Application of the Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and Electromagnetic (EM34-3) Geophysical Tools and Sedimentology for the Evaluation of the Subsurface of Sites Earmarked for Aquaculture Ponds in the Amazon Region of Northern Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation
1.2. Contributions
1.3. Organization
2. Materials and Methods
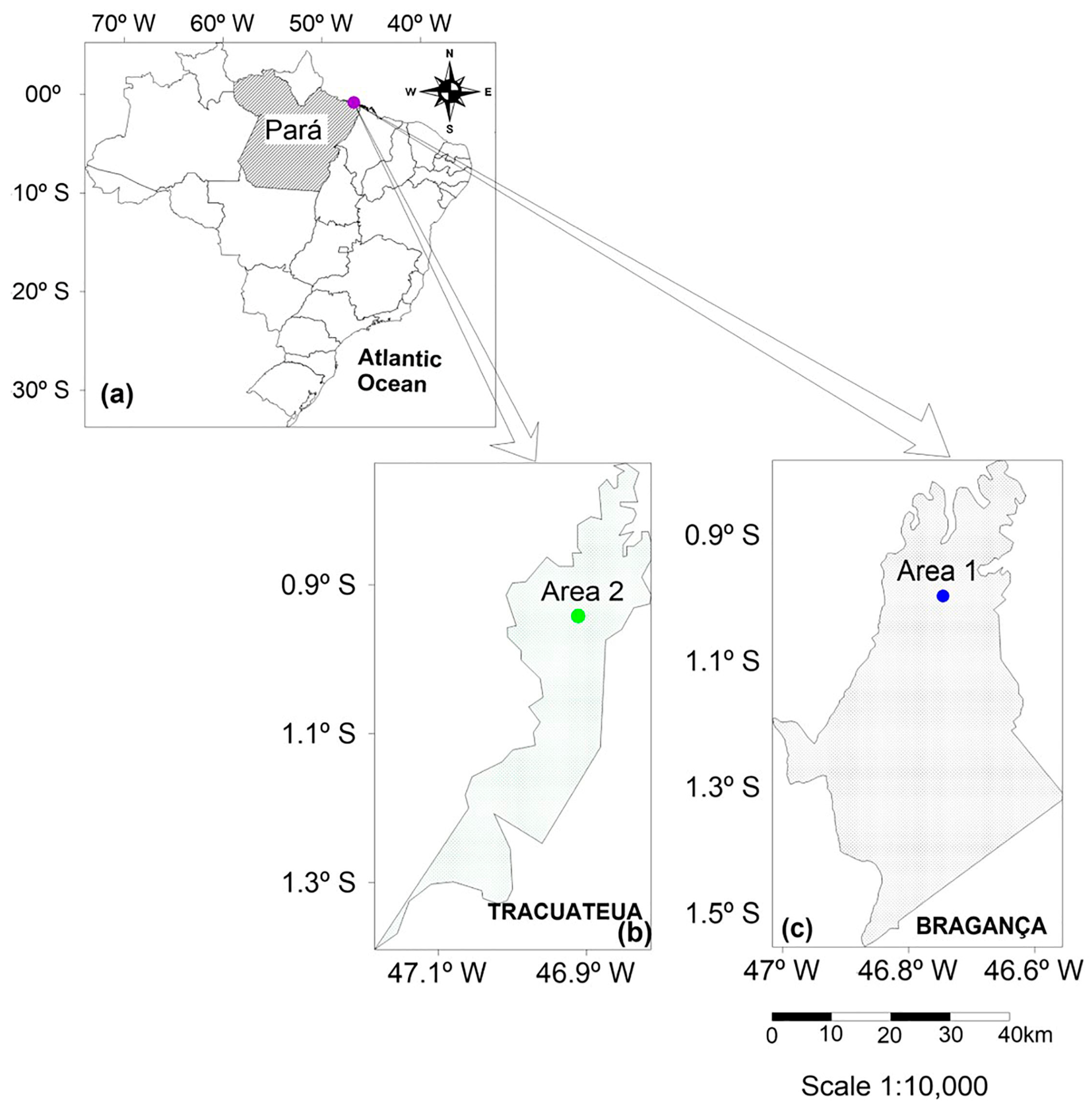
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
2.3. Electromagnetic Induction (EMI)
2.4. Standard Penetration Test (SPT)
2.5. Sampling and Data Acquisition
2.5.1. Acquisition of Data by GPR
2.5.2. EMI Data Acquisition
2.5.3. Sedimentological Analyses of the Soil Samples
- Two subsamples of approximately 300 mL of the soil were placed in two transparent 2 L jars (Jar Sedimentation Method);
- The samples were then ground up with a rod to eliminate the air trapped in the soil and record the volume of the material in the container;
- A total of 1500 mL of water was added to each container to homogenize the soil and dissociate all the particles present in the sample. After decanting for 24 h, the proportions of gravel, sand, silt, and clay present in the soil were determined and measured.
2.5.4. Standard Penetration Test
2.6. Data Processing
2.6.1. GPR
2.6.2. EMI
3. Results
3.1. Area 1
3.2. Area 2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calixto, E.S.; dos Santos, D.F.B.; Lange, D.; Galdiano, M.S.; Rahman, I.U. Aquaculture in Brazil and worldwide: Overview and perspectives. J. Environ. Anal. Prog. 2020, 5, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAPA (Ministério da Agricultura, Pecuária e Abastecimento). Plano Nacional de desenvolvimento da aquicultura—PNDA; Departamento de Ordenamento e Desenvolvimento da Aquicultura: Brasília, Brazil, 2017. Available online: https://www.gov.br/agricultura/pt-br/assuntos/mpa/aquicultura-1/plano-nacional-de-desenvolvimento-da-aquicultura-pnda-2022-2032/documento-pnda-30122022-1-_m.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2023). (In Portuguese)
- Aheto, D.W.; Acheampong, E.; Odoi, J.O. Are small-scale freshwater aquaculture farms in coastal areas of Ghana economically profitable? Aquac. Int. 2019, 27, 785–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapader, M.A.; Hasan, M.M.; Sarker, B.S.; Rana, E.U.; Bhowmik, S. Comparison of soil nutrients, pH and electrical conductivity among fish ponds of different ages in Noakhali, Bangladesh. Korean J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 44, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhhala, I.; Bahida, A.; Nhhala, H.; Chadli, H.; Baldan, D.; Wahbi, M.; Erraioui, H. Site selection for fish farming using integrated GIS-spatial multi-criteria evaluation and carrying capacity approaches: Case study of M’diq bay, Morocco. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2022, 26, 807–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Pu, R.; Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Ai, S.; Yang, Y. Mapping Coastal Aquaculture Ponds of China Using Sentinel SAR Images in 2020 and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMBRAPA (Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária). Piscicultura de água Doce: Multiplicando Conhecimentos; EMBRAPA: Brasília, Brazil, 2013; 440p, Available online: https://www.infoteca.cnptia.embrapa.br/handle/doc/1082280 (accessed on 29 August 2023). (In Portuguese)
- SEBRAE (Serviço Brasileiro de Apoio às Micro e Pequenas Empresas). Como Iniciar Piscicultura Com Espécies Regionais, 1st ed.; SEBRAE: Brasília, Brazil, 2013; Available online: https://bibliotecas.sebrae.com.br/chronus/ARQUIVOS_CHRONUS/bds/bds.nsf/b7c92dacee0fbaec6c77bbb438c6ab64/$File/4510.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2023). (In Portuguese)
- Jayanthi, M.; Thirumurthy, S.; Samynathan, M.; Manimaran, K.; Duraisamy, M.; Muralidhar, M. Assessment of land and water ecosystems capability to support aquaculture expansion in climate-vulnerable regions using analytical hierarchy process based geospatial analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SENAR (Serviço Nacional de Aprendizagem Rural). Aquicultura: Planejamento e Legalização de Projetos Aquícolas, 2nd ed.; SENAR: Brasília, Brazil, 2018; 84p. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Hadipour, A.; Vafaie, F.; Hadipour, V. Land suitability evaluation for brackish water aquaculture development in coastal area of Hormozgan, Iran. Aquac. Int. 2014, 23, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GESAMP (IMO/FAO/UNESCO-IOC/WMO/WHO/IAEA/UN/UNEP). Joint group of experts on the scientific aspects of marine environmental Protection. Planning and management for sustainable coastal aquaculture development. FAO Rep. Stud. 2001, 68, 90. [Google Scholar]
- SEBRAE (Serviço Brasileiro de Apoio às Micro e Pequenas Empresas). Aquicultura: Um mercado em crescimento no Brasil e no mundo. 2022. Available online: https://sebrae.com.br/sites/PortalSebrae/artigos/aquicultura-um-mercado-em-crescimento-no-brasil-e-no-mundo,ac99bb738c910810VgnVCM100000d701210aRCRD (accessed on 21 September 2023). (In Portuguese).
- PEIXE BR. Associação Brasileira de Piscicultura. Anuário PEIXE BR da Piscicultura 2023. São Paulo (SP). Brazil. 2023. Available online: https://www.peixebr.com.br/anuario/ (accessed on 21 September 2023). (In Portuguese).
- Valenti, W.C.; Barros, H.P.; Moraes-Valenti, P.; Bueno, G.W.; Cavalli, R.O. Aquaculture in Brazil: Past, present and future. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 19, 100611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, G.; Stead, S.M. Governance and offshore aquaculture in multi-resource use settings. In Aquaculture Perspective of Multi-Use Sites in the Open Ocean; Buck, B.H., Langan, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapieve, D.R.; Maggi, M.F.; Mercante, E.; Francisco, H.R.; Oliveira, D.D.D.; Luiz Junior, O.J. Use of geotechnologies for aquaculture site selection: Suitability factors and constraints for production in ground-excavated ponds. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2023, 5, 160–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, L.; Middelboe, A.L.; Kaas, H.; Ross, L.G.; Telfer, T.C. Use of geographic information systems for aquaculture and recommendations for the development of spatial tools. Rev. Aquacult. 2019, 12, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, J.; Boss, E.; Weatherbee, R.; Thomas, A.C.; Brady, D.; Newell, C. Oyster Aquaculture Site Selection using Landsat 8-Derived Sea Surface Temperature, Turbidity, and Chlorophyll a. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Boss, E.; Kiffney, T.; Hesketh, G.; Bourdin, G.; Fan, D.; Brady, D.C. Oyster Aquaculture Site Selection Using High-Resolution Remote Sensing: A Case Study in the Gulf of Maine, United States. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 802438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradipta, A.; Soupios, P.; Kourgialas, N.; Doula, M.; Dokou, Z.; Makkawi, M.; Alfarhan, M.; Tawabini, B.; Kirmizakis, P.; Yassin, M. Remote Sensing, Geophysics, and Modeling to Support Precision Agriculture—Part 1: Soil Applications. Water 2022, 14, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitella, G.; Rossi, R.; Loperte, A.; Satriani, A.; Lapenna, V.; Perniola, M.; Amato, M. Geophysical Techniques for Plant, Soil, and Root Research Related to Sustainability. In The Sustainability of Agro-Food and Natural Resource Systems in the Mediterranean Basin; Vastola, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; 397p. [Google Scholar]
- Besson, A.; Cousin, I.; Bourennane, H.; Nicoullaud, B.; Pasquier, C.; Richard, G.; Dorigny, A.; King, D. The spatial and temporal organization of soil water at the field scale as described by electrical resistivity measurements. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, K.J.M.; Oliva, P.A.C.; da Rocha, H.O.; Mendes, R.d.A.; da Costa, A.C.G.; Miranda, C.d.S.; Almeida, N.d.O. Evaluation of the contamination of the subsurface and groundwater by monoaromatic hydrocarbons in an eastern Amazonian town in northern Brazil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, L.F.S.; Oliva, P.A.C.; El Robrini, M.; dos Reis Junior, J.A. Contribution of ground penetrating radar in the study of an Amazon tide channel, influenced by macro tide. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2022, 116, 103776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacha, D.d.C.S.; Santos, S.; Mendes, R.d.A.; Rocha, C.C.d.S.; Corrêa, J.A.; Cruz, J.C.R.; Abrunhosa, F.A.; Oliva, P.A.C. Evaluation of the contamination of the soil and water of an open dump in the Amazon Region, Brazil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, C.N.d.C., Jr.; El Robrini, M.; Oliva, P.A.C. Experimental survey of the Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) in the study of the Aturiaí river (Bragança Coastal Plain, northeast of Pará). Res. Soc. Dev. 2020, 9, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, L.A.P.; Gandolfo, O.C.B. Geofísica aplicada. In Geologia de Engenharia e Ambiental: Métodos e técnicas, 1st ed.; Oliveira, A.M.S., Monticeli, J.J., Eds.; ABGE—Associação Brasileira de Geologia de Engenharia and Ambiental: São Paulo, Brazil, 2018; Volume 2, pp. 314–333. [Google Scholar]
- Utsi, E.C. Ground Penetrating—Radar Theory and Practice. Butterworth-Heinemann; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Haynie, K.L.; Khan, S.D. Shallow subsurface detection of buried weathered hydrocarbons using GPR and EMI. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.A.; Özürlan, G.; Şengül, E. Delineation of soil and groundwater contamination using geophysical methods at a waste disposal site in Çanakkale, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 135, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chira, O.P.; Barbalho, D.P.; Cruz, J.C.R. Environmental study of the Bragança City landfill (Brazil) applying Ground Penetrating Radar. In Proceedings of the 21st European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics (EAGE 2015), Turin, Italy, 6–10 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales, R.M.; Martínez-Pagan, P.; Faz, A.; Moreno-Cornejo, J. Environmental Monitoring Using Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) in the Subsoil of Three Former Petrol Stations in SE of Spain. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 3757–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jol, H.M. (Ed.) Ground Penetrating Radar: Theory and Applications; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.A.; Özürlan, G.; Balkaya, Ç. Geoelectrical investigation of seawater intrusion in the coastal urban area of Çanakkale, NW Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearey, P.; Brooks, M.; Hill, I. An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration; Blackwell Science Ltd.: London, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.L.; Annan, A.P. Ground-penetrating radar for high-resolution mapping of soil and rock stratigraphy. Geophys. Prospect. 1989, 37, 531–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolittle, J.A.; Brevik, E.C. The use of electromagnetic induction techniques in soils studies. Geoderma 2014, 223–225, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, E.D.; Doro, K.O.; Iserhien-Emekeme, R.E.; Atakpo, E.A. Using geophysics to guide the selection of suitable sites for establishing sustainable earthen fishponds in the Niger-Delta region of Nigeria. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chira, P.A.; Texeira, F.d.A.d.S.; Pena, R.T.; dos Reis Júnior, J.A. Application of the Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and sedimentology for evaluation of the subsoil for the excavation of fish farming ponds in the municipality of Bragança, Northeastern Pará, Brazil. In Proceedings of the 17o Simpósio de Geologia da Amazônia. Geotecnologias e Sustentabilidade: A Geologia na Amazônia atual, Santarém, Pará, Brazil, 23–25 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pathirana, S.; Lambot, S.; Krishnapillai, M.; Cheema, M.; Smeaton, C.; Galagedara, L. Ground-Penetrating Radar and Electromagnetic Induction: Challenges and Opportunities in Agriculture. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBGE (Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística). Divisão Regional do Brasil em Regiões Geográficas Imediatas e regiões Geográficas Intermediárias. Rio de Janeiro. 2017. Available online: https://biblioteca.ibge.gov.br/index.php/biblioteca-atalogo?view=detalhes&id=2100600 (accessed on 5 September 2022). (In Portuguese)
- Aranha, L.G.; Lima, H.P.; Souza, J.M.P.; Marinho, R.K. Origem and evolução das bacias de Bragança-Viseu, São Luís and Ilha Nova. In Origem and Evolução de Bacias Sedimentares; Raja Gabaglia, G.P., Milani, E.J., Eds.; Petrobrás: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1990; pp. 221–233. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Costa, J.B.S.; Hasui, Y. Evolução geológica da Amazônia. In Contribuições a Geologia da Amazônia; Costa, M.L., Angélica, R.S., Eds.; Brazilian Society of Geology/FINEP: Belém, Brazil, 1997; pp. 15–90. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Costa, J.B.S.; Borges, M.S.; Bermeguy, R.L.; Fernandes, J.M.G.; Costa Júnior, P.S.; Costa, M.L. Evolução cenozóica da região de Salinópolis, nordeste do estado do Pará. Geociências 1993, 12, 353–372. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Igreja, H.L.S. Aspectos tectono-sedimentares do Fanerozóico do nordeste do Pará e nordeste do Maranhão. Ph.D. Thesis, Federal University of Pará, Belem, Brazil, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- de Moraes, B.C.; da Costa, J.M.N.; da Costa, A.C.L.; Costa, M.H. Variação espacial and temporal da precipitação no estado do Pará. Acta Amaz. 2005, 35, 207–214. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, A.; Costa, R.M.; Liang, T.H.; Pereira, L.C.C.; Ribeiro, M.J.S. Spatial and temporal distribution in density and biomass of two Pseudodiaptomus species (Copepoda: Calanoida) in the Caeté River Estuary (Amazon region-North of Brazil). Braz. J. Biol. 2006, 66, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annan, A.P. Electromagnetic principles of Ground Penetrating Radar. In Ground Penetrating Radar—Theory and Applications; Jol, H.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 3–40. [Google Scholar]
- McNeill, J.D. Electromagnetic Terrain Conductivity at Low Induction Numbers; Technical Note TN-6; Geonics Limited: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 1980; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, B.; Mahmood, H.S.; Quraishi, M.Z.; Hoogmoed, W.B.; Mouazen, A.M.; Van Henten, E.J. Sensing Soil Properties in the Laboratory, In Situ, and On-Line: A Review. Adv. Agron. 2012, 114, 155–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.A.; Aquino, W.F.; Dourado, J.C. Aplicação do método eletromagnético indutivo (EM) no monitoramento de contaminantes em subsuperfície. Rev. Bras. Geofísica 2007, 25, 413–420. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas (ABNT). Norma Brasileira NBR 6484. Solo-Sondagens de Simples reconhecimento com SPT—Método de Ensaio. 2001. Available online: https://engenhariacivilfsp.files.wordpress.com/2014/11/spt-metodo_de_ensaio_nbr_6484.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2022). (In Portuguese).
- GEOSCAN. GEOSCAN Geology and Geophysics Cia. Standard Penetration Test (SPT): Know All the Procedures. 2022. Available online: https://www.geoscan.com.br/blog/spt/ (accessed on 16 August 2022). (In Portuguese).
- Google Earth Pro 2021. Available online: https://www.google.com/earth/versions/ (accessed on 13 June 2021).
- Basudha, C.h.; Singh, R.K.; Sureshchandra, N.; Soranganba, N.; Sobita, N.; Singh, T.B.; Singh, L.K.; Singh, I.M.; Prakash, N. Fish Farm Design and Pond Construction for Small Scale Fish Farming in Manipur; Technical Bulletin No. RCM(TB)-12, ICAR Research Complex for NEH Region; Manipur Centre: Imphal, India, 2019; pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, C.E. Bottom Soils, Sediment, and Pond Aquaculture; Springer Science + Business Media Dordrecht: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, J.C.P.; Costa, J.d.O. Análise do Solo: Determinações, Cálculos and Interpretação; Empresa de Pesquisa Agropecuária de Minas Gerais (EPAMIG Sul de Minas): Lavras, Brazil, 2012; pp. 1–14. Available online: http://www.bibliotecaflorestal.ufv.br/bitstream/handle/123456789/10529/EPAMIG_An%c3%a1lise-do-solo-determina%c3%a7%c3%b5es-c%c3%a1lculos-e-interpreta%c3%a7%c3%a3o.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 14 May 2020).
- PLLENO. Plleno Arquitetura E Construções. Geotechnical Survey Report requested by the Federal University of Pará (Brazil) for the Northeast Pará Aquaculture Research Center (CEANPA). 2015. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- da Rocha, H.O.; Silva, M.W.C.; Marques, F.L.T.; Leite Filho, D.C. Magnetic gradiometry and ground penetrating radar applied in Estearia of Penalva (MA). Geol. USP Sér. Cient. 2015, 15, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.R., Jr.; Castro, D.L.; Jesus, T.E.S.; Lima Filho, F.P. Characterization of collapsed paleocave systems using GPR attributes. J. Appl. Geophys. 2014, 103, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelf, R. Where is True Time Zero? In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Grounds Penetrating Radar, Delft, The Netherlands, 21–24 June 2004; pp. 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Annan, A.P. Transmission dispersion and GPR. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 1996, 2, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMBRAPA (Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária). Recomendações de calagem e adubação para o estado do Pará, 2nd ed.; Brasil, E.C., Cravo, M.d.S., Viégas, I.d.J.M., Eds.; EMBRAPA: Brasília, Brazil, 2020; 424p. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- McNeill, J.D. Electrical Conductivity of Soils and Rock; Technical Note TN-5; Geonics Limited: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Sonkamble, S.; Chandra, S. GPR for earth and environmental applications: Case studies from India. J. Appl. Geophys. 2021, 193, 104422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, C.; Alcalá, F.J.; Carvalho, J.M.; Ribeiro, L. Current uses of ground penetrating radar in groundwater-dependent ecosystems research. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 868–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, H.; Doolittle, J. Soil layering and preferential flow impacts on seasonal changes of GPR signals in two contrasting soils. Geoderma 2014, 213, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nováková, E.; Karous, M.; Zajíček, A.; Karousová, M. Evaluation of ground penetrating radar and vertical electrical sounding methods to determine soil horizons and bedrock at the locality Dehtáře. Soil Water Res. 2013, 8, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doetsch, J.; Linde, N.; Pessognelli, M.; Green, A.G.; Günther, T. Constraining 3-D electrical resistance tomography with GPR reflection data for improved aquifer characterization. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 78, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simeoni, M.; Galloway, P.; O’neil, A.; Gilkes, R. A procedure for mapping the depth to the texture contrast horizon of duplex soils in south-western Australia using ground penetrating radar, GPS and kriging. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2009, 47, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Ortiz, D.; Pereira, M.; Martin-Crespo, T.; Rial, F.I.; Novo, A.; Lorenzo, H.; Vidal, J.R. Joint use of GPR and ERI to image the subsoil structure in a sandy coastal environment. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 56, 956–960. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, R.F.; Oliva, P.A.C.; Gomes, K.P.; Correia, K.A.; Pena, R.T.; da Silva, R.P. Application of geophysical tools for evaluation of adequate ponds for Aquaculture. In Proceedings of the 82nd EAGE Annual Conference & Exhibition, EAGE, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 18–21 October 2021. Paper Number 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafi, J.; Waheed, K.N.; Mirza, Z.S.; Zafarullah, M. Assessment of soil quality for aquaculture activities from four divisions of Punjab, Pakistan. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2021, 31, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswathy, R.; Ravisankar, T.; Ravichandran, P.; Vimala, D.D.; Jayanthi, M.; Muralidhar, M.; Manohar, C.; Vijay, M.; Santharupan, T.C. Assessment of soil and source water characteristics of disused shrimp ponds in selected coastal states of India and their suitability for resuming aquaculture. Indian J. Fish. 2016, 63, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, N.; Mussaa, B.; Masood, Z.; UR-Rehman, H.; Ullah, A.; Majeed, A. Study of Some Physiochemical Properties of Soil in Fish Pond at Circuit House, District Sibi of Province Balochistan, Pakistan. Glob. Vet. 2015, 14, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, W.S.; White, M.V.; Norris, H.A.; Berrigan, M.E. Hard clam (Mercenaria spp.) aquaculture in Florida, USA: Geographic information system applications to lease site selection. Aquac. Eng. 2000, 23, 203–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.K.; Kumar, P.; Pant, D.; Mohanty, R.K. Land suitability modelling for enhancing fishery resource development in Central Himalayas (India) using GIS and multi-criteria evaluation approach. Aquac. Eng. 2018, 83, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, R.; Mustafa, F.B.; Bhassu, S.; Azhar, N.A.A.; Bwadi, B.E.; Ahmad, N.S.B.N.; Ajeng, A.A. Evaluation of water and soil qualities for giant freshwater prawn farming site suitability by using the AHP and GIS approaches in Jelebu, Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia. AIMS Geosci. 2021, 7, 507–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, H.R.; Corrêia, A.F.; Feiden, A. Classification of Areas Suitable for Fish Farming Using Geotechnology and Multi-Criteria Analysis. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf 2019, 8, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghmashhadi, A.H.; Azizi, A.; Hoseinkhani, M.; Zahedi, S.; Cirella, G.T. Aquaculture Site Selection of Oncorhynchus Mykiss (Rainbow Trout) in Markazi Province Using GIS-Based MCDM. ISPRS Int. J Geo-Inf 2022, 11, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilpour-Poodeh, S.; Ghorbani, R.; Hosseini, S.A.; Salmanmahiny, A.; Rezaei, H.; Kamyab, H. A multi-criteria evaluation method for sturgeon farming site selection in the southern coasts of the Caspian Sea. Aquaculture 2019, 513, 734416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laama, C.; Bachari, N.E.I. Evaluation of site suitability for the expansion of mussel farming in the Bay of Souahlia (Algeria) using empirical models. J. Appl. Aquac. 2018, 31, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Krishnan, P.; Suryavanshi, A.S.; Choudhury, S.B.; Kantharajan, G.; Srinivasa Rao, C.; Manjulatha, C.; Babu, D.E. Identification of Suitable Aquaculture Sites Using Large-Scale Land Use and Land Cover Maps Factoring the Prevailing Regulatory Frameworks: A Case Study from India. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2021, 49, 725–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupandan, A.G.; Gernez, P.; Palmer, S.; Thomas, Y.; Barillé, L. Exploring South African Pacific oyster mariculture potential through combined Earth observation and bioenergetics modelling. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 24, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIAGAS. Groundwater Information System-CPRM/Geological Survey of Brazil (SGB). 2021. Available online: http://siagasweb.cprm.gov.br/layout/index.php (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- de Benedetto, D.; Montemurro, F.; Diacono, M. Repeated geophysical measurements in dry and wet soil conditions to describe soil water content variability. Sci. Agric. 2020, 77, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajícová, K.; Chuman, T. Application of ground penetrating radar methods in soil studies: A review. Geoderma 2019, 343, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.R.d.R.; Vidal-Torrado, P.; Modolo, A.J. Use of Ground Penetrating Radar to study spatial variability and soil stratigraphy. Eng. Agrícola 2019, 39, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minet, J.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Lambot, S.; Vanclooster, M. Temporal stability of soil moisture patterns measured by proximal ground-penetrating radar. Hydrol Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 10, 4063–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Lin, H.; Doolittle, J. Repeated electromagnetic induction surveys for determining subsurface hydrologic dynamics in an agricultural landscape. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1750–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taioli, F.; dos Santos, M.G.M.; Assine, M.L.; Mendes, D. How Ground Penetrating Radar helps to understand the Nhecolândia lakes landscape in the Brazilian Pantanal wetland. Braz. J. Geol. 2021, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Tang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Drahota, J. Using the electromagnetic induction survey method to examine the depth to clay soil layer (Bt horizon) in playa wetlands. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Ruiz, A.; Linde, N.; Keller, T.; Or, D. A review of geophysical methods for soil structure characterization. Rev. Geophys. 2019, 56, 672–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X. Experimental study of soil compaction effects on GPR signals. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 126, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz, E.; Shaw, R.K.; Gimenez, D.; Williams, C.A.; Kenny, L. Use of ground-penetrating radar to determine depth to compacted layer in soils under pasture. In Digital Soil Morphometrics; Hartemink, A., Minasny, B., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, N.R.; Costa, J.L.; Balzarini, M.; Angelini, H. Delineation of management zones with measurements of soil apparent electrical conductivity in the Southeastern Pampas. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 93, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.; Van Leeuwen, C.; Saussez, S.; Van Durmen, R.; Bogaert, P.; Moghadas, D.; de Rességuier, L.; Delvaux, B.; Vereecken, H.; Lambot, S. High-resolution imaging of a vineyard in south of France using ground-penetrating radar, electromagnetic induction and electrical resistivity tomography. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 78, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loperte, A.; Satriani, A.; Bavusi, M.; Lapenna, V.; Dellungo, S.; Sabelli, R.; Gizzi, F.T. Geophysical prospecting in archaeology: Investigations in SantaVenera, south suburb of Poseidonia-Paestum, Campania, southern Italy. J. Geophys. Eng. 2011, 8, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral, F.J.; Terrón, J.M.; Silva, J.R.M. Delineation of management zones using mobile measurements of soil apparent electrical conductivity and multivariate geostatistical techniques. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 106, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.; Basso, B.; Celano, G.; Bitella, G.; Morelli, C.; Rossi, R. In situ detection of tree root distribution and biomass by multi-electrode resistivity imaging. Tree Physiol. 2008, 28, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, Y.; Hubbard, S.S. Hydrogeophysics. Water Science and Technology Library; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L.; Plant, R.E. Applications of apparent soil electrical conductivity in precision agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, H.; Fleige, H.; Rabbel, W.; Horn, R. Applicability of geophysical prospecting methods for mapping soil compaction variability of soil texture on farm land. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2005, 168, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, S.; Grote, K.; Rubin, Y. Mapping the volumetric soil water content of a California vineyard using high-frequency GPR ground wave data. Lead. Edge 2002, 21, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradipta, A.; Soupios, P.; Kourgialas, N.; Doula, M.; Dokou, Z.; Makkawi, M.; Alfarhan, M.; Tawabini, B.; Kirmizakis, P.; Yassin, M. Remote Sensing, Geophysics, and Modeling to Support Precision Agriculture—Part 2: Irrigation Management. Water 2022, 14, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Depth (m) | SPT Probes SP 01 and SP 02 |
|---|---|
| 0–4.769 | Sandy silt, yellow |
| 4.77–9.299 | Medium clay with pebbles |
| 9.30–10.45 | Coarse sand, reddish and yellow |
| Depth (m) | SPT Probe SP 03 |
|---|---|
| 0–4.769 | Sandy silt, yellow |
| 4.77–9.299 | Medium clay with pebbles |
| 9.30–10.50 | Coarse sand, reddish and yellow |
| Depth (m) | Lithology [60] | Wave Velocity (m/ns) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–4.769 | Sandy silt, yellow | 0.092 | 10.63 |
| 4.77–8.5 | Medium clay with pebbles | 0.070 | 18.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pena, R.W.T.; Oliva, P.A.C.; Abrunhosa, F.A. Application of the Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and Electromagnetic (EM34-3) Geophysical Tools and Sedimentology for the Evaluation of the Subsurface of Sites Earmarked for Aquaculture Ponds in the Amazon Region of Northern Brazil. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11107. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131911107
Pena RWT, Oliva PAC, Abrunhosa FA. Application of the Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and Electromagnetic (EM34-3) Geophysical Tools and Sedimentology for the Evaluation of the Subsurface of Sites Earmarked for Aquaculture Ponds in the Amazon Region of Northern Brazil. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(19):11107. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131911107
Chicago/Turabian StylePena, Ramon Wagner Torres, Pedro Andrés Chira Oliva, and Fernando Araújo Abrunhosa. 2023. "Application of the Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and Electromagnetic (EM34-3) Geophysical Tools and Sedimentology for the Evaluation of the Subsurface of Sites Earmarked for Aquaculture Ponds in the Amazon Region of Northern Brazil" Applied Sciences 13, no. 19: 11107. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131911107
APA StylePena, R. W. T., Oliva, P. A. C., & Abrunhosa, F. A. (2023). Application of the Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) and Electromagnetic (EM34-3) Geophysical Tools and Sedimentology for the Evaluation of the Subsurface of Sites Earmarked for Aquaculture Ponds in the Amazon Region of Northern Brazil. Applied Sciences, 13(19), 11107. https://doi.org/10.3390/app131911107








