The Effects of 8 Aerobic Endurance Training Weeks of 4vs.4+GK Small-Sided Games versus Traditional Training on Physical Fitness and Skills among U18 Football Players
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Design of Research
2.2. Participants
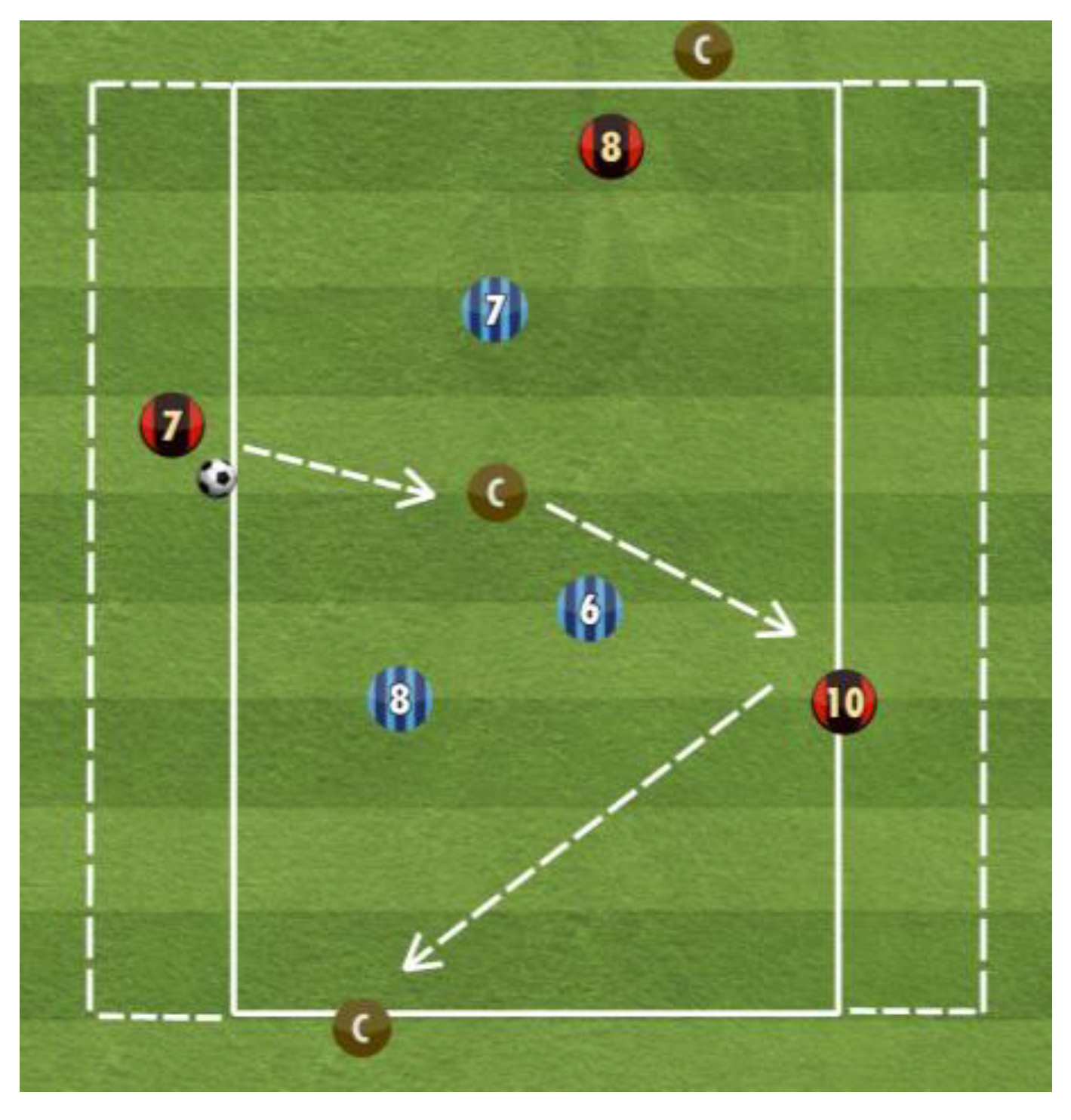
2.3. Test Applied
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. VO2max
3.2. Tests of 10 m Sprint and 20 m Sprint
3.3. Agility Tests
3.4. Tests of Total Distance, High-Speed Running and Very-High-Speed Running Recorded during a Small-Sided Game
3.5. Independent Comparative Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edis, Ç.; Vural, F.; Vurgun, H. The Importance of Postural Control in Relation to Technical Abilities in Small-Sided Soccer Games. J. Hum. Kinet. 2016, 53, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freire, L.A.; de Brito, M.A.; Esteves, N.S.; Tannure, M.; Slimani, M.; Znazen, H.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Brito, C.J.; Soto, D.A.S.; Gonçalves, D.; et al. Running Performance of High-Level Soccer Player Positions Induces Significant Muscle Damage and Fatigue Up to 24 h Postgame. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 708725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellal, A.; Varliette, C.; Owen, A.; Chirico, E.N.; Pialoux, V. Small-sided games versus interval training in amateur soccer players: Effects on the aerobic capacity and the ability to perform intermittent exercises with changes of direction. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 2712–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, A.; Roqueta, E.; Tarrago, J.R.; Seirullo, F.; Cos, F. Training in team sports: Coadjuvant training in the FCB. Apunts. Educ. Fis. Y Deporte 2019, 138, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, P.; Engel, F.A.; Holmberg, H.C.; Sperlich, B. A Meta-Comparison of the Effects of High-Intensity Interval Training to Those of Small-Sided Games and Other Training Protocols on Parameters Related to the Physiology and Performance of Youth Soccer Players. Sports Med. Open 2019, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massamba, A.; Dufour, S.P.; Favret, F.; Hureau, T.J. Small-Sided Games Are Not as Effective as Intermittent Running to Stimulate Aerobic Metabolism in Prepubertal Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2021, 16, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rodenas, J.; Calabuig, F.; Aranda, R. Effect of the Game Design, the Goal Type and the Number of Players on Intensity of Play in Small-Sided Soccer Games in Youth Elite Players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2015, 49, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bompa, T.O.; Buzzichelli, C. Periodization: Theory and Methodology of Training; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pino-Ortega, J.; Oliva-Lozano, J.M.; Rico-González, M. Comparison of the validity and reliability of local positioning systems against other tracking technologies in team sport: A systematic review. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part P. J. Sports Eng. Technol. 2022, 236, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, K.; Araújo, D.; Correia, V.; Vilar, L. How small-sided and conditioned games enhance acquisition of movement and decision-making skills. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2013, 41, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sousa, H.; Gouveia, É.R.; Marques, A.; Sarmento, H.; Pestana, M.; Quintal, T.; Lopes, H.; Ihle, A. The Influence of Small-Sided Football Games with Numerical Variability in External Training Load. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, F.M.; Marcora, S.M.; Castagna, C.; Reilly, T.; Sassi, A.; Iaia, F.M.; Rampinini, E. Physiological and performance effects of generic versus specific aerobic training in soccer players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2006, 27, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hill-Haas, S.V.; Dawson, B.; Impellizzeri, F.M.; Coutts, A.J. Physiology of small-sided games training in football: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köklü, Y.; Cihan, H.; Alemdaroğlu, U.; Dellal, A.; Wong, D.P. Acute effects of small-sided games combined with running drills on internal and external loads in young soccer players. Biol. Sport 2020, 37, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouertatani, Z.; Selmi, O.; Marsigliante, S.; Aydi, B.; Hammami, N.; Muscella, A. Comparison of the Physical, Physiological, and Psychological Responses of the High-Intensity Interval (HIIT) and Small-Sided Games (SSG) Training Programs in Young Elite Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthof, S.B.H.; Frencken, W.G.P.; Lemmink, K.A. A Match-Derived Relative Pitch Area Facilitates the Tactical Representativeness of Small-Sided Games for the Official Soccer Match. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santos, S.; Jiménez, S.; Sampaio, J.; Leite, N. Effects of the Skills4Genius sports-based training program in creative behavior. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machado, G.; Da Costa, I.T. TacticUP Video Test for Soccer: Development and Validation. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellal, A.; Chamari, K.; Owen, A.L.; Wong, D.P. Influence of technical instructions on the physiological and physical demands of small-sided soccer games. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2011, 11, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellal, A.; da Silva, C.D.; Hill-Haas, S.; del Wong, P.; Natali, A.J.; De Lima, J.R.; Bara Filho, M.G.; Marins, J.J.; Garcia, E.S.; Chamari, K. Heart rate monitoring in soccer: Interest and limits during competitive match play and training, practical application. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 2890–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dellal, A.; Hill-Haas, S.; Lago-Penas, C.; Chamari, K. Small-sided games in soccer: Amateur vs. professional players’ physiological responses, physical, and technical activities. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köklü, Y.; Aşçi, A.; Koçak, F.U.; Alemdaroğlu, U.; Dündar, U. Comparison of the physiological responses to different small-sided games in elite young soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1522–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Dios-Álvarez, V.; Lorenzo-Martínez, M.; Padrón-Cabo, A.; Rey, E. Small-sided games in female soccer players: A systematic review. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2022, 62, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujalance-Moreno, P.; Latorre-Román, P.Á.; García-Pinillos, F. A systematic review on small-sided games in football players: Acute and chronic adaptations. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 921–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, F.M.; Sarmento, H. Combining small-sided soccer games and running-based methods: A systematic review. Biol. Sport 2021, 38, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, J.; Hofman, B.N.; Pasquarelli, B.N.; Leonardi, T.J. Proposals and effects of training using small-sided games for young soccer players: A narrative review. Motriz. Rev. De Educ. Física 2022, 28, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.M.; Silva, A.F.; Kawczyński, A.; Yıldız, M.; Chen, Y.S.; Birlik, S.; Nobari, H.; Akyildiz, Z. Physiological and locomotor demands during small-sided games are related to match demands and physical fitness? A study conducted on youth soccer players. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.M.; Soylu, Y.; Arslan, E.; Kilit, B.; Garrett, J.; van den Hoek, D.; Badicu, G.; Filipa Silva, A. Can high-intensity interval training and small-sided games be effective for improving physical fitness after detraining? A parallel study design in youth male soccer players. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, M.V.; Botelho, G.M.; Gonçalves, B.S.; Sampaio, J.E. Physiological responses and activity profiles of football small-sided games. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Quintana, J.S.; Casamichana, D.; Castellano, J.; Calleja-González, J.; Jukić, I.; Ostojić, S.M. The influence of ball-touches number on physical. Kinesiology 2013, 45, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Nayıroğlu, S.; Yılmaz, A.K.; Silva, A.F.; Silva, R.; Nobari, H.; Clemente, F.M. Effects of small-sided games and running-based high-intensity interval training on body composition and physical fitness in under-19 female soccer players. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, E.; Orer, G.E.; Clemente, F.M. Running-based high-intensity interval training vs. small-sided game training programs: Effects on the physical performance, psychophysiological responses and technical skills in young soccer players. Biol. Sport 2020, 37, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faude, O.; Steffen, A.; Kellmann, M.; Meyer, T. The effect of short-term interval training during the competitive season on physical fitness and signs of fatigue: A crossover trial in high-level youth football players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runacres, A.; Mackintosh, K.A.; McNarry, M.A. The effect of constant-intensity endurance training and high-intensity interval training on aerobic and anaerobic parameters in youth. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 2492–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, M.J.S.P.S.R. Managing high-speed running load in professional soccer players: The benefit of high-intensity interval training supplementation. Sport Perform. Sci. Rep. 2019, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Manzi, V.; Impellizzeri, F.; Castagna, C. Aerobic fitness ecological validity in elite soccer players: A metabolic power approach. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dello Iacono, A.; McLaren, S.J.; Macpherson, T.W.; Beato, M.; Weston, M.; Unnithan, V.B.; Shushan, T. Quantifying Exposure and Intra-Individual Reliability of High-Speed and Sprint Running During Sided-Games Training in Soccer Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 371–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos Rebelo, A.N.; Silva, P.; Rago, V.; Barreira, D.; Krustrup, P. Differences in strength and speed demands between 4v4 and 8v8 small-sided football games. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 2246–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los Arcos, A.; Vázquez, J.S.; Martin, J.; Lerga, J.; Sánchez, F.; Villagra, F.; Zulueta, J.J. Effects of Small-Sided Games vs. Interval Training in Aerobic Fitness and Physical Enjoyment in Young Elite Soccer Players. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.F.; Oliveira, R.; Ceylan, H.I.; Akyildiz, Z.; González-Fernández, F.T.; Nobari, H.; Yıldız, M.; Birlik, S.; Clemente, F.M. Effects of a small-sided games training program in youth male soccer players: Variations of the locomotor profile while interacting with baseline level and with the accumulated load. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makar, P.; Praça, G.; Kawczyński, A.; Akyildiz, Z.; Yıldız, M.; Aquino, R.; Clemente, F.M. Testing the effects of 4-week training programs based on extreme and medium-sided soccer games: A study focusing on change-of-direction, vertical jump height and locomotor profile. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.M.; Praça, G.M.; Aquino, R.; Castillo, D.; Raya-González, J.; Rico-González, M.; Afonso, J.; Sarmento, H.; Silva, A.F.; Silva, R.; et al. Effects of pitch size on soccer players’ physiological, physical, technical, and tactical responses during small-sided games: A meta-analytical comparison. Biol. Sport 2023, 40, 111–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.M.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Sarmento, H.; Praça, G.M.; Afonso, J.; Silva, A.F.; Rosemann, T.; Knechtle, B. Effects of Small-Sided Game Interventions on the Technical Execution and Tactical Behaviors of Young and Youth Team Sports Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 667041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, C.H.; Hwang-Bo, K.; Jee, H. Technical and Physical Activities of Small-Sided Games in Young Korean Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 2164–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.F.; González-Fernández, F.T.; Aquino, R.; Akyildiz, Z.; Vieira, L.P.; Yıldız, M.; Birlik, S.; Nobari, H.; Praça, G.; Clemente, F.M. Analyzing the within and between Players Variability of Heart Rate and Locomotor Responses in Small-Sided Soccer Games Performed Repeatedly over a Week. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gantois, P.; Piqueras-Sanchiz, F.; Cid, M.J.F.A.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Castillo, D.; Nakamura, F.Y. The effects of different small-sided games configurations on heart rate, rating of perceived exertion, and running demands in professional soccer players. Eur. J. Sport. Sci. 2022, 8, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mara, J.K.; Thompson, K.G.; Pumpa, K.L. Physical and Physiological Characteristics of Various-Sided Games in Elite Women’s Soccer. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trecroci, A.; Boccolini, G.; Duca, M.; Formenti, D.; Alberti, G. Mental fatigue impairs physical activity, technical and decision-making performance during small-sided games. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, C.; Akenhead, R.; Thomas, K. Time-motion analysis of acceleration demands of 4v4 small-sided soccer games played on different pitch sizes. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2014, 33, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparkes, W.; Turner, A.; Weston, M.; Russell, M.; Johnston, M.; Kilduff, L. Neuromuscular, Biochemical, Endocrine, and Mood Responses to Small-Sided Games’ Training in Professional Soccer. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 2569–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ric, A.; Hristovski, R.; Gonçalves, B.; Torres, L.; Sampaio, J.; Torrents, C. Timescales for exploratory tactical behaviour in football small-sided games. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferraz, R.; Gonçalves, B.; Coutinho, D.; Oliveira, R.; Travassos, B.; Sampaio, J.; Marques, M.C. Effects of Knowing the Task’s Duration on Soccer Players’ Positioning and Pacing Behaviour during Small-Sided Games. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, J.; Travassos, B.; Gonçalves, B.; Mourão, P.; Viana, J.L.; Sampaio, J. Exploring the Effects of Playing Formations on Tactical Behavior and External Workload During Football Small-Sided Games. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 2024–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntianu, V.-A.; Abalașei, B.-A.; Nichifor, F.; Dumitru, I.-M. The Correlation between Psychological Characteristics and Psychomotor Abilities of Junior Handball Players. Children 2022, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusa, F.S.; Badau, A.; Badau, D.; Trambitas, C.; Brinzaniuc, K. Investigating the deformation parameters of PVC fitness balls in relation to the height and body mass index of the users. Mater. Plast. 2017, 54, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantau, C.; Nae, C.; Hantau, C.; Neagu, N. Formation Strategy for the Young Handball Players. Procedia Social. Behav. Sci. 2013, 93, 1936–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hantau, C.; Hatzimanouil, D.; Giannakos, A. The Impact of Dynamic Games on the Coordination Development. Marathon 2015, 7, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Gherghel, A.; Badau, D.; Badau, A.; Moraru, L.; Manolache, G.M.; Oancea, B.M.; Tifrea, C.; Tudor, V.; Costache, R.M. Optimizing the Explosive Force of the Elite Level Football-Tennis Players through Plyometric and Specific Exercises. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, A.L.; Newton, M.; Shovlin, A.; Malone, S. The Use of Small-Sided Games as an Aerobic Fitness Assessment Supplement Within Elite Level Professional Soccer. J. Hum. Kinet. 2020, 71, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riboli, A.; Esposito, F.; Coratella, G. Small-Sided Games in Elite Football: Practical Solutions to Replicate the 4-min Match-Derived Maximal Intensities. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2023, 37, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryanoosh, F.; Alishavandi, H.; Nemati, J.; Basereh, A.; Jowhari, A.; Asad-Manesh, E.; Oliveira, R.; Brito, J.P.; Prieto-González, P.; García-Calvo, T.; et al. Effect of interval and continuous small-sided games training on the bio-motor abilities of young soccer players: A comparative study. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čaušević, D.; Rani, B.; Gasibat, Q.; Čović, N.; Alexe, C.I.; Pavel, S.I.; Burchel, L.O.; Alexe, D.I. Maturity-Related Variations in Morphology, Body Composition, and Somatotype Features among Young Male Football Players. Children 2023, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albina, A.M.; Buga, A.A.M.; Ion, L.; Burchel, L.O. How introducing isoinertial exercises using a flywheel can improve the training of athletes: A systematic review. Bull. Transilv. Univ. Braşov Ser. IX Sci. Hum. Kinet. 2023, 16, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboli, A.; Dellal, A.; Esposito, F.; Coratella, G. Can small-sided games assess the training-induced aerobic adaptations in elite football players? J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2022, 62, 1313–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalen, T.; Sandmæl, S.; Stevens, T.G.A.; Hjelde, G.H.; Kjøsnes, T.N.; Wisløff, U. Differences in Acceleration and High-Intensity Activities Between Small-Sided Games and Peak Periods of Official Matches in Elite Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Testing | N | M ± SD mL/kg/min | CV (%) | Median | Asymmetry Coefficient (β) | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Initial | 20 | 55.68 ± 4.38 | 7.87 | 54.73 | 0.22 | 6.688 | <0.0005 |
| Final | 20 | 61.44 ± 2.66 | 4.33 | 61.84 | −0.15 | |||
| Control | Initial | 20 | 57.34 ± 1.95 | 3.40 | 57.85 | −0.26 | 0.763 | >0.05 |
| Final | 20 | 57.51 ± 2.35 | 4.08 | 58.11 | −0.26 |
| Group | Variable | Testing | N | M ± SD |
CV (%) | Median |
Asymmetry Coefficient (β) | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | 10 m sprint (s) | Initial | 20 | 1.91 ± 0.08 | 4.28 | 1.90 | 0.23 | 10.855 | <0.0005 |
| Final | 20 | 1.79 ± 0.06 | 3.53 | 1.78 | 0.11 | ||||
| 20 m sprint (s) | Initial | 20 | 3.17 ± 0.10 | 3.03 | 3.15 | 0.24 | 2.220 | <0.025 | |
| Final | 20 | 3.15 ± 0.12 | 3.81 | 3.13 | 0.18 | ||||
| Control | 10 m sprint (s) | Initial | 20 | 1.85 ± 0.12 | 6.60 | 1.84 | 0.07 | 4.656 | <0.0005 |
| Final | 20 | 1.77 ± 0.08 | 4.30 | 1.77 | −0.01 | ||||
| 20 m sprint (s) | Initial | 20 | 3.15 ± 0.21 | 6.77 | 3.09 | 0.27 | 2.873 | <0.005 | |
| Final | 20 | 3.07 ± 0.14 | 4.57 | 3.04 | 0.21 |
| Group | Variable | Testing | N | M ± SD | CV (%) | Median | Asymmetry Coefficient (β) | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment | Illinois Agility Test (s) | Initial | 20 | 15.72 ± 0.36 | 2.27 | 15.81 | −0.23 | 9.905 | <0.0005 |
| Final | 20 | 15.04 ± 0.18 | 1.18 | 15.04 | −0.03 | ||||
| Short Dribbling Test (s) | Initial | 20 | 11.87 ± 0.47 | 3.94 | 11.86 | 0.02 | 9.847 | <0.0005 | |
| Final | 20 | 11.30 ± 0.55 | 4.84 | 11.35 | −0.10 | ||||
| Control | Illinois Agility Test (s) | Initial | 20 | 15.71 ± 0.41 | 2.59 | 15.90 | −0.46 | 2.201 | <0.025 |
| Final | 20 | 15.67 ± 0.43 | 2.75 | 15.81 | −0.32 | ||||
| Short Dribbling Test (s) | Initial | 20 | 11.89 ± 0.51 | 4.25 | 11.93 | −0.09 | 1.059 | >0.05 | |
| Final | 20 | 11.88 ± 0.51 | 4.29 | 11.95 | −0.15 |
| Variable | Testing | N | M ± SD | CV (%) | Median | Asymmetry Coefficient (β) | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Distance (m) | Initial | 20 | 2201.65 ± 121.57 | 5.52 | 2216 | −118.00 | 6.941 | <0.0005 |
| Final | 20 | 2373.15 ± 104.79 | 4.42 | 2349 | 0.23 | |||
| High-Speed Running (m) | Initial | 20 | 146.60 ± 29.33 | 20.00 | 140.50 | 0.21 | 4.985 | <0.0005 |
| Final | 20 | 191.90 ± 37.14 | 19.36 | 195.50 | −0.10 | |||
| Very-High-Speed Running (m) | Initial | 20 | 4.25 ± 6.81 | 160.12 | 0 | 0.63 | 1.532 | >0.05 |
| Final | 20 | 5.25 ± 5.96 | 113.60 | 2.50 | 0.46 |
| Variable | Testing | Group | N | Median ± SD | CV (%) | Coef. ω2 | SD | d | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VO2max (mL/kg/min) | Initial testing | Experiment | 20 | 55.68 ± 4.38 | 7.87 | 0.034 | 3.389 | −0.489 | 1.546 | >0.05 |
| Control | 20 | 57.34 ± 1.95 | 3.40 | 3.4% | ||||||
| Final testing | Experiment | 20 | 61.44 ± 2.66 | 4.33 | 0.372 | 2.508 | 1.57 | 4.966 | <0.0005 | |
| Control | 20 | 57.51 ± 2.35 | 4.08 | 37.20% | ||||||
| 10 m speed (s) | Initial testing | Experiment | 20 | 1.91 ± 0.08 | 4.28 | 0.07 | 0.104 | 0.635 | 2.008 | <0.05 |
| Control | 20 | 1.85 ± 0.12 | 6.60 | 7.0% | ||||||
| Final testing | Experiment | 20 | 1.79 ± 0.06 | 3.53 | −0.008 | 0.07 | 0.257 | 0.815 | >0.05 | |
| Control | 20 | 1.77 ± 0.08 | 4.30 | −0.8% | ||||||
| 20 m speed (s) | Initial testing | Experiment | 20 | 3.17 ± 0.10 | 3.03 | −0.019 | 0.165 | 0.158 | 0.498 | >0.05 |
| Control | 20 | 3.15 ± 0.21 | 6.77 | −1.9% | ||||||
| Final testing | Experiment | 20 | 3.15 ± 0.12 | 3.81 | 0.077 | 0.130 | 0.662 | 2.086 | <0.025 | |
| Control | 20 | 3.07 ± 0.14 | 4.57 | 7.7% | ||||||
| Illinois Agility Test (s) | Initial testing | Experiment | 20 | 15.72 ± 0.36 | 2.27 | −0.025 | 0.383 | 0.029 | 0.091 | >0.05 |
| Control | 20 | 15.71 ± 0.41 | 2.59 | 2.5% | ||||||
| Final testing | Experiment | 20 | 15.04 ± 0.18 | 2.59 | 0.476 | 0.330 | −1.93 | 6.109 | <0.0005 | |
| Control | 20 | 15.67 ± 0.43 | 2.75 | 47.6% | ||||||
| Short Dribbling Test (s) | Initial testing | Experiment | 20 | 11.86 ± 0.46 | 3.94 | −0.025 | 0.487 | −0.053 | 0.169 | >0.05 |
| Control | 20 | 11.89 ± 0.47 | 3.94 | 2.5% | ||||||
| Final testing | Experiment | 20 | 11.30 ± 0.55 | 4.84 | 0.217 | 0.529 | −1.10 | 3.480 | <0.005 | |
| Control | 20 | 11.88 ± 0.51 | 4.29 | 21.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaharia, G.; Badau, D.; Tudor, V.; Costache, R.; Geambasu, A.; Damian, M.; Giurgiu, L.; Damian, C.; Ursu, V.E.; Rusu, R.G.; et al. The Effects of 8 Aerobic Endurance Training Weeks of 4vs.4+GK Small-Sided Games versus Traditional Training on Physical Fitness and Skills among U18 Football Players. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7963. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137963
Zaharia G, Badau D, Tudor V, Costache R, Geambasu A, Damian M, Giurgiu L, Damian C, Ursu VE, Rusu RG, et al. The Effects of 8 Aerobic Endurance Training Weeks of 4vs.4+GK Small-Sided Games versus Traditional Training on Physical Fitness and Skills among U18 Football Players. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(13):7963. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137963
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaharia, Gabriel, Dana Badau, Virgil Tudor, Raluca Costache, Adina Geambasu, Mirela Damian, Laura Giurgiu, Cosmin Damian, Vasile Emil Ursu, Razvan Gheorghe Rusu, and et al. 2023. "The Effects of 8 Aerobic Endurance Training Weeks of 4vs.4+GK Small-Sided Games versus Traditional Training on Physical Fitness and Skills among U18 Football Players" Applied Sciences 13, no. 13: 7963. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137963
APA StyleZaharia, G., Badau, D., Tudor, V., Costache, R., Geambasu, A., Damian, M., Giurgiu, L., Damian, C., Ursu, V. E., Rusu, R. G., Hasmasan, I. T., Stoian, I., & Tifrea, C. (2023). The Effects of 8 Aerobic Endurance Training Weeks of 4vs.4+GK Small-Sided Games versus Traditional Training on Physical Fitness and Skills among U18 Football Players. Applied Sciences, 13(13), 7963. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137963








