A Semi-Empirical Model for Sound Absorption by Perforated Plate Covered Open Cell Foam and Improvements from Optimising the Perforated Plate Parameters
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
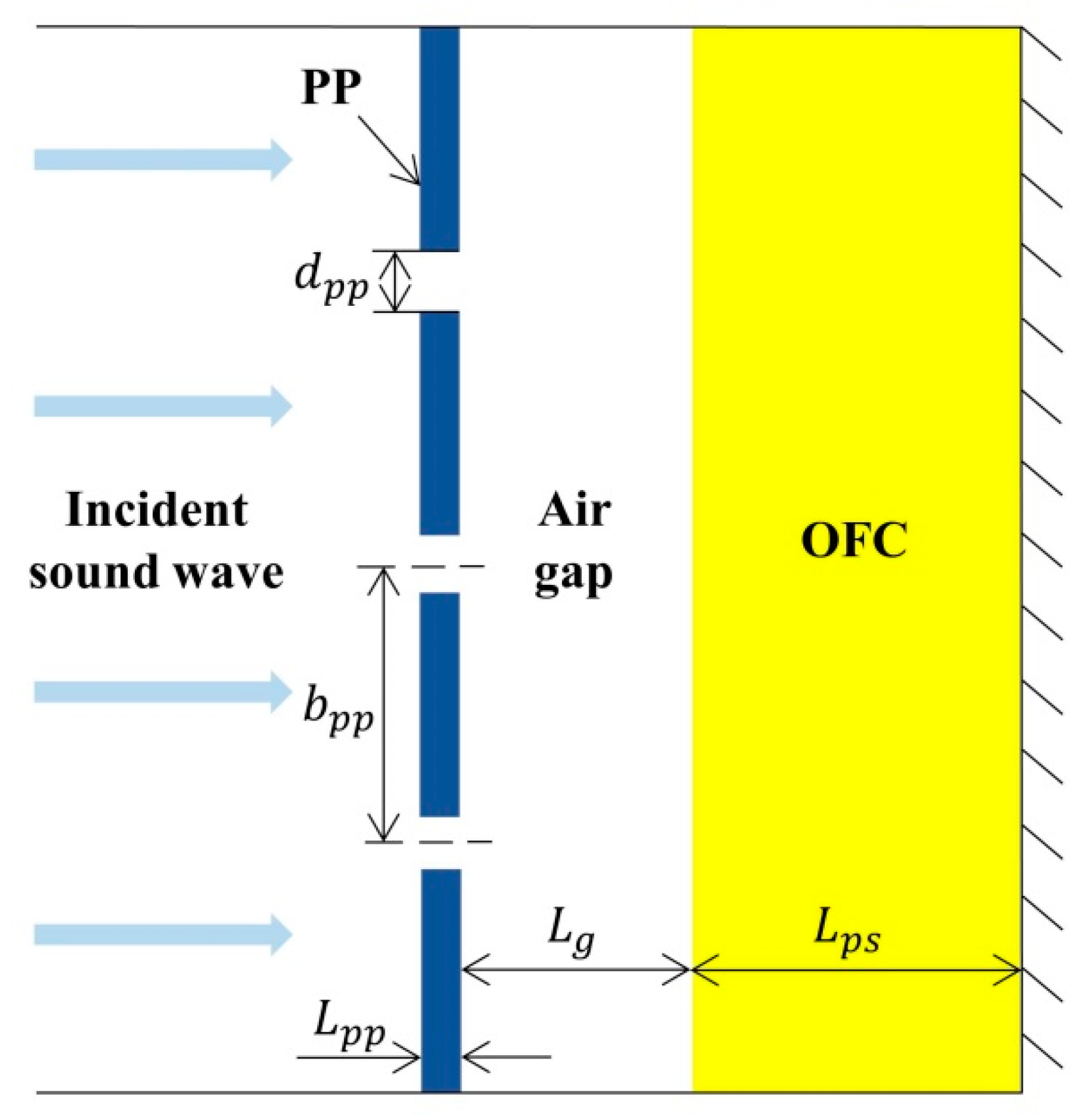
2. The Sound Absorption Model of the Composite Structure
3. Experimental Validation and Discussions
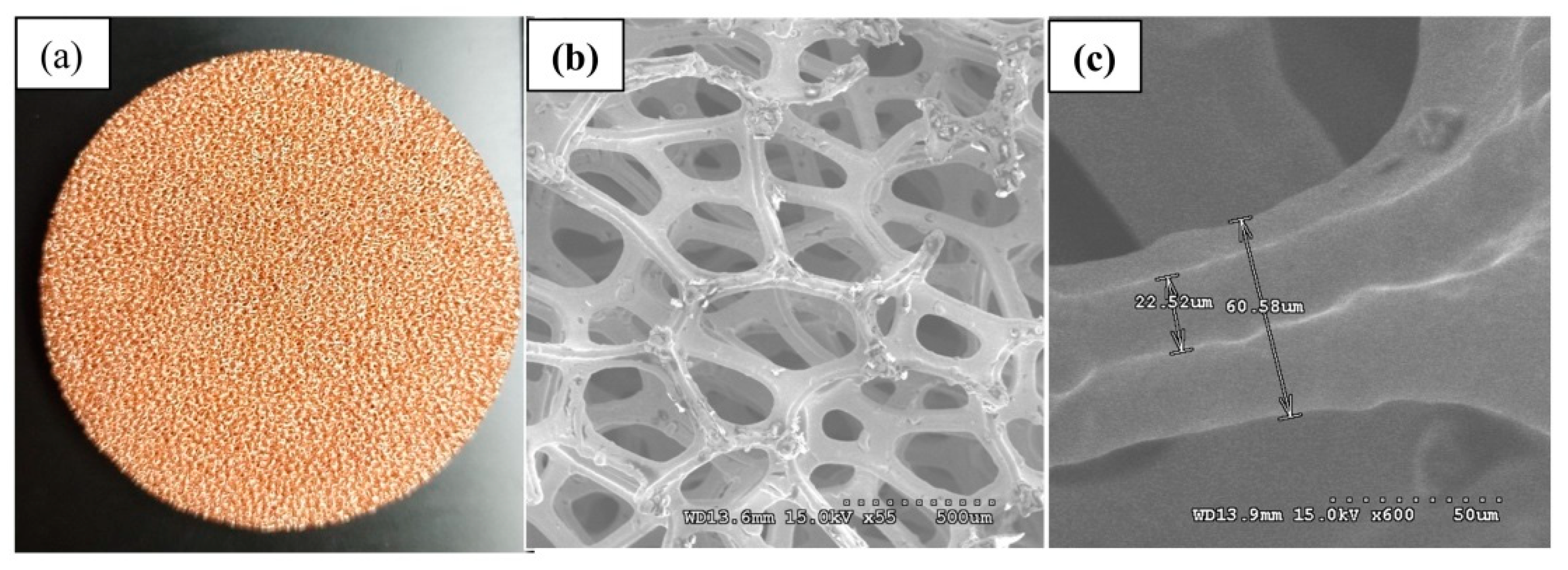
3.1. The PP Specimen Preparation
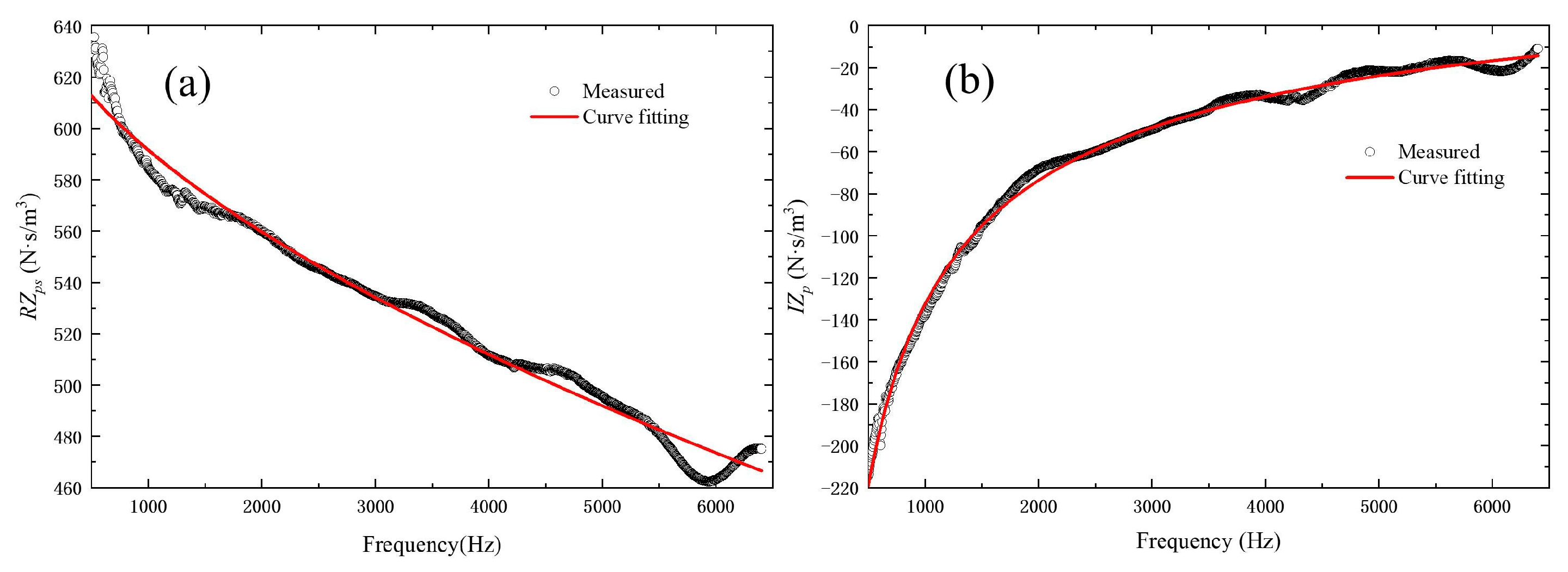
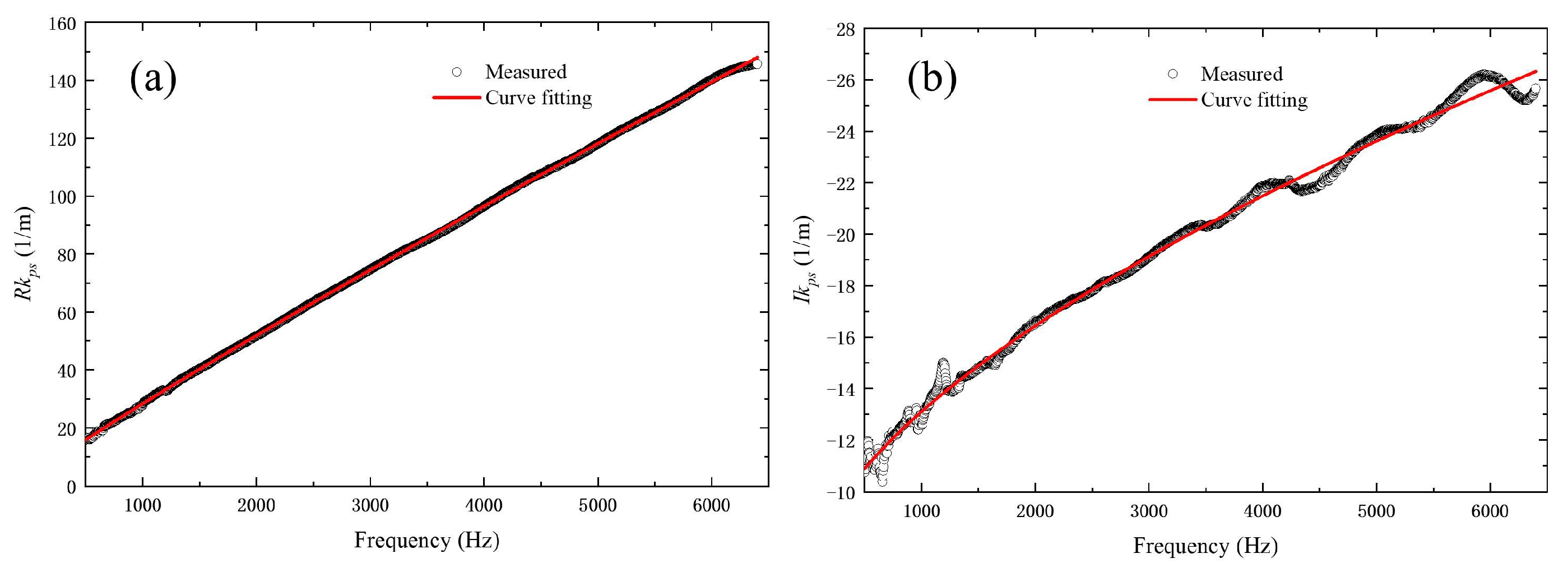
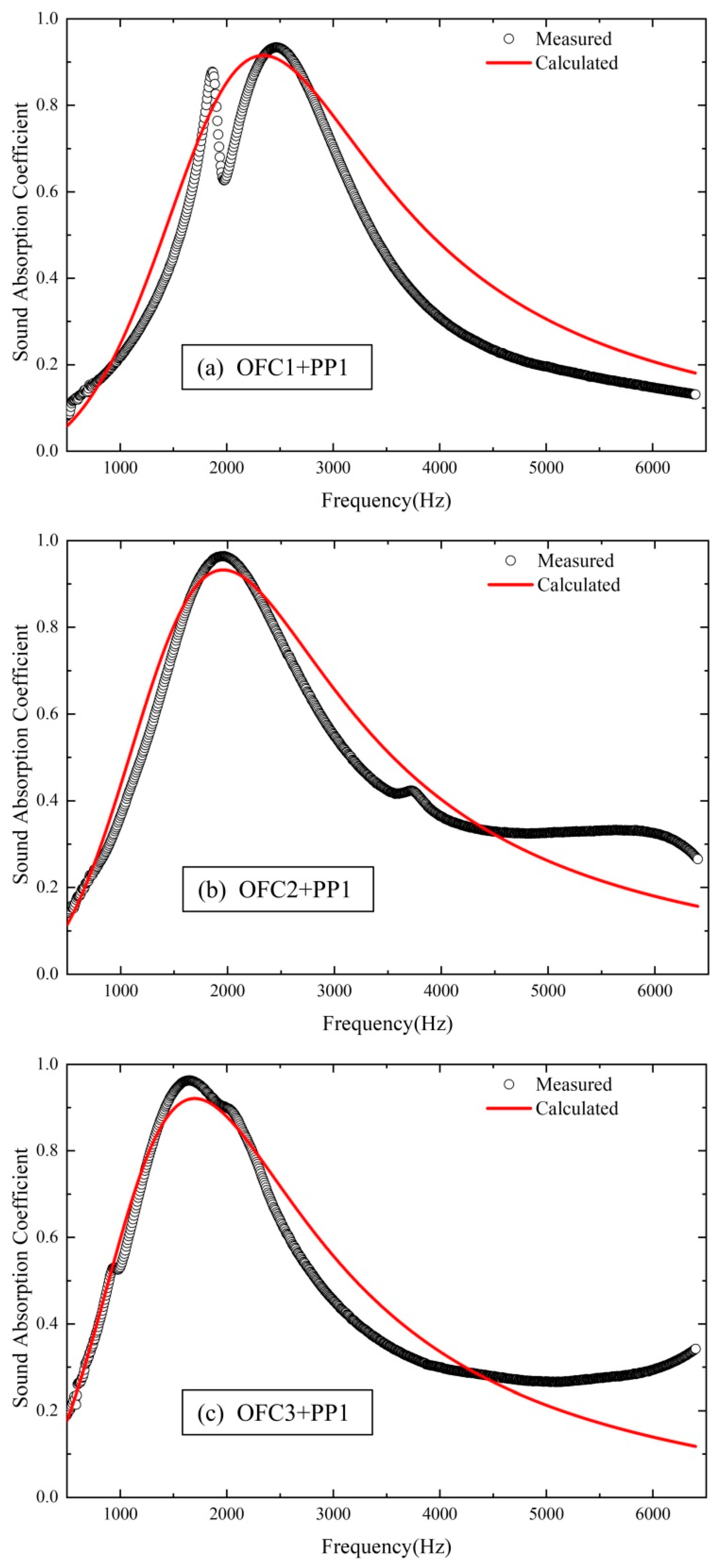
3.2. Results and Discussions
4. Lower-Frequency Absorptivity Optimization of the Composite Structure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atalla, N.; Sgard, F. Modeling of perforated plates and screens using rigid frame porous models. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 303, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F. Sound absorption of a porous material with a perforated facing at high sound pressure levels. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 425, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannemann, M.; Kucher, M.; Kunze, E.; Modler, N.; Knobloch, K.; Enghardt, L.; Sarradj, E.; Höschler, K. Experimental Study of Advanced Helmholtz Resonator Liners with Increased Acoustic Performance by Utilising Material Damping Effects. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, L. Theory of Sound II; Macmillan: London, UK, 1929. [Google Scholar]
- Maa, D.Y. Theory and design of Micro-perforated panel sound-absorbing constructions. Sci. Sin. 1975, 18, 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Maa, D.Y. Potential of microperforated panel absorber. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 2861–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Brocklesby, M.W. Feasibility of applying micro-perforated absorbers in acoustic window systems. Appl. Acoust. 2005, 66, 669–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Chen, W. Pilot study on compact wideband micro-perforated muffler with a serialparallel coupling mode. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 148, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mana, A.A.; Sonti, V.R. Sound radiation from a perforated panel set in a baffle with a different perforation ratio. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 372, 317–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, N.; Kong, D.Y.; Zhang, X.X. Pilot study on wideband sound absorber obtained by adopting a serial-parallel coupling manner. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 124, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yairi, M.; Sakagami, K.; Takebayashi, K.; Masayuki, M. Excess sound absorption at normal incidence by two microperforated panel absorbers with different impedance. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2011, 32, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, H.-S.; Ma, P.-S.; Kim, B.-K.; Kim, S.-R.; Lee, S.-H. Low-frequency sound absorption of elastic micro-perforated plates in a parallel arrangement. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 460, 114884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Rubini, P.; Qin, Q. A Porous Media Model for the Numerical Simulation of Acoustic Attenuation by Perforated Liners in the Presence of Grazing Flows. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Lee, E.W.M.; Ng, C.F. Sound absorption of a finite flexible micro-perforated panel backed by an air cavity. J. Sound Vib. 2005, 287, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laly, Z.; Atalla, N.; Meslioui, S.-A. Acoustical modeling of micro-perforated panel at high sound pressure levels using equivalent fluid approach. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 427, 134–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duponta, T.; Leclairea, P.; Pannetonb, R.; Umnova, O. A microstructure material design for low frequency sound absorption. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 136, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, J. Static and dynamic airflow resistance properties of porous metals. In Proceedings of the ICSV20, Bangkok, Thailand, 7–11 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cobo, P.; Espinosa, F.M. Proposal of cheap microperforated panel absorbers manufactured by infiltration. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M. The impact of the neck material on the sound absorption performance of Helmholtz resonators. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 6843–6857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, H.; Cobo, P.; Dupont, T.; Martin, B.; Leclaire, P. Acoustic properties of plates with unevenly distributed macroperforations backed by woven meshes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 3138–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Zhan, J.X.; Fard, M.; Davy, J.L. Acoustic properties of multilayer sound absorbers with a 3D printed micro-perforated panel. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 121, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Ren, S.W.; Xin, F.X.; Lu, T.J. Sound absorption coefficient optimization of gradient sintered metal fiber felts. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2016, 59, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.L.; Sun, J.; Tang, H.P.; Wang, J.Z.; Ao, Q.B.; Bao, T.F.; Song, W.D. Gradient-structural optimization of metal fiber porous materials for sound absorption. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, T.N.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhu, J. Numerical and analytical solutions for sound propagation and absorption in porous media at high sound pressure levels. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 1436–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mareze, P.H.; Brandão, E.; Fonseca, W.D.; Silva, O.M.; Lenzi, A. Modeling of acoustic porous material absorber using rigid multiple micro-ducts network. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 443, 376–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaru, A.J. Enhancing the sound absorption performance of porous metals using tomography images. Appl. Acoust. 2019, 143, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, T.N. Calculation of sound absorption characteristics of porous sintered fiber metal. Appl. Acoust. 2009, 70, 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.H.; Yoon, G.H. Absorption performance optimization of perforated plate using multiple-sized holes and a porous separating partition. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 120, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.K.; Chang, D.Q.; Liu, B.L. Enhanced low- to mid-frequency sound absorption using parallel-arranged perforated plates with extended tubes and porous material. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 127, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Xin, F.X.; Lu, T.J. Sound Absorption Optimization of Graded Semi-Open Cellular Metals by Adopting the Genetic Algorithm Method. J. Vib. Acoust. 2014, 136, 061007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delany, M.E.; Bazley, E.N. Acoustical properties of fibrous absorbent materials. Appl. Acoust. 1970, 3, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.Y.; Blaser, D.A. Transfer function method of measuring in-duct acoustic properties, II. Experiment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 68, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.F.; Shen, X.M.; Zhang, X.N.; Yang, X.C.; Yin, Q.; Liu, A.X. Influences of compression ratios on sound absorption performance of porous nickel–iron alloy. Metals 2018, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, P.; Azimian, M.; Wiegmann, A.; Zarrebini, M. Experimental and computational analysis of sound absorption behavior in needled nonwovens. J. Sound. Vib. 2018, 426, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Yu, X.; Song, X.; Ang, L.Y.L.; Cui, F.S.; Lee, H.P. Microstructure-based experimental and numerical investigations on the sound absorption property of open-cell metallic foams manufactured by a template replication technique. Mater. Design. 2018, 137, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.C.; Wu, J.H.; Cai, Y.Q. Study on dynamic effective parameters of bilayer perforated thin-plate acoustic metamaterials. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2021, 35, 2150048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, V.G.V.; Irwan; Wijayono, A.; Mohamad, J.; Yusuf, Y. A novel theoretical modeling for predicting the sound absorption of woven fabrics using modification of sound wave equation and genetic algorithm. Autex. Res. J. 2022, 22, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, V.T.; Özcan, E.; Parkes, A.J.; Sreekumar, A.; Jaouen, L.; Bécot, F.-X. Comparison of heuristics and metaheuristics for topology optimisation in acoustic porous materials. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 150, 3164–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


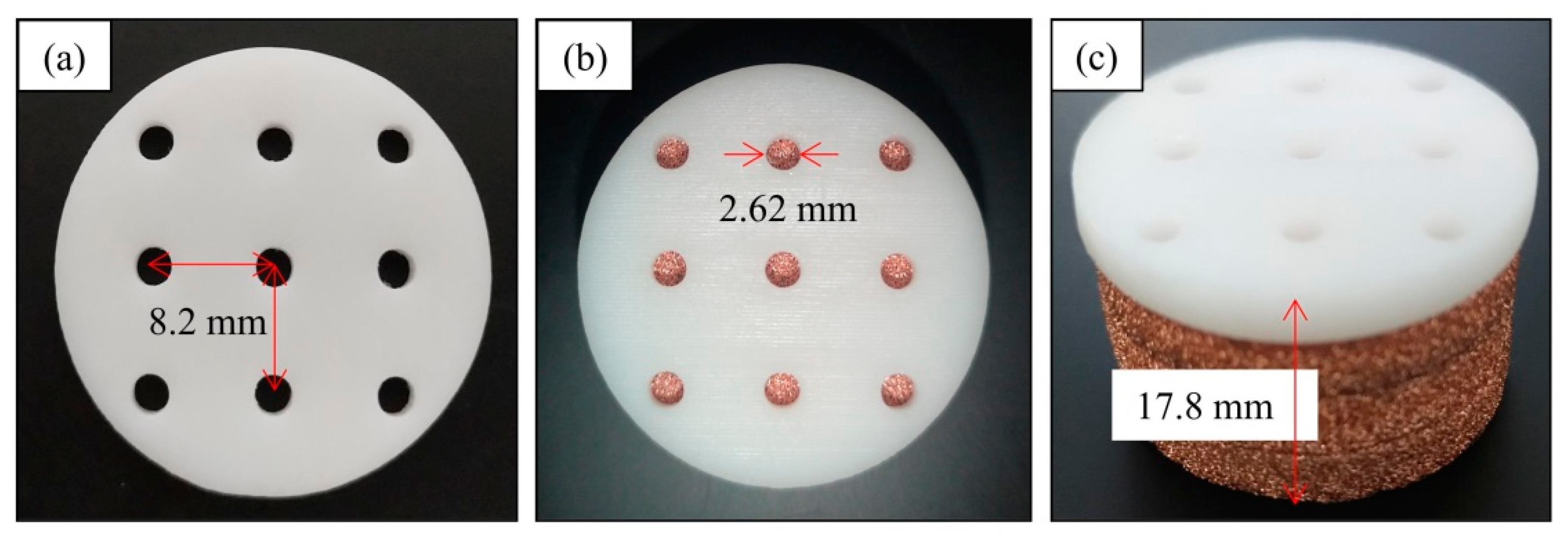

| Sample Number | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| OFC1 | 94.9 | 4.98 | 28.36 |
| OFC2 | 95.1 | 9.93 | 28.42 |
| OFC3 | 94.8 | 14.22 | 28.26 |
| Number | OFC1 | OFC3 |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Number | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP1 | 6.18 | 2.02 | 5.1 | 1.02 | 28.58 |
| Sample Number | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PP2 | 7.35 | 2.62 | 8.2 | 2.57 | 28.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Chen, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, J. A Semi-Empirical Model for Sound Absorption by Perforated Plate Covered Open Cell Foam and Improvements from Optimising the Perforated Plate Parameters. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010078
Zhang J, Chen T, Zhang B, Zhu J. A Semi-Empirical Model for Sound Absorption by Perforated Plate Covered Open Cell Foam and Improvements from Optimising the Perforated Plate Parameters. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(1):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010078
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Junzhe, Tianning Chen, Bo Zhang, and Jian Zhu. 2023. "A Semi-Empirical Model for Sound Absorption by Perforated Plate Covered Open Cell Foam and Improvements from Optimising the Perforated Plate Parameters" Applied Sciences 13, no. 1: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010078
APA StyleZhang, J., Chen, T., Zhang, B., & Zhu, J. (2023). A Semi-Empirical Model for Sound Absorption by Perforated Plate Covered Open Cell Foam and Improvements from Optimising the Perforated Plate Parameters. Applied Sciences, 13(1), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13010078






