Ion Exchange MIEX® GOLD Resin as a Promising Sorbent for the Removal of PFAS Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pre-Treatment of MIEX® GOLD Resin
2.3. Removal of PFAS Compounds by MIEX® GOLD Resin
2.4. PFAS Loading Capacity of MIEX® GOLD Resin
2.5. Interference of Tannic Acid, Humic Acid, Sulfates, and Nitrates in PFAS Removal
2.6. Regeneration of MIEX® GOLD Resin
2.7. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
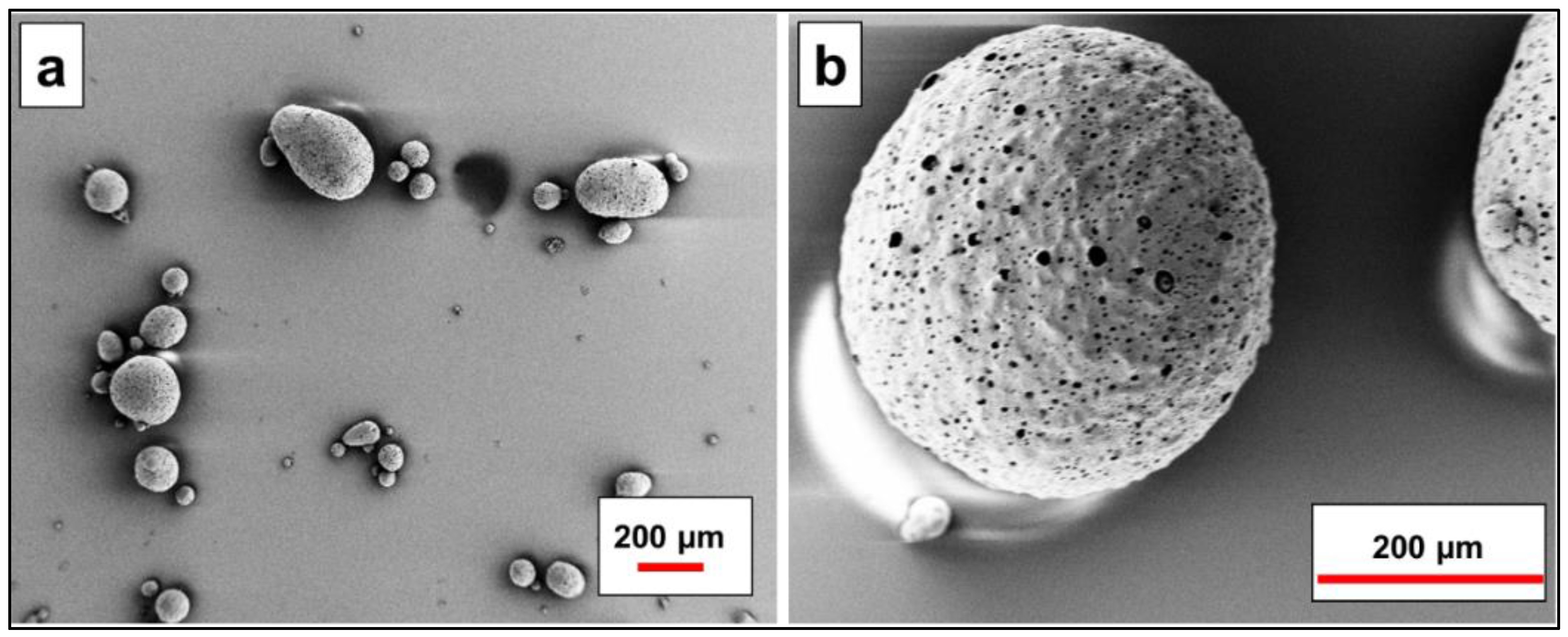
3.1. Characterization of MIEX® GOLD
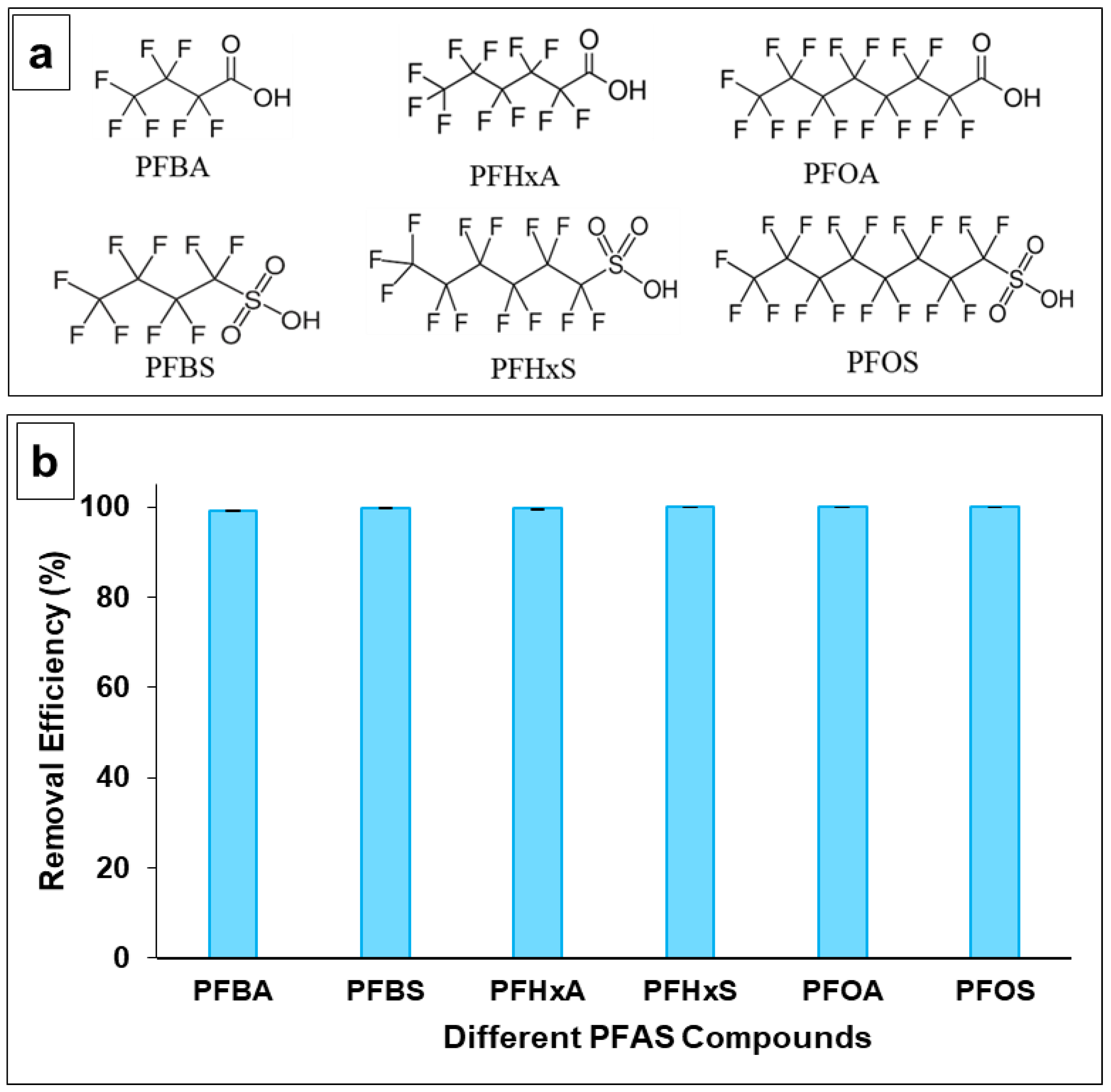
3.2. PFAS Removal Efficiency of MIEX® GOLD Resin
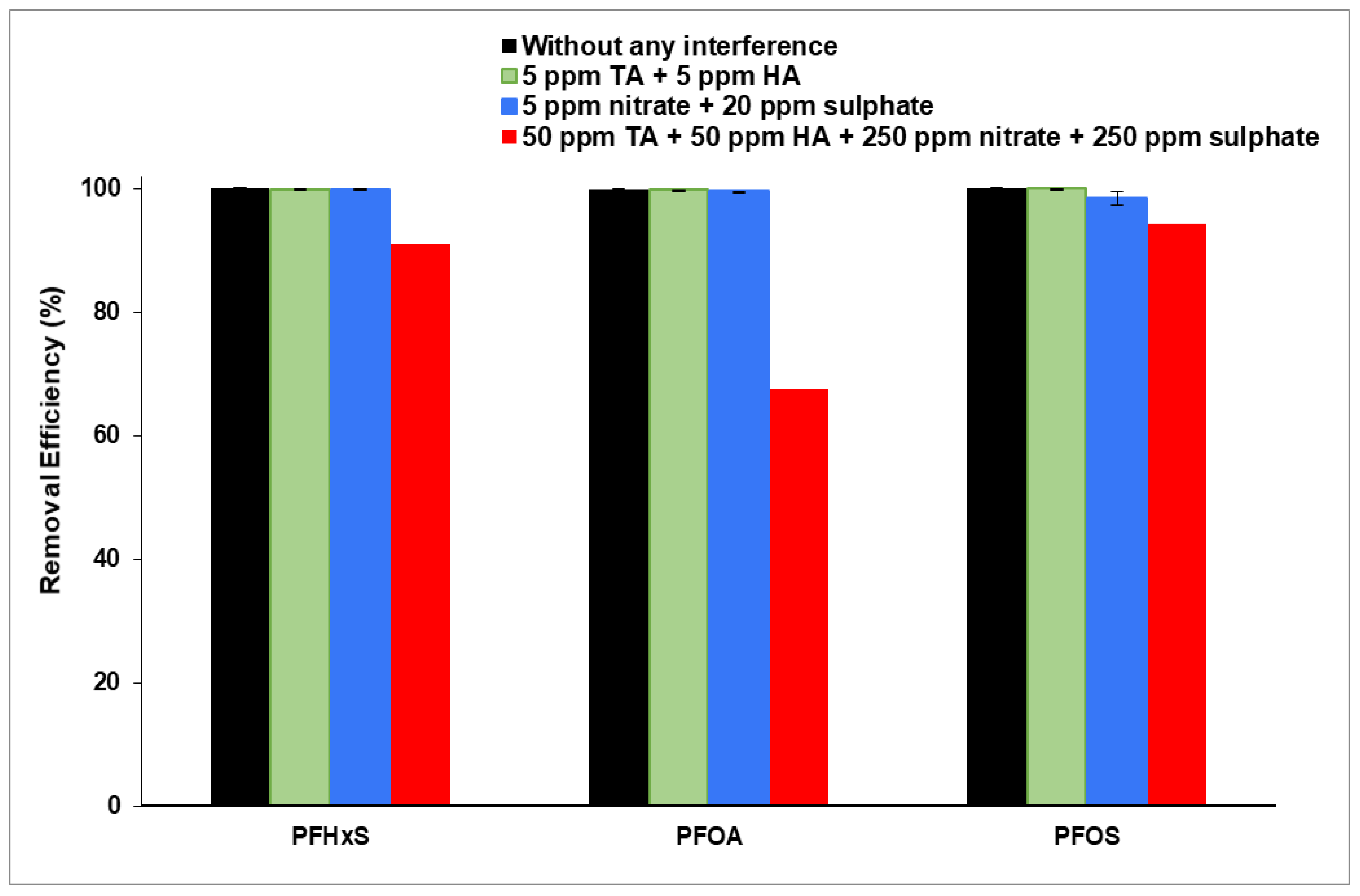
3.3. Interference of Organic and Inorganic Matter on PFAS Removal
3.3.1. Interference of Organic Matter in PFAS Removal
3.3.2. Interference of Inorganic Matter on PFAS Removal
3.3.3. Interference of Highly Concentrated NOM and Inorganic Matter on PFAS Removal
3.4. Regeneration of MIEX® GOLD Resin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maimaiti, A.; Deng, S.; Meng, P.; Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G. Competitive adsorption of perfluoroalkyl substances on anion exchange resins in simulated AFFF-impacted groundwater. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallen, C.; Eaglesham, G.; Drage, D.; Nguyen, T.H.; Mueller, J. A mass estimate of perfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) release from Australian wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucharzyk, K.H.; Darlington, R.; Benotti, M.; Deeb, R.; Hawley, E. Novel treatment technologies for PFAS compounds: A critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 204, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelch, K.E.; Reade, A.; Wolffe, T.A.; Kwiatkowski, C.F. PFAS health effects database: Protocol for a systematic evidence map. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, N.B.; Khalid, A.; Tian, Y.; Ayres, C.; Sabaraya, I.V.; Pietari, J.; Hanigan, D.; Chowdhury, I.; Apul, O.G. Removal of poly- and per-fluoroalkyl substances from aqueous systems by nano-enabled water treatment strategies. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 5, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, N.A.; Rodriguez-Freire, L.; Keswani, M.; Sierra-Alvarez, R. Effect of chemical structure on the sonochemical degradation of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs). Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaggia, A.; Conte, L.; Falletti, L.; Fant, M.; Chiorboli, A. Use of strong anion exchange resins for the removal of perfluoroalkylated substances from contaminated drinking water in batch and continuous pilot plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCleaf, P.; Englund, S.; Östlund, A.; Lindegren, K.; Wiberg, K.; Ahrens, L. Removal efficiency of multiple poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) in drinking water using granular activated carbon (GAC) and anion exchange (AE) column tests. Water Res. 2017, 120, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkola, N.; Sainio, P. Survey of perfluorinated alkyl acids in Finnish effluents, storm water, landfill leachate and sludge. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7979–7987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaine, A.C.; Rich, C.D.; Sedlacko, E.M.; Hundal, L.S.; Kumar, K.; Lau, C.; Mills, M.A.; Harris, K.M.; Higgins, C.P. Perfluoroalkyl acid distribution in various plant compartments of edible crops grown in biosolids-amended soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7858–7865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurwadkar, S.; Dane, J.; Kanel, S.R.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Cawdrey, R.W.; Ambade, B.; Struckhoff, G.C.; Wilkin, R. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in water and wastewater: A critical review of their global occurrence and distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, D.S.; Sjödin, M.; Hellstrandh, M.; Norinder, U.; Nikiforova, V.; Lindberg, J.; Wincent, E.; Bergman, Å.; Cotgreave, I.; Kos, V.M. Cellular accumulation and lipid binding of perfluorinated alkylated substances (PFASs)—A comparison with lysosomotropic drugs. Chem. Interact. 2018, 281, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousins, I.T.; DeWitt, J.C.; Glüge, J.; Goldenman, G.; Herzke, D.; Lohmann, R.; Miller, M.; Ng, C.A.; Scheringer, M.; Vierke, L.; et al. Strategies for grouping per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) to protect human and environmental health. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2020, 22, 1444–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, C.; Kappleman, W.; DiGuiseppi, W. Ecological Considerations of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS). Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2017, 3, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.F.; Anderson, W.B.; Peldszus, S.; Huck, P.M. Ion-Exchange Treatment of Perfluorinated Carboxylic Acids in Water: Comparison of Polystyrenic and Polyacrylic Resin Structures and Impact of Sulfate on Their Performance. ACS ES&T Water 2022, 2, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.-M.; Pan, C.-G.; Yin, C.; Yu, K. Insights into the Understanding of Adsorption Behaviors of Legacy and Emerging Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) on Various Anion-Exchange Resins. Toxics 2023, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, S. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Treatment Techniques in Removing Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Water; UPTEC: Porto, Portugal, 2014; p. 66. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, E.C.A. Removal of Perfluorinated Compounds by Anion Exchange: Factors Affecting Resin Performance and Regeneration. Master’s Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, 2014. Available online: http://www.lib.ncsu.edu/resolver/1840.16/9334 (accessed on 3 March 2014).
- Park, M.; Daniels, K.D.; Wu, S.; Ziska, A.D.; Snyder, S.A. Magnetic ion-exchange (MIEX) resin for perfluorinated alkylsubstance (PFAS) removal in groundwater: Roles of atomic charges for adsorption. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ortiz, C.; Gadea, I.S.; Varó-Galvañ, P.; Maestre-Pérez, S.; Prats-Rico, D. Effect of magnetic ion exchange (MIEX®) on removal of emerging organic contaminants. Chemosphere 2018, 208, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, R.; Senanayake, G.; Dharmasiri, L.; Mathes, J.; Kim, D. A preliminary batch study of sorption kinetics of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions by a magnetic ion exchange (MIEX®) resin and determination of film/pore diffusivity. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X. Response surface methodology directed adsorption of chlorate and chlorite onto MIEX resin and study of chemical properties. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 2454–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Ji, W.; Yang, M.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, X. The study of bromate adsorption onto magnetic ion exchange resin: Optimization using response surface methodology. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 17, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Hua, M.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; Shuang, C.; Li, A. Preparation of permanent magnetic resin crosslinking by diallyl itaconate and its adsorptive and anti-fouling behaviors for humic acid removal. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanga, Y.; Liua, Q.; Hea, Y.; Tangb, M.; Lia, A.; Fana, J. Sorption of tribromophenol with magnetic ion exchange resin: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 113, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateia, M.; Alsbaiee, A.; Karanfil, T.; Dichtel, W.R. Efficient PFAS Removal by Amine-Functionalized Sorbents: Critical Review of the Current Literature. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadee, K.; O’Leary, B.; Smith, P.; Slunjski, M.; Bourke, M. World’s first magnetic ion exchange (MIEX®) water treatment plant to be installed in Western Australia. In American Water Works Association Conference Proceedings; American Water Works Association Tennessee: Louisville, KY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, P.; Fang, X.; Maimaiti, A.; Yu, G.; Deng, S. Efficient removal of perfluorinated compounds from water using a regenerable magnetic activated carbon. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; Liang, Y. Adsorption of perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) from aqueous solution—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chularueangaksorn, P. Study on Effective Adsorption Conditions for Perfluorinated Compounds (PFCs) Removal in Municipal and Industrial Wastewaters in Thailand and Japan. Ph.D. Thesis, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Deng, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, G. Removal of perfluorinated carboxylates from washing wastewater of perfluorooctanesulfonyl fluoride using activated carbons and resins. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, K.; Roy, A.; Yu, G. Understanding the adsorption of PFOA on MIL-101(Cr)-based anionic-exchange metal-organic frameworks: Comparing dft calculations with aqueous sorption experiments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8657–8665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lv, L.; Lan, P.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Zhang, W. Effect of effluent organic matter on the adsorption of perfluorinated compounds onto activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 225–226, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Cheng, J.; Vecitis, C.D.; Hoffmann, M.R. Sorption of perfluorochemicals to granular activated carbon in the presence of ultrasound. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 2250–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Deng, S.; Bei, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of perfluorinated compounds on various adsorbents—A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, Q.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, X. Magnetic ion exchange resin for effective removal of perfluorooctanoate from water: Study of a response surface methodology and adsorption performances. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29267–29278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodard, S.; Berry, J.; Newman, B. Ion exchange resin for PFAS removal and pilot test comparison to GAC. Remediat. J. 2017, 27, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PFAS | Removal Efficiency (%) without Interference | Std (±) | Removal Efficiency (%) in 20 ppm Sulfate + 5 ppm Nitrate | Std (±) | Removal Efficiency (%) in 5 ppm Humic Acid + 5 ppm Tannic Acid | Std (±) | Removal Efficiency (%) in Inorganic and NOM at High Concentration * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFHxS | 100 | 0 | 99.88 | 0.09 | 99.82 | 0.02 | 91.00 |
| PFOA | 99.91 | 0.04 | 99.50 | 0.09 | 99.79 | 0.01 | 67.42 |
| PFOS | 100 | 0 | 98.40 | 1.00 | 99.94 | 0.90 | 94.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamanna, T.; Mahon, P.J.; Hockings, R.K.; Alam, H.; Raymond, M.; Smith, C.; Clarke, C.; Yu, A. Ion Exchange MIEX® GOLD Resin as a Promising Sorbent for the Removal of PFAS Compounds. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6263. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106263
Tamanna T, Mahon PJ, Hockings RK, Alam H, Raymond M, Smith C, Clarke C, Yu A. Ion Exchange MIEX® GOLD Resin as a Promising Sorbent for the Removal of PFAS Compounds. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(10):6263. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106263
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamanna, Tasnuva, Peter J. Mahon, Rosalie K. Hockings, Husna Alam, Matt Raymond, Craig Smith, Craig Clarke, and Aimin Yu. 2023. "Ion Exchange MIEX® GOLD Resin as a Promising Sorbent for the Removal of PFAS Compounds" Applied Sciences 13, no. 10: 6263. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106263
APA StyleTamanna, T., Mahon, P. J., Hockings, R. K., Alam, H., Raymond, M., Smith, C., Clarke, C., & Yu, A. (2023). Ion Exchange MIEX® GOLD Resin as a Promising Sorbent for the Removal of PFAS Compounds. Applied Sciences, 13(10), 6263. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106263






