Thermodynamic Behavior of As, Pb, and As during the Vacuum Carbothermal Reduction of Copper Anode Slime
Abstract
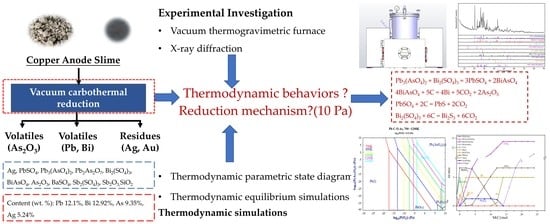
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Characterization
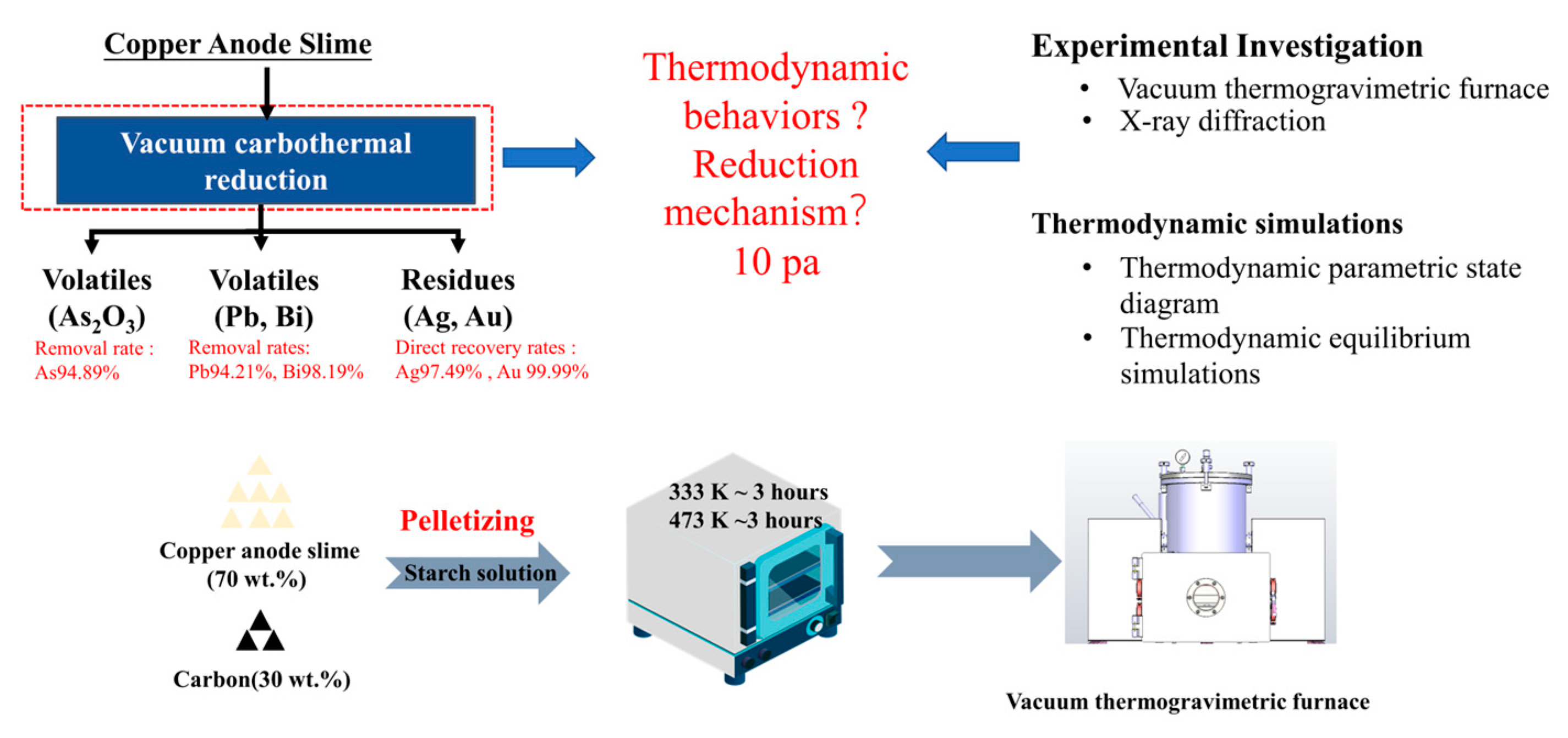
2.2. Vacuum Thermogravimetry Tests
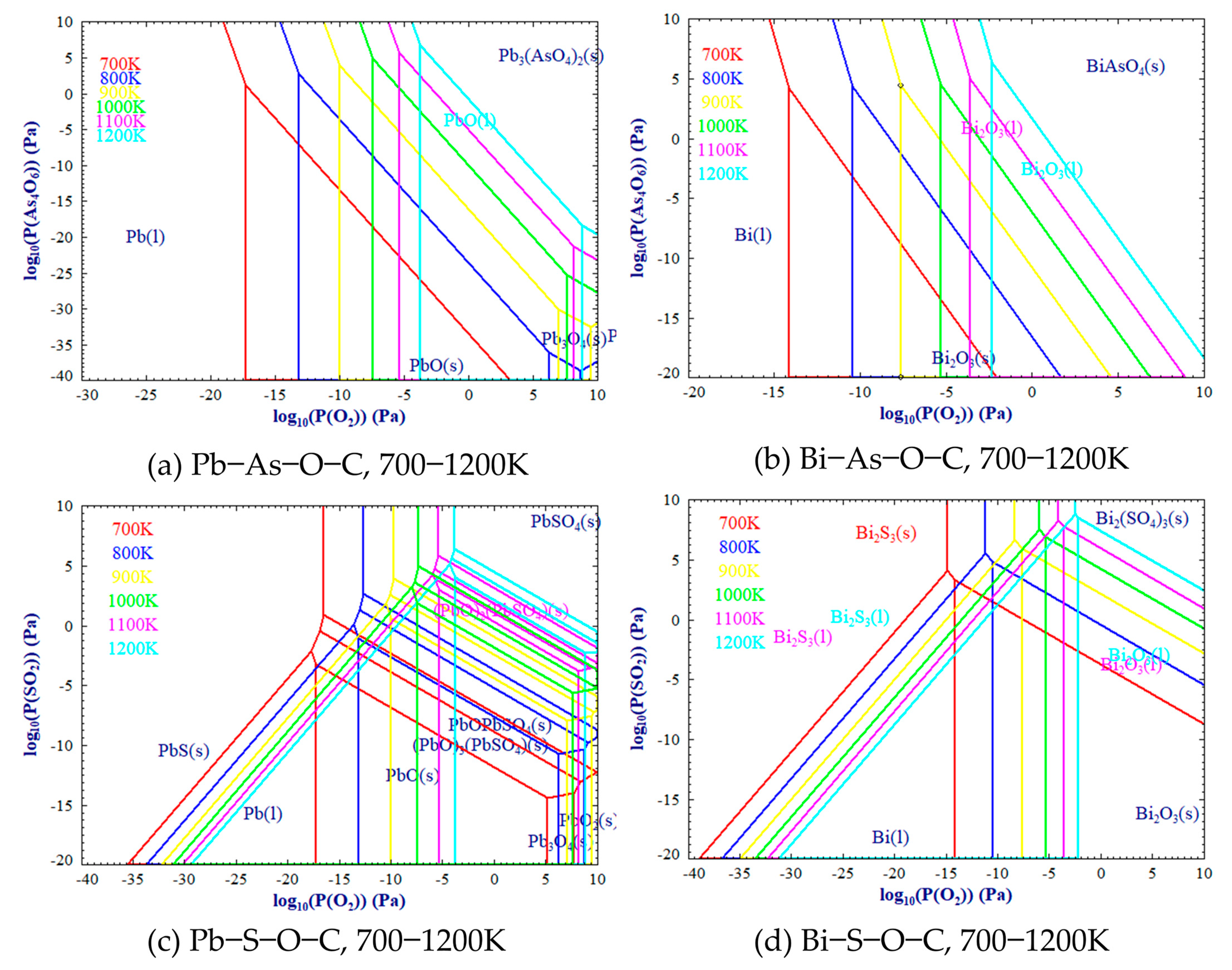
2.3. Thermodynamic Simulations
3. Results
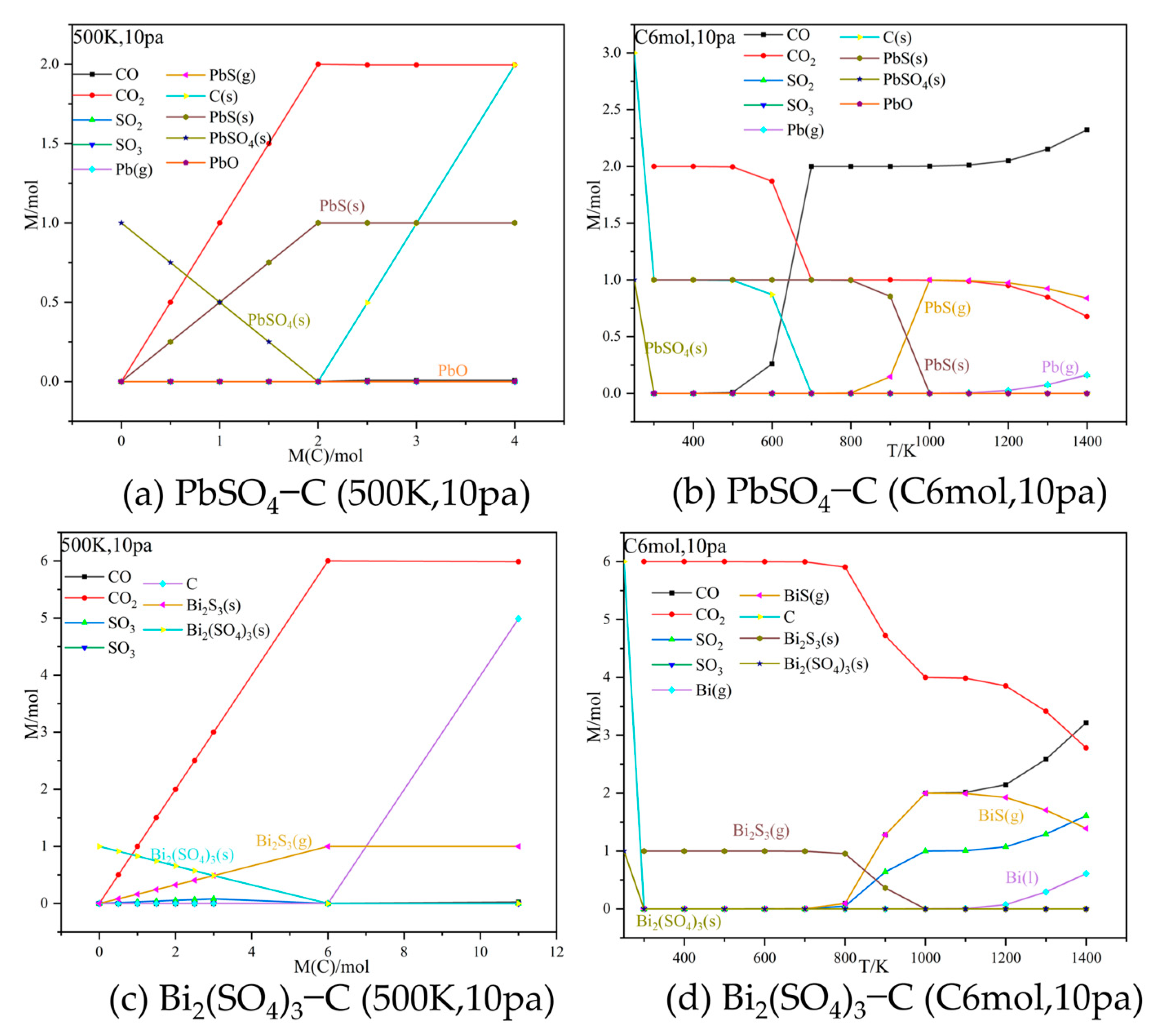
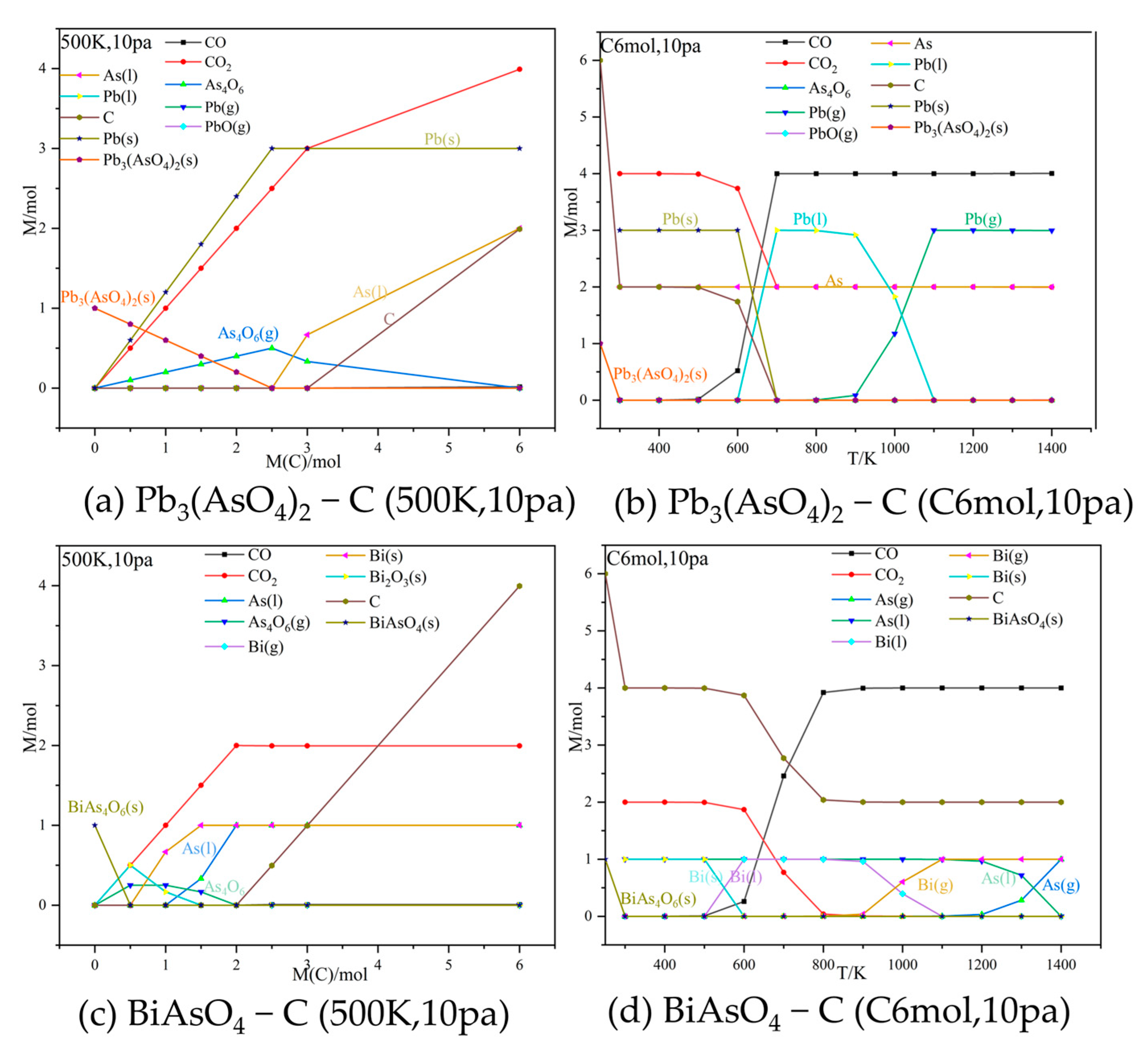
3.1. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Simulations
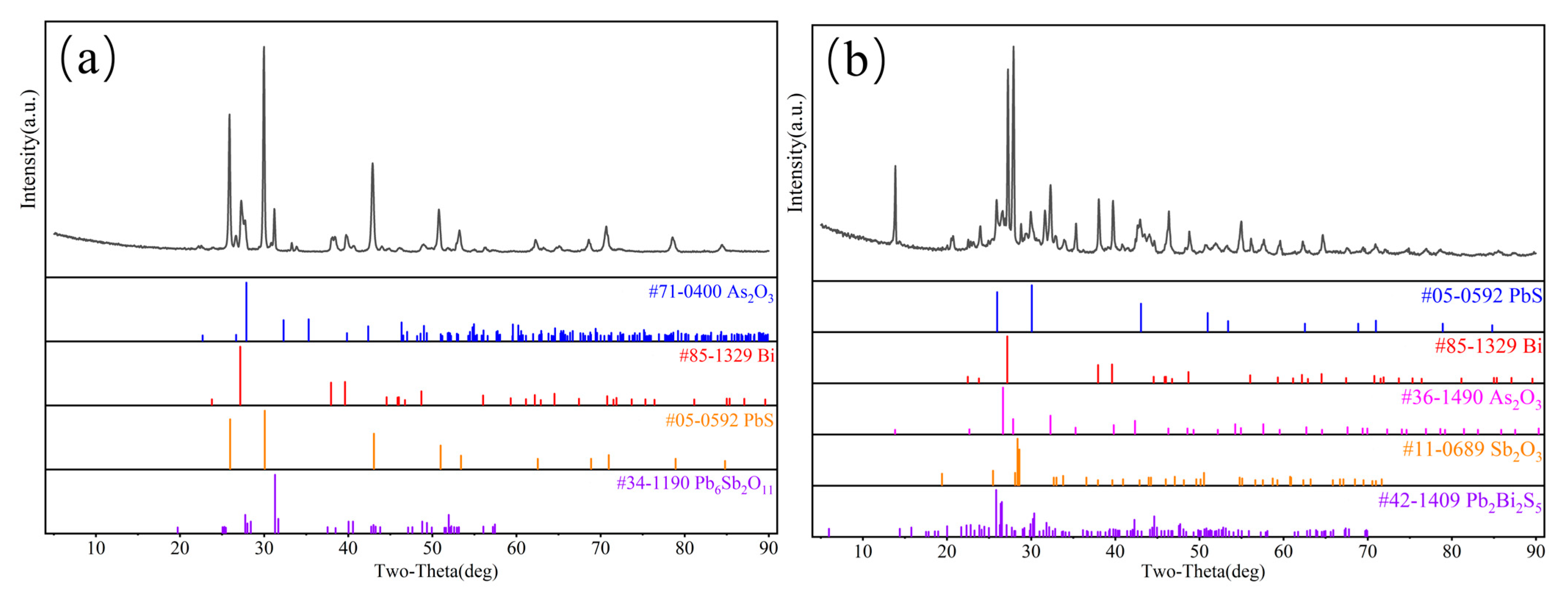
3.2. Vacuum Carbothermal Reduction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, L.; Wang, Y.L.; Yu, Y.; Fu, G.Y.; Han, P.W.; Sun, Z.H.I.; Ye, S.F. An Environmentally Friendly Process to Selectively Recover Silver from Copper Anode Slime. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 187, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Geological Survey. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/periodicals/mcs2022/mcs2022-copper.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- Bin, W.; Lu, Y. Gui Jin Shu Ye Jin Xue; Central South University Press: Changsha, China, 2011; ISBN 978-7-5487-0223-8. [Google Scholar]
- China Gold Association in the First Quarter of 2022, Raw Gold Production within China Reached 83.401 Tons, of Which 65.009 Tons Was Mineral Gold and 18.392 Tons. Available online: http://www.cngold.org.cn/newsinfo.aspx?ID=3632 (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Kilic, Y.; Kartal, G.; Timur, S. An Investigation of Copper and Selenium Recovery from Copper Anode Slimes. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 124, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.D.; Sohn, S.H.; Lee, M.S. A Review on the Recovery of Noble Metals from Anode Slimes. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2020, 41, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhu, N.; Xian, J.; Xi, Y.; Li, F.; Wu, P.; Chen, Y. A Green Process for Simultaneously Efficient Base Metals Removal and Precious Metals Enrichment from Copper Anode Slime. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 180, 106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.T.; Dutrizac, J.E. Mineralogical Characterization of a Copper Anode and the Anode Slimes from the La Caridad Copper Refinery of Mexicana de Cobre. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2005, 36, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Jiang, T.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y. Comprehensive Recoveries of Selenium, Copper, Gold, Silver and Lead from a Copper Anode Slime with a Clean and Economical Hydrometallurgical Process. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 393, 124762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Z.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, B.; Liu, G.; Yang, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y. Eco-Friendly and Efficient Extraction of Valuable Elements from Copper Anode Mud Using an Integrated Pyro-Hydrometallurgical Process. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, L.; Wang, S.D.; Wang, H.; Wu, G.D. Extraction of Platinum and Gold from Copper Anode Slimes by a Process of Chlorinating Roasting Followed by Chlorinating Leaching. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2020, 56, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanuki, S.; Minami, N.; Arai, K.; Izaki, T.; Majima, H. Oxidative Leaching Treatment of Copper Anode Slime in a Nitric Acid Solution Containing Sodium Chloride. Mater. Trans. JIM 1989, 30, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanlarian, M.; Rashchi, F.; Saba, M. A Modified Sulfation-Roasting-Leaching Process for Recovering Se, Cu, and Ag from Copper Anode Slimes at a Lower Temperature. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kurniawan, K.; Chung, K.W.; Kim, S. Metallurgical Process for Total Recovery of All Constituent Metals from Copper Anode Slimes: A Review of Established Technologies and Current Progress. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 27, 2160–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.A.; Segarra, M.; Espiell, F. Selective Leaching of Arsenic and Antimony Contained in the Anode Slimes from Copper Refining. Hydrometallurgy 1996, 41, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuiping, Y.; Juner, W.; Huanran, Z.; Hang, C.; Chen, Y. Furnace Extraction Technology of Copper Anode Slime by Caldo Furnace Method; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2019; ISBN 978-7-5024-8038-7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W. Study on the Treatment of Copper and Lead Anode Sludge by Alkaline Oxidation Method. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, W.D.; Lee, M.S. Development of a Hydrometallurgical Process for the Recovery of Gold and Silver Powders from Anode Slime Containing Copper, Nickel, Tin, and Zinc. Gold Bull. 2019, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, J.; Jana, R.K.; Sanyal, S.K. Processing of Copper Electrorefining Anode Slime: A Review. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2013, 118, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, W.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, J.; Yang, B. A Selective Volatilization and Condensation Process for Extracting Precious Metals from Noble Lead. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jiang, W.; Cha, G.; Deng, J.; Guo, X.; Huang, D.; Xu, B.; Yang, B. Recovery of Associated Precious Metals from By-Products of Lead and Copper Smelting. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2021, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Shi, T.; Yang, B.; Yang, J.; Jiang, W. Research Status on Treatment and Utilization of Arsenic Containing Dust. J. Kunming Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2019, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Xu, B.; Deng, J.; Jiang, W.; Liu, D.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Kong, L.; Yang, J. Method for Recovering Valuable Metal from Copper Anode Slime. Patent 202111191251, 28 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.L.; Deng, J.H.; Jiang, W.L.; Zha, G.Z.; Yang, B. Removal of Arsenic, Lead and Bismuth from Copper Anode Slime by a One-Step Sustainable Vacuum Carbothermal Reduction Process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 310, 123059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FactSage Modules. The Equilib Module. Available online: https://www.factsage.com/fs_equilib.php (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- FactSage Modules. The Phase Diagram Module. Available online: https://www.factsage.com/fs_pd.php (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Howard, S.M. Three-Dimensional Predominance Volume Diagrams: The Ni-As-S-O System. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 2332–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
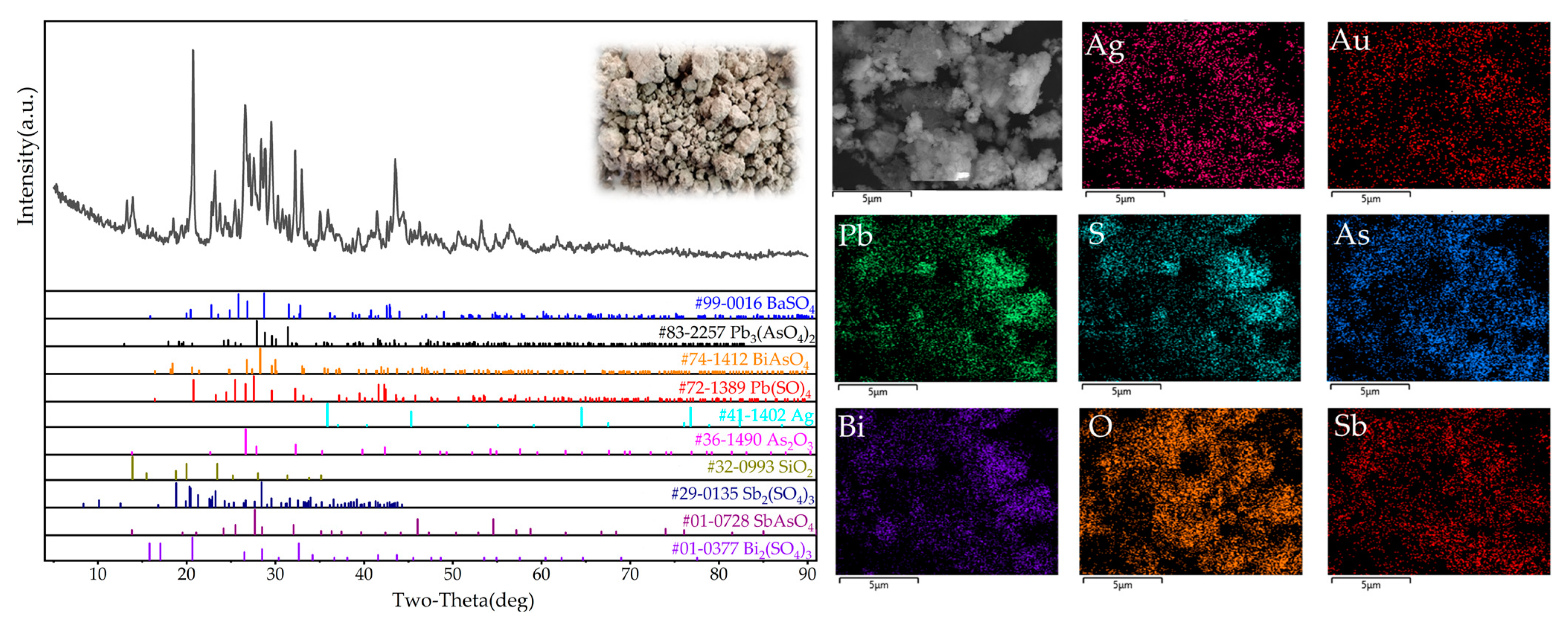



| Resource | Ag | Au | As | Pb | Bi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| La Caridad Copper Refinery [8] | 15.4 | 0.04 | 5.00 | 14.80 | 1.20 |
| Qinghai Copper Industry Co. [9] | 5.00 | 0.15 | 2.12 | 28.5 | 4.61 |
| Sarkuysan Copper, Turkey [5] | 2.80 | 0.23 | 3.93 | 12.93 | 0.15 |
| Medium-scale copper smelter in western China [10] | 5.36 | 0.16 | 2.38 | 28.65 | 3.86 |
| Yunnan [11] | 4.79 | 0.18 | 6.21 | 3.18 | 3.15 |
| Toyama, Japan [12] | 17.00 | 1.04 | 0.41 | 35.10 | – |
| Tehran, Iran [13] | 7.07 | 0.08 | 0.42 | 4.42 | 0.08 |
| Noranda (Canada) [14] | 19.50 | 0.18 | 1.14 | 8.00 | 0.77 |
| IMI Refinery (UK) [14] | 5.50 | 0.07 | 3.50 | 22.00 | 0.50 |
| INCO (USA) [14] | 6.37 | 0.12 | 0.50 | 1.70 | 0.14 |
| La Caridad Copper Refinery (Mexico) [8] | 15.40 | 0.04 | 5.00 | 14.80 | 1.20 |
| Rio Tinto Minera Copper Refinery, Huelva (Spain) [15] | 14.54 | 0.38 | 3.41 | 2.89 | 0.76 |
| Element | Ag | Au (g/t) | Bi | Pb | As | Ba | S | O * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw materials | Content (wt. %) | 5.24 | 927.9 | 12.92 | 12.1 | 9.35 | 7.64 | 6.94 | 15.52 |
| Element | Sb | Te | Se | Cu | Ni | Fe | Zn | ||
| Content (wt. %) | 4.94 | 1.64 | 0.71 | 0.7 | 0.41 | 0.27 | 0.007 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, J.; Zha, G.; Liu, D.; He, J.; Jiang, W. Thermodynamic Behavior of As, Pb, and As during the Vacuum Carbothermal Reduction of Copper Anode Slime. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5878. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13105878
Deng J, Zha G, Liu D, He J, Jiang W. Thermodynamic Behavior of As, Pb, and As during the Vacuum Carbothermal Reduction of Copper Anode Slime. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(10):5878. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13105878
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Juhai, Guozheng Zha, Dachun Liu, Jilin He, and Wenlong Jiang. 2023. "Thermodynamic Behavior of As, Pb, and As during the Vacuum Carbothermal Reduction of Copper Anode Slime" Applied Sciences 13, no. 10: 5878. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13105878
APA StyleDeng, J., Zha, G., Liu, D., He, J., & Jiang, W. (2023). Thermodynamic Behavior of As, Pb, and As during the Vacuum Carbothermal Reduction of Copper Anode Slime. Applied Sciences, 13(10), 5878. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13105878