Test–Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change in Chester Step Test and 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test in Long COVID Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. CST
2.3. One-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test
2.4. Study Procedures
2.5. Sample Size Calculation
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
Test–Retest Reliability
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghebreyesus, T.A. Alocución de Apertura Del Director General de La OMS En La Rueda de Prensa Sobre La COVID-19 Celebrada El 11 de Marzo de 2020; Discursos del Director General de la OMS; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zaim, S.; Chong, J.H.; Sankaranarayanan, V.; Harky, A. COVID-19 and Multiorgan Response. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2020, 45, 100618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitrago-Garcia, D.; Egli-Gany, D.; Counotte, M.J.; Hossmann, S.; Imeri, H.; Ipekci, A.M.; Salanti, G.; Low, N. Occurrence and Transmission Potential of Asymptomatic and Presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections: A Living Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machhi, J.; Herskovitz, J.; Senan, A.M.; Dutta, D.; Nath, B.; Oleynikov, M.D.; Blomberg, W.R.; Meigs, D.D.; Hasan, M.; Patel, M.; et al. The Natural History, Pathobiology, and Clinical Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infections. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 359–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriatopoulou, M.; Korompoki, E.; Fotiou, D.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Kastritis, E.; Terpos, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Organ-Specific Manifestations of COVID-19 Infection. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carfì, A.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F. Gemelli against COVID-19 Post-Acute Care Study Group. Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 603–605.
- Greenhalgh, T.; Knight, M.; A’Court, C.; Buxton, M.; Husain, L. Management of Post-Acute COVID-19 in Primary Care. BMJ 2020, 370, m3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenforde, M.W.; Kim, S.S.; Lindsell, C.J.; Rose, E.B.; Shapiro, N.I.; Files, D.C.; Gibbs, K.W.; Erickson, H.L.; Steingrub, J.S.; Smithline, H.A.; et al. Symptom Duration and Risk Factors for Delayed Return to Usual Health among Outpatients with COVID-19 in a Multistate Health Care Systems Network—United States, March–June 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Kessel, S.A.M.; Olde Hartman, T.C.; Lucassen, P.L.B.J.; Van Jaarsveld, C.H.M. Post-Acute and Long-COVID-19 Symptoms in Patients with Mild Diseases: A Systematic Review. Fam. Pract. 2022, 39, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniou, K.M.; Vasarmidi, E.; Russell, A.M.; Andrejak, C.; Crestani, B.; Delcroix, M.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T.; Poletti, V.; Sverzellati, N.; Vitacca, M.; et al. European Respiratory Society Statement on Long COVID Follow-Up. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Castro, R.; Solis-Navarro, L.; Sitjà-Rabert, M.; Vilaró, J. Functional Limitations Post-COVID-19: A Comprehensive Assessment Strategy. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2021, 57, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.E.; Spruit, M.A.; Troosters, T.; Puhan, M.A.; Pepin, V.; Saey, D.; McCormack, M.C.; Carlin, B.W.; Sciurba, F.C.; Pitta, F.; et al. An Official European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society Technical Standard: Field Walking Tests in Chronic Respiratory Disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1428–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez-Cortés, R.; Rivera-Lillo, G.; Arias-Campoverde, M.; Soto-García, D.; García-Palomera, R.; Torres-Castro, R. Use of Sit-to-Stand Test to Assess the Physical Capacity and Exertional Desaturation in Patients Post COVID-19. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2021, 18, 1479973121999205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekman, E.; Mesters, I.; Gosselink, R.; Klaassen, M.P.M.; Hendriks, E.J.M.; Van Schayck, O.C.P.; De Bie, R.A. The First Reference Equations for the 6-Minute Walk Distance over a 10 m Course. Thorax 2014, 69, 867–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fell, B.; Hanekom, S.; Heine, M. A Modified Six-Minute Walk Test (6MWT) for Low-Resource Settings-a Cross-Sectional Study. Heart Lung 2022, 52, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olezene, C.S.; Hansen, E.; Steere, H.K.; Giacino, J.T.; Polich, G.R.; Borg-Stein, J.; Zafonte, R.D.; Schneider, J.C. Functional Outcomes in the Inpatient Rehabilitation Setting Following Severe COVID- 19 Infection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peroy-Badal, R.; Sevillano-Castaño, A.; Torres-Castro, R.; García-Fernández, P.; Maté-Muñoz, J.L.; Dumitrana, C.; Sánchez Rodriguez, E.; de Frutos Lobo, M.J.; Vilaró, J. Comparison of Different Field Tests to Assess the Physical Capacity of Post-COVID-19 Patients. Pulmonology, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.P.; Sim, J.; Eston, R.G.; Hession, R.; Fox, R. Reliability and Validity of Measures Taken during the Chester Step Test to Predict Aerobic Power and to Prescribe Aerobic Exercise. Br. J. Sports Med. 2004, 38, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bennett, H.; Parfitt, G.; Davison, K.; Eston, R. Validity of Submaximal Step Tests to Estimate Maximal Oxygen Uptake in Healthy Adults. Sport. Med. 2016, 46, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karloh, M.; Corrêa, K.S.; Martins, L.Q.; Araujo, C.L.P.; Matte, D.L.; Mayer, A.F. Chester Step Test: Assessment of Functional Capacity and Magnitude of Cardiorespiratory Response in Patients with COPD and Healthy Subjects. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2013, 17, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilarinho, R.; Caneiras, C.; Montes, A.M. Measurement Properties of Step Tests for Exercise Capacity in COPD: A Systematic Review. Clin. Rehabil. 2021, 35, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strassmann, A.; Steurer-Stey, C.; Lana, K.D.; Zoller, M.; Turk, A.J.; Suter, P.; Puhan, M.A. Population-Based Reference Values for the 1-Min Sit-to-Stand Test. Int. J. Public. Health 2013, 58, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotake, T.; Dohi, N.; Kajiwara, T.; Sumi, N.; Koyama, Y.; Miura, T. An Analysis of Sit-to-Stand Movements. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1993, 74, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millington, P.J.; Myklebust, B.M.; Shambes, G.M. Biomechanical Analysis of the Sit-to-Stand Motion in Elderly Persons. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1992, 73, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gross, M.M.; Stevenson, P.J.; Charette, S.L.; Pyka, G.; Marcus, R. Effect of Muscle Strength and Movement Speed on the Biomechanics of Rising from a Chair in Healthy Elderly and Young Women. Gait Posture 1998, 8, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevillano-Castaño, A.; Peroy-Badal, R.; Torres-Castro, R.; Gimeno-Santos, E.; Fernández, P.G.; Vila, C.G.; Alfaro, A.A.; Álvarez, R.D.D.; Vilaró, J.; Blanco, I. Is There a Learning Effect on 1-Min Sit-to-Stand Test in Post-COVID-19 Patients? ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozalevli, S.; Ozden, A.; Itil, O.; Akkoclu, A. Comparison of the Sit-to-Stand Test with 6 Min Walk Test in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haley, S.M.; Fragala-Pinkham, M.A. Interpreting Change Scores of Tests and Measures Used in Physical Therapy. Phys. Ther. 2006, 86, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for Reporting Observational Studies. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Crouch, R. 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2019, 39, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, S.D.; Eliasziw, M.; Donner, A. Sample Size and Optimal Designs for Reliability Studies. Stat. Med. 1998, 17, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, J.P. Quantifying Test-Retest Reliability Using the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient and the SEM. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2005, 19, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.Y.; Sheu, C.F.; Protas, E.J. Test-Retest Reliability and Measurement Errors of Six Mobility Tests in the Community-Dwelling Elderly. Asian J. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2009, 4, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, J.; Howard, J.; Wallace, E.; Elborn, S. Reliability, Repeatability, and Sensitivity of the Modified Shuttle Test in Adult Cystic Fibrosis. Chest 2000, 117, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saremi, M.; Khayati, F.; Mousavi, F. Validity and Reliability of the Chester Step Test for Prediction of the Aerobic Capacity among Iranian Students. J. Occup. Health Epidemiol. 2018, 7, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, A.; Oliveira, A.; Ferreira, P.G.; Martins, V.; Marques, A. Reliability and Validity of the Chester Step Test in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease. Pulmonology, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Camargo, A.A.; Justino, T.; de Andrade, C.H.S.; Malaguti, C.; Dal Corso, S. Chester Step Test in Patients with COPD: Reliability and Correlation with Pulmonary Function Test Results. Respir. Care 2011, 56, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Özden, F.; Coşkun, G.; Bakırhan, S. The Test-Retest Reliability and Concurrent Validity of the Five Times Sit to Stand Test and Step Test in Older Adults with Total Hip Arthroplasty. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 142, 111143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, L.S.; Palombaro, K.M. Modified 30-Second Sit-to-Stand Test: Reliability and Validity in Older Adults Unable to Complete Traditional Sit-to-Stand Testing. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2020, 43, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, J.; Meng, S.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Tsang, R.C.C.; El-Ansary, D.; Han, J.; Jones, A.Y.M. Reliability and Validity of Sit-to-Stand Test Protocols in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 841453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combret, Y.; Prieur, G.; Boujibar, F.; Gravier, F.E.; Smondack, P.; Le Roux, P.; Bonnevie, T.; Medrinal, C.; Reychler, G. Validity and Reliability of the One-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test for the Measurement of Cardio-Respiratory Responses in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Pulmonology 2022, 28, 137–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A. Functional Status in the COVID-19 Era: ALERT, ALERT, ALERT! Pulmonology 2021, 27, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, A.E.; Malaguti, C.; Hoffman, M.; Lahham, A.; Burge, A.T.; Dowman, L.; May, A.K.; Bondarenko, J.; Graco, M.; Tikellis, G.; et al. Home-Based or Remote Exercise Testing in Chronic Respiratory Disease, during the COVID-19 Pandemic and beyond: A Rapid Review. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2020, 17, 1479973120952418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalbosco-Salas, M.; Torres-Castro, R.; Leyton, A.R.; Zapata, F.M.; Salazar, E.H.; Bastías, G.E.; Díaz, M.E.B.; Allers, K.T.; Fonseca, D.M.; Vilaró, J. Effectiveness of a Primary Care Telerehabilitation Program for Post-COVID-19 Patients: A Feasibility Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides-Cordoba, V.; Barros-Poblete, M.; Vieira, R.P.; Mazzucco, G.; Fregonezi, G.; Torres-Castro, R. Provision of Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Latin America 18 Months after the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Survey of the Latin American Thoracic Association. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2022, 19, 14799731221104102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, A.; Denehy, L.; Benjemaa, A.; Crowe, J.; Bruns, E.; Hall, T.; Traill, A.; Edbrooke, L. Feasibility and Safety of the 30-Second Sit-to-Stand Test Delivered via Telehealth: An Observational Study. PM&R 2023, 15, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Castro, R.; Núñez-Cortés, R.; Larrateguy, S.; Alsina-Restoy, X.; Barberà, J.A.; Gimeno-Santos, E.; García, A.R.; Sibila, O.; Blanco, I. Assessment of Exercise Capacity in Post-COVID-19 Patients: How Is the Appropriate Test Chosen? Life 2023, 13, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisó-Almirall, A.; Brito-Zerón, P.; Conangla Ferrín, L.; Kostov, B.; Moragas Moreno, A.; Mestres, J.; Sellarès, J.; Galindo, G.; Morera, R.; Basora, J.; et al. Long COVID-19: Proposed Primary Care Clinical Guidelines for Diagnosis and Disease Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura-Ortí, E.; Martínez-Olmos, F.J. Test-Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change Scores for Sit-to-Stand-to-Sit Tests, the Six-Minute Walk Test, the One-Leg Heel-Rise Test, and Handgrip Strength in People Undergoing Hemodialysis. Phys. Ther. 2011, 91, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwenk, M.; Gogulla, S.; Englert, S.; Czempik, A.; Hauer, K. Test-Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change of Repeated Sit-to-Stand Analysis Using One Body Fixed Sensor in Geriatric Patients. Physiol. Meas. 2012, 33, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapo, R.O.; Morris, A.H.; Gardner, R.M. Reference Spirometric Values Using Techniques and Equipment That Meet ATS Recommendations. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1981, 123, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankinson, J.L.; Odencrantz, J.R.; Fedan, K.B. Spirometric Reference Values from a Sample of the General U. S. Population. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henricson, E.; Abresch, R.; Han, J.J.; Nicorici, A.; Keller, E.G.; Elfring, G.; Reha, A.; Barth, J.; McDonald, C.M. Percent-Predicted 6-Minute Walk Distance in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy to Account for Maturational Influences. PLoS Curr. 2012, 4, RRN1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mean ± SD | (95% CI) Min–Max | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 51.6 ± 9.3 | (50.6 to 57.0) 33–79 |
| Weight (kg) | 84.0 ± 18.1 | (78.6 to 89.6) 45.1–125.0 |
| Height (cm) | 165.2 ± 9.4 | (162.3 to 165.2) 145–186 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30.5 ± 5.1 | (29.0 to 32.2) 17.4–40.2 |
| Hospitalisation (days) | 21.4 ± 39.0 | (9.2 to 33.5) 10.0–191.0 |
| Chester Test | Sit-to-Stand | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | p-Value | Trial 1 | Trial 2 | p-Value | ||
| Saturation Basal (%) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | 96.4 ± 1.8 (95.8–97.0) | 96.2 ± 2.0 (95.5–96.9) | 0.545 | 96.5 ± 1.4 (96.08–96.9) | 96.7 ± 1.3 (96.2–97.1) | 0.344 |
| (min–max) | (90.0–99.0) | (90.0–100.0) | (93.0–99.0) | (92.0–99.0) | |||
| Heart Rate Basal (lpm) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | 84.0 ± 14.8 (79.2–88.8) | 85.6 ± 14.4 (81.0–90.3) | 0.488 | 83.6 ± 13.7 (79.3–87.9) | 84.7 ± 13.8 (80.4–89.0) | 0.455 |
| (min–max) | (51–114) | (51–112) | (54–108) | (59–115) | |||
| Saturation Final (%) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | 94.6 ± 2.5 (93.8–95.4) | 94.6 ± 2.6 (93.8–95.52) | 0.833 | 93.8 ± 3.3 (92.8–94.9) | 91.4 ± 14.2 (87.0–95.9) | 0.327 |
| (min–max) | (89.0–99.0) | (89.0–98.0) | (87.0–99.0) | (85.0–99.0) | |||
| Heart Rate Final (lpm) | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | 108.3 ± 19.4 (102.1–114.5) | 109.5 ± 18.3 (103.6–115.4) | 0.384 | 118.4 ± 27.7 (109.7–127.0) | 118.8 ± 27.2 (110.3–127.3) | 0.655 |
| (min–max) | (65–146) | (62–146) | (77–155) | (73–160) | |||
| BORG | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | 3.9 ± 1.8 (3.2–4.5) | 4.0 ± 1.8 (3.4–4.6) | 0.626 | 4.4 ± 1.8 (3.9–5.0) | 5.1 ± 1.9 (4.1–5.7) | 0.413 |
| (min–max) | (0–7) | (0–8) | (0–7) | (0–7) | |||
| Fatigue LL | Mean ± SD (95% CI) | 4.0 ± 2.1 (3.3–4.7) | 4.3 ± 1.8 (3.7–4.9) | 0.381 | 4.4 ± 2.1 (3.7–5.2) | 4.5 ± 2.4 (3.8–5.1) | 0.983 |
| (min–max) | (0–8) | (0–8) | (0–10) | (0–9) | |||
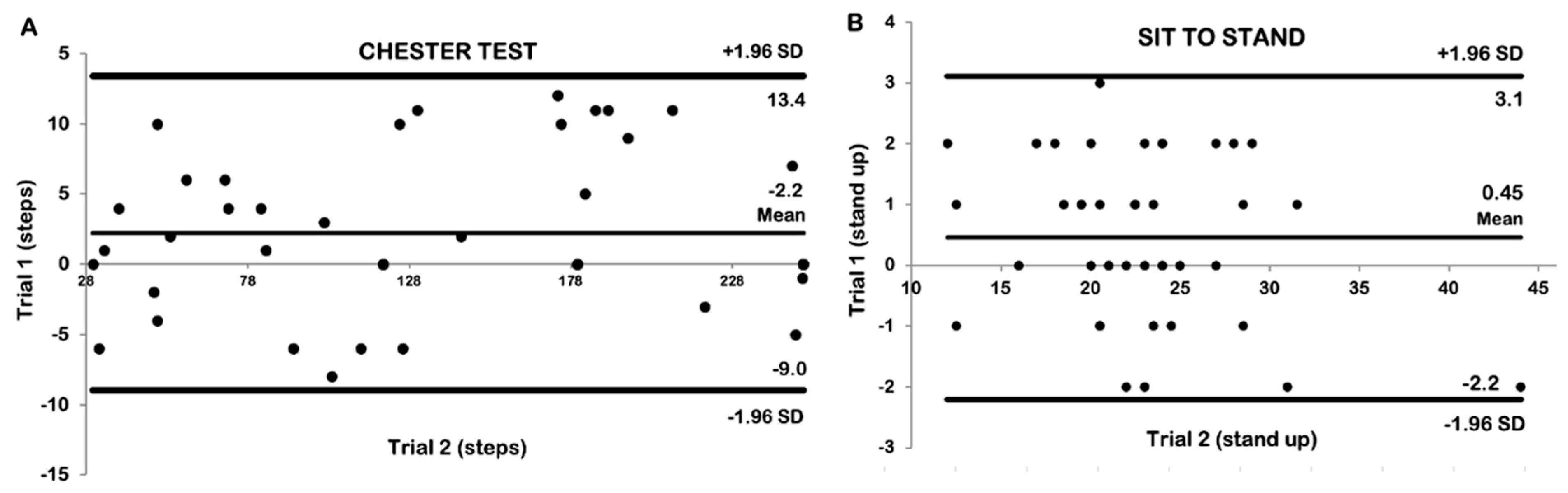
| Test–Retest Reliability for Chester Step (Trial 1 vs. Trial 2) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | ICC (95% CI) | SEM | MDC90 | MDC95 | ||
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | p | ||||
| 137.76 ± 72.16 | 138.80 ± 73.35 | 0.093 | 0.96 (0.93 to 0.98) | 7.27 | 16.96 (12%) | 20.15 (15%) |
| Test–retest reliability for sit-to-stand (Trial 1 vs. Trial 2) | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | ICC (95% CI) | SEM | MDC90 | MDC95 | ||
| Trial 1 | Trial 2 | p | ||||
| 22.47 ± 5.93 | 22.85 ± 5.58 | 0.196 | 0.98 (0.96 to 0.99) | 0.81 | 1.89 (8%) | 2.71 (12%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sevillano-Castaño, A.I.; Peroy-Badal, R.; Torres-Castro, R.; Cañuelo-Márquez, A.M.; Rozalén-Bustín, M.; Modrego-Navarro, Á.; De Sousa-De Sousa, L.; Ramos-Álvarez, J.J.; Maté-Muñoz, J.L.; García-Fernández, P. Test–Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change in Chester Step Test and 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test in Long COVID Patients. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8464. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148464
Sevillano-Castaño AI, Peroy-Badal R, Torres-Castro R, Cañuelo-Márquez AM, Rozalén-Bustín M, Modrego-Navarro Á, De Sousa-De Sousa L, Ramos-Álvarez JJ, Maté-Muñoz JL, García-Fernández P. Test–Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change in Chester Step Test and 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test in Long COVID Patients. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(14):8464. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148464
Chicago/Turabian StyleSevillano-Castaño, Ana Isabel, Renata Peroy-Badal, Rodrigo Torres-Castro, Ana María Cañuelo-Márquez, Manuel Rozalén-Bustín, Ángel Modrego-Navarro, Luis De Sousa-De Sousa, Juan José Ramos-Álvarez, José Luis Maté-Muñoz, and Pablo García-Fernández. 2023. "Test–Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change in Chester Step Test and 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test in Long COVID Patients" Applied Sciences 13, no. 14: 8464. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148464
APA StyleSevillano-Castaño, A. I., Peroy-Badal, R., Torres-Castro, R., Cañuelo-Márquez, A. M., Rozalén-Bustín, M., Modrego-Navarro, Á., De Sousa-De Sousa, L., Ramos-Álvarez, J. J., Maté-Muñoz, J. L., & García-Fernández, P. (2023). Test–Retest Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change in Chester Step Test and 1-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test in Long COVID Patients. Applied Sciences, 13(14), 8464. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13148464








