Velocity Control of a Multi-Motion Mode Spherical Probe Robot Based on Reinforcement Learning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Structure
2.2. Dynamic Modeling
- During movement, MMSPR rolls without slipping, and its mass is decomposed into the mass of the shell and the pendulum: , ;
- The centroid of MMSPR coincides with its geometric center;
- The two degrees of freedom do not mutually interfere, and the longitudinal axis does not rotate.
3. Controller Design
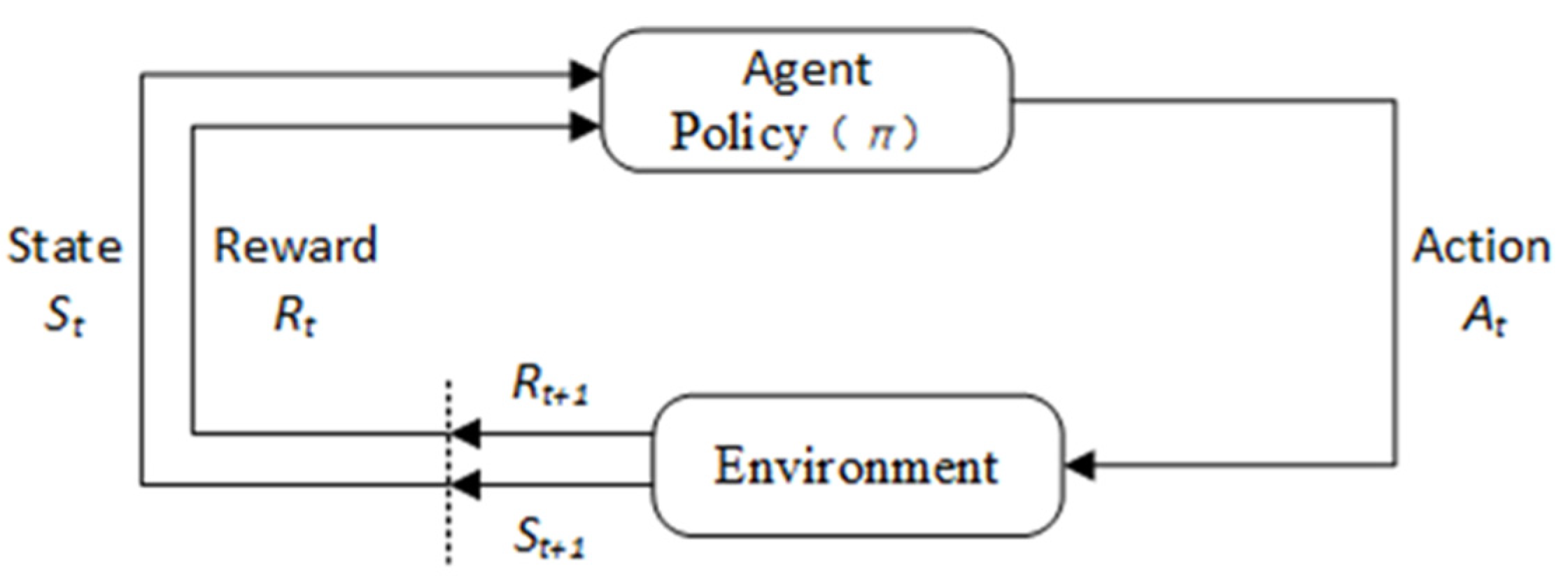
3.1. Reinforcement Learning
3.2. SAC Algorithm
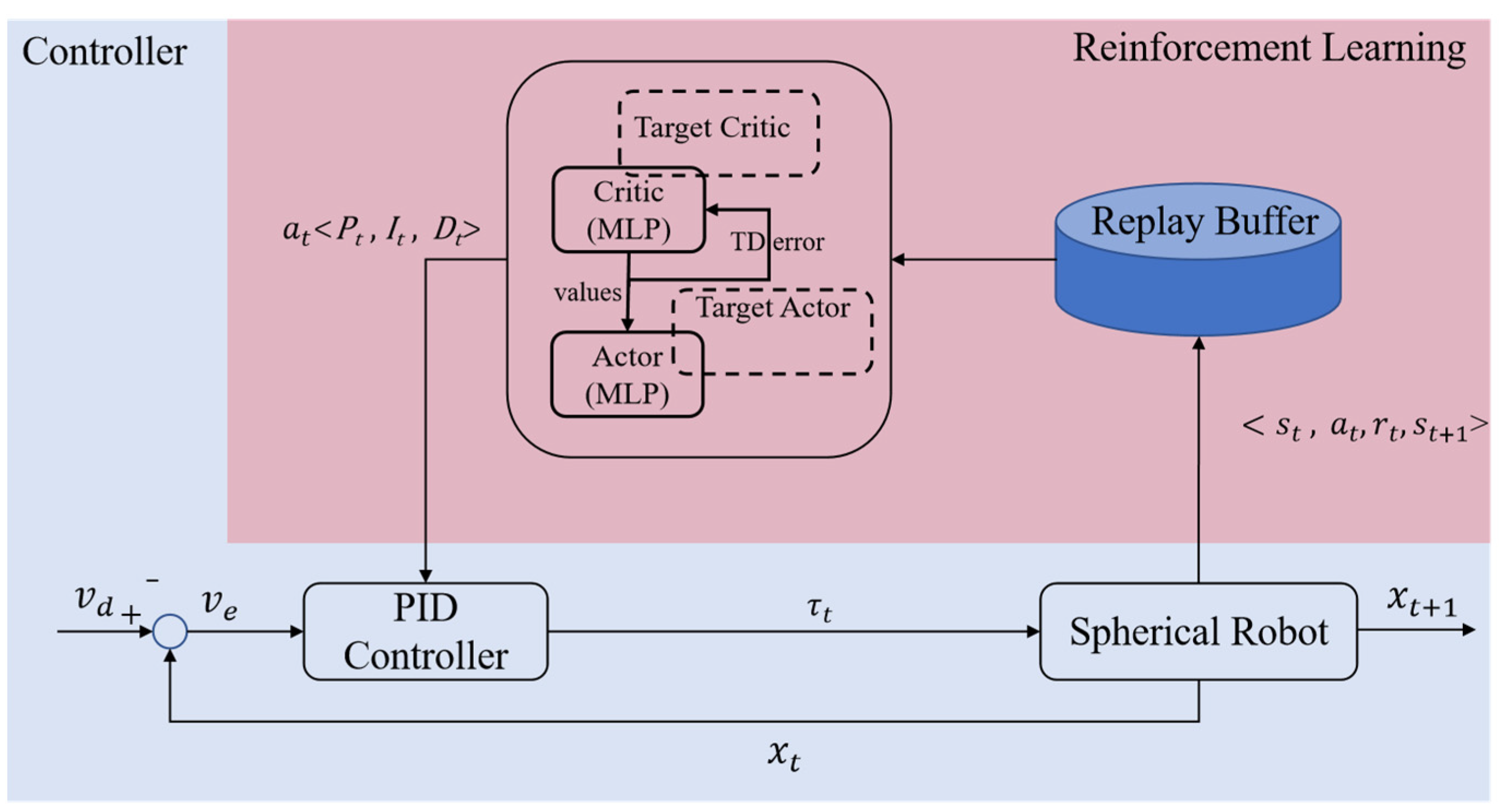
3.3. Adaptive PID Controller Based on Reinforcement Learning
4. Simulations
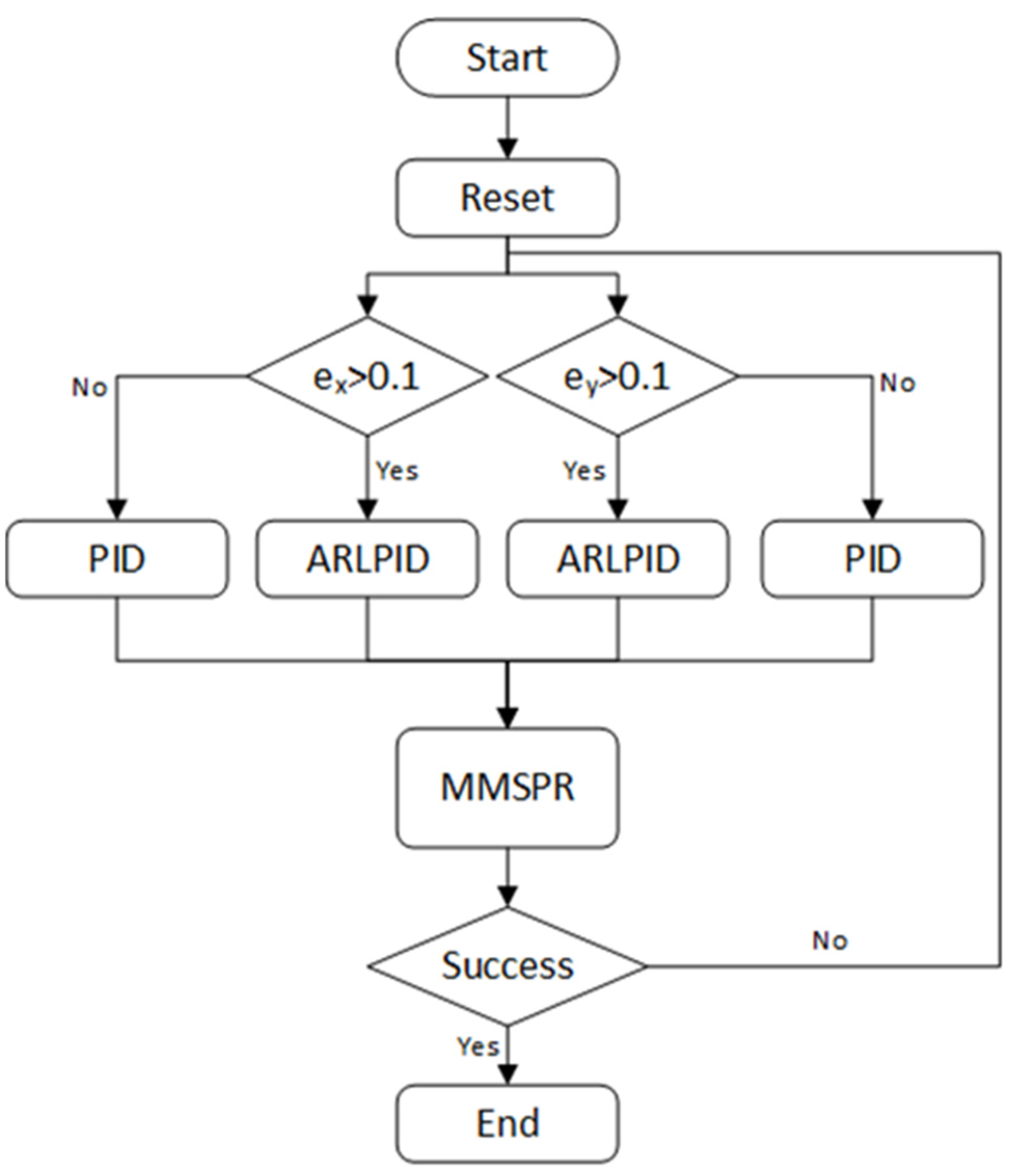
4.1. Simulation Environment
4.2. Simulation Results and Analysis
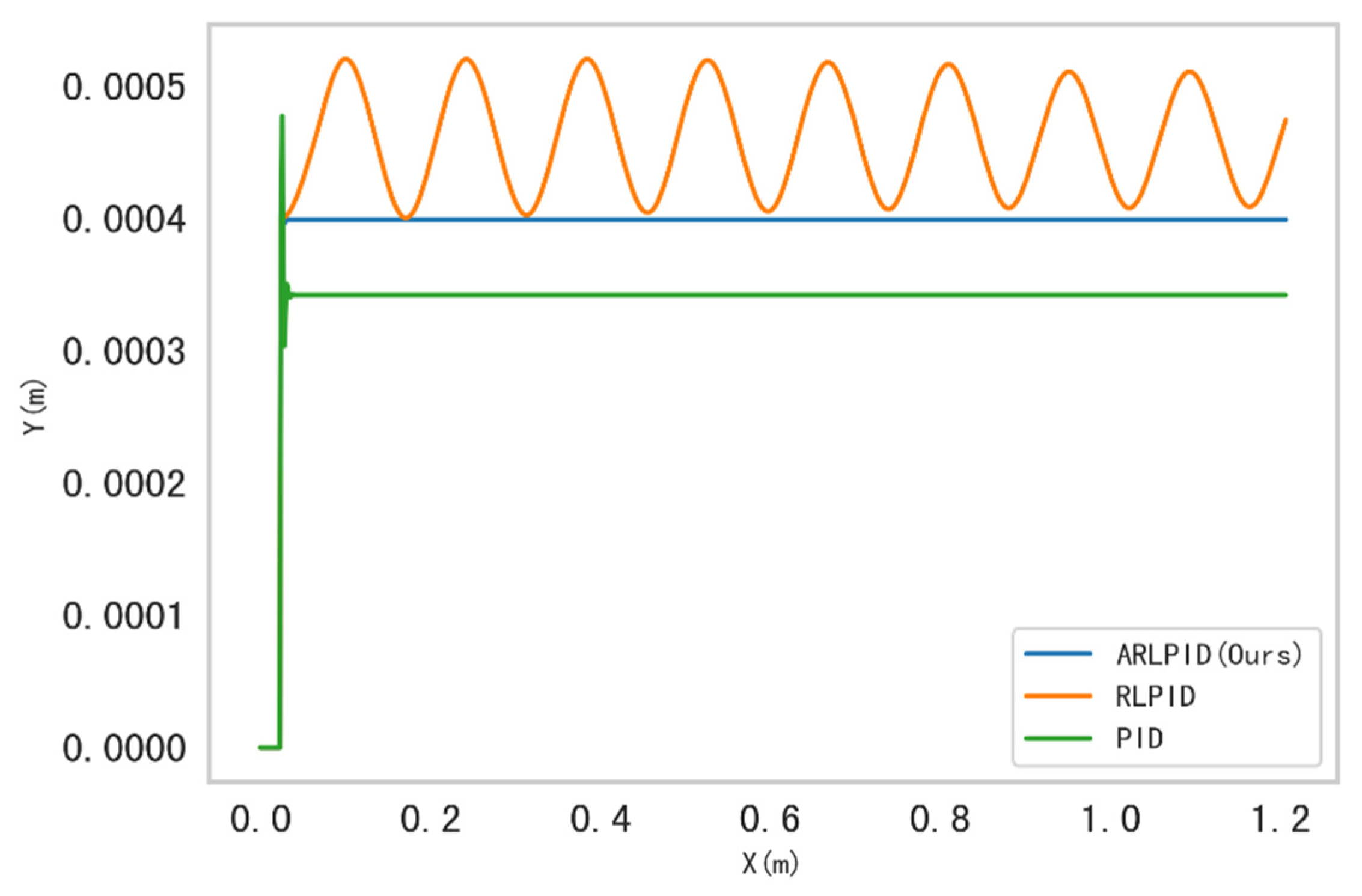
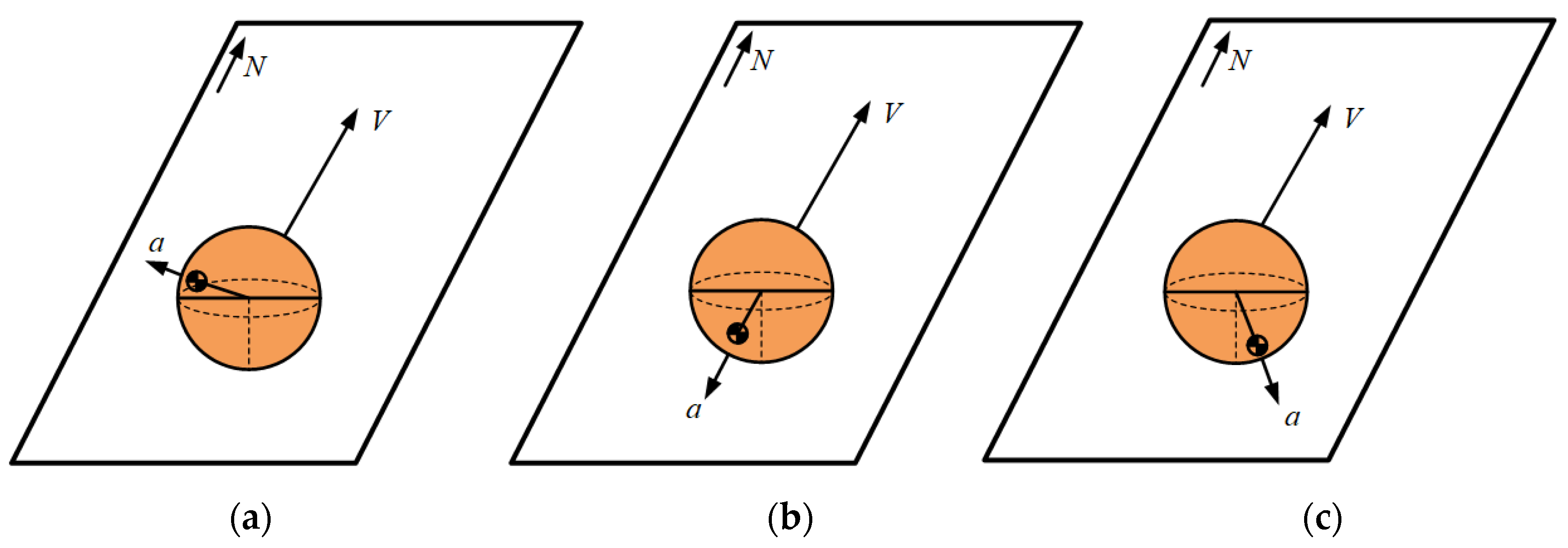
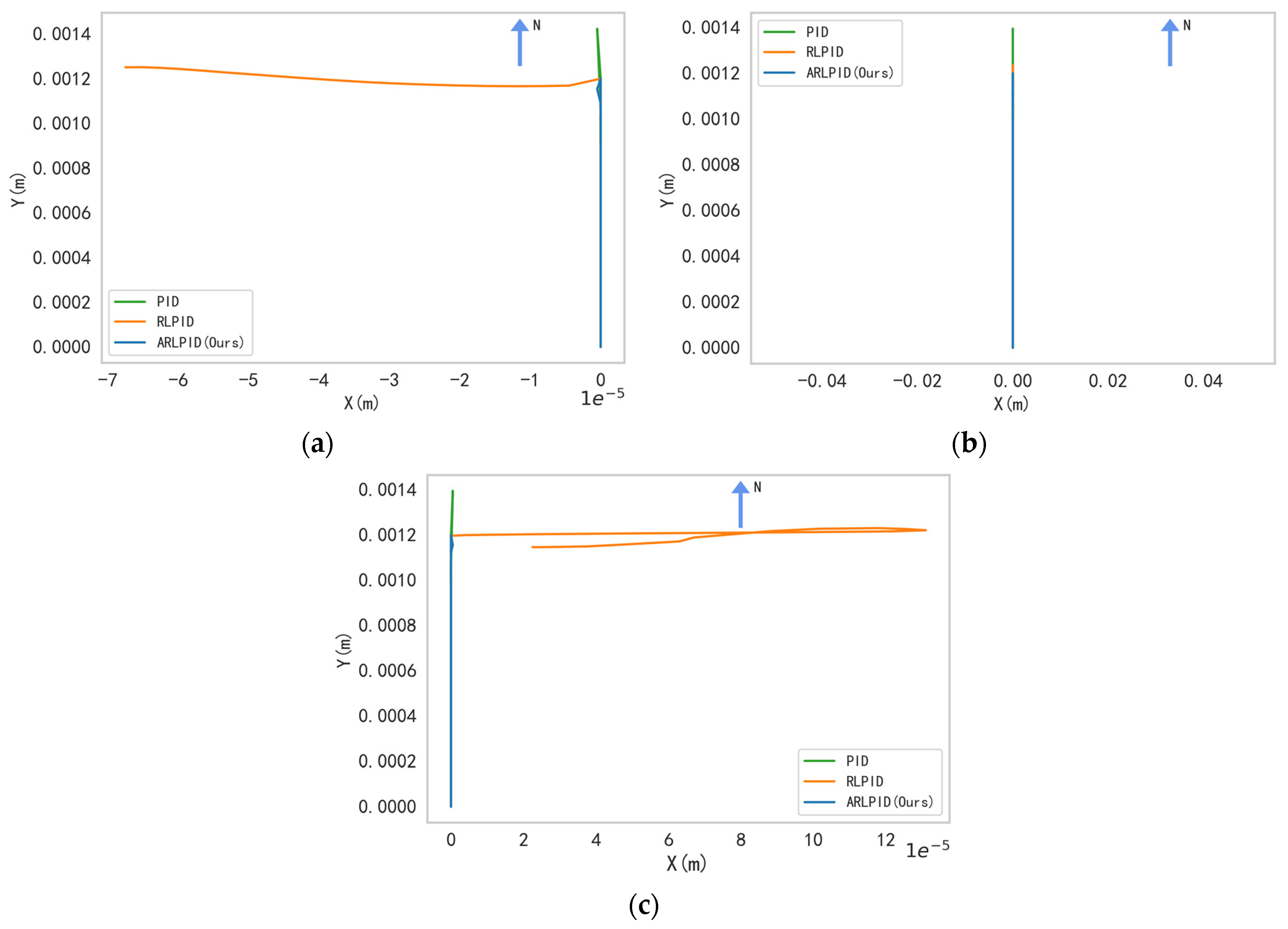
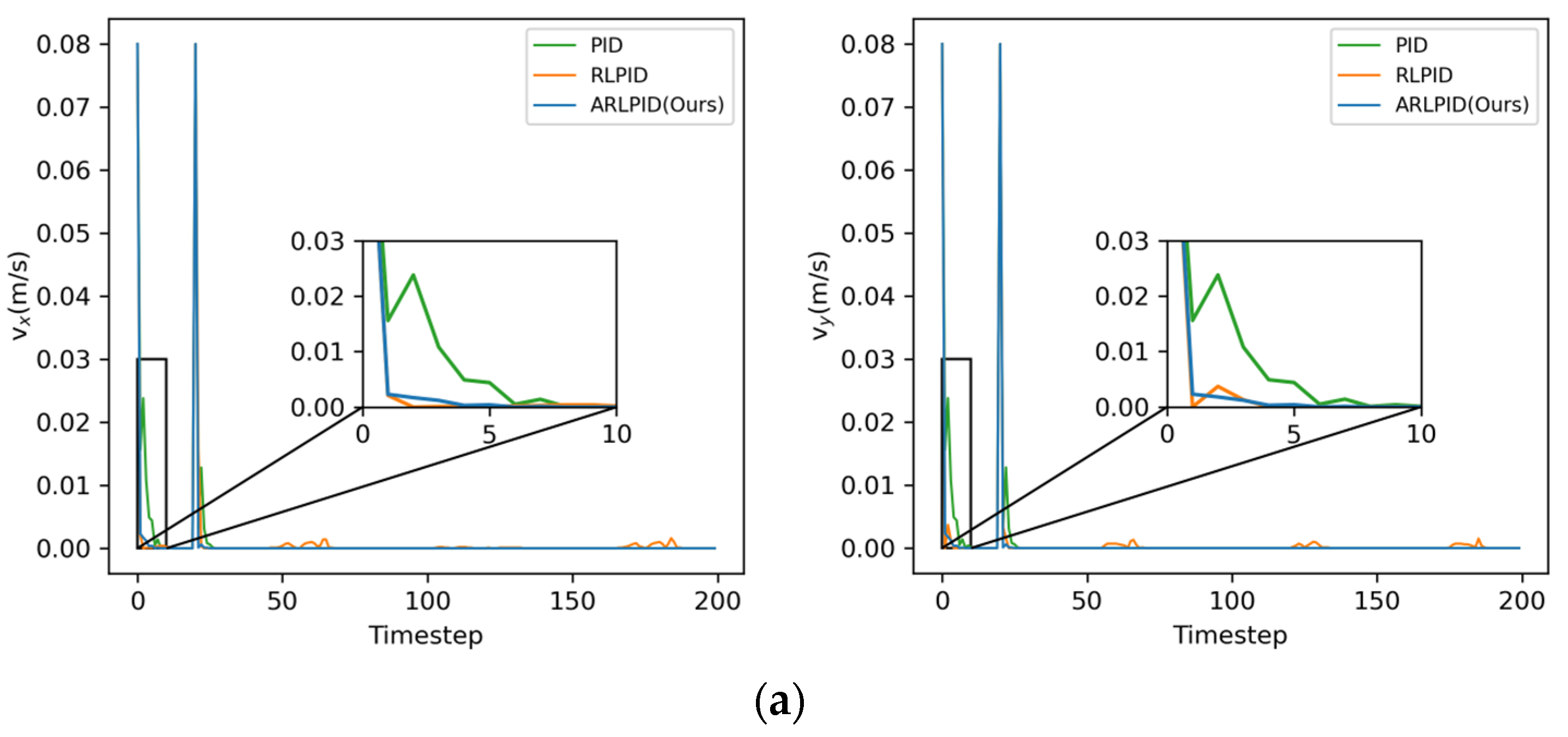
4.2.1. Motion Stability
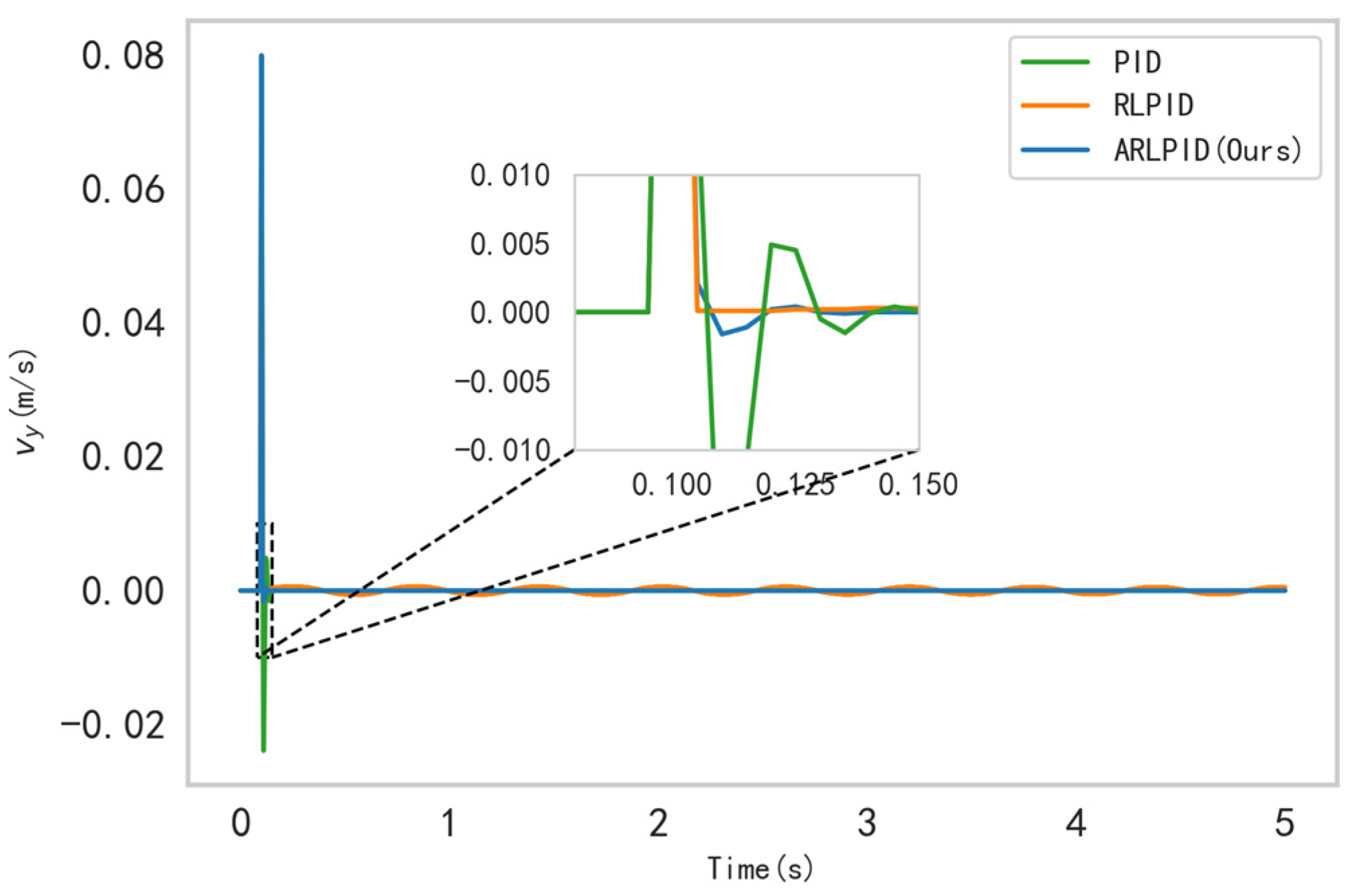
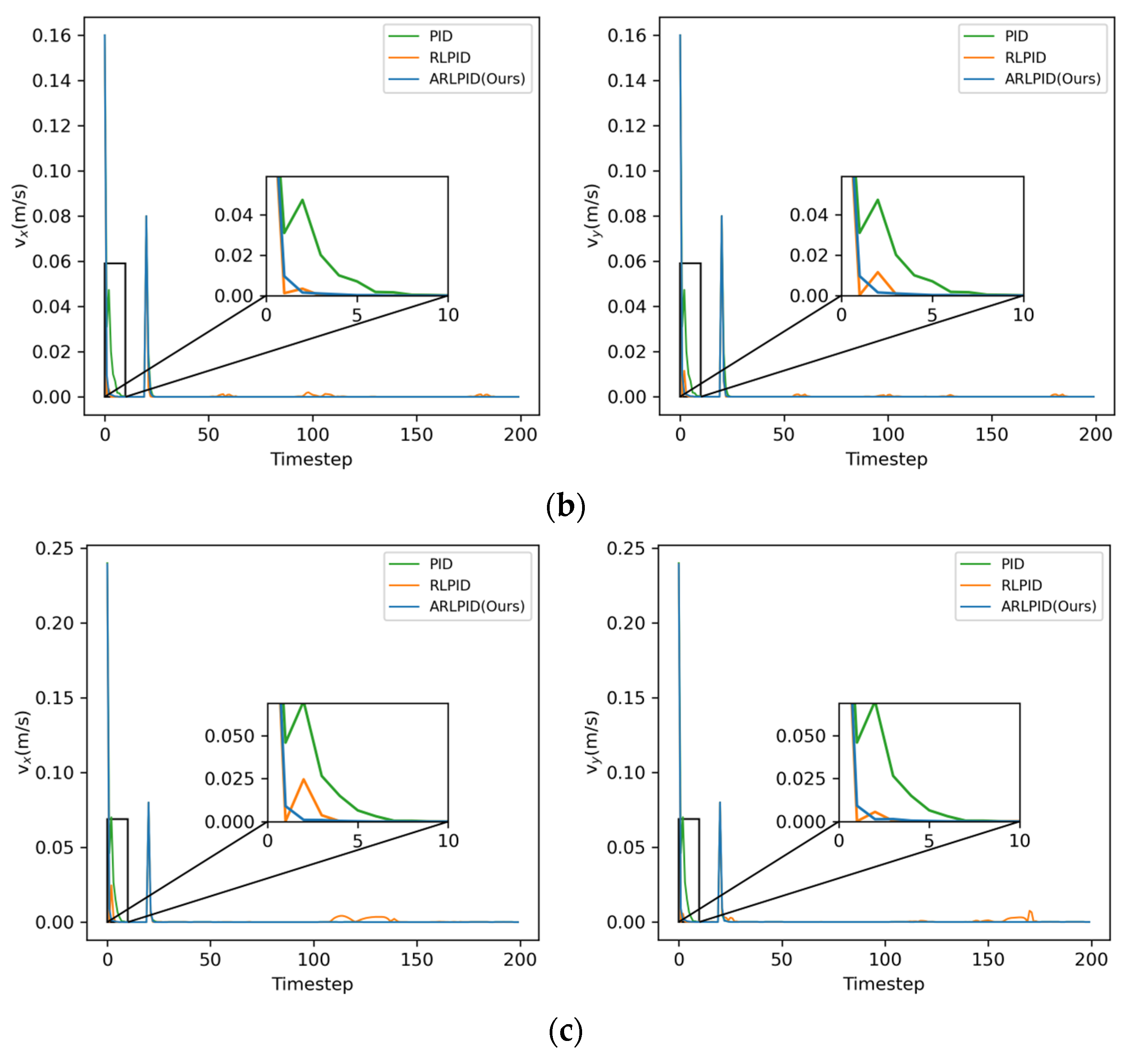
4.2.2. Rapidly Brake
Postures
Velocities
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sagsoz, I.H.; Eray, T. Design and Kinematics of Mechanically Coupled Two Identical Spherical Robots. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2023, 108, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sun, H.; Ma, L.; Gao, P.; Huo, D.; Wang, Z.; Sun, P. Special spherical mobile robot for planetary surface exploration: A review. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Zhan, Q. Design and modelling of an amphibious spherical robot attached with assistant fins. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Guo, S.; Pan, S.; Bao, P.; Duan, L. Design, Implementation and Control of an Amphibious Spherical Robot. J. Bionic Eng. 2022, 19, 1736–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangapur, I.; Prasad, B.K.S.; Suresh, R. Design and Development of Spherical Spy Robot for Surveillance Operation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 171, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, F.O.; Caron, S. Roball, the Rolling Robot. Auton. Robot. 2002, 12, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.R.; Naderi, D. Dynamic modeling and trajectory planning for a mobile spherical robot with a 3Dof inner mechanism. Mech. Mach. Theory 2013, 64, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, A.V.; Kilin, A.A.; Mamaev, I.S. An omni-wheel vehicle on a plane and a sphere. Nelin. Dinam. 2011, 7, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moazami, S.; Palanki, S.; Zargarzadeh, H. Design, Modeling, and Control of Norma: A Slider & Pendulum-Driven Spherical Robot. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1908.02243. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Li, B.; Wang, F.; Luo, B.; Jiao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, P. Design and Analysis of the Rolling and Jumping Compound Motion Robot. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, C.; Niu, S.; Wang, P.; Wu, H.; Li, B. Design and Analysis of a Spherical Robot with Rolling and Jumping Modes for Deep Space Exploration. Machines 2022, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, M. Design and performance evaluation of a spherical robot assisted by high-speed rotating flywheels for self-stabilization and obstacle surmounting. J. Mech. Robot. 2021, 13, 061001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-J.; Chang, C.-L.; Ho, J.-H.; Lin, P.-C. Design and implementation of a novel spherical robot with rolling and leaping capability. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 171, 104747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-B.; Beigi, A.; Yousefpour, A.; Rajaee, F.; Jahanshahi, H.; Bekiros, S.; Martinez, R.A.; Chu, Y. Recurrent Neural Network-Based Robust Nonsingular Sliding Mode Control With Input Saturation for a Non-Holonomic Spherical Robot. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 188441–188453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuna, L.; Frasca, M.; Buscarino, A. Optimal and Robust Control: Advanced Topics with MATLAB®; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Xu, Y.-G.; Wu, B. Smooth Fractional Order Sliding Mode Controller for Spherical Robots with Input Saturation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, W.; Chang, C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, P.; Li, B. Attitude control of multi-motion mode spherical probe robots based on decoupled dynamics. In Proceedings of the Advances in Guidance, Navigation and Control; Yan, L., Duan, H., Deng, Y., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 5850–5861. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Sun, H.; Song, J. Fractional-order adaptive integral hierarchical sliding mode control method for high-speed linear motion of spherical robot. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 66243–66256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Hu, Y.; Su, S.; Guo, S.; Xing, H.; Hou, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Xia, D. A Fuzzy PID Algorithm for a Novel Miniature Spherical Robots with Three-dimensional Underwater Motion Control. J. Bionic Eng. 2020, 17, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, C.; Guo, S. A novel step optimal path planning algorithm for the spherical mobile robot based on fuzzy control. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 1394–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, C.; Guo, S. Path optimization method for the spherical underwater robot in unknown environment. J. Bionic Eng. 2020, 17, 944–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guan, X.; Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Hu, T.; Ren, W.; Hao, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. Multi-terrain velocity control of the spherical robot by online obtaining the uncertainties in the dynamics. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guan, X.; Hu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, S.; Wang, Y.; Hao, J.; Li, G. Direction and trajectory tracking control for nonholonomic spherical robot by combining sliding mode controller and model prediction controller. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 11617–11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayacan, E.; Bayraktaroglu, Z.Y.; Saeys, W. Modeling and control of a spherical rolling robot: A decoupled dynamics approach. Robotica 2012, 30, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamis, N.N.; Embong, A.H.; Ahmad, S. Modelling and Simulation Analysis of Rolling Motion of Spherical Robot. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 260, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Ren, X.; Guo, Q. Balance and velocity control of a novel spherical robot with structural asymmetry. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2021, 52, 3556–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J.; Liu, J. Improve PID controller through reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE CSAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference (CGNCC), Xiamen, China, 10–12 August 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Q.; Tang, R.; Gou, S.; Zhang, W. A PID Gain Adjustment Scheme Based on Reinforcement Learning Algorithm for a Quadrotor. In Proceedings of the 2020 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Shenyang, China, 27–29 July 2020; pp. 6756–6761. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yin, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X. Trajectory Tracking Control for Mobile Robots Using Reinforcement Learning and PID. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 2020, 44, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Yamamoto, T. Design of a Reinforcement Learning PID Controller. IEEJ Trans. Elec. Electron. Eng. 2021, 16, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, H.; Hwang, K.; Lim, S. Deep Reinforcement Learning Based Dynamic Proportional-Integral (PI) Gain Auto-Tuning Method for a Robot Driver System. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 31043–31057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarnoja, T.; Zhou, A.; Abbeel, P.; Levine, S. Soft Actor-Critic: Off-Policy Maximum Entropy Deep Reinforcement Learning with a Stochastic Actor. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.01290. [Google Scholar]





| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Learning rate of actor | 0.001 |
| Actor network | 128 × 128 |
| Learning rate of critic | 0.0005 |
| Critic network | 128 × 128 |
| Discount () | 0.99 |
| Batch size | 128 |
| Max_epoch | 1000 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Length of an episode | 200 steps |
| Soft target update () | 0.005 |
| Replay_buffer_size | 1,000,000 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| M, the mass of shell | 0.2 kg |
| m, the mass of pendulum | 0.6 m |
| R, the radius of sphere | 0.08 m |
| L, the length of swing arm | 0.023 m |
| g, the acceleration of gravity | 9.81 m/s2 |
| Algorithms | Success Rate |
|---|---|
| ARLPID (ours) | 100% |
| Torque_RL | 0% |
| RLPID | 91% |
| Scenarios | Velocity | PID | RLPID | ARLPID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The first scenario | 0.04 s | 0.01 s | 0.03 s | |
| 0.01 s | 0.01 s | 0.01 s | ||
| The second scenario | 0.035 s | 0.01 s | 0.025 s | |
| 0.00 s | 0.00 s | 0.00 s | ||
| The third scenario | 0.035 s | 0.01 s | 0.025 s | |
| 0.01 s | 0.08 s | 0.01 s |
| Initial Velocity | Error | PID | RLPID | ARLPID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.08 m/s | 0.065 s | 0.065 s | 0.045 s | |
| 0.065 s | 0.025 s | 0.045 s | ||
| 0.16 m/s | 0.06 s | 0.02 s | 0.04 s | |
| 0.06 s | 0.03 s | 0.04 s | ||
| 0.24 m/s | 0.055 s | 0.03 s | 0.045 s | |
| 0.055 s | 0.035 s | 0.045 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, W.; Li, B.; Cao, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, M.; Chang, C.; Peng, S. Velocity Control of a Multi-Motion Mode Spherical Probe Robot Based on Reinforcement Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8218. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148218
Ma W, Li B, Cao Y, Wang P, Liu M, Chang C, Peng S. Velocity Control of a Multi-Motion Mode Spherical Probe Robot Based on Reinforcement Learning. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(14):8218. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148218
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Wenke, Bingyang Li, Yuxue Cao, Pengfei Wang, Mengyue Liu, Chenyang Chang, and Shigang Peng. 2023. "Velocity Control of a Multi-Motion Mode Spherical Probe Robot Based on Reinforcement Learning" Applied Sciences 13, no. 14: 8218. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148218
APA StyleMa, W., Li, B., Cao, Y., Wang, P., Liu, M., Chang, C., & Peng, S. (2023). Velocity Control of a Multi-Motion Mode Spherical Probe Robot Based on Reinforcement Learning. Applied Sciences, 13(14), 8218. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148218






