Abstract
Pupil tracking plays a crucial role in various applications, including human–computer interactions, biometric identification, and Autostereoscopic three-dimensional (3D) displays, such as augmented reality (AR) 3D head-up displays (HUDs). This study aims to explore and compare advancements in pupil-tracking techniques using event camera imaging. Event cameras, also known as neuromorphic cameras, offer unique benefits, such as high temporal resolution and low latency, making them well-suited for capturing fast eye movements. For our research, we selected fast classical machine-learning-based computer vision techniques to develop our remote pupil tracking using event camera images. Our proposed pupil tracker combines local binary-pattern-features-based eye–nose detection with the supervised-descent-method-based eye-nose alignment. We evaluate the performance of event-camera-based techniques in comparison to traditional frame-based approaches to assess their accuracy, robustness, and potential for real-time applications. Consequently, our event-camera-based pupil-tracking method achieved a detection accuracy of 98.1% and a tracking accuracy (pupil precision < 10 mm) of 80.9%. The findings of this study contribute to the field of pupil tracking by providing insights into the strengths and limitations of event camera imaging for accurate and efficient eye tracking.
1. Introduction
Pupil tracking is a fundamental task in computer vision, human–computer interactions, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR) display systems. It plays a crucial role in enabling various applications, including gaze estimation [], attention tracking [], biometric identification [], and Autostereoscopic three-dimensional (3D) displays, such as AR 3D head-up displays (HUDs) []. Eye pupil tracking is also useful in psychology and medicine. Researchers have used it to identify conditions, like stress, by studying how the eyes move and other related body signals []. Extensive research has been conducted on head-mounted eye-pupil tracking, a close-range eye-tracking technology primarily designed for wearable devices [,,]. Additionally, remote eye-tracking has also garnered significant attention in the research community. Remote pupil tracking enables the monitoring and analysis of eye movements from a distance without requiring any physical contact with the user. This non-intrusive technology finds applications in various fields, including human–computer interactions [], psychological studies [], Autostereoscopic 3D displays [], and AR 3D HUDs in automobiles [], offering valuable insights into users’ visual attention and cognitive processes. The advancements in remote eye-tracking techniques have paved the way for more practical and non-intrusive implementations in real-world scenarios. While previous studies have extensively utilized traditional frame-based camera systems, sometimes with the integration of near-infrared (NIR) light, for remote pupil-tracking tasks [,], they inherently possess certain limitations, particularly in capturing fast and subtle eye movements that are vital for comprehending cognitive processes and human behavior.
Recently, the emergence of event camera imaging has piqued the interest of the computer vision community due to its unique capabilities for dynamic vision tasks. Event cameras asynchronously capture pixel-level intensity changes, or events, triggered by significant changes in the scene, such as motion. This novel sensing modality offers distinct advantages over conventional frame-based cameras, including a high temporal resolution, low latency, and low power consumption. These properties make event cameras highly attractive for capturing fast eye movements, such as rapid eye movements and subtle eye motions, which are often missed or blurred in frame-based systems []. One of the key characteristics of event cameras is their ability to represent motion through positive and negative pixel intensity changes. Positive events represent increases in intensity, while negative events signify decreases. As a result, event cameras provide a sparse representation of the scene, focusing solely on the changes occurring in the environment when motion occurs (Figure 1). This unique feature allows event cameras to excel in capturing dynamic scenes with reduced redundancy and minimized motion blur, making them particularly well-suited for tasks, like pupil tracking, where fast eye movements are critical for accurate analysis [].

Figure 1.
Examples of event camera imaging (left) capturing different levels of motion compared to frame-based Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) camera (right). The 1st row shows examples of minimal motion, the 2nd row shows subtle motion, and the 3rd row shows large motion with verifiable eye shape. As depicted in the examples, event cameras effectively capture the pixel-level intensity changes corresponding to motion, providing a clear representation of dynamic events and enhancing the accuracy of pupil-tracking algorithms.
In this paper, considering the potential of event camera imaging, we focus on developing remote pupil-tracking techniques using event cameras for Autostreoscopic 3D displays and AR 3D HUDs. Using knowledge from traditional frame-based eye-tracking, our primary goal is to assess the viability of pupil tracking using event cameras. By integrating event camera data with our previous frame-based methods [,], we emphasize the promise of event-camera-based tracking. Through this research, we explore the benefits, challenges, and limits of using event camera imaging for remote pupil tracking.
2. Proposed Method
In our previous work [,], we successfully developed an eye-tracking method designed for faces in diverse environments and user conditions. This method involved 11-point eye-nose shape tracking, which was based on the supervised descent method (SDM) [] for non-occluded faces. Building on the success of our previous work that extensively employed machine-learning-based computer vision algorithms for pupil tracking, we now extend our approach to utilize the unique capabilities of event camera imaging. In this section, we describe how we adapt and apply our previously developed machine-learning-based algorithm to the context of event camera data. Specifically, we present the design of our novel pupil-tracking algorithm, which incorporates feature extraction, eye–nose detection, and alignment methods tailored specifically for event camera imaging. By building upon the principles established in frame-based eye-tracking research and combining them with the insights from our previous work on bare-face eye tracking, we aim to unlock the potential of event camera imaging for more sophisticated and effective pupil tracking. This novel approach holds promise for advancing eye-tracking technologies and expanding their applications in various real-world scenarios.
2.1. Event Camera Imaging
Event cameras stand out due to their asynchronous capture of events—instantaneous pixel intensity variations caused by scene changes. Their defining characteristics and suitability for eye-tracking applications are further detailed in this section.
The key characteristic of event cameras is their asynchronous operation, where they capture pixel-level intensity changes, known as “events,” triggered by significant changes in the scene, such as motion. This unique sensing mechanism allows event cameras to react instantly to motion, leading to high temporal resolution and low latency. Unlike frame-based cameras that capture entire frames at fixed time intervals, event cameras produce events in real-time, providing a sparse and efficient representation of dynamic scenes. Another advantage of event cameras is their low power consumption. Traditional cameras often consume substantial power due to continuous image capture and processing, whereas event cameras only generate events when there is motion, significantly reducing power requirements. In terms of the data format, event cameras produce streams of events with precise timestamps, intensity changes, and corresponding pixel locations. This data format contrasts with conventional cameras, which produce sequences of static frames. Event camera data are highly suitable for capturing fast and subtle eye movements, such as rapid eye movements and subtle eye motions, which can be crucial for accurate eye tracking (Figure 2). By leveraging the unique capabilities of event camera imaging, we aim to enhance pupil-tracking performance, particularly in scenarios involving rapid eye movements and real-time applications.
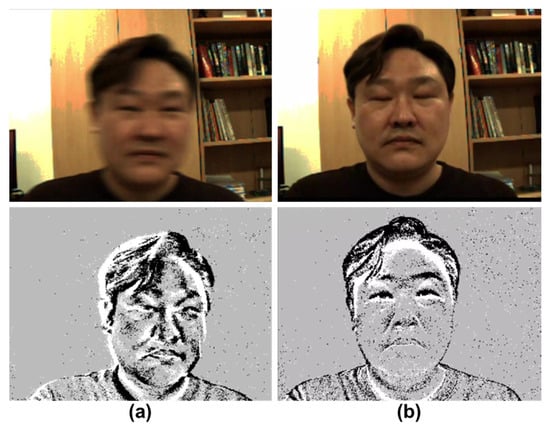
Figure 2.
Illustration of the advantages of event cameras over conventional RGB-frame-based cameras. The 1st row shows examples of RGB-frame-based images, and the 2nd row shows corresponding images from the event camera images. (a) Rapid movement: while the RGB image shows motion blur due to swift movement, the event camera captures the eye’s shape without any motion blur. (b) Quick eye movement: demonstrating the capability of the event camera to capture rapid eye movements. During a fast blink, the RGB image lags and still depicts the eye as closed, whereas the event camera swiftly captures the moment, revealing the actual open state of the eye during this time.
Figure 3 showcases the event camera used in our proposed method: the DAVIS 346 by Inivation []. This state-of-the-art event camera plays a crucial role in our research, enabling us to capture pixel-level intensity changes with exceptional precision. The DAVIS 346 event camera operates asynchronously, allowing it to respond instantaneously to motion events. Specifically, it processes a bandwidth of 12 million events per second, and its minimum latency is approximately 20 microseconds. Moreover, when converting these events for visualization purposes, they are typically aggregated to form event frames at a user-defined rate, similar to the event frame concept that accumulates events over a predefined interval to visualize them in a 2D image format. For our experiments, we chose to visualize these frames at 30 fps. The DAVIS 346 offers a resolution of 346 × 260 pixels, a dynamic range of 120 dB, minimum latency of 20 μs, and 180 mA power consumption at 5V DC. For our training and testing purposes, the images captured with the DAVIS 346 were resized to a resolution of 640 × 480 pixels to optimize the performance of our algorithms.
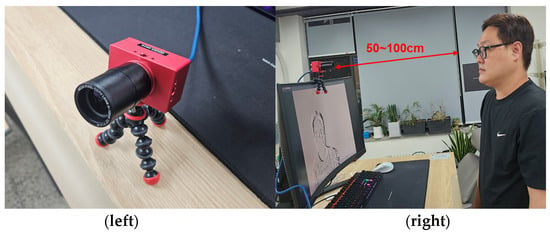
Figure 3.
The event camera used in our proposed method: Inivation’s DAVIS 346 (left) []. The experimental setup for remote pupil tracking, demonstrating the distance range between the event camera imaging device and the user’s face, spanning from 50 to 100 cm (right).
In addition to presenting the event camera itself, Figure 3 also illustrates the experimental setup we used for remote pupil tracking. The distance range between the event camera imaging device and the user’s face spans from 50 to 100 cm. Designed for Autostereoscopic 3D PC displays and vehicular AR 3D HUD systems, this distance was selected to guarantee the best pupil-tracking results in these settings. In our evaluations, participants with eyeglasses posed no issues for our methodology; however, sunglasses that occlude the eyes were excluded. Our system, developed for both Autostereoscopic 3D displays and AR 3D HUDs and utilizing the high dynamic range of event cameras, is expected to function efficiently outdoors. Yet, direct outdoor evaluations were not part of this study. This setup ensures that we can efficiently monitor and analyze the eye movements from a certain distance without the need for physical contact with the user. The remote pupil-tracking approach offers non-intrusive and user-friendly eye-tracking solutions for various real-world scenarios. With the DAVIS 346 event camera’s capabilities and the remote pupil tracking setup, we are well-equipped to explore the potential of event camera imaging for advanced pupil-tracking tasks. These features enable us to effectively capture and analyze eye movements, especially in challenging conditions, thereby paving the way for more accurate and efficient eye-tracking solutions.
2.2. Pupil-Tracking Algorithm
In our research, the creation of event frames is an important step. By accumulating events over a 33 ms interval, we translate this information into a visual format familiar to standard frame-based systems. The flowchart in Figure 4 starts with data from the event camera. These data are collected over the 33 ms period to form the event frame. Once the frame accumulates events for the set 33 ms interval, it is passed on to the next stage for processing. After forming the event frame, our method first identifies and localizes the eye–nose region within the frame. This detection step utilizes cascaded Adaboost classifiers with multi-block local binary patterns (LBPs) for the robust and efficient recognition of the eye region. Upon successful detection of the eye–nose region, our system activates the SDM-based eye–nose shape alignment. The next tracking checker block ensures that our tracking is maintained over consecutive frames and verifies the validity of the tracking. For the tracking checker, we utilize Scale-Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) features extracted around 11 landmarks on bare faces and use a support vector machine (SVM) to ascertain the success of tracking. When the eye tracking fails, it restarts the detection mode, which scans the whole image to find the eye–nose area with a relatively lower speed (16 ms), compared to the tracking mode (5 ms), which utilized a small region of interest from the eye tracking success in the previous camera frame. Therefore, it is desirable to maintain the tracking mode at each frame without the execution of the detection module, in terms of the overall system latency. The above processes yield the final eye coordinates, allowing our system to effectively and efficiently track pupils in dynamic environments. The entire process, from event frame formulation to the extraction of the final eye coordinates, is illustrated in Figure 4.
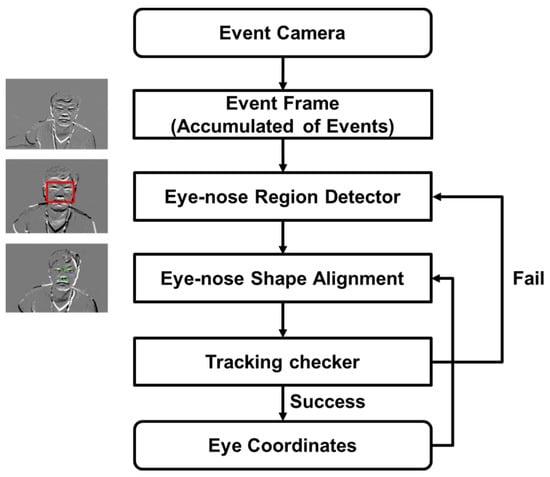
Figure 4.
Flowchart of the proposed pupil-tracking method based on event camera imaging. This visual representation details the process, starting from event frame generation, moving to eye–nose detection and alignment, and ending with the tracking checker.
We are expanding on the success of our previously developed eye-tracking method [,], which demonstrated effectiveness in diverse environmental settings and with different users. The foundation of our previous approach relied on 11-point eye–nose shape tracking, employing SIFT features [], the SDM []. A concise list of the main features we employed includes the following: (1) 11-point eye-nose shape tracking—this technique selects the most significant landmark points within the entire facial structure, chosen specifically for their role in enhancing the accuracy of eye alignment, (2) SDM regression with the SIFT feature—optimized for central processing unit (CPU) efficiency; SDM uses a 4-stage regression to transition from an average to an optimal facial shape. SDM focuses on a series of descent directions to minimize non-linear square functions of landmarks. This regression-based approach not only reduces computational cost but also enhances the alignment accuracy, presenting shape alignment as an optimization task. We efficiently regress the initial pupil positions from the detected eye–nose regions to their optimal pupil center positions, along with other eye–nose landmark points, enabling swift and accurate tracking. Given the demands of real-time applications and the challenges posed by various light conditions, eye occlusion, head movements, and limited computing resources, we opted for a comprehensive and efficient machine-learning-based computer vision approach. This approach includes utilizing the speed advantage of the SDM [] and cascaded Adaboost classifiers [,] with multiblock LBP [] for eye–nose region detection, offering a robust alternative to more computationally intensive methods.
Furthermore, our previous studies [,] have demonstrated the substantial speed advantage of the SDM-based eye tracking method over various convolutional neural-network (CNN)-based algorithms. While CNNs exhibit remarkable performance in computer vision tasks, they often demand significant computational resources and result in longer processing times, making them less suitable for real-time applications. In contrast, our chosen approach, which utilized a multi-block LBP-based detector and SDM-based aligner, exhibited faster and more efficient performance, particularly on conventional CPUs in PCs or mobile tablets with limited graphic processing unit (GPU) resources [,]. The LBP-based detector enabled straightforward and practical eye–nose region detection, while the SDM-based aligner ensured accurate and real-time eye center position tracking. This capability was essential for capturing rapid eye movements during pupil-tracking tasks. Our previous studies [,] highlighted that the SDM-based eye tracking achieved an impressive speed of 4 ms per 640 by 480 image resolution with CPU usage. In comparison, various CNN-based algorithms, such as ESR (15 ms, CPU) [], DVLN (15 ms, CPU) [], and LAB (2.6 s, CPU) [], required significantly more time under the same conditions. The superior speed and efficiency of our method make it highly suitable for real-time eye-tracking applications, especially when dealing with rapid eye movements, dynamic environments, and limited computing resources.
In the context of event camera imaging, we have adapted and applied our previously developed machine-learning-based computer vision algorithm for pupil tracking. Our new algorithm is specifically designed to work with event camera data and includes feature extraction, eye–nose detection, and alignment methods. By combining insights from frame-based eye-tracking research with our knowledge from bare-face eye tracking, our goal is to effectively utilize the unique capabilities of event camera imaging. The main components of our tracking system are divided into three stages: (1) eye–nose region detection from event camera images, which accumulate asynchronous events during a fixed time, (2) tracking the eye center position based on the detected eye–nose region, and (3) a tracker-checker for fast tracking. For eye–nose region detection, we employ the error-based learning (EBL) method [], using cascaded Adaboost classifiers with multiblock LBP. This approach is designed to make optimal use of standard CPUs found in personal computers (PCs) or mobile tablets with limited GPU resources. Upon successful eye–nose region detection, the eye center position tracking mode is activated. We use a coarse-to-fine strategy to infer the pupil center location through the use of the SDM with SIFT features, followed by pupil position refinement through the pupil-segmentation module. The SDM-based shape alignments rely on 11 landmark points that cover the eyes and nose areas.
To enhance pupil-tracking performance using event cameras, we developed a specialized event camera image database (DB) and implemented efficient learning methods. The DB was created by capturing real-world videos using the DAVIS 346 event camera, and the videos were categorized into three motion levels as shown in Figure 1: minimal motion, subtle motion, and large motion with verifiable eye shape. For training the eye–nose region detector, we utilized images from both the subtle and large motion categories. We employed the EBL method to efficiently detect eye–nose regions from the event camera images. Typically, the EBL method, which is inherently iterative, progresses through three stages refining and reducing large datasets to essential samples. Due to the limited number of images available in the DB, we focused on the early and middle stages of the EBL training process, leaving out the final matured stage []. As for the eye–nose region aligner, we concentrated solely on the large motion category for training. The aligner needs to accurately handle eye shapes under significant motion, making the large motion DB more suitable for this purpose. The specialized event camera image DB played a crucial role in training both the eye–nose region detector and aligner. By incorporating distinct motion categories, we ensured that the algorithms could effectively adapt to different motion levels and diverse eye shapes encountered in real-world scenarios. As a result, while the performance may not be considered superior, our fine-tuned detector and aligner have shown great potential in leveraging event camera imaging for pupil tracking. Indeed, one of the most notable achievements of our event-camera-based pupil-tracking method is its ability to capture rapid eye movements that are challenging for traditional RGB-frame-based systems. The event camera’s asynchronous operation and high temporal resolution allow it to detect and respond instantly to pixel-level intensity changes triggered by motion events. This unique sensing mechanism enables us to accurately track fast eye movements, which are often difficult for conventional frame-based cameras to capture.
3. Experimental Results
To evaluate the performance of event camera-based pupil tracking, we conducted comprehensive experiments using a diverse dataset that includes various eye movement scenarios and lighting conditions. We compared the results obtained from our proposed event-camera-based method with our previous frame-based eye-tracking algorithms []. The experimental results convincingly showcased the potential of event camera imaging in significantly enhancing the accuracy and robustness of pupil tracking, especially during rapid eye movements. Our proposed method was implemented using C++ and tested solely based on CPU computations on a Windows PC. Remarkably, the algorithms achieved an impressive speed of 200 frames per second at a 640 × 480 resolution with a 2.0 GHz CPU, showcasing their real-time capabilities and practical suitability for various applications. Table 1 summarizes the pupil-tracking specification. The eye–nose detection uses a cascaded Adaboost classifier combined with multiblock LBP, incorporating nine boosting substages. For pupil localization, the aligner adopts an SDM-based 11-point eye–nose-alignment technique that integrates SIFT features through a 4-step regression. These predefined 11 points include the left eye’s outer and inner corners, its center; the right eye’s outer and inner corners, its center; and the nasion, pronasale, left alare, subnasale, and right alare. We assessed the precision of our algorithm by computing the disparity between the ground truth and the tracked pupil centers. This method provides a direct quantitative measure of the algorithm’s performance by identifying how closely our tracking aligns with known truth values. To relate these disparities to real-world measurements, we utilized the inter-pupil distance (IPD) as a reference. Assuming an IPD of 65 mm, which is a general average for adults, we converted pixel distances into physical distances, enabling us to accurately estimate the positions of the pupils in real-world units. Consequently, our event-camera-based pupil-tracking method achieved a detection accuracy of 98.1% and a tracking accuracy (pupil precision < 10 mm) of 80.9%. The detection accuracy was on par with existing RGB-frame-camera-based pupil-tracking methods, while the tracking accuracy, though slightly lower than frame-camera-based algorithms, proved reasonable and promising for an initial exploration of event-camera-based pupil tracking. A summary of these results is provided in Table 2.

Table 1.
Pupil tracking specification.

Table 2.
Performance of the proposed event-camera-based pupil-tracking method. For a comparison, previous RGB-frame-camera-based method [] performance is also shown.
The dataset employed for our proposed method was thoughtfully constructed, consisting of real-world videos captured using the DAVIS 346 event camera. To train the eye–nose region detector, we used a combination of images from both the subtle and large motion categories of the event camera dataset. We efficiently detected eye–nose regions in the event camera images using the EBL method []. Due to the limited number of available images in the dataset, our focus was on the early and middle stages of the EBL training process, excluding the final matured stage. Specifically, the detector training incorporated 3608 event camera images along with 3949 negative non-face background images. For the eye–nose region aligner, we exclusively concentrated on the large motion category of the event camera dataset during training. The aligner’s primary task was to accurately handle eye shapes under significant motion, making the large motion DB particularly well-suited for this purpose. The event camera alignment training comprised 2273 events with verifiable eye shape.
By constructing and utilizing this specialized event camera dataset, we ensured the algorithms’ adaptability to challenging real-world scenarios involving various eye movements and head poses. The proposed algorithm was evaluated based on a video DB captured in a normal office environment with illumination ranging from 100 to 400 lux, using the DAVIS346 event camera. The DB consisted of videos categorized into three distinct motion levels, each having a verifiable eye shape. To assess the algorithm’s performance, a test set comprising 474 face images with large movements was utilized. These rigorous tests allowed us to validate the algorithm’s capabilities in handling real-world scenarios with different motion levels and lighting conditions, particularly emphasizing its proficiency in accurately tracking pupils during rapid eye movements (Figure 5). Table 3 provides a summary of the training and testing DBs used for the evaluation of our algorithm.
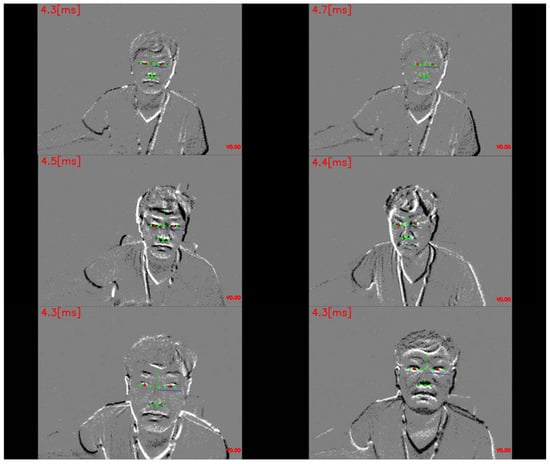
Figure 5.
Experimental results obtained from event camera face images with verifiable eye shapes due to large movements. The pupil-tracking algorithm demonstrated successful performance across various face motions.

Table 3.
Training and testing DB for the proposed event-camera-based pupil-tracking method.
4. Discussion
In this study, the primary objective was assessing how existing algorithms perform when applied to event camera imaging. Our approach used machine-learning-based computer vision methods, including a multi-block LBP-based detector and SDM-based aligner, to achieve real-time and efficient pupil-tracking performance. For our experiments, we aggregated events into frames at 30 fps to accurately represent eye movements. This rate was chosen for its visual clarity and its compatibility with our SDM-based keypoint alignment. Our algorithm, utilizing the SDM, showed optimal performance with data aggregated at this rate. We evaluated the algorithm’s capabilities using a comprehensive dataset that included various eye movement scenarios, and we compared the results with our previous frame-based eye-tracking algorithms. While our event camera-based approach achieved a nearly equivalent detection accuracy of 98.1%, closely matching the 99.4% achieved by traditional RGB frame camera methods [], there was a noticeable decline in the tracking accuracy. The tracking accuracy dropped from 99.4% with the RGB-frame-camera-based method [] to 80.9% in our proposed approach. To further quantify our results, we computed the precision and recall for our method. The precision achieved was 100%, and the recall was 80.89%. Based on our testing, the confusion matrix related to our approach has been detailed in Figure 6. Our true negative value was zero, consistent with our test dataset that did not contain any images without pupils. A notable point from our results is the zero false positives. This can be attributed to the intrinsic nature of event cameras, which do not output any pixel value in static backgrounds. Hence, there is no activation unless there is motion. This characteristic eliminates the chances of false positive detections in areas with no movement, showing one of the significant advantages of utilizing event cameras. Since event cameras might not consistently provide uniform shape information, SDM can sometimes fail in its regression tasks, leading to less precise tracking. Moreover, our tracker checker tends to discard tracking instances when the shape information is unclear, especially during non-insufficient movements. Our choice of the AdaBoost-based eye–nose detection combined with the SDM-based pupil alignment was intentionally selected. This conventional method was chosen driven by our primary aim: to examine the feasibility of well-established remote eye-tracking algorithms on rapidly functioning event cameras. As demonstrated in our previous research on RGB-frame-based cameras [], while advanced deep learning methods may offer improved results, our technique can operate efficiently on CPUs, eliminating the necessity for high-priced GPUs. However, methods, like AdaBoost and SDM, have limitations when confronting outliers, noise, occlusions, and other challenging scenarios compared to newer deep learning techniques. A further study focusing on deep neural networks designed for event cameras is required.
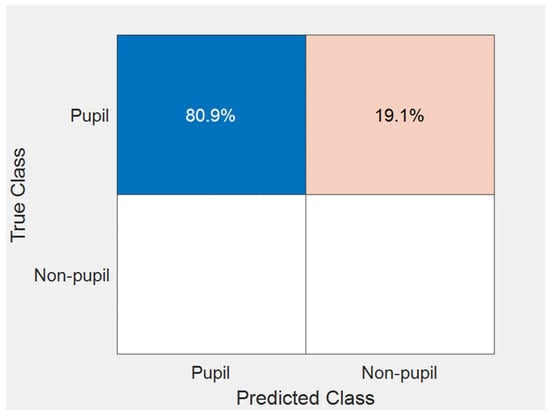
Figure 6.
Confusion matrix for the proposed pupil localization.
Figure 7 showcases some failure cases of the proposed method. In Figure 7a, we observe a scenario with minimal movements and an obscured eye shape, leading to the detector’s failure in detecting the eye–nose region. Similarly, Figure 7b presents a case where the eye shape is visible, but the algorithm encounters challenges in the alignment and tracker-checker components, resulting in tracking failure. These instances illustrate the complexities and limitations associated with event camera imaging, particularly when dealing with scenarios involving minimal movements and obscured eye shapes. Additionally, Table 4 summarizes our algorithm’s performance across movement levels. In the large movement category, we achieved a detection accuracy of 98% and a tracking accuracy of 80.9%, illustrating our system’s ability to track pupils during quick eye motions. For a range from minimal to large movements, the detection accuracy was reduced to 69.1% and tracking to 52.7%, emphasizing the tracking challenges with varying motion intensities. A comparison between our proposed event-camera-based method and state-of-the-art RGB-frame-camera-based techniques [,,,] is also listed in Table 5.
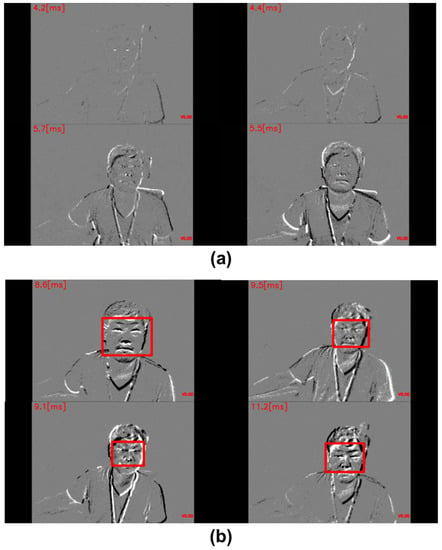
Figure 7.
Failure cases of the proposed event-camera-based pupil tracking method. (a) Minimal movements with obscured eye shape, leading to a failure in eye–nose region detection. (b) Visible eye shape, but failure in the alignment and tracker-checker components.

Table 4.
Performance comparison of the proposed event-camera-based pupil-tracking method on different movement levels.

Table 5.
Comparison between previous RGB-frame-camera-based studies and the proposed method.
Despite the algorithm’s successes in handling rapid eye movements and achieving real-time capabilities, there are areas for improvement. One notable limitation is the reduced accuracy when dealing with subtle or minimal movements. When there is minimal-to-no head movement, the nature of event cameras, which primarily respond to changes in the scene, might produce sparse events, complicating eye–nose detection. Our research successfully detected pupil movements across a 1 m range using event cameras, as evidenced in the Figure 1, Figure 5, and Figure 6 shown in the manuscript. However, we recognize the resolution limitation of the DAVIS 346 and anticipate improvements with next-generation high definition (HD) event cameras. These situations may lead to partial occlusion or insufficient motion cues, making it challenging for the algorithm to accurately detect and track pupils. Furthermore, the algorithm’s performance was dependent on the quality and availability of data in the training dataset. The limited number of available images in the event camera dataset for training the detector and aligner may have influenced the algorithm’s performance on certain motion levels. Another consideration is the trade-off between speed and accuracy. While our proposed method achieved remarkable real-time performance at 200 frames per second at a 640 × 480 resolution with a 2.0 GHz CPU, there is room for improving the accuracy at the expense of processing speed. For specific applications that require higher precision, optimizations to balance speed and accuracy should be explored. In this study, our primary goal was to assess the feasibility of using event cameras for remote eye tracking, positioning our work as a preliminary exploration in this domain. We acknowledge that a comprehensive comparison with other eye-tracking methods and a more extensive validation were not undertaken. Additionally, to overcome these limitations and further enhance the algorithm’s performance, several strategies can be considered. In this research, we emphasized computational efficiency, favoring methods, like SDM, Adaboost, and LBP. However, to further optimize the performance of our algorithm, considering diverse strategies is important. As deep learning continues to develop with new lightweight networks coming out, adapting or customizing these networks specifically for event cameras could be beneficial. By using recent advanced deep neural networks [,], the algorithm could potentially handle subtle movements more effectively and enhance its robustness in challenging scenarios with obscured eye shapes. Additionally, utilizing the graph structure, especially through approaches, like the graph Fourier transform as discussed in ref. [], can be adopted to improve tracking capabilities, offering a richer representation of data relationships. Moreover, efforts to expand the training dataset with a more diverse range of event camera data could be undertaken. By collecting data from various real-world environments and users, the algorithm can better adapt to different motion levels and lighting conditions, ultimately leading to improved generalization and performance.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our proposed event-camera-based pupil-tracking algorithm demonstrated promising results in accurately tracking pupils during rapid eye movements, with real-time capabilities. Specifically, our method reached a detection accuracy rate of 98.1% and a tracking accuracy, where the pupil difference was less than 10 mm, at 80.9%. However, there are challenges to overcome, particularly in handling subtle movements and occluded eye shapes. Future research could focus on expanding the dataset for training and investigating new machine learning techniques to improve the algorithm’s performance across diverse eye movement scenarios and lighting conditions. By addressing these challenges, event-camera-based pupil tracking holds great potential for advancing eye-tracking technologies and enabling new applications in various real-world settings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.K. and J.J.; methodology, D.K. and Y.K.L.; software, D.K.; validation, D.K. and Y.K.L.; formal analysis, J.J.; investigation, Y.K.L.; resources, D.K.; data curation, J.J.; writing—original draft preparation, D.K.; writing—review and editing, Y.K.L. and J.J.; visualization, Y.K.L.; supervision, J.J.; project administration, D.K.; funding acquisition, D.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No. 2022R1F1A1074056); this work was supported by the 2023 Hongik University Research Fund. This work was supported by the Ministry of Education (MOE) and a Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (MOTIE) (P0022165, High-Speed Semiconductor IC Design and Test/Signal Integrity Professional Training Project).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yiu, Y.-H.; Aboulatta, M.; Raiser, T.; Ophey, L.; Flanagin, V.L.; Zu Elenburg, P.; Ahmadi, S.-A. DeepVOG: Open-source pupil segmentation and gaze estimation in neuroscience using deep learning. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 324, 108307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaramagkas, V.; Giannakakis, G.; Ktistakis, E.; Manousos, D.; Karatzanis, I.; Tachos, N.S.; Tripoliti, E.; Marias, K.; Fotiadis, D.I.; Tsiknakis, M. Review of eye tracking metrics involved in emotional and cognitive processes. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 16, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asish, S.M.; Kulshreshth, A.K.; Borst, C.W. User identification utilizing minimal eye-gaze features in virtual reality applications. Virtual Worlds 2022, 1, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Ma, L. Real-Time Eye Tracking for Bare and Sunglasses-Wearing Faces for Augmented Reality 3D Head-Up Displays. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 125508–125522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.S.; Reisi, F.; Daliri, M.R.; Shalchyan, V. Stress Detection Using Eye Tracking Data: An Evaluation of Full Parameters. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 118941–118952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, W.-L.; Kuo, T.-L.; Chang, C.-C.; Fan, C.-P. Deep-learning-based pupil center detection and tracking technology for visible-light wearable gaze tracking devices. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozomitu, R.G.; Păsărică, A.; Tărniceriu, D.; Rotariu, C. Development of an Eye Tracking-Based Human-Computer Interface for Real-Time Applications. Sensors 2019, 19, 3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiago, S.; Fuhl, W.; Kasneci, E. PuRe: Robust pupil detection for real-time pervasive eye tracking. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2018, 170, 40–50. [Google Scholar]
- Majaranta, P.; Bulling, A. Eye tracking and eye-based human–computer interaction. In Advances in Physiological Computing; Springer: London, UK, 2014; pp. 39–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.J.; Mountstephens, J.; Teo, J. Emotion recognition using eye-tracking: Taxonomy, review and current challenges. Sensors 2020, 20, 2384. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.; Heo, J. Content-Aware Eye Tracking for Autostereoscopic 3D Display. Sensors 2020, 20, 4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braiden, B.; Rose, J.; Eizenman, M. Hybrid eye-tracking on a smartphone with CNN feature extraction and an infrared 3D model. Sensors 2020, 20, 543. [Google Scholar]
- Gallego, G.; Delbruck, T.; Orchard, G.; Bartolozzi, C.; Taba, B.; Censi, A.; Leutenegger, S.; Davison, A.J.; Conradt, J.; Danilidis, K.; et al. Event-based vision: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 154–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuehan, X.; De la Torre, F. Supervised descent method and its applications to face alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 53–539. [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS346. Available online: https://inivation.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/DAVIS346.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2023).
- Lowe, D. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.; Jones, M.J. Robust real-time face detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 57, 137–154. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, V.; Jones, M. Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Chu, R.; Xiang, S.; Liao, S.; Li, S.Z. Face detection based on multi-block lbp representation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometrics, Seoul, Korea, 27–29 August 2007; pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Wei, Y.; Wen, F.; Sun, J. Face alignment by explicit shape regression. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2014, 107, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenyan, W.; Yang, S. Leveraging intra and inter-dataset variations for robust face alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 150–159. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Qian, C.; Yang, S.; Wang, Q.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, Q. Look at boundary: A boundary-aware face alignment algorithm. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2129–2138. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.H.; Kittler, J.; Awais, M.; Huber, P.; Wu, X.J. Wing loss for robust facial landmark localisation with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2235–2245. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Bo, L.; Fuxin, L. Adaptive wing loss for robust face alignment via heatmap regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6971–6981. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, S.; Sun, K.; Wu, W.; Qian, C.; Jia, J. Aggregation via separation: Boosting facial landmark detector with semi-supervised style translation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 10153–10163. [Google Scholar]
- Kujur, A.; Raza, Z.; Khan, A.A.; Wechtaisong, C. Data Complexity Based Evaluation of the Model Dependence of Brain MRI Images for Classification of Brain Tumor and Alzheimer’s Disease. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 112117–112133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Madendran, R.K.; Thirunavukkarasu, U.; Faheem, M. D2PAM: Epileptic Seizures Prediction Using Adversarial Deep Dual Patch Attention Mechanism. 2023. Available online: https://ietresearch.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/action/showCitFormats?doi=10.1049%2Fcit2.12261 (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Belda, J.; Vergara, L.; Safont, G.; Salazar, A.; Parcheta, Z. A New Surrogating Algorithm by the Complex Graph Fourier Transform (CGFT). Entropy 2019, 21, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).