Assessment of the Central Nervous System in Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) Using Magnetic Resonance (MR) Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Patients, Materials, and Methods
2.1. Structural Examinations
2.2. 1H MRS Examinations
2.3. DWI Examinations
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Data
3. Results
3.1. Structural Examination
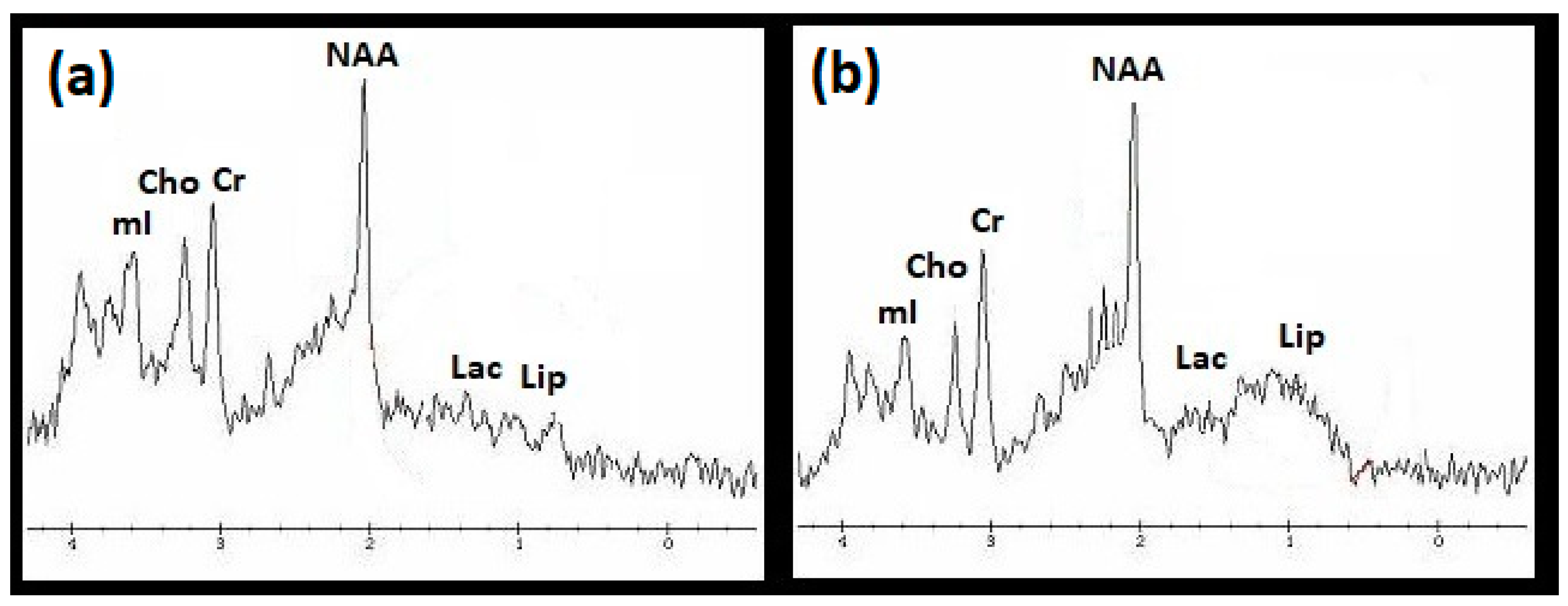
3.2. 1H MRS Examination
- Higher Lip/Cr concentrations in the frontal lobes (p < 0.001), basal ganglia (p < 0.001), cerebellum (p < 0.05), and in the whole brain (p < 0.001);
- Lower NAA/Cr concentrations in the frontal lobes (p < 0.05) and in the basal ganglia (p < 0.01);
- Lower Cho/Cr concentrations in the basal ganglia (p < 0.01), cerebellum (p < 0.05), and in the whole brain (p < 0.05);
- Lower mI/Cr concentrations in the frontal lobes (p < 0,05), basal ganglia (p < 0.05), hippocampi (p < 0.05), and in the whole brain (p < 0.001).
3.3. DWI Examination
4. Discussion
4.1. Structural Examination
4.2. 1H MRS Examination
4.3. DWI Examination
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huss, M. Chronische Alkoholskrankheit oder Alcoholismus Chronicus: Ein Beitrag zur Kenntniss der Vergiftungs-Krankheiten; Van Dem Busch, G., Ed.; Kessinger Publishing: Whitefish, MT, USA, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Abel, E.L. Was the fetal alhohol syndrome recognized by the Greek and Romans? Alcohol Alcohol. 1999, 34, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freind, J. The History of Physick: From the Time of Galen, to the Beginning of the Sixteenth Century. Chiefly with Regard to Practice. In a Discourse Written to Doctor Mead; Gale ECCO: London, UK, 1726. [Google Scholar]
- Watney, J. Mother’s Ruin: A History of Gin; Owen: London, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Lancereaux, E. De l’Alcoolisme et de Ses Conséquences au Point de Vue de L’état Physique, Intellectuel et Moral des Populations. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculté de Paris, Paris, France, 1878. [Google Scholar]
- Lemoine, P.; Harousseau, H.; Borteyru, J.P.; Menuet, J.C. Les enfantes de parents alcoholiques: Anomalies observees a propos de 127 cas. Quest Med. 1968, 21, 476–482. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, K.; Smith, D.; Ulleland, C.; Streissguth, A. Pattern of malformation in offspring of chronic alcoholic mothers. Lancet 1973, 301, 1267–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, E.L. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome. From Mechanism to Prevention; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Streissguth, A.P.; O’Malley, K. Neuropsychiatric implications and long-term consequences of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Semin. Clin. Neuropsychiatry 2000, 5, ascnp0050177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, H.M.; Streissguth, A.P. Identifying maternal self-reported alcohol use associated with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astley, S.J. Diagnostic Guide for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. The 4-Digit Diagnostic Code TM, 3rd ed.; University of Washinghton: Seattle, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, E.P.; Clarren, S.; Weinberg, J.; Jonsson, E. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder: Management and Policy Perspectives of FASD; Wiley-Blackwell: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Astley, S.J.; Aylward, E.H.; Olson, H.C.; Kerns, K.; Brooks, A.; Coggins, T.E.; Davies, J.; Dorn, S.; Gendler, B.; Jirikowic, T.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging outcomes from a comprehensive magnetic resonance study of children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 1671–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biffen, S.C.; Warton, C.M.R.; Lindinger, N.; Randall, S.R.; Lewis, C.E.; Molteno, C.D.; Jacobson, J.L.; Jacobson, S.W.; Meintjes, E.M. Reductions in corpus callosum volume partially mediate effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on IQ. Front. Neuroanat. 2018, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, S.W.; Jacobson, J.L.; Molteno, C.D.; Warton, C.M.; Wintermark, P.; Hoyme, H.E.; De Jong, G.; Taylor, P.; Warton, F.; Lindinger, N.M.; et al. Heavy Prenatal Alcohol Exposure is Related to Smaller Corpus Callosum in Newborn MRI Scans. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dyląg, K.A.; Sikora-Sporek, A.; Bańdo, B.; Boroń-Zyss, J.; Drożdż, D.; Dumnicka, P.; Przybyszewska, K.; Sporek, M.; Walocha, J.W.; Wojciechowski, W.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings among children with fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS), partial fetal alcohol syndrome (pFAS) and alcohol related neurodevelopmental disorders (ARND). Przegl. Lek. 2016, 73, 605–609. [Google Scholar]
- Inkelis, S.M.; Moore, E.M.; Bischoff-Grethe, A.; Riley, E.P. Neurodevelopment in adolescents and adults with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASD): A magnetic resonance region of interest analysis. Brain Res. 2020, 1732, 146654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bookstein, F.L.; Streissguth, A.P.; Sampson, P.D.; Connor, P.D.; Barr, H.M. Corpus callosum shape and neuropsychological deficits in adult males with heavy fetal alcohol exposure. NeuroImage 2002, 15, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donald, K.A.; Eastman, E.; Howells, F.M.; Adnams, C.; Riley, E.P.; Woods, R.P.; Narr, K.L.; Stein, D.J. Neuroimaging effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on the developing human brain: A magnetic resonance imaging review. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2015, 27, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Phillips, O.R.; Kan, E.; Sulik, K.K.; Mattson, S.N.; Riley, E.P.; Jones, K.L.; Adnams, C.M.; May, P.A.; O’Connor, M.J.; et al. Callosal Thickness Reductions Relate to Facial Dysmorphology in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2012, 36, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sowell, E.R.; Thompson, P.M.; Mattson, S.N.; Tessner, K.D.; Jernigan, T.L.; Riley, E.P.; Toga, A.W. Voxel-based morphometric analyses of the brain in children and adolescents prenatally exposed to alcohol. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treit, S.; Beaulieu, C. Imaging Brain Structure in FASD. In Ethical and Legal Perspectives in Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASD); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 77–93. [Google Scholar]
- Treit, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, D.; Baugh, L.; Rasmussen, C.; Andrew, G.; Pei, J.; Beaulieu, C. Sexual dimorphism of volume reduction but not cognitive deficit in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: A combined diffusion tensor imaging, cortical thickness and brain volume study. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 15, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemingway, S.J.A.; Davies, J.K.; Jirikowic, T.; Olson, E.M. What proportion of the brain structural and functional abnormalities observed among children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder is explained by their prenatal alcohol exposure and their other prenatal and postnatal risks? Adv. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 7, 41. [Google Scholar]
- Sowell, E.R.; Thompson, P.M.; Mattson, S.N.; Tessner, K.D.; Jernigan, T.L.; Riley, E.P.; Toga, A.W. Regional brain shape abnormalities persist into adolescence after heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Cereb. Cortex. 2002, 12, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Archibald, S.L.; Fennema-Notestine, C.; Gamst, A.; Riley, E.P.; Mattson, S.N.; Jernigan, T.L. Brain dysmorphology in individuals with severe prenatal alcohol exposure. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2001, 43, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meintjes, E.M.; Narr, K.L.; Van Der Kouwe, A.J.; Molteno, C.D.; Pirnia, T.; Gutman, B.; Woods, R.P.; Thompson, P.M.; Jacobson, J.L.; Jacobson, S.W. A tensor-based morphometry analysis of regional differences in brain volume in relation to prenatal alcohol exposure. NeuroImage Clin. 2014, 5, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Little, G.; Beaulieu, C. Multivariate models of brain volume for identification of children and adolescents with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dodge, N.C.; Thomas, K.G.F.; Meintjes, E.M.; Molteno, C.D.; Jacobson, J.L.; Jacobson, S.W. Reduced Hippocampal Volumes Partially Mediate Effects of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure on Spatial Navigation on a Virtual Water Maze Task in Children. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 44, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roediger, D.J.; Krueger, A.M.; de Water, E.; Mueller, B.A.; Boys, C.A.; Hendrickson, T.J.; Schumacher, M.J.; Mattson, S.N.; Jones, K.L.; Lim, K.O.; et al. Hippocampal subfield abnormalities and memory functioning in children with fetal alcohol Spectrum disorders. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2020, 83, 106944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boronat, S.; Sanchez-Montanez, A.; Gomez-Barros, N.; Jacas, C.; Martinez-Ribot, L.; Vázquez, E.; Del Campo, M. Correlation between morphological MRI findings and specific diagnostic categories in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 60, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, E.M.; Aliani, M. Metabolomics and fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fagerlund, Å.; Heikkinen, S.; Autti-Rämö, I.; Korkman, M.; Timonen, M.; Kuusi, T.; Riley, E.P.; Lundbom, N. Brain metabolic alterations in adolescents and young adults with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 2097–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Plessis, L.; Jacobson, J.L.; Jacobson, S.W.; Hess, A.T.; van der Kouwe, A.; Avison, M.J.; Molteno, C.D.; Stanton, M.E.; Stanley, J.A.; Peterson, B.S.; et al. An in vivo 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy study of the deep cerebellar nuclei in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cichocka, M.; Urbanik, A. Widmo protonowej spektroskopii rezonansu magnetycznego (1H MRS) mózgu dorosłego człowieka. Inż. Fiz. Med. 2017, 6, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, R.D.; Vasconcelos, M.M.; Faleiros, L.O.; Cruz, L.C., Jr.; Domingues, R.C.; Brito, A.R.; Werner, J., Jr.; Herdy, G.V. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2009, 67, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Neill, J.; O’Connor, M.J.; Yee, V.; Ly, R.; Narr, K.; Alger, J.R.; Levitt, J.G. Differential neuroimaging indices in prefrontal white matter in prenatal alcohol-associated ADHD versus idiopathic ADHD. Birth Defects Res. 2019, 111, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortese, B.M.; Moore, G.J.; Bailey, B.A.; Jacobson, S.W.; Delaney-Black, V.; Hannigan, J.H. Magnetic resonance and spectroscopic imaging in prenatal alcohol-exposed children: Preliminary findings in the caudate nucleus. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2006, 28, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howells, F.M.; Donald, K.A.; Roos, A.; Woods, R.P.; Zar, H.J.; Narr, K.L.; Stein, D.J. Reduced glutamate in white matter of male neonates exposed to alcohol in utero: A 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolozza, A.; Treit, S.; Beaulieu, C.; Reynolds, J.N. Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter and correlates to eye movement control and psychometric testing in children with prenatal alcohol exposure. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, A.; Wedderburn, C.J.; Fouche, J.-P.; Subramoney, S.; Joshi, S.H.; Woods, R.P.; Zar, H.J.; Narr, K.L.; Stein, D.J.; Donald, K.A. Central white matter integrity alterations in 2–3-year-old children following prenatal alcohol exposure. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 225, 108826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Lebel, C. Evaluation of Brain Alterations and Behavior in Children with Low Levels of Prenatal Alcohol Exposure. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e225972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, P.; Reynolds, J.E.; Ben Gibbard, W.; McMorris, C.; Tortorelli, C.; Lebel, C. Trajectories of brain white matter development in young children with prenatal alcohol exposure. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2022, 43, 4145–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebel, C.; Rasmussen, C.; Wyper, K.; Walker, L.; Andrew, G.; Yager, J.; Beaulieu, C. Brain diffusion abnormalities in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fryer, S.L.; Schweinsburg, B.C.; Bjorkquist, O.A.; Frank, L.R.; Mattson, S.N.; Spadoni, A.D.; Riley, E.P. Characterization of white matter microstructure in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2009, 33, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
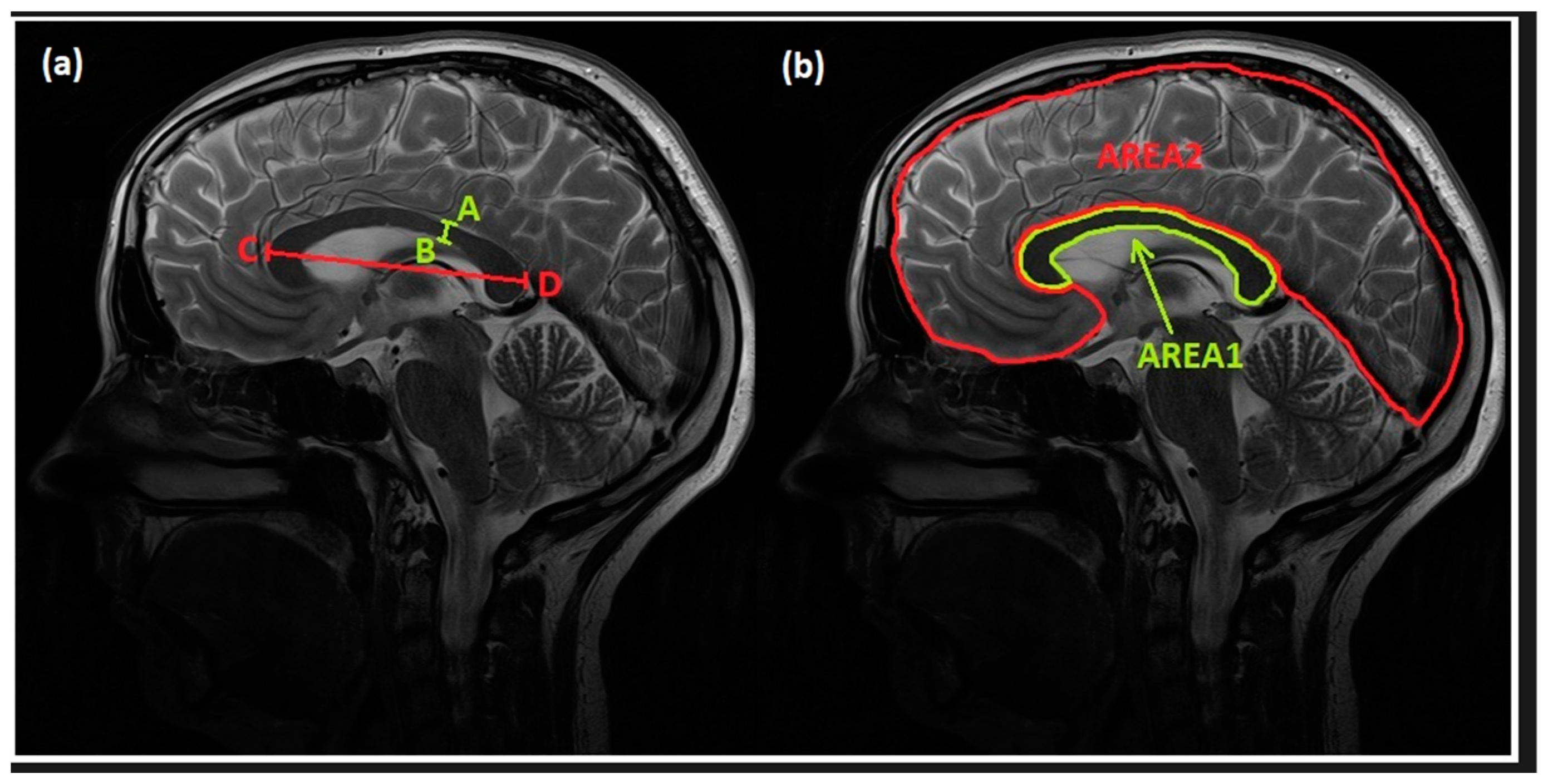
| Parameter | Control Group | FASD Group | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| AB (mm) | 3.72 ± 0.82 | 2.92 ± 0.99 | <0.001 * |
| CD (mm) | 69.21 ± 4.0 | 65.14 ± 4.59 | <0.001 * |
| AREA1 (mm2) | 4.98 ± 0.59 | 4.29 ± 1.01 | <0.001 * |
| AREA2 (mm2) | 95.29 ± 8.55 | 90.13 ± 8.57 | <0.001 * |
| AREA1/AREA2 | 0.05 ± 0.005 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | <0.01 * |
| DWI | ADC | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FASD Mean | Controls Mean | p | FASD Mean | Controls Mean | p | |
| frontal lobes | 212.71 ± 33.36 | 195.44 ± 34.99 | 0.01 * | 0.0007 ± 0.0000 | 0.0007 ± 0.0001 | 0.73 |
| basal ganglia | 195.72 ± 34.47 | 179.48 ± 36.42 | 0.03 * | 0.0007 ± 0.0000 | 0.0007 ± 0.0000 | 0.25 |
| hippocampi | 251.96 ± 47.58 | 234.23 ± 44.56 | 0.06 | 0.0009 ± 0.0006 | 0.0010 ± 0.0001 | 0.33 |
| cerebellum | 298.15 ± 61.79 | 278.57 ± 58.87 | 0.11 | 0.0008 ± 0.0001 | 0.0007 ± 0.0001 | 0.09 |
| mean value from all the studied VOIs | 231.28 ± 37.18 | 213.84 ± 35.59 | 0.02 * | 0.0008 ± 0.0000 | 0.0008 ± 0.0000 | 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urbanik, A.; Nardzewska-Szczepanik, M.; Jadczak-Szumiło, T.; Ostrogórska, M. Assessment of the Central Nervous System in Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) Using Magnetic Resonance (MR) Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7303. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127303
Urbanik A, Nardzewska-Szczepanik M, Jadczak-Szumiło T, Ostrogórska M. Assessment of the Central Nervous System in Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) Using Magnetic Resonance (MR) Techniques. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(12):7303. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127303
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrbanik, Andrzej, Monika Nardzewska-Szczepanik, Teresa Jadczak-Szumiło, and Monika Ostrogórska. 2023. "Assessment of the Central Nervous System in Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) Using Magnetic Resonance (MR) Techniques" Applied Sciences 13, no. 12: 7303. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127303
APA StyleUrbanik, A., Nardzewska-Szczepanik, M., Jadczak-Szumiło, T., & Ostrogórska, M. (2023). Assessment of the Central Nervous System in Children with Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) Using Magnetic Resonance (MR) Techniques. Applied Sciences, 13(12), 7303. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13127303






