HGF Spatial–Spectral Fusion Method for Hyperspectral Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
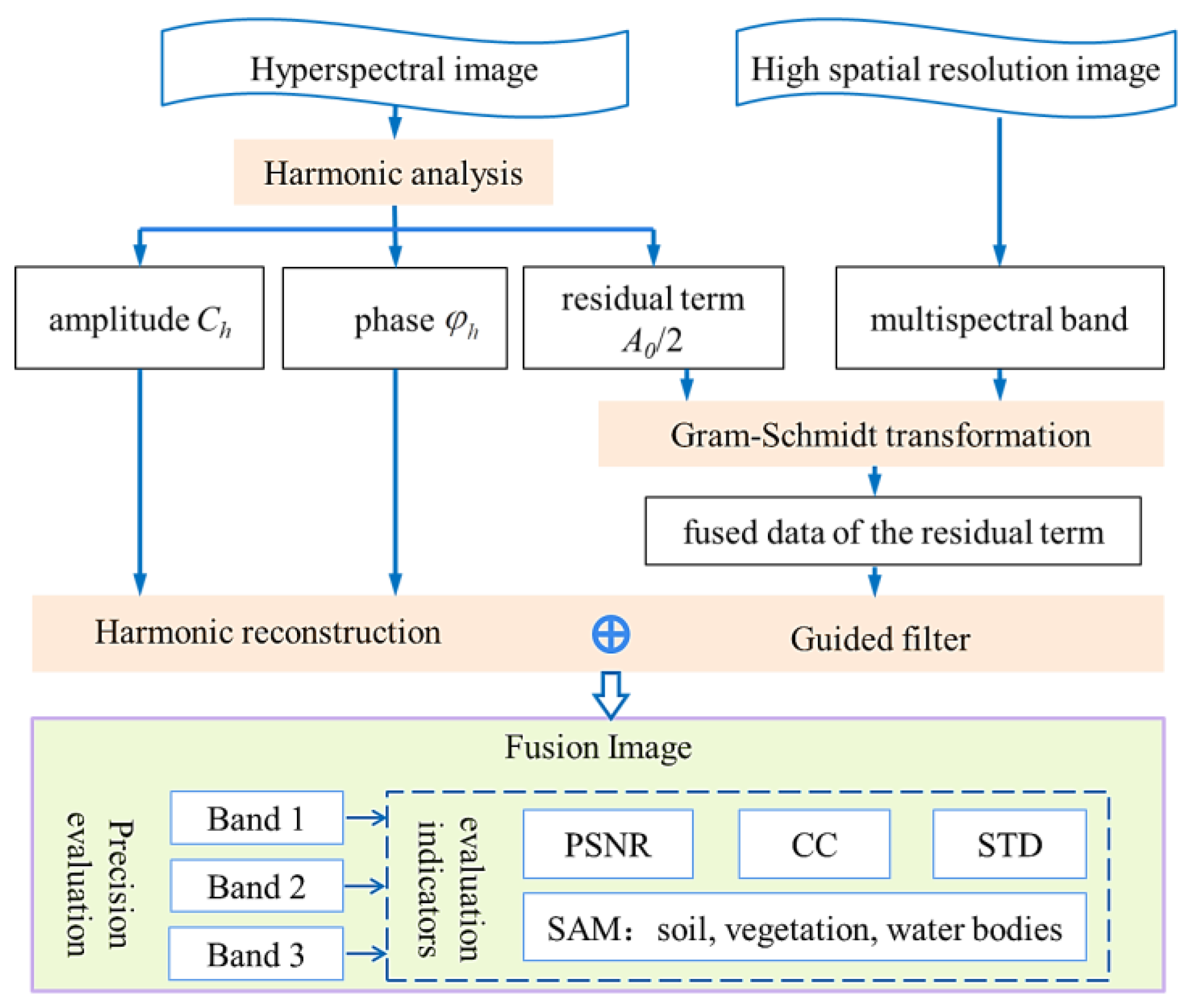
2. HGF Model
2.1. Data and Preprocessing
2.2. Fusion Algorithm of Hyperspectral Images
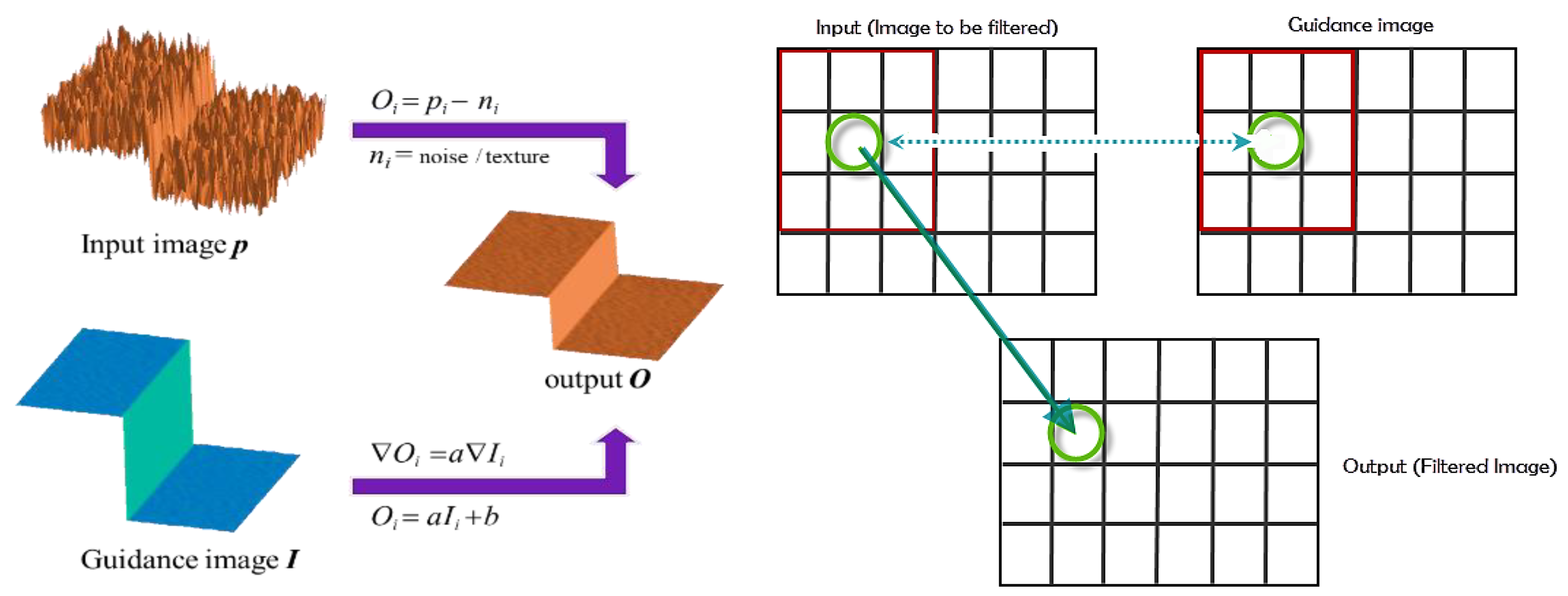
2.3. Guided Filtering
2.4. Evaluation Metrics
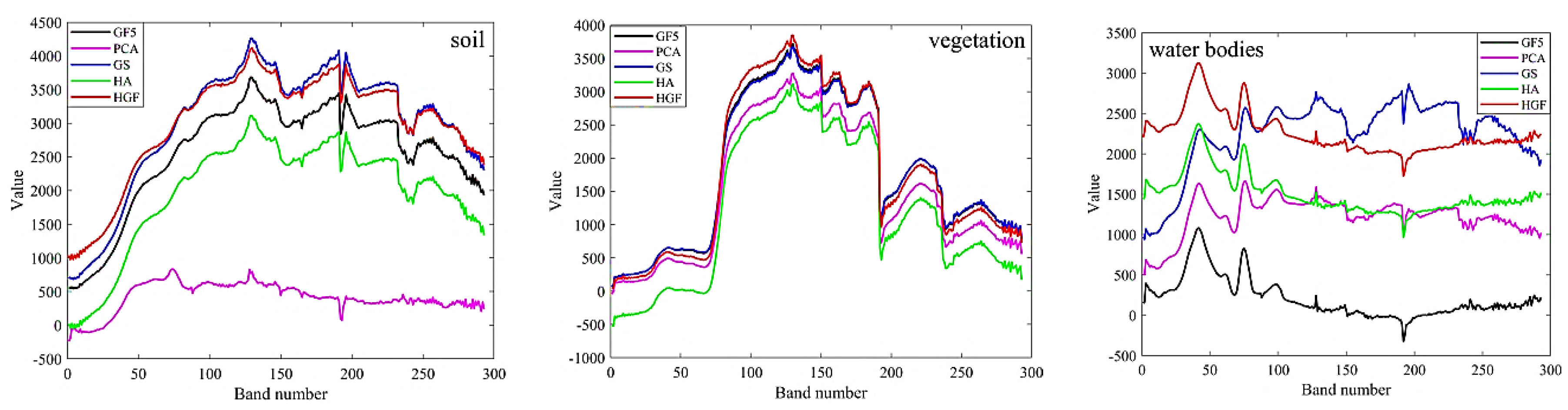
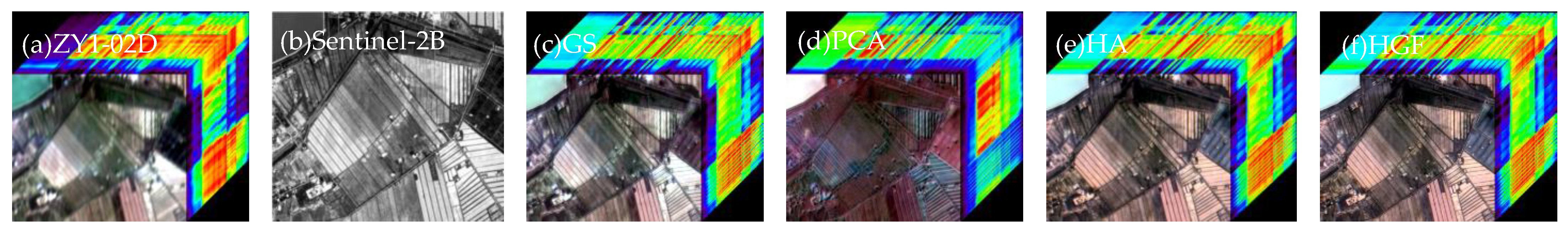
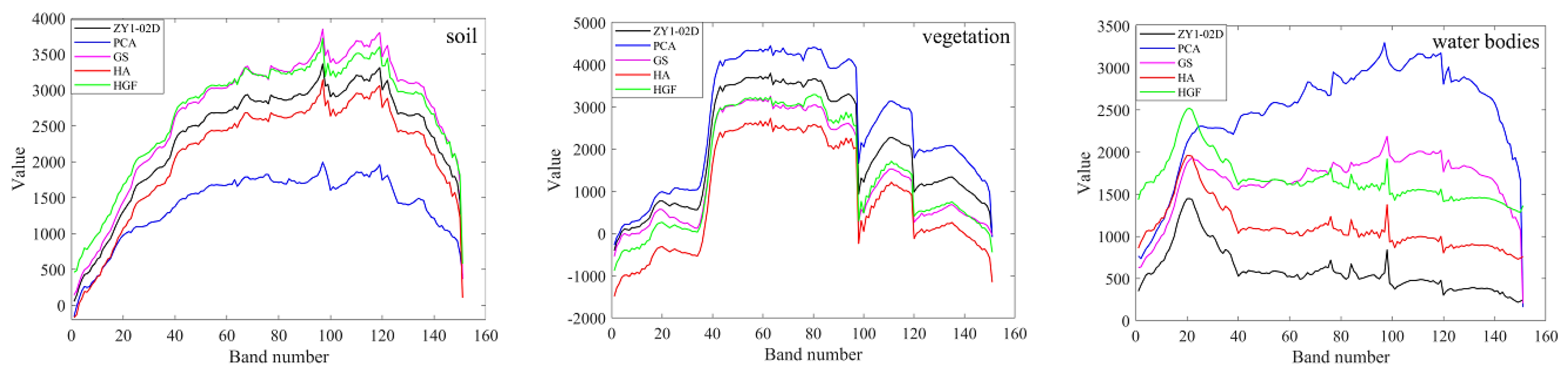
3. Results and Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Future Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Shen, H. Progress and future of remote sensing data fusion. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2016, 20, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Sun, W.; Ren, K.; Yang, G.; Shao, F.; Fu, R. Spatial-spectral fusion of GF-5/GF-1 remote sensing images based on multiresolution analysis. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2020, 24, 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Loncan, L.; De Almeida, L.B.; Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Briottet, X.; Chanussot, J.; Dobigeon, N.; Fabre, S.; Liao, W.; Licciardi, G.A.; Simoes, M. Hyperspectral Pansharpening: A Review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2015, 3, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivone, G.; Alparone, L.; Chanussot, J.; Mura, M.; Garzelli, A.; Licciardi, G.A.; Restaino, R.; Wald, L. A Critical Comparison among Pansharpening Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2565–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xiao, L.; Wei, Z.; Liu, H.; Tang, S. A New Pan-Sharpening Method with Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 12, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Tuia, D.; Mou, L.; Xia, G.S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Fraundorfer, F. Deep Learning in Remote Sensing: A Comprehensive Review and List of Resources. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2018, 5, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, S.; Qu, J.; Dong, W.; Zhang, T. Pansharpening Based on Multi-Branch CNN. Acta Opt. Sin. 2021, 41, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zheng, K.; Yao, J.; Gao, L.; Hong, D. Deep Unsupervised Blind Hyperspectral and Multispectral Data Fusion. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, K.R.; Ghamisi, P.; Rasti, B.; Scheunders, P.; Gloaguen, R. Unsupervised Data Fusion with Deeper Perspective: A Novel Multisensor Deep Clustering Algorithm. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Xue, Z.; Jia, T.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L. A harmonic analysis model of small target detection of hyperspectral imagery. Acta Geod. Et. Cartogr. Sin. 2013, 42, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Qian, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, L. A new algorithm on hyperspectral image fusion based on the harmonic analysis. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2014, 43, 547–553. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Yang, K.; Luo, W.; Zhang, Y. Fusion algorithm for hyperspectral remote sensing image combined with harmonic analysis and Gram-Schmidt transform. Acta Geod. Et. Cartogr. Sin. 2015, 44, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, G.; Yang, S.; Hang, X.; Fan, X. Road intersections and structure extraction method based on trajectory data. Sci. Technol. Ind. 2021, 21, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Li, S.; Li, A.; Zhang, B.; Chen, J. Deep fusion of hyperspectral images and multi-source remote sensing data for classification with convolutional neural network. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2021, 25, 1489–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Du, P.J.; Fu, P.J.; Zhang, P.; Tang, P.F.; Zheng, H.R.; Meng, Y.P.; Li, E.Z. Attention-Aware Dynamic Self-Aggregation Network for Satellite Image Time Series Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Yang, Y.; Ma, D.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z. Fusion and evaluation of “Zhuhai -1” hyperspectral data and GF-2 image. Technol. Innov. Appl. 2022, 12, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Cui, Z. Medical Image Fusion Based on Guided Filtering and Sparse Representation. J. Univ. Electron. Sci. Technol. China 2022, 51, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qi, Z.; Sun, W.; Li, S. Infrared image enhancement algorithm based on feature fusion. Opt. Tech. 2022, 48, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Meng, X.; Tian, X. Parallel design of object detection method for ground object segmentation based on Hi3559A platform. Electron. Des. Eng. 2022, 30, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Du, P.; Lin, C.; Fu, P.; Wang, X.; Bai, X.; Zheng, H.; Xia, J.; Samat, A. An Improved Feature Set for Hyperspectral Image Classification: Harmonic Analysis Optimized by Multiscale Guided Filter. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 3903–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Cui, X.; Liu, C. Inversion estimation of soil organic matter content based on GF-5 hyperspectral remote sensing image. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 3539–3545. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gu, X.; Zhou, X.; Ma, Y.; Xuan, X. Quantitative inversion of soil organic matter and total nitrogen content based on differential transformation. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2020, 48, 220–225. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.; Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Du, Q.; Du, P.; Pan, C. Estimation of the spatial distribution of heavy metal in agricultural soils using airborne hyperspectral imaging and random forest. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 382, 120987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Cheng, H. Application and development of hyperspectral remote sensing technology to determine the heavy metal content in soil. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 2699–2709. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Arnon, K.; Chen, J.; Han, W. Inversion of Soil Moisture Content from Hyperspectra Based on Ridge Regression. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 240–248. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, T.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Guan, W.; He, G.; Pan, D.; Liu, X. Construction of chlorophyll hyperspectral inverse model of alpine grassland community in Eastern Qilian Mountains. Grassl. Turf 2021, 41, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, P.; Zhang, W.; Yang, K.; Meng, F. A novel spectral analysis method for distinguishing heavy metal stress of maize due to copper and lead: RDA and EMD-PSD. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
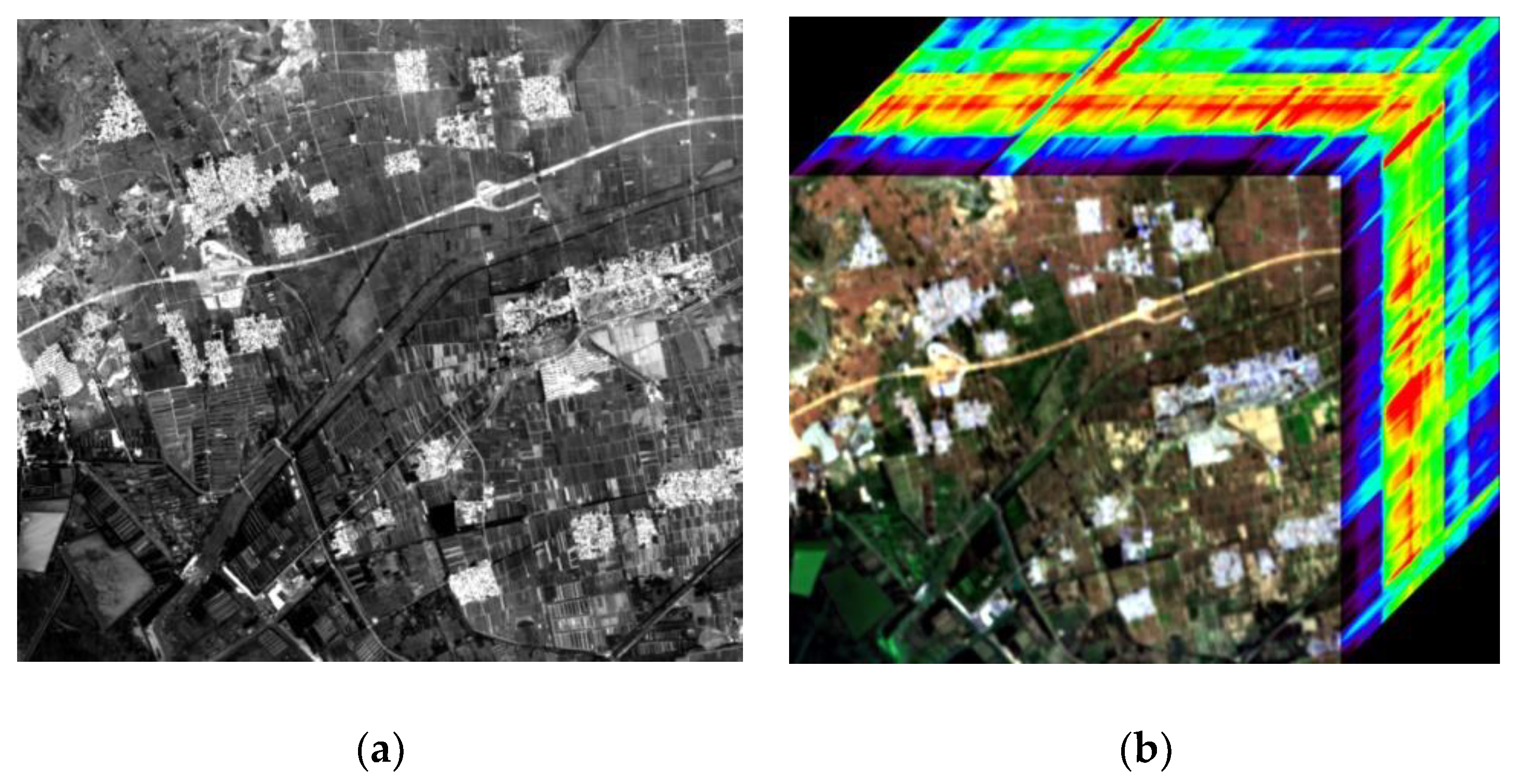


| GF-1: Band 4 | GF-5 | Sentinel-2B: Band 4 | ZY1-02D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acquisition time | 25 May 2019 | 29 May 2019 | 20 June 2020 | 28 June 2020 |
| Pixel | 8 m | 30 m | 10 m | 30 m |
| Spectral resolution | _ | VNIR: 5 nm SWIR: 10 nm | _ | VNIR: 10 nm SWIR: 20 nm |
| Dims | 510 × 455 × 1 | 136 × 121 × 303 | 420 × 354 × 1 | 140 × 118 × 151 |
| Wavelength Range | 390–730 nm | 730–1400 nm | 1400–2260 nm | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | PCA | GS | HA | HGF | PCA | GS | HA | HGF | PCA | GS | HA | HGF | ||
| Evaluation metrics | CC | −0.14 | 0.86 | 0.74 | 0.79 | 0.08 | 0.76 | 0.93 | 0.82 | −0.62 | 0.71 | 0.82 | 0.85 | |
| STD | 0.90 | 3.64 | 2.82 | 4.22 | 1.10 | 3.75 | 2.92 | 3.91 | 3.48 | 4.29 | 2.65 | 4.59 | ||
| PSNR | 13.92 | 19.80 | 13.68 | 18.02 | 8.35 | 15.63 | 13.75 | 16.78 | 9.14 | 15.69 | 13.62 | 17.62 | ||
| SAM | Soil | 0.39 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |
| Building | 0.26 | 0.01 | 0.47 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | ||
| Vegetation | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.49 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 0.01 | ||
| Water bodies | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.35 | 0.79 | 0.84 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 0.87 | ||
| Wavelength Range | 390–730 nm | 730–1400 nm | 1400–2260 nm | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | PCA | GS | HA | HGF | PCA | GS | HA | HGF | PCA | GS | HA | HGF | |
| Evaluation metrics | CC | −0.53 | 0.79 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.10 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.78 | −0.57 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.79 |
| STD | 0.89 | 2.40 | 2.81 | 2.73 | 0.56 | 1.89 | 1.85 | 1.89 | 1.42 | 3.79 | 3.51 | 3.45 | |
| PSNR | 14.40 | 20.76 | 13.64 | 18.87 | 11.04 | 18.06 | 13.61 | 18.17 | 12.32 | 18.81 | 13.42 | 18.89 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, B. HGF Spatial–Spectral Fusion Method for Hyperspectral Images. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010034
Fu P, Zhang Y, Meng F, Zhang W, Zhang B. HGF Spatial–Spectral Fusion Method for Hyperspectral Images. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(1):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010034
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Pingjie, Yuxuan Zhang, Fei Meng, Wei Zhang, and Banghua Zhang. 2023. "HGF Spatial–Spectral Fusion Method for Hyperspectral Images" Applied Sciences 13, no. 1: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010034
APA StyleFu, P., Zhang, Y., Meng, F., Zhang, W., & Zhang, B. (2023). HGF Spatial–Spectral Fusion Method for Hyperspectral Images. Applied Sciences, 13(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010034









