ocenica | Nannochloropsis oculata | Chlorella sorokiniana | |
| Control medium | 0.046 d ± 0.001 | 0.029 e ± 0.001 | 0.005 e ± 0.001 |
| Medium + 105 °C once | 0.054 c ± 0.005 | 0.103 d ± 0.001 | 0.096 c ± 0.002 |
| Medium + 105 °C twice | 0.085 b ± 0.003 | 0.152 b ± 0.001 | 0.105 b ± 0.002 |
| Medium + 121 °C once | 0.099 a ± 0.003 | 0.099 d ± 0.003 | 0.116 a ± 0.001 |
| Medium + 121 °C twice | 0.046 d ± 0.005 | 0.126 c ± 0.007 | 0.109 b ± 0.004 |
| Medium + 24 h | 0.053 c ± 0.003 | 0.165 a ± 0.007 | 0.068 d ± 0.005 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nallapan Maniyam, M.; Abdullah, H.; Ahmad, M.F.; Hashim, E.F.; Sjahrir, F.; Komatsu, K.; Kuwahara, V.S.; Yaacob, N.S. Malaysian Virgin Soil Extracts as Natural Growth Enhancer for Targeted Green Microalgae Species. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12084060
Nallapan Maniyam M, Abdullah H, Ahmad MF, Hashim EF, Sjahrir F, Komatsu K, Kuwahara VS, Yaacob NS. Malaysian Virgin Soil Extracts as Natural Growth Enhancer for Targeted Green Microalgae Species. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(8):4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12084060
Chicago/Turabian StyleNallapan Maniyam, Maegala, Hasdianty Abdullah, Mohd Fadzli Ahmad, Emi Fazlina Hashim, Fridelina Sjahrir, Kazuhiro Komatsu, Victor S. Kuwahara, and Nor Suhaila Yaacob. 2022. "Malaysian Virgin Soil Extracts as Natural Growth Enhancer for Targeted Green Microalgae Species" Applied Sciences 12, no. 8: 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12084060
APA StyleNallapan Maniyam, M., Abdullah, H., Ahmad, M. F., Hashim, E. F., Sjahrir, F., Komatsu, K., Kuwahara, V. S., & Yaacob, N. S. (2022). Malaysian Virgin Soil Extracts as Natural Growth Enhancer for Targeted Green Microalgae Species. Applied Sciences, 12(8), 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12084060