Abstract
Green roofs are considered to be one of the optimal tools for saving energy and protecting the environment in developed countries. In this paper, an analysis of the possible application of green roofs on existing residential buildings with flat roofs is presented. In the economic analysis, models of existing buildings in Belgrade, with two different types of green roofs, are studied. A key indicator of investment profitability in this investigation is the net present value (NPV) of the green roof project. Besides the private economic impact, other aspects of green roof applications, significant for sustainable development, have been highlighted. The values of the reductions in the annual energy needed for heating and cooling are compared for different scenarios. A maximum energy saving of 22% in the heating season is determined in the building energy simulation program for the model with an intensive green roof. Life cycle profit analysis was based on the probabilistic approach. The corresponding variance-based sensitivity analysis determined the impact of various parameters on the final result. In all models, the first order sensitivity index, which measures the impact of the number of residential units on the NPV, ranges from 12.2% to 63.6%. Sensitivity analysis showed that the benefit of property value increase has the highest influence on the calculated NPV in scenarios that account for this benefit. The obtained results in those scenarios indicate that the most probable NPV at the end of the life cycle is EUR 43/m2 and EUR 82/m2 for extensive and intensive green roofs, respectively.
1. Introduction
The building sector is responsible for about 40% of total global final energy use in some developed countries as well as 40% of total greenhouse gas emissions [1]. Additionally, in the Republic of Serbia, residential households have a 35% share in the total amount of energy consumption [2]. It is therefore clear that significant improvement in energy savings can be achieved by the increase in energy efficiency in this sector.
Despite the unnatural environment of modern cities, they should provide comfort to their inhabitants. The goal of optimizing energy consumption and protecting the environment should also be accomplished. New solutions have emerged in the construction strategy as a result of growing populations in cities [3]. Their aim is to reduce the impact of considerable energy needs while maintaining or improving citizens’ quality of life. Due to the constant increase in urbanization, it is necessary to optimize building areas and their use. Fulfilling these demands can generally be achieved through various approaches. Retrofitting measures in residential buildings with different aspects and challenges with the importance of cost-effectiveness are discussed in references [4,5]. However, greenery systems provide additional social and environmental value, with great potential to mitigate some negative aspects of urban housing. An overview of different greenery systems and the effectiveness of their application in different climates are presented in reference [6].
Green roofs, the practical tool of the urban greening concept, are structures that are covered with a vegetation layer. The growth of different forms of vegetation on top of buildings thus provides aesthetic, environmental, and economic benefits [7,8]. Additionally, green roofs have a positive effect on improving the global microclimate in cities, reducing noise levels and purifying rainwater and air inside the building. They are also a living space for various animals and insects, and they can be used for food production. It is important to emphasize that green roofs can improve the thermal performance of buildings, so they are a great option for potential energy savings [9] through reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling [10]. Even though validation of the results of the simulation model [11] is valuable confirmation in research on green roofs, reference [12] argued that there is a lack of experimental results in terms of energy savings in the literature. Data for measuring the effects of green roofs are further discussed in the Section 2.
There are three types of green roofs, depending on usage, maintenance requirements, and structural considerations: intensive, semi-intensive, and extensive. Green roofs consist of the following layers (from bottom to top of the construction): protective board, waterproof membrane, drainage layer, filter, vegetation substrate, and plants. Besides the essential layers, green roofs can include additional filters [7], root barriers, thermal insulation, and irrigation systems (above or inside the soil layer).
Since growing medium represents a relatively thin layer in the case of extensive green roofs, they are easily feasible and lightweight. Consequently, they serve aesthetic, remedial, or technical purposes, and, compared to other types of green roofs, their maintenance and construction costs are lower. In addition to traditional green areas, intensive green roofs can provide similar amenities, usually arranged as parks or gardens. However, their initial and maintenance costs are considerably higher due to their significant weight and irrigation requirements. Furthermore, their waterproofing layers are more reliable, and the energy efficiency of the adjacent spaces of building is substantially improved.
Besides all the above advantages, an important aspect of the applying of green roofs is reflected in the economic benefits. Many studies, such as [7,13,14], claim that the probability of profit of a green roof is much higher than its potential financial losses. Thereby, the study conducted in reference [13] should be emphasized, whose probabilistic net present value (NPV) analysis shows that there is a low financial risk for installing any type of green roof. Additionally, many other investigations [14,15,16] demonstrate that at the end of its lifetime, the NPV for the green roof is significantly lower when compared with conventional roofs. Determination of NPV of green roofs is usually analyzed through private or social (and environmental) benefits or taking into account both economic impacts, which often implies considering diversified cost and benefit effects. This paper deals with the analysis of the impact of green roofs on the energy performance of the existing building in the center of Belgrade. The potential private benefits of installing a green roof on such a flat roof are indicated.
It can be said that green roofs are not widely represented in Serbia and that there is great potential for its application. This includes, among other things, the conversion of flat roofs to green rooftops on the existing buildings. According to a recent investigation [17], the distribution of the flat roof in the building stock in the Republic of Serbia is about 20%. However, in the central urban area of the capital city of Belgrade, that number reaches as much as 40%. Therefore, the economic feasibility of applying of a green roof system to this type of building is presented in this paper.
Commonly, governments have a leading role in the implementation of green roofs. Therefore, the lack of institutional incentives can be a potential barrier to the implementation of a green roof system, especially for existing buildings. For the greenery project implementation, the barriers are similar to standard renovation projects. They are categorized as market, organizational, and economic related, and even in developed countries, policies are different for overcoming these issues [18]. In order to decrease the energy efficiency gap, reference [19] emphasizes that barriers’ inner complex relations and transforming nature must be approached dynamically. Additionally, these obstacles could be further amplified in green roof implementation in countries with an undeveloped green industry. Fortunately, there are many examples of good practices in the world in terms of policies, programs, and projects that encourage the development and implementation of green roofing [20,21,22]. In Belgrade, the policy of supporting the use of green roofs is reflected through the strategic goals of the Development Strategy of the City of Belgrade 2021 and the pilot project “Green roof of public buildings in the city of Belgrade”. In green roof implementation, policies are categorized as direct and indirect financial incentives but also ecological compensation measures with the aim to be integrated into standard development strategies, as presented in ref. [23]. In ref. [22], the incentive policies (mainly concentrated in Europe and North America) were classified into six different categories: tax reductions, financing, construction permits, sustainability certification, obligations by law, and agile administrative processes. In the distinct analysis for southeast Europe [24], state building typology, climate, period of construction, building service, and user behavior are determined as the main considerations for building retrofit packages. In this paper, the focus is on existing residential buildings with a flat roof in the urbanized area, with the presumption that the conclusions could be applied to some extent to other categories of residential buildings with a flat roof. The purpose of this type of research is also to provide background for the possible large-scale implementation as the cost-benefit analysis is regarded as helpful in raising awareness of environmental goods and in increasing the transparency of policymaking [25].
2. An Overview of the Impacts of Green Roofs
Private benefits of green roofs are categorized as buildings’ increased aesthetic value, improved sound insulation, extended membrane longevity, and reduced consumption of energy. Further, they enable LEED certification bonuses [26], along with bringing psychological and health benefits. In addition to the individual level, green roof installations also affect the public (environmental and social benefits).
Constructing a green roof can lead to a decrease in energy needed for cooling and heating, which may vary depending on the analyzed climate zone, green roof type, and building envelope. In [27], results are categorized according to their location, where maximum energy savings are obtained in intensive green roofs comparison to black roofs, especially over non-insulated roofs, reaching to 84% energy savings in the cooling season and 48% in the heating season. Similar comparison (white, black, and green roofs) is analyzed in but these types of roofs are not widely spread in the location of the presented analysis. In this paper, the impact of green roofs is investigated in Belgrade, where the climate is considered to be Cfa according to and to Koppen–Geiger climate classification system [28]. It should be emphasized that the presented data from the literature mainly reflect energy savings only for the floor under the green roof, which is also taken into account in the economic analysis in the presented paper. Ref. [29] found that the installation of a rooftop garden in a building in Singapore could result in a saving of up to 15% in the annual energy consumption. Total energy savings in the range of 24 to 35% were the result of investigation performed in hot-humid climate areas [30]. The comparison presented in [31] ranks green roof performance above the traditional roof with an insulation layer (5–14% energy saving) in the experimental analysis performed during the cooling season in Spain. A specific study in cold and hot climate zones [32] concluded that application of green roofs leads to an annual reduction in heating load by 36.5% to 55% and an annual reduction in cooling load by 27.7% to 35.8%. Based on a comprehensive literature review related to this topic, ref. [6] concluded that the maximum energy savings of greenery systems are found during summer. In contrast, for winter conditions, the results can vary and are dependent on the conditions in which the research was conducted.
The high absorption of solar radiation in urban areas may cause heat island effects. As a consequence, the temperature in the city center is significantly higher than in the surrounding rural areas [33]. This temperature difference is usually larger at night than during the day and this urban heat island (UHI) effect indirectly increases building cooling demand [34]. Still, the effects of UHI have been recognized since the 19th century [35], and today, how their negative impacts are reflected in the social, economic, and environmental aspects is especially considered. Compared to standard flat roofs, this effect could be mitigated due to the reduction in heat flux in the green roof structure. Consequently, for buildings that are not heavily insulated, the reduction in the peak indoor temperature can reach 7 °C [36] during the cooling season. Feng [26] presented the results of the simulations indicating that the green roof concept in Toronto and New York can reduce the average temperature of the roof by 1–2 °C. In addition, in ref. [37], it is calculated that in Venice, the temperature could be 4 °C lower if the green permeable surface were used instead of existing roofs. The numerical model for Belgrade [38] showed that with a different type of green roof structure, the reduction in temperature varies from 0.5 to 1.5 °C and 0.5 to 1.8 °C for the roof and pedestrian level, respectively. In the recent study of the summer thermal performance of a lightweight extensive green roof system with rock mineral wool substrate in Belgrade [39], a maximum outdoor roof surface temperature reduction of 27.5 °C was observed, while the average air temperature decrease was 1.6 °C.
In urban areas, the public (social and environmental) benefits of green roof are indisputable. Managing water runoff quantity, reduction in pollution alongside urban noise, and enabling the preservation of habitats [40,41] represent the most essential public gains. Studies quantifying biodiversity increase with the green roof [42,43] reported green roof limited effect and different factors that influence biodiversity. The comparison of the hydrological and water quality performance of green roofs that are presented in [44], shows that they behave differently in different climate zones. The green roof system shows promising results as a substantial tool for removing the air polluting particles in urban areas, as explained in [45], but a model for indication of removal level in Toronto [46] and Chicago [47] showed limitations of green roof impact as they cannot fully replace the widespread urban removal of green areas. Assessment of health risk caused by air pollution in Belgrade [48] proved high exceedance of level PM10 particles, which generally can be modestly mitigated by wider application of green roofs [49].
Besides obvious environmental benefits, the presence in vegetation surroundings is good for mental health, providing general comfort from various aspects. It is noted in [50] that evaluating the mental health aspect of green roof implementation must be a multidisciplinary task as it is influenced by other benefits as well.
3. Costs and Benefits of Green Roof
The economic benefits of applying green roofs are an important aspect of the usage of this technology. Cost-benefit studies can be an essential tool for city planners and public decision-makers in promoting green roofs and support for draft bills [22]. There is a wide range of costs that depend on various factors, such as the type and size of the roof, weather conditions of the location, building characteristics, etc. There are also possible barriers to the application of green roofs [40] primarily related to increasing maintenance, design, and construction cost as well as the possible structural limit exceedance, which can cause serious problems in practice.
Comprehensive research provides multifunction nature of green roofs in both the private and social sectors. In the presented economic model, only the private cost/benefit effect is examined in detail. It is based on the relevant references from literature and also on the consideration of local conditions and practices. For the initial cost of extensive green roofs (EGR), the value varies in different ranges: USD 130–165/m2 [13], USD 70–100/m2 [51], USD 60–110/m2 [14], USD 53–214/m2 [22], or about USD 172 /m2, proposed in [52]. The estimated range for the intensive green roof (IGR) is USD 160–540/m2 [13,22], or USD 100–240/m2 suggested in [51]. In [9], it is indicated that the cost of retrofitting of the existing building (with EGR) depends in the wide range (USD 60–180/m2) on the specification but also the condition of the existing waterproofing layer.
According to ref. [13], property value increase is relatively close to installation cost, i.e., it can be evaluated as an increase of 2–5% for EGR to 10–20% for IGR. So, it is estimated that this increase is USD 132–648/m2, depending on the type of green roof. On the other hand, ref. [53] estimated an increase of 16.2% in rental prices in buildings with green roofs. For property value increase, the most influential parameter is an aesthetic improvement, although it depends on access and ownership regime [54], and it is taken into a calculation as a one-off benefit or annual benefit in the case of renting. Without directly estimating property value, in ref. [26], the aesthetic benefits (USD 2.6–32.2/m2) and the benefit of acoustic improvement (USD 43/m2) in the building are separately analyzed and quantified, added up to USD 72.2/m2/40 years. In the economic analysis conducted in this paper, these types of benefits are considered to be incorporated into property value increase. These benefits are conservatively estimated for the apartment below the green roof, and for the other apartments in the considered building, this value is further reduced by 50%.
For IGR, operating and maintenance cost is one of the main concerns of potential investors, while EGR has minimum operating requirements. These costs have notably dispersed value range in the literature overview. In refs. [13,27], this value ranges from USD 0.7 to 13.5/m2 per year for different types of green roofs. In ref. [52], this value is set to USD 2.9/m2, while in ref. [16] this value is universally proposed as USD 5/m2 per year. For markets and industries that are not yet developed, the higher values are more suitable. Given that green roofs in Serbia are not yet sufficiently represented, the higher value is adopted in the economic model.
The lifespan of the green roof can vary from 40 to 55 years [13,15]. Therefore, in addition to maintenance costs, replacement after the projected lifetime could be included in the analysis. However, the conventional flat roof is usually replaced or reconstructed in 20 years, or twice as often as green roofs. Consequently, the membrane longevity benefit is proposed as much as USD 160/m2 in ref. [13], although this value is significantly lower (USD 20–43/m2) in refs. [55,56,57]. The replacement cost of the green roof at the end of its service life [52] is approximately evaluated as one-third of the green roof installation cost, but it is not included in the presented economic model since the analysis of one life cycle is performed. As it is stated previously, the uncertainty of project cost/benefit outcome is one of the main barriers in the wider application of green roofs. Property value increase due to greenery systems also depends on people’s preferences and access [20], so its financial contribution is dependent on a specific type of implementation and pricing models. Furthermore, even neighboring residential areas (with a view to green areas) have this benefit [58] in the case of a substantial greening project. In the investigations presented in refs. [13,14,20,26,59,60,61], the property value increase is counted as a benefit, while in refs. [7,15,16,30,52] authors do not account it directly or neglect that benefit. Thus, in the analysis presented in this paper both approaches are used to determination the NPV of green roof projects at the end of the life cycle.
4. Application of Green Roof on the Existing Building
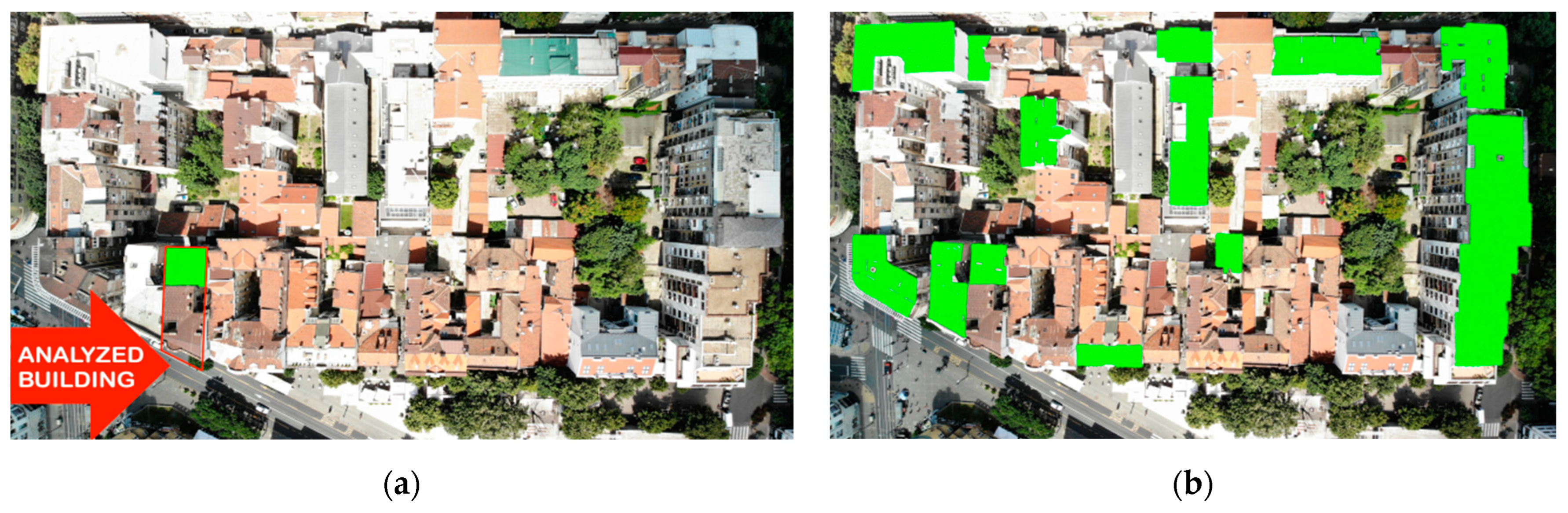
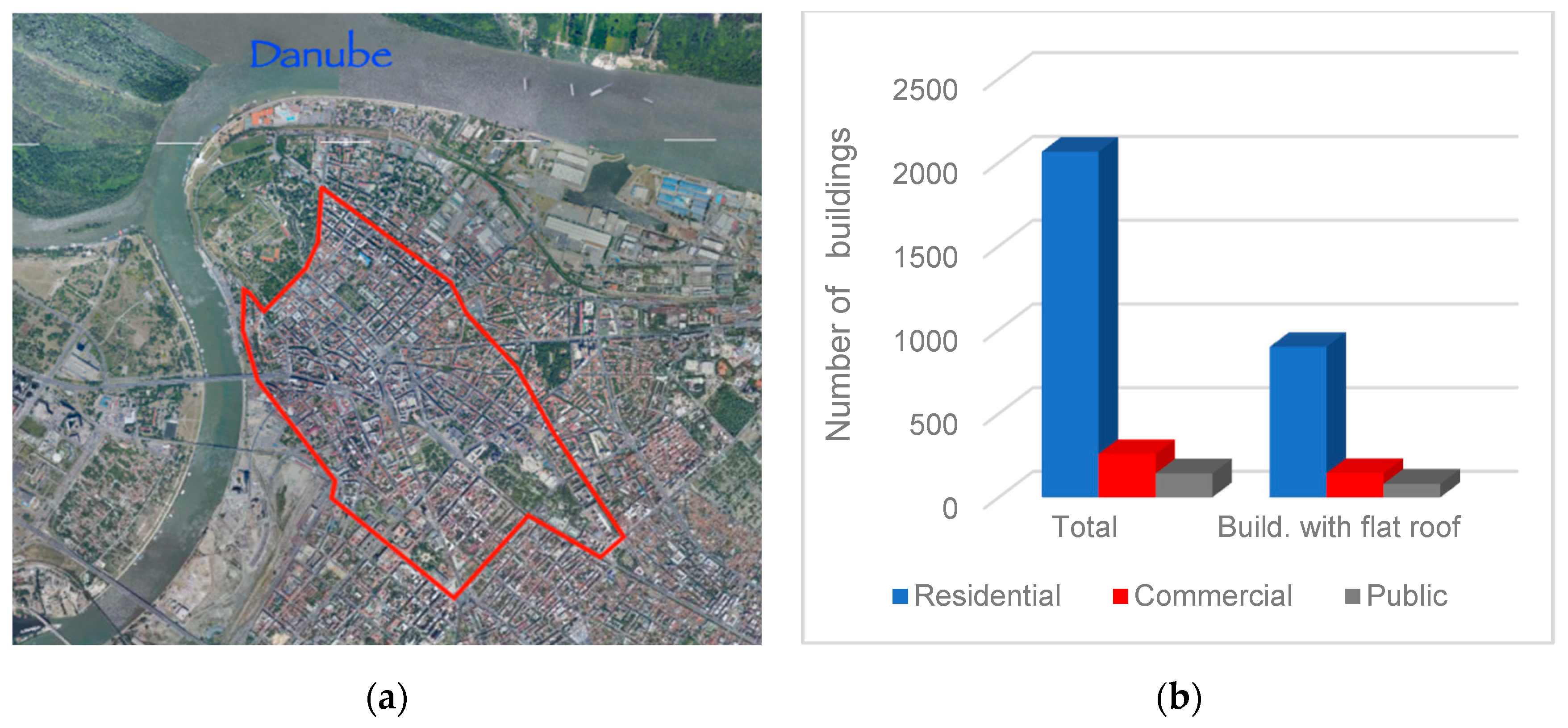
While it is certainly beneficial to incorporate green roofs into the initial design of new buildings, it is equally important to explore the feasibility and advantages of retrofitting existing buildings. Even though the share of buildings with flat roofs built in Serbia before 1945 is not high [17], a significant number of these buildings are located in the center of Belgrade. Due to their urban architectural value, these buildings are occasionally protected by city and state regulations and this too applies to the building analyzed in this investigation. Furthermore, the strict city center (Figure 1a) has great potential for wider implementation of the green roofs, according to data obtained during the research performed for this paper. The investigated area covers about 2.82 million square meters, of which (public) green areas are only 0.21 million square meters. By mapping the buildings with flat roofs in this zone (Figure 1), it is concluded that 45% of the buildings have flat roofs, with a total area of about 330,000 m2. It is indicative that the flat roof area in the observed zone is about 50% larger than the area of the existing parks. In a study from 2016 in Thessaloniki, green roof potential reaches 2.29 km2 compared to 0.66 km2 of the existing vegetation areas [62].
Figure 1.
(a) City center (red outline) from which detailed data is acquired. (b) Summary of the building stock in analyzed zone.
Figure 1b gives a summary of the building stock in the analyzed zone. The highest share in presented data belongs to residential buildings; hence, the absolute highest number of flat roof buildings is detected in that type. About 43% of them have such a roof with a total area of 194,000 m2. On the other hand, 55% of commercial buildings in this zone have a flat roof (total area 69,000 m2), as do 56% of public buildings (total area 67,000 m2). Since current city regulations predict a budget for investing in the greening of public buildings, it is clear that there is great potential for such investments as well.
Model and Parameters
The potential of constructing of green roof on a flat roof is evaluated through project that predicts the removal of layers of the roof structure, enabling additional load on the roof without structural implications. A correlative study in ref. [9] implies that removing traditional paving slabs and gravel on the roof could provide enough capacity for EGR with decent thickness. An additional problem arises if a live load is considered, where ref. [63] proposes a wide range of values of imposed load on accessible flat roofs, depending on National Annexes, up to 2 kN/m2. Specifically, ref. [64] recommends a live load of up to 4.79 kN/m2 for accessible roof gardens in a saturated condition, limiting its adequacy for existing roof structures. On the other hand, for inaccessible green roofs, the live load is in the range of 0.5–0.96 kN/m2 [64], which corresponds to existing capacity according to standards used for analyzed building stock. Data provided in [17,65] revealed flat roof structure typology in Serbia; hence, it can also be relevant for considered urbanized area—the center of Belgrade. Distinct types of roof coverings are observed; still, the overall characteristics are similar and they can be classified (Table 1) on two types according to the top outside layer. Since the weight of various types of green roofs demands different capacities of the roof structure, it can be estimated that for installing EGR, removing all the layers above the concrete laid to fall would be sufficient in certain types of flat roof structures. On the other hand, if that remaining layer is also removed, in some cases it would increase capacity, enabling setting up of semi-intensive or IGR. Table 1 indicates the possibility of installation of IGR (without strengthening the structure) is lower (than EGR). Additionally, ref. [66] argues that an EGR can be the most efficient solution in buildings’ greenery concept. Nevertheless, analyzing the IGR economic implications is also important especially in the investigated building that has an even higher capacity (than presented in Table 1) for the vertical load on the flat roof structure. More precisely, the possible removal of all layers above the surface of the structural plate would provide 4 kN/m2 of additional weight.

Table 1.
Characteristic layers and weight of different types of flat roofs according to [17].
The object of the analysis is a four-story residential building with eight residential units with a total area of 771 m2. Given the insufficient thermal insulation in this building, it can be used as an appropriate example for energy efficiency improvement. Contemplated measures are represented in the form of the application of an EGR and IGR, which was previously discussed, only on the part of the existing roof that is flat (Figure 2).

Figure 2.
Micro location and the possible green roof implementation: (a) on the roof of the analyzed building; (b) on the entire block of buildings.
The installation of a green roof in the proposed models would be performed after the removal of all non-structural elements above the last slab in the building. Consequently, the weight of the new roof structure would be reduced compared to the weight of the existing roof. The estimated mass of the proposed types (Table 2) of the green roof ranges from 125 kg/m2 (EGR) to 250 kg/m2 (IGR). In general, additional capacity can be introduced to account for the increase in load due to the saturation of soil and maintenance loading [59]. Regarding the uniqueness of building typology and condition, structural analysis or survey is recommended in most cases [67], especially in the potentially active seismic area, where the additional load on the roof has global implications on the whole building structure.

Table 2.
Properties of EGR and IGR layers in numerical model.
The configuration of the model of EGR and IGR structures and its properties are shown in Table 2, where the highest values of parameter correspond to the IGR model, and the lowest to EGR model. The thickness of the layer is marked as d, density with ρ, specific heat with c, and thermal conductivity with λ. Thus, the variation in the composition of the green roof layer can give different outcomes in thermal properties and numerical models [68,69,70,71], which modifies the peak cooling load and energy consumption. However, since the aim of the paper is a general approach in the profitability of the analyzed project, detailed variation of the layer properties is not performed. As presented later in the conducted sensitivity analysis, the dependence of the calculated energy cost reduction indicated the overall importance of the savings achieved by installing a green roof.
Energy efficiency measures consider different levels of thermal envelope retrofitting, and the effects of those actions are usually determined relative to the current state. Results of greening the roof can additionally improve energy consumption, even after the possible usual measures of energy renovating in the buildings—the so-called business as usual (BAU) scenario. In the model of partial renovation (flat roof renovating excluded) assumed in ref. [65], the BAU scenario predicted 20% of heating energy savings, which can be compared with the energy savings in the presented analysis. On the other hand, in ref. [72], 15% of energy savings represents a low renovation scenario, and 45% of energy savings represents a moderate renovation scenario. Furthermore, for the analyzed building, potential additional thermal envelope retrofitting is limited because the design of the street façade of the analyzed building is protected due to its urban architectural value. In addition, a significant part of the external walls represents the party wall with surrounding buildings which may be the obstacle for other buildings in the urbanized center.
For verification of different rehabilitation measures, distinct scenarios are proposed in Table 3. A probabilistic Monte Carlo simulation [73] is performed to calculate the life cycle NPV of different projects. These calculated values represent the possible investment profitability indicator from the point of view of different residential unit owners, expressed in EUR/m2 of green roof area compared to the current state of the building thermal envelope.

Table 3.
Scenarios for economic analysis.
Although various social (public) benefits could be accounted for in the economic analysis, the local circumstances in practice do not strongly support this type of expectation, especially for residential buildings. The existing city development strategy includes activities and a budget for green roof projects of public buildings, but detailed plans have not been completed, so some values are not easy to determine. Therefore, in the presented analysis of energy renewal of the existing object, only personal (private) benefits are taken into account, as given in Table 4. The outcome of the following analysis could also represent the indication for the level of public financial subsidy programs after evaluating the feasibility of the proposed projects as shown at the end of this section. The benefits relate to the apartment under the green roof predominately, but other residential units are also interested in this type of project. As explained in ref. [74], the influence in other adjacent zones of the building is manifested in the reduction in the peak of cooling energy demand to some extent. However, this impact of the green roofs is neglected in the calculation of benefits for other residential units (models 2 and 4). It is important to emphasize that models for NPV calculation are determined by uniformly dividing the costs (marked with * in Table 4) of investment, maintenance and, consequently, the roof membrane longevity value (as a benefit) to all residential units. These adjusted prices used in the economic analysis represent a realistic scenario, according to the local city regulation on housing, where investment and maintenance costs are distributed equally among all apartments.

Table 4.
Input parameters and their function in probabilistic analysis.
In summary, for models 1 IGR and 1 EGR, all parameters from Table 4 are used, except parameter 3. For models 2 IGR and 2 EGR, only parameters 1, 2, 6, and 7 are used in the LCC and sensitivity analysis. For models 3 IGR and 3 EGR, all parameters 1–7 from Table 4 are used. Models 4 IGR and 4 EGR include parameters 1, 2, 6, 7, and 50% of the parameter 3 value.
The variation of different cost and benefit values in the analysis, presented in Table 4, is based on the previous overview of different sources. The life cycle of the green roof is also varied from 40 to 55 years, and the discount rate is assumed in a uniform variation range of 4–8% in the economic analysis. As is already mentioned, scenario models 2 and 4 (all residential units except RU under the green roof) do not have the benefit of reduced energy for heating and cooling due to green roofs. Furthermore, the property value benefit for model 4 is reduced to 50% compared to the corresponding model 3. Based on the reviewed economic analysis from the literature [13,30,55,75], and the local tariff system, the price of the energy reduction is adopted as 0.08 EUR/kWh.
5. Results and Discussion
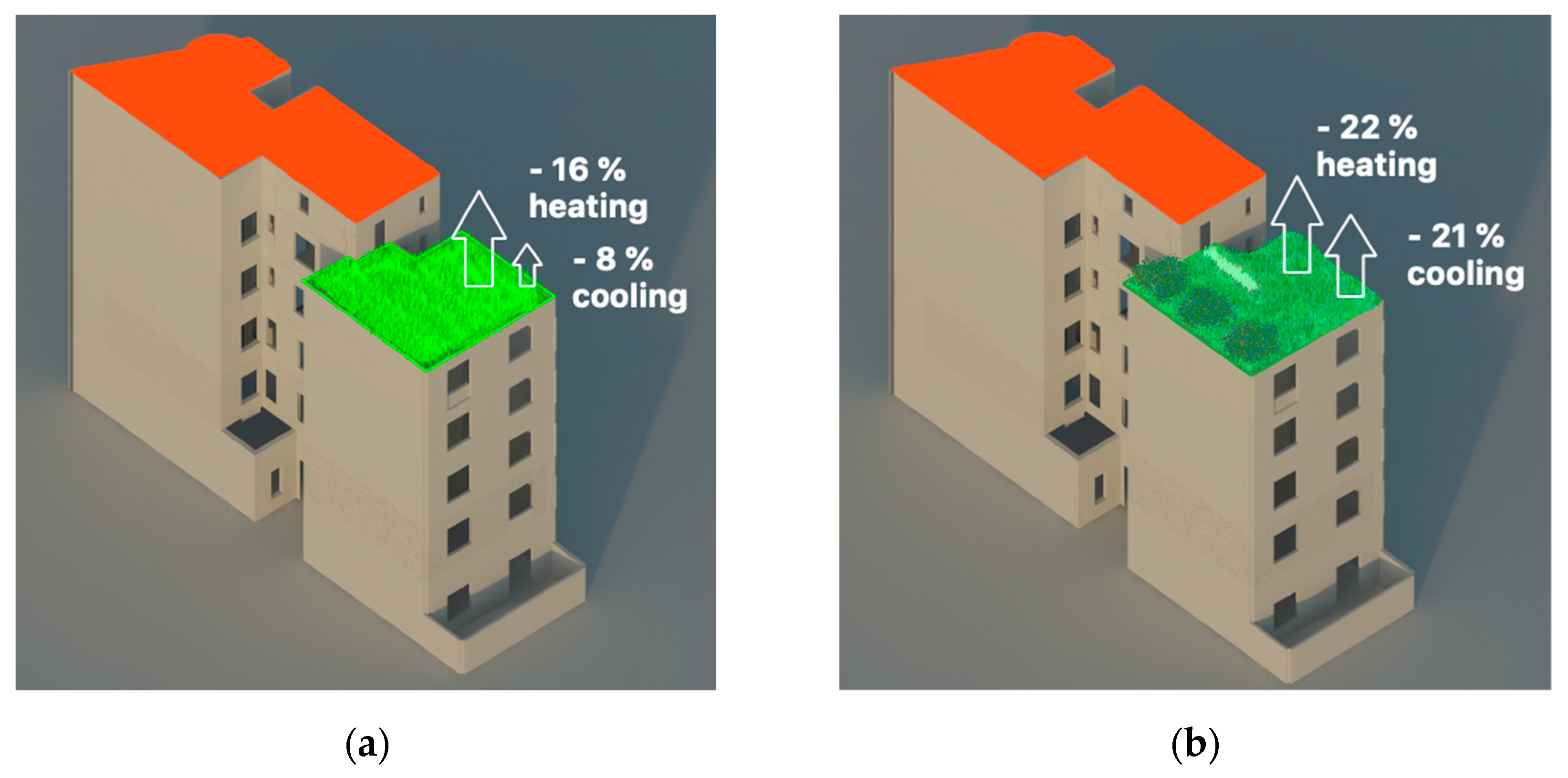
EnergyPlus 9.1.0 software with the EcoRoof model [76] was used for the computation of the heating and cooling energy needs. Different outcomes for the reduction in the building’s annual energy need for cooling and heating (for the last floor) are demonstrated in Table 5 and Figure 3. As a result of the currently insufficient thermal insulation, the analyzed apartment can potentially reduce the consumption up to 22% of heating and 21% of cooling energy with the implementation of IGR compared to the current state (Figure 3b), which is in the range of savings obtained in BAU scenario measures. On the other hand, IGR models reduce the need for cooling energy significantly more than the proposed EGR model. In the corresponding economic analysis, the yearly benefits of heating and cooling energy reductions, for models with EGR and IGR, are presented in Table 5.

Table 5.
Energy need reduction and results from probabilistic analysis for different scenarios.
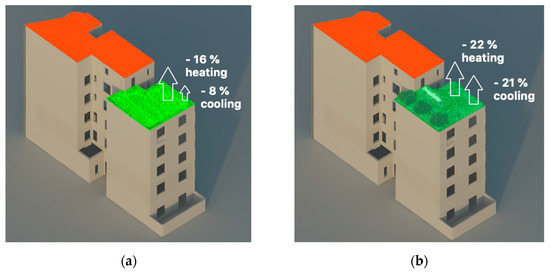
Figure 3.
Reduction in energy need (percentage) for cooling and heating compared to the current state of the apartment under the (green) roof obtained with: (a) EGR and (b) IGR.
The results of the economic analysis are presented in Table 5. Based on the presented input data for the apartment under the green roof, the life cycle NPV for model 3 is computed in the range of EUR 17/m2 to EUR 132/m2, depending on the type of the roof when the property value increase is accounted as a benefit. By analyzing the models without this benefit, it can be said that there are dominantly negative outcomes of NPV values for scenarios 1 and 2, which may be the case with similar location and envelope properties. It is important to emphasize that the analyzed object has eight residential units, and for similar energy performance buildings with a higher number of RU, individual users (investors) could have lower installation costs but lower benefits from membrane longevity as well. Therefore, sensitivity analysis evaluated the impact of this parameter. Since the social benefits, but also the costs, are excluded from the NPV model in this paper, corresponding life cycle assessment analysis should incorporate the negative aspects of old roof disposal aspects as well.
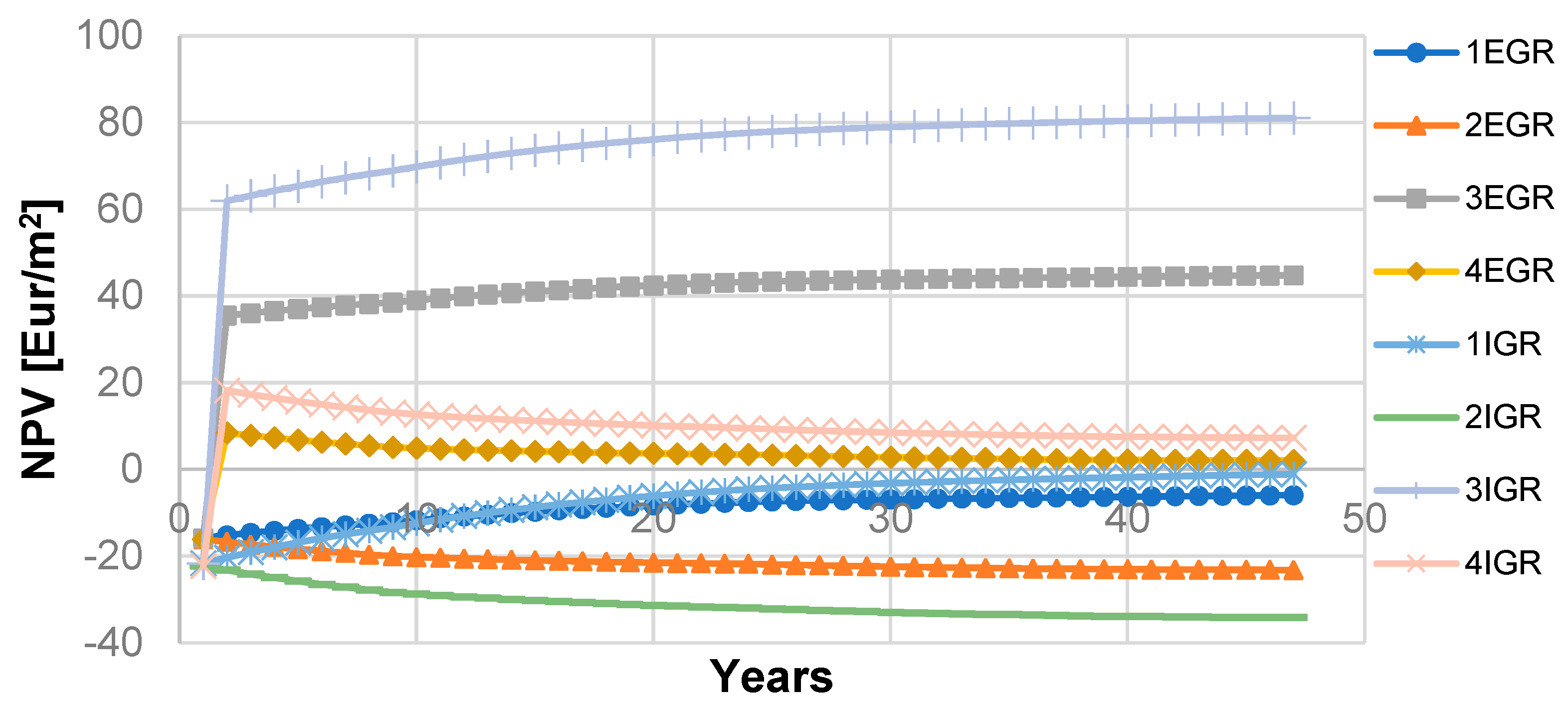
Since the uniform variations included an estimated green roof lifespan of 40 to 55 years, in Figure 4, the most probable result for NPV of the life cycle projected to 47 years is presented for all models. These results indicate that energy savings are not the crucial aspect of the economic benefits of investment, even for the model with the IGR. Based on the calculation, it is clear that the payback period is not more than one year for the models incorporating this benefit. This outcome is expected because the increase of the property value has become significantly higher than the initial costs—if it is distributed on all residential units of the building. An analogous observation is in accordance with sensitivity analysis. Moreover, the property value increase broadly determines the outcome of the NPV at the end of the life cycle, and the shape of the LCC curve is depicting the asymptotic tendency of the final result (Figure 4.). The influence of a number of residential units is analyzed through sensitivity analysis. For the different numbers of RU, the NPV value curve tends to increase or decrease with a high rate for all models, which will be indicated in the sensitivity analysis. For an individual investor (number of RU = 1) in the equivalent model, the NPV value would further decrease to EUR −176/m2, EUR −254/m2, EUR −124/m2, and EUR −170/m2, for models 1 EGR, 1 IGR, 3 EGR, and 3 IGR, respectively. LCC analysis can present different results depending on the climate and economic parameters, but various costs and benefits that are included in the calculation could alter the results as well. In ref. [14], the most probable NPV for installation of EGR on detached house was calculated as USD 351/m2, with significant benefits obtained by thermal envelope improvement. In the first scenario in ref. [55], where property with a constructed green roof is being used after construction, the most probable NPV is calculated as USD 173/m2 and USD 213/m2 for EGR and IGR, respectively. In the second scenario where property is being sold after construction, the most probable NPV is calculated as USD −16/m2 and USD −41/m2 for EGR and IGR, respectively The most probable NPV calculated in ref. [13] was USD 291/m2 and USD 611/m2 for EGR and IGR, respectively. However, it should be noted that the corresponding analysis, presented in ref. [13], included additional benefits in the form of avoidance of infrastructure cost. Moreover, in compared results from the literature [13,14,55], the distribution of costs on other RUs was not analyzed.
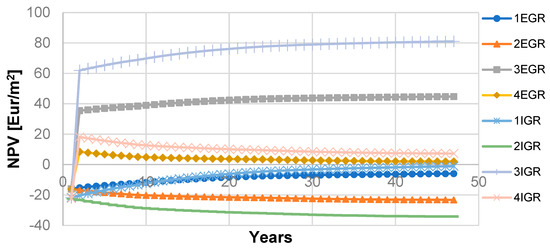
Figure 4.
The life cycle of green roof—N = 47 years—calculated NPV for proposed models—most probable scenario for different models.
Sensitivity analysis was based on the variance-based method [77] that was implemented in the Python library [78]. Sensitivity analysis is one of the tools in the impact assessment procedure recommended by regulatory documents [79]. The proposed method enables the calculation of the first (Si) and the second order (Sij) sensitivity indices, as well as total effects index. Besides parameters from Table 4, additional significant factors are taken into account in Table 6. First-order sensitivity indices of parameters for NPV indicate the greatest influence of the property value increase on the outcome, while the benefit of the heating energy reduction is only significant for models 1 EGR and 1 IGR. This is due to the poor current state of the thermal envelope of the building, but this effect is less pronounced in models 3 EGR and 3 IGR. As is the case with similar numerical analyses, the discount rate also has a notable impact on the formation of NPV results given that the life cycle of a green roof is high. Second-order sensitivity indices, which determine interactions between parameters, are insignificant for the presented analysis and hence the total sensitivity indices are close to the first-order.

Table 6.
First-order sensitivity indices for different parameters in life cycle analysis.
It is clear that the estimated life cycle period, within a range from 40 to 55 years, also does not significantly affect the outcome, although the membrane longevity parameter has a higher probability to occur twice for a green roof with a longer lifespan. That remark is consistent with the shape of the NPV curve presented in Figure 4, which is almost constant after 40 years. For models 2 and 4 (without the benefits of energy reduction), the most dominant factor is the number of RUs and the increase in the value of the properties, respectively. Although installation cost is a parameter with the highest value in all models, it is not the most influential since it is distributed to all residential units. The most influential economic factors in sensitivity analysis in [13] was discount rate, while the property value was the most important non-economic factor in LCC model from private perspective. In the first scenario in [55], the most influential parameters were discount rate and energy savings, while in the second scenario, initial cost and property value increase were the most decisive parameters in the NPV calculation. On the other hand, in ref. [14], the most important factors for NPV were maintenance cost and discount rate.
Based on the results obtained in sensitivity analysis, the presented approach could be extended to different typologies of buildings in future research as it would give different absolute and relative values of parameters in life cycle analysis.
6. Conclusions
This paper presented the analysis of the potential application of green roofs in urban areas and the economic effects for private users on a specific example of a building in Belgrade. Since the city center is always the most affected by the UHI effect, the significant potential for increasing the current state of the green area is revealed. This possibility is perceived through the high percentage of buildings with a flat roof in the observed area, and their capacity for additional loading after removing current layers of the roof structure. Energy efficiency calculation is performed in the EnergyPlus 9.1.0 software, and it referred to the energy savings of the apartment under the proposed green roof. In the presented study, application of green roofs reduces the energy need for heating and cooling up to 22% and 21%, respectively. Those results are in the agreement with those reported in the literature. Since the variance-based approach is used in sensitivity analysis, a relatively small difference in parameter values is amplified, resulting in the reduction in cooling energy being insignificant in comparison to the heating energy reduction. Although this approach is efficient and enables calculation of second-order effects in the sensitivity analysis, no such dependence on factors is observed.
The economic profitability analysis took into account other relevant benefits and costs for the private users through a probabilistic lifecycle approach. This paper aimed to emphasize personal gain by focusing on individual benefits for different users as it predominantly affects investment comprehension. Hence, the presented investigation also provided insight into economic interest from the perspective of distinct RUs of existing buildings that aim for green roof renovation. By examining the top floor of such a building, it becomes evident that implementing a green roof can enhance energy efficiency to a comparable or even greater extent than traditional energy renovations (as per the BAU scenario). The proposed concept of cost distribution led to a positive life cycle NPV even for other residential units if the property value increase is counted as a benefit. Moreover, positive implications are identified at the public level, which should activate local authorities to significantly stimulate green roof implementation projects for existing and new buildings. The relevance of the number of residential units taking part in the investment is determined, and it is concluded that for the individual investor, the NPV of the project would decrease substantially. Although in the presented analysis, property value increase is conservatively estimated, it is the most influential factor in NPV models that include this benefit, with a high probability of negative values in all other models. Therefore, in those models, additional social benefits must be included in the project to be profitable. Moreover, in future research, this benefit must be determined precisely with an appropriate pricing model and market analysis for existing buildings. The presented typology of flat roofs indicates EGR as the most practical solution for existing buildings, as was concluded in analogous research. According to data related to the load capacity of existing roofs, it can be seen that there is limited possibility for installing IGR. Nevertheless, its environmental impact and higher NPV (in most cases) could motivate investors and decision-makers to support these types of projects.
These conclusions imply the existence of the influential role of local authorities and government in generating such projects through a subsidy policy, tax abatements, and official programs for different social benefits in both the public and private building sectors.
Author Contributions
Z.P.: conceptualization, methodology, supervision, numerical analysis, writing—original draft preparation; S.C.: investigation, data curation, numerical analysis; S.I.: investigation, formal analysis, visualization; D.S.: validation, revision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technological Development, Republic of Serbia, through Project 200092.
Data Availability Statement
All the original data will be available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Berardi, U. Building Energy Consumption in US, EU, and BRIC Countries. Procedia Eng. 2015, 118, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Todorovic, M.; Rajčić, A. Energy Efficiency Manual for Buildings; GIZ—Deutsche Gesellschaft fur Internationale Zusammenarbeit: Belgrade, Serbia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. World Urbanization Prospects The 2018 Revision; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Manzoor, B.; Othman, I.; Sadowska, B.; Sarosiek, W. Zero-Energy Buildings and Energy Efficiency towards Sustainability: A Bibliometric Review and a Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felius, L.C.; Dessen, F.; Hrynyszyn, B.D. Retrofitting towards Energy-Efficient Homes in European Cold Climates: A Review. Energy Effic. 2020, 13, 101–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, B.; Tenpierik, M.J.; Van Den Dobbelsteen, A. The Impact of Greening Systems on Building Energy Performance: A Literature Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K. Green Roofs: A Critical Review on the Role of Components, Benefits, Limitations and Trends. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatian, O.; Sopian, K.; Salleh, E.; Lim, C.H.; Riffat, S.; Saadatian, E.; Toudeshki, A.; Sulaiman, M.Y. A Review of Energy Aspects of Green Roofs. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 23, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castleton, H.F.; Stovin, V.; Beck, S.B.M.; Davison, J.B. Green Roofs; Building Energy Savings and the Potential for Retrofit. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 1582–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, M.; Di Perna, C.; Di Giuseppe, E. Green Roof Yearly Performance: A Case Study in a Highly Insulated Building under Temperate Climate. Energy Build. 2012, 55, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowski, P.; Nawalany, G. Analysis of Energy Exchange with the Ground in a Two-Chamber Vegetable Cold Store, Assuming Different Lengths of Technological Break, with the Use of a Numerical Calculation Method—A Case Study. Energies 2020, 13, 4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, P. The Effectiveness of Green Roofs in Reducing Building Energy Consumptions across Different Climates. A Summary of Literature Results. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 151, 111523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, F.; Hewage, K. Probabilistic Social Cost-Benefit Analysis for Green Roofs: A Lifecycle Approach. Build. Environ. 2012, 58, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulubeyli, S.; Arslan, V. Economic Viability of Extensive Green Roofs through Scenario and Sensitivity Analyses: Clients’ Perspective. Energy Build. 2017, 139, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.; Adriaens, P.; Talbot, F.B. Green Roof Valuation: A Probabilistic Economic Analysis of Environmental Benefits. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.L.S.; Chow, T.T. Energy and Economic Performance of Green Roof System under Future Climatic Conditions in Hong Kong. Energy Build. 2013, 64, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, M.; Ignjatovic, D.; Radivojević, A.; Rajcic, A. Atlas of Multifamily Housing in Serbia Energy Efficiency in Public Buildings View Project Creating the Network of Knowledge Labs for Sustainable and Resilient Environments-KLABS View Project; Faculty of Architecture, University of Belgrade, GIZ—Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit: Belgrade, Serbia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Amoruso, G.; Donevska, N.; Skomedal, G. German and Norwegian Policy Approach to Residential Buildings’ Energy Efficiency—A Comparative Assessment. Energy Effic. 2018, 11, 1375–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, J.; Reindl, K. Understanding Barriers to Energy-Efficiency Renovations of Multifamily Dwellings. Energy Effic. 2018, 11, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, S.W.; Callaghan, C.; Kuhn, M.E.; Arch, B.; Bass, B. Greenbacks from Green Roofs: Forging a New Industry in Canada; Peck & Associates: Wellesley, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Crncevic, T.; Sekulic, M. Green Roofs in the Context of Climate Changes—Review of New Experience. Arhit. i Urban. 2012, 36, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberalesso, T.; Oliveira Cruz, C.; Matos Silva, C.; Manso, M. Green Infrastructure and Public Policies: An International Review of Green Roofs and Green Walls Incentives. Land Use Policy 2020, 96, 104693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, G. Green Roof Policies: Tools for Encouraging Sustainable Design; British Columbia Society of Landscape Architects: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Novikova, A.; Csoknyai, T.; Szalay, Z. Low Carbon Scenarios for Higher Thermal Comfort in the Residential Building Sector of South Eastern Europe. Energy Effic. 2018, 11, 845–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnhardt, A.; Grothmann, T.; Wagner, J. Cost-Benefit Analysis: What Limits Its Use in Policy Making and How to Make It More Usable? A Case Study on Climate Change Adaptation in Germany. Environ. Sci. Policy 2022, 137, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Hewage, K.N. Economic Benefits and Costs of Green Roofs. In Nature Based Strategies for Urban and Building Sustainability; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 307–318. ISBN 9780128123249. [Google Scholar]
- Manso, M.; Teotónio, I.; Silva, C.M.; Cruz, C.O. Green Roof and Green Wall Benefits and Costs: A Review of the Quantitative Evidence. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World Map of the Köppen-Geiger Climate Classification Updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, N.H.; Cheong, D.K.W.; Yan, H.; Soh, J.; Ong, C.L.; Sia, A. The Effects of Rooftop Garden on Energy Consumption of a Commercial Building in Singapore. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Asif, M.; Hassanain, M.; Babsail, M.; Sanni-Anibire, M. Energy and Economic Evaluation of Green Roofs for Residential Buildings in Hot-Humid Climates. Buildings 2017, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, J.; Pérez, G.; Castell, A.; Solé, C.; Cabeza, L.F. Green Roofs as Passive System for Energy Savings in Buildings during the Cooling Period: Use of Rubber Crumbs as Drainage Layer. Energy Effic. 2014, 7, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Lei, Y.; Gu, X. Building Energy Impacts of Simple Green Roofs in the Hot Summer and Cold Winter Climate Zone: Suzhou as a Study Case. Procedia Eng. 2017, 205, 2918–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, V.; Evola, G.; Marletta, L. Energy Savings in Buildings or UHI Mitigation? Comparison between Green Roofs and Cool Roofs. Energy Build. 2016, 114, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackhurst, M.; Hendrickson, C.; Matthews, H.S. Cost-Effectiveness of Green Roofs. J. Archit. Eng. 2010, 16, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I.D. Why Should Urban Heat Island Researchers Study History? Urban Clim. 2019, 30, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokogiannakis, G.; Tietje, A.; Darkwa, J. The Role of Green Roofs on Reducing Heating and Cooling Loads: A Database across Chinese Climates. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 11, 604–610. [Google Scholar]
- Peron, F.; De Maria, M.M.; Spinazzè, F.; Mazzali, U. An Analysis of the Urban Heat Island of Venice Mainland. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2015, 19, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalošević, M.D.; Komatina, M.S.; Miloš, M.V.; Rudonja, N.R. Green Roofs and Cool Materials as Retrofitting Strategies for Urban Heat Island Mitigation—Case Study in Belgrade, Serbia. Therm. Sci. 2018, 2018, 2309–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostadinović, D.; Jovanović, M.; Bakić, V.; Stepanić, N.; Todorović, M. Experimental Investigation of Summer Thermal Performance of the Green Roof System with Mineral Wool Substrate. Build. Environ. 2022, 217, 109061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C.; Yeung, K.K.A. A Comprehensive Study of Green Roof Performance from Environmental Perspective. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2014, 3, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, B.; Seshadri, S.; Mathewos, E.; Gebreyesus, T. Impact of Green Roofs on Urban Living. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2018, 8, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.G. The Application of the Biosphere Reserve Concept to Urban Areas: The Case of Green Rooftops for Habitat Network in Seoul. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1023, 187–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrader, S.; Böning, M. Soil Formation on Green Roofs and Its Contribution to Urban Biodiversity with Emphasis on Collembolans. Pedobiologia 2006, 50, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akther, M.; He, J.; Chu, A.; Huang, J.; van Duin, B. A Review of Green Roof Applications for Managing Urban Stormwater in Different Climatic Zones. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suszanowicz, D.; Kolasa-Wiȩcek, A. The Impact of Green Roofs on the Parameters of the Environment in Urban Areas-Review. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, B.A.; Bass, B. Estimates of Air Pollution Mitigation with Green Plants and Green Roofs Using the UFORE Model. Urban Ecosyst. 2008, 11, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, Q.; Gong, P. Quantifying Air Pollution Removal by Green Roofs in Chicago. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7266–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perišić, M.; Rajšić, S.; Šoštarić, A.; Mijić, Z.; Stojić, A. Levels of PM10-Bound Species in Belgrade, Serbia: Spatio-Temporal Distributions and Related Human Health Risk Estimation. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, L.F.M.; Jensen, M.B. Benefits of Green Roofs: A Systematic Review of the Evidence for Three Ecosystem Services. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 28, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.J.H.; Lee, K.E.; Sargent, L.; Johnson, K.A.; Rayner, J.; Farrell, C.; Miller, R.E.; Williams, N.S.G. Appraising the Psychological Benefits of Green Roofs for City Residents and Workers. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 44, 126399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.R.A.; Ahmad, H.; Rosley, M.S.F. Green Roof: Its Awareness Among Professionals and Potential in Malaysian Market. Procedia—Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 85, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproul, J.; Wan, M.P.; Mandel, B.H.; Rosenfeld, A.H. Economic Comparison of White, Green, and Black Flat Roofs in the United States. Energy Build. 2014, 71, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichihara, K.; Cohen, J.P. New York City Property Values: What Is the Impact of Green Roofs on Rental Pricing? Lett. Spat. Resour. Sci. 2011, 4, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekrle, M.; Liberalesso, T.; Macháč, J.; Matos Silva, C. The Economic Value of Green Roofs: A Case Study Using Different Cost–Benefit Analysis Approaches. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 413, 137531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdiyar, A.; Tabatabaee, S.; Sadeghifam, A.N.; Mohandes, S.R.; Abdullah, A.; Meynagh, M.M. Probabilistic Private Cost-Benefit Analysis for Green Roof Installation: A Monte Carlo Simulation Approach. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 20, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdiyar, A.; Tabatabaee, S.; Yahya, K.; Mohandes, S.R. A Probabilistic Financial Feasibility Study on Green Roof Installation from the Private and Social Perspectives. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 58, 126893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, V.; Votsis, A.; Perrels, A.; Lehvävirta, S. Cost-Benefit Analysis of Green Roofs in Urban Areas: Case Study in Helsinki; Ilmatieteen Laitos: Helsinki, Finland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Noor, N.M.; Asmawi, M.Z.; Abdullah, A. Sustainable Urban Regeneration: GIS and Hedonic Pricing Method in Determining the Value of Green Space in Housing Area. Procedia—Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 170, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, S.; Catania, F.; Gagliano, A.; Sciuto, G. A Comprehensive Study on Green Roof Performance for Retrofitting Existing Buildings. Build. Environ. 2018, 136, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomalty, R.; Komorowski, B. The Monetary Value of the Soft Benefits of Green Roofs; Smart Cities Research Services: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Porsche, U.; Köhler, M. Life Cycle Cost of Green Roofs—A Comparison of Germany, USA, and Brazil; Latin American Renewable Energy Fair (LAREF): Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Karteris, M.; Theodoridou, I.; Mallinis, G.; Tsiros, E.; Karteris, A. Towards a Green Sustainable Strategy for Mediterranean Cities: Assessing the Benefits of Large-Scale Green Roofs Implementation in Thessaloniki, Northern Greece, Using Environmental Modelling, GIS and Very High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Data. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 510–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1991-1-1; Eurocode 1: Actions on Structures—Part 1-1: General Actions—Densities, Self-Weight, Imposed Loads for Buildings. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 1991.
- Dvorak, B. Comparative Analysis of Green Roof Guidelines and Standards in Europe and North America. J. Green Build. 2011, 6, 170–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, A.; Szalay, Z.; Feiler, J.; Jovanović, M. The Typology of the Residential Building Stock in Serbia and Modelling Its Low-Carbon Transformation. In Support for Low-Emission Development in South Eastern Europe (SLED); Regional Environmental Center: Skopje, Macedonia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, T.; Keeler, A. Life-Cycle Cost-Benefit Analysis of Extensive Vegetated Roof Systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munby, B. Feasibility Study for the Retrofitting of Green Roofs. In Civil and Structural Engineering; University of Sheffield: Sheffield, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Eksi, M.; Rowe, D.B.; Wichman, I.S.; Andresen, J.A. Effect of Substrate Depth, Vegetation Type, and Season on Green Roof Thermal Properties. Energy Build. 2017, 145, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianella, A.; Aye, L.; Chen, Z.; Williams, N.S.G. Substrate Depth, Vegetation and Irrigation Affect Green Roof Thermal Performance in a Mediterranean Type Climate. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, Z.; Yang, J.; Tang, M.; Feng, C. An Experimental Study on the Thermal and Energy Performance of Self-Sustaining Green Roofs under Severe Drought Conditions in Summer. Energy Build. 2022, 261, 111953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Jim, C.Y.; Chen, A.; Li, X. A Random Effects Model to Optimize Soil Thickness for Green-Roof Thermal Benefits in Winter. Energy Build. 2021, 237, 111953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapf, O.; Antoniou, T.; D’angiolella, R. Renovating Belgrade—A Framework for Exploring the Potential to Renovate the City of Belgrade; APO: Hawthorn, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Firestone, M.; Fenner-Crisp, P.; Barry, T.; Bennett, D.; Chang, S.; Callahan, M.; Burke, A.; Barnes, D.; Wood, W.P.; Knott, S.M. Guiding Principles for Monte Carlo Analysis Technical Panel Office of Prevention, Pesticides, and Toxic Substances Risk Assessment Forum Staff; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Saiz, S.; Kennedy, C.; Bass, B.; Pressnail, K. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of Standard and Green Roofs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4312–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulubeyli, S.; Arslan, V.; Kazaz, A. Comparative Life Cycle Costing Analysis of Green Roofs: The Regional Aspect. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2017, 5, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailor, D.J. A Green Roof Model for Building Energy Simulation Programs. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltelli, A.; Annoni, P.; Azzini, I.; Campolongo, F.; Ratto, M.; Tarantola, S. Variance Based Sensitivity Analysis of Model Output. Design and Estimator for the Total Sensitivity Index. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2010, 181, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, T.; Usher, W.; Herman, J. Toward SALib 2.0: Advancing the Accessibility and Interpretability of Global Sensitivity Analyses. Socio-Environ. Syst. Model. 2022, 4, 18155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Committee of European Securities Regulators (CESR). Guidelines on Impact Assessment for EU Lamfalussy Level 3 Committees; ESMA: Paris, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).