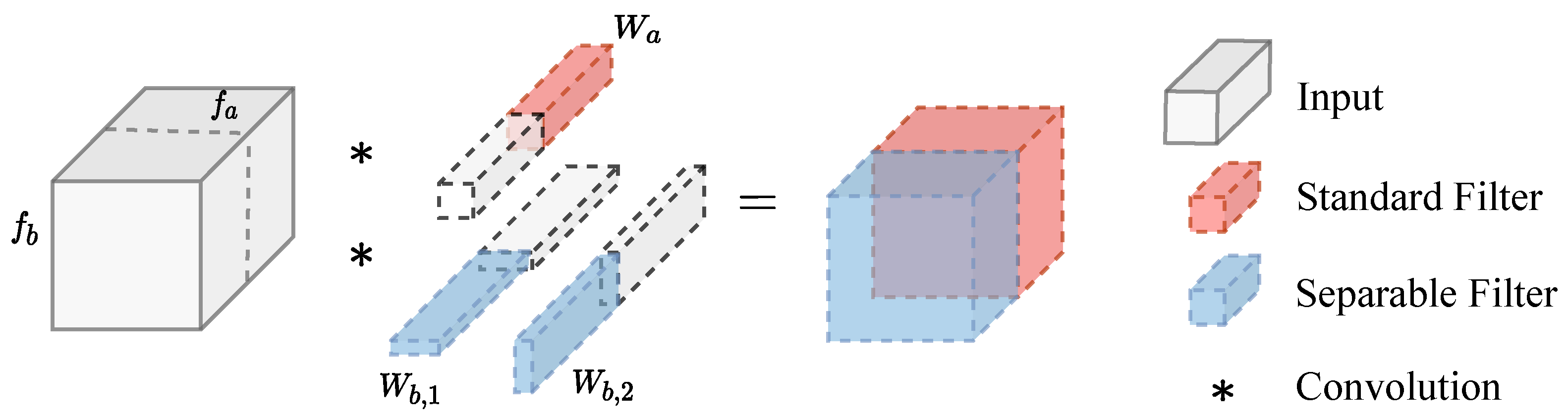Abstract
Semantic segmentation is increasingly being applied on mobile devices due to advancements in mobile chipsets, particularly in low-power consumption scenarios. However, the lightweight design of mobile devices poses limitations on the receptive field, which is crucial for dense prediction problems. Existing approaches have attempted to balance lightweight designs and high accuracy by downsampling features in the backbone. However, this downsampling may result in the loss of local details at each network stage. To address this challenge, this paper presents a novel solution in the form of a compact and efficient convolutional neural network (CNN) for real-time applications: our proposed model, local spatial perception convolution (LSPConv). Furthermore, the effectiveness of our architecture is demonstrated on the Cityscapes dataset. The results show that our model achieves an impressive balance between accuracy and inference speed. Specifically, our LightSeg, which does not rely on ImageNet pretraining, achieves an mIoU of 76.1 at a speed of 61 FPS on the Cityscapes validation set, utilizing an RTX 2080Ti GPU with mixed precision. Additionally, it achieves a speed of 115.7 FPS on the Jetson NX with int8 precision.
1. Introduction
Unmanned systems, including autonomous driving and industrial robots, have experienced significant advancements in recent years. These systems heavily rely on sensors and intelligent algorithms to perform tasks such as object recognition and tracking. Semantic segmentation plays a crucial role in obtaining semantic information for such systems, as it assigns a label to each pixel on an image, representing its semantic class, such as “road”, “building”, or “person”. However, performing semantic segmentation on low-power devices poses challenges due to limited computing resources. To achieve real-time performance on these devices, efficient and compact deep-learning models are required to extract semantic information while keeping computational complexity low.
To address this challenge, researchers have proposed various approaches for lightweight neural networks, including lightweight design, model compression, and network architecture searching (NAS).
While depth-wise convolution is commonly used to reduce computational costs, group convolution is employed to address information disfluency, where an output channel is derived from only a small part of the input channel. The MobileNet [1,2,3] and ShuffleNet [4,5] series utilize channel shuffle, respectively, to improve information quality and reduce computational complexity. However, channel shuffle introduces memory access disruptions and additional latency.
In addition to computational efficiency, contextual information is crucial for image segmentation. Recent studies have introduced self-attention mechanisms, such as non-local [6] and DANet [7,8], to capture local, multi-scale, and global contexts. Inspired by ResNeXt [9], RegSeg [10] employs a D block with dilated convolutions to increase the receptive field without sacrificing local information. However, dilated convolutions can introduce drawbacks such as the “Gridding effect” [11,12], which compromises pixel-level dense prediction tasks.
To overcome these challenges, this study proposes a novel block called “local spatial perception convolution” (LSPConv), which utilizes spatial separable convolutions to decompose a large kernel into the outer product of two vectors. A standard convolution is employed to extract local features simultaneously. LSPConv aims to reduce model complexity and parameter count. LSPConv achieves a 26.7% reduction in parameters while achieving a speedup of up to 61 FPS on the RTX 2080Ti GPU (Graphics Processing Unit).
Based on LSPConv, an LSPBlock is introduced to enhance the receptive field while reducing computation. Leveraging these modules, a real-time semantic segmentation model called LightSeg is proposed. LightSeg achieves impressive performance on different devices and settings. It achieves 115.7 FPS on embedded devices when performing int8 inference, which is demonstrating its efficiency in resource-constrained environments. On the RTX 2080Ti, LightSeg achieves a reasoning speed of 61 FPS using mixed precision, even with a larger input resolution of 1024 × 2048. These results highlight the optimized inference capabilities of LightSeg across embedded devices and precision modes.
In summary, this study contributes in three key areas:
- It proposes the novel local spatial perception convolution (LSPConv) to extract both global and local features.
- It introduces the LSP Block, based on LSPConv, to enhance the receptive field while reducing computation.
- It presents LightSeg, a real-time semantic segmentation model, achieving high inference speeds on embedded devices and GPUs, demonstrating its efficiency and versatility.
2. Related Works
2.1. Semantic Segmentation
Semantic segmentation has been a focus of research in computer vision, and several models have contributed significantly to this field.
The fully convolutional network (FCN) [13] was a pioneering network that extended end-to-end convolutional networks to semantic segmentation tasks. It introduced a deconvolutional layer for upsampling, enabling the network to recover spatial information lost during downsampling. Another influential model, U-Net [14], built upon the FCN architecture by incorporating skip connections to combine high-level semantic information with coarse and fine surface details. While FCN adds corresponding pixel values, U-Net performs concatenation on its channels.
The Deeplab series, including Deeplab [15], DeeplabV2 [16], and DeeplabV3 [17], have made significant contributions to semantic segmentation. These models introduced hole convolution, which increases the field of view without sacrificing spatial resolution. Deeplab models also incorporate Atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) [16] to extract multi-scale features using multiple dilation rates. Additionally, they leverage fully connected conditional random fields [15] (CRFs) to refine segmentation results and improve boundary smoothness.
However, recent advancements in semantic segmentation have explored limitations inherent in CNN methods, which primarily rely on local information processing. To overcome these limitations, researchers have started to incorporate Transformer schemes such as VIT [18], SETR [19], TransUNET [20], and SegFormer [21]. These models tokenize the input image, enabling the exploitation of global information for better semantic segmentation performance.
2.2. Real-Time Semantic Segmentation
Real-time semantic segmentation requires efficient models that can process images quickly without sacrificing accuracy. Researchers have explored different strategies to achieve real-time performance.
To avoid introducing additional branches for obtaining contextual information and expanding the field of perception, some models have adopted skip connections [22] to preserve image information. Additionally, lightweight segmentation networks based on transformer structures have introduced new ideas for real-time semantic segmentation. For example, EdgeNeXt [23] and Mobile-Former [24] propose novel architectures that leverage transformer principles while maintaining computational efficiency.
In contrast, the RegSeg [10] model proposes the D block to enhance contextual information and increase the receptive field. These modules enable real-time semantic segmentation by avoiding additional computational overhead.
3. Methods
3.1. Overall Architecture
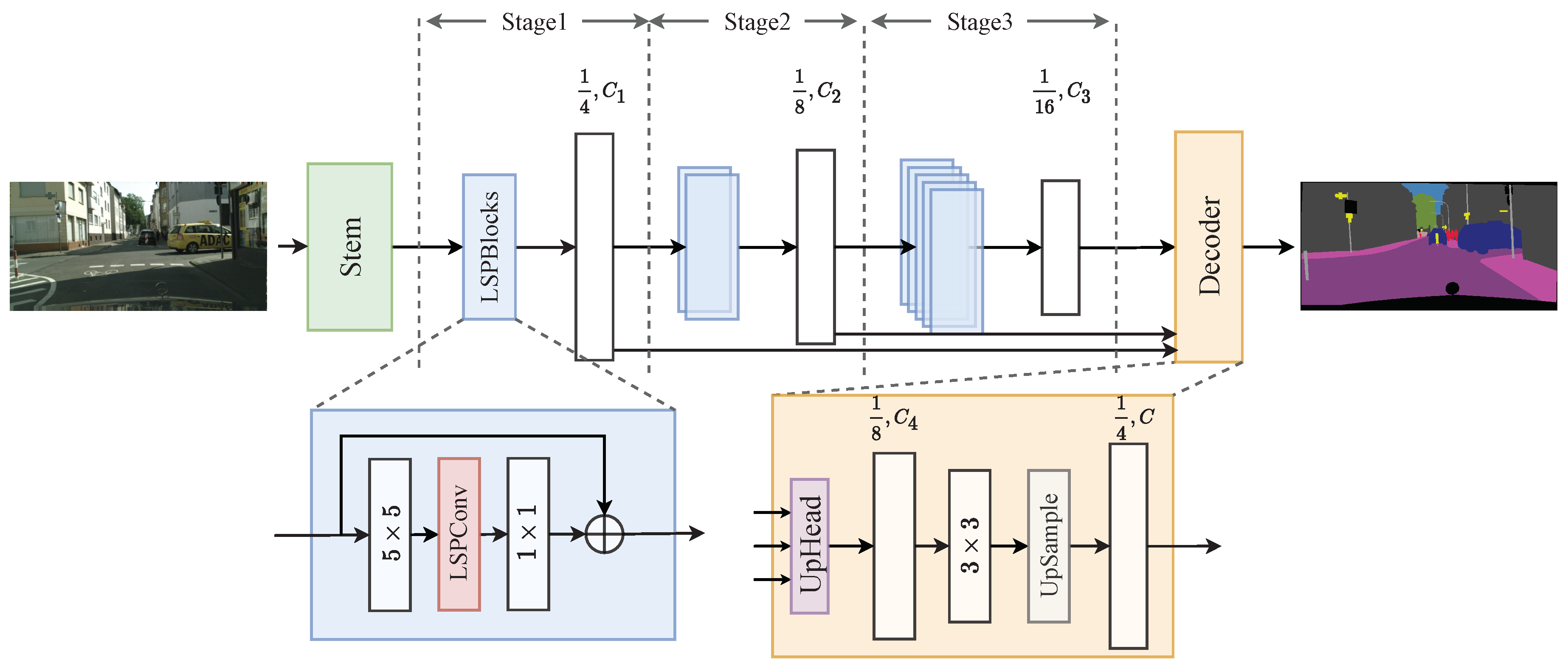
The overall architecture of LightSeg is depicted in Figure 1, which follows a standard segmentation network design consisting of an encoder and a decoder. The encoder module is responsible for extracting meaningful semantic features from the input image, capturing essential information about the image’s content and context. These extracted features are then forwarded to the decoder module, which utilizes them to make a pixel-wise classification for the entire image by effectively leveraging the rich semantic information encoded in the extracted features.
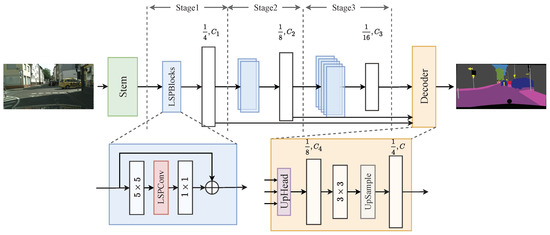
Figure 1.
Network structure diagram of LightSeg, illustrating the encoder-decoder architecture. Each stage is stacked with an LSPBlock module for robust feature extraction. The UpHead module serves as the multi-scale feature fusion module.
Our network architecture starts with a stem module, which consists of a convolution. This module performs downsampling and reduces the size of the input feature map. Extensive experiments and analysis have shown that this downsampling process has little impact on the overall accuracy of the network [25] because the network effectively captures and retains essential information for accurate predictions. Moreover, the resulting lower spatial resolution improves inference speed. Subsequently, multi-level features are extracted from the original resolution of 1/4, 1/8, and 1/16. These features undergo a fusion process facilitated by the UpHead module, which combines them into a unified representation. Finally, a convolutional layer is employed to predict the segmentation mask at a 1/4 resolution. It is important to note that the Decoder consists of C segmentation classes.
3.2. Local Spatial Perception Convolution
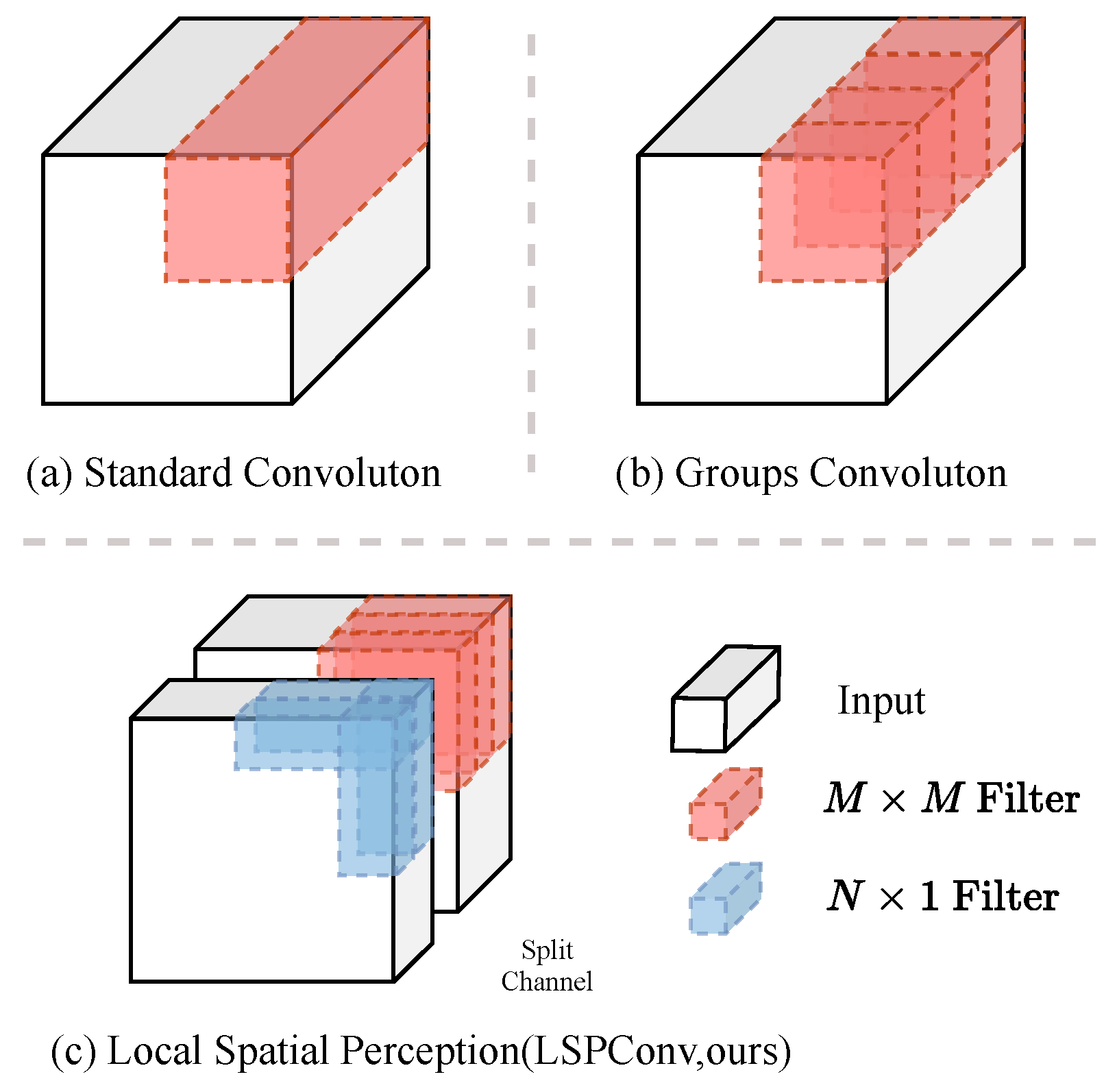
This paper introduces a novel neural convolution architecture called “Local Spatial Perception Convolution (LSPConv)” that integrates local perception and long-range dependency capturing. Figure 2 illustrates the basic structure of LSPConv, highlighting its distinctive features compared to ordinary convolutions.
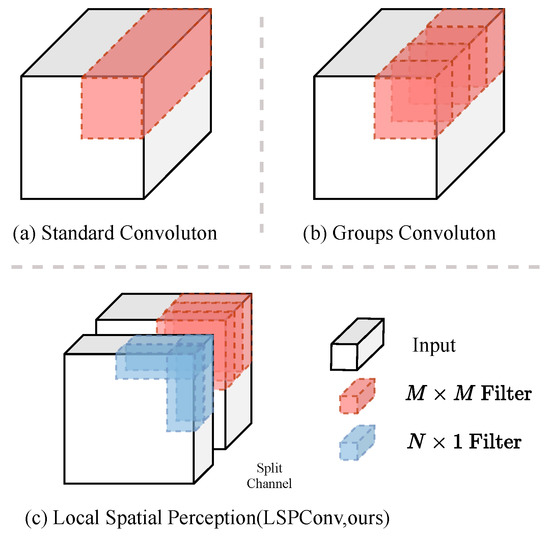
Figure 2.
The figure illustrates the distinction between feature extraction methods: standard convolution, grouped convolution, and our proposed LSPConv module. In standard convolution, a small kernel size is applied uniformly across all channels for feature extraction. Grouped convolution divides the input channels into groups, performing feature extraction using standard convolution within each group. In contrast, our LSPConv module partitions the channels into two groups, utilizing standard convolution for one group and spatial separable convolution for the other group.
The LSPConv module aims to extract more informative features from the input feature map by applying different types of convolutions to different parts of the input channels. Specifically, the input feature map is divided into two channel parts, and , which are processed separately using different convolutional layers. The mathematical expression is shown in Equation (1). Figure 3 provides a more visual demonstration of this process.
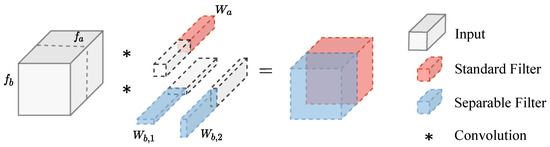
Figure 3.
Illustration of the LSPConv module. The input feature map is split into two channel parts, and , which are processed separately using different convolutional layers. The output feature maps and are then concatenated and passed through a nonlinear activation function to obtain the final output feature map .
For , a standard convolutional layer with weight parameters and bias parameters is applied. This operation produces the output feature map .
For , a depthwise separable convolutional layer is used, which consists of a depthwise convolutional layer. The depthwise convolution applies a separate filter to each input channel. In this case, the depthwise convolutional layer applied a filter represented by the weight parameters and to the input feature map , The output feature map of this operation is denoted as .
Finally, the output feature maps and are concatenated along the channel axis to form the final output feature map using the concatenation operator .
3.3. Local Spatial Perception Block
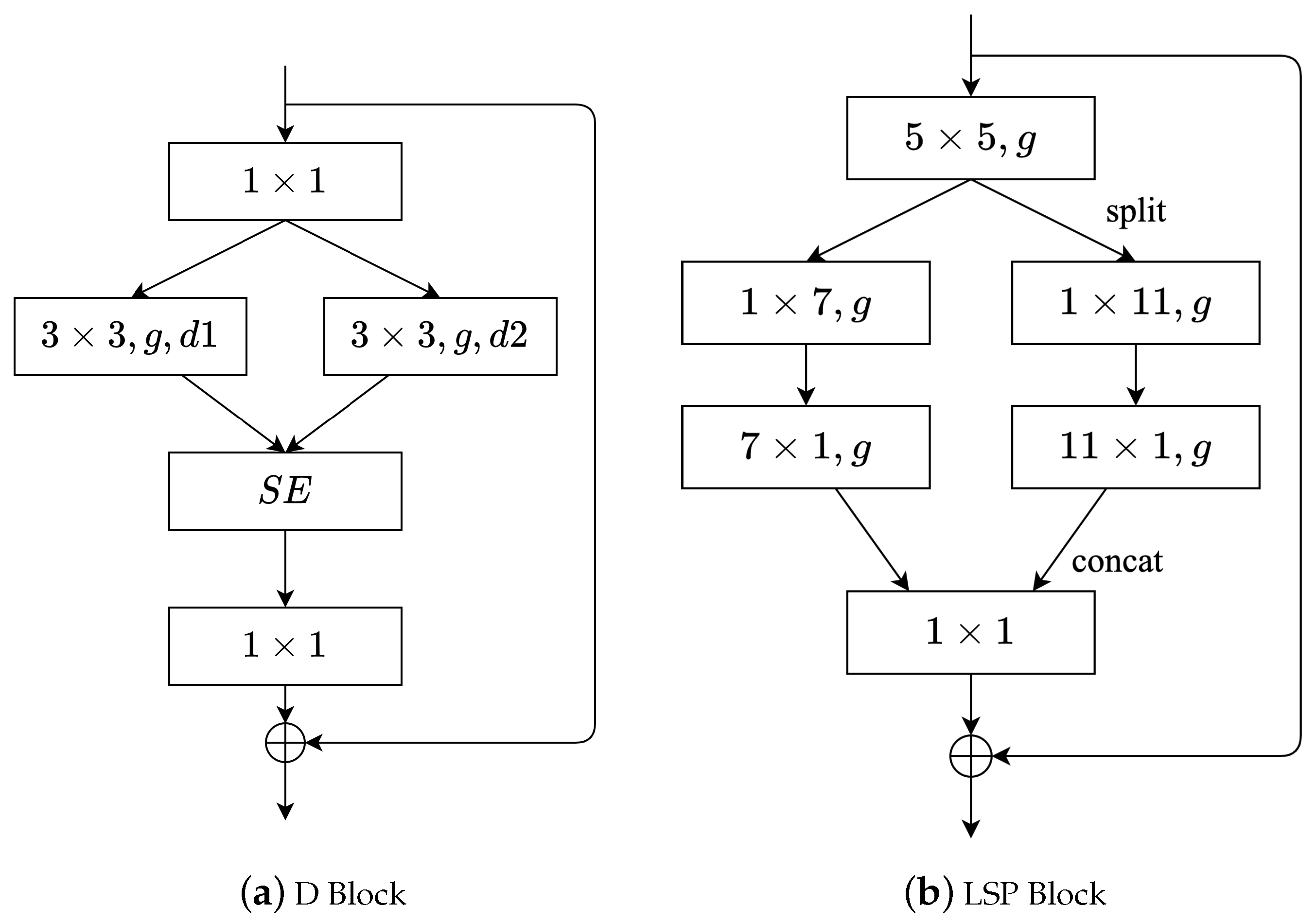
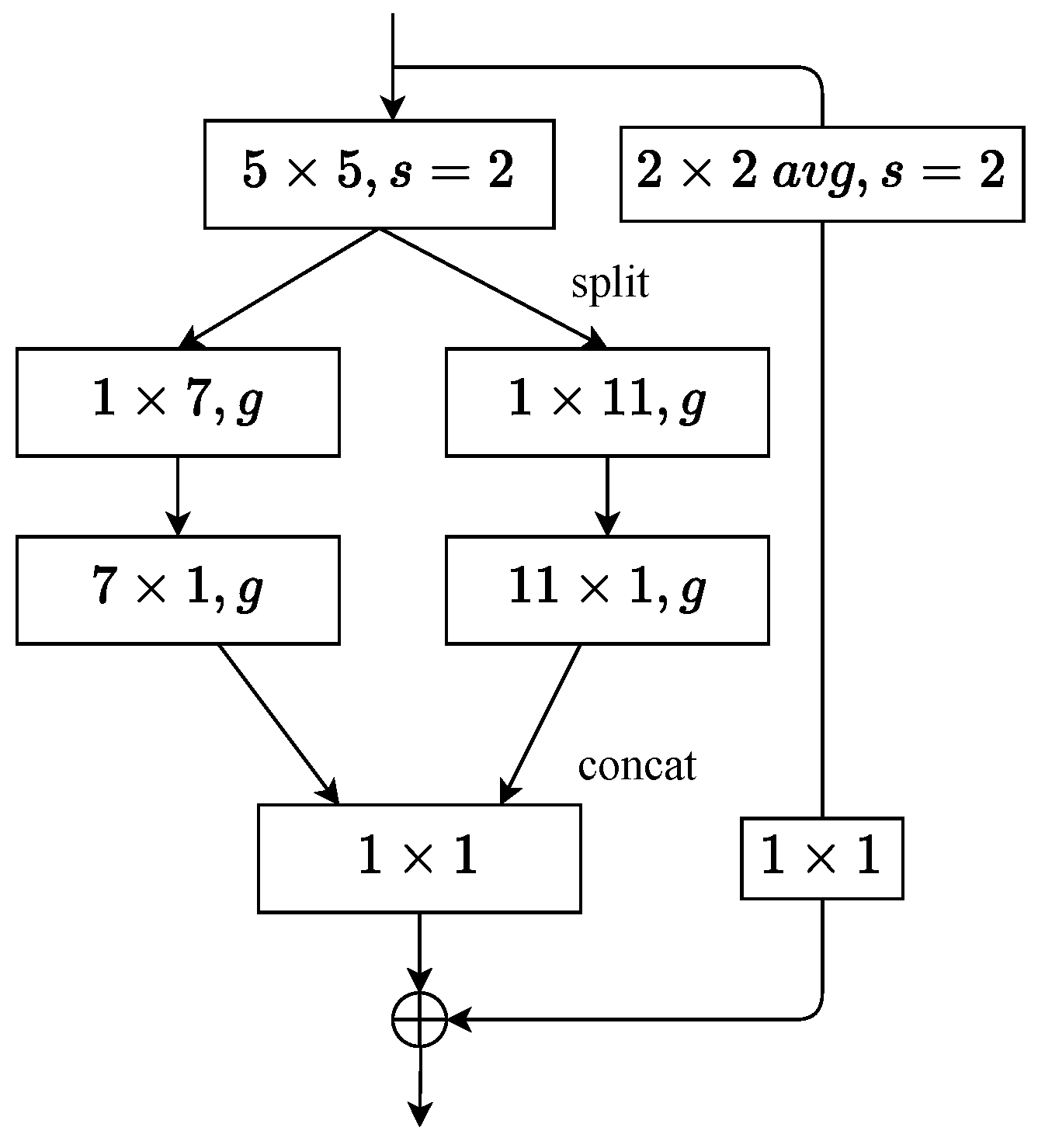
A new network block named LSPBlock was designed based on LSPConv. Figure 4b illustrates the difference between LSPBlock and DBlock [10]. LSPBlock maintains the same number of input and output channels. First, LSPBlock applies a standard convolution to extract features from the input. Then, the input with w channels is split into two groups, each group including channels. A standard convolution is applied to one group while the other group undergoes spatial separable convolution. Next, LSPBlock concatenates the outputs of the two groups and finally applies a pointwise convolution to fuse different channel features. Notably, the LSPBlock module was not used in the early stages of the network, and other modules were adopted instead. Additionally, similar to the convolutions with the parameter g shown in LightSeg, group convolutions were also used to reduce the number of parameters and computational complexity.
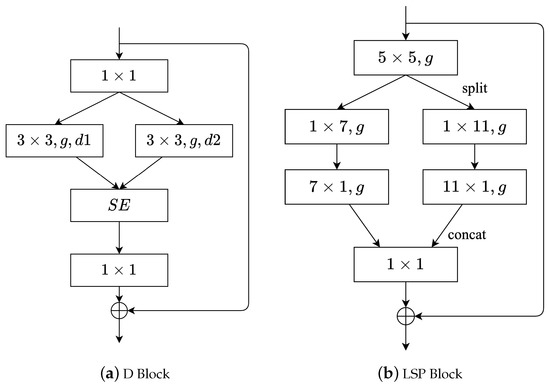
Figure 4.
Comparison of LightSeg’s LSP block and ResSeg D block. The symbol g denotes the size of the group convolution, while the symbols and represent the dilation rates of the dilated convolutions.
Assuming the input feature X has C channels and the configuration of spatially separable convolution size is m, the number of parameters P in the LSP block can be calculated as follows when the stride is 1:
where represents the number of parameters in a convolutional layer, represents the number of parameters in a spatially separable convolutional layer with kernel size m, represents the number of parameters in a convolutional layer, and P represents the total number of parameters in the LSP block.
A typical LightSeg Encoder is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The architectures of lightseg-base and lightseg-large, where denotes repeating the corresponding block for n times.
In the initial stage of the network, i.e., stem, stage 4, the standard convolution was used to extract feature information from the input.
Downsampling is performed at the beginning of each stage by applying the s block with stride = 2 (). The network is structured as Figure 5, and features are downsampled at the first standard convolution. The above steps are performed to reduce the image resolution as quickly as possible and increase the network speed.
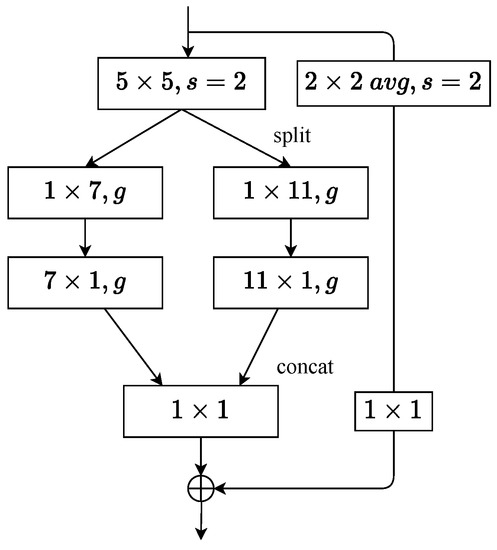
Figure 5.
The symbol s denotes the stride of the convolution. When the stride is set to 2 using the LSPBlock, a average pooling operation is performed for downsampling, followed by a convolutional layer for channel transformation.
Table 2 demonstrates a comparison between LSPBlock and DBlock [10] in terms of parameter quantity and inference speed. The kernel shape denotes the distinct specifications of the LSPBlock and DBlock kernels. It should be noted that the core purpose of the DBlock is to modify the dilation rate of the kernel, without altering its size. As a result, there is only one row dedicated to the DBlock in the table. The input channel was set to 64, with the output channel equal to the input channel. The input image size was 116. The results showed that LSPBlock significantly reduced the inference time at the same receptive field.

Table 2.
Paramete and Benchmark: The table illustrates a comparison between LSPBlock and DBlock in terms of parameter quantity and benchmark metrics. The symbol “↓” indicates that a smaller value in the column is preferred, while the symbol “↑” indicates that a larger value in the column is preferred. The color of the text indicates the ranking, with red indicating the best and blue indicating the second-best.
3.4. Hierarchical Feature Decoding and Fusion
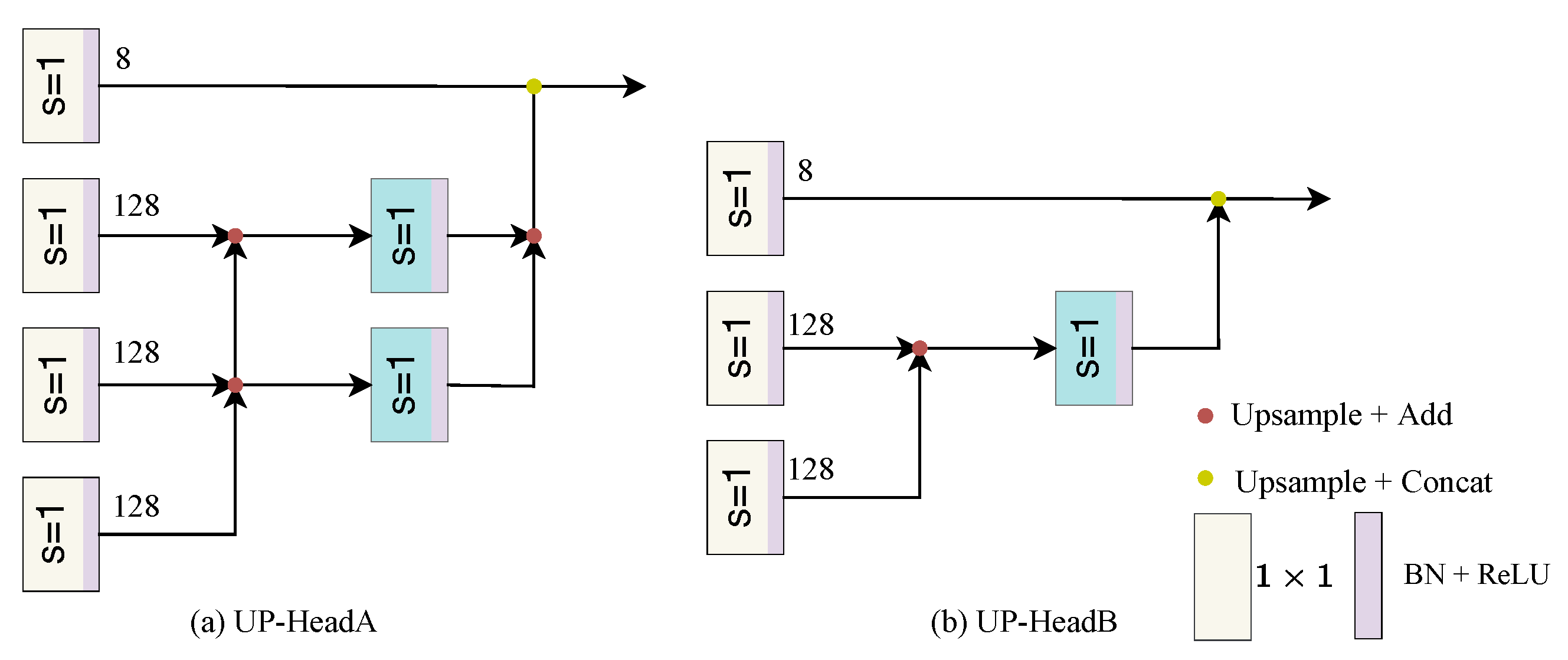
The Up-Head approach was used to decode features from different levels of the encoder. Drawing from the experience of DeeplabV3+ [26], we use convolutions were used to reduce the dimensionality of low-level features, minimizing the weakening of high-level features. Two sizes of Up-Head were designed to suit different scenarios. Specifically, the final 1/4, 1/8, and 1/16 features from the backbone were selected as inputs, and different convolutional operations and upsampling techniques were used to fuse the features. For example, a convolution is first applied [1 × 1, 128] on the 1/16 feature for dimensionality reduction, which then undergoes upsampling and is added to the 1/4 feature. Subsequently, [3 × 3, 64] convolution is used for feature fusion, and the 1/4 feature is finally concatenated with the output as input to the SegHead. The SegHead typically consists of a convolutional layer for final feature mapping. The UpHead structure is illustrated in Figure 6. This simple decoder provides a convenient parameter search paradigm and can be easily inserted into existing networks to search for optimal performance.
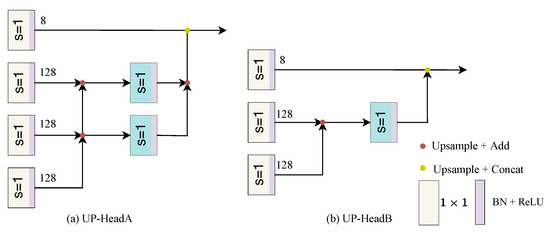
Figure 6.
The Up-Head approach enables the decoding of features from various levels of the encoder. The diagram depicts the process of fusing features from the final 1/4, 1/8, and 1/16 stages of the backbone.
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
Cityscapes [27] is a large-scale street view dataset. The semantic segmentation dataset contains 2975 images for training, 500 images for validation, and 1525 images for testing. The objects in the images were divided into 19 categories, with an image size of .
CamVid [28,29] is a dataset consisting of street scene images. It contains 367 images for training, 101 for validation, and 233 for testing. We specifically focus on using 11 predefined classes while assigning the ignore label = 255 to all other classes. During our training process, we train the model on the trainval set and evaluate its performance on the test set. The images in the CamVid dataset have a standardized size of 720 × 960 pixels.
4.2. Training Setup and Parameters
Our CNN network uses a momentum of 0.9, an initial learning rate of 0.05, and a weight decay of 0.0001 in the Pytorch 1.11.0 framework and CUDA 11.3 (Compute Unified Device Architecture). The input image resolution was cropped to 768 × 768, and the learning rate was adjusted by the poly strategy when doing the training. Random resize was applied in the range to the Cityscapes dataset and images were randomly cropped to [768] with a 50% probability RandomHorizontalFlip, Furthermore, a set of simplified RandAug [30] operations (auto-contrast, equalization, rotation, color, contrast, luminance, and sharpness) was applied. In addition, a category uniform sampling [31] method was applied for category enhancement sampling, with uniform percent = 0.5, and the model was initialized using Pytorch’s default initialization method. A single NVIDIA RTX 2080Ti GPU was trained with 1000 epochs at a batch size of 8. The NVIDIA Jetson Xavier NX with 21 TOPS was used to test the FPS in a real deployment.
The following loss function Equation (3) was employed to supervise the network:
Given an input data point x and its corresponding true label y, the loss L is computed as a vector of individual losses for each class in the output. The individual loss for class n is obtained by taking the negative logarithm of the softmax probability of the model output for class n. The softmax probability is calculated by exponentiating the output scores and normalizing them by the sum of exponentiated scores over all classes. The loss for class n is only considered if its corresponding label is not marked as an ignore index.
When performing the ablation experiments, only 400 epochs were trained. Since no pre-training was performed on ImageNet, all the experiments were averaged three times.
4.3. LSPBlock Ablation Studies
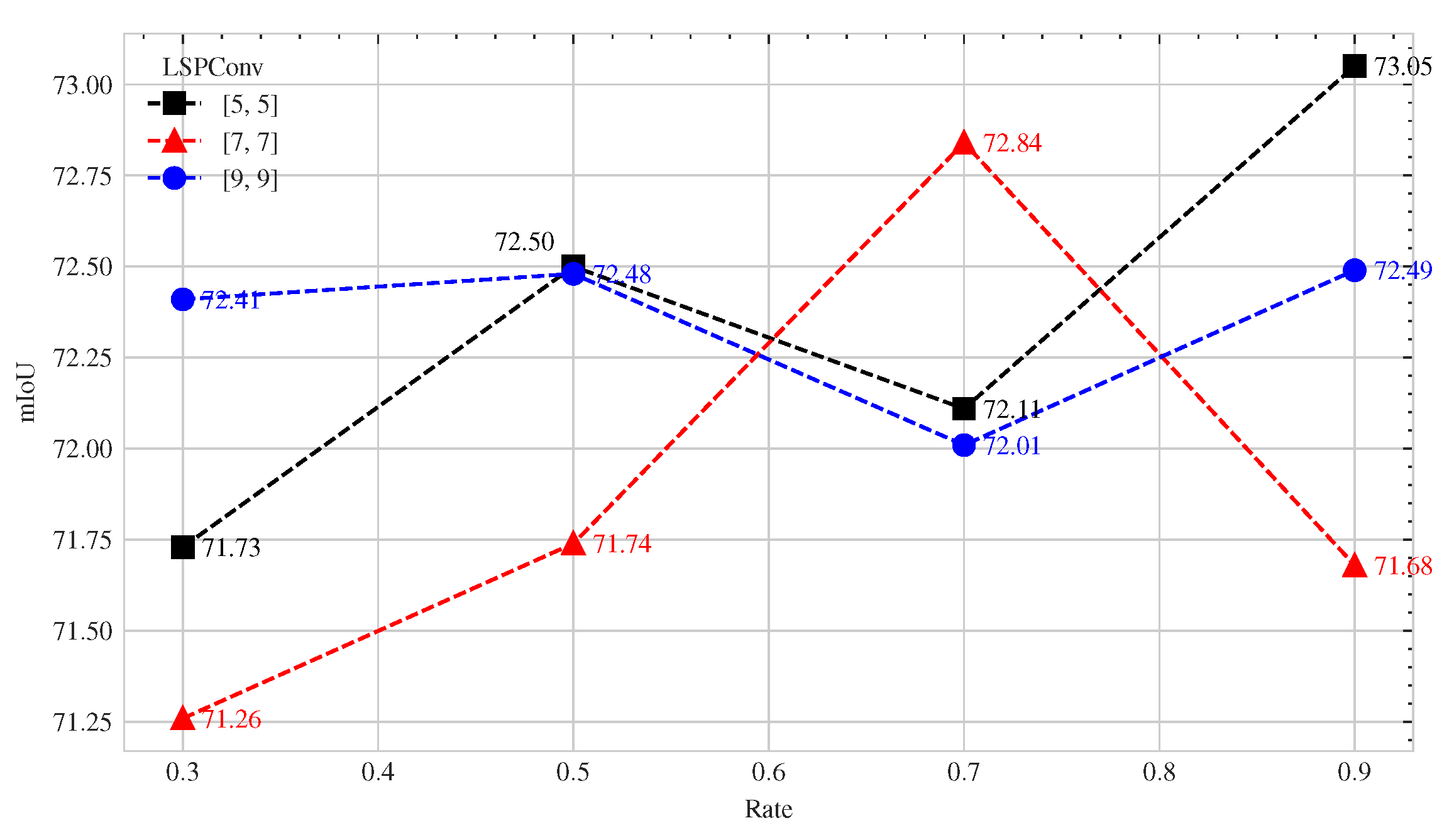
Experiments on the sizes and numbers of the kernels were conducted for the last 13 blocks with the same experimental settings. In the notation [m], m represents the LSPConv size. The rate indicates the ratio of NormConv to the number of blocks in Stage 4. For example, a rate of 0.3 indicates that NormConv was used for the first four () blocks in Stage 4 and LSPConv for the remaining nine blocks. The experiment results are displayed in Figure 7.
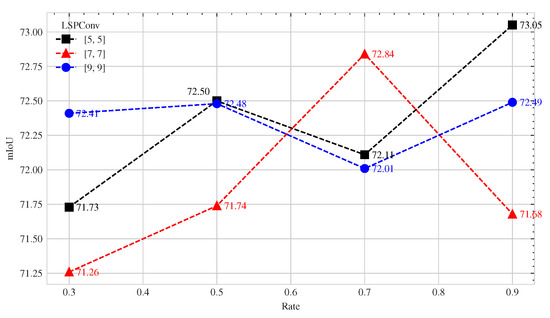
Figure 7.
The effect of the proportion of LSPConv on network performance for different kernel sizes.
The results in Figure 7 show that the proportion of LSPConv has a significant effect on the performance of the network. For larger kernel sizes, using a higher proportion of LSPConv can lead to improved performance. Conversely, the improvement in performance may not be as significant for smaller kernel sizes. This indicates that the choice of LSPConv proportion is dependent on the kernel size and should be adjusted accordingly for optimal performance.
4.4. LSPBlock Location Ablation Studies
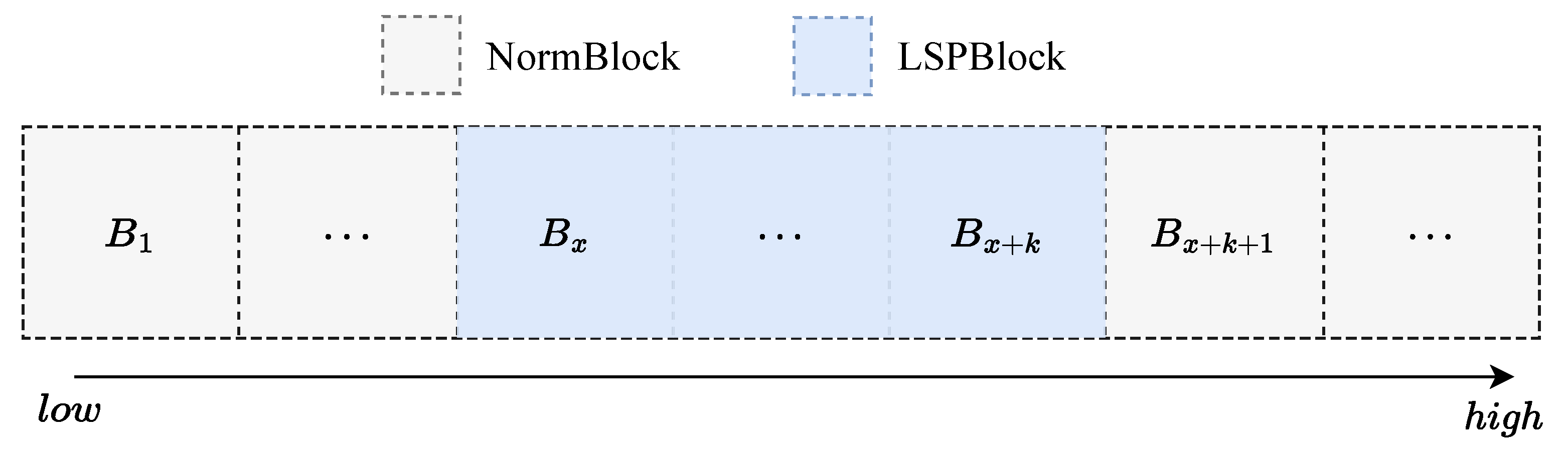
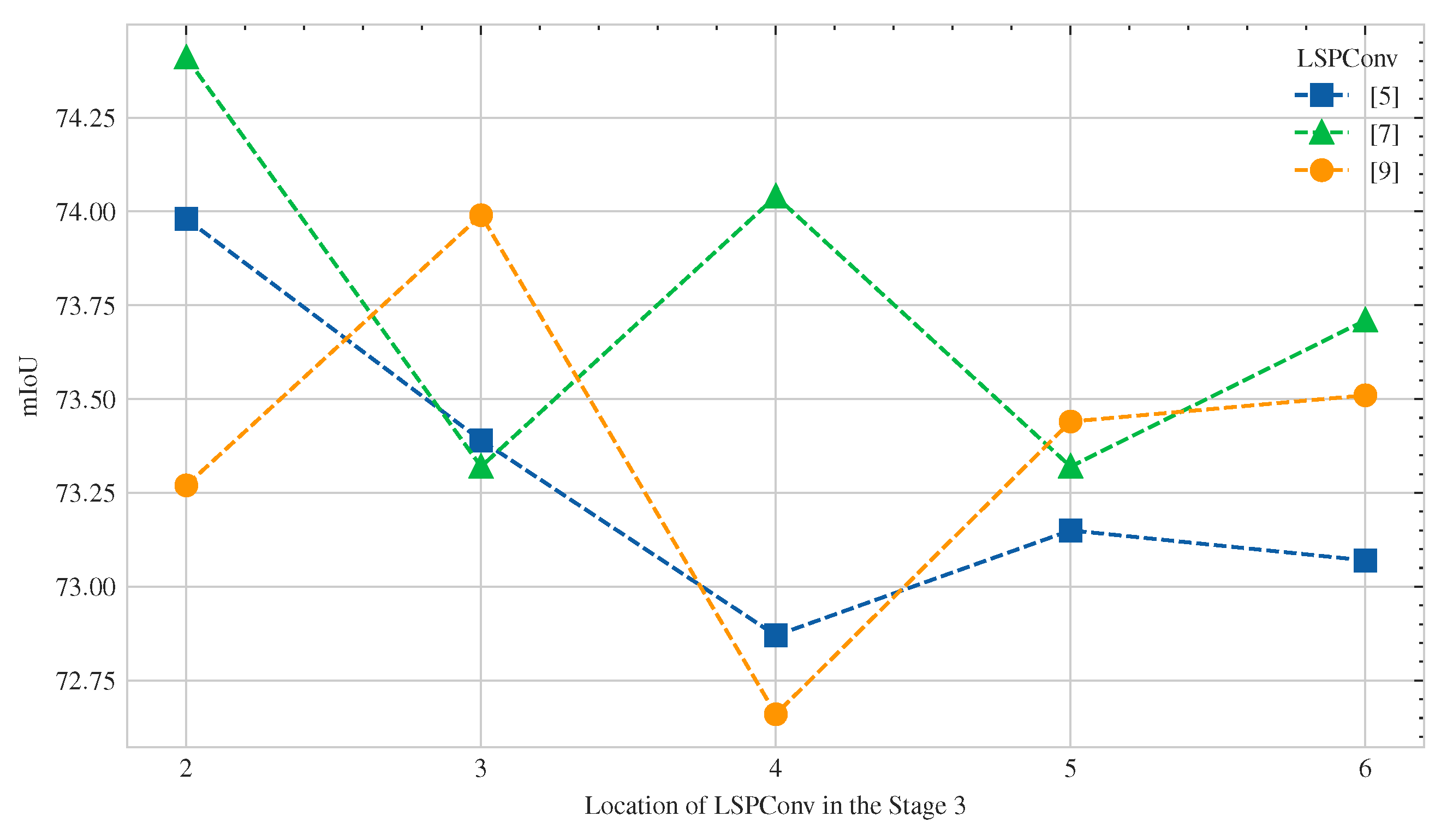
In addition, the effects of location within the network on network performance were investigated for LSPConvs of different sizes. Therefore, the network performance was tested with LSPConvs of different sizes located at different depths of the network. Figure 8 shows the experimental setup for the location ablation study, where represents the x-th block (from 1 to 7) and k represents the length of LSPBlock, which was set to 5 in the experiments. Figure 9 shows the results of the location ablation study for LSPConv placement.
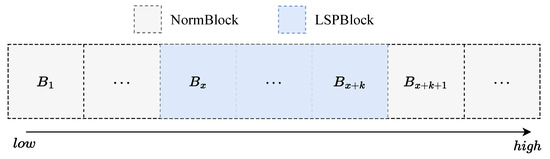
Figure 8.
We conducted experiments on the positions of different sizes of LSPBlocks in Stage 3 to investigate the preference of different kernel sizes for network depth. In the experiments, k represents the length of consecutive LSPBlocks, while x represents the starting block of using LSPBlock.
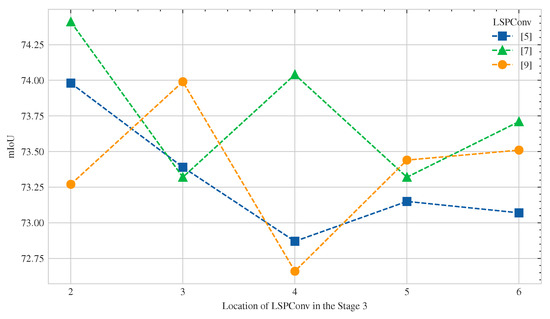
Figure 9.
We conducted experiments with three different kernel sizes of LSPBlock, namely 5, 7, and 9. The horizontal axis represents the starting position of five consecutive LSPBlocks in Stage 3, while the vertical axis represents the mIoU metric.
The results of the experiments showed that the position of LSPConv in the network affects the effectiveness of different kernel sizes. Specifically, deeper layers in the network may be more effective for larger kernel sizes, while shallower layers may be more effective for smaller kernel sizes.
This finding could be attributed to the receptive field of the convolution operation. As the receptive field of a convolutional layer increases with network depth, it becomes more capable of capturing more spatial information in the input image. Therefore, the deeper layers with a larger receptive field could be more effective for larger kernel sizes. On the other hand, shallower layers may be more effective for smaller kernel sizes since they can capture local features better than deeper layers.
4.5. Block Ablation Studies
The encoder based on spatially separable convolution was compared with Regseg’s encoder. To ensure fairness, RegSeg’s decoder was used for both CNNs in the comparison. The FPS and GFLOPs for each test experiment were tested on an RTX 2080Ti. For 3 × 2048 × 1024 input images, the spatially separable convolution-based model showed a reduction in GFLOPs of about 14.14% and an increase in FPS of 52.36%. mIoU was reduced by about 2.56% compared to Regseg (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Comparison of frames per second (FPS) and Gigaflops (GFLOPs) with 3 × 2048 × 1024 Image Resolution.
4.6. Timing Setup and Parameters
An RTX 2080Ti GPU was used to time LightSeg in mixed-precision mode. PyTorch 1.10.0 and CUDA 11.3 were used. The input size was 1 × 3 × 1024 × 2048 on Cityscapes 10 iterations were processed as a warm-up before officially starting the test, and the inference times were averaged over the next 100 iterations.
Jetson Xavier NX used Pytorch 1.11.0 Jetpack 5.0.2-b231 and accelerated with TensorRT.
4.7. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
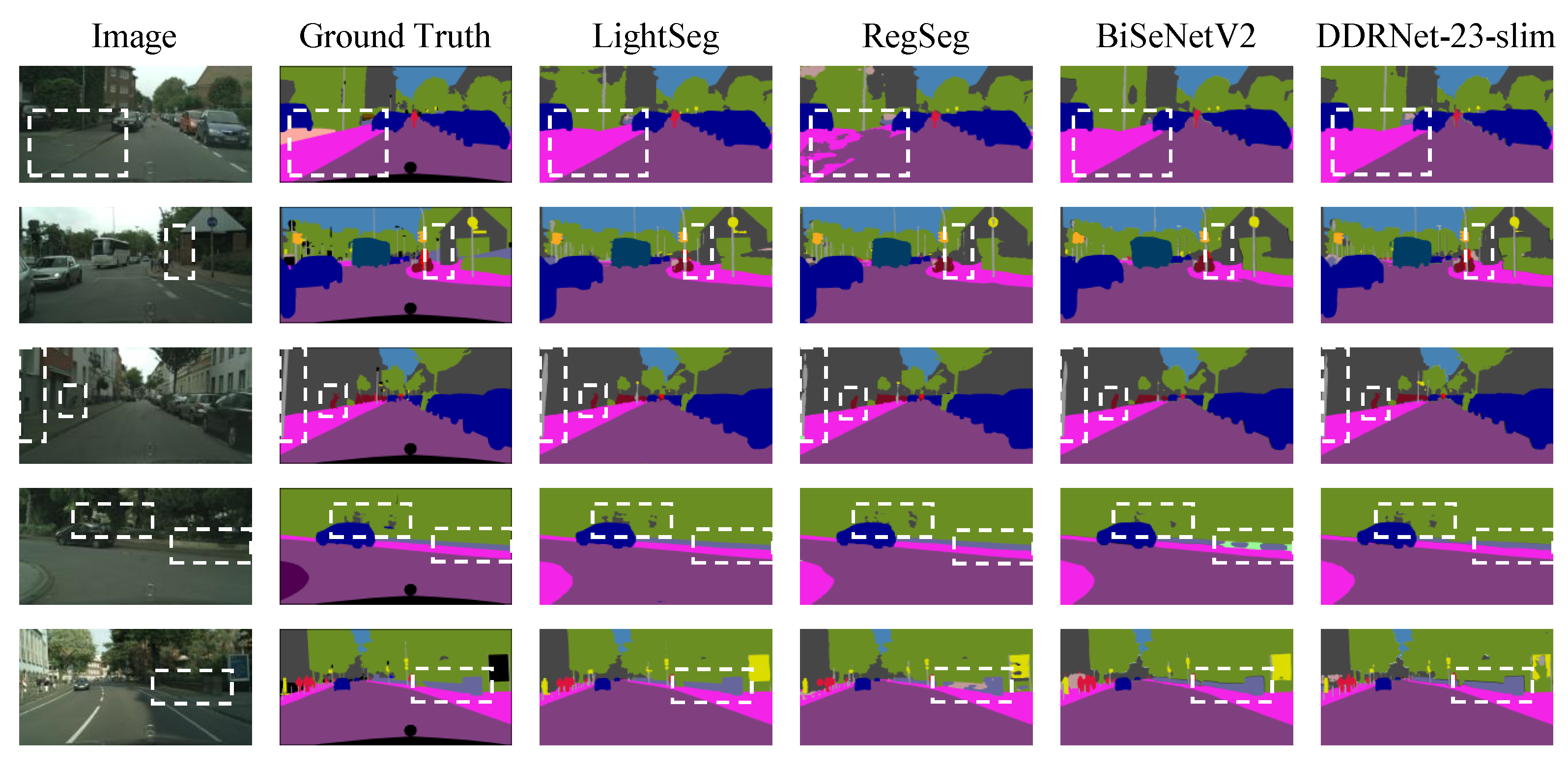
In Table 4, our model was compared with other lightweight real-time semantic segmentation models, revealing leading results in both speed and complexity. Here, “IM” indicates that the model was pre-trained on ImageNet. Notably, our model achieved a 16% faster inference speed and a nearly 56% reduction in complexity compared to the previous state-of-the-art model RegSeg, while maintaining a similar MIoU performance. Furthermore, the model was deployed using TensorRT on Jetson NX, achieving a score of 115.7 FPS and outperforming most of the results in Table 4. Notably, the improvements in speed and complexity can be attributed to the design of our LSPBlock and UpHead modules, which effectively reduce computational and memory costs while maintaining segmentation accuracy. Figure 10 displays the visual results of LightSeg and Regseg under different scenarios.

Table 4.
Comparison with state-of-the-art methods on Cityscapes. IM means ImageNet. † indicates that the deployment uses TensorRT benchmark.
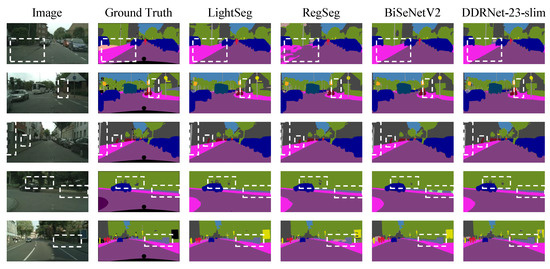
Figure 10.
Visual results comparison of LightSeg and Regseg on Cityscapes validation set under various scenarios. The visualization results clearly indicate the superiority of our network over RegSeg in accurately capturing elongated objects. Moreover, the inherent local spatial perception ability of LSPConv significantly enhances the segmentation performance for large-scale objects.
As shown in Table 5, our proposed method, LightSeg, achieves mIOU of 77.1% on the challenging CamVid test set while operating at an impressive speed of 99.4 FPS. This performance improvement is significant when compared to the previous state-of-the-art (SOTA) model, DDRNet-23 [36], as our method achieves a 5% increase in speed. Moreover, in comparison to RegSeg, our approach demonstrates a substantial speed boost of 42%.

Table 5.
Comparison with state-of-the-art methods on Camvid, IM: ImageNet, C: Cityscapes.
4.8. Effective Receptive Field Analysis
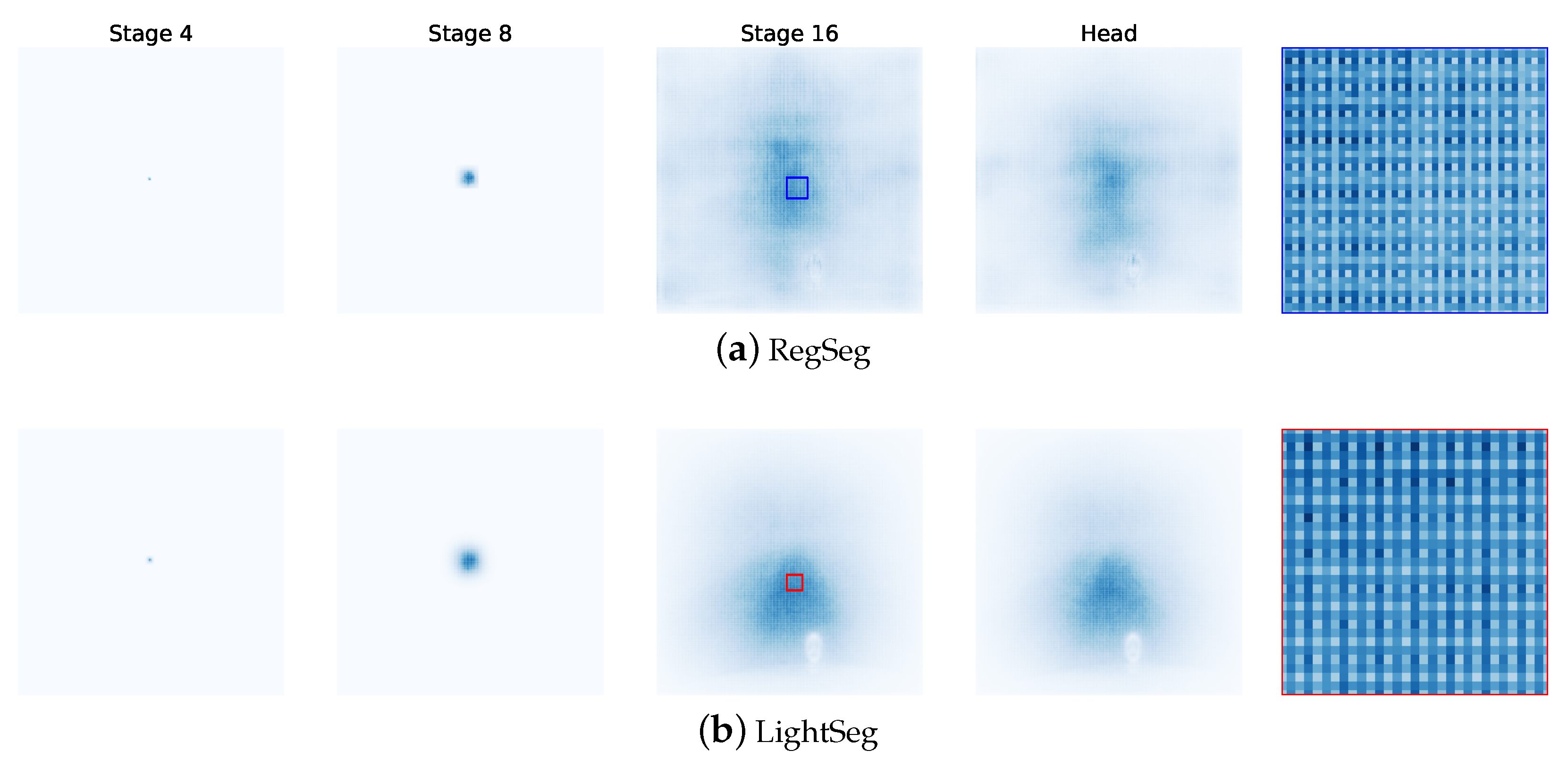
The receptive fields of RegSeg and LightSeg were visualized to demonstrate how our network effectively addresses the “Gridding Effect” [12] issue in RegSeg.
The visualization results are shown in Figure 11; the darker colors indicate that the coordinates are focused within the receptive field of the corresponding feature kernel. Based on the visualization results, the following conclusions can be drawn:
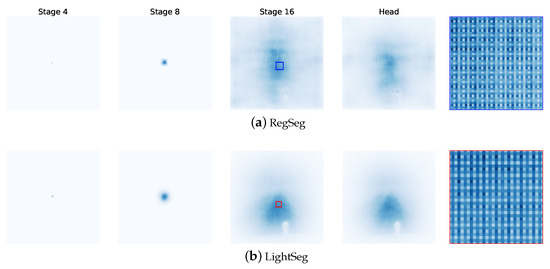
Figure 11.
Effective receptive field (ERF) Analysis on Cityscapes. The depth of color represents the degree of influence of the input image on the target value. A darker color indicates a significant influence, while a lighter color indicates a minimal impact on the target value.
- The D Block in RegSeg effectively increases the receptive field, but also causes sparse gradients due to its dilated convolution structure, resulting in the “Gridding Effect”.
- Both LightSeg and RegSeg exhibited relatively small ERFs in the early stages of the network.
- In Stage 3, LightSeg showed a global receptive field while still maintaining a strong focus on local regions.
5. Conclusions
This paper introduces LSPConv, a novel convolutional neural network (CNN) module specifically designed for intelligent recognition and detection on mobile devices. LSPConv effectively addresses the challenge of limited receptive field in lightweight designs by employing spatial separable convolutions with large kernels in the encoder, while also capturing local information using local convolutions. The proposed LSPBlock further enhances the network’s receptive field without the drawbacks of dilated convolutions and reduces computational complexity through depthwise separable convolutions.
By performing spatial separable convolutions channel-wise and fusing features using point-wise convolutions, the proposed approach achieves real-time performance on low-power embedded platforms. This results in a 41% reduction in the number of parameters compared to standard convolution, while increasing inference speed by 30%, thereby improving efficiency for deployment on unmanned systems with limited computational resources.
Experiments on kernel size combinations reveal that incorporating large kernels in the initial stage using LSPConv does not significantly improve network performance. Therefore, the kernel size is gradually increased in the LSPBlock of stage 3.
Evaluation of the Cityscapes dataset demonstrates the effectiveness of our model. Compared to DDRNet-23 [36], our model achieves nearly a 13% speedup while sacrificing only 1.7% accuracy compared to RegSeg. These results highlight the efficiency and accuracy achieved by our LSPConv-based approach in real-time semantic segmentation tasks on resource-constrained mobile devices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.L. and J.L.; methodology, X.L. and J.L.; software, J.L. and Z.G.; validation and J.L.; formal analysis, J.L.; investigation, X.L. and J.L.; resources, X.L. and Z.J.; data curation, J.L. and Z.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, J.L., X.L. and Z.J.; visualization, J.L. and Z.G.; supervision, Z.J.; project administration, Z.J.; funding acquisition, Z.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61876049, 62172118) and Nature Science Key Foundation of Guangxi (2021GXNSFDA196002); in part by the Sichuan Regional Innovation Cooperation Project (2021YFQ0002); in part by the Guangxi Key Laboratory of Image and Graphic Intelligent Processing under Grants (GIIP2004) and Student’s Platform for Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program under Grant (S202210595177, 202210595029).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
For the Cityscape dataset, the data supporting reported results can be found at the following link: https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com/ (accessed on 12 May 2023). The dataset is publicly available for research purposes and can be downloaded upon registration on the website. For CamVid dataset, the data supporting reported results can be found at the following link: http://mi.eng.cam.ac.uk/research/projects/VideoRec/CamVid/ (accessed on 20 June 2023). The dataset is publicly available for research purposes and can be downloaded upon registration on the website.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| FCN | Fully Convolutional Networks |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| LSPConv | Local Spatial Perception Convolution |
| LSPBlock | Local Spatial Perception Block |
| CUDA | Compute Unified Device Architecture (a parallel computing platform by NVIDIA) |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| FPS | Frames Per Second (the number of frames processed or displayed per second) |
| GFlops | Gigaflops (the number of billions of floating-point operations per second) |
| mIoU | Mean Intersection over Union (a metric used to evaluate the accuracy of segmentation models) |
| TensorRT | Tensor Runtime (an optimization and inference engine for deep learning models) |
References
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L. Mobilenetv2: The next generation of on-device computer vision networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Xiong, R.; Shen, Y.; Jin, C.; Wang, Y. Intelligent generation of Peking opera facial masks with deep learning frameworks. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, M.; Bai, S.; Huang, T.; Bai, X. Asymmetric non-local neural networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 593–602. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Lou, X.; Chan, C.A.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W. A semantic and emotion-based dual latent variable generation model for a dialogue system. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2023, 8, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1492–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R. Rethinking Dilated Convolution for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 4674–4683. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V.; Funkhouser, T. Dilated residual networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 472–480. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Chen, P.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, Z.; Hou, X.; Cottrell, G. Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 1451–1460. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected crfs. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.7062. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Lu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, X.; Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Feng, J.; Xiang, T.; Torr, P.H.; et al. Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 6881–6890. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, S. LRD-SLAM: A Lightweight Robust Dynamic SLAM Method by Semantic Segmentation Network. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 7332390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, M.; Shaker, A.; Cholakkal, H.; Khan, S.; Zamir, S.W.; Anwer, R.M.; Shahbaz Khan, F. Edgenext: Efficiently amalgamated cnn-transformer architecture for mobile vision applications. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, M.; Dong, X.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z. Mobile-former: Bridging mobilenet and transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 July 2022; pp. 5270–5279. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Haitao, H.; Li, A.; Mansourian, A. Impact of data processing on deriving micro-mobility patterns from vehicle availability data. Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2021, 97, 102913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The Cityscapes Dataset for Semantic Urban Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brostow, G.J.; Shotton, J.; Fauqueur, J.; Cipolla, R. Segmentation and Recognition Using Structure from Motion Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Marseille, France, 12–18 October 2008; pp. 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Brostow, G.J.; Fauqueur, J.; Cipolla, R. Semantic Object Classes in Video: A High-Definition Ground Truth Database. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2008, 30, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, hlSeattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 702–703. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Sapra, K.; Reda, F.A.; Shih, K.J.; Newsam, S.; Tao, A.; Catanzaro, B. Improving semantic segmentation via video propagation and label relaxation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 8856–8865. [Google Scholar]
- Si, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, F.; Yu, G.; Lu, F. Real-time semantic segmentation via multiply spatial fusion network. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.07217. [Google Scholar]
- Orsic, M.; Kreso, I.; Bevandic, P.; Segvic, S. In defense of pre-trained imagenet architectures for real-time semantic segmentation of road-driving images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 12607–12616. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Gong, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. FasterSeg: Searching for Faster Real-time Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.10917. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Bisenet: Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, H.; Hong, Y.; Sun, W.; Jia, Y. Deep Dual-Resolution Networks for Real-Time and Accurate Semantic Segmentation of Traffic Scenes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 3448–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Lai, S.; Huang, J.; Wei, X.; Chai, Z.; Luo, J.; Wei, X. Rethinking bisenet for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 9716–9725. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.; Sun, P.; Cheng, G.; Xie, S.; Li, X.; Shi, J. Graph-guided architecture search for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, hlSeattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 4203–4212. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, J.; Yao, T.; Liu, D.; Mei, T. Customizable architecture search for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 11641–11650. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, S.; Couprie, C.; Kokkinos, I. Deep spatio-temporal random fields for efficient video segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8915–8924. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, G.; Shen, C.; Sang, N. Bisenet v2: Bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3051–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).