Abstract
Connected vehicles in vehicular networks will lead to a smart and autonomous transportation system. These vehicles have a large number of applications that require wireless connectivity by using cellular vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X). The infrastructure of C-V2X comprises multiple roadside units (RSUs) that provide direct connectivity with the on-road vehicles. Vehicular traffic applications are mainly categorized into three major groups such as emergency response traffic, traffic management and infotainment traffic. Vehicles have limited processing capabilities and are unable to process all tasks simultaneously. To process these offloaded tasks in a short time, fog servers are placed near the RSUs. However, it is sometimes not possible for the fog computing server to process all offloaded tasks. In this work, a utility function for the RSU to process these offloaded tasks is designed. In addition, a knapsack-based task scheduling algorithm is proposed to optimally process the offloaded tasks. The results show that the proposed scheme helps fog nodes to optimally scrutinize the high-priority offloaded tasks for task execution resulting in more than 98% of emergency tasks beingprocessed by fog computing nodes.
1. Introduction
The vehicular network is a vital component of future smart cities. Smart connectivity in vehicular networks helps in traffic management, increased safety, and better infotainment systems [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Efficient traffic management reduces traffic congestion, resulting in reduced carbon emissions thus improving atmospheric conditions in future smart cities with reduced accidents [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. In addition, route guidance applications, predictive maintenance of vehicles and infotainment services will benefit from vehicular networks [20,21,22,23,24].
Vehicular networks are comprised of vehicle’s built-in on-board units (OBU), geographical placement of roadside units (RSU) and city traffic command centres (TCC) [18,25]. Vehicles communicate through their wireless transceivers called OBUs, which are responsible for transmitting and receiving all types of vehicle information. In vehicle to vehicle (V2V), vehicles communicate with each other through their OBUs. RSUs are geographically located across roads in such a way that vehicles during their journey remain connected with one of the RSU located on the road. These RSUs are backward connected with the TCC through the Internet cloud for collecting and analyzing the traffic data and also providing infotainment services to the vehicles.
With the rapid growth of 5G wireless technology, the concept of autonomous vehicles has become a reality [26,27,28,29,30,31]. One of the key features of the 5G cellular vehicle-to-everything (C-V2X) standard is the reduced latency needed for the autonomous driving application. However, to cope up with these latency requirements, C-V2X has to propose some modifications in its medium access control and physical layers.
Vehicular communication relies on wireless technologies such as cellular communications, thus leading to intelligent transportation systems (ITS). ITS offers multiple smart services such as unmanned autonomous vehicle driving, online gaming, augmented and virtual reality. Most of these services require high computational capability and do not compromise delay. Moreover, an increase in high traffic applications along with simultaneous multiple tasking is expected from vehicles in the near future. To meet these challenges, the vehicles require high computational and battery sources. Though offloading high computational tasks and data traffic through the Internet cloud solves these challenges, computing at remote locations through centralized cloud-based Internet access may cause significant delays that are not acceptable in delay-sensitive applications of ITS.
To mitigate these delay-sensitive issues, computing servers are deployed on each RSU location and are connected with each RSU to behave as a fog node. These fog nodes have abundant caching and computational capability to perform vehicles tasks with cache and computing capabilities [32,33,34,35]. However, the fast speed with a limited coverage area provides shorter connectivity time for vehicles with RSUs and is a major constraint in task computation. Moreover, due to a large number of different varieties of tasks, a fog node cannot execute all tasks simultaneously. This causes a delay in the execution of some tasks that are not required for different applications and may badly affect the performance of the vehicular networks.
In this work, an efficient task execution by fog node () that gives task preference in accordance with time constraints is proposed . An algorithm along with a superframe structure is designed to fulfill these requirements. The salient features of the are given below:
- 1.
- Screen out those offloaded tasks that are about to leave the RSU coverage area. The screen-out tasks are forwarded to a cloud server for task execution.
- 2.
- A utility function is designed for the rest of the offloaded task requests according to task preferences and the remaining time of attachment with the RSU.
- 3.
- If task requests are more than the execution capacity of the fog node, tasks are optimally scrutinized according to their utility function by applying the 0/1 knapsack algorithm. The scrutinized tasks are executed at the fog node, and the rest of the tasks are forwarded to the cloud for processing.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 discusses fog computing and different research about task offloading schemes. The system model is discussed in Section 3 The proposed task execution policy is examined in Section 4. The performance of the proposed scheme is evaluated in Section 5, and Section 6 concludes the paper.
2. Related Works
The concept of fog computing is preferred over cloud computing due to nearby processing with reduced delay. That is why there are multiple research studies on the prospects of fog computing. In vehicular networks, the placement of a server adjacent to a RSU creates a fog node. The utility of fog computing is being heavily studied due to its high utilities in vehicular networks such as content caching and task processing.
An intelligent technique for task offloading to edge nodes by using a finite horizon Markov decision has been proposed for vehicular networks [36]. The main focus of this work determines the transition probabilities to offload the task to that edge node by considering driver behaviour, communication behaviour and road topology. The authors claim that their proposed task offloading scheme reduces delay significantly.
In [37], a double bipartite matching task offloading algorithm is proposed for high-speed vehicles that are categorized in three different states. In this work, vehicles offload tasks to their nearby edge node, and the edge node can further forward the offloaded task to the next edge node that is in the direction of vehicle movement. However, the authors have not considered the task processing capacity of the next edge node.
The authors in [38] proposed a task offloading scheme by optimizing the fog node selection. The authors execute the offloaded tasks through a load balancing technique by introducing fiber wireless technology in which all RSUs are backwardly connected through fiber with a software-defined network for information management and a centralized network. The software-defined networking node forwards the offloaded tasks to the edge node by applying the game theory. The authors in this work reduce the delay by applying offloading techniques that includes complex and costly fiber wireless technology. Moreover, the offloaded tasks are routed to a software-defined network through roadside units, causing unnecessary delay.
Chao et al., in [39] proposed a mobility aware task offloading scheme by considering the maximum allowed latency of an offloaded task along with the communication and computing capabilities of allocated fog node resources. The authors proposed a greedy scheme to assign tasks to other nearby vehicles in addition to a bipartite matching algorithm and claimed that their proposed scheme reduces the execution time of offloaded tasks. In [40], an adaptive learning task offloading algorithm was proposed for offloading task execution of vehicles. The algorithm is based on the multi armed bandit theory to minimize the offloaded task delay.
All the abovementioned task offloading schemes for vehicular networks are either based on vehicle to vehicle bases or offer different load balancing schemes on different criteria basis. However, no one has proposed an efficient task offloading scheme for fog node, and no one has discussed the processing capacity of fog computing nodes. In this work, an optimal task offloading scheme is proposed by considering the task processing capacity of fog computing nodes.
3. System Model
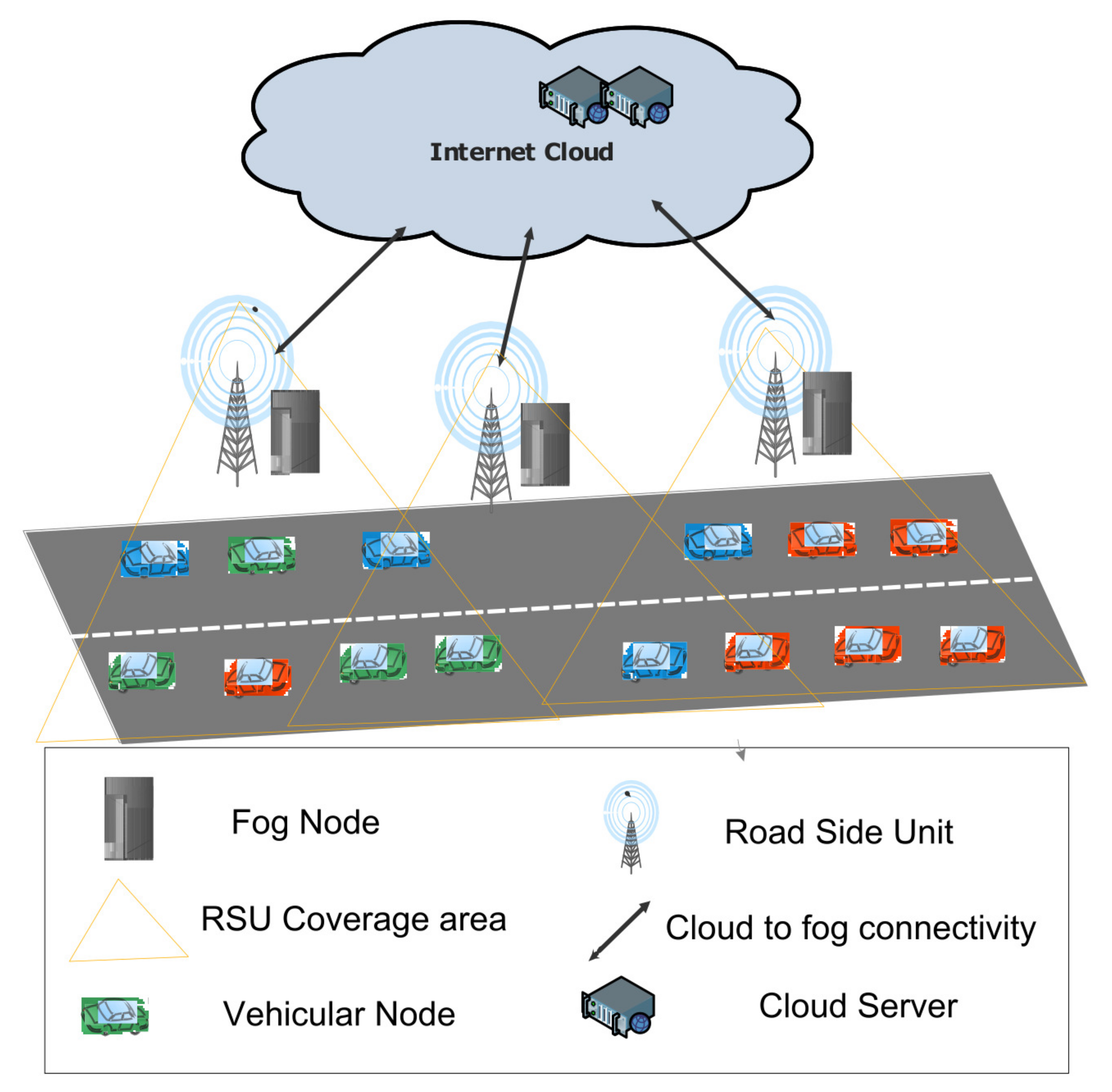
The system model used in this paper is shown in Figure 1. All vehicles are connected with RSUs by using V2I communication. These RSUs are placed on the roadside at different geographical areas to provide the coverage area of the complete highway. These RSUs are attached with servers for efficient computing to make them fog-computing nodes. These fog nodes are backwardly connected with the Internet cloud. Vehicles move with uniform velocity, and the expected time of attachment with each RSU is the same. Vehicles have one or more different types of tasks that are required to be executed. These tasks are mainly divided into three different types, such as emergency or safety tasks, traffic management tasks and infotainment tasks. The time sensitivity of execution of each type of task varies along with their task size. Vehicles want to offload these tasks for timely execution.

Figure 1.
System model.
In this work, we consider R RSUs, and each RSU is connected with V vehicles on the road. Each vehicle attached with a RSU has one to three tasks for execution. These tasks are categorized as , and and are prioritized from low to high priority level, respectively. T is the total number of tasks that are required to be executed and are calculated as:
The downloading data rate for a vehicle to download a task solution from a fog node is computed as:
where is the signal to noise ratio between the vehicle and the fog computing node.
The data rate for downloading executed tasks from a cloud node such as TCCC is calculated as:
where is the signal to noise ratio between a vehicle and a cloud node. We assume that there are multiple channels available in each fog node to transmit all executed tasks simultaneously without considering any queuing delay. We used the path loss propagation model along with Nakagami-m multipath fading [41] to find the RSU coverage range.
4. Proposed Task Execution Policy
This work proposes an efficient task execution policy for fog nodes () that executes those tasks that are offloaded by vehicles during their journey in vehicular networks. Fog nodes located near RSUs execute these offloaded tasks to minimize the task delay. A fog node has limited processing capability compared to cloud servers, and tasks beyond its capacity cannot be processed. In addition, there are different categories of tasks with varying delay constraints. It is therefore required that the fog node optimally scrutinize these offloaded tasks to execute in accordance with their task emergency. optimally scrutinizes offloaded tasks according to their sizes and priorities in the following way:
- A task selection policy is introduced by excluding offloaded tasks of those vehicles that are about to leave the fog node coverage area.
- A utility function of the fog node determines the priority for all offloaded tasks by all vehicles in the range of the RSU.
- An optimal selection of offloaded tasks to be executed by the fog node are determined by applying a 0/1 knapsack algorithm.
4.1. Task Selection Policy
A fog node in after regular intervals calculates the total number of received tasks and makes the decision whether to process these tasks on its own or forward them to the cloud server based on the following conditions:
- 1.
- If the vehicle’s remaining time of attachment with the RSU is less than its executed task downloaded time, then the task is forwarded to the cloud for task execution, and the cloud is supposed to download the task to a fog node placed at the vehicle’s next attached RSU.
- 2.
- If all the valid requested tasks are less than its task execution capacity, then it processes all tasks itself, and no task will be forwarded to the cloud server.
A complete task processing criteria is shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: Task processing Criteria |
 |
If requested tasks are more than the task execution capacity, then it optimally scrutinizes tasks to be performed at the fog node by applying 0/1 knapsack, and the rest of the tasks are forwarded to the cloud server. The value of 0/1 knapsack in the proposed scheme is derived from a utility function that is computed by the fog node for each offloaded task.
4.2. Fog Node Utility Function
The utility function is calculated to determine the value of each vehicle’s offloaded task. The utility function is based on the task priority and the remaining time of attachment of the vehicle with the requested fog node. The higher the priority of the tasks, the higher its utility value will be. Similarly, the smaller the time of attachment of the vehicle with the requested fog node, the higher its value will be. In case two vehicles offload the same priority tasks to the fog node, then the fog node prefers to execute those tasks that are going to leave this fog node earlier first.
The fog node computes a utility function for each task offloaded by vehicles by considering the task sensitivity and the vehicle’s remaining time of attachment with that fog node. Suppose there are two emergency tasks; then, priority should be given to the one that is about to leave the RSU.
For the ith vehicle offloaded task, the fog node calculates its utility function according to its task priority () and its remaining time of contact with the fog node. The utility function of ith vehicle () is calculated as:
where is calculated as:
where is the remaining distance of ith vehicles before leaving the fog node that can be determined from GPS, and is the speed of the vehicle.
The fog node in , after computing the utility function, applies, the 0/1 knapsack algorithm to optimally scrutinize the offloaded tasks for execution.
4.3. 0/1 Knapsack for Task Scheduling
Fog nodes have limited execution capacity, and if requested tasks are more than their capacity then they need to scrutinize delay-sensitive tasks.
Optimal scrutiny of different-sized task requests in the fixed data execution capacity of the fog node is solved by the 0/1 knapsack algorithm. The decision is based on the utility function of each offloaded task request as discussed in Section 4.2.
Suppose the task execution capacity of a fog node is C data/cycle, and there are different sizes of K task requests by V vehicular nodes. These K tasks are categorized into three types of tasks as infotainment, traffic management and emergency tasks and are prioritized from low, medium and high, respectively. If each of V vehicle attached with the RSU, sends one to three task requests to the fog node, then the knapsack optimization technique is applied with the following constraint:
- The requested offloaded tasks of V vehicles, with t requested tasks by each vehicle should be less than the task capacity C and is represented as:
- The scrutinized tasks are selected with maximum value such as utility.
The knapsack optimizes the scrutiny process by filling a knapsack table, and from this table, an optimal task with higher utility values is selected. A complete knapsack algorithm is shown in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2: Task Selection Criteria |
 |
5. Performance Evaluation
In this section, the performance of is evaluated in different prospects. The offloaded tasks are categorized in three levels of priority. Each vehicle attached with the fog node is randomly chosen to offload one to three tasks of different levels to its fog node as discussed in Section 3. The performance of is evaluated in different scenarios, and it is compared with the following three task offloading schemes:
- 1.
- Tasks of different vehicles are offloaded to a fog node for task computation. Offloaded tasks are processed by following the smallest task first (STF) algorithm. This allows the fog node to start executing tasks from the smallest tasks and keeps on executing the tasks to the task processing capacity of the fog node. The remaining tasks are forwarded to the cloud for computation and execution.
- 2.
- In the second scheme, a fog node executes tasks by following the longest task first (LTF) algorithm. Contrary to STF, LTF allows a fog node to start executing from the longest task execution and keeps on processing to the task processing capacity of the fog node. The remaining tasks are forwarded to the cloud for computation and execution.
- 3.
- The fog node processes offloaded tasks up to its processing capacity by applying first come first serve (FCFS) mechanism, and the rest of the tasks are forwarded to the cloud for processing and execution.
We developed a simulation environment to evaluate the performance of the proposed technique with two other schemes. The detailed simulation setup along with its different parameter values are described in Section 5.1 and results are discussed in Section 5.2.
5.1. Simulation Parameters and Performance Metrics
The performance of the proposed work was evaluated using simulations conducted in MATLAB. The model used for simulations was discussed in Section 3. In this simulation, task offloading with different task types was performed. These task sizes are ranged from 5 kB to 20 kB for sensitive tasks, 12 kB to 30 kB for traffic management tasks, and 20 kB to 50 kB for infotainment tasks. The coverage area of a fog node was taken as 200 m.
The data rate for the downlink between the fog node and the vehicle is 8 Mbps. However, the downloading data rate of a vehicle from a cloud server is 2 Mbps. A fog computing node has limited processing capability and can execute 500 kBytes of tasks simultaneously, However, the cloud has unlimited processing capacity.
A list of salient simulation parameters are shown in Table 1. In this work, a Monte-Carlo-based simulation was performed for fair comparative analysis of . The results are obtained as an average of iterations.

Table 1.
Simulation parameters.
5.2. Results and Discussion
In this subsection, the performance of our proposed is analyzed and compared with STF, LTF and task processing with FCFS. The comparative results are obtained to calculate the task processing time and number of tasks performed along with their percentages for all three varieties of tasks individually.
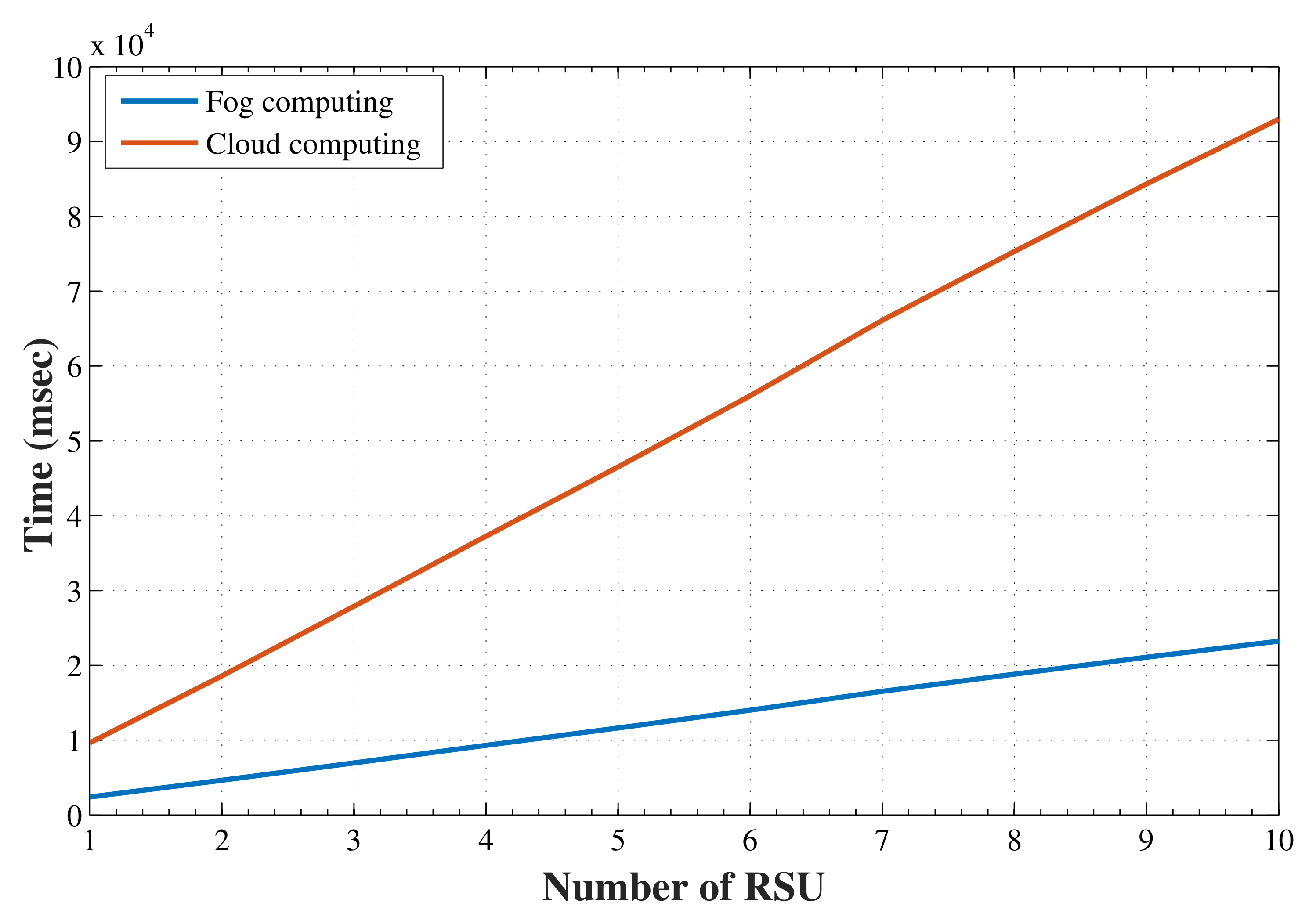
Fog-computing nodes are preferred over cloud-computing servers due to the close proximity of vehicles. Fog nodes provide better downloading data rates compared to cloud servers that are remotely placed and require Internet bandwidth to access. The tasks offloaded by vehicles are preferred to be executed by a fog node compared to the remotely placed cloud servers. Figure 2 shows a comparative analysis of task execution time between cloud servers and fog nodes. It is evident from the results that fog nodes compute the same tasks with considerably less time compared to the cloud servers.

Figure 2.
Task execution time in fog and cloud servers for varying number of RSUs.
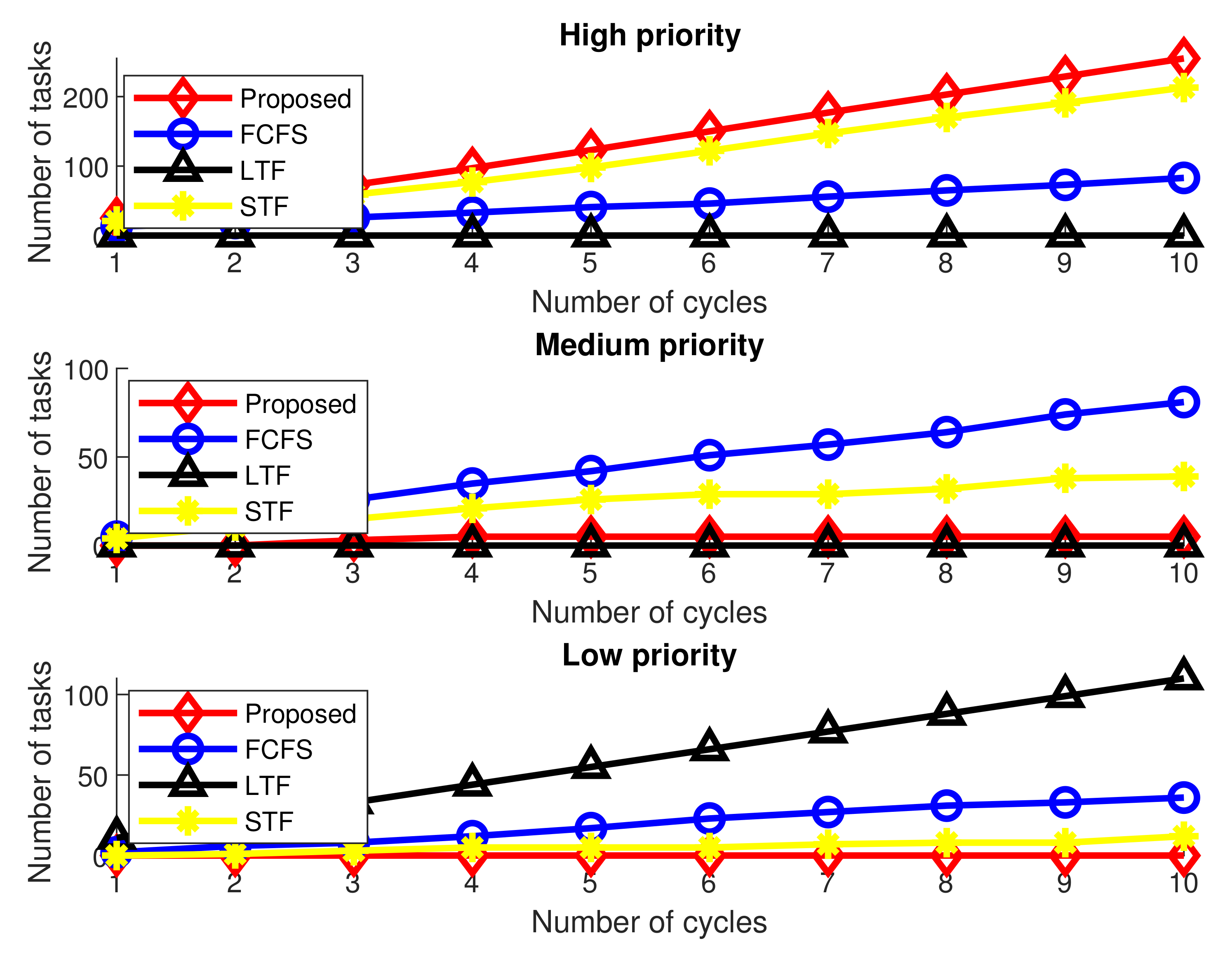
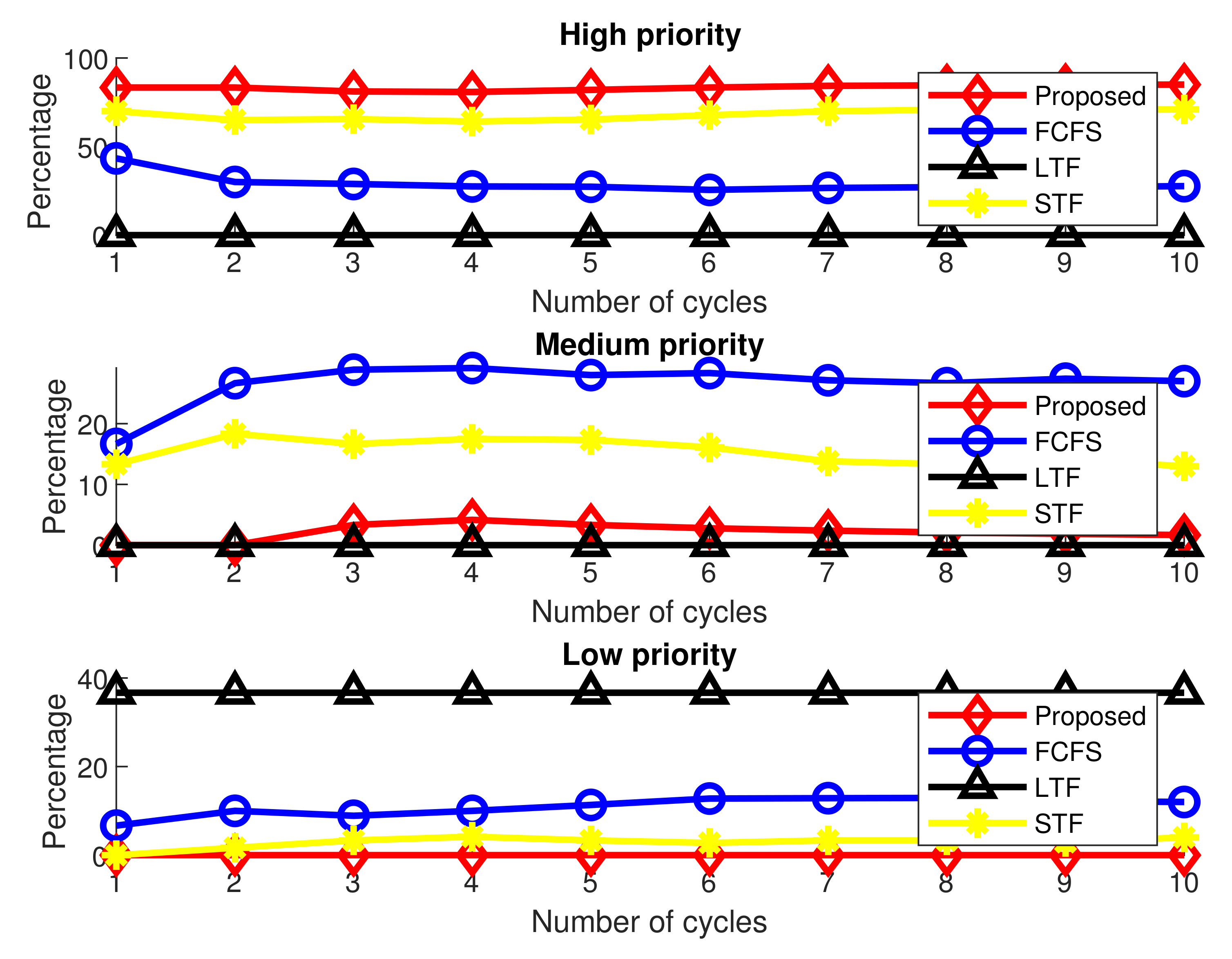
Figure 3 and Figure 4 show a comparative analysis of the number and percentages of tasks performed by fog-computing nodes for a fixed number of offloaded tasks in different processing cycles, respectively. There are 90 offloaded tasks in each processing cycle, 30 each for high, medium and low-priority tasks. Both figures are comprised of three subfigures for three types of offloaded tasks.

Figure 3.
Number of tasks performed by fog nodes in different processing cycles.

Figure 4.
Percentage of tasks performed by fog nodes in different processing cycles.
Figure 3 shows that for high-priority emergency tasks, allows fog computing nodes to compute a maximum number of tasks compared to the other three schemes. For moderate- and low-priority tasks, forwards almost all the tasks to the cloud for processing as it almost reaches the processing capacity of fog nodes. However, LTF has the lowest number of high-priority tasks among all schemes. This is due to the fact that the size of most of the low-priority tasks is larger compared to the other two priority types. On the other hand, STF also processes the majority of the high-priority tasks due to their smaller task sizes but less than the proposed scheme. However, FCFS allows the fog node to execute all three types of tasks according to their random arrival.
The results shown in Figure 4 represent the task processing percentages of these schemes for different priorities of tasks individually. The results show that executes about 84% of the high-priority tasks in all execution cycles. However, it only execute 3.5% of medium-priority tasks and none of the low-priority tasks is executed, whereas STF executes 70% of the high-priority tasks that is followed by FCFS and LTF. FCFS allows the fog node to process all three types of tasks, and LTF is top in processing most of the low-priority tasks, and executing 38% of these tasks.
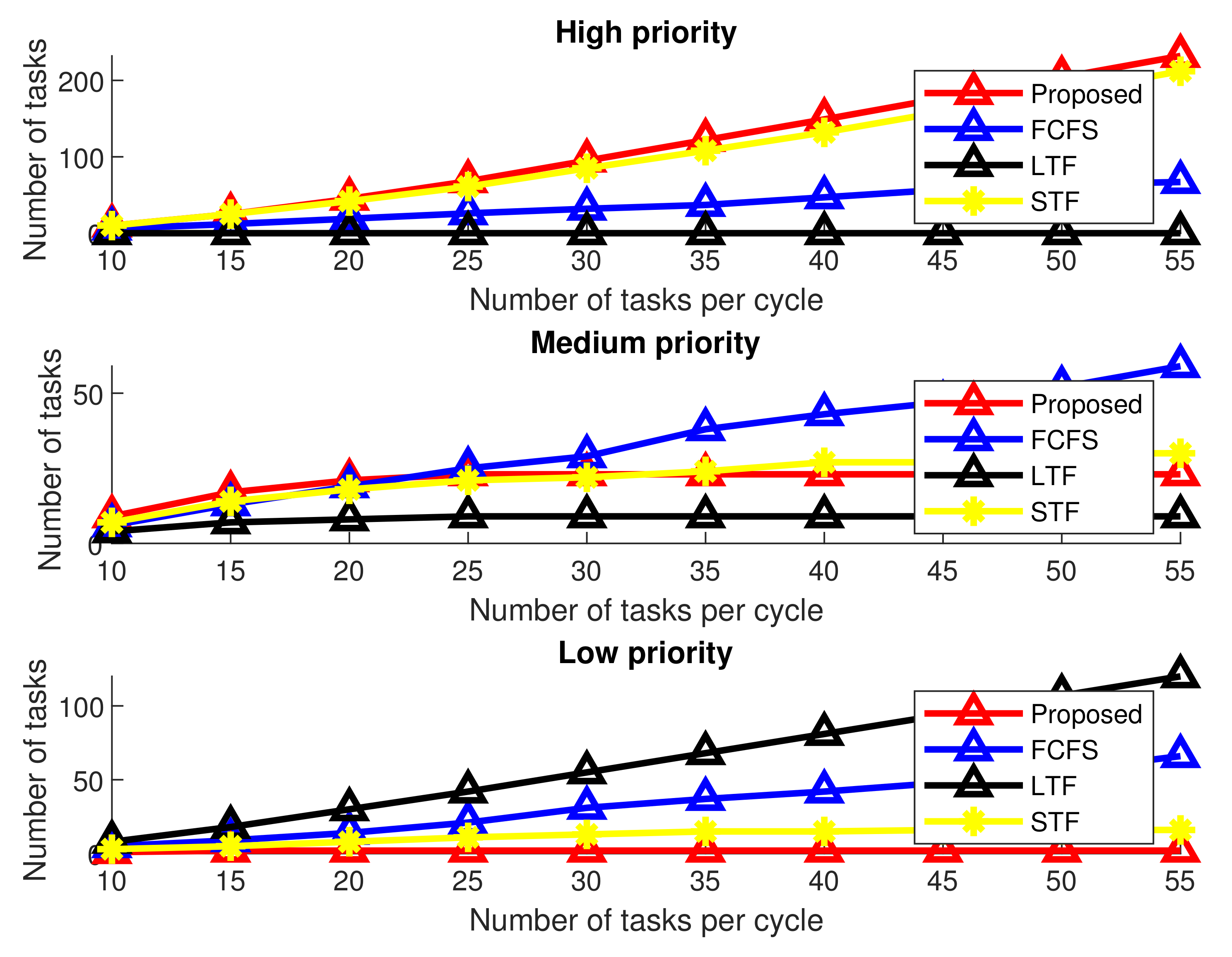
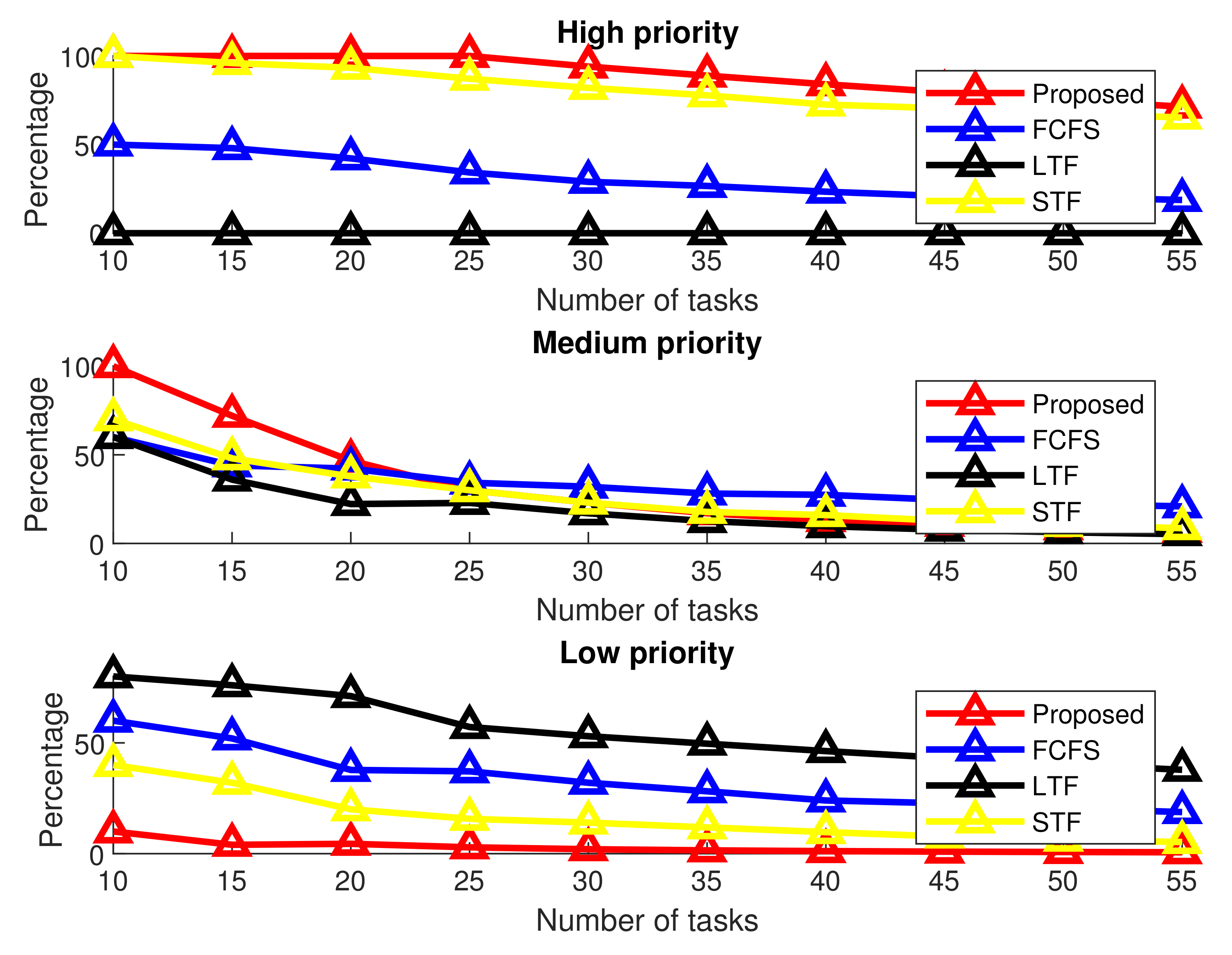
Figure 5 and Figure 6 show comparative performance analysis of with the other three schemes for a varying number of offloaded tasks and percentage of tasks performed by fog node in different processing times, respectively. All three different priorities of tasks are shown in subfigures separately. The number of tasks in each figure is incremented by five, and the processed tasks are accumulated by adding the current tasks to previously processed tasks.

Figure 5.
Number of tasks performed by fog nodes for varying number of tasks.

Figure 6.
Percentage of tasks performed by fog nodes for varying number of tasks.
Figure 5 shows the number of accumulated tasks processed by fog nodes. The results show that the proposed knapsack-based assists fog nodes process all high-priority tasks until the number of tasks reach 25 out of 234 of the 325 processed high-priority tasks at which point the number of high-priority tasks is gradually increased to 55. On the other hand, all three schemes execute a lower number of high-priority tasks. For medium-priority tasks, helps the fog node process more tasks compared to the other three schemes in each processing cycle when the number of offloaded tasks is within the range of 20. However, processing tasks in the proposed scheme are less than the other three schemes when number of tasks increases from this limit. This is due to the fact that intelligently scrutinizes the tasks for task execution. For low-priority task results, the number of offloaded tasks processed by is far less than the other three schemes because does not process any of the low-priority tasks because it has already processed most of the high-priority tasks by applying the 0/1 knapsack algorithm.
Results shown in Figure 6 verify that the fog node performs 100% of offloaded high-priority tasks in when the number of tasks is 25 compared to 91%, 38% and 0% of tasks for STF, FCFS and LTF, respectively. When the number of tasks is increased to 55 with an increase of 5 tasks in each cycle, an overall 72% of high-priority tasks are processed compared to 66%, 21% and 0% of high-priority tasks for STF, FCFS and LTF, respectively. For medium-priority tasks, for the initial 10 tasks, the proposed scheme is 100%, more than the rest of the other three schemes. However, for low-priority tasks, the number of processed tasks in is less than all three schemes and the processed tasks are at 10% compared to 20%, 70% and 90% of tasks in STF, FCFS and LTF, respectively.
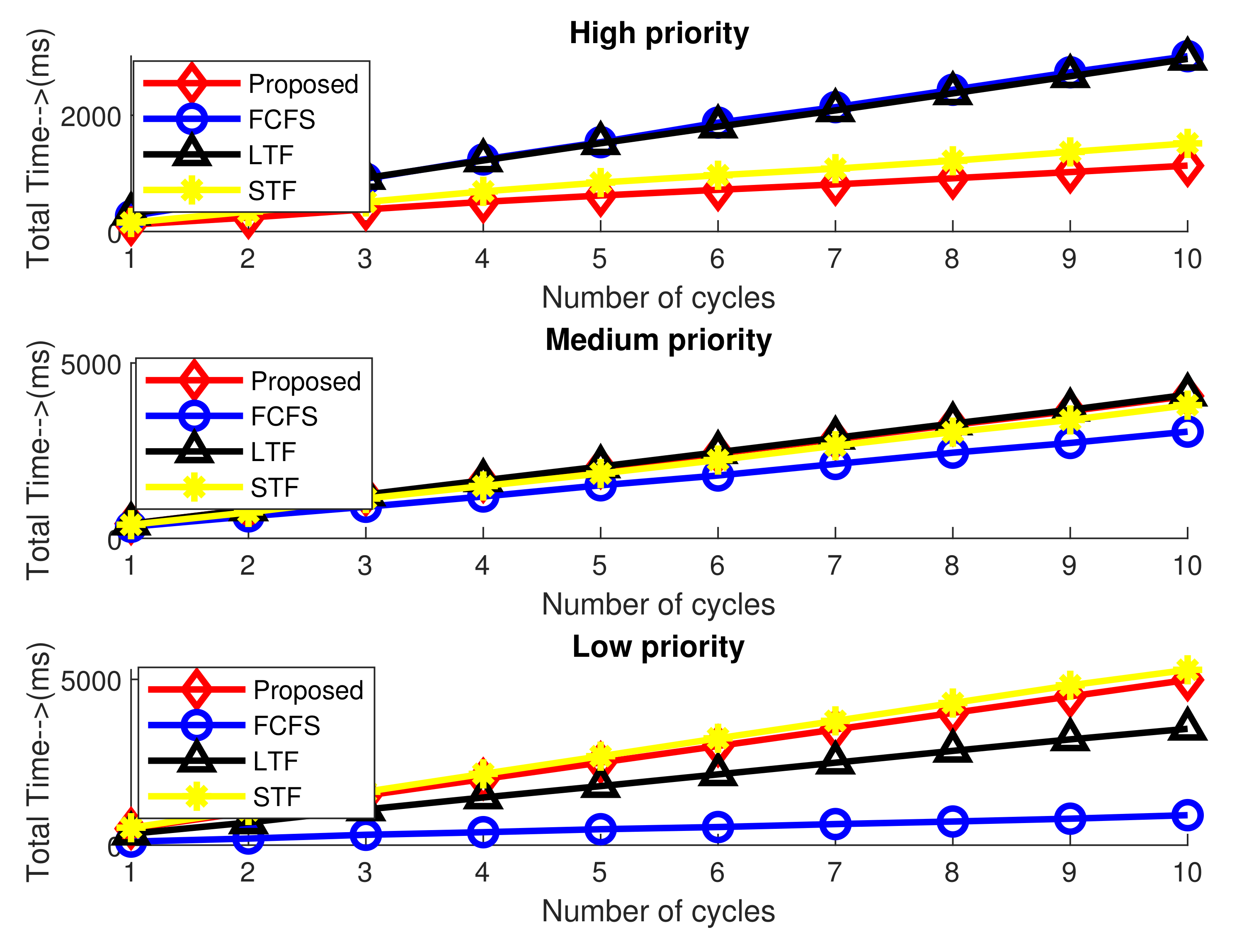
Figure 7 analyzes the task completion time of compared to the other three schemes. The total task processing time is defined as the total time required to download the processed task by vehicles from the fog node or from the cloud server. The total processing time is the sum of all processed tasks downloading time of vehicles by adding the previous processing time to current processing time. The results show that the task completion time for high-priority tasks in is much less than in STF, FCFS3 and LJF because the majority of these tasks are processed by the fog node itself, and only a few are forwarded to the cloud. However, accumulated task execution time for low-priority tasks is higher than the rest of the scheme because most of these tasks are forwarded to the cloud for task processing.

Figure 7.
Accumulated processing task time for different processing cycles.
It is evident from the results that our proposed scheme accommodates most of the highest priority tasks as compared to all other competitive schemes for varying numbers of processing cycles and for varying tasks in each processing cycle. This results in reduced execution time for the highest priority offloaded tasks as it allows the fog node to execute most of these tasks within its processing capacity.
6. Conclusions
Fog computing nodes are preferred over cloud computing servers for faster processing of tasks. In this paper, we proposed an efficient task execution for a fog node () that allowed fog computing nodes to optimally scrutinize the offloaded tasks by applying the knapsack optimization technique. A utility function is calculated for all offloaded vehicular task nodes that are based on their task priority and the time of attachment with the fog node. The key idea is to optimally execute most of the time-sensitive tasks by the fog computing node for faster processing and less sensitive tasks to be forwarded to the cloud. The proposed scheme is compared with FCFS and random processing techniques. The results show that the proposed scheme allows fog nodes to execute more than 98% of high-priority tasks, 47% of medium-priority tasks with an average task processing time of less than 12 ms and 62 ms, respectively, by compromising low-priority tasks.
Author Contributions
This article was prepared through the collective efforts of all the authors. Conceptualization, A.N.A., M.A.J., M.H.A.H., M.B.K., A.K.J.S., M.A. and U.F.; critical review, A.N.A., M.A.J., M.H.A.H., M.B.K., A.K.J.S., M.A. and U.F.; writing—original draft, A.N.A. and M.A.J.; writing—review and editing, M.H.A.H., M.B.K., A.K.J.S., M.A. and U.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University for funding this work through Research Group no. RG-21-07-06.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University for funding this work through Research Group no. RG-21-07-06.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Javed, M.A.; Zeadally, S.; Hamida, E.B. Data analytics for Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems. Veh. Commun. 2019, 15, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Abolhasan, M.; Ni, W.; Lipman, J.; Jamalipour, A. A Hybrid-Fuzzy Logic Guided Genetic Algorithm (H-FLGA) Approach for Resource Optimization in 5G VANETs. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 6964–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjevic, M.; Winkenbach, M. Characterizing urban last-mile distribution strategies in mature and emerging e-commerce markets. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 133, 164–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Quan, Y.; Shen, X.S.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Wang, W.; Dev, K. A Privacy-Enhanced Retrieval Technology for the Cloud-assisted Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 4981–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeadally, S.; Javed, M.A.; Hamida, E.B. Vehicular Communications for ITS: Standardization and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag. 2020, 4, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, A.A.; Sadiq, A.S.; Mirjalili, S.; Ghafoor, K.Z. Nonlinear-based Chaotic Harris Hawks Optimizer: Algorithm and Internet of Vehicles application. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 109, 107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Rahim, M.; Javed, M.A.; Ghabban, F.; Ameerbakhsh, O.; Alfadli, I. A D2D assisted multi-hop data dissemination protocol for inter-UAV communication. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2021, 34, e4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrar Ghafoor, K.; Kong, L.; Zeadally, S.; Sadiq, A.S.; Epiphaniou, G.; Hammoudeh, M.; Bashir, A.K.; Mumtaz, S. Millimeter-Wave Communication for Internet of Vehicles: Status, Challenges, and Perspectives. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 8525–8546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Imran, M.; Nasser, N.; Shoaib, M. Self-Aware Autonomous City: From Sensing to Planning. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, P.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. Kinematic Information Aided User-Centric 5G Vehicular Networks in Support of Cooperative Perception for Automated Driving. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 40195–40209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, F.; Javed, M.A.; Ngo, D.T. Performance Analysis of Cooperative V2V and V2I Communications Under Correlated Fading. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 3476–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, S.A.; Hajisami, A.; Krishnan, H.; Ahmed-Zaid, F.; Moradi-Pari, E. V2V System Congestion Control Validation and Performance. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 2102–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, B.; Murphy, F.; Mullins, M.; Ryan, C. Connected and autonomous vehicles: A cyber-risk classification framework. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2019, 124, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Alvi, A.N.; Khan, M.Z.; Javed, M.A.; Alhazmi, O.H.; Bouk, S.H. A novel superframe structure and optimal time slot allocation algorithm for IEEE 802.15.4—Based Internet of things. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2020, 16, 1550147720984645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Jin, C.; Alazab, M.; Yeh, K.H.; Wang, H.; Gadekallu, T.R.R.; Wang, W.; Su, C. On the Design of Blockchain-based ECDSA with Fault-tolerant Batch Verication Protocol for Blockchain-enabled IoMT. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Shabir, M.W.; Javed, M.A.; Imran, M. Intelligent energy prediction techniques for fog computing networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 111, 107682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, K.M.; Nadeem, M.; Sadiq, A.S.; Alghushami, A.; Khan, I.; Rabie, K. Smart Handoff Technique for Internet of Vehicles Communication using Dynamic Edge-Backup Node. Electronics 2020, 9, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahim, M.; Ali, S.; Alvi, A.N.; Javed, M.A.; Imran, M.; Azad, M.A.; Chen, D. An intelligent content caching protocol for connected vehicles. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2021, 32, e4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, A.S.; Khan, S.; Ghafoor, K.Z.; Guizani, M.; Mirjalili, S. Transmission power adaption scheme for improving IoV awareness exploiting: Evaluation weighted matrix based on piggybacked information. Comput. Netw. 2018, 137, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, U.M.; Javed, M.A.; Zeadally, S.; ul Islam, S. Energy efficient fog computing for 6G enabled massive IoT: Recent trends and future opportunities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.A.; Zeadally, S. AI-Empowered Content Caching in Vehicular Edge Computing: Opportunities and Challenges. IEEE Netw. 2021, 35, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, J.; Ali, B.; Javed, M.A. Stable Matching for Selection of Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces in Multiuser MISO Systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2748–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazab, M.; Lakshmanna, K.; G, T.R.; Pham, Q.V.; Reddy Maddikunta, P.K. Multi-objective cluster head selection using fitness averaged rider optimization algorithm for IoT networks in smart cities. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 43, 100973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.A.; Khan, M.Z.; Zafar, U.; Siddiqui, M.F.; Badar, R.; Lee, B.M.; Ahmad, F. ODPV: An Efficient Protocol to Mitigate Data Integrity Attacks in Intelligent Transport Systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 114733–114740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.; Javed, M.A.; Alvi, A.N.; Imran, M. An efficient caching policy for content retrieval in autonomous connected vehicles. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 140, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, I.; Khan, L.U.; Kazmi, S.M.A.; Imran, M.; Guizani, N.; Hong, C.S. Autonomous Driving Cars in Smart Cities: Recent Advances, Requirements, and Challenges. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacHardy, Z.; Khan, A.; Obana, K.; Iwashina, S. V2X Access Technologies: Regulation, Research, and Remaining Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 1858–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Kawamoto, Y.; Kato, N.; Liu, J. Future Intelligent and Secure Vehicular Network Toward 6G: Machine-Learning Approaches. Proc. IEEE 2020, 108, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, G.; Choudhury, B.; Park, J. IEEE 802.11bd & 5G NR V2X: Evolution of Radio Access Technologies for V2X Communications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 70169–70184. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, C.; Yu, K.; Aloqaily, M.; Alazab, M.; Lv, Z.; Mumtaz, S. Attribute-Based Encryption with Parallel Outsourced Decryption for Edge Intelligent IoV. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 13784–13795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.U.; Javed, M.A.; Nguyen, T.N.; Khan, S.; Elhalawany, B.M. Energy-Efficient Resource Allocation for 6G Backscatter-Enabled NOMA IoV Networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousafzai, A.; Yaqoob, I.; Imran, M.; Gani, A.; Noor, R.M. Process migration-based computational offloading framework for IoT-supported mobile edge/cloud computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 7, 4171–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javed, M.A.; Nafi, N.S.; Basheer, S.; Aysha Bivi, M.; Bashir, A.K. Fog-Assisted Cooperative Protocol for Traffic Message Transmission in Vehicular Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 166148–166156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fida, M.H.; Lian, Z.; Yin, Z.; Pham, Q.V.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Dev, K.; Su, C. Secure-Enhanced Federated Learning for AI-Empowered Electric Vehicle Energy Prediction. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Pham, Q.V.; Prabadevi, B.; Deepa, N.; Dev, K.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Ruby, R.; Liyanage, M. Industry 5.0: A survey on enabling technologies and potential applications. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2021, 26, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Cui, Q.; Tao, X.; Wang, S. MDP-based Task Offloading for Vehicular Edge Computing under Certain and Uncertain Transition Probabilities. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 3296–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, G.; Yan, J. Fog Computing Model and Efficient Algorithms for Directional Vehicle Mobility in Vehicular Network. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 2599–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Task Offloading in Vehicular Edge Computing Networks: A Load-Balancing Solution. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 2092–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhong, W.; Xie, S. Efficient Mobility-Aware Task Offloading for Vehicular Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 26652–26664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Guo, X.; Song, J.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, X.; Niu, Z. Adaptive Learning-Based Task Offloading for Vehicular Edge Computing Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 3061–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The European Telecommunications Standards Institute. ETSI TR 102 861 v1.1.1—Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS)—STDMA Recommended Parameters and Settings for Cooperative ITS; Access Layer Part; Technical Report; ETSI: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).