Abstract
Liquid-based cytology (LBC) plays a crucial role in the effective early detection of cervical cancer, contributing to substantially decreasing mortality rates. However, the visual examination of microscopic slides is a challenging, time-consuming, and ambiguous task. Shortages of specialized staff and equipment are increasing the interest in developing artificial intelligence (AI)-powered portable solutions to support screening programs. This paper presents a novel approach based on a RetinaNet model with a ResNet50 backbone to detect the nuclei of cervical lesions on mobile-acquired microscopic images of cytology samples, stratifying the lesions according to The Bethesda System (TBS) guidelines. This work was supported by a new dataset of images from LBC samples digitalized with a portable smartphone-based microscope, encompassing nucleus annotations of 31,698 normal squamous cells and 1395 lesions. Several experiments were conducted to optimize the model’s detection performance, namely hyperparameter tuning, transfer learning, detected class adjustments, and per-class score threshold optimization. The proposed nucleus-based methodology improved the best baseline reported in the literature for detecting cervical lesions on microscopic images exclusively acquired with mobile devices coupled to the µSmartScope prototype, with per-class average precision, recall, and F1 scores up to 17.6%, 22.9%, and 16.0%, respectively. Performance improvements were obtained by transferring knowledge from networks pre-trained on a smaller dataset closer to the target application domain, as well as including normal squamous nuclei as a class detected by the model. Per-class tuning of the score threshold also allowed us to obtain a model more suitable to support screening procedures, achieving F1 score improvements in most TBS classes. While further improvements are still required to use the proposed approach in a clinical context, this work reinforces the potential of using AI-powered mobile-based solutions to support cervical cancer screening. Such solutions can significantly impact screening programs worldwide, particularly in areas with limited access and restricted healthcare resources.
1. Introduction
Cervical cancer has been responsible for registering 605,000 new cases in 2020, resulting in approximately 342,000 deaths worldwide. It is the fourth most frequently diagnosed cancer and the fourth leading cause of cancer death in women [1,2]. Over the past years, cytology screening tests have enabled a strong decrease in cervical cancer deaths, contributing to reducing its incidence by 60–90% and the death rate by 90% [3]. Nevertheless, difficulties experienced by health facilities due to a shortage of specialized staff and equipment are increasing the interest in developing computer-aided diagnosis (CADx) systems for cervical screening.
A recent review article [4] analyzed the approaches used for the tasks associated with examining microscopic images from cervical cytology smears, namely focus and adequacy assessment, region of interest segmentation, and lesion classification. Regarding segmentation and classification tasks, the authors point out that, despite the relatively good performance exhibited by binary or low-class classification approaches, the slow processing times and the considerable quantity of misclassifications or false positives reported for multi-class problems can make the algorithms unusable in a clinical environment. Additionally, the authors concluded that most works disregard adequacy assessment, while others only implement some techniques to detect and remove unwanted objects such as inflammatory cells or blood, with this topic being scarcely addressed in the literature.
Considering the limitations identified in the existing literature, the authors of the current work proposed a nucleus-based approach for the automated adequacy assessment of cervical cytology smears [5]. In this work, major focus was given to the cellularity evaluation of the cytological samples since low squamous cellularity is the most common cause for the identification of specimens as unsatisfactory. In particular, the proposed approach automatically detects, counts, and calculates the average number of squamous nuclei in images from liquid-based cytology (LBC) samples and consequently classifies it as adequate or inadequate based on the cellularity threshold established in The Bethesda System (TBS)—a minimum of 5000 well-preserved squamous nuclei (3.8 per microscopic field at 40× magnification) to consider a specimen as adequate for diagnosis [5].
Therefore, this paper aims to study the impact and feasibility of using a nucleus-based deep learning approach to detect different TBS classes of cervical lesions in mobile-acquired microscopic images of LBC samples. In particular, this work starts by contributing with a new annotated dataset of images from LBC samples digitalized with a portable smartphone-based microscope, which supported the development of a novel approach to detect the nuclei of cervical lesions on mobile-acquired microscopic images of cytology samples. Several experiments were conducted to optimize the performance of the developed lesion detection network, namely (i) hyperparameter optimizations, namely learning rate (LR) and batch size (BS); (ii) transfer learning optimizations through weight initialization from networks pre-trained on closer and distant application domains; (iii) detected class optimizations through the inclusion of normal squamous nuclei as a class detected by the model; and (iv) per-class tuning of post-processing parameters, like score threshold. A comparison between the performance achieved by the proposed nucleus-based methodology and a previous region-based work (which considered entire cells and cell aggregates as regions to detect) [6] that used the same dataset for cervical lesion detection is provided, thus supporting the contributions of this work.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 1 summarizes the motivation and objectives of the work; Section 2 outlines the relevant related work present in the literature; in Section 3, the datasets used are described; Section 4 presents the methodology, including the system overview and the proposed approach to expand its capabilities from sample adequacy assessment to nucleus-based detection and classification of cervical lesions; and throughout Section 5, results are drawn alongside the discussion. Finally, Section 6 summarizes the developed work, followed by a conclusion and future work.
2. Related Work
Cell detection, segmentation, and counting are computer vision tasks well addressed in the literature. While all these tasks allow us to obtain the number of cells, the most suitable approach for a specific problem depends on the target goal. In particular, the detection task provides the localization in the form of a bounding box and the respective class, while density estimation only gives the final number of objects. Alternatively, segmentation approaches allow for obtaining the mask and respective class of the detected objects.
For such tasks, the state-of-the-art approaches proposed in the literature mostly rely on machine learning and deep learning methods. Works such as [7,8,9] propose approaches based on deep learning, such as U-Net and feature pyramid network (FPN) networks, to perform cell detection and segmentation. A single-shot detector (SSD) in pair with a convolutional neural network (CNN) to localize and count different blood cell types was addressed in [10]. Furthermore, microscopy cell counting based on density estimation employing fully convolutional regression networks was proposed in [11]. In all approaches mentioned above, the authors reported results with performances comparable with human specialists.
Until [5], a less explored field in the literature was related to automated smear adequacy assessment, i.e., the development of computational methods to ensure that cervical samples are adequate for further analysis. In [12], the authors describe an AI-assistive diagnostic solution to improve cervical liquid-based thin-layer cell-smear diagnosis according to clinical TBS criteria. The developed system consists of five AI models which are employed to detect and classify the lesions. A You-Only-Look-Once (YOLO)v3 model was used for target detection, Xception, and patch-based models to cope with the high number of false positives detected and U-net for nucleus segmentation. The final classification was performed via two ensembled XGboost models, being developed and evaluated using a dataset of 80,000 LBC samples collected from five medical institutes. Regarding quality assessment, the procedure is applied to the entire sample and comprises focus, contrast, and quantitative cell evaluations. For this task, a simpler approach was followed: the Otsu thresholding method is initially used to separate the cells from the background, and the cell-to-overall-area ratio is then used to obtain a rough number of cells in the sample. The average accuracy of 99.11% was reported on the task of sample classification as satisfactory or unsatisfactory. However, it must be noted that TBS guidelines were not strictly followed since this method estimates the total number of cells in the sample, including other types of nuclei, aside from squamous nuclei, that should not be considered to assess sample cellularity.
Still on the topic of using deep-learning-based approaches to detect and classify cervical lesions, several recent works proved its feasibility to support cervical cancer screening, with proposed approaches that explored the usage of different deep convolutional neural networks ([13,14]) and architectures, such as MobileNet [15,16], EfficientNet [15,17], as well as newly proposed networks, like the series-parallel fusion network (SPFNet) [18], Cervical Ensemble Network (CEENET) [19], or EfficientNet Fuzzy Extreme-Learning Machine (EN-FELM) [20]. Despite the promising results of these previous works, it should be noted that the vast majority do not take into account limitations like restricted computational resources to run the models. Additionally, most of them require the usage of high-end digital pathology whole-slide imaging (WSI) scanners, which are equipment not generally accessible in areas with limited access and restricted financial resources. As an alternative to regular microscopes and WSI scanners, the development of low-cost, portable microscopes that enable microscopy-based diagnosis has also emerged in the literature. In particular, and leveraged by the impressive evolution in the quality of the cameras, processing power, and memory, smartphone-based solutions are being explored to implement cost-effective platforms for microscopic inspection of samples [21]. A wide range of applications has also been used to test the feasibility of affordable approaches based on smartphones, including the screening of blood smears [22] or the detection of parasites [23,24,25] and viruses [26].
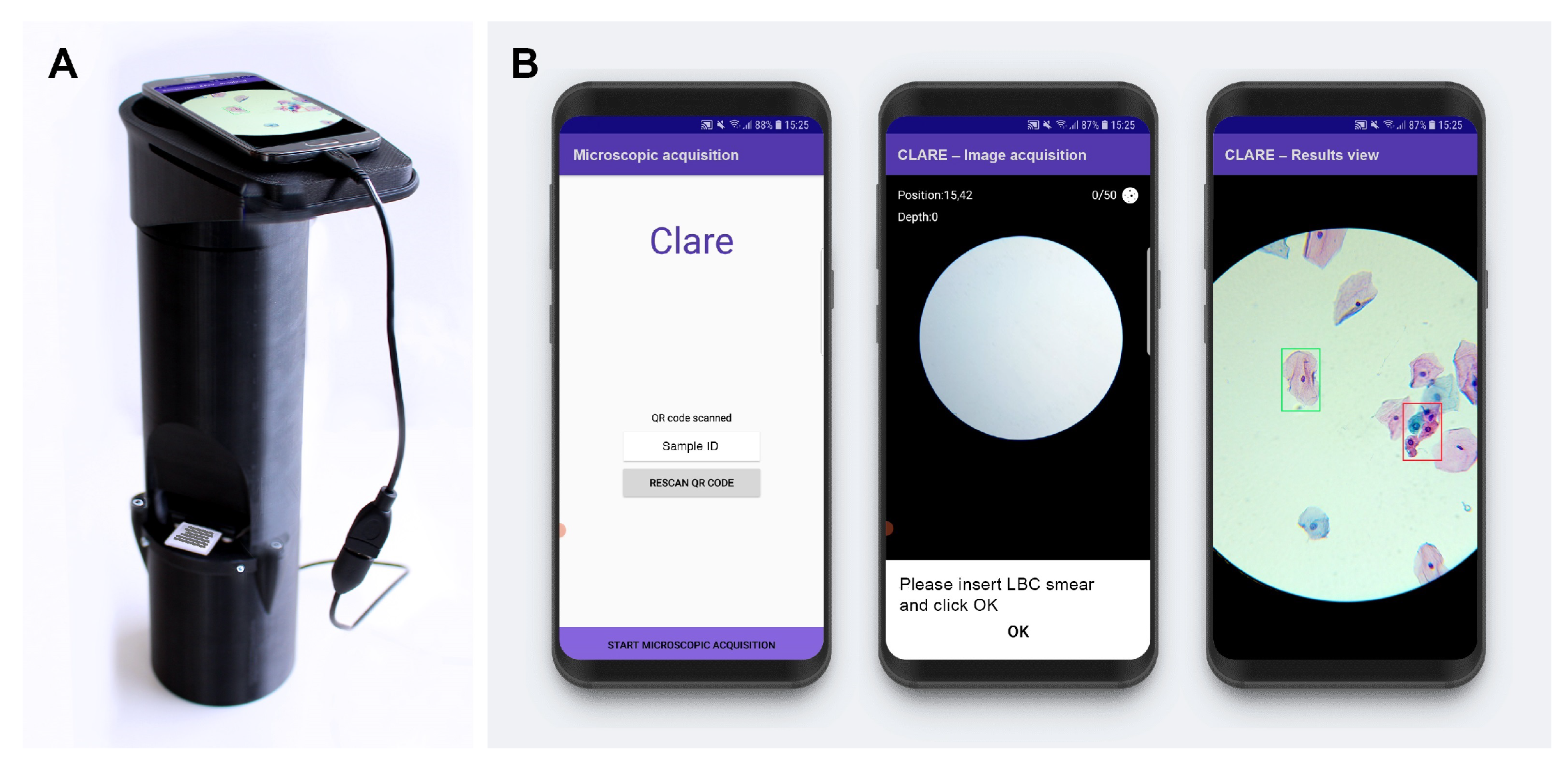
Regarding the cervical cytology use case, a device called µSmartScope [27,28] was adapted for the digitalization of cervical cytology samples [29,30], (Figure 1). This device is a fully automated, 3D-printed smartphone microscope tailored to support microscopy-based diagnosis in areas with limited access. The device aims to decrease the burden of manual microscopy examination by being fully powered and controlled by a smartphone, in addition to the motorized stage.
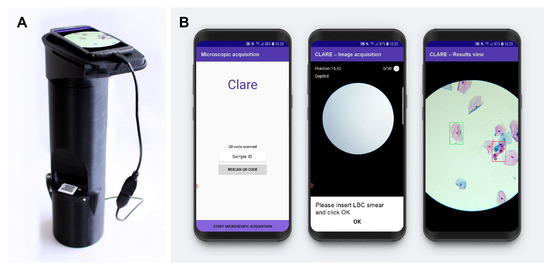
Figure 1.
Mobile-based framework for automated cervical cytology screening: (A) µSmartScope with smartphone attached and LBC sample inserted; (B) smartphone application screenshots (from [6]).
Supported by such devices for cervical cytology, a recent work [6] proposed a region-based approach for the mobile detection of cervical lesions. This work used the public dataset SIPAKMED and a new private dataset acquired with the uSmartScope (hereinafter referred as Region-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset), depicted in Figure 1. Promising results for cervical cancer screening have been achieved using a Faster R-CNN model with a ResNet50 backbone while also focusing on being a cost-effective Internet of Things (IoT)-based solution. Nevertheless, the authors identified the low data volume and high structure variability of the region-based dataset as the major bottlenecks of the study. Thus, this work follows this research stream and explores the development of a nucleus-based approach for automated adequacy assessment and cervical lesion detection using LBC samples digitalized with the µSmartScope device that strictly follows the TBS guidelines on both tasks.
3. Dataset
Although there are some publicly available datasets with cervical cell annotations, such as Herlev [31], SIPaKMeD [32], Cervix93 [33], and ISBI Challenges [34,35], they are not adequate for the tasks of nucleus and lesion detection. On the one hand, Herlev only contains isolated images of cells, with annotations by abnormality of the cell. Some datasets, such as the Cervix93, the ISBI Challenges, and the SipakMeD databases, comprise images of microscopic fields with information regarding the nucleus regions but do not provide annotations regarding the cervical lesions in those fields. In contrast, the more recent CRIC [36] dataset includes images of microscopic fields with annotated cervical lesions, yet with no information concerning the nuclei structures.
In view of the shortcomings of the existing public datasets, recent works presented two additional datasets acquired with the µSmartScope device: (i) the Adequacy Assessment Dataset [5], which consists of 41 samples with 42,387 manually annotated nuclei in terms of cell type, and (ii) the Region-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset [6], which consists on 21 samples with 927 manually annotated regions in terms of cervical lesions (single cells and cell aggregates). Given that this work aims to develop a nucleus-based approach for cervical lesion detection, none of these datasets entirely fulfilled that purpose. Thus, a new dataset was created, hereinafter referred to as the Nucleus-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset.
3.1. Nucleus-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset
To create a new dataset annotated in terms of nuclei with cervical lesions, the following TBS classes were considered: atypical squamous cell of undetermined significance (ASC-US); low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL); atypical squamous cell, cannot rule out high-grade lesion (ASC-H); high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL); and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). It should be noted that the Region-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset already provides annotations for these same classes, although not for nuclei but for entire cells and cell aggregates. Contrarily, the Adequacy Assessment Dataset provides nucleusi annotations but in terms of cell types, not cervical lesions.
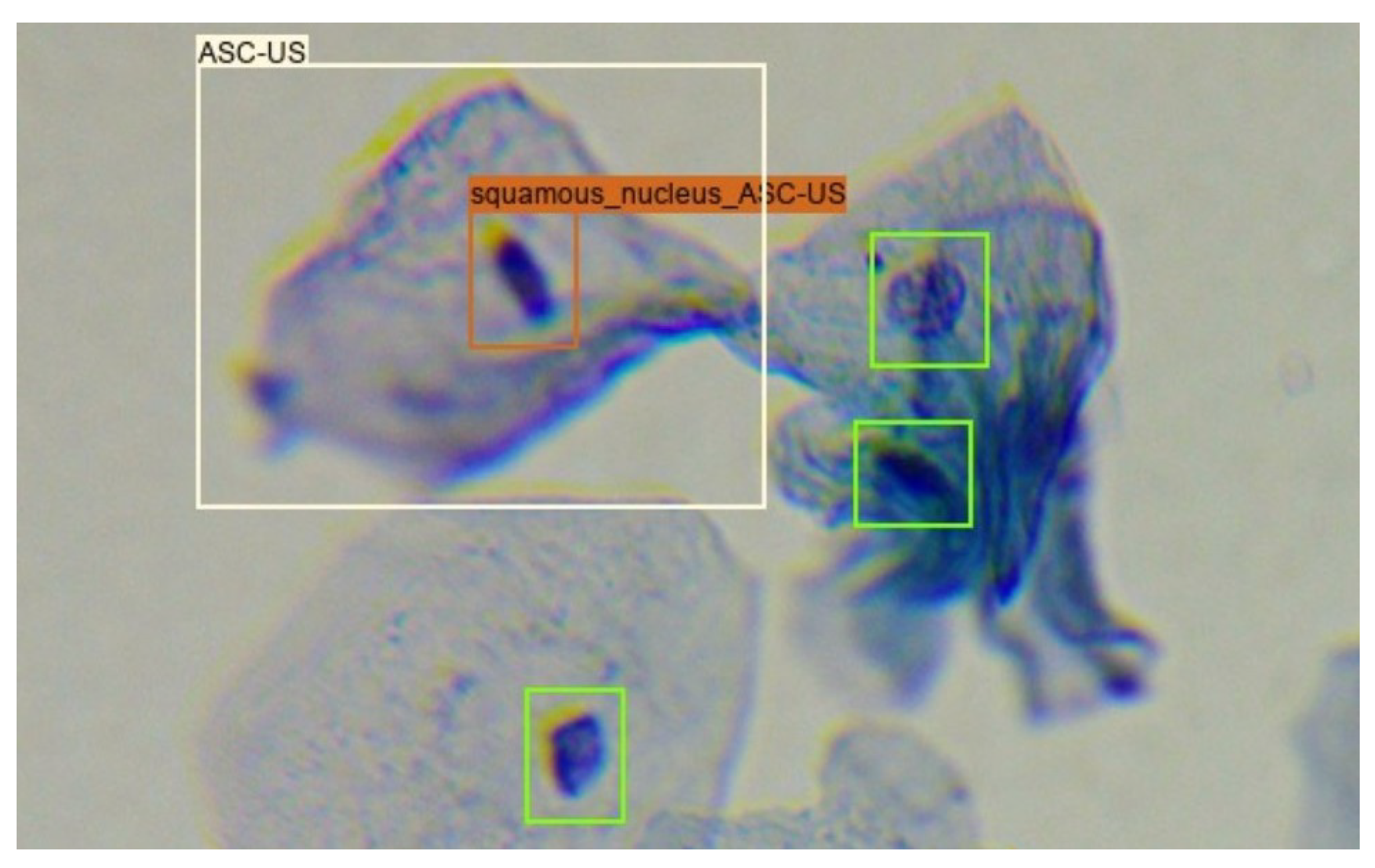
Given that around 30% of the images in the Region-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset are also present in the Adequacy Assessment Dataset, the overlap between the annotation of these two datasets was explored. Only squamous nucleus annotations from the Adequacy Assessment Dataset were considered since the previously referred cervical lesion classes are only present on this type of cells. In the new dataset, the cervical lesion class of each squamous nucleus annotation inside an annotated cervical lesion region was considered equal to the class of the region annotation that encompassed it, as shown in Figure 2.
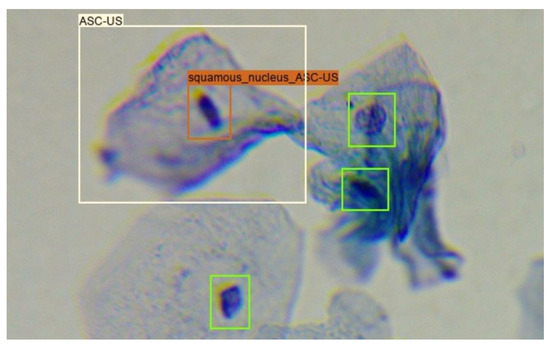
Figure 2.
Creation of the Nucleus-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset: green boxes correspond to squamous nucleus annotations present in the Adequacy Assessment Dataset; white box corresponds to lesion annotations present in the Region-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset; orange box corresponds to the transformation of a squamous nucleus annotation to an ASC-US nucleus annotation.
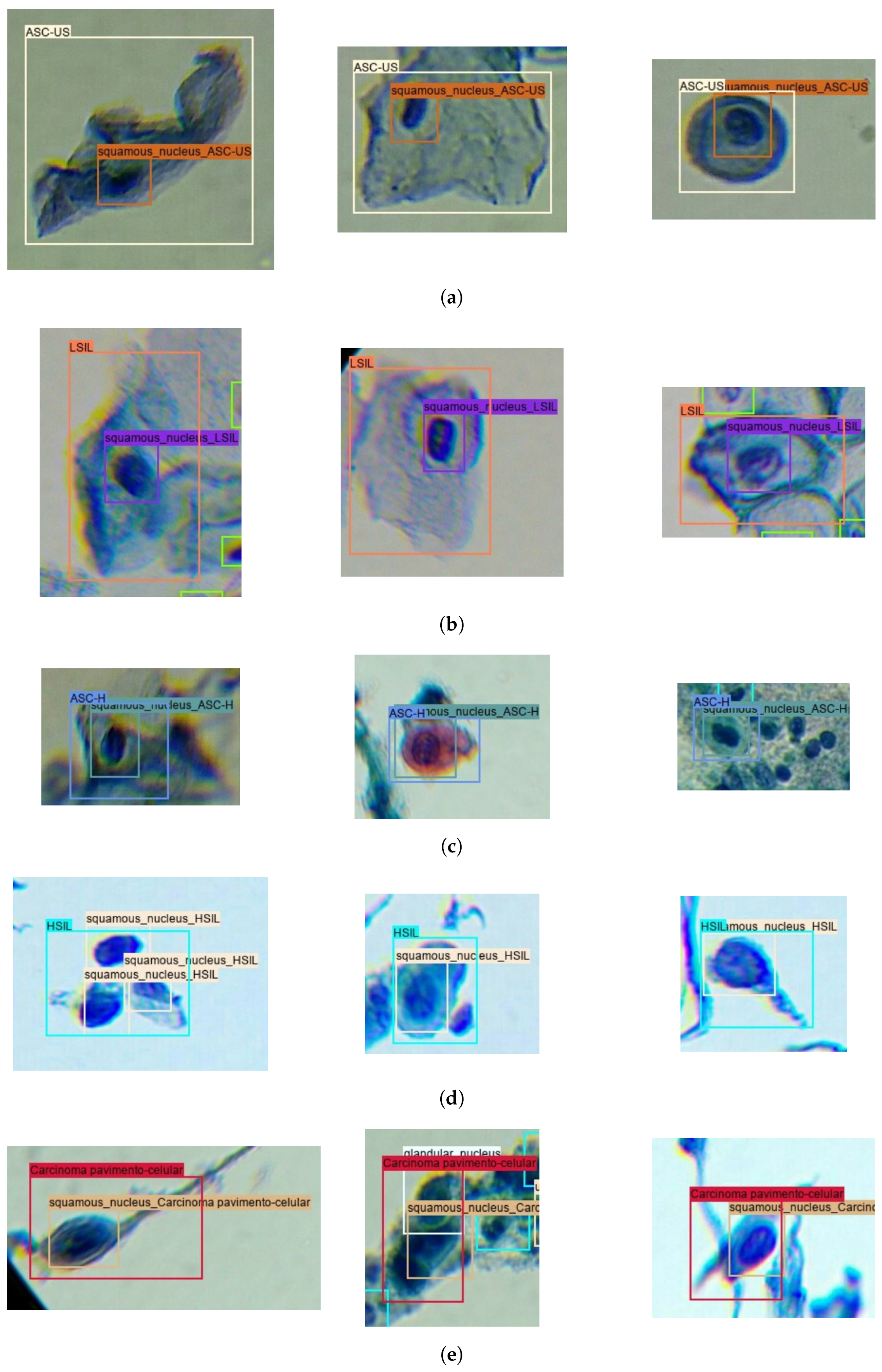
To take advantage of the full extent of cervical lesion annotations from the Region-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset, an automatic annotation strategy was applied to the subset of images without overlap with the Adequacy Assessment Dataset. In particular, the best-performing model for squamous nucleus detection proposed in [5] was used to detect the squamous nuclei on that subset, with the same process mentioned above being further applied to attribute the cervical lesion label to all nucleus detections inside annotated cervical lesion regions. Figure 3 provides examples of nucleus and region annotations for each TBS class.
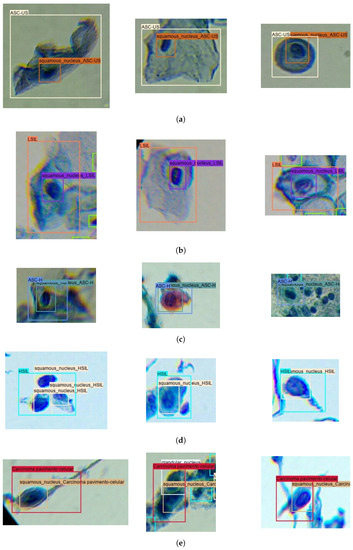
Figure 3.
Illustrative examples of nucleus and region annotations for each TBS class in the Nucleus-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset: (a) ASC-US; (b) LSIL; (c) ASC-H; (d) HSIL; and (e) SCC.
Table 1 depicts the final number of region and nucleus annotations per TBS lesion class for the Nucleus-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset. The higher number of nucleus annotations is justified by annotated regions in the Region-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset that encompass more than one cell, leading to several nucleus lesion annotations per region. Nevertheless, it can be observed that this dataset suffers from class imbalance for both nucleus and region annotations.

Table 1.
Per-class distribution of nuclei and regions annotations of Nucleus-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset.
Regarding dataset split, the train/test division will be equal to the previously reported for the Region-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset [6], including the usage of a patch-slicing operation (i.e., images are sliced into patches of fixed dimensions). Similarly to that previous work, the SCC and HSIL types of lesions were merged in a single class (HSIL-SCC) due to the demarcated under-representation of the SCC class and similar clinical diagnosis flow for both classes. The number of empty patches (i.e., the patches with no annotations or only normal annotations) used for training was balanced through the downsampling of these patches in the training data, and Table 2 shows the final data distribution for the nucleus annotations. Even though the annotation type was refactored from regions to nuclei, the test set images are exactly the same, which allows us to make a fair comparison between the performance of the region-based approach from that previous work [6] and the nucleus-based approach proposed in this work.

Table 2.
Distribution of nucleus annotations per TBS class for the training and test sets of the Nucleus-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset (after patch slicing).
4. Methodology
This work aims to contribute to the development of a cost-effective mobile-based solution for cervical lesion screening, building upon previous work that addressed nucleus detection for automated adequacy assessment of cytological samples [5] and region detection for the identification of cervical lesions [6]. A new nucleus-based deep learning approach is proposed to detect cervical lesions in images from LBC samples digitalized with the portable microscope µSmartScope [28].
4.1. Mobile-Based Framework for Cervical Cytology Screening: Pipeline Overview
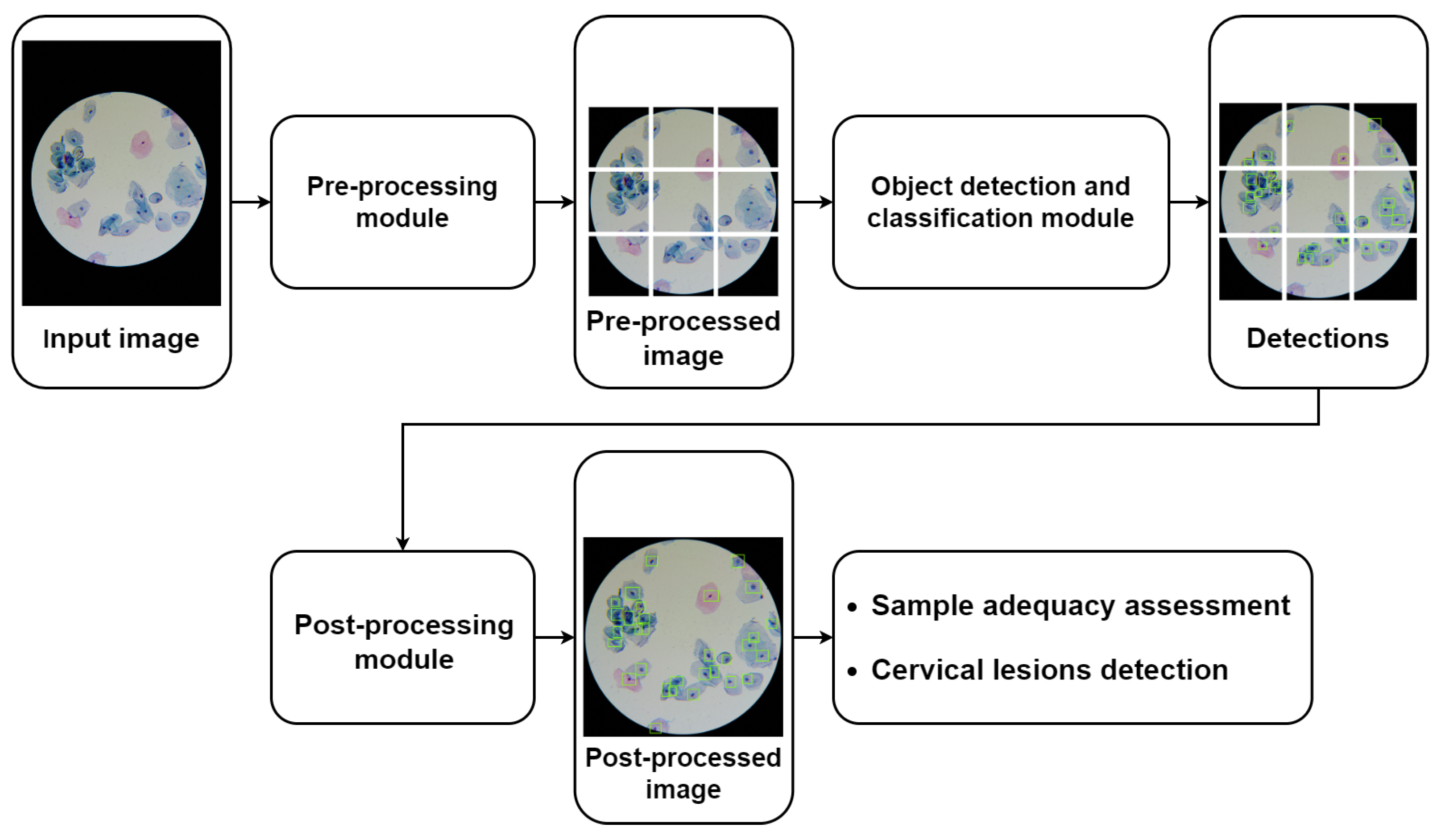
Figure 4 depicts the general pipeline of the mobile-based solution for automated cervical cytology screening, in which the nucleus-based cervical lesion detection module proposed in this work can be integrated. The proposed pipeline starts with a pre-processing module to ensure that the input images meet the demands presented by the detection models in terms of input standardization and computational limitations, which includes the following image processing steps: (i) optical disk segmentation (according to the approach proposed in [24]); (ii) cropping the region of interest in accordance with the optic disk segmentation mask; and (iii) patch slicing (320 × 320 pixels) with adjustable patch overlap percentage. As shown in Figure 4, the pipeline can comprise different object detection and classification modules that can be coupled together in the same framework to serve different purposes; e.g., the nucleus-based model previously proposed can be used for automated adequacy assessment of cytological samples [5], while the nucleus-based deep learning approach proposed in this work can be used to detect cervical lesions in images of LBC samples digitalized with the portable microscope µSmartScope [28]. Since this device uses an objective magnification of 40×, several images of different microscopic fields must be acquired for each slide to cover a representative sample area. Finally, the pipeline also includes a post-processing module responsible for the harmonization of the model’s outputs, namely to merge the patches of each microscopic field into a single image, which allows defining the following parameters: (i) NMS threshold and (ii) score threshold for each detected class.
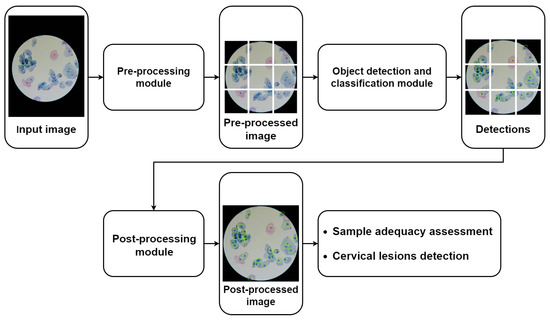
Figure 4.
General pipeline of the mobile-based solution for automated cervical cytology screening.
As shown in Figure 4, the pre-processing module is responsible for slicing the images into patches of fixed dimensions, with the possibility of overlap. Patches are then fed to the object detection model, and outputs are collected. Since each patch will pass individually through the model, the outputs (bounding boxes and respective classifications) will be in reference to the patch. Therefore, to obtain the compiled results for each microscopic field, they must be transferred to a global reference by combining into a single image the outputs of the associated patches. For scenarios with overlapped patches, the detected objects with two or more overlapped predictions are handled using a non-maximum suppression (NMS) algorithm to eliminate the duplicates. In the end, the image-level information of all images that belong to the same slide is then aggregated to provide an overall report regarding the detected cervical lesions for each sample.
4.2. Nucleus-Based Cervical Lesion Detection Model
The recognition of cervical lesions in cytological samples is performed by searching for cellular structures with abnormal morphological properties, typically associated with specific lesion levels [37]. Given the promising results obtained in [5] by a nucleus-based approach for automated adequacy assessment, that work was used as a reference starting point. In particular, this previous work provided a comparative analysis between three different meta-architecture/backbone combinations for the detection model: (i) SSD with a Mobilenet v2 backbone; (ii) RetinaNet with a Resnet50 backbone; and (iii) EfficientNet D0. The best-performing model for automatically detecting squamous nuclei was the RetinaNet Resnet50. This object detection model uses a ResNet50 backbone and a feature pyramid network (FPN) to capture multi-scale features, predicts object presence and class labels using anchor boxes at different feature map levels, and employs a focal loss to address class imbalance, giving more weight to challenging examples. Given this model’s promising results and suitability for our target scenario, it was selected as the basis for the approach proposed in the present work. It should be noted that we aim to deploy and execute the model locally on the smartphone, so this model selection also took into account the lightness of the RetinaNet/ResNet50 architecture (i.e., it needs to be suitable for the computational power available on regular Android devices) and the availability of the model in the Tensorflow Object Detection API (to ensure model compatibility to run on Android devices by converting to TensorFlow Lite). Additionally, and similarly to [5], the momentum optimizer, the Huber localization loss, and the focal cross-entropy classification loss were also used to train the model in the new dataset of lesion nuclei described in Section 3.1. Details regarding the remaining training settings optimized in this work are provided in Section 4.2.1 and Section 4.2.2.
Moreover, considering the high impact of the model-centric optimizations that led to the best-performing model in [5], an analogous analysis was conducted for the trained nucleus-based lesion detection model, further explained in Section 4.2.3 and Section 4.2.5.
4.2.1. Training Optimizations
For training and evaluation purposes, the Nucleus-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset was split at the sample-level, with an 80% to 20% ratio for training and testing, respectively. The selected split ratio balances enough data for training and a representative subset for evaluating model performance. Three-fold cross-validation with random split at the image-level was used for hyperparameter tuning, with a number of folds particularly suitable for smaller datasets (like the one created in this work) allowing us to obtain stable performance estimates while balancing computational efficiency and variance reduction. This process involved a random search process to optimize the batch size (8 and 16) and the learning rate (from 1 × 10−1 to 1 × 10−5), which allowed us to explore a wide range of values through a low number of experiments [38]. The randomly generated combinations of batch sizes and learning rate values explored in this work are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Combinations of learning rate and batch size values considered for hyperparameter tuning.
All experiments were conducted on NVIDIA® A16 GPU (virtualized with 8 GB of VRAM) and an AMD EPYC 7302 CPU, being adapted the training steps in each experiment to ensure a similar number of training epochs (around 100).
4.2.2. Transfer Learning Optimizations
To accelerate network convergence and the learning process, the usage of transfer learning techniques was explored through weight initialization by fine-tuning the network pre-trained on two distinct settings: (i) using the large-scale (Common Objects in Context) COCO public dataset [39] for object detection of categories distant from the target application domain and (ii) using the Adequacy Assessment Dataset [5] for the nucleus-based detection of squamous nuclei, i.e., a similar cervical cytology context. The motivation behind the selection of these two scenarios is two-fold: first, to assess the impact of transferring knowledge from distant and closer application domains, and second, to avoid vanishing or exploding gradient problems caused by random weight initialization, which can lead to improperly initialized weights that might negatively affect the training.
4.2.3. Detected Classes Optimization
The impact of including and excluding the normal squamous nuclei as a class detected by the model was studied. This study was motivated by the visual similarities between normal and abnormal squamous nuclei, aiming to assess if detecting normal nuclei could eventually help the learning process toward more robust discrimination of lesions’ nuclei. Nevertheless, as depicted in Table 1, including the normal squamous nuclei as a class, even when performed only on patches that already contain other abnormal class on the train subset, turns the dataset highly imbalanced, which may hinder the model training process.
4.2.4. Model Evaluation
The evaluation of the models was performed in two stages: during the training process and for the assessment of the final system. The first, focused on finding the optimal hyperparameters and training settings, was carried out at the patch level using the validation sets. Two object detection metrics were used—the mean average precision (mAP@0.50IoU) per class and the average recall (AR@10), averaged over the three cross-validation folds of the dataset. In contrast, the latter evaluation stage aimed to assess the overall performance of the final system. It was conducted on the test set at the image level, after combining the detection results for all the patches of each image. To support the critical analysis of the results, additional information was considered, namely false negatives (FN), false positives (FP), true positives (TP), and the respective confusion matrix. This allowed us to inspect supplementary performance metrics, such as accuracy, specificity, F1 score, and Youden’s index.
4.2.5. Post-Processing Optimizations
After finding the optimal hyperparameter values and model settings based on the average cross-validation performance, the best-performing model was re-trained on the whole training set and further optimized in terms of post-processing parameters. With the goal of improving the model’s image-level performance on the test set, the impact of the prediction score threshold and optimizing it separately for each class was explored. In this process, score threshold values between 0.05 and 0.95 with 0.01 steps were tested. The F1 score was used as the main criterion for selecting the optimal score threshold of each class since it considers the trade-off between precision and recall. It should be noted that other relevant post-processing parameters could also be tuned, namely the percentage of overlap of sliced patches, the minimum intersection over union (IoU) applied to suppress overlapping boxes in the non-maximum suppression (NMS) stage, and the minimum IOU between the predicted and ground truth objects to consider a true positive prediction. Nevertheless, given the similar context of the previous adequacy assessment work where these parameters were already optimized [5], the same values of the best-performing model reported were used, namely a patch overlap of 29%, NMS threshold of 0.97, and IoU threshold of 0.1.
5. Results and Discussion
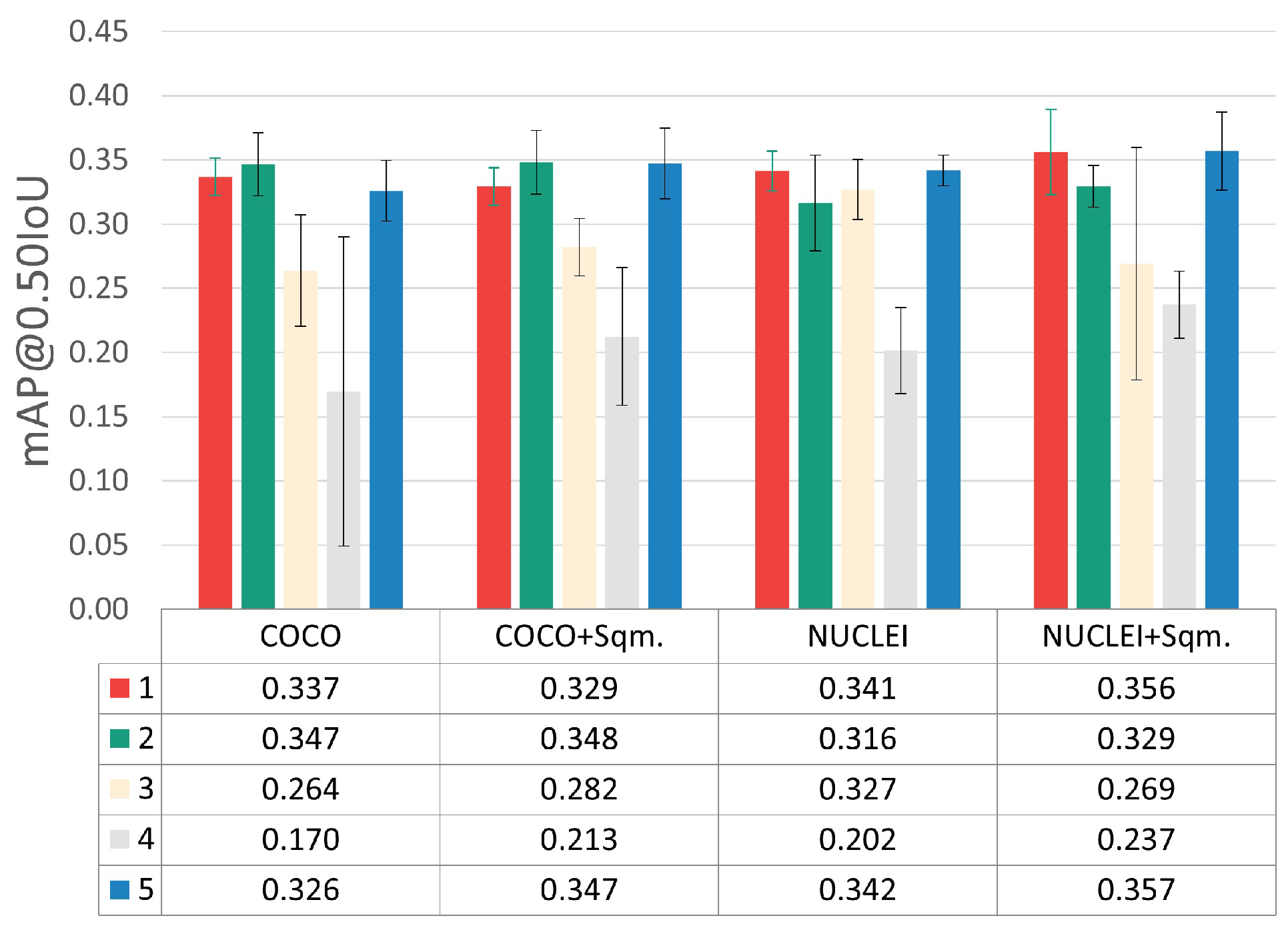
The results obtained during model training at the patch level on the validation set are depicted in Figure 5. This figure merges the results achieved through three-fold cross-validation for the different optimization steps, namely hyperparameter tuning, transfer learning strategy, and detected classes adjustments. The results for each optimization step are separately discussed in the following sub-sections.
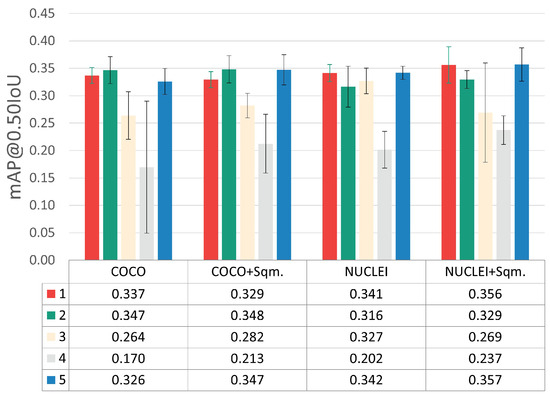
Figure 5.
mAP@0.50IoU results for the different optimization steps. (i) Hyperparameter tuning: each color represents a different combination, according to the indexes used in Table 3. (ii) Transfer learning: weight initialization using models pre-trained on the Adequacy Assessment (NUCLEI) and COCO Datasets. (iii) Detected class adjustments: exclusion and inclusion of normal squamous nucleus class (+Sqm.).
5.1. Training Optimizations
Considering the five different LR-BS combinations tested (see Table 3), the hyperparameter combinations with indexes 1, 2, and 5 clearly provided the best results, with minor mAP@0.50IoU differences between them. Nevertheless, it was considered that the best and most consistent performance was achieved by combination 5 (LR = 4.862 × 10−5 and BS = 16).
5.2. Transfer Learning Optimizations
Regarding the results of the transfer learning experiments through weight initialization, the fine-tuning of the network pre-trained on the Adequacy Assessment Dataset (NUCLEI) yielded better results when compared to the COCO experiments. With these experiments, it was concluded that transferring knowledge from a smaller dataset of a closer applications domain (i.e., a similar cervical cytology context) brought more benefits than using large-scale public dataset with categories distant from the target application domain. It should be noted that the COCO Dataset, despite its myriad object classes, does not include any microscopy images or cellular structures.
5.3. Detected Class Optimizations
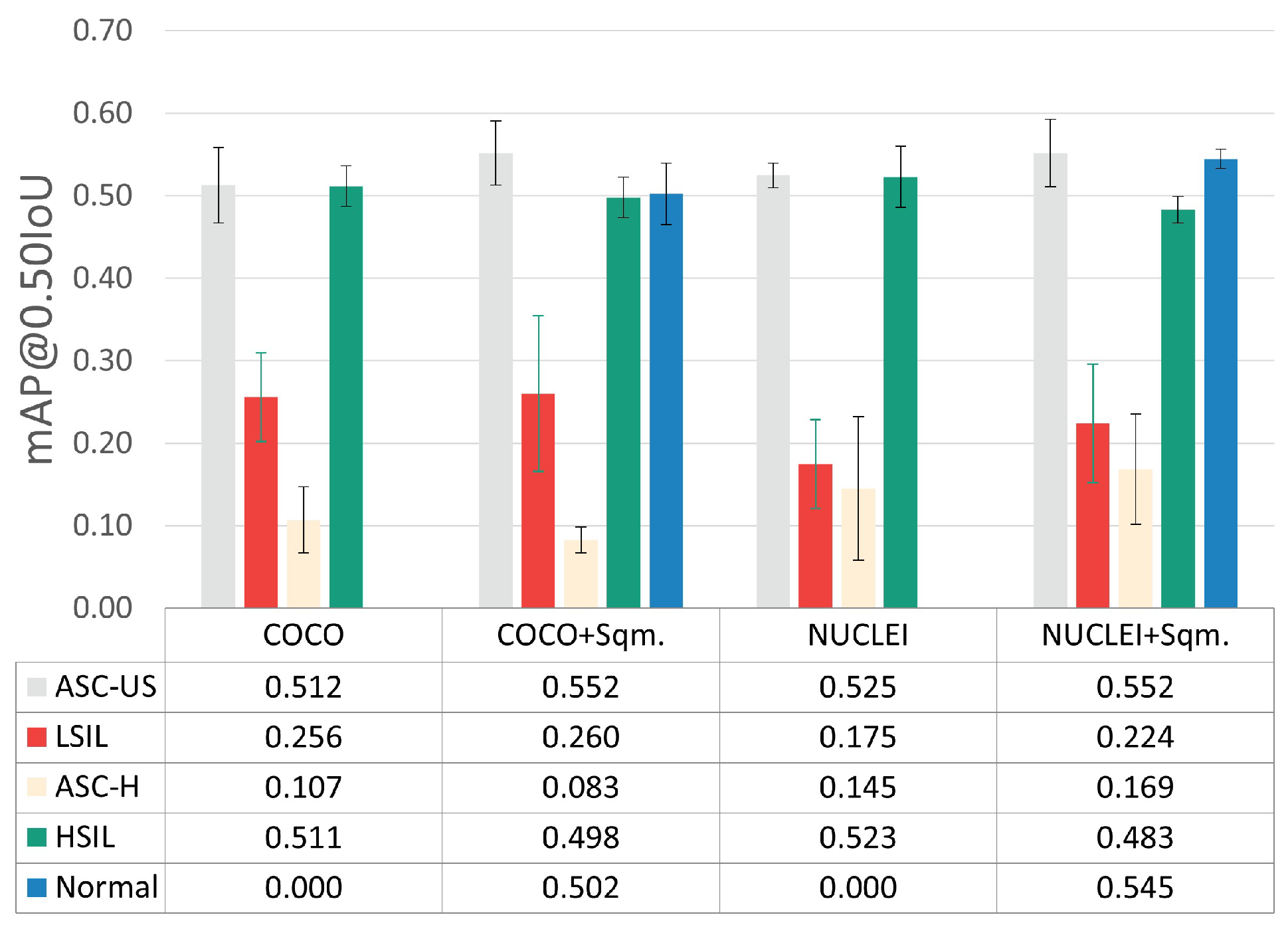
To assess the impact of including and excluding normal squamous nuclei as a detected class, the per-class mAP@0.50IoU results were also examined (see Figure 6), given the demarcated data imbalance imposed by the inclusion of this class (see Table 1).
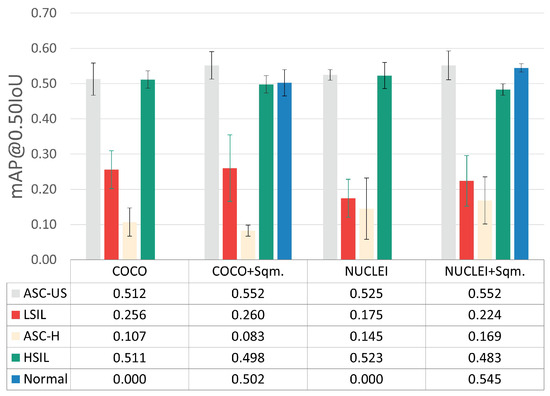
Figure 6.
Per-class mAP@0.50IoU results for the best hyperparameter combination.
The experiments with the normal squamous nucleus class (+Sqm.) achieved slightly better mAP@0.50IoU for the ASC-US and ASC-H classes while simultaneously providing a lower overall standard deviation between cross-validation folds. Thus, the inclusion of the normal squamous nucleus class, which seems to help the learning process toward more robust discrimination of lesions’ nuclei, was selected
5.4. Data Augmentation
As depicted in Table 2, the Nucleus-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset is highly imbalanced, with a positive correlation between the number of annotations for each class and the respective detection performance (see Figure 6) being observable. Therefore, the underrepresented classes were augmented via random basic image transformations, such as 90-degree rotation, horizontal and vertical flips, blur, and sharpening. Table 4 shows the number of annotations before and after the data augmentation procedure.

Table 4.
Number of annotation and patches before and after data augmentation.
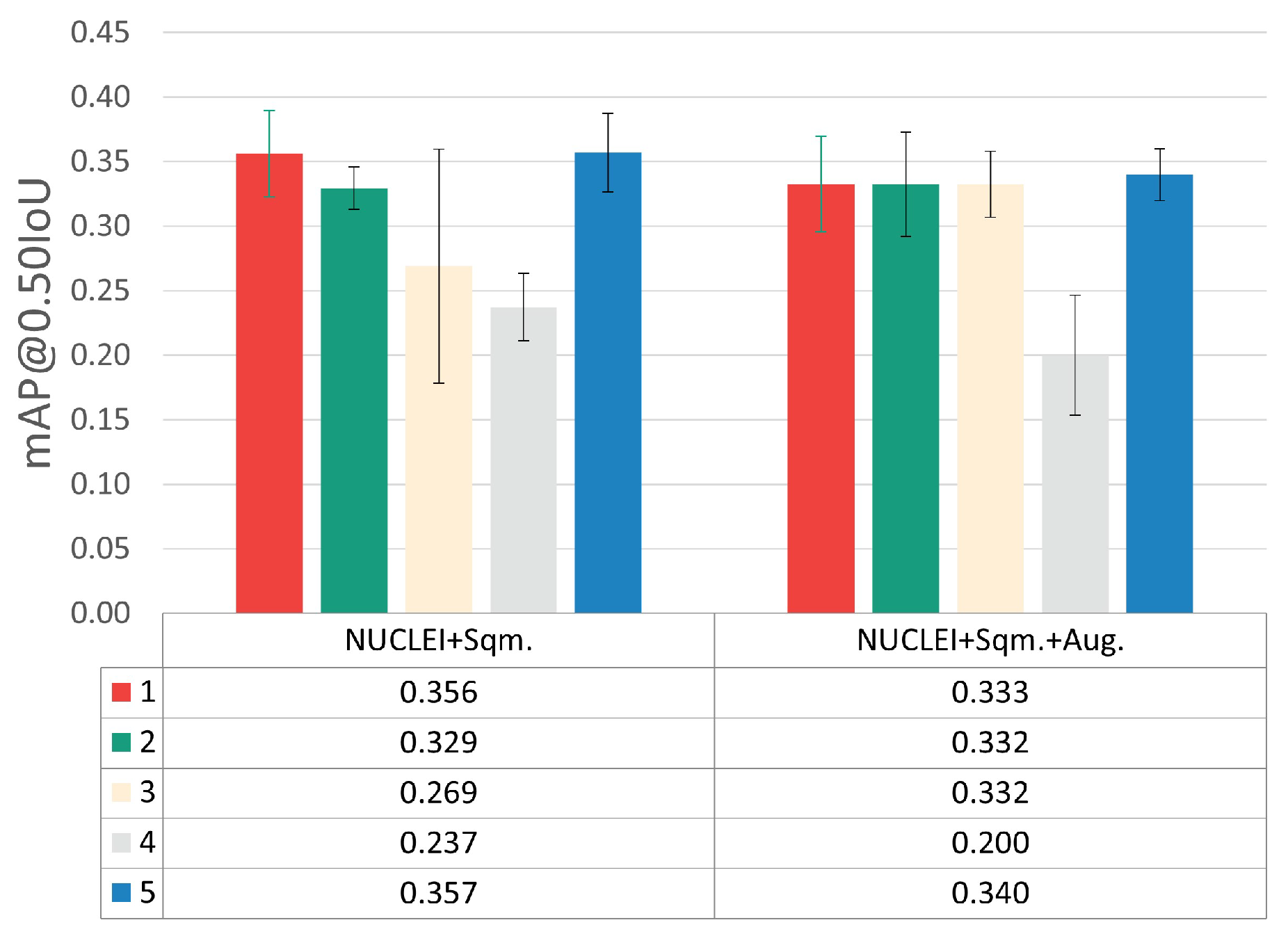
Using the augmented version of the dataset, a new set of experiments was performed by using the best transfer learning approach previously found (NUCLEI pre-trained model) and training with the five different LR-BS combinations detailed in Table 3. The results depicted in Figure 7 indicate that the data augmentation strategy did not improve detection performance.
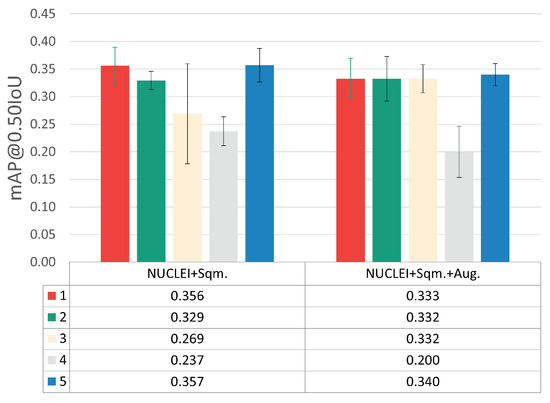
Figure 7.
mAP@0.50IoU results for each LR-BS combination, with and without data augmentation.
One possible cause for this outcome might be the large volume of instances generated through basic image manipulation that was added to the highly underrepresented classes, which probably provided mostly redundant information. This leads us to conclude that the usage of data augmentation via basic image manipulations in the target scenario negatively affects the model’s generalization capability by potentially infusing bias during model training. Nevertheless, alternative data augmentation approaches that promote higher and more reliable per-class variability should be explored in the future, for instance, generative deep learning, such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) or latent diffusion models.
5.5. Nucleus-Based versus Region-Based Approaches
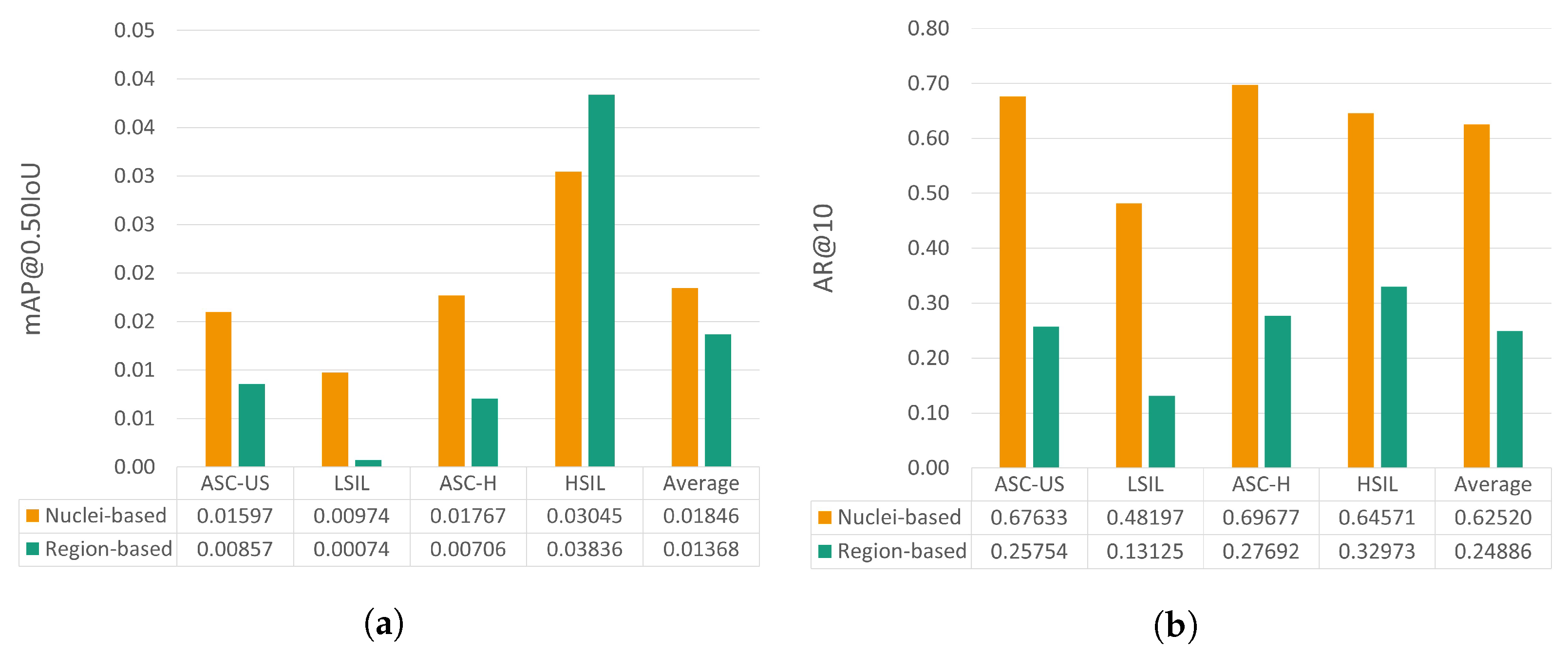
This section provides a comparative analysis between the performance achieved by the proposed nucleus-based methodology and the previously reported region-based approach [6]. To allow the benchmarking of these two deep learning strategies for mobile-based cervical lesion detection, the test set used is the same for both approaches, thus allowing a fairer comparison. Nevertheless, it should be noted that the patch size and the number of annotations per class are not the same due to the annotation refactor detailed in Section 3.1. The results regarding mAP@0.50IoU and AR@10 can be observed in Figure 8.
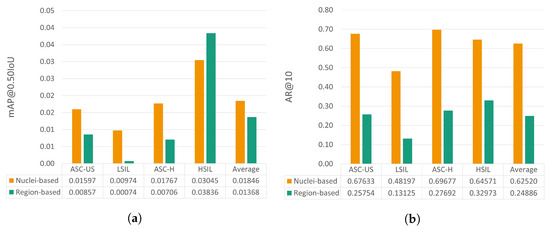
Figure 8.
mAP@0.50IoU (a) and AR@10 (b) results for the test set for the proposed nucleus-based and the previously proposed region-based approaches [6].
Analyzing the relative performance gain for each metric, it is possible to see that the proposed nucleus-based approach allows an mAP@0.50IoU increase ranging from 53.6% to 1216.2%, except for the HSIL class, with a decrease of 20.6%. Regarding AR@10, the nucleus-based approach also brought clear performance improvements, from 95.8% to 267.2% for the different classes.
5.6. Post-Processing Optimizations
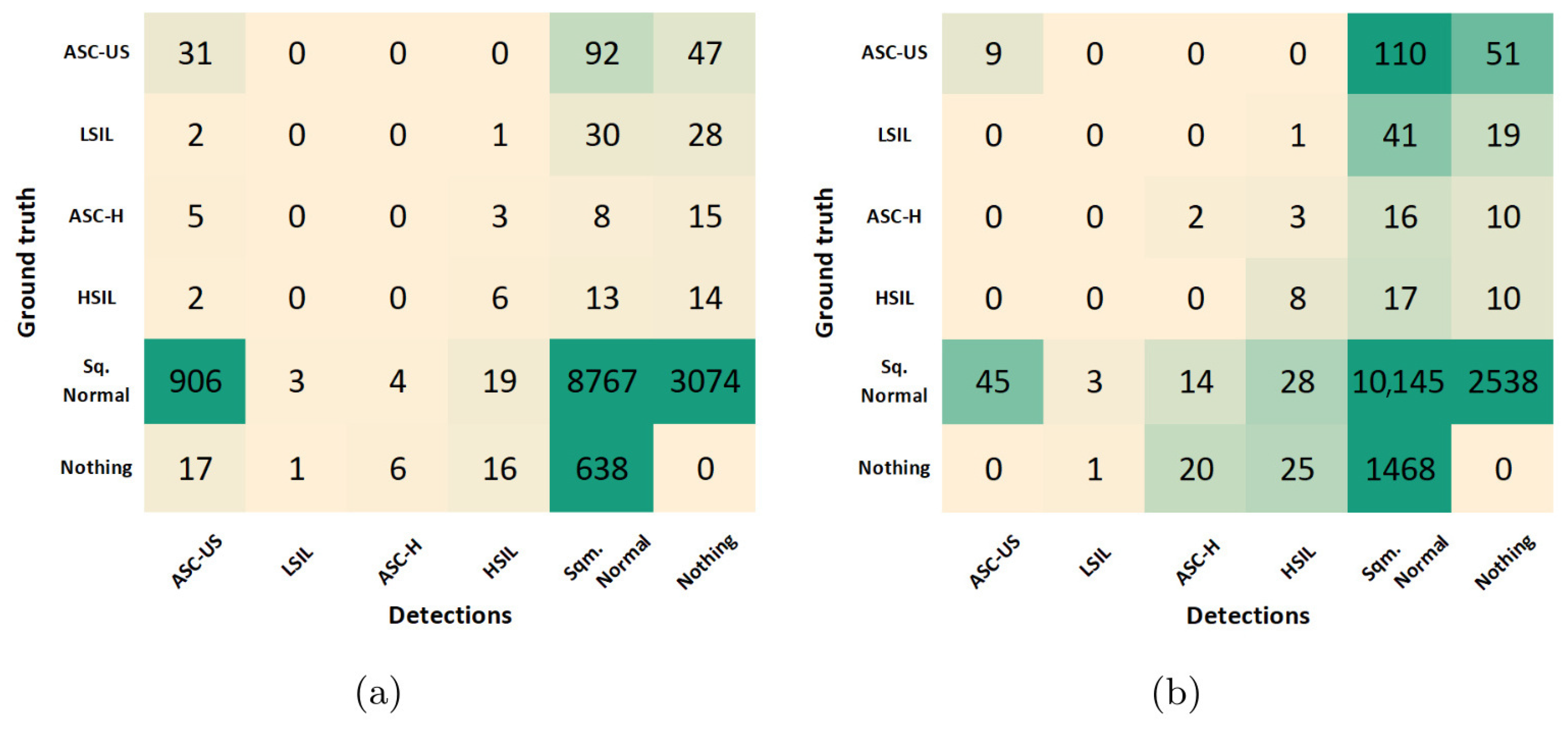
The results reported in the previous sections allowed us to select the best combination of optimization steps during model training, which maximized the cervical lesion detection performance at the patch-level on the validation set. Using the best-performing model achieved after training, the class-wise optimization of the prediction score threshold was further explored to improve the model’s image-level performance on the test set. The confusion matrices obtained for the best-performing model before and after the score threshold optimization are depicted in Figure 9.
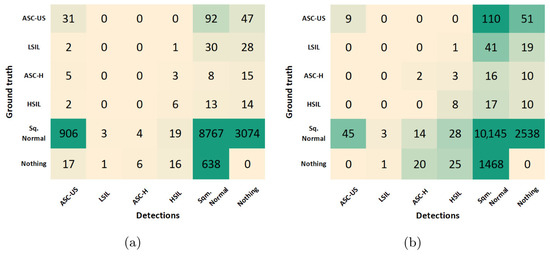
Figure 9.
Confusion matrices for the best-performing model before (a) and after (b) the score threshold optimization.
To support the critical analysis of these results, additional performance metrics were extracted from both confusion matrices, namely accuracy, specificity, F1 score, and Youden’s index (see Table 5). Due to the class imbalance of the dataset, the F1 score was used as the primary criterion for selecting the optimal score threshold for each class. This led to F1 score improvements in all classes, except for LSIL, with still no TPs detected. In particular, the F1 score of ASC-US class increased 47% due to a favorable decrease of 887 FPs, but with the compromise of losing 22 TPs. On the other hand, the F1 score of normal squamous nuclei (Sqm. Normal) increased 5% due to a favorable increase of 1376 TPs, but with the shortcoming of detecting 871 additional FPs. However, similar behavior was verified in the ASC-H and HSIL classes, with just residual increases in both TPs and FPs.

Table 5.
Performance metrics for the best-performing model before and after the score threshold optimization.
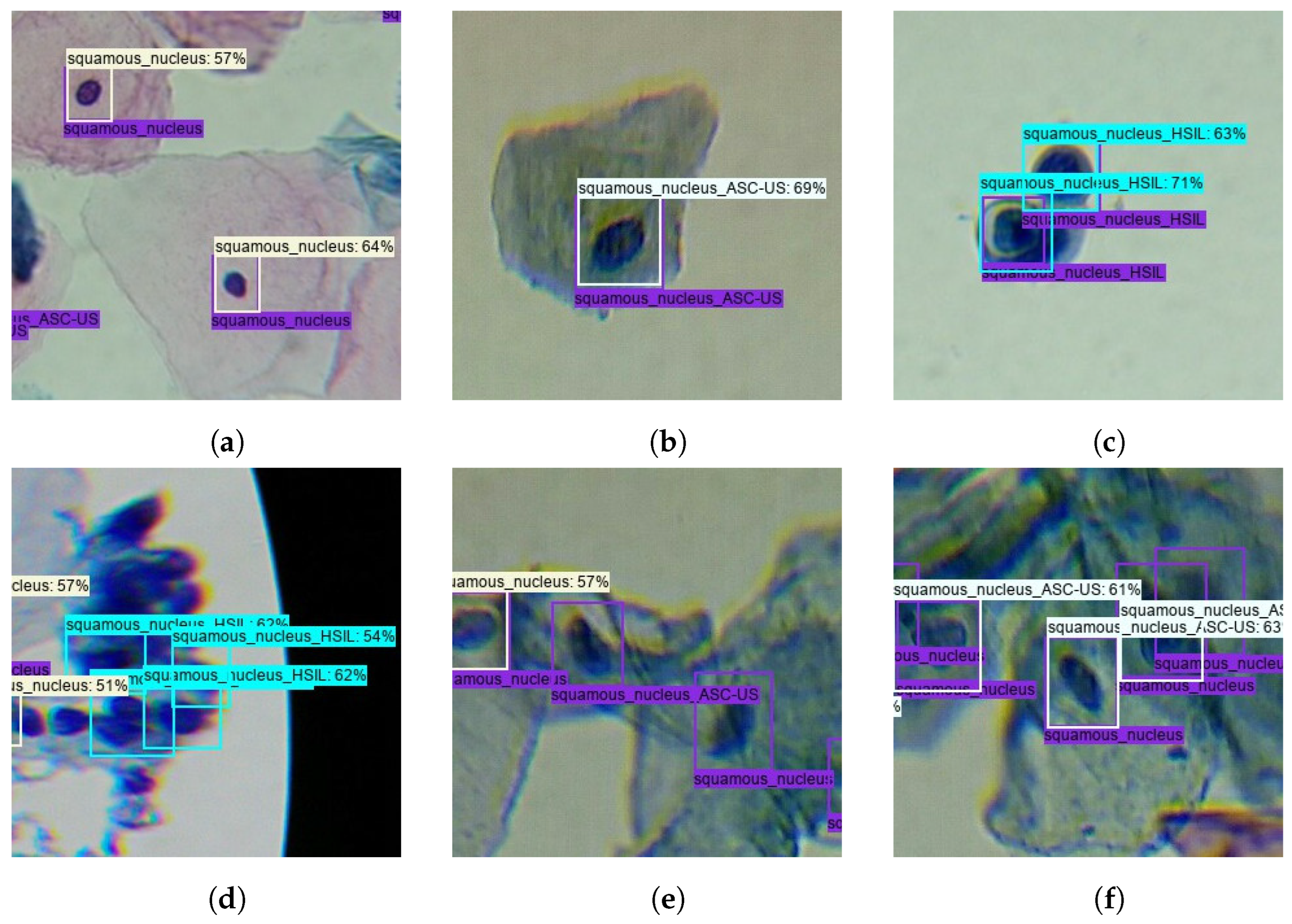
From the clinical point of view, the described trade-offs between TPs and FPs seem to benefit the usage of the model after optimization for screening purposes. First, because Sqm. Normal detections are not cervical lesions, they do not represent priority findings that need to be mandatorily reviewed by the screening cytopathologists. For this reason, the significant increase of FPs for the Sqm. After optimization, the normal class on the model does not necessarily cause overhead in the clinical flow. And second, the demarcated decrease in ASC-US FPs on the model after optimization could actually have a relevant impact on its suitability to support clinical decisions because these are abnormal findings that need to be reviewed by cytopathologists, forcing them to constantly review large numbers of FPs, which can lead to an unfeasible overhead in the screening process. Thus, the performance improvements verified for the lesion classes demonstrated the benefits of the data and model-centric optimizations applied during training and post-processing steps, resulting in a more robust lesion detection system with potential to streamline the clinical workflow of cervical screening processes. Some illustrative examples of correctly and incorrectly classified images on the test set are shown in Figure 10.
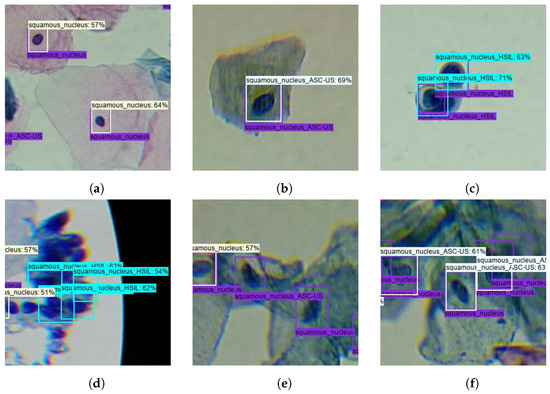
Figure 10.
Illustrative examples of correctly and incorrectly classified images on the test set: (a) True-positive Normal Sqm. (b) True-positive ASC-US. (c) True-positive HSIL. (d) False-positive HSIL. (e) False-negative ASC-US and Normal Sqm. (f) Misclassified Normal Sqm.
In summary, this work contributes to the advancement of mobile-based cervical cytology screening by demonstrating the potential of using nucleus-based approaches that can represent a complementary crucial tool to increase the wide spread of cervical cytology screening and the early and accurate diagnosis of cervical dysplasias. By expanding the coverage of screening programs in underserved areas, these tools can contribute to decreasing the extension of excisional treatments, which are responsible for adverse effects like increased risk of preterm delivery, lower birth weight, or preterm premature rupture of membrane before 37 weeks of pregnancy [40]. These tools can also be coupled to the analysis of risk factors like HPV persistence and the positivity of surgical resection to leverage a more widespread early detection of recurrence after surgical treatment [41]. At the same time, the authors acknowledge that future work needs to be carried out to improve the performance of the proposed method. Currently, the state of the art for mobile-based solutions for cervical cancer screening is still far from reaching clinical usage due to the particular limitations of this scenario, like lack of large publicly mobile-acquired datasets, limited mobile-acquired image quality, and the restricted computational power of mobile-based solutions for portable microscopic screening. In particular, the requirement of locally executing the detection models on mobile devices dramatically limits the selection of suitable meta-architecture/backbone combinations, which must be simultaneously lightweight and compatible to run on mobile devices. These limitations should be considered when comparing the performance and maturity of such mobile-based solutions with solutions that operate under optimal, well-controlled laboratory conditions, which usually have access to images acquired with high-end microscopic equipment and unrestricted computational resources.
6. Conclusions and Future Work
In this paper, a new nucleus-based deep learning approach was proposed to detect different TBS classes of cervical lesions on mobile-acquired microscopic images of LBC samples. A RetinaNet model with a ResNet50 backbone was used, and several experiments were conducted to optimize the detection model’s performance, starting by optimizing the learning rate and batch size hyperparameters. In terms of transfer learning, transferring knowledge from networks pre-trained on a smaller dataset closer to the target application domain brought more benefits when compared with an experiment with a large-scale public dataset with categories distant from the tarobtain application domain. Detected classes optimizations were also explored by including normal squamous nuclei as a class detected by the model, which improved the learning process toward more robust discrimination of lesions’ nuclei. Finally, the per-class tuning of the score threshold in the post-processing step also allowed us to obtain a model more suitable to support screening procedures, allowing performance improvements in terms of the F1 score in most of the considered classes.
A comparison between the performance achieved by the proposed nucleus-based methodology and a region-based approach previously proposed was also provided, achieving clear performance improvements regarding both mAP@0.50IoU and AR@10 metrics on the same dataset. Despite the apparent success of the proposed approach, it should be noted that the Nucleus-Based Cervical Lesion Dataset created in the ambit of this work still has clear limitations. While the reported experiments regarding data augmentation through basic image manipulations did not improve the detection performance, alternative strategies should be explored in the future like state-of-the-art generative deep learning approaches such as GANs and latent diffusion models to promote higher and more reliable per-class variability. The authors also aim to experiment with additional meta-architecture/backbone combinations, such as object detection models from the YOLO series.
In summary, the proposed nucleus-based strategy for cervical lesion detection presents a step further in developing a cost-effective mobile framework for cervical cancer screening. Although further improvements are still required to embed the proposed approach in a reliable and robust decision support system for cervical cancer screening, this work reinforces the potential of using AI-powered portable solutions to automatically scan and analyze LBC samples. Such solutions can significantly impact screening programs worldwide, particularly in areas with limited access and restricted healthcare resources.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.M., A.S. and L.R.; methodology, V.M., A.S., P.V. and L.R.; software, V.M.; validation, V.M., A.S., P.V. and L.R.; formal analysis, V.M., A.S., P.V. and L.R.; investigation, V.M., A.S., P.V. and L.R.; data curation, V.M.; writing—original draft preparation, V.M. and L.R.; writing—review and editing, V.M., A.S., P.V., T.O. and L.R.; visualization, V.M., A.S. and L.R.; supervision, P.V. and L.R.; project administration, T.O. and L.R.; funding acquisition, T.O. and L.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the project Transparent Artificial Medical Intelligence (TAMI), co-funded by Portugal 2020 framed under the Operational Programme for Competitiveness and Internationalisation (COMPETE 2020), Fundação para a Ciência and Technology (FCT), Carnegie Mellon University, and the European Regional Development Fund under Grant 45905.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Approval of all ethical and experimental procedures and protocols was granted by the Ethics Committee of the Portuguese Oncology Institute of Porto (Approval ID: 101/021). All methods were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Data Availability Statement
In light of involved patients’ privacy concerns, the cervical lesion dataset utilized in the aforementioned studies will remain private. However, the research team is currently undertaking efforts to create a new dataset that is based on similar data to the original cervical lesion dataset, with the aim of making it publicly available.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Anatomical Pathology Service of the Portuguese Oncology Institute – Porto (IPO-Porto).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Sqm. | Squamous nuclei |
| Aug. | Augmented |
| LBC | Liquid-Based Cytology |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| TBS. | The Bethesda System |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Diagnosis |
| COCO | Common Objects in Context |
| FPN | Feature Pyramid Network |
| SSD | Single-Shot Detector |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| YOLO | You Only Look Once |
| WSI | Whole-Slide Imaging |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| ASC-US | Atypical Squamous Cell of Undetermined Significance |
| LSIL | Low-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion |
| ASC-H | Atypical Squamous Cell, cannot rule out High-grade lesion |
| HSIL | High-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion |
| SCC | Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| 3D | Three Dimensions |
| NMS | Non-Maximum Suppression |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| VRAM | Video Random Access Memory |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
| AR | Average Recall |
| AP | Average Precision |
| mAP | Mean Average Precision |
| FN | False Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| TP | True Positive |
| LR | Learning Rate |
| BS | Batch Size |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| SPFNet | Series-Parallel Fusion Network |
| CEENET | Cervical Ensemble Network |
| EN-FELM | EfficientNet Fuzzy Extreme-Learning Machine |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Cancer Today. 2021. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/fact-sheets-cancers (accessed on 11 February 2021).
- Marth, C.; Landoni, F.; Mahner, S.; McCormack, M.; Gonzalez-Martin, A.; Colombo, N. Cervical cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Conceição, T.; Braga, C.; Rosado, L.; Vasconcelos, M.J.M. A Review of Computational Methods for Cervical Cells Segmentation and Abnormality Classification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5114. [Google Scholar]
- Mosiichuk, V.; Viana, P.; Oliveira, T.; Rosado, L. Automated Adequacy Assessment of Cervical Cytology Samples Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the Iberian Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, Aveiro, Portugal, 4–6 May 2022; Pinho, A.J., Georgieva, P., Teixeira, L.F., Sánchez, J.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 156–170. [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio, A.F.; Rosado, L.; Vasconcelos, M.J.M. Towards the Mobile Detection of Cervical Lesions: A Region-Based Approach for the Analysis of Microscopic Images. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 152188–152205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, T.; Mai, D.; Bensch, R.; Çiçek, d.; Abdulkadir, A.; Marrakchi, Y.; Böhm, A.; Deubner, J.; Jaeckel, Z.; Seiwald, K.; et al. U-Net: Deep learning for cell counting, detection, and morphometry. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, C.X.; Sultan, M.M.; Pande, V.S. Using Deep Learning for Segmentation and Counting within Microscopy Data. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.10548. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, J.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, C.; Bednarz, T.; Sowmya, A.; Liang, X. Selective Detection and Segmentation of Cervical Cells. In Proceedings of the ICBBT’19: 2019 11th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 29–31 May 2019; pp. 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tsai, J.; Ho, W. Automatic identifying and counting blood cells in smear images by using single shot detector and Taguchi method. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 22 (Suppl. 5), 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Noble, J.; Zisserman, A. Microscopy cell counting and detection with fully convolutional regression networks. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2018, 6, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, X.; Ong, K.H.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Young, D.; Su, Y.; Shang, B.; Peng, L.; et al. Hybrid AI-assistive diagnostic model permits rapid TBS classification of cervical liquid-based thin-layer cell smears. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshisundaram, N.; Govindaraj, D. An Automatic Method for Identification of Cervical Cancer based on Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Knowledge Discovery in Concurrent Engineering (ICECONF), Chennai, India, 5–7 January 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, C.; Padmashree, S.; Bhavani, R.; Priya, R. Detection and Identification of Cervical Cancer on Elephant Herding Optimization on Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 2nd Mysore Sub Section International Conference (MysuruCon), Mysuru, India, 16–17 October 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, D.; Rezende, M.; Bianchi, A.; Carneiro, C.; Luz, E.; Moreira, G.; Ushizima, D.; Medeiros, F.; Souza, M. A Deep Learning Ensemble Method to Assist Cytopathologists in Pap Test Image Classification. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingöl, H. NCA -based hybrid convolutional neural network model for classification of cervical cancer on gauss-enhanced pap-smear images. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2022, 32, 1978–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Master, O.; Ganatra, A.; Kotecha, K. Cervical cancer detection in pap smear whole slide images using convNet with transfer learning and progressive resizing. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Zhang, G.; Mu, C.; Guan, B.; Wang, M. In Proceedings of the Cervical Cancer Cell Detection Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Network, Shenyang, China, 27–29 July 2020; pp. 6527–6532. [CrossRef]
- Subarna, T.; Sukumar, P. Detection and classification of cervical cancer images using CEENET deep learning approach. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 43, 3695–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suphalakshmi, A.; Appathurai, A.; Jeyam, A.; Subramanian, M. Cervical cancer classification using efficient net and fuzzy extreme learning machine. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 43, 6333–6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, S.; Sindhoora; Melanthota, K.; Arbaaz.; Vaz, J.; Kadambalithaya, V.; Hussain, I.; Dutta, S.; Mazumder, N. Recent trends in smartphone-based detection for biomedical applications: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 2389–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haan, K.; Ceylan Koydemir, H.; Rivenson, Y.; Tseng, D.; Van Dyne, E.; Bakic, L.; Karinca, D.; Liang, K.; Ilango, M.; Gumustekin, E.; et al. Automated screening of sickle cells using a smartphone-based microscope and deep learning. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, L.; Correia da Costa, J.M.; Elias, D.; Cardoso, J. Automated Detection of Malaria Parasites on Thick Blood Smears via Mobile Devices. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 90, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, L.; Costa, J.M.C.d.; Elias, D.; Cardoso, J.S. Mobile-Based Analysis of Malaria-Infected Thin Blood Smears: Automated Species and Life Cycle Stage Determination. Sensors 2017, 17, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmström, O.; Linder, N.; Ngasala, B.; Mårtensson, A.; Linder, E.; Lundin, M.; Moilanen, H.; Suutala, A.; Diwan, V.; Lundin, J. Point-of-care mobile digital microscopy and deep learning for the detection of soil-transmitted helminths and Schistosoma haematobium. Glob. Health Action 2017, 10, 1337325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Qi, H.; Luo, W.; Tseng, D.; Ki, S.; Wan, Z.; Göröcs, Z.; Bentolila, L.; Wu, T.T.; Sun, R.; et al. Fluorescent Imaging of Single Nanoparticles and Viruses on a Smart Phone. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9147–9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, L.; Oliveira, J.; Vasconcelos, M.J.M.; da Costa, J.M.C.; Elias, D.; Cardoso, J.S. μSmartScope: 3D-printed Smartphone Microscope with Motorized Automated Stage. In Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies—BIODEVICES, (BIOSTEC 2017), Porto, Portugal, 21–23 February 2017; INSTICC. SciTePress: Lisbon, Portugal, 2017; pp. 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosado, L.; Silva, P.T.; Faria, J.; Oliveira, J.; Vasconcelos, M.J.M.; da Costa, J.M.C.; Elias, D.; Cardoso, J.S. μSmartScope: Towards a Fully Automated 3D-printed Smartphone Microscope with Motorized Stage. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. Book Ser. 2018, 4, 19–44. [Google Scholar]
- Brandão, P.; Silva, P.T.; Parente, M.; Rosado, L. µSmartScope: Towards a low-cost microscopic medical device for cervical cancer screening using additive manufacturing and optimization. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2021, 236, 267–279. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, C.; Silva, P.T.; Rosado, L.; Mota, L.; Martins, J. The Design Thinking Process in the Development of an Intelligent Microscopic Equipment. In Proceedings of the Advances in Design and Digital Communication II, Cham, Switzerland, 4–6 November 2022; pp. 170–182. [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen, J.; Norup, J.; Dounias, G.; Bjerregaard, B. Pap-smear Benchmark Data For Pattern Classification. Nat. Inspired Smart Inf. Syst. (NiSIS) 2005, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Plissiti, M.; Dimitrakopoulos, P.; Sfikas, G.; Nikou, C.; Krikoni, O.; Charchanti, A. Sipakmed: A New Dataset for Feature and Image Based Classification of Normal and Pathological Cervical Cells in Pap Smear Images. In Proceedings of the 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 3144–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phoulady, H.A.; Mouton, P.R. A New Cervical Cytology Dataset for Nucleus Detection and Image Classification (Cervix93) and Methods for Cervical Nucleus Detection. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.09651. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Carneiro, G.; Bradley, A. An Improved Joint Optimization of Multiple Level Set Functions for the Segmentation of Overlapping Cervical Cells. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Carneiro, G.; Bradley, A.; Ushizima, D.; Nosrati, M.S.; Bianchi, A.; Carneiro, C.; Hamarneh, G. Evaluation of Three Algorithms for the Segmentation of Overlapping Cervical Cells. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 21, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, M.T.; Tobias, A.H.G.; Silva, R.; Oliveira, P.H.C.; Medeiros, F.N.S.; Ushizima, D.M.; Carneiro, C.M.; Bianchi, A.G.C. Cric searchable image database as a public platform for conventional pap smear cytology data. Nat. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, R.; Wilbur, D.C. The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology: Definitions, Criteria, and Explanatory Notes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstra, J.; Bengio, Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Monti, M.; D’Aniello, D.; Scopelliti, A.; Tibaldi, V.; Santangelo, G.; Colagiovanni, V.; Giannini, A.; Palaia, I.; Perniola, G.; Giancotti, A.; et al. Relationship between cervical excisional treatment for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and obstetrical outcome. Minerva Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 73, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, A.; Di Donato, V.; Sopracordevole, F.; Ciavattini, A.; Ghelardi, A.; Vizza, E.; D’Oria, O.; Simoncini, T.; Plotti, F.; Casarin, J.; et al. Outcomes of High-Grade Cervical Dysplasia with Positive Margins and HPV Persistence after Cervical Conization. Vaccines 2023, 11, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).