Effects of Processing Conditions on the Properties of Porous Diatomite Granules Prepared by Sodium Alginate Gelation
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
| SiO2 * | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2O + K2O | Loss of Ignition (1000 °C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 92.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 2.5 | 0.2 |
3. Results
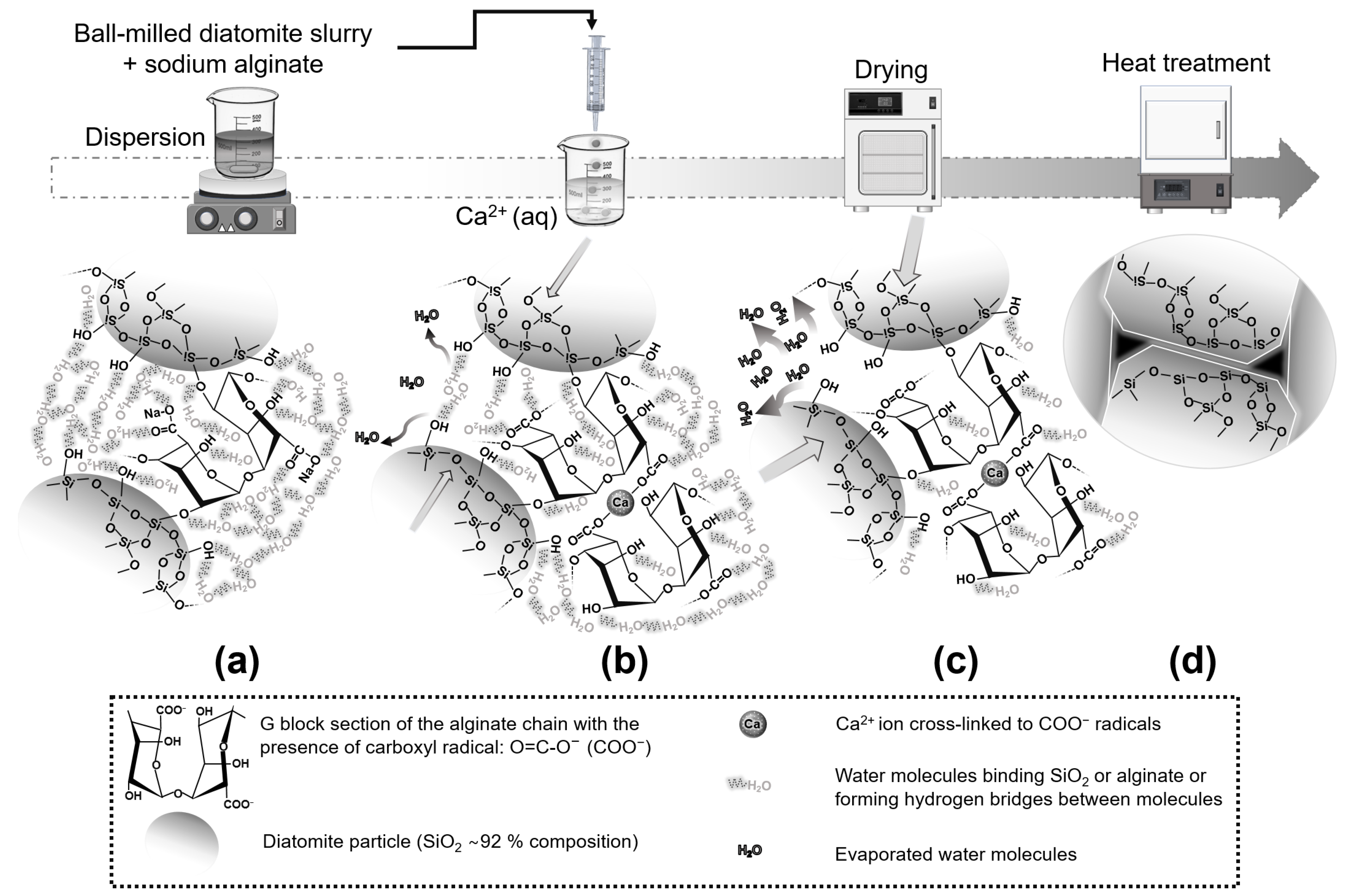
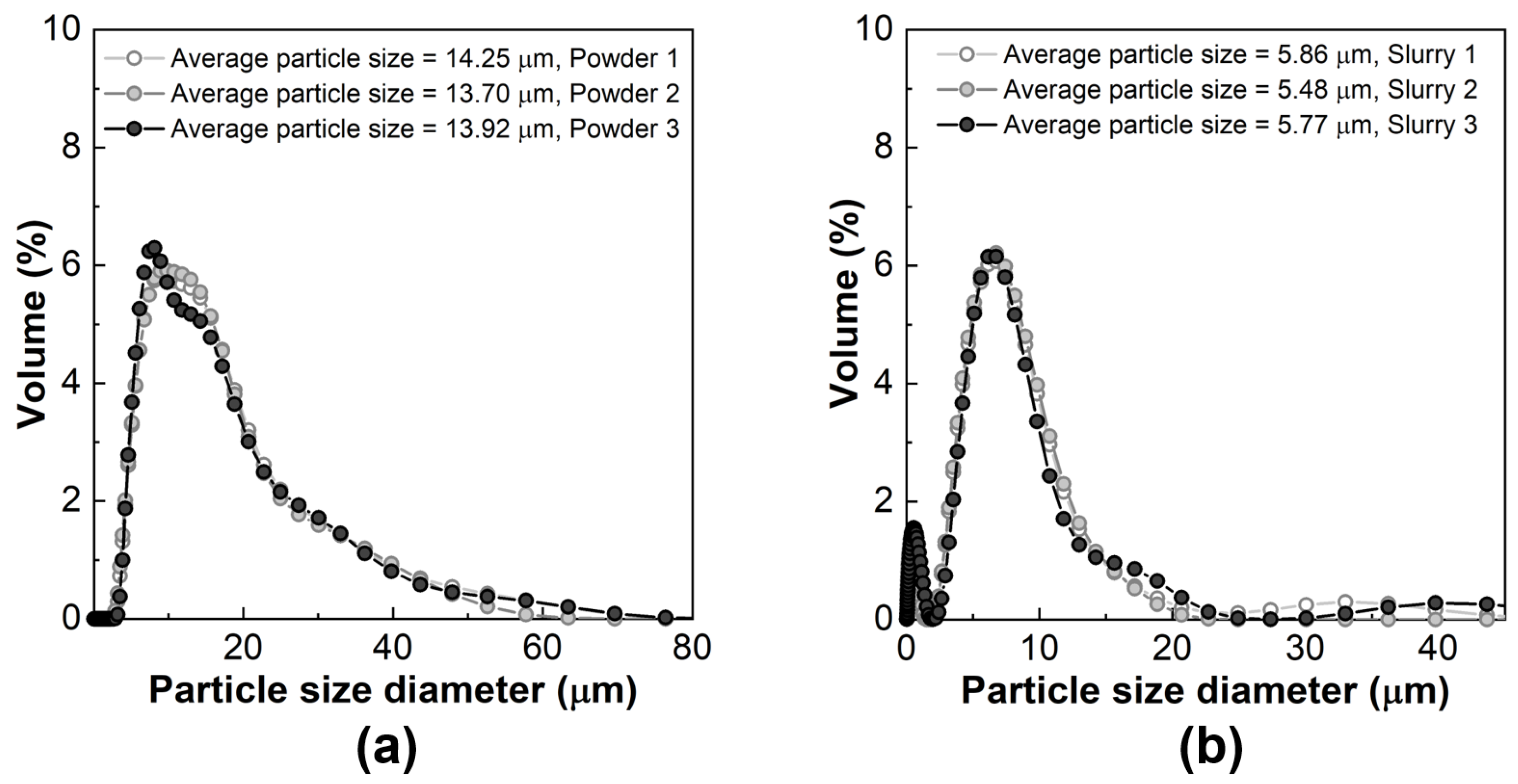
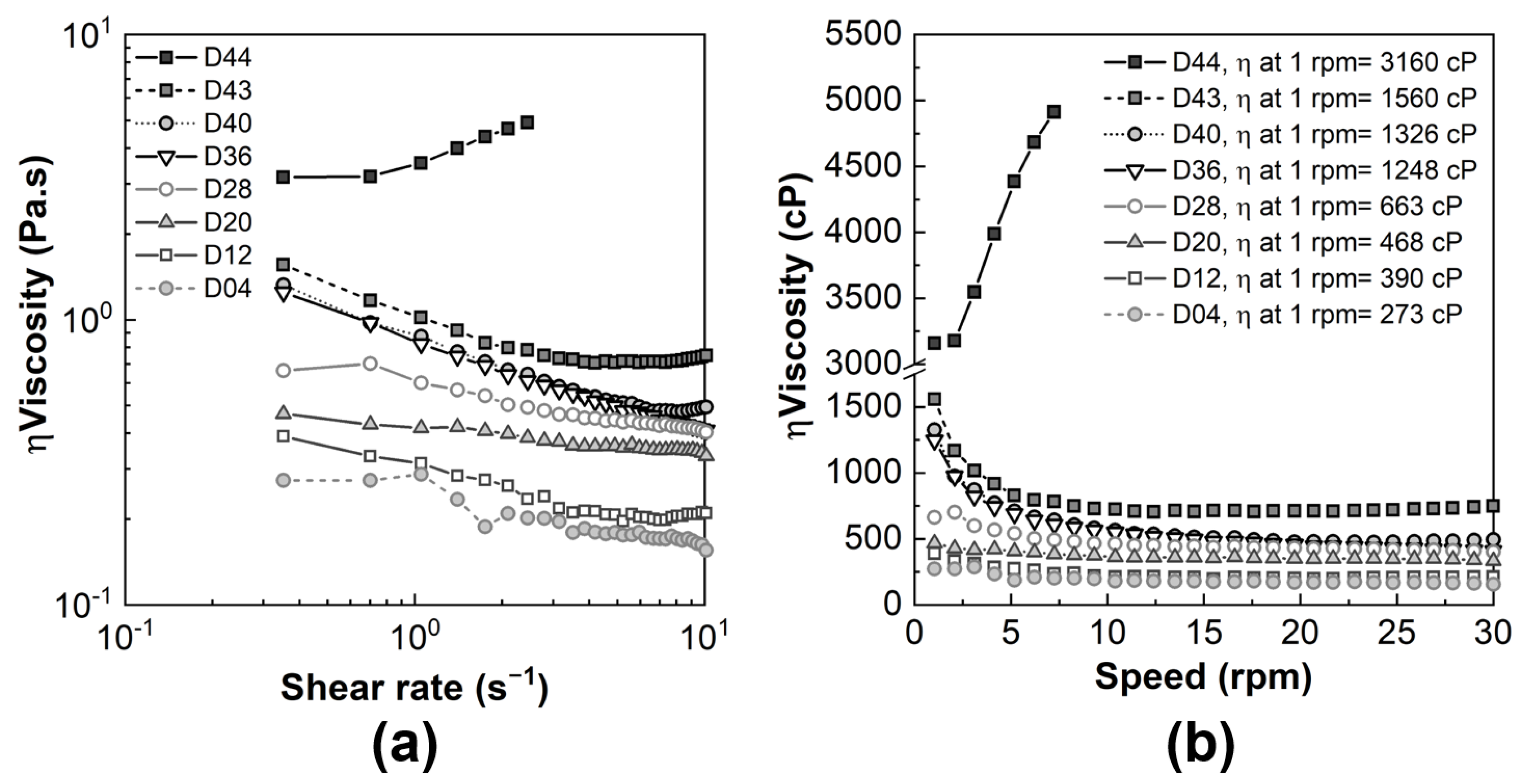
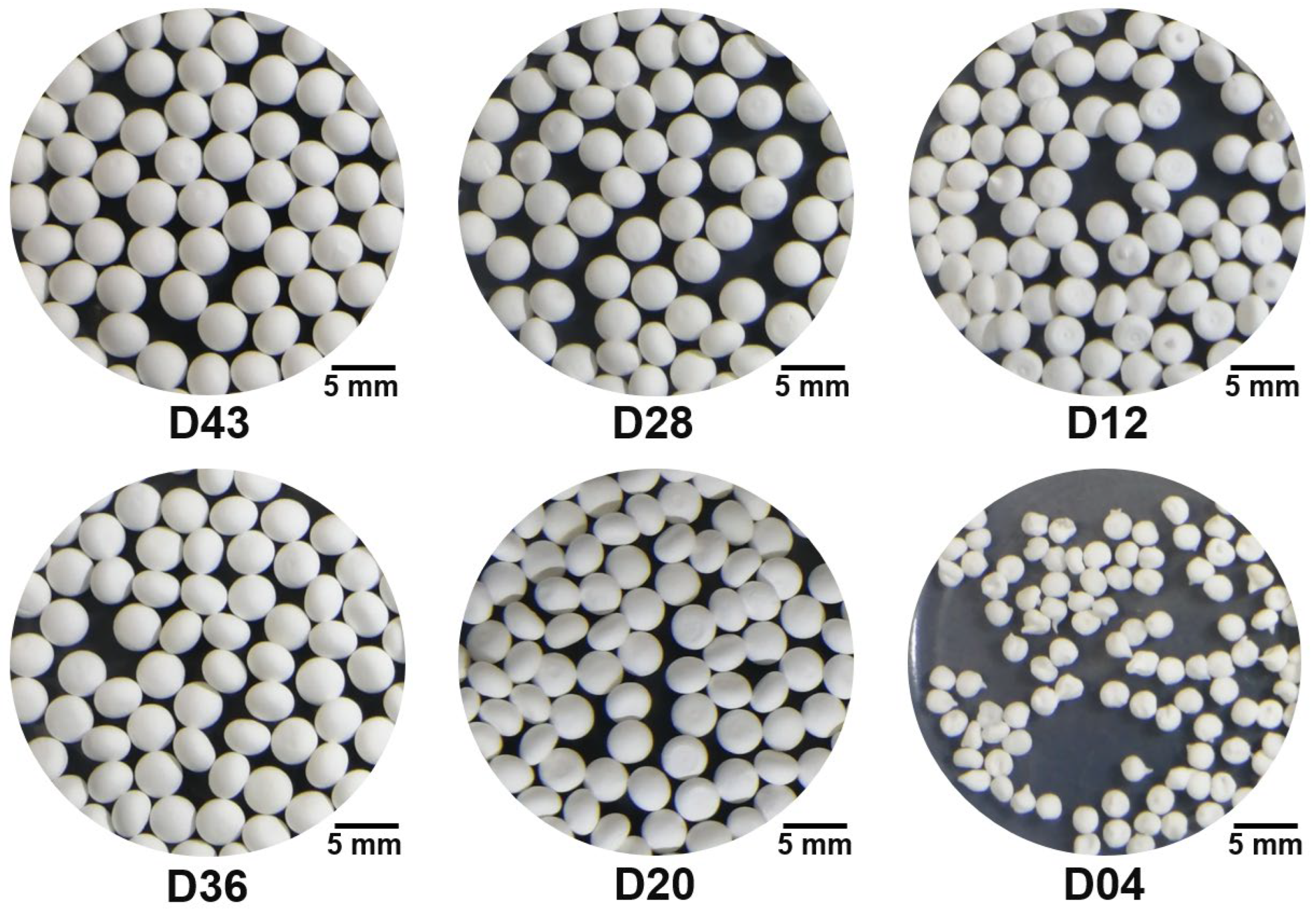
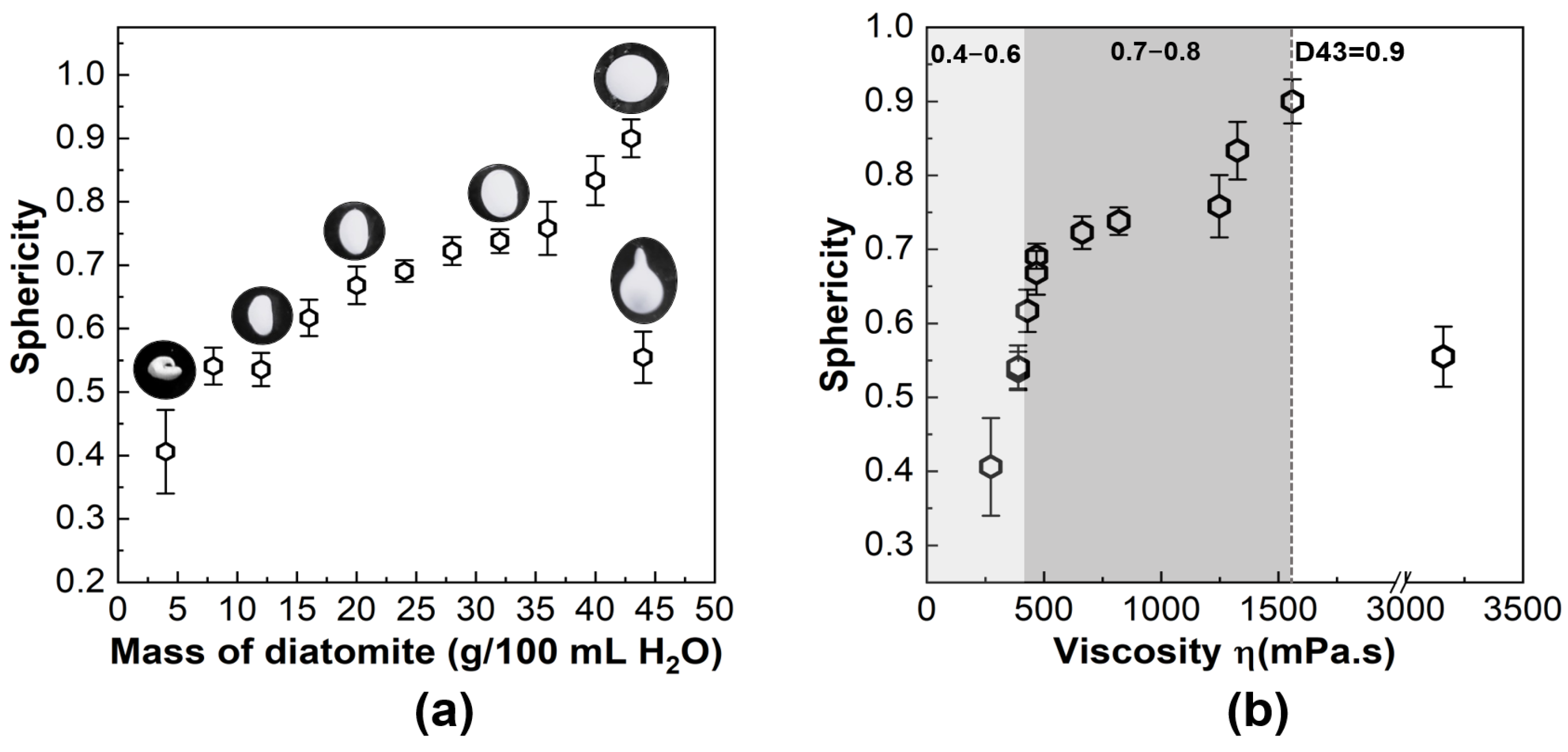
3.1. Characterization of Diatomite Powders, Diatomite/Sodium Alginate Dispersions and Resultant Granules
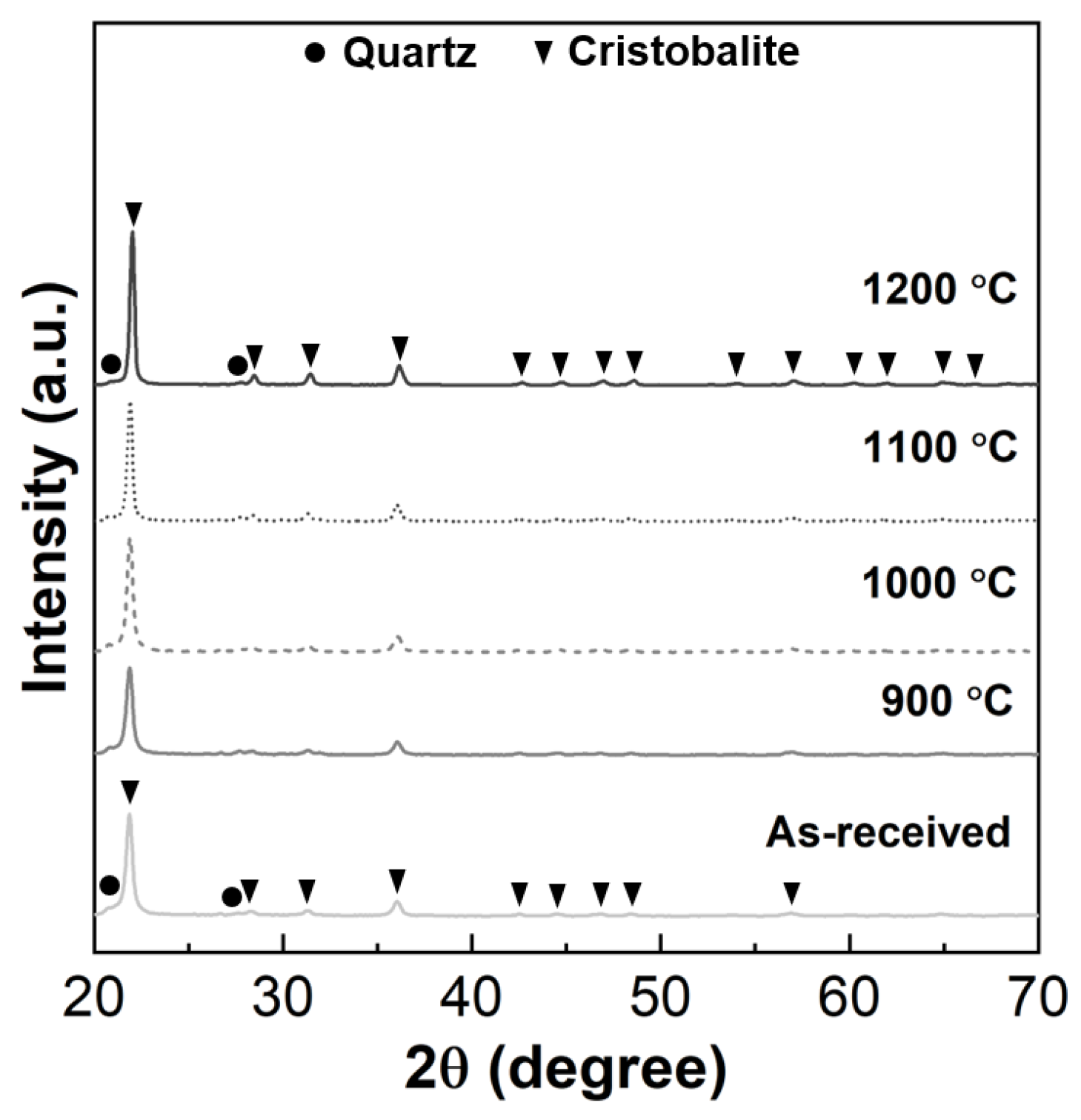
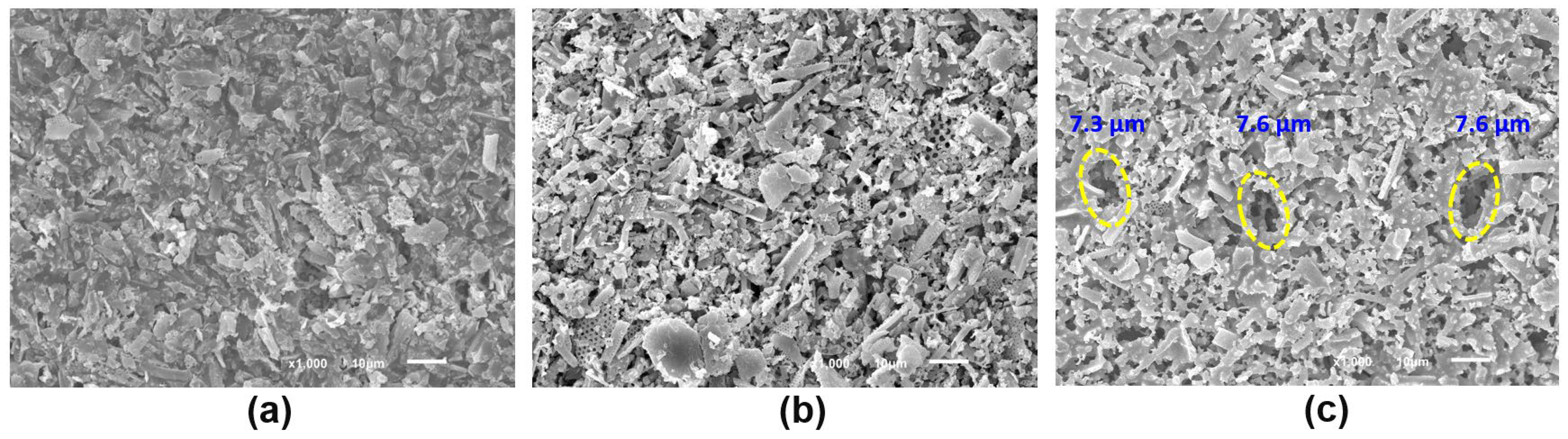
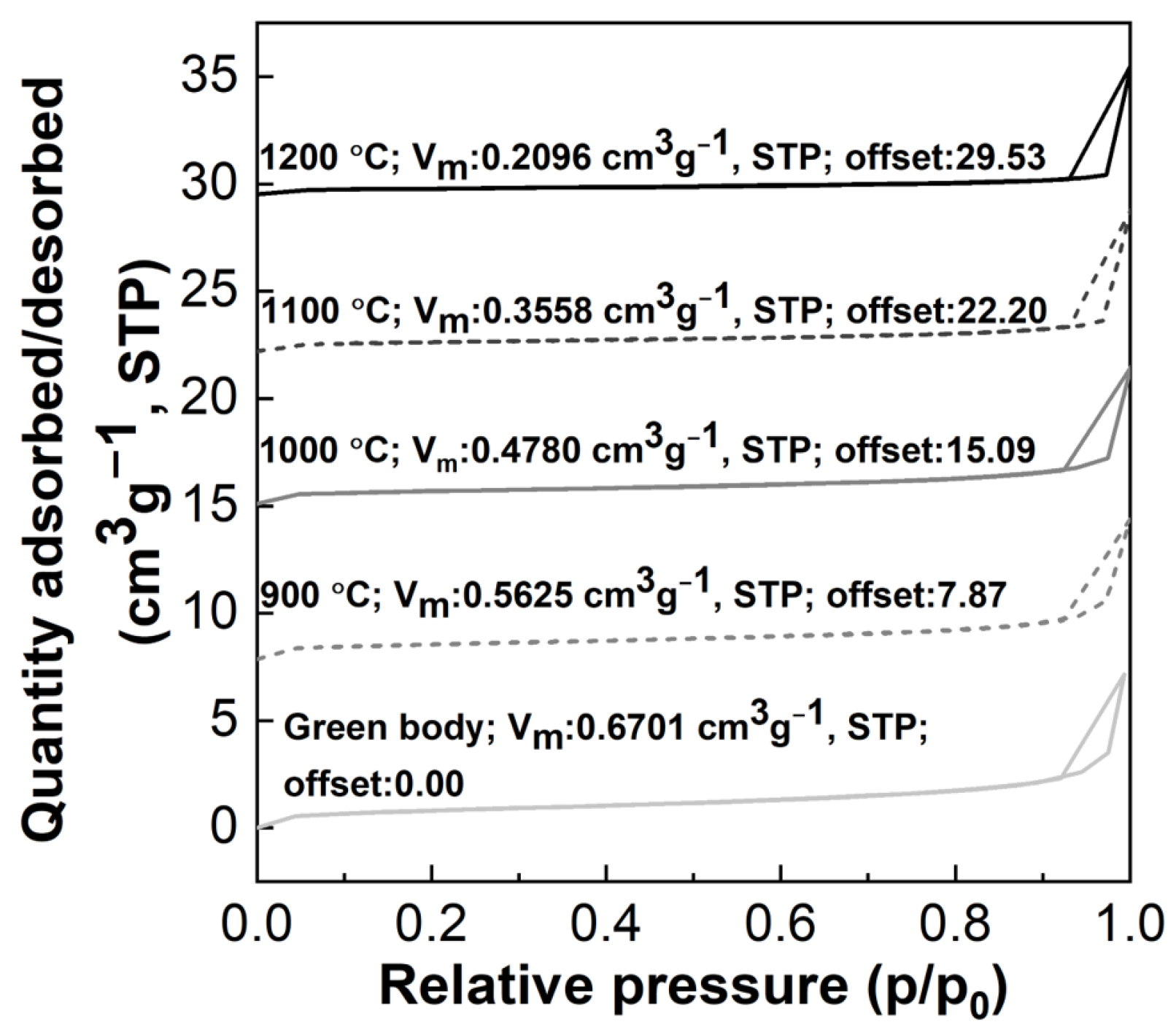
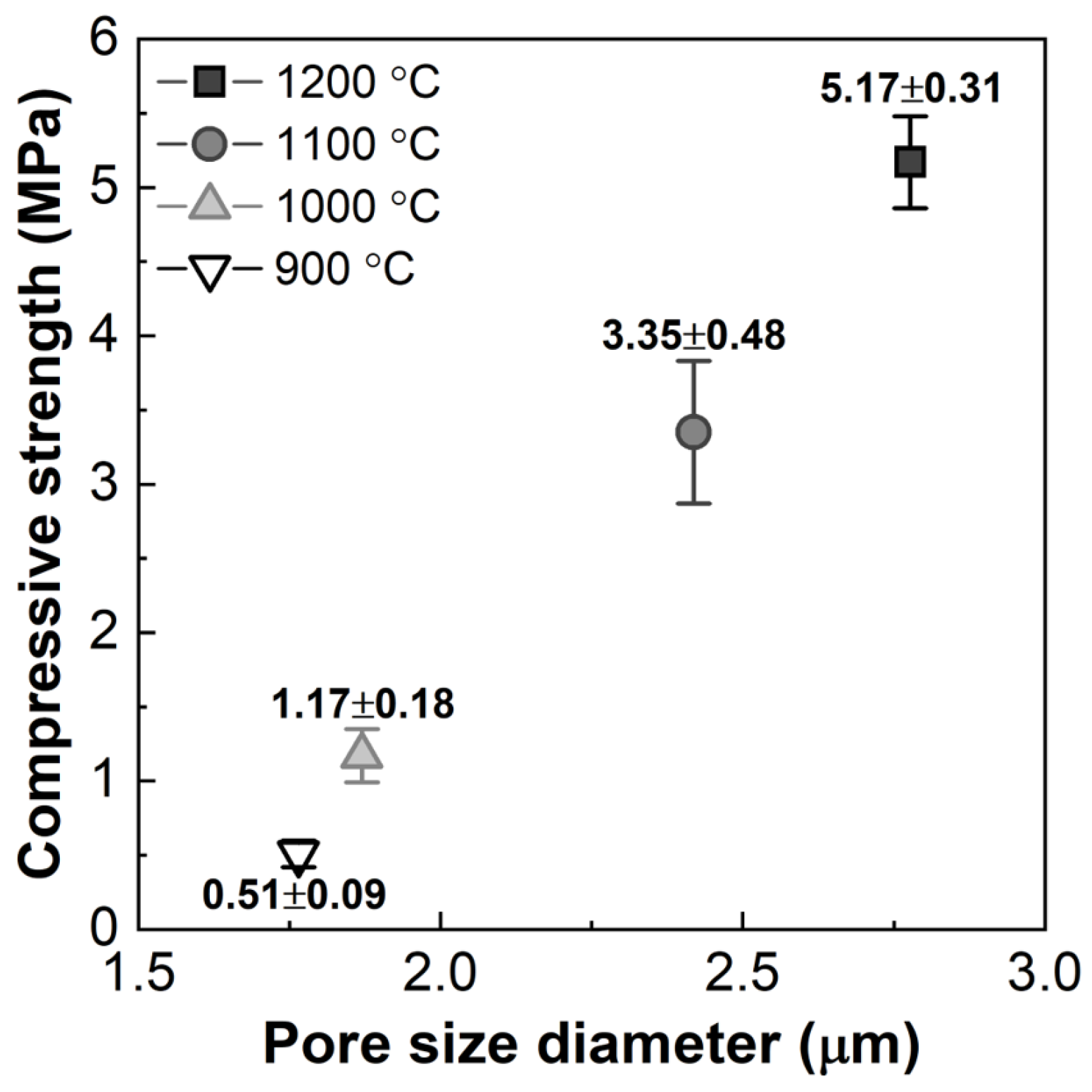
3.2. Effect of the Heat-Treatment Temperature on the Properties of the Porous Diatomite Granules
| Designation | Total Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) | BET Specific Surface Area (m2 g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| D43-0 | 0.0107 | 14.70 | 2.92 |
| D43-9 | 0.0091 | 14.83 | 2.45 |
| D43-10 | 0.0088 | 16.94 | 2.08 |
| D43-11 | 0.0089 | 23.01 | 1.55 |
| D43-12 | 0.0081 | 35.34 | 0.91 |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohji, T.; Fukushima, M. Macro-porous ceramics: Processing and properties. Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, 57, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, N.N.; Ola, O.; Xia, Y.D.; Zhu, Y.Q. Porous ceramics: Light in weight but heavy in energy and environment technologies. Mat. Sci. Eng. R 2021, 143, 100589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.; Atashi, H.; Tabrizi, F.F. Parametric investigation of γ-alumina granule preparation via the oil-drop route. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 1356–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Lin, Y.S. Sol-gel synthesis of silicalite/γ-alumina granules. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 4944–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, P.; Vakifahmetoglu, C.; Costacurta, S. Fabrication of ceramic components with hierarchical porosity. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5425–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Chu, C.M.; Chan, E.S.; Ravindra, P. Synthesis and characterization of millimetric gamma alumina spherical particles by oil drop granulation method. J. Porous Mat. 2012, 19, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, S.H.; Yap, D.K.Y.; Mansir, N.; Islam, A.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H. Facile Recoverable and Reusable Macroscopic Alumina Supported Ni-based Catalyst for Efficient Hydrogen Production. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, E.; Alarcón, A.; Xuriguera, E.; Guilera, J. Shaping of Porous CeO2 Powders into Highly Active Catalyst Carriers. ACS Appl. Eng. Mater. 2023, 1, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, M.J.; Du, H.C.; Wang, B.C.; Li, Y.L.; Huan, W.W. Highly effective catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene compounds with gold nanoparticle-immobilized hydroxyapatite nanowire-sintered porous ceramic beads. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 4601–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patcas, F.C.; Garrido, G.I.; Kraushaar-Czarnetzki, B. CO oxidation over structured carriers: A comparison of ceramic foams, honeycombs and beads. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 3984–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Ravindra, P.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Chan, E.S. Development of a procedure for spherical alginate-boehmite particle preparation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2013, 24, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Ravindra, P.; Teo, S.H.; Sivasangar, S.; Chan, E.S. Biodiesel synthesis over millimetric γ-Al2O3/KI catalyst. Energy 2015, 89, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilov, Z.R.; Shkrabina, R.A.; Koryabkina, N.A. New technology for production of spherical alumina supports for fluidized bed combustion. Catal. Today 1999, 47, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilov, Z.R.; Shkrabina, R.A.; Koryabkina, N.A. Hydrocarbon-ammonia moulding-a new technology for production of combustion catalysts. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 1997, 14, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.G.; Ma, J.T.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Hao, S.C.; Deng, C.S.; Liu, B. A comparative study of small-size ceria-zirconia microspheres fabricated by external and internal gelation. J. Sol. Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiknejad, D. Synthesis optimization, structural evolution and optical properties of hierarchical nanoporous alumina microspheres prepared by continuous soft chemistry method. J. Porous Mat. 2013, 20, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buelna, G.; Lin, Y.S. Sol-gel-derived mesoporous γ-alumina granules. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1999, 30, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.C.; Feng, J.T.; Zhang, X.M.; Lin, Y.J.; Evans, D.G.; Li, D.Q. Preparation of high purity spherical γ-alumina using a reduction-magnetic separation process. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2008, 69, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangar, B.V.; Nagarajan, K.; Krishnan, R.V.; Pandit, A.B. Preparation of Alumina and Alumina-Ceria Microspheres using an Internal Gelation Process and their Characterization. Trans. Indian Ceram. Soc. 2012, 71, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couland, M.; Fourcaudot, S.; Abril, R.J.; Fernandez-Carretero, A.; Somers, J. Novel Production Route of Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Fuel Kernels and Pellets for Nuclear Fuel Applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.Q.; Ma, J.T.; Zhou, X.W.; Zhao, X.Y.; Hao, S.C.; Deng, C.S.; Li, G.X. Fabrication of CeO2-Nd2O3 microspheres by internal gelation process using M(OH)m and [MCit·xH2O] (M=Ce3+, Ce4+, and Nd3+) as precursors. J. Sol. Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.G.; Ma, J.T.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Hao, S.C.; Deng, C.S.; Liu, B. Preparation of ceria-stabilized zirconia microspheres by external gelation: Size control. J. Sol. Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.R.; Han, K.B.; Voicu, V.; Matei, V.; Ciuparu, D. Impregnation of Catalytic Active Components in an Ammonia Solution During Granulation of Aluminium Hydroxide Gel by Sol-Gel Method in Hydrocarbon-Ammonia Moulding Column. Rev. Chim. 2012, 63, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.C.; Tang, C.T. Preparation and application of granular ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst for the removal of hazardous trichloroethylene. J. Hazard Mater. 2007, 142, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Ban, J.Y.; Choung, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Abimanyu, H.; Yoo, K.S. Sol-gel synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of mesoporous TiO2/γ-Al2O3 granules. J. Sol. Gel Sci. Technol. 2007, 44, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.G.; Xie, W.F.; Tu, Z.B.; Zhang, F.; Quan, S.Q.; Liu, L. N-TiO2/gamma-Al2O3 Granules: Preparation, Characterization and Photocatalytic Activity for the Degradation of 2,4-Dichlorophenol. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.S.; Wang, C.L.; Li, Y.J.; Xu, M.Z.; Jia, H. Microfluidic fabrication of ZrO2 microspheres using improved external gelation aided by polyacrylamide networks. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 21576–21581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backov, R. Combining soft matter and soft chemistry: Integrative chemistry towards designing novel and complex multiscale architectures. Soft Matter 2006, 2, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prouzet, E.; Khani, Z.; Bertrand, M.; Tokumoto, M.; Guyot-Ferreol, V.; Tranchant, J.F. An example of integrative chemistry: Combined gelation of boehmite and sodium alginate for the formation of porous beads. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2006, 96, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danks, A.E.; Hall, S.R.; Schnepp, Z. The evolution of ‘sol-gel’ chemistry as a technique for materials synthesis. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.Q.; Lu, W.; Mata, A.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y.P. Egg-box model-based gelation of alginate and pectin: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergeeva, A.; Vikulina, A.S.; Volodkin, D. Porous Alginate Scaffolds Assembled Using Vaterite CaCO3 Crystals. Micromachines 2019, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, S.; Talbot, D.; Bee, A. Preparation and effect of Ca2+ on water solubility, particle release and swelling properties of magnetic alginate films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 305, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.B.; Fang, Y.P.; Vreeker, R.; Appelqvist, I.; Mendes, E. Reexamining the egg-box model in calcium-alginate gels with X-ray diffraction. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, B.A.; Barbut, S.; Lim, L.T.; Marcone, M.F. Effect of Various Gelling Cations on the Physical Properties of “Wet” Alginate Films. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, E562–E567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; He, H.P.; Wei, G.L.; Liu, D.; Liang, X.L.; Chen, T.H.; Zhu, J.X.; Zhu, R.L. An efficient catalyst of manganese supported on diatomite for toluene oxidation: Manganese species, catalytic performance, and structure activity relationship. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 239, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, C.Y.; Ha, J.H.; Lee, J.; Song, I.H.; Kwon, S.H. Effect of Processing Conditions on the Properties of Reticulated Porous Diatomite-Kaolin Composites. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.B.; Deng, L.L.; Yuan, P.; Liu, D.; Yuan, W.W.; Liu, P.; He, H.P.; Li, Z.H.; Chen, F.R. Surface silylation of natural mesoporous/macroporous diatomite for adsorption of benzene. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 448, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Liu, D.; Fan, M.D.; Yang, D.; Zhu, R.L.; Ge, F.; Zhu, J.X.; He, H.P. Removal of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] from aqueous solutions by the diatomite-supported/unsupported magnetite nanoparticles. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 173, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarci, F.; Turan, D.; Ozcelik, B.; Poncelet, D. The influence of solution viscosities and surface tension on calcium-alginate microbead formation using dripping technique. Food Hydrocolloid 2017, 62, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.S.; Lee, B.B.; Ravindra, P.; Poncelet, D. Prediction models for shape and size of ca-alginate macrobeads produced through extrusion-dripping method. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Gu, J.Y.; Peng, Z.S.; Dai, X.Y.; Liu, Q.B.; Zhu, G.Q. Discrete element modeling of particles sphericity effect on sand direct shear performance. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 18754:2013; Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics)—Determination of Density and Apparent Porosity. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 1–7.
- Lucio, M.D.S.; Kultayeva, S.; Kim, Y.W.; Song, I.H. Effects of SiC whisker addition on mechanical, thermal, and permeability properties of porous silica-bonded SiC ceramics. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2022, 19, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Kim, H.N.; Park, Y.J.; Ko, J.W.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, H.D. Fabrication of transparent MgAl2O4 spinel through homogenous green compaction by microfluidization and slip casting. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 13354–13360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olhero, S.M.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Influence of particle size distribution on rheology and particle packing of silica-based suspensions. Powder Technol. 2004, 139, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, S.; Ha, J.H.; Lee, J.; Song, I.H.; Moon, K.S. Effect of the Zirconia Particle Size on the Compressive Strength of Reticulated Porous Zirconia-Toughened Alumina. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, S.; Ha, J.H.; Lee, J.; Song, I.H.; Moon, K.S. Effect of the Sintering Temperature on the Compressive Strengths of Reticulated Porous Zirconia. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, C.S.; Zheng, W.; Wu, J.M.; Yan, C.Z.; Shi, Y.S. Effects of particle size distribution and sintering temperature on properties of alumina mold material prepared by stereolithography. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 6069–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.C.; Hu, K.H.; Wang, H.Y.; Nie, L.; Feng, Q.; Lu, Z.G.; Li, P.J.; Lu, K. The effect of particle size distribution on the microstructure and properties of Al2O3 ceramics formed by stereolithography. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 21600–21609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Elimelech, M. Complexation between dissolved silica and alginate molecules: Implications for reverse osmosis membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 605, 118109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.H.; Liang, J.C.; Fukuda, S.; Zhu, L.J.; Wang, S.R. Sodium alginate-silica composite aerogels from rice husk ash for efficient absorption of organic pollutants. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 159, 106424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Wu, P.Y. Exploring the hydrogen-bond structures in sodium alginate through two-dimensional correlation infrared spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, B.M.; Skylaris, C.K.; Green, N.G. Acid-base dissociation mechanisms and energetics at the silica-water interface: An activationless process. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 451, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, U.A.; Nagarsenker, M.S. Characterization of Gelatin-Sodium Alginate Complex Coacervation System. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 71, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutin, A.; Lima, N.; Lopez, F.; Carvalho, M. Stability of Silica Nanofluids at High Salinity and High Temperature. Powders 2023, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Yang, J.; Ferreira, J.M.F. Effect of dispersant concentration on slip casting of cordierite-based glass ceramics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 241, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.B.; Kang, W.L.; Wu, H.R.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, P.X.; Zhang, X.F.; Sarsenbekuly, B. Stability, rheological property and oil-displacement mechanism of a dispersed low-elastic microsphere system for enhanced oil recovery. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 8118–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.J.; Brady, J.F. Shear thickening in colloidal dispersions. Phys. Today 2009, 62, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.P.; da Silveira, P.H.P.M.; Braga, F.D.; Monteiro, S.N. Fabric Impregnation with Shear Thickening Fluid for Ballistic Armor Polymer Composites: An Updated Overview. Polymers 2022, 14, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.F.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Zou, X.Q.; Zhou, W.D.; Guo, J.; Ye, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.H. Adsorption Properties of Calcium Alginate-Silica Dioxide Hybrid Adsorbent to Methylene Blue. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 2114–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voo, W.P.; Ooi, C.W.; Islam, A.; Tey, B.T.; Chan, E.S. Calcium alginate hydrogel beads with high stiffness and extended dissolution behaviour. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 75, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murer, M.; Formica, G.; Milicchio, F.; Morganti, S.; Auricchio, F. A coupled multiphase Lagrangian-Eulerian fluid-dynamics framework for numerical simulation of Laser Metal Deposition process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 3269–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixinho, J.; Lefevre, G.; Coudert, F.X.; Hurisse, O. Water evaporation in silica colloidal deposits. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 408, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Kooij, H.M.; van de Kerkhof, G.T.; Sprakel, J. A mechanistic view of drying suspension droplets. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 2858–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labowska, M.B.; Skrodzka, M.; Sicinska, H.; Michalak, I.; Detyna, J. Influence of Cross-Linking Conditions on Drying Kinetics of Alginate Hydrogel. Gels 2023, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreeker, R.; Li, L.B.; Fang, Y.P.; Appelqvist, I.; Mendes, E. Drying and Rehydration of Calcium Alginate Gels. Food Biophys. 2008, 3, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.G.; Ma, J.T.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Hao, S.C.; Deng, C.S. Precisely Controlling Preparation of Ceria-Stabilized Zirconia Microspheres of similar to ~ 100 µm by External Gelation. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2016, 13, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupkova, J.; Valaskova, M.; Studentova, S. Influence of acid-treated talc and Na2CO3 flux on mineralogical phase composition and porosity in steatite ceramics. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2017, 14, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapiaggi, M.; Pagliari, L.; Pavese, A.; Sciascia, L.; Merli, M.; Francescon, F. The formation of silica high temperature polymorphs from quartz: Influence of grain size and mineralising agents. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 4547–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Liu, X.Q.; Meng, G.Y. Sintering kinetics of porous ceramics from natural diatomite. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 88, 1826–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.M.; Bao, L.H.; Cheng, Y.S.; Dunphy, D.R.; Li, X.D.; Brinker, C.J. Aerosol-assisted synthesis of monodisperse single-crystalline alpha-cristobalite nanospheres. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1293–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Pan, J.F.; Jiang, X.G.; Jiang, Y.G. Bio-manufacturing technology based on diatom micro- and nanostructure. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 3836–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponjic, A.; Stankovic, M.; Majstorovic, J.; Matovic, B.; Ilic, S.; Egelja, A.; Kokunesoski, M. Porous ceramic monoliths based on diatomite. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 9745–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, P.D.; Belini, G.B.; Mambrini, G.P.; Yamaji, F.M.; Waldman, W.R. Thermal degradation of calcium and sodium alginate: A greener synthesis towards calcium oxide micro/nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, F.; Rehman, Y.; Bergstrom, L. A study of the sintering of diatomaceous earth to produce porous ceramic monoliths with bimodal porosity and high strength. Powder Technol. 2010, 201, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittemore, O.J.; Sipe, J.J. Pore growth during the initial stages of sintering ceramics. Powder Technol. 1974, 9, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, S.; Mirkazemi, S.M.; Rezaie, H.; Vahidshad, Y.; Trasatti, S. A comparative study on the thermal stability, textural, and structural properties of mesostructured γ-Al2O3 granules in the presence of La, Sn, and B additives. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 6638–6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ha, J.H.; Lee, J.; Song, I.H. Enhanced mechanical strength of talc-containing porous kaolin prepared by a replica method. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2021, 58, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, F.U.A.; Supit, S.W.M. Compressive strength and durability of high-volume fly ash concrete reinforced with calcium carbonate nanoparticles. In Fillers and Reinforcements for Advanced Nanocomposites; Dong, Y., Umer, R., Lau, A.K.-T., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015; pp. 275–307. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.W.; Yuan, P.; Liu, D.; Deng, L.L.; Zhou, J.M.; Yu, W.B.; Chen, F.R. A hierarchically porous diatomite/silicalite-1 composite for benzene adsorption/desorption fabricated via a facile pre-modification in situ synthesis route. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 294, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.V.; Gadipelli, S.; Wood, B.; Ramisetty, K.A.; Stewart, A.A.; Howard, C.A.; Brett, D.J.L.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F. Characterization of the adsorption site energies and heterogeneous surfaces of porous materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 10104–10137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Scharf, D.; Graule, T.; Clemens, F.J. Granulation processing parameters on the mechanical properties of diatomite-based porous granulates. Powder Technol. 2014, 263, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, D.V.; Ramanan, M.V. Experimental analysis of CO2 reduction using low surface area carbon beads (CB) and Ca/CB catalyst by thermocatalytic gasification for fuel gas production. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 7319–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sosa Lucio, M.D.; Oh, E.-J.; Ha, J.-H.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.-J.; Song, I.-H. Effects of Processing Conditions on the Properties of Porous Diatomite Granules Prepared by Sodium Alginate Gelation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169474
Sosa Lucio MD, Oh E-J, Ha J-H, Lee J, Lee H-J, Song I-H. Effects of Processing Conditions on the Properties of Porous Diatomite Granules Prepared by Sodium Alginate Gelation. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(16):9474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169474
Chicago/Turabian StyleSosa Lucio, Maria Dolores, Eun-Ji Oh, Jang-Hoon Ha, Jongman Lee, Hong-Joo Lee, and In-Hyuck Song. 2023. "Effects of Processing Conditions on the Properties of Porous Diatomite Granules Prepared by Sodium Alginate Gelation" Applied Sciences 13, no. 16: 9474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169474
APA StyleSosa Lucio, M. D., Oh, E.-J., Ha, J.-H., Lee, J., Lee, H.-J., & Song, I.-H. (2023). Effects of Processing Conditions on the Properties of Porous Diatomite Granules Prepared by Sodium Alginate Gelation. Applied Sciences, 13(16), 9474. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13169474





