A Bidirectional LSTM-RNN and GRU Method to Exon Prediction Using Splice-Site Mapping
Abstract
:1. Introduction
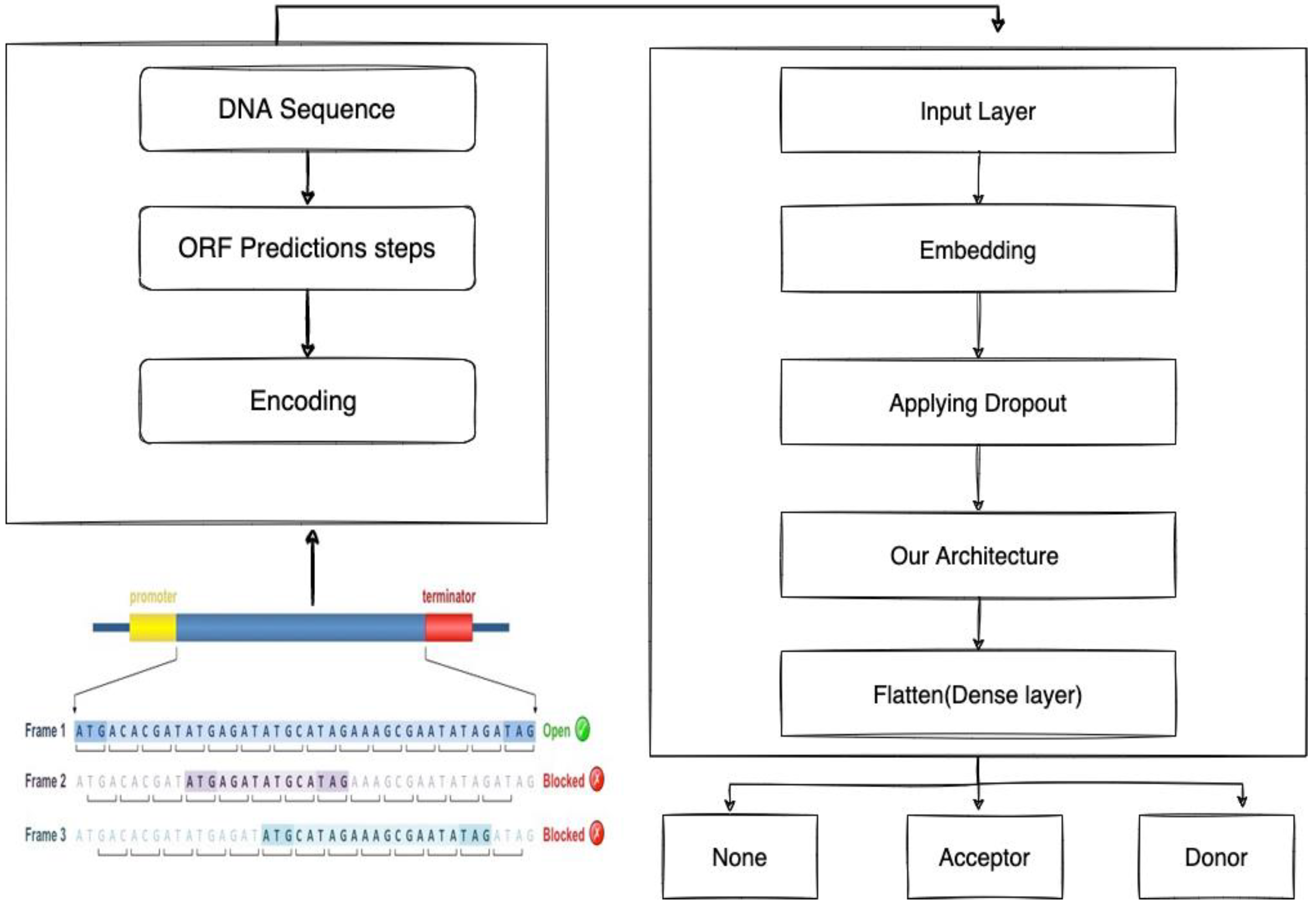
2. Methodology of Research
2.1. Data Acquisition and Training
2.1.1. Identifying the Donor and Acceptor of Splice Sites
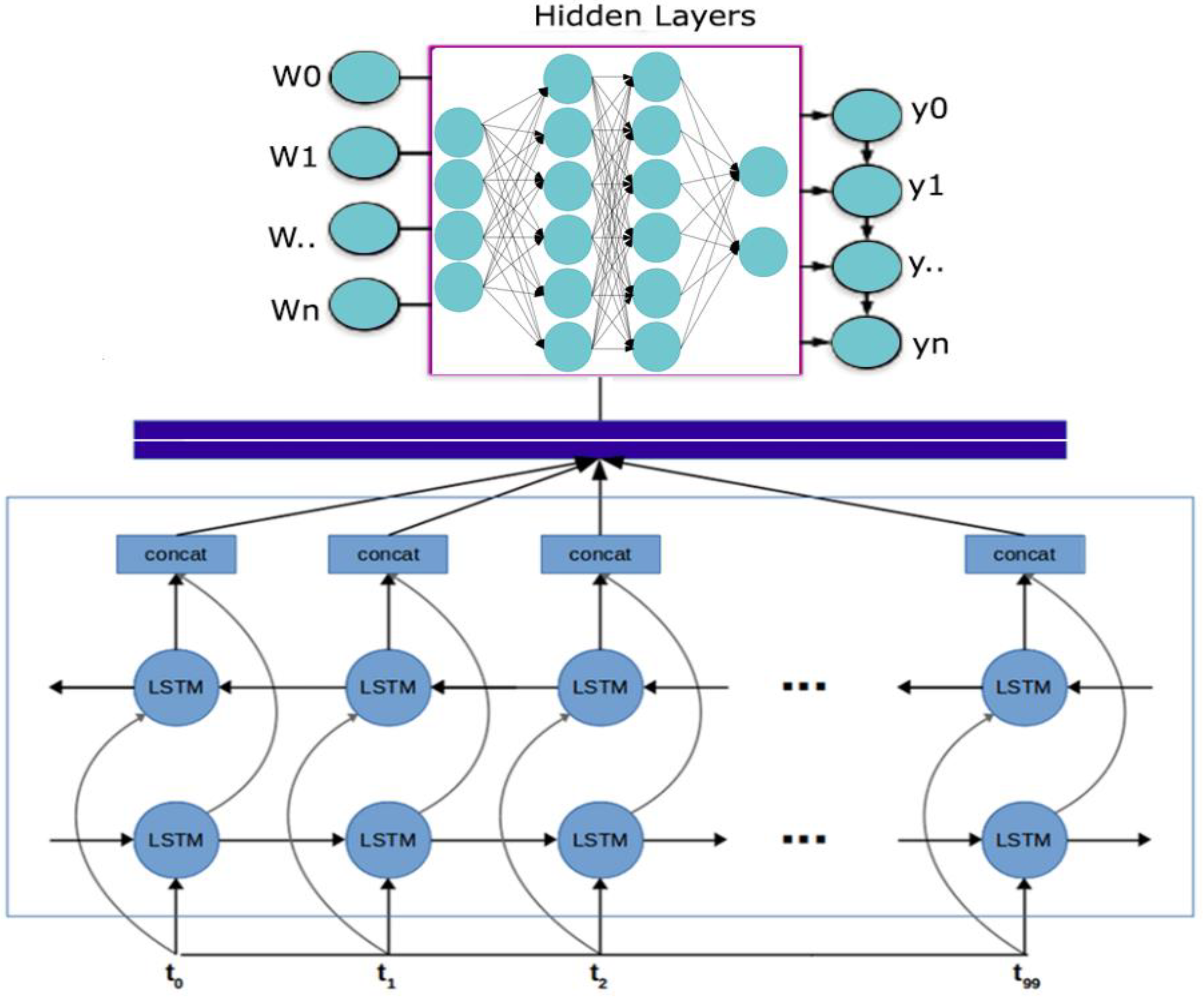
2.1.2. Bidirectional LSTM-RNN and GRU Model Preparation
3. Discussion and Results
3.1. Training for Bidirectional LSTM-RNN and GRU Model
3.2. Testing Results for the Bidirectional LSTM-RNN and GRU Model
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, A.; Chaudhry, M. Review and Analysis of Stock Market Data Prediction Using Data mining Techniques. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON), Mathura, India, 22–23 October 2021; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Bauchet, G.J.; Bett, K.E.; Cameron, C.T.; Campbell, J.D.; Cannon, E.K.; Cannon, S.B.; Carlson, J.W.; Chan, A.; Cleary, A.; Close, T.J.; et al. The future of legume genetic data resources: Challenges, opportunities, and priorities. Legum. Sci. 2019, 1, e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorrell, M.I.; Lineback, J.E. Using Shapes & Codes to Teach the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology: A Hands-On Inquiry-Based Activity. Am. Biol. Teach. 2019, 81, 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, A. Characterizing the hnRNP Q Complex and Its Activity in Asymmetric Neural Precursor Cell Divisions during Cerebral Cortex Development. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Guelph, Guelph, ON, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pudova, D.S.; Toymentseva, A.A.; Gogoleva, N.E.; Shagimardanova, E.I.; Mardanova, A.M.; Sharipova, M.R. Comparative Genome Analysis of Two Bacillus pumilus Strains Producing High Level of Extracellular Hydrolases. Genes 2022, 13, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertea, M.; Lin, X.; Salzberg, S.L. GeneSplicer: A new computational method for splice site prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ptok, J.; Müller, L.; Theiss, S.; Schaal, H. Context matters: Regulation of splice donor usage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 194391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Lee, C. Alternative splicing and RNA selection pressure—Evolutionary consequences for eukaryotic genomes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, W.M.; Tobin, K.; Ritchie, S. Chapter 5: Learn as You Build: Integrating Science in Innovative Design. Counterpoints 2001, 177, 135–172. [Google Scholar]
- Shoka, A.A.E.; Dessouky, M.M.; El-Sherbeny, A.S.; El-Sayed, A. Fast Seizure Detection from EEG Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 7th International Japan-Africa Conference on Electronics, Communications, and Computations, (JAC-ECC), Alexandria, Egypt, 15–16 December 2019; pp. 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Delalleau, O.; Roux, N. The curse of highly variable functions for local kernel machines. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2005, 18, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Katiyar, R.N.; Singh, D.B. Splice-Site Identification for Exon Prediction Using Bidirectional Lstm-Rnn Approach. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7285987/ (accessed on 21 April 2022).
- Choi, S.; Cho, N.; Kim, K.K. Non-canonical splice junction processing increases the diversity of RBFOX2 splicing isoforms. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2022, 144, 106172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-C.; Feng, J.-W. Development and Application of Artificial Neural Network. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2018, 102, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastri, B.J.; Tait, A.N.; de Lima, T.F.; Pernice, W.H.P.; Bhaskaran, H.; Wright, C.D.; Prucnal, P.R. Photonics for artificial intelligence and neuromorphic computing. Nat. Photon. 2021, 15, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Nath, R.; Singh, D.B. Prediction of Eukaryotic Exons using Bidirectional LSTM-RNN based Deep Learning Model. Int. J. 2021, 9, 275–278. [Google Scholar]
- Hapudeniya, M. Artificial Neural Networks in Bioinformatics. Sri Lanka J. Bio-Med. Inform. 2010, 1, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ostmeyer, J.; Cowell, L. Machine learning on sequential data using a recurrent weighted average. Neurocomputing 2018, 331, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldi, P.; Brunak, S. Bioinformatics: The Machine Learning Approach. In Bioinformatics: The Machine Learning Approach; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; p. 452. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, J.; Goomer, R.; Singh, A.K. Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Network (LSTM-RNN) Based Workload Forecasting Model for Cloud Datacenters. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 125, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsauer, H.; Schäfl, B.; Lehner, J.; Seidl, P.; Widrich, M.; Adler, T.; Gruber, L.; Holzleitner, M.; Pavlović, M.; Sandve, G.; et al. Hopfield networks is all you need. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.02217. [Google Scholar]
- Sulehria, H.K.; Zhang, Y. Hopfield Neural Networks: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 6th WSEAS International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Knowledge Engineering and Data Bases, Corfu Island, Greece, 16–19 February 2007; Volume 6, pp. 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bakrawy, L.M.; Cifci, M.A.; Kausar, S.; Hussain, S.; Islam, M.A.; Alatas, B.; Desuky, A.S. A Modified Ant Lion Optimization Method and Its Application for Instance Reduction Problem in Balanced and Imbalanced Data. Axioms 2022, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagheer, A.; Kotb, M. Unsupervised pre-training of a deep LSTM-based stacked autoencoder for multivariate time series forecasting problems. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kavitha, S.; Sanjana, N.; Yogajeeva, K.; Sathyavathi, S. Speech Emotion Recognition Using Different Activation Function. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advancements in Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computing and Automation (ICAECA), Kumaraguru College of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India, 8–9 October 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.; Schmidhuber, J. Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM and other neural network architectures. Neural Netw. 2005, 18, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkani-Tür, D.; Tür, G.; Celikyilmaz, A.; Chen, Y.N.; Gao, J.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.Y. Multi-domain joint semantic frame parsing using bi-directional rnn-lstm. In Proceedings of the 17th Annual Meeting of the International Speech Communication Association (INTERSPEECH), San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 September 2016; pp. 715–719. [Google Scholar]
- Cifci, M.A.; Aslan, Z. Deep learning algorithms for diagnosis of breast cancer with maximum likelihood estimation. In International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 486–502. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.; Lee, T.; Na, B.; Yoon, S. DNA-Level Splice Junction Prediction using Deep Recurrent Neural Networks. 2015. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/1512.05135 (accessed on 12 February 2022).
- Lee, T.; Yoon, S. Boosted Categorical Restricted Boltzmann Machine for Computational Prediction of Splice Junctions. 2015; pp. 2483–2492. Available online: http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/leeb15.html (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Augustauskas, R.; Lipnickas, A. Pixel-level Road Pavement Defects Segmentation Based on Various Loss Functions. In Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications (IDAACS), Cracow, Poland, 22–25 September 2021; Volume 1, pp. 292–300. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.-H.; Pyun, J.-Y. ECG Identification for Personal Authentication Using LSTM-Based Deep Recurrent Neural Networks. Sensors 2020, 20, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasser, M.; Salim, N.; Hamza, H.; Saeed, F.; Rabiu, I. Improved deep learning-based method for molecular similarity searching using stack of deep belief networks. Molecules 2020, 26, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, L.; Pittman, R.; Shen, X. LCD: A Fast-Contrastive Divergence Based algorithms for Restricted Boltzmann Machine. Neural Netw. 2018, 108, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Ke, R.; Pu, Z.; Wang, Y. Stacked bidirectional and unidirectional LSTM recurrent neural network for forecasting network-wide traffic state with missing values. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 118, 102674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xuan, Z.; Zhen, Z.; Li, K.; Wang, T.; Shi, M. A day-ahead P.V. power forecasting method based on LSTM-RNN model and time correlation modification under partial daily pattern prediction framework. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 212, 112766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khine, W.L.K.; Aung, N.T.T. Aspect Level Sentiment Analysis Using Bi-Directional LSTM Encoder with the Attention Mechanism. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Collective Intelligence, Da Nang, Vietnam, 30 November–3 December 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 279–292. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, B.; Kim, M.; Harerimana, G.; Kang, S.U.; Kim, J.W. Bi-LSTM model to increase accuracy in text classification: Combining Word2vec CNN and attention mechanism. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Chromosome No. | RefSeq (CBI) | No. of ORFs |
|---|---|---|
| I | NC_011601 | 91 |
| II | NC_011602 | 99 |
| III | NC_011603 | 97 |
| IV | NC_011604 | 93 |
| V | NC_011605 | 104 |
| VI | NC_011606 | 114 |
| VII | NC_011607 | 122 |
| VIII | NC_011608 | 98 |
| Layer | Output Shapes | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Embed (input_dim) | (None, 64, 64) | 400 |
| Dropout (0.25) | (None, 64, 64) | 0 |
| Batch Normalization | (None, 128) | 59,122 |
| Flatten layer | (None, 3) | 512 |
| Total Parameters Trainable Parameters Non-Trainable Parameters | 69,657 | |
| 69,647 | ||
| 10 |
| X/Y | Training (80%) | Testing (20%) |
|---|---|---|
| X_train | (88,814, 70) | (22,241, 70) |
| Y_train | (88,814, 3) | (22,241, 3) |
| Predicted | Genome Annotation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exons | Introns | Exons | Introns | |
| Number | 4618 | 681 | 4231 | 681 |
| Average Length | 1370 | 89 | 1716 | 89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
CANATALAY, P.J.; Ucan, O.N. A Bidirectional LSTM-RNN and GRU Method to Exon Prediction Using Splice-Site Mapping. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094390
CANATALAY PJ, Ucan ON. A Bidirectional LSTM-RNN and GRU Method to Exon Prediction Using Splice-Site Mapping. Applied Sciences. 2022; 12(9):4390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094390
Chicago/Turabian StyleCANATALAY, Peren Jerfi, and Osman Nuri Ucan. 2022. "A Bidirectional LSTM-RNN and GRU Method to Exon Prediction Using Splice-Site Mapping" Applied Sciences 12, no. 9: 4390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094390
APA StyleCANATALAY, P. J., & Ucan, O. N. (2022). A Bidirectional LSTM-RNN and GRU Method to Exon Prediction Using Splice-Site Mapping. Applied Sciences, 12(9), 4390. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12094390






