Safety and Energy Implications of Setback Control in Operating Rooms during Unoccupied Periods
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- Maintaining the required positive pressure. It is necessary to control both the supply and return airflow (many old systems do not include the latter).
- -
- Maintaining an appropriate ventilation rate to remove contaminants from cleaning activities.
- -
- The control of unoccupied periods through occupancy sensors, timers, light switches, etc.
- -
- Rapid transition from unoccupied periods to occupied operations while maintaining the indoor set temperature and humidity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Study
- Preheating and heating coils: work with hot water from natural gas boilers.
- Cooling coil: works with cold water from vapor compression, air-condensed chillers.
- Vapor injection unit: connected to the hospital’s steam distribution system.
- Supply and exhaust fans, dampers, and filters.
2.2. Tests Performed
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
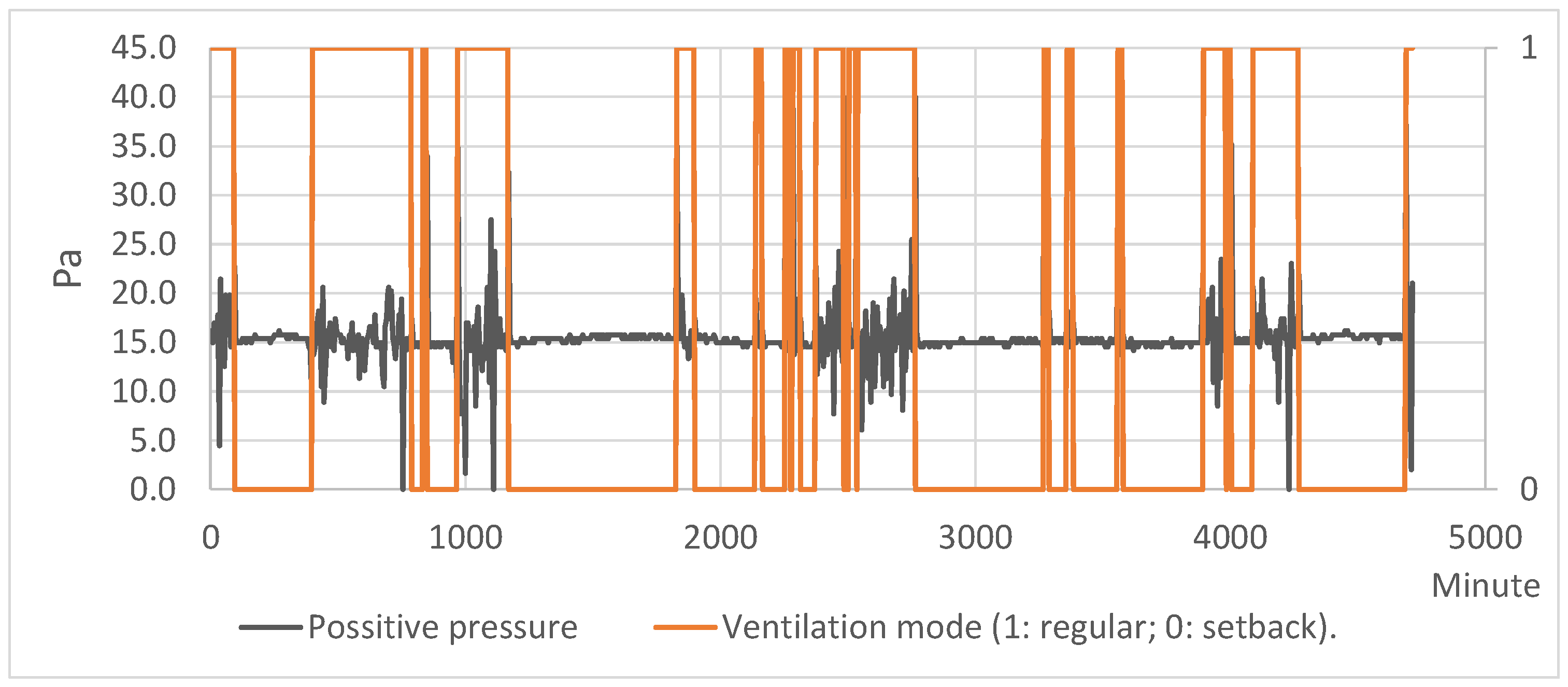
3.1. Pressure Relationships
3.2. Energy and Emissions Savings
3.3. Annual Estimations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EPTA. Guidelines for energy efficiency in hospitals. EMAS Inf. Technol. Hosp. 2007, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- ASHRAE. Chapter 9. Health care facilities. In ASHRAE Handbook—HVAC Applications; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Capolongo, S.; Settimo, G.; Gola, M.; Mele, A.; Tolino, B.; D’Alessandro, D.; Fara, G.M.; Bonadonna, L.; Briancesco, R.; Coccia, A.M.; et al. Indoor Air Quality in Healthcare Facilities; Capolongo, S., Settimo, G., Gola, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yau, Y.H.; Ng, W.K. A comparison study on energy savings and fungus growth control using heat recovery devices in a modern tropical operating theatre. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 1850–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejero-González, A.; DeFreitas-Barros-Galvão, V.M.; Zarzuelo-Sánchez, A.M.; SanJosé-Alonso, J.F. Energy use optimization in ventilation of operating rooms during inactivity periods. Build. Res. Inf. 2021, 49, 308–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Sanz-Calcedo, J.; Al-Kassir, A.; Yusaf, T. Economic and environmental impact of energy saving in healthcare buildings. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Short, C.A.; Al-Maiyah, S. Design strategy for low-energy ventilation and cooling of hospitals. Build. Res. Inf. 2009, 37, 264–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanish Standard UNE 100713:2005 Instalaciones de Acondicionamiento de Aire en Hospitales. 2015. Available online: https://www.une.org/encuentra-tu-norma/busca-tu-norma/norma/?c=N0034264 (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- ANSI/ASHRAE/ASHE Standard 170-2021; Ventilation of Health Care Facilities. ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2021; Volume 54.
- ASHRAE. HVAC Design Manual for Hospitals and Clinics, 2nd ed.; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gormley, T.; Markel, T.A.; Jones, H.; Greeley, D.; Ostojic, J.; Clarke, J.H.; Abkowitz, M.; Wagner, J. Cost-benefit analysis of different air change rates in an operating room environment. Am. J. Infect. Control 2017, 45, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, J.E.; Reynolds, G.L.; Montag, G.M.; Braymen, D.T.; Rasmussen, R.W. Ventilation requirements in hospital operating rooms—Part II: Energy and economic implications. ASHRAE Trans. 1986, 92, 427–449. [Google Scholar]
- Tschudi, W.; Faulkner, D.; Hebert, A. Energy Efficiency Strategies for Cleanrooms without Compromising Environmental conditions. ASHRAE Trans. 2005, 111, 476–484. [Google Scholar]
- Castro Ruiz, F.; San José-Alonso, J.F.; Villafruela Espina, J.M.; Guijarro Rubio, Á. Manual de Diseño de la Climatización y Ventilación de Quirófanos y Habitaciones en Centros Hospitalarios en Castilla y León; Mata Digital: Valladolid, Spain, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.J.; Chang, T.B.; Lai, C.M.; Liu, Z.Y. Performance improvement of airflow distribution and contamination control for an unoccupied operating room. Int. Build. Perform. Simul. Assoc. 2012. Available online: http://www.ibpsa.org/proceedings/asim2012/0130.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- Cacabelos-Reyes, A.; López-González, J.L.; González-Gil, A.; Febrero-Garrido, L.; Eguía-Oller, P.; Granada-Álvarez, E. Assessing the energy demand reduction in a surgical suite by optimizing the HVAC operation during off-use periods. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loomans, M.G.L.C.; Molenaar, P.C.A.; Kort, H.S.M.; Joosten, P.H.J. Energy demand reduction in pharmaceutical cleanrooms through optimization of ventilation. Energy Build. 2019, 202, 109346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porowski, M. Energy optimization of HVAC system from a holistic perspective: Operating theater application. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 182, 461–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Barroso Moreno, G.; García-Sanz Calcedo, J.; González, A.G.; Salgado, D.R. Sustainable solutions for thermal energy saving in hospital operating theatres. E3S Web Conf. 2019, 85, 01002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- John, D.A.; Faris, E.; Sipes, J.M.; Pich, D.; Holdaway, R.G.; Richardson, G.; Tosh, M.M. ASHRAE Design Guide for Air Terminal Units. Selection, Application, Control, and Commissioning; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Spanish Standard UNE 171340:2020 Validación y Cualificación de Salas de Ambiente Controlado en Hospitales. 2021. Available online: https://www.une.org/encuentra-tu-norma/busca-tu-norma/norma?c=N0064465 (accessed on 14 April 2022).
- Rey-Martínez, F.J.; SanJosé-Alonso, J.F.; Velasco-Gómez, E.; Tejero-González, A.; Esquivias, P.M.; Rey-Hernández, J.M. Energy consumption reduction of a chiller plant by adding evaporative pads to decrease condensation temperature. Energies 2020, 13, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASHRAE. Chapter 1: Psychrometrics. In ASHRAE Fundamentals; ASHRAE: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- IDAE. Factores de emisión de CO2 y coeficientes de paso a energía primaria de diferentes fuentes de energía final consumidas en el sector de edificios en España. In Documento reconocido del Reglamento de Instalaciones Térmicas en los Edificios (RITE); Government of Spain: Madrid, Spain, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C. Ventilation Performance in Operating Rooms: A Numerical Assessment. Ph.D. Thesis, KTH, School of Architecture and the Built Environment (ABE), Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
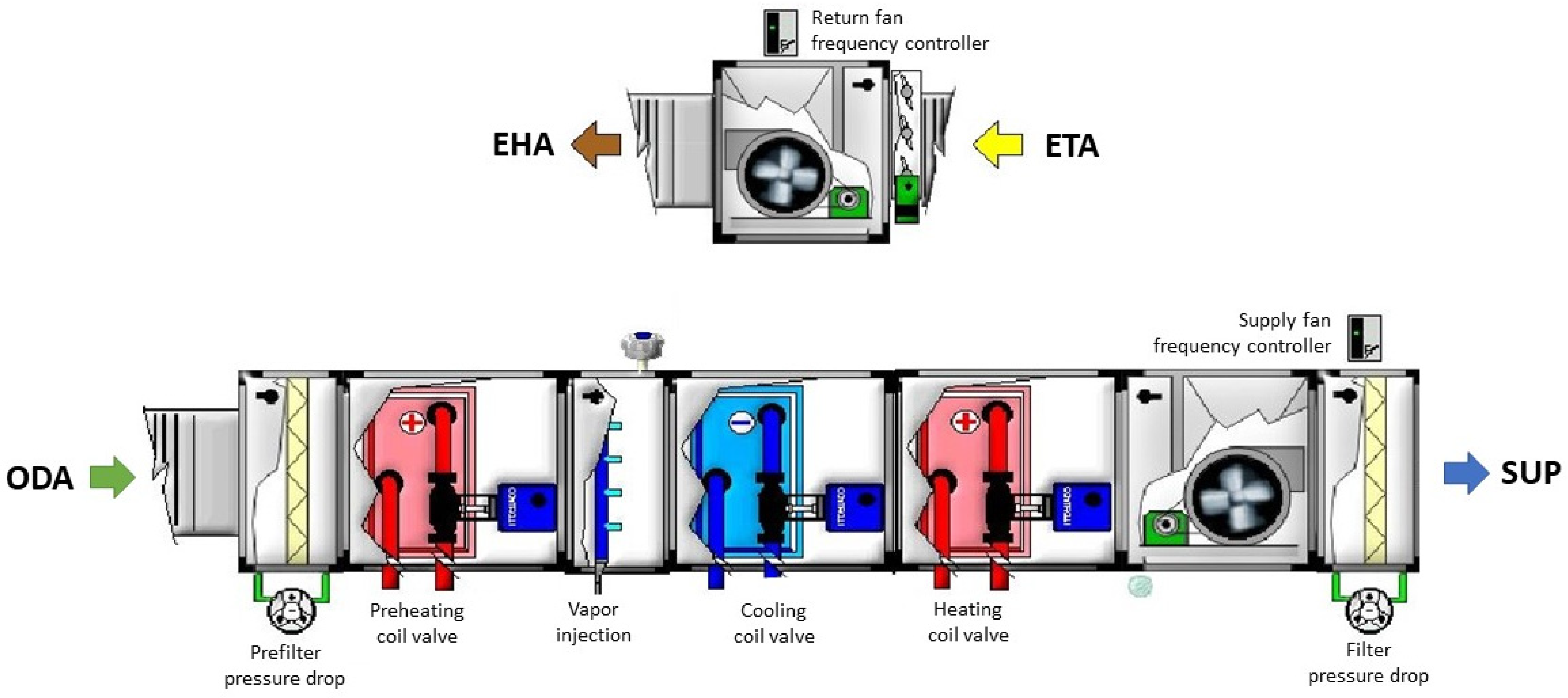
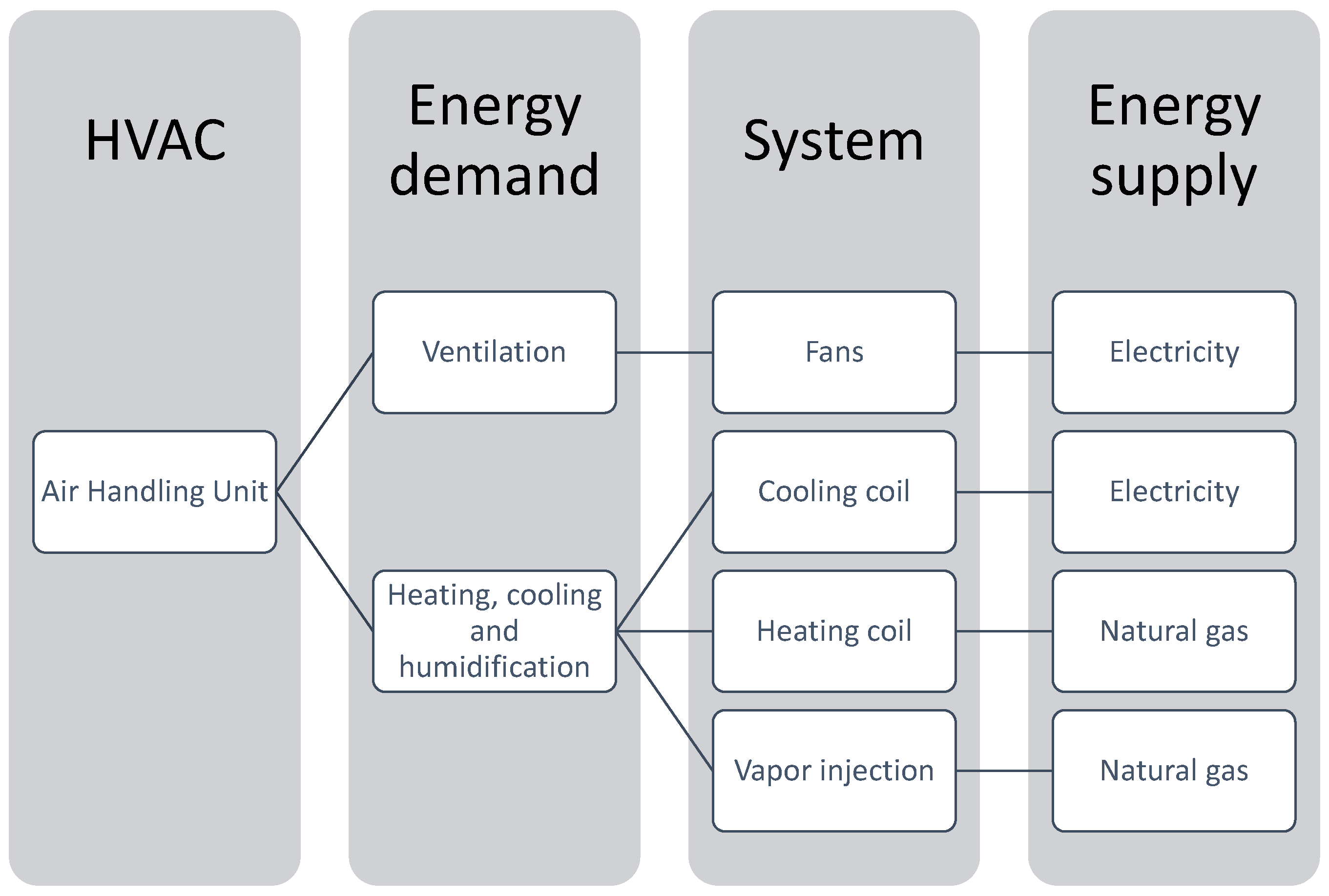
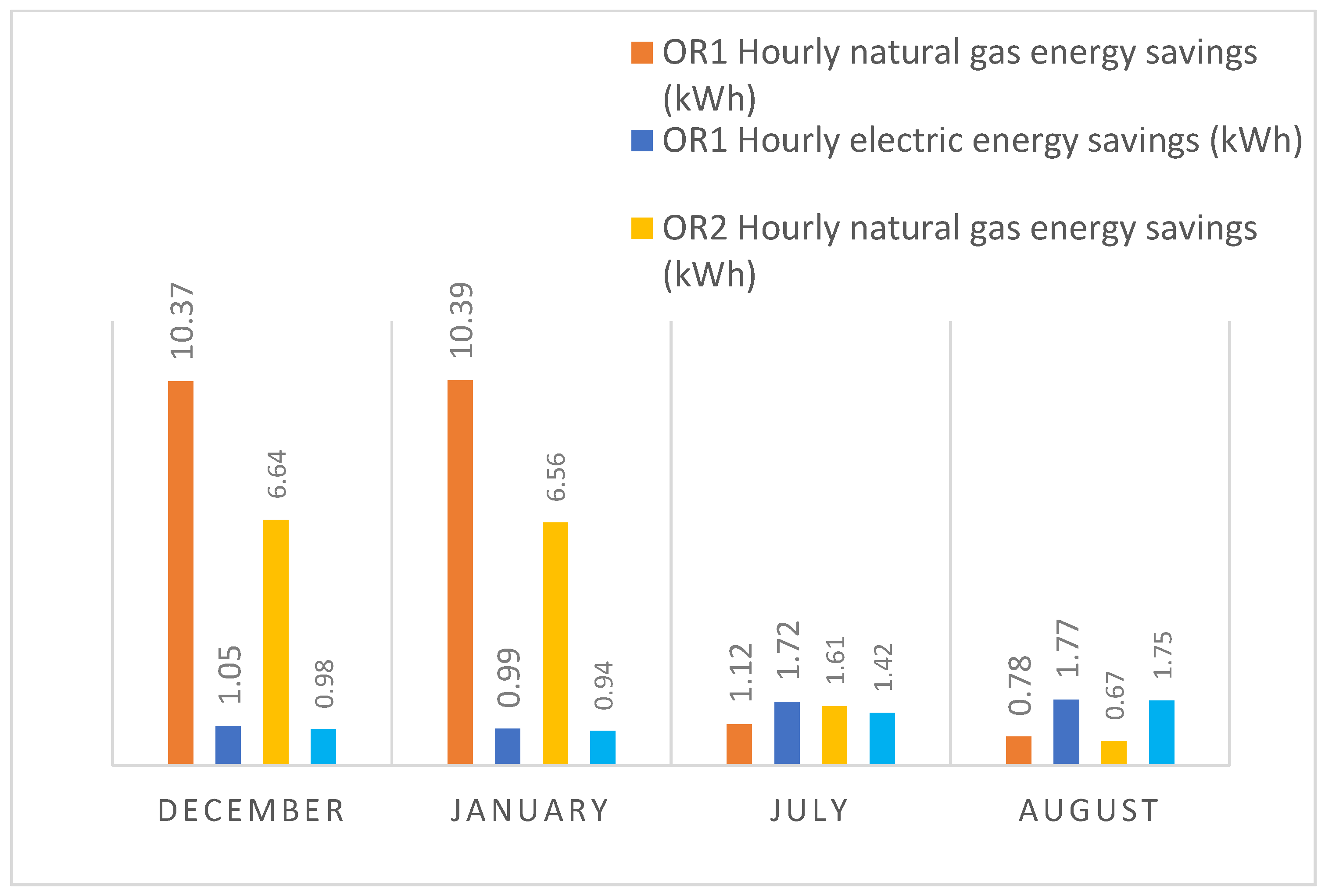
| Measured Conditions | Variables |
|---|---|
| AHU operating conditions | Supply fan frequency converter (Hz) Return fan frequency converter (Hz) Pre-heating coil valve (%) Humidifier (%) Cooling coil valve (%) Heating coil valve (%) |
| Indoor conditions | Dry Bulb Temperature (°C) Relative Humidity (%) Overpressure (Pa) |
| Supply conditions | Dry Bulb Temperature (°C) Relative Humidity (%) Volume airflow (m3/h) |
| Outdoor conditions | Dry Bulb Temperature (°C) Relative Humidity (%) |
| Controlled Variables | Set Value |
|---|---|
| Supply volume airflow | 2500 m3/h |
| Indoor overpressure | 15 Pa |
| Supply Dry Bulb Temperature | During occupation: 22.0 °C During non-occupation: 19.0 °C (winter), 25 °C (summer) Min. 14.0 °C Max. 28.0 °C |
| Supply Relative Humidity | Max. 60% |
| Indoor Relative Humidity | 35% |
| Test | Duration (hours) | Dates |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 78.7 | 7–10 December |
| 2 | 83.3 | 17–21 January |
| 3 | 13.6 | 7–8 April |
| 4 | 65.5 | 26–29 July |
| 5 | 83 | 15–19 August |
| Standard | OR Type/Ventilation Mode | Minimum Total Air (ach) 1 | Pressure Relationship to Adjacent Areas | Minimum Pressure Differential |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNE 171340:2020 (Spain) [21] | High risk ORs/ unidirectional airflows | 20 | 20 | 6 Pa |
| High risk ORs/ mixing ventilation | 20 | 15 | ||
| General | 15 | 10 | ||
| ANSI/ASHRAE/ASHE Standard 170-2021 (USA) [9] | All ORs/Unidirectional airflow | 20 | Positive | 2.5 Pa |
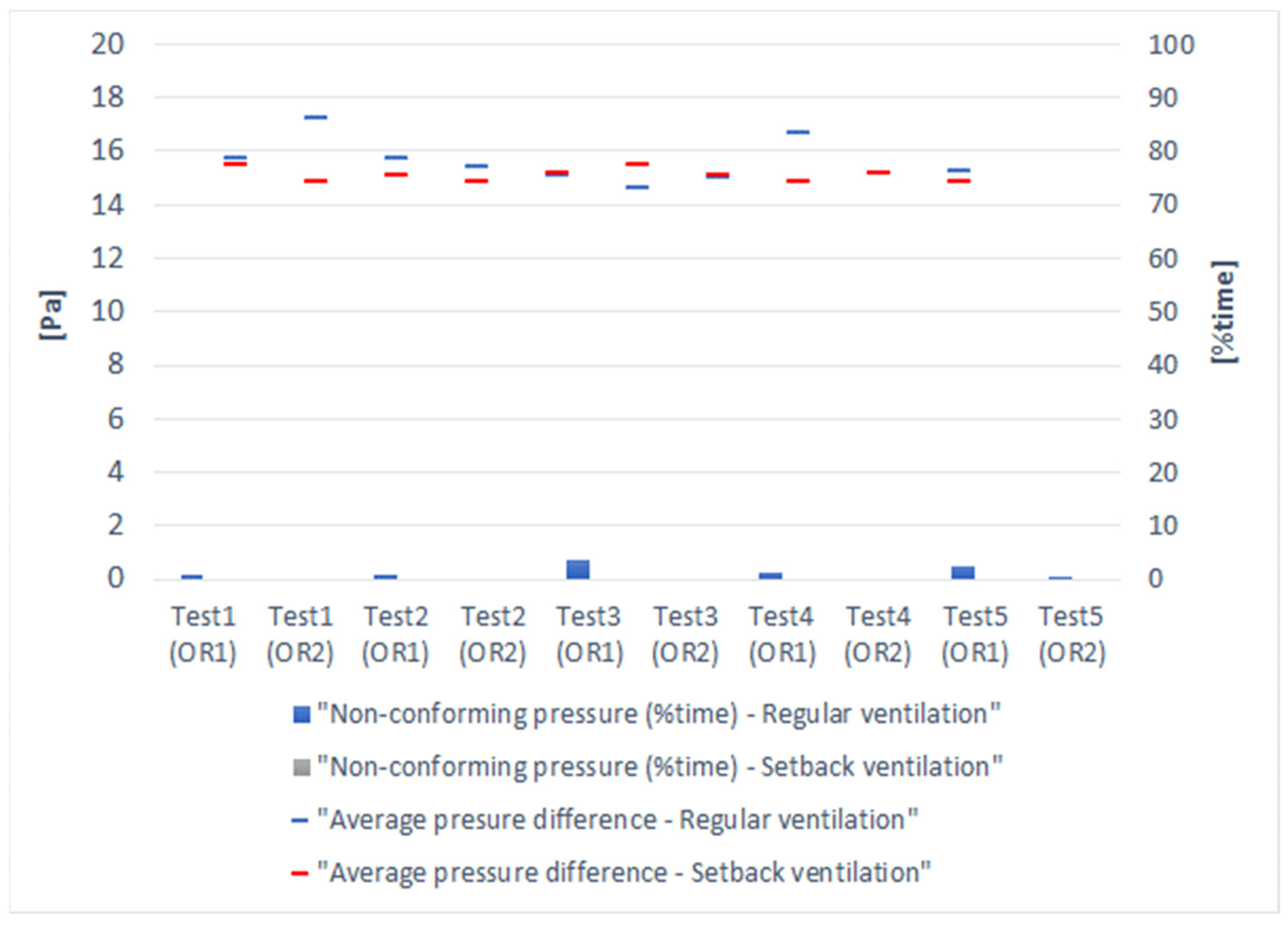
| Test | OR | Ventilation Mode | Total Time (h) | Average Pressure Difference (ΔP) | Average Values Nonconforming Pressure Differences 1 (Pa) | Minimum Values Nonconforming Pressure Differences 1 (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | OR1 | Regular | 26.5 | 15.7 | 1.4 | 0.0 |
| Setback | 52.2 | 15.5 | na | na | ||
| OR2 | Regular | 0.8 | 17.2 | na | na | |
| Setback | 77.9 | 14.9 | na | na | ||
| 2 | OR1 | Regular | 24.1 | 15.7 | 1.3 | 0.0 |
| Setback | 59.2 | 15.1 | na | na | ||
| OR2 | Regular | 8.7 | 15.4 | na | na | |
| Setback | 74.6 | 14.9 | na | na | ||
| 3 | OR1 | Regular | 13.6 | 15.1 | 1.7 | 0.0 |
| Setback | 0.0 | na | na | na | ||
| OR2 | Regular | 5.9 | 14.6 | na | na | |
| Setback | 7.2 | 15.4 | na | na | ||
| 4 | OR1 | Regular | 20.0 | 15.0 | 1.1 | 0.0 |
| Setback | 45.5 | 15.1 | na | na | ||
| OR2 | Regular | 4.5 | 16.7 | na | na | |
| Setback | 60.9 | 14.8 | na | na | ||
| 5 | OR1 | Regular | 40.7 | 15.2 | 1.3 | 0.0 |
| Setback | 42.3 | 15.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ||
| OR2 | Regular | 8.3 | 15.2 | 0.9 | 0.1 | |
| Setback | 74.7 | 14.8 | na | na |
| Test | OR | Setback Operation (%Time) | Natural Gas Energy Savings (kWh) | Fans Electric Energy Savings (kWh) | Total Electric Energy Savings (kWh) | Total Carbon Emissions (kgCO2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | OR1 | 66% | 541.0 | 54.9 | 54.9 | 149.1 |
| OR2 | 99% | 517.4 | 76.7 | 76.7 | 150.6 | |
| 2 | OR1 | 71% | 614.9 | 58.6 | 58.6 | 168.2 |
| OR2 | 90% | 489.3 | 70.1 | 70.1 | 141.6 | |
| 3 | OR1 | 0% | na | na | na | na |
| OR2 | 55% | 155.5 | 29.4 | 29.4 | 47.3 | |
| 4 | OR1 | 69% | 50.8 | 47.5 | 78.4 | 28.1 |
| OR2 | 93% | 97.9 | 60.5 | 86.5 | 43.7 | |
| 5 | OR1 | 51% | 32.9 | 41.6 | 75.0 | 21.7 |
| OR2 | 90% | 50.2 | 71.6 | 130.8 | 35.8 |
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (h) | 8 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 7 | 1 | 2 |
| Standard deviation (h) | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 1.9 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 2.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tejero-González, A.; López-Pérez, H.; Espí-García, F.; Navas-Gracia, L.M.; SanJosé-Alonso, J.F. Safety and Energy Implications of Setback Control in Operating Rooms during Unoccupied Periods. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094098
Tejero-González A, López-Pérez H, Espí-García F, Navas-Gracia LM, SanJosé-Alonso JF. Safety and Energy Implications of Setback Control in Operating Rooms during Unoccupied Periods. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(9):4098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094098
Chicago/Turabian StyleTejero-González, Ana, Héctor López-Pérez, Fernando Espí-García, Luis M. Navas-Gracia, and Julio F. SanJosé-Alonso. 2022. "Safety and Energy Implications of Setback Control in Operating Rooms during Unoccupied Periods" Applied Sciences 12, no. 9: 4098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094098
APA StyleTejero-González, A., López-Pérez, H., Espí-García, F., Navas-Gracia, L. M., & SanJosé-Alonso, J. F. (2022). Safety and Energy Implications of Setback Control in Operating Rooms during Unoccupied Periods. Applied Sciences, 12(9), 4098. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094098







