Distinguishing Malignant Melanoma and Benign Nevus of Human Skin by Retardance Using Mueller Matrix Imaging Polarimeter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Preparation of Human Skin Specimens
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Vectorial Retardance Imaging
3. Results and Discussion
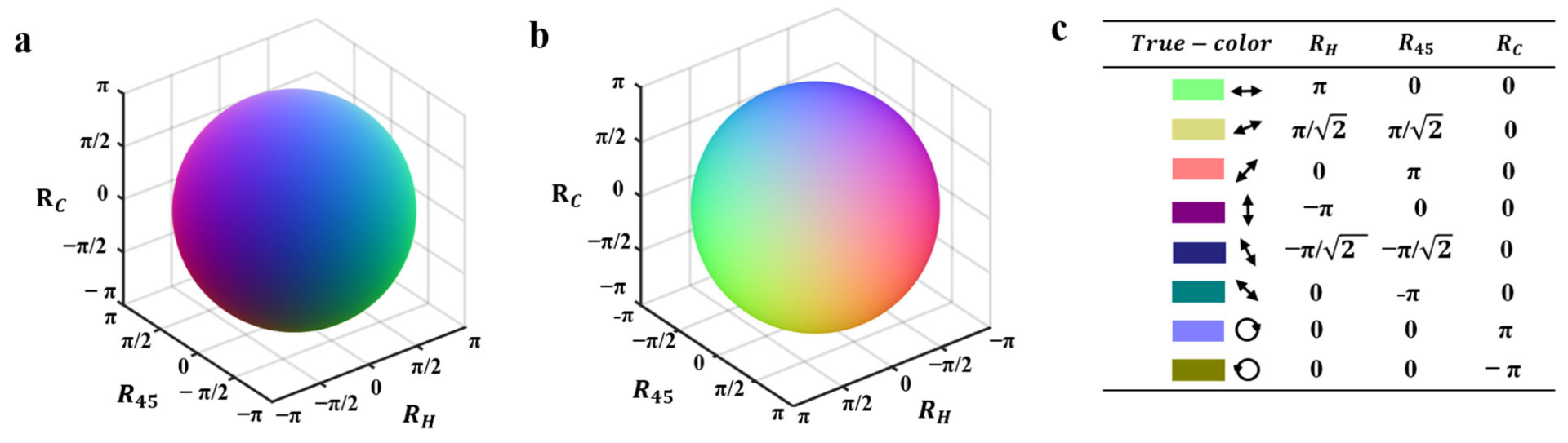
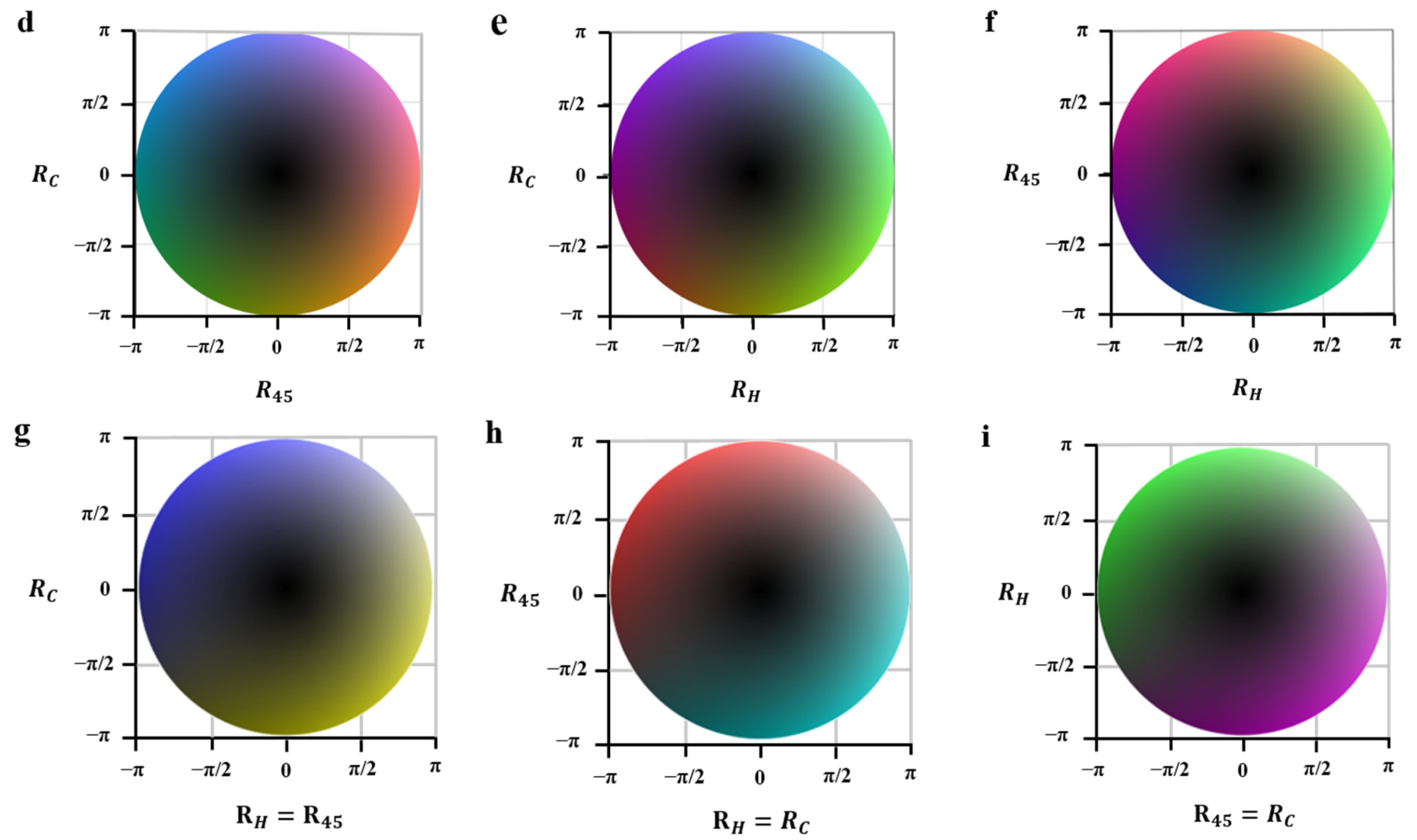
3.1. Test Experiment of True-Color Vectorial Retardance Imaging by a Vortex Retarder
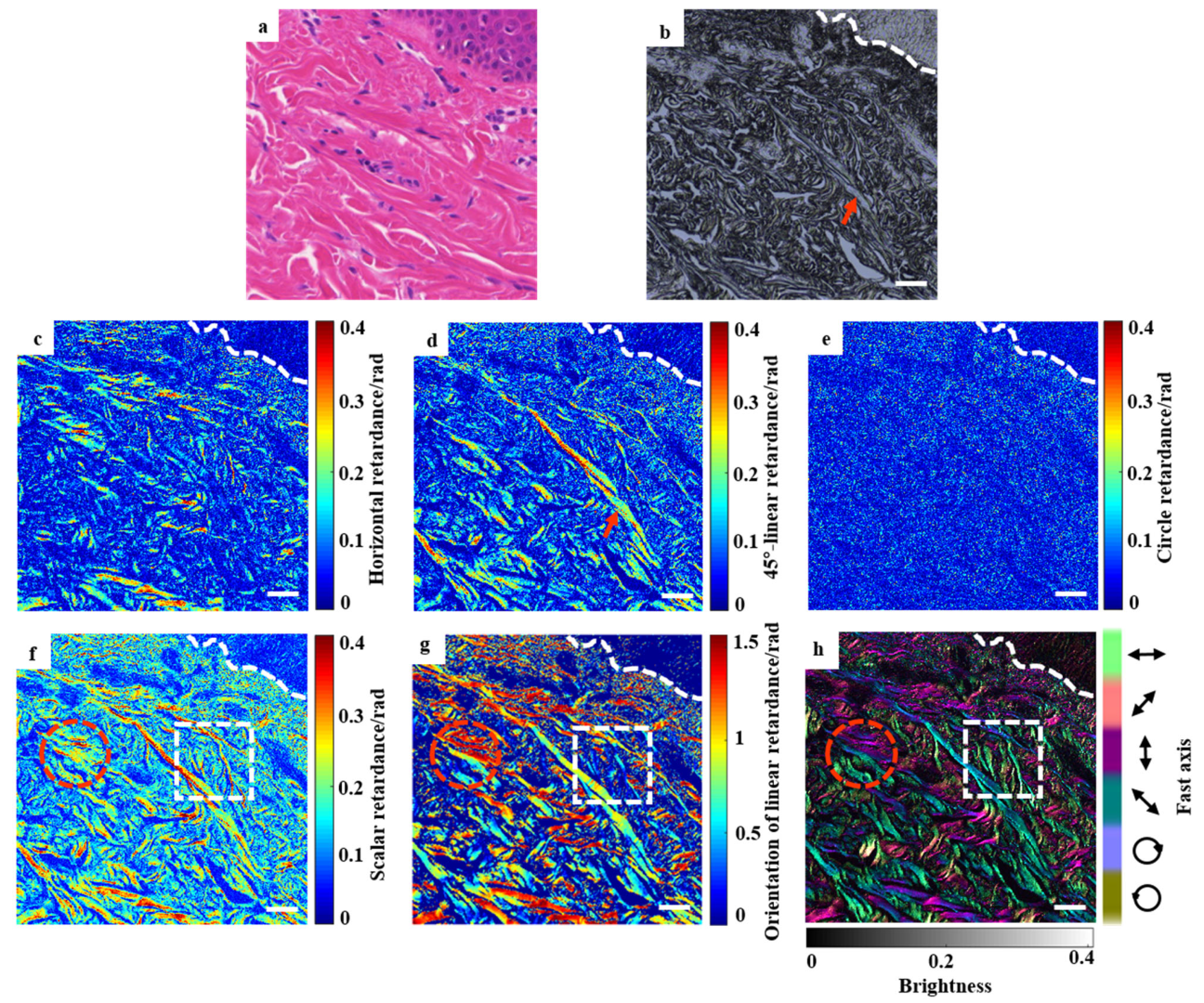
3.2. Discrimination of Different Human Skin Tissues Using Vectorial Retardance
3.2.1. Quantitative Classification
3.2.2. Qualitative Assessment by True-Color Vectorial Retardance Imaging
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, M.; Singh, D.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Vaccarella, S.; Meheus, F.; Cust, A.E.; de Vries, E.; Whiteman, D.C.; Bray, F. Global Burden of Cutaneous Melanoma in 2020 and Projections to 2040. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babino, G.; Lallas, A.; Longo, C.; Moscarella, E.; Alfano, R.; Argenziano, G. Dermoscopy of melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer. G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 150, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kornek, T.; Augustin, M. Skin cancer prevention. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2013, 11, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, M.A.; Zakaria, A.; Nizran, P. Skin Cancer. Prim. Care 2015, 42, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OCatalano, O.; Roldán, F.A.; Varelli, C.; Bard, R.; Corvino, A.; Wortsman, X. Skin cancer: Findings and role of high-resolution ultrasound. J. Ultrasound 2019, 22, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marghoob, N.G.; Liopyris, K.; Jaimes, N. Dermoscopy: A Review of the Structures That Facilitate Melanoma Detection. J. Am. Osteopat. Assoc. 2019, 119, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobos, M. Histopathologic classification and prognostic factors of melanoma: A 2021 update. G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 156, 300–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, S. Clinical applications of reflectance confocal microscopy in the management of cutaneous tumors. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas 2008, 99, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, R.P.; Rabinovitz, H.S.; Oliviero, M.; Kopf, A.W.; Saurat, J.H. Dermoscopy of pigmented skin lesions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 52, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, C.; Haenssle, H.A. Non-invasive tools for the diagnosis of cutaneous melanoma. Ski. Res. Technol. 2017, 23, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.Q.; Ma, S.J.; Mo, Y.; Huo, S.T.; Wen, Y.Q.; Chen, Q. Comparison of dermoscopy and reflectance confocal microscopy for the diagnosis of malignant skin tumours: A meta-analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broggi, G.; Verzì, A.E.; Lacarrubba, F.; Micali, G.; Caltabiano, R. Horizontal Histopathology Correlation with In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy in Inflammatory Skin Diseases: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Datto, M.; Duncavage, E.J.; Kulkarni, S.; Lindeman, N.I.; Roy, S.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Wolff, D.J.; Younes, A.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation and Reporting of Sequence Variants in Cancer: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology, American Society of Clinical Oncology, and College of American Pathologists. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouzin, M.; Marini, M.; Chirico, G.; Granucci, F.; Mingozzi, F.; Colombo, R.; D’alfonso, L.; Sironi, L.; Collini, M. Melanin concentration maps by label-free super-resolution photo-thermal imaging on melanoma biopsies. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 1173–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sober, A.J.; Fitzpatrick, T.B.; Mihm, M.C.; Wise, T.G.; Pearson, B.J.; Clark, W.H.; Kopf, A.W. Early recognition of cutaneous melanoma. JAMA 1979, 242, 2795–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christos, P.J.; A Oliveria, S.; Berwick, M.; Guerry, D.; E Elder, D.; Synnestvedt, M.; A Fine, J.; Barnhill, R.L.; Halpern, A.C. Signs and symptoms of melanoma in older populations. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2000, 53, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Maloufi, S.; Louie, D.C.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Q.; Lee, T.K.; Tang, S. Investigating the depolarization property of skin tissue by degree of polarization uniformity contrast using polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 5073–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasooriya, P.R.; Mendis, B.R.R.N.; Lombardi, T. A Case Series on Intraoral Blue Nevi with a Literature Review-Based Clinico-Pathologic Comparison of Intraoral Blue Nevi with Other Oral Melanocytic Nevi. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtenay, L.A.; González-Aguilera, D.; Lagüela, S.; Del Pozo, S.; Ruiz-Mendez, C.; Barbero-García, I.; Román-Curto, C.; Cañueto, J.; Santos-Durán, C.; Cardeñoso-Álvarez, M.E.; et al. Hyperspectral imaging and robust statistics in non-melanoma skin cancer analysis. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 5107–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horobin, R.; Kiernan, J. Conn’s Biological Stains: A Handbook of Dyes, Stains and Fluorochromes for Use in Biology and Medicine; BIOS Scientific Publishers: Milton Park, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, K.Y.; Smith, E.R.; Booth, J.; Compton, R.G.; Brennan, C.M.; Atherton, J.H. Kinetics and Mechanism of Dyeing Processes: The Dyeing of Cotton Fabrics with a Procion Blue Dichlorotriazinyl Reactive Dye. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 186, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantine, V.S.; Mowry, R.W. Selective staining of human dermal collagen. I. An analysis of standard methods. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1968, 50, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, M.F.G.; Ghosh, N.; Moriyama, E.H.; Wilson, B.C.; Vitkin, I.A. Proof-of-principle demonstration of a Mueller matrix decomposition method for polarized light tissue characterization in vivo. J. Biomed. Opt. 2009, 14, 014029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehbinder, J.; Haddad, H.; Deby, S.; Teig, B.; Nazac, A.; Novikova, T.; Pierangelo, A.; Moreau, F. Ex vivo Mueller polarimetric imaging of the uterine cervix: A first statistical evaluation. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 071113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arifler, D.; Pavlova, I.; Gillenwater, A.; Richards-Kortum, R. Light Scattering from Collagen Fiber Networks: Micro-Optical Properties of Normal and Neoplastic Stroma. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 3260–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prockop, D.J.; Kivirikko, K.I. Collagens: Molecular biology, diseases and potentials for therapy. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 64, 403–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubry, L.; Sy, K.; Sayd, T.; Ferraro, V. Collagen Peptides-Minerals Complexes from the Bovine Bone by-Product to Prevent Lipids Peroxidation in Meat and Butter and to Quench Free Radicals—Influence of Proteases and of Steam Sterilisation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, I.; Velasquez, P.; Fernandez-Pousa, C.R.; Sanchez-Lopez, M.M. Jones matrix method for predicting and optimizing the optical modulation properties of a liquid-crystal display. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 3697–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schucht, P.; Lee, H.R.; Mezouar, H.M.; Hewer, E.; Raabe, A.; Murek, M.; Zubak, I.; Goldberg, J.; Kovari, E.; Pierangelo, A.; et al. Visualization of white matter fiber tracts of brain tissue sections with wide-field imaging Mueller polarimetry. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 4376–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Akkin, T.; Magnain, C.; Wang, R.; Dubb, J.; Kostis, W.J.; A Yaseen, M.; Cramer, A.; Sakadžić, S.; Boas, D. Polarization sensitive optical coherence microscopy for brain imaging. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 2213–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.L.; Nguyen, D.T.; Le, T.H.; Phan, Q.-H.; Pham, T.-T. Characterization of healthy and cancerous human skin tissue utilizing Stokes–Mueller polarimetry technique. Opt. Commun. 2021, 480, 126460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.W.; Taberner, A.J.; Nash, M.P.; Nielsen, P. Quantifying optical anisotropy in soft tissue membranes using Mueller matrix imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2021, 26, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancelin, S.; Nazac, A.; Ibrahim, B.H.; Dokládal, P.; Decencière, E.; Teig, B.; Haddad, H.; Fernandez, H.; Schanne-Klein, M.C.; De Martino, A. Determination of collagen fiber orientation in histological slides using Mueller microscopy and validation by second harmonic generation imaging. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 22561–22574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, H.; Sun, Y.; He, H.; Chen, B.; He, C.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H. Distinguishing tissue structures via polarization staining images based on different combinations of Mueller matrix polar decomposition parameters. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2022, 152, 106955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; He, H.; Zeng, N.; Du, E.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; He, Y.; Ma, H. Characterizing the microstructures of biological tissues using Mueller matrix and transformed polarization parameters. Biomed. Opt. Express 2014, 5, 4223–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierangelo, A.; Nazac, A.; Benali, A.; Validire, P.; Cohen, H.; Novikova, T.; Ibrahim, B.H.; Manhas, S.; Fallet, C.; Antonelli, M.R.; et al. Polarimetric imaging of uterine cervix: A case study. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 14120–14130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, A.M.; Naoun, K.; Louis-Dorr, V.; Mala, L.; Raspiller, A. Linear dichroism of the retinal nerve fiber layer expressed with Mueller matrices. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Vitkin, I.A. Tissue polarimetry: Concepts, challenges, applications, and outlook. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 110801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, L.; Yu, X.; Meng, D.; Gu, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z. Mueller Matrix Decomposition and Image for Non-Destructive Testing of UAVs Skin. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.T. Physical Optics; Publishing House of Electronics Industry: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; He, C.; Liao, R.; Zeng, N.; Liu, S.; Ma, H. Division of focal plane polarimeter-based 3 × 4 Mueller matrix microscope: A potential tool for quick diagnosis of human carcinoma tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 056002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushenko, Y.A.; Gorskii, M.P.; Dubolazov, A.V.; Motrich, A.V.; Ushenko, V.A.; Sidor, M.I. Spatial-frequency Fourier polarimetry of the complex degree of mutual anisotropy of linear and circular birefringence in the diagnostics of oncological changes in morphological structure of biological tissues. Quantum Electron. 2012, 42, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.N.; Phan, Q.H.; Le, T.H.; Pham, T.T. Classification of human skin cancer using Stokes-Mueller decomposition method and artificial intelligence models. Optik 2022, 249, 168239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; He, H.; Chang, J.; Dong, Y.; Liu, S.; Zeng, N.; He, Y.; Ma, H. Characterizing microstructures of cancerous tissues using multispectral transformed Mueller matrix polarization parameters. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 2934–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, G.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Li, Y. Quantitatively characterizing the microstructural features of collagen fiber bundles with or without tenocytes by Mueller imaging polarimeter. In Proceedings of the Biomedical Imaging and Sensing Conference 2021, Online, 20–22 April 2021; Volume 11925, pp. 99–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, P.; Xu, J.; Wang, R.K. Imaging and visualization of the polarization state of the probing beam in polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 113, 231101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huard, S. Polarization of Light; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, D. Polarized Light, 2nd ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chipman, R.A.; Lam, W.S.T.; Young, G. Polarized Light and Optical Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, O.N.; Arce-Diego, J.L. Mueller matrix differential decomposition. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 1942–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, C.; Shao, C.; He, H.; He, C.; Ma, H. Evaluating Tissue Mechanical Properties Using Quantitative Mueller Matrix Polarimetry and Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, B.; Wan, J.; Si, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Ma, H. Polarization imaging-based radiomics approach for the staging of liver fibrosis. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 1564–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, B.; Rehbinder, J.; Dellinger, J.; Heinrich, C.; Torzynski, M.; Spenlé, C.; Bagnard, D.; Zallat, J. Monitoring subcutaneous tumors using Mueller polarimetry: Study on two types of tumors. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 6055–6065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, C.; Rehbinder, J.; Zallat, J. Revisiting the generalized polar decomposition of Mueller matrices. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2020, 37, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatenko, D.N.; Shkirin, A.V.; Lobachevsky, Y.P.; Gudkov, S.V. Applications of Mueller Matrix Polarimetry to Biological and Agricultural Diagnostics: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Yao, W.; Myers, K.M.; Vink, J.Y.; Wapner, R.J.; Hendon, C.P. Analyzing three-dimensional ultrastructure of human cervical tissue using optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 1090–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chue-Sang, J.; Holness, N.; Gonzalez, M.; Greaves, J.; Saytashev, I.; Stoff, S.; Gandjbakhche, A.; Chernomordik, V.V.; Burkett, G.; Ramella-Roman, J.C. Use of Mueller matrix colposcopy in the characterization of cervical collagen anisotropy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 121605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, K.; Ashraf, S.; Ahmad, S.; Ikram, M. Ex vivo characterization of normal and adenocarcinoma colon samples by Mueller matrix polarimetry. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 056012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, A.M.; Chung, J.R.; Baba, J.S.; Spiegelman, C.H.; Amoss, M.S.; Cote, G.L. Mueller matrix imaging for cancer detection. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37439), Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2003; Volume 2, pp. 1027–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, I.; Khaliq, A.; Iqbal, M.; Khan, S. Mueller matrix polarimetry for characterization of skin tissue samples: A review. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 30, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.L.; Huynh, T.N.; Nguyen, D.T.; Vo, T.V.; Hien, P. Characterization of healthy and nonmelanoma-induced mouse utilizing the Stokes-Mueller decomposition. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 125003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhou, G.; Liu, L.; Zheng, M. Hybrid calibration method of a wide-view-angle Mueller polarimeter for hyper-numerical-aperture imaging systems. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2020, 18, 081202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, C.; Zhou, G.; Li, L. High-fidelity and rapid cellular-level Mueller matrix imaging for tissue identification with unstained sections. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Ma, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, A.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, G.; Li, Y. Research on the Reliability of Mueller Imaging Polarimeter in pathological diagnosis. Acta Optica Sinica. 2022, 42, 1512002. [Google Scholar]
- Maitra, S.; Gartley, M.G.; Kerekes, J.P. Relation between degree of polarization and Pauli color coded image to characterize scattering mechanisms. Polariz. Meas. Anal. Remote Sens. X SPIE 2012, 8364, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, J.; Marjanovic, M.; Chaney, E.J.; Cradock, K.A.; Higham, A.M.; Liu, Z.G.; Gao, Z.; Boppart, S.A. Differentiation of breast tissue types for surgical margin assessment using machine learning and polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 3021–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Mesa, K.J.; South, F.A.; Chaney, E.J.; Spillman, D.R.; Barkalifa, R.; Marjanovic, M.; Carney, P.S.; Higham, A.M.; et al. Complementary use of polarization-sensitive and standard OCT metrics for enhanced intraoperative differentiation of breast cancer. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 6519–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.Y.; Chipman, R.A. Interpretation of Mueller matrices based on polar decomposition. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1996, 13, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffar, M.; Pradhan, A. Mapping of Retardance, Diattenuation and Polarizance vector on Poincare Sphere for Diagnosis and Classification of Cervical Precancer. J. Biophotonics 2020, 13, e201960139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.W.; Lin, C.J. A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2002, 13, 415–425. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.W.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. A practical Guide to Support Vector Classification. 2003, 1396–1400. Available online: https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/papers/guide/guide.pdf (accessed on 19 May 2016).
- Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.; Hao, J.; Yu, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, W.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Lin, Z.; et al. Label-free identification of human coronary atherosclerotic plaque based on three-dimensional quantitative assessment of multiphoton microscopy images. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 2979–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Thai, T.C.; Castellano, T.; Gunderson, C.C.; Moore, K.; Mannel, R.S.; Liu, H.; Zheng, B.; Qiu, Y. Developing a new radionics-based CT image marker to detect lymph node metastasis among cervical cancer patients. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 197, 105759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnemari, S.; Alshammari, M. Detecting Phishing Domains Using Machine Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Luo, C.; Lv, X.; Shi, Y.; Yang, J.; Meng, X.; Chen, C.; Su, J.; et al. Raman spectroscopy combined with machine learning algorithms for rapid detection Primary Sjögren’s syndrome associated with interstitial lung disease. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 40, 103057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Hwang, H.; Sohn, B.; Park, K.; Han, K.; Ahn, S.S.; Lee, W.; Chu, M.K.; Heo, K.; Lee, S.K. Development and Validation of MRI-Based Radiomics Models for Diagnosing Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy. Korean J. Radiol. 2022, 23, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, Y.; Li, S.; Guo, F.; Xue, H.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xie, W.; Zhu, F. Predicting renal function recovery and short-term reversibility among acute kidney injury patients in the ICU: Comparison of machine learning methods and conventional regression. Ren. Fail. 2022, 44, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Wei, T.; Fan, R.; Su, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Qi, Y.; Li, X. Development and validation of a machine learning model to predict venous thromboembolism among hospitalized cancer patients. Asia Pac. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2022, 9, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borovkova, M.; Peyvasteh, M.; Dubolazov, O.; Ushenko, Y.; Ushenko, V.; Bykov, A.; Deby, S.; Rehbinder, J.; Novikova, T.; Meglinski, I. Complementary analysis of Mueller-matrix images of optically anisotropic highly scattering biological tissues. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. 2018, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Naqa, I.; Grigsby, P.; Apte, A.; Kidd, E.; Donnelly, E.; Khullar, D.; Chaudhari, S.; Yang, D.; Schmitt, M.; Laforest, R.; et al. Exploring feature-based approaches in PET images for predicting cancer treatment outcomes. Pattern Recognit. 2009, 42, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaynes, E.T. Probability Theory: The Logic of Science; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y. Limit Error and Confidence Level in Sampling; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Park, W.J.; Park, J.B. History and application of artificial neural networks in dentistry. Eur. J. Dent. 2018, 12, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, F.G.; Guo, W.B.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.L.; Li, M. Risk prediction model for early postoperative death in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study based on random forest algorithm and logistic regression. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 4, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Zhou, J.; Chung, C.T.; Lee, R.O.Y.; Bazoukis, G.; Letsas, K.P.; Wong, W.T.; Wong, I.C.K.; Mok, N.S.; Liu, T.; et al. Comparing the Performance of Published Risk Scores in Brugada Syndrome: A Multi-center Cohort Study. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2022, 47, 101381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayalibay, B.; Jensen, G.; Smagt, P. CNN-based segmentation of medical imaging data. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.03056. [Google Scholar]
- Suhail, Z.; Denton, E.R.E.; Zwiggelaar, R. Classification of micro-calcification in mammograms using scalable linear Fisher discriminant analysis. Med Biol. Eng. Comput. 2018, 56, 1475–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffar, M.; Pradhan, A. Spatial autocorrelation analysis on two-dimensional images of Mueller matrix for diagnosis and differentiation of cervical precancer. J. Biophotonics 2020, 13, e202000006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.; He, H.; Zeng, N.; Sun, M.; Guo, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Ma, H. Mueller matrix polarimetry for differentiating characteristic features of cancerous tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 76013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Pradhan, A. Mueller decomposition images for cervical tissue: Potential for discriminating normal and dysplastic state. Opt Express. 2009, 17, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Wood, M.F.G.; Vitkin, I.A. Mueller matrix decomposition for extraction of individual polarization parameters from complex turbid media exhibiting multiple scattering, optical activity, and linear birefringence. J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 044036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNichols, R.J.; Coté, G.L. Optical glucose sensing in biological fluids: An overview. J. Biomed. Opt. 2000, 5, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; He, H.; Lin, J.; Dong, Y.; Chen, D.; Ma, H.; Elson, D.S. Assessment of tissue polarimetric properties using Stokes polarimetric imaging with circularly polarized illumination. J. Biophotonics 2018, 11, e201700139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, P.; Schwarz, T. Dermatologie Venerologie: Grundlagen. Klinik. Atlas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Q. Spectropolarimetric imaging for pathological analysis of skin. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, D236–D246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Sun, L.; Zhang, E. Depth selectivity for the assessment of microstructure by polarization studies. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safrani, A.; Aharon, O.; Mor, S.; Arnon, O.; Rosenberg, L.; Abdulhalim, I. Skin biomedical optical imaging system using dual wavelength polarimetric control with liquid crystals. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 026024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ney, M.; Abdulhalim, I. Modeling of reflectometric and ellipsometric spectra from the skin in the terahertz and submillimeter waves region. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 067006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon, O.; Abdulhalim, I.; Arnon, O.; Rosenberg, L.; Dyomin, V.; Silberstein, E. Differential optical spectropolarimetric imaging system assisted by liquid crystal devices for skin imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 086008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ney, M.; Abdulhalim, I. Ultrahigh polarimetric image contrast enhancement for skin cancer diagnosis using InN plasmonic nanoparticles in the terahertz range. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 125007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, L.; Yitzhaky, Y.; Abdulhalim, I. Classification of skin moles from optical spectropolarimetric images: A pilot study. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 111403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuleil, M.J.; Abdulhalim, I. Tunable achromatic liquid crystal waveplates. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 5487–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuleil, M.J.; Abdulhalim, I. Broadband ellipso-polarimetric camera utilizing tunable liquid crystal achromatic waveplate with improved field of view. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 12011–12024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Aisheh, M.; Abutoama, M.; Abuleil, M.J.; Abdulhalim, I. Fast tunable metamaterial liquid crystal achromatic waveplate. Nanophotonics 2023, 12, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Ning, T.; Long, C.; Zhou, G. Optimal design for a broadband Stokes polarimeter of liquid crystal variable retarders. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 7490–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Normal | BE | MM | Total | Mean Age | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients | 21 | 20 | 23 | 64 | 68 ± 12 |
| Cases | 853 | 851 | 847 | 2551 |
| Train Set | Test Set | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | BE | MM | Total | Normal | BE | MM | Total | |
| Cases | 500 | 500 | 500 | 1500 | 353 | 351 | 347 | 1051 |
| SVM Classifier | Retardance-Related Parameters | Cross-Validation Accuracy | Prediction Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classifier I | 82.80% | 81.64% | |
| Classifier II | 87.40% | 84.30% | |
| Classifier III | 87.20% | 85.92% | |
| Classifier IV | 88.33% | 87.92% | |
| Classifier V | 95.20% | 84.11% | |
| Classifier VI | 95.33% | 82.97% | |
| Classifier VII | 96.27% | 85.16% | |
| Classifier VIII | () | 98.60% | 96.19% |
| Number | Polarimetric Imaging Techniques | Polarization Parameters | Polarization Staining Methods |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MMIP [33] | Scalar retardance Azimuth of the slow axis | False-color imaging by one parameter |
| 2 | MMIP [34] | Diattenuation Linear retardance Azimuth of the slow axis | True-color imaging by several parameters |
| 3 | DoFP polarization microscope [41] | Degree of linear polarization Angle of polarization | True-color imaging by several parameters |
| 4 | PS-OCT [47] | Stokes parameters | True-color imaging by several parameters |
| 5 | Stokes polarimeter [96] | Stokes parameters | True-color imaging by several parameters |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Chen, G.; Li, Y. Distinguishing Malignant Melanoma and Benign Nevus of Human Skin by Retardance Using Mueller Matrix Imaging Polarimeter. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6514. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116514
Wang W, Chen G, Li Y. Distinguishing Malignant Melanoma and Benign Nevus of Human Skin by Retardance Using Mueller Matrix Imaging Polarimeter. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(11):6514. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116514
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wen’ai, Guoqiang Chen, and Yanqiu Li. 2023. "Distinguishing Malignant Melanoma and Benign Nevus of Human Skin by Retardance Using Mueller Matrix Imaging Polarimeter" Applied Sciences 13, no. 11: 6514. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116514
APA StyleWang, W., Chen, G., & Li, Y. (2023). Distinguishing Malignant Melanoma and Benign Nevus of Human Skin by Retardance Using Mueller Matrix Imaging Polarimeter. Applied Sciences, 13(11), 6514. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13116514






