Thermochemical Analysis of Hydrogenation of Pd-Containing Composite Based on TiZrVNbTa High-Entropy Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Alloy and Fiber Preparation
2.2. Palladium Coating Obtaining
2.3. Hydrogen Sorption Properties
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy
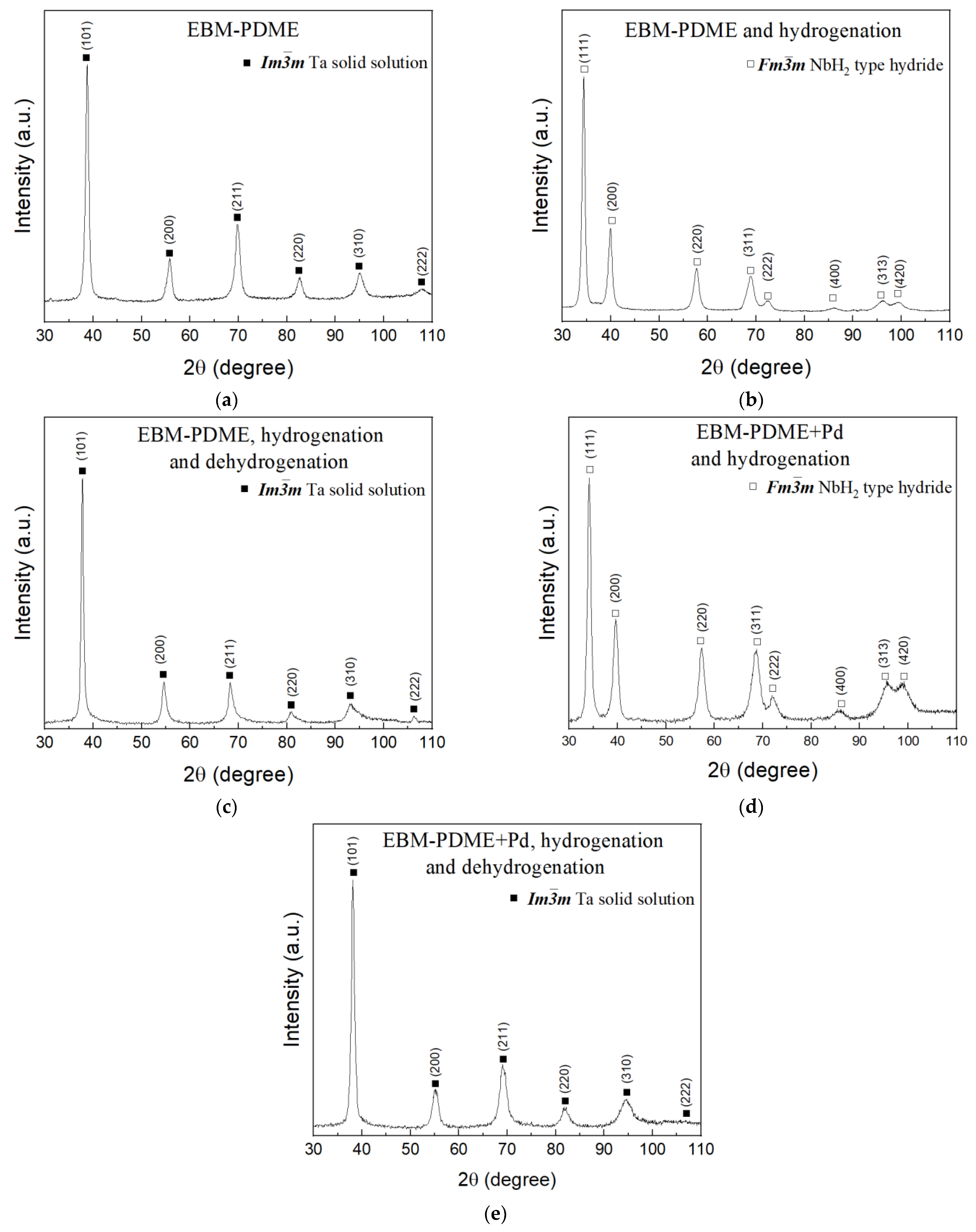
2.5. X-ray Phase Analysis
2.6. Time-of-Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Palladium Coating
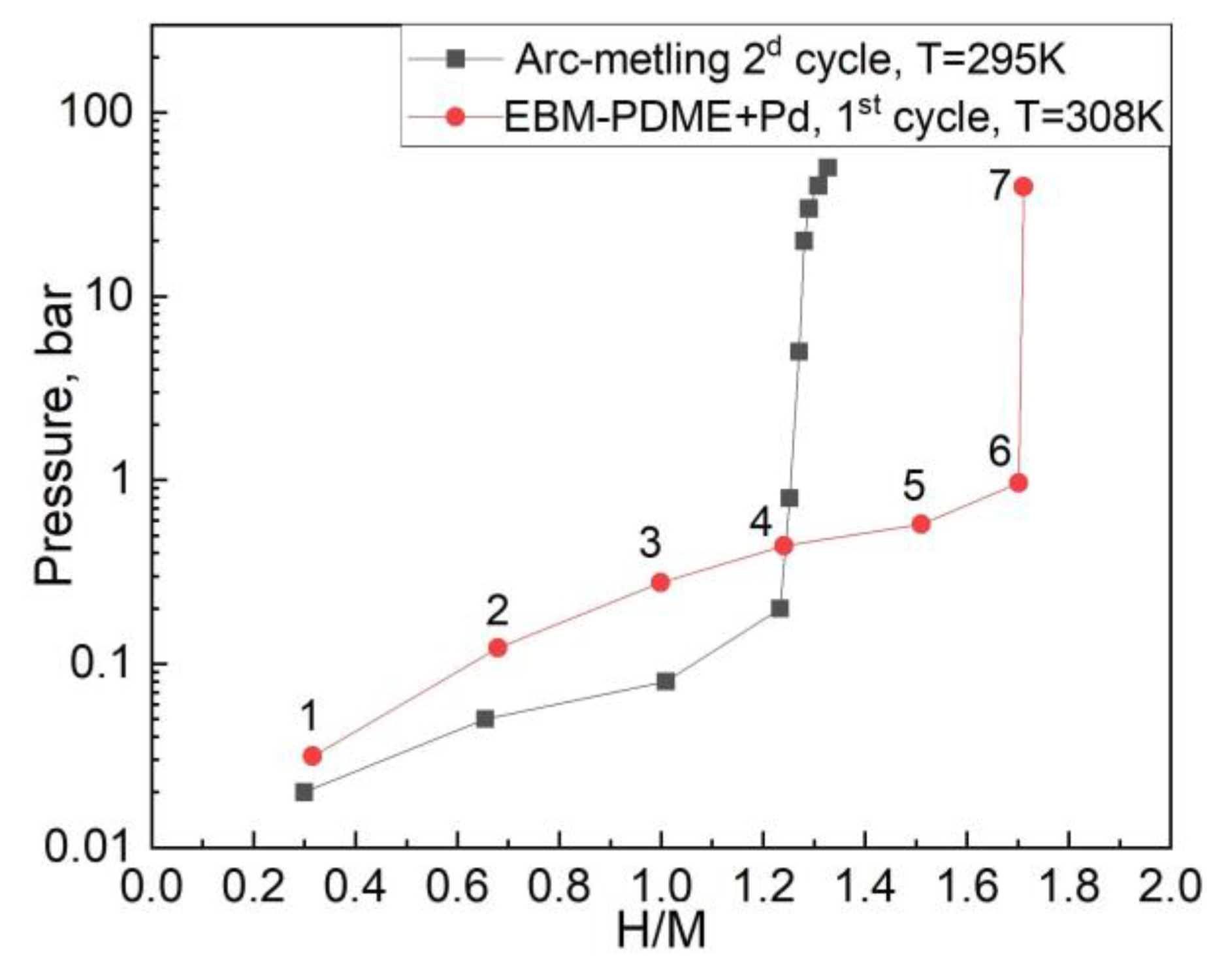
3.2. Hydrogen Sorption Properties
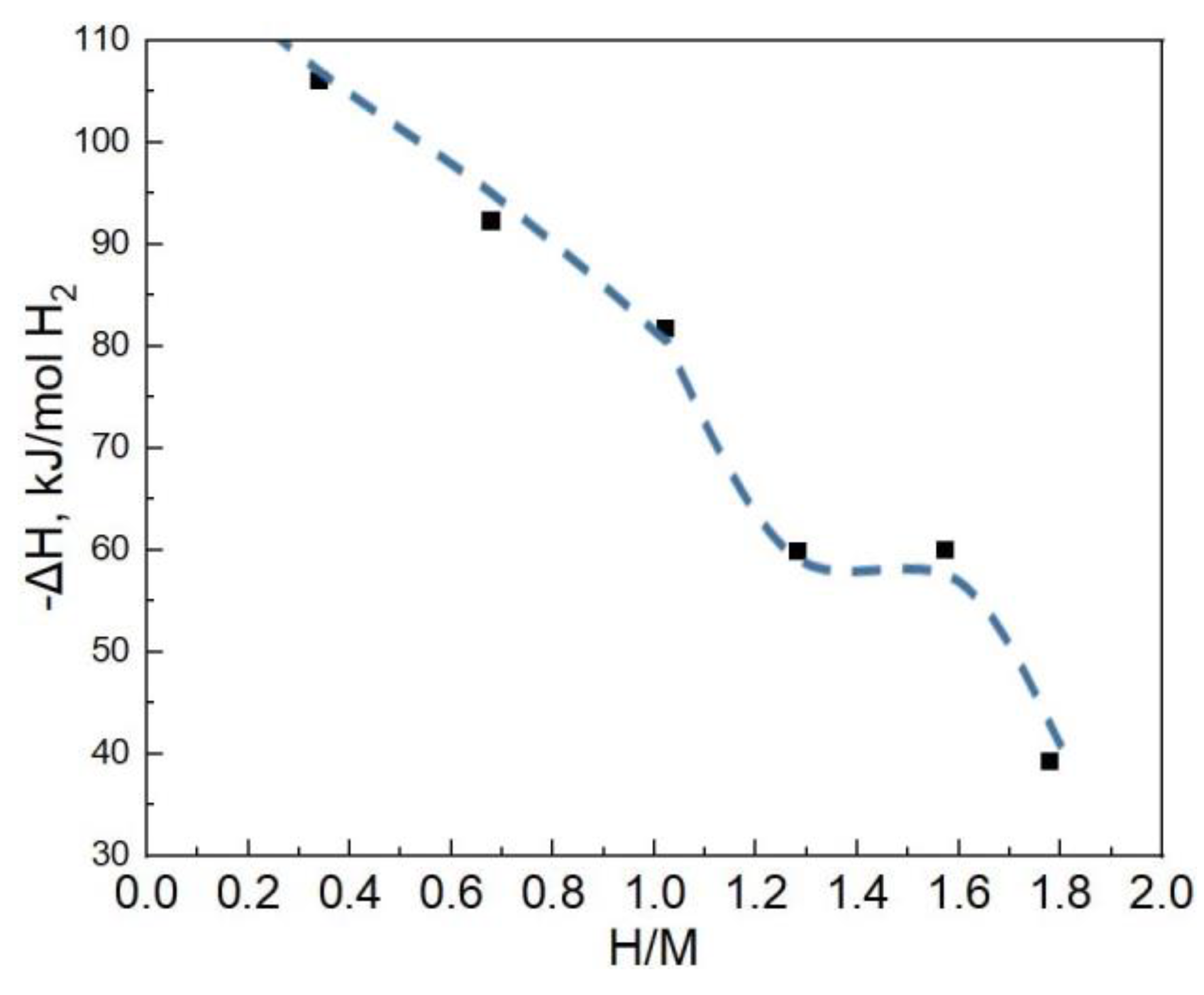
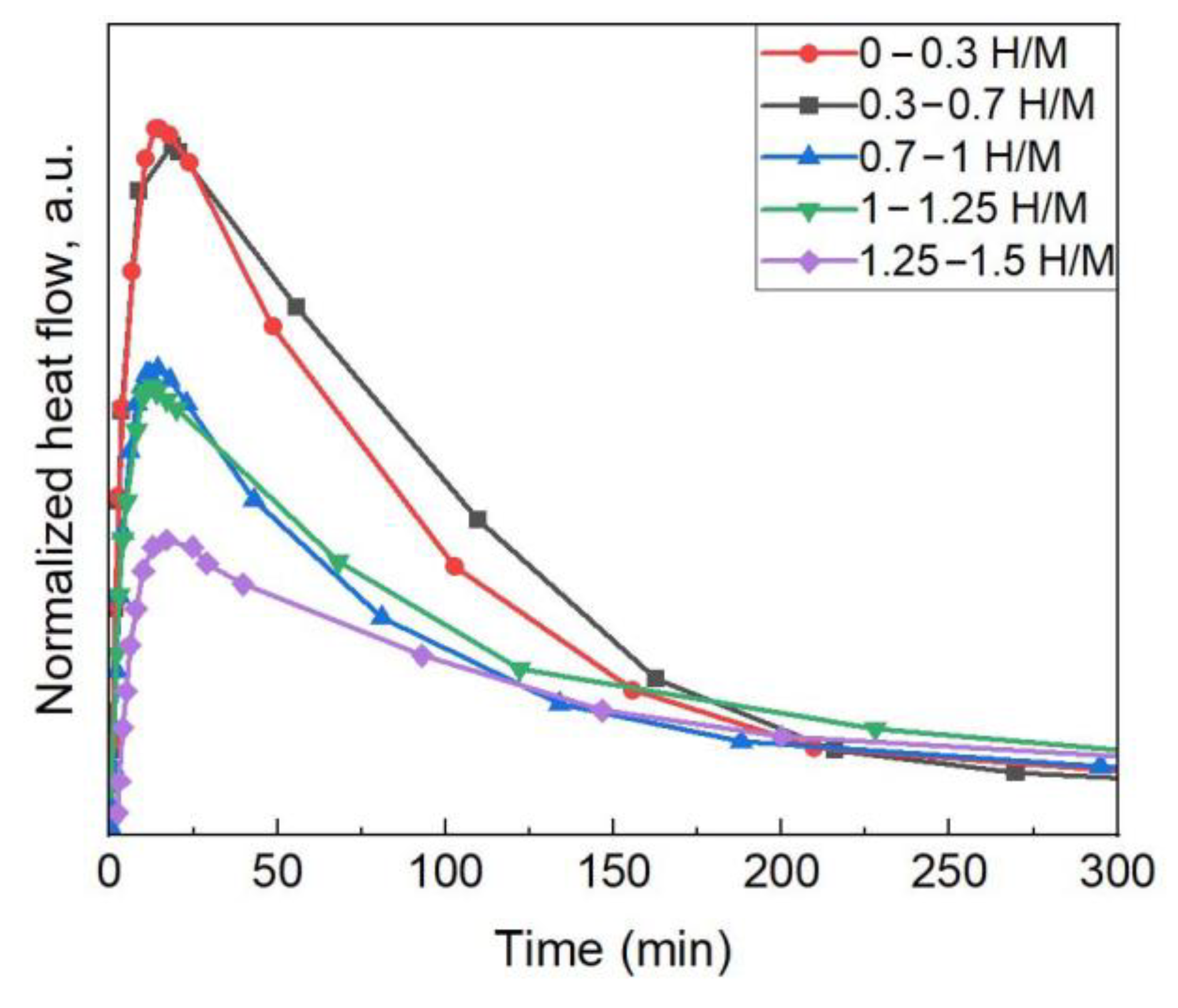
3.3. Calorimetric Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Huot, J.; Jasmina, G.; Nikola, N. Recent progress on the development of high entropy alloys (HEAs) for solid hydrogen storage: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 11236–11249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorban, V.; Shaginyan, R.; Krapivka, N.; Firstov, S. Superhard vacuum coatings based on high-entropy alloys. Powder Met. Met. Ceram. 2016, 54, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ming, K.; Kang, J.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Bi, X. High entropy alloy as a highly active and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 279, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Gu, J.; Sun, Y.; Ji, W.; Fu, Z. Self-supported high-entropy alloy electrocatalyst for highly efficient H2 evolution in acid condition. J. Mater. 2020, 6, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, T.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Krishna, N. High-Entropy Alloys for Solid Hydrogen Storage: Potentials and Prospects. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2022, 7, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlberg, M.; Karlsson, D.; Zlotea, C.; Jansson, U. Superior hydrogen storage in high entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, K.; Fukai, Y. High-pressure studies of high-concentration phases of the TiH system. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 231, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, G.; Nygård, M.; Pavan, A.; Montero, J.; Henry, P.; Sørby, M.; Witman, M.; Stavila, V.; Zlotea, C.; Hauback, B.; et al. Elucidating the effects of the composition on hydrogen sorption in TiVZrNbHf-based high-entropy alloys. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 60, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, F.; Balcerzak, M.; Winkelmann, F.; Zepon, G.; Felderhoff, M. Review and outlook on high-entropy alloys for hydrogen storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 5191–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. Prediction of high-entropy stabilized solid-solution in multi-component alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.; Raabe, D.; Ritchie, R. High-entropy alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troparevsky, M.; Morris, J.; Kent, P.; Lupini, A.; Stocks, G. Criteria for Predicting the Formation of Single-Phase High-Entropy Alloys. Phys. Rev. X 2015, 5, 011041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Troparevsky, M.; Morris, J.; Daene, M.; Wang, Y.; Lupini, A.; Stocks, G. Beyond Atomic Sizes and Hume-Rothery Rules: Understanding and Predicting High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 2015, 67, 2350–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.; Middleburgh, S.; McGregor, A.; Cortie, M. Predicting the formation and stability of single phase high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2016, 104, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, K.; Li, H.; Kilmametov, A.; Floriano, R.; Borchers, C. High-pressure torsion for synthesis of high-entropy alloys. Metals 2021, 11, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floriano, R.; Zepon, G.; Edalati, K.; Fontana, G.; Mohammadi, A.; Ma, Z.; Contieri, R. Hydrogen storage in TiZrNbFeNi high entropy alloys, designed by thermodynamic calculations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 33759–33770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobko, M.; Lushnikov, S.; Verbetsky, V.; Agafonov, S. Structure of (ZrTi)0.5(VCrFe(Ni0.9Cu0.1))0.5- and (ZrTi)0.5(VMoFeNi)0.5-Based Deuterides. Inorg. Mater. 2020, 56, 1106–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepon, G.; Leiva, D.; Strozi, R.; Bedoch, A.; Figueroa, S.; Ishikawa, T.; Botta, W. Hydrogen-induced phase transition of MgZrTiFe0.5Co0.5Ni0.5 high entropy alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 1702–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Liu, H.; Pan, X.; Lu, T.; Zhu, T.; Luo, G. Hydrogen isotope permeation and retention behavior in the CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 522, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, C.; Luo, H.; Raabe, D.; Li, Z. Hydrogen resistance of a 1 GPa strong equiatomic CoCrNi medium entropy alloy. Corros. Sci. 2022, 167, 108510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotea, C.; Sow, M.; Ek, G.; Couzinié, J.; Perrière, L.; Guillot, I.; Bourgon, J.; Møller, K.; Jensen, T.; Akiba, E. Hydrogen sorption in TiZrNbHfTa high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 775, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.; Chun, C.; Lee, J.Y. Observation of the defects induced by hydrogen absorption and desorption in LaNi5. Acta Metall. Mater. 1995, 43, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Hirota, M.; Yamaguchi, M. Lattice defects introduced during hydrogen absorption–desorption cycles and their effects on P–C characteristics in some intermetallic compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 330, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, Y.; You, L.; Cao, X.; Lu, Z.; Song, X. Investigation on the activation mechanism of hydrogen absorption in TiZrNbTa high entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 781, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, G.; Zepon, G.; Edalati, K.; Mohammadi, A.; Ma, Z.; Li, H.; Floriano, R. Crystal structure and hydrogen storage properties of AB-type TiZrNbCrFeNi high-entropy alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 13555–13565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Prasad, Y.; Krishna, M. Notable hydrogen storage in Ti–Zr–V–Cr–Ni high entropy alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 22893–22900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygård, M.; Ek, G.; Karlsson, D.; Sahlberg, M.; Sørby, M.; Hauback, B. Hydrogen storage in high-entropy alloys with varying degree of local lattice strain. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 29140–29149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunce, I.; Polanski, M.; Bystrzycki, J. Structure and hydrogen storage properties of a high entropy ZrTiVCrFeNi alloy synthesized using Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 12180–12189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhong, B.; Xiao, H.; Ye, X.; Lu, L.; Guan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, C. Effect of degassing treatment on the deuterium permeability of Pd-Nb-Pd composite membranes during deuterium permeation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 190, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phair, J.; Donelson, R. Developments and design of novel (non-palladium-based) metal membranes for hydrogen separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2006, 45, 5657–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Min, R.; Zhao, P.; Misra, R.; Huang, P.; Zou, Y.; Chu, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Sun, L. Design of Nb-based multi-phase alloy membranes for high hydrogen permeability and suppressed hydrogen embrittlement. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Shao, Y.; Li, J.; Yao, K. Microstructure. phase stability and mechanical properties of Nb–Ni–Ti–Co–Zr and Nb–Ni–Ti–Co–Zr–Hf high entropy alloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2015, 25, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lundin, C.; Lynch, F.; Magee, C. A correlation between the interstitial hole sizes in intermetallic compounds and the thermodynamic properties of the hydrides formed from those compounds. J. Less-Common Met. 1977, 56, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitani, S.; Yonezu, I.; Saito, T.; Furukawa, N.; Akiba, E.; Hayakawa, H.; Ono, S. Relation between equilibrium hydrogen pressure and lattice parameters in pseudobinaryZr Mn alloy systems. J. Less-Common Met. 1991, 172, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, F.; Joubert, J.; Latroche, M.; Percheron-Guégan, A. Intermetallic compounds as negative electrodes of Ni/MH batteries. Appl. Phys. A 2001, 72, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galey, B.; Auroux, A.; Sabo-Etienne, S.; Dhaher, S.; Grellier, M.; Postole, G. Improved hydrogen storage properties of Mg/MgH2 thanks to the addition of nickel hydride complex precursors. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 28848–28862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdonosova, E.; Klyamkin, S.; Zadorozhnyy, V.; Zadorozhnyy, M.; Geodakian, K.; Gorshenkov, M.; Kaloshkin, S. Calorimetric study of peculiar hydrogenation behavior of nanocrystalline TiFe. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorozhnyy, V.; Berdonosova, E.; Gammer, C.; Eckert, J.; Zadorozhnyy, M.; Bazlov, A.; Klyamkin, S. Mechanochemical synthesis and hydrogenation behavior of (TiFe) 100-xNix alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 796, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.; Lototsky, M.; Davids, M.; Linkov, V.; Yartys, V.; Solberg, J. Chemical surface modification for the improvement of the hydrogenation kinetics and poisoning resistance of TiFe. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somo, T.; Davids, M.; Lototskyy, M.; Hato, M.; Modibane, K. Improved hydrogenation kinetics of TiMn1.52 alloy coated with palladium through electroless deposition. Materials 2021, 14, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serov, M. Microcrystalline and amorphous alloys obtained by the method of rapid quenching of melt. Tekhnol. Legk. Splav. 2008, 4, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Korol, A.; Zadorozhnyy, V.; Zadorozhnyy, M.; Bazlov, A.; Berdonosova, E.; Serov, M.; Savvotin, I. Production of multi-principal-component alloys by pendent-drop melt extraction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorozhnyy, V.; Tomilin, I.; Berdonosova, E.; Gammer, C.; Zadorozhnyy, M.; Savvotin, I.; Shchetinin, I.; Zheleznyi, M.; Novikov, A.; Bazlov, A.; et al. Composition design. synthesis and hydrogen storage ability of multi-principal-component alloy TiVZrNbTa. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 901, 163638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarac, B.; Zadorozhnyy, V.; Ivanov, Y.; Spieckermann, F.; Klyamkin, S.; Berdonosova, E.; Serov, M.; Kaloshkin, S.; Greer, A.; Sarac, A.; et al. Transition metal-based high entropy alloy microfiber electrodes: Corrosion behavior and hydrogen activity. Corros. Sci. 2021, 193, 109880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovleva, N.; Ganich, E.; Rumyantseva, T.; Semenenko, K. Interaction mechanism of hydrogen with the CaCu5-type crystal structure intermetallic compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 1996, 241, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelekhov, E.; Sviridova, T. Programs for X-ray analysis of polycristals. J. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2000, 42, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, J.; Ek, G.; Laversenne, L.; Nassif, V.; Zepon, G.; Sahlberg, M.; Zlote, C. Hydrogen storage properties of the refractory Ti–V–Zr–Nb–Ta multi-principal element alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 835, 155376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
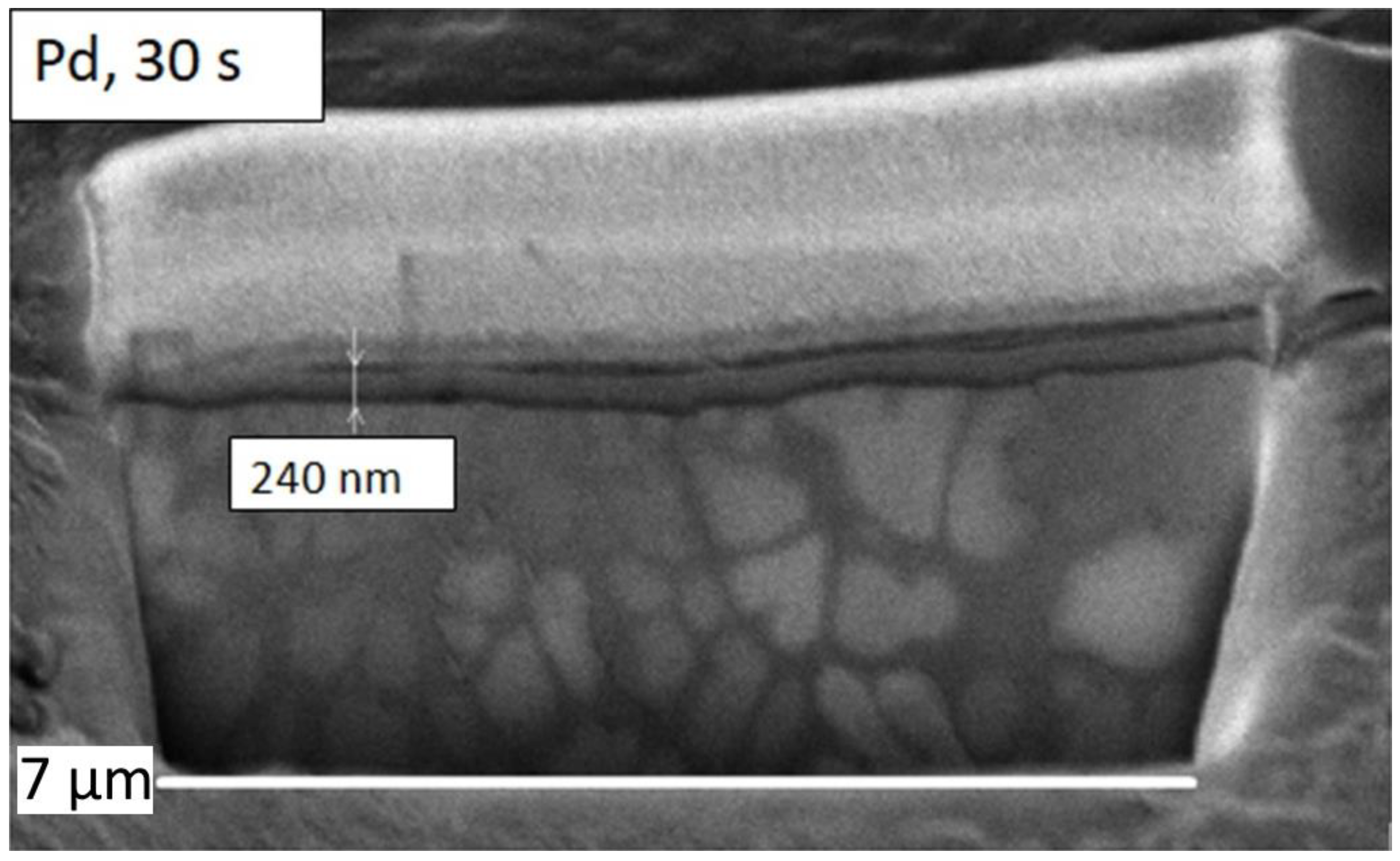
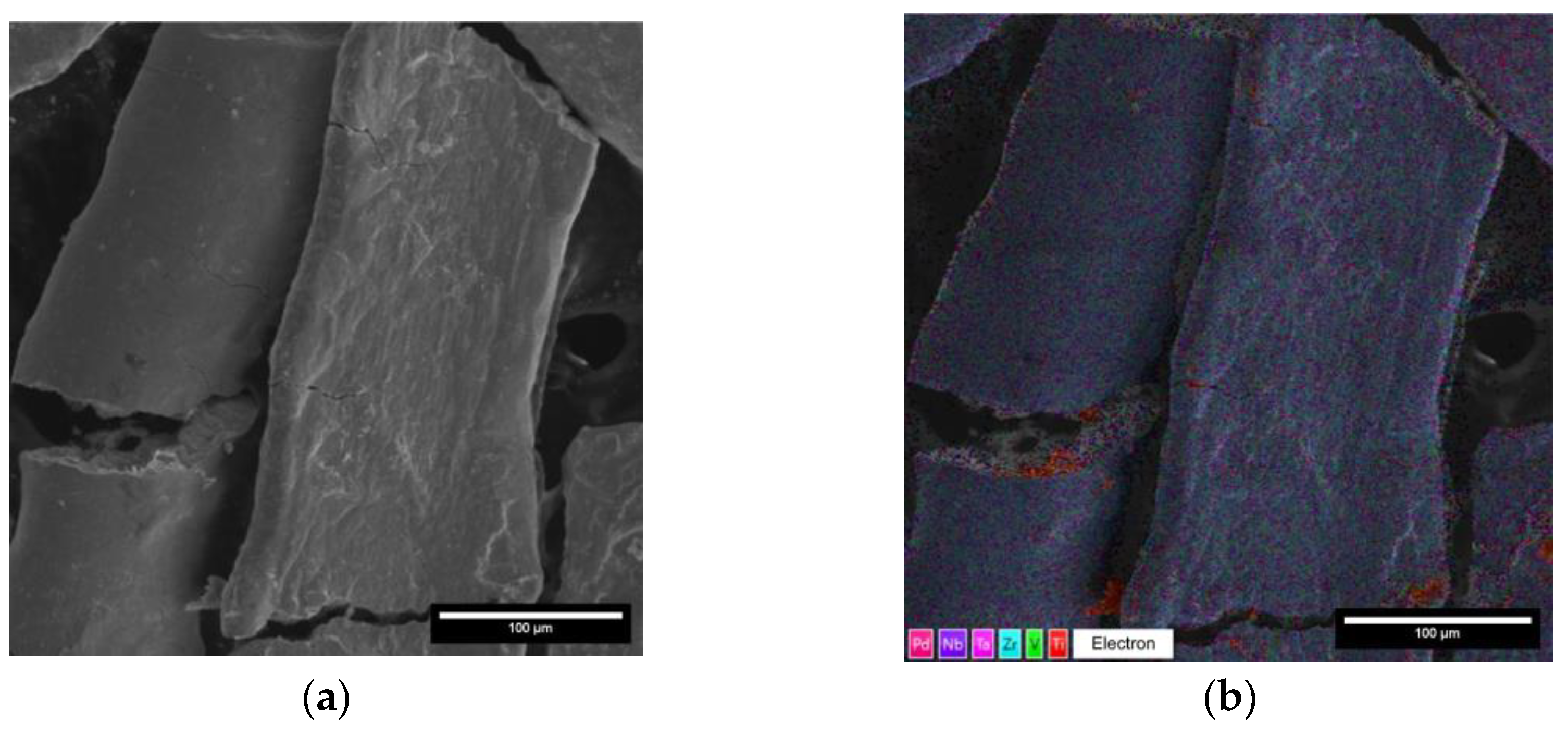
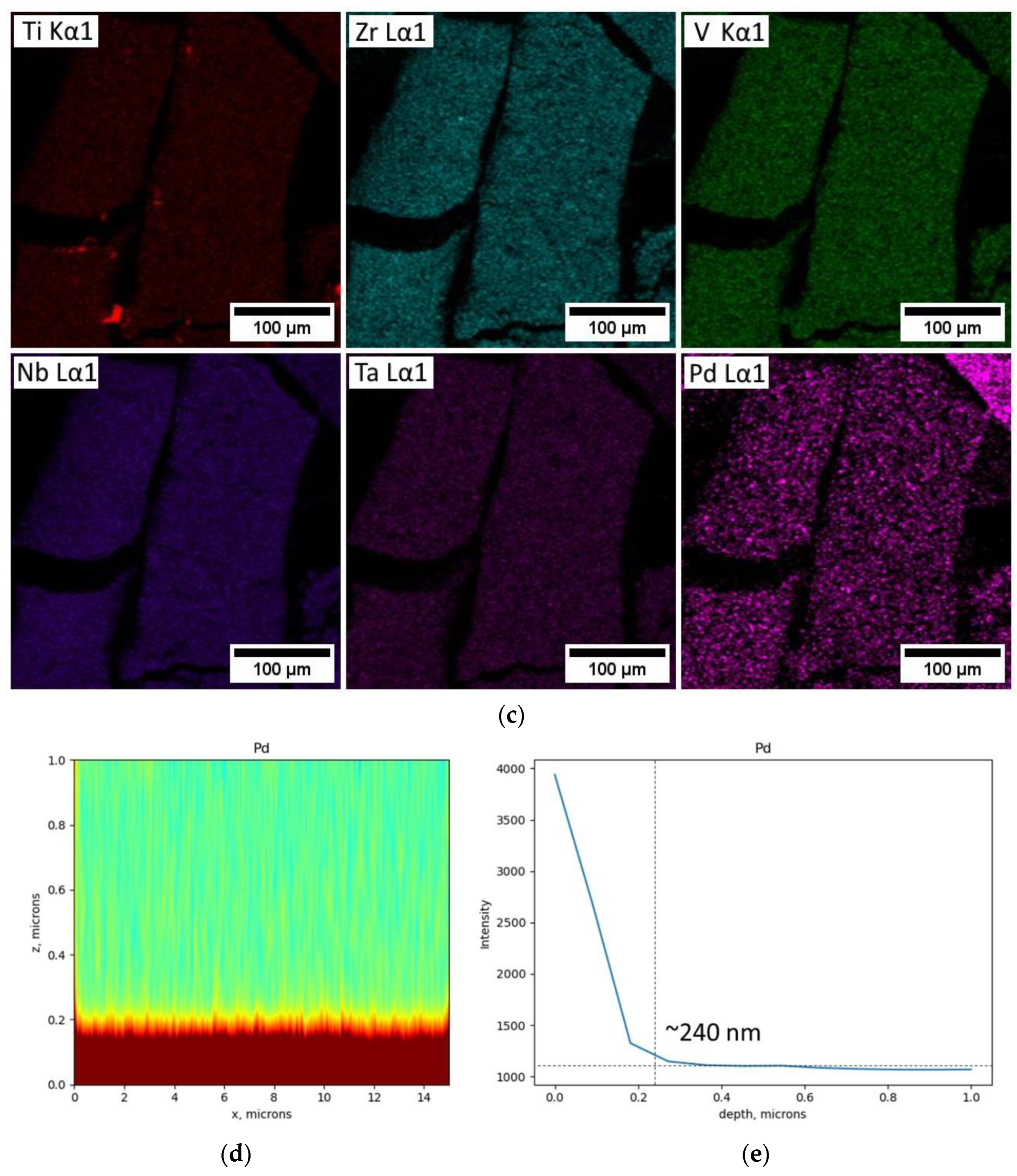
| Element | Set Composition, at. % | Defined Composition, at. % |
|---|---|---|
| Ti | 20 | 18.1 |
| Zr | 20 | 19.7 |
| V | 20 | 19.2 |
| Nb | 20 | 21.5 |
| Ta | 20 | 21.5 |
| Sample | Space Group | Phase Content, % | Unit Cell Parameters, nm | Crystallite Size, nm | V, nm3 | ΔV/V0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As prepared | ||||||
| TiZrVNbTa | m | 100 | a = 0.3301(5) | ˃200 | 0.0359(3) | - |
| After hydrogenation | ||||||
| TiZrVNbTa | m | 100 | a = 0.4539(3) | ˃200 | 0.0935(2) | 30.2 |
| Pd@TiZrVNbTa | m | 100 | a = 0.4538(1) | ˃200 | 0.0935(1) | 30.2 |
| TiZrVNbTa * | m | 95 | a = 0.4517(5) | ˃200 | 0.0922(4) | 27.3 |
| Pnnn | 5 | a = 0.4795(7) b = 0.4829(4) c = 0.3450(2) | ˃200 | 0.0799(3) | 22.1 | |
| After dehydrogenation | ||||||
| TiZrVNbTa | m | 100 | a = 0.3321(2) | 100 | 0.0366(6) | 1.9 |
| Pd@TiZrVNbTa | m | 100 | a = 0.3314(4) | 100 | 0.0364(2) | 1.4 |
| TiZrVNbTa * | m | 95 | a = 0.3304(2) | 40 | 0.0361(5) | 0.6 |
| m | 5 | a = 0.3395(7) | 50 | 0.0391(2) | 8.2 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Savvotin, I.; Berdonosova, E.; Korol, A.; Zadorozhnyy, V.; Zadorozhnyy, M.; Statnik, E.; Korsunsky, A.; Serov, M.; Klyamkin, S. Thermochemical Analysis of Hydrogenation of Pd-Containing Composite Based on TiZrVNbTa High-Entropy Alloy. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9052. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169052
Savvotin I, Berdonosova E, Korol A, Zadorozhnyy V, Zadorozhnyy M, Statnik E, Korsunsky A, Serov M, Klyamkin S. Thermochemical Analysis of Hydrogenation of Pd-Containing Composite Based on TiZrVNbTa High-Entropy Alloy. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(16):9052. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169052
Chicago/Turabian StyleSavvotin, Ivan, Elena Berdonosova, Artem Korol, Vladislav Zadorozhnyy, Mikhail Zadorozhnyy, Evgeniy Statnik, Alexander Korsunsky, Mikhail Serov, and Semen Klyamkin. 2023. "Thermochemical Analysis of Hydrogenation of Pd-Containing Composite Based on TiZrVNbTa High-Entropy Alloy" Applied Sciences 13, no. 16: 9052. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169052
APA StyleSavvotin, I., Berdonosova, E., Korol, A., Zadorozhnyy, V., Zadorozhnyy, M., Statnik, E., Korsunsky, A., Serov, M., & Klyamkin, S. (2023). Thermochemical Analysis of Hydrogenation of Pd-Containing Composite Based on TiZrVNbTa High-Entropy Alloy. Applied Sciences, 13(16), 9052. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169052









