Real-Time Interaction for 3D Pixel Human in Virtual Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a novel pixel-style avatar to solve segmented human real-time 3D visualization problems in a virtual environment.
- We use 3D pose data to generate a 3D pixel avatar arm and use high-resolution facial video to reflect facial expressions, enabling more realistic interactions and intuitive communication.
2. Related Works
2.1. Avatars in Virtual Meetings
2.2. Pixel-Style Art
2.3. Human Matting and Segmentation
2.4. Pose Estimation
3. Pixel-Style Avatar Generation Method
3.1. Matting and Pose Estimation Methods
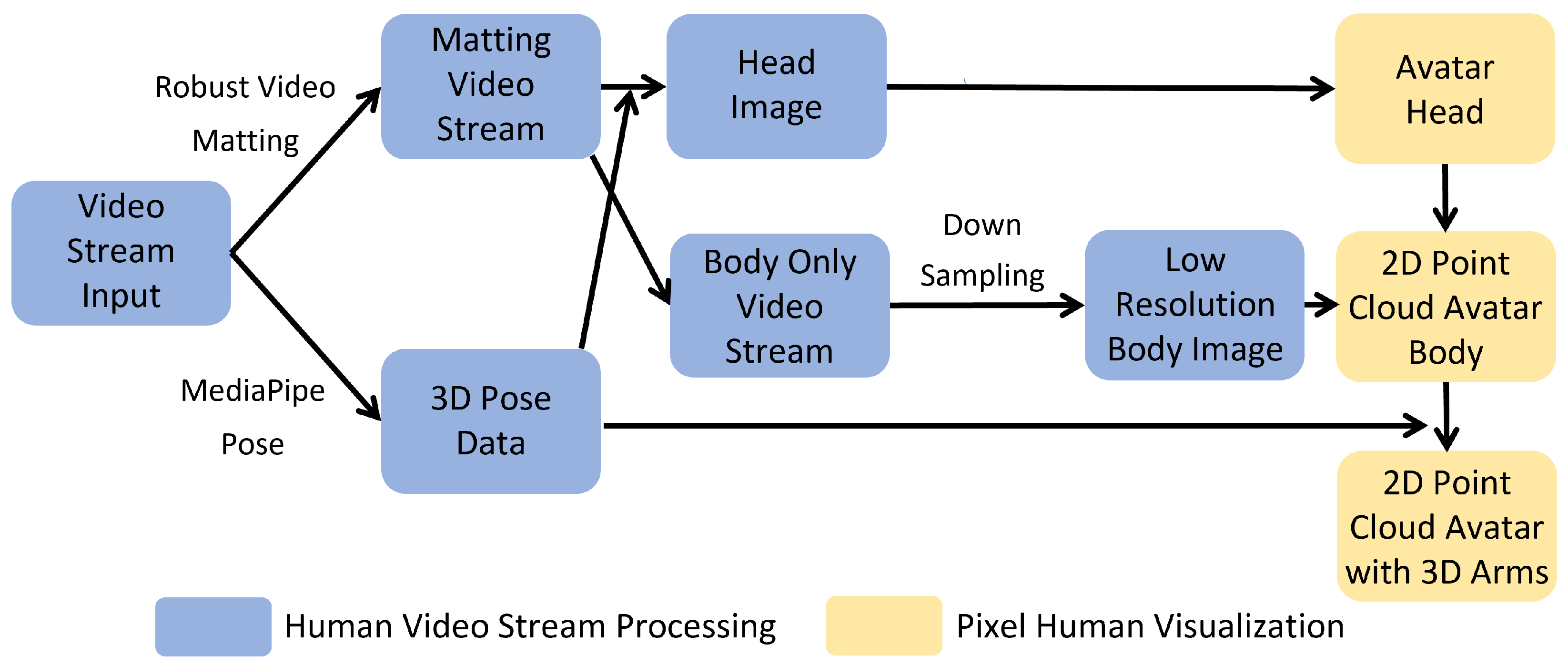
3.2. Human Video Stream Processing
3.3. Pixel Human Visualization
3.3.1. 2D Head Visualization
3.3.2. Point Cloud Body Visualization
3.3.3. Interactive Arm Generation
4. Implemented Experiences
5. Experiments and Results
5.1. Environments and Participants
5.2. Comparative Experiment
- Q1.
- Can the avatar reflect the shape and texture of the arms of a real person?
- Q2.
- How was the interactive experience with the virtual objects?
- Q3.
- How realistic was the meeting? Was there a feeling of coexisting in the same space with other participants?
5.3. Usability Experiment
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zoom. Available online: https://zoom.us/ (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Spatial—Metaverse Spaces That Bring Us Together. Available online: https://spatial.io/ (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Chen, G.; Tong, X.; Guo, B. VirtualCube: An Immersive 3D Video Communication System. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2022, 28, 2146–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azure Kinect DK. Available online: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/kinect-dk/#overview (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Minecraft Image Converter Online. Available online: https://minecraftart.netlify.app/ (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Make Pixel Art in Seconds with Machine Learning. Available online: https://inikolaeva.medium.com/make-pixel-art-in-seconds-with-machine-learning-e1b1974ba572 (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Intel® RealSense™. Available online: https://www.intelrealsense.com/ (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Oculus VR Headsets, Games & Equipment—Meta Quest. Available online: https://store.facebook.com/en/quest/ (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Han, B.; Kim, G.J. AudienceMR: Extending the Local Space for Large-Scale Audience with Mixed Reality for Enhanced Remote Lecturer Experience. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakanen, M.; Alavesa, P.; van Berkel, N.; Koskela, T.; Ojala, T. “Nice to see you virtually”: Thoughtful design and evaluation of virtual avatar of the other user in AR and VR based telexistence systems. Entertain. Comput. 2022, 40, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- PixelMe: Convert Your Photo into Pixelart. Available online: https://pixel-me.tokyo/en/ (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Iseringhausen, J.; Weinmann, M.; Huang, W.; Hullin, M.B. Computational parquetry: Fabricated style transfer with wood pixels. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2020, 39, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Sun, K.; Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Huang, Y.; Yan, Y. Blendmask: Top-down meets bottom-up for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 8573–8581. [Google Scholar]
- Ranftl, R.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Koltun, V. Vision transformers for dense prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 12179–12188. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, S.; Jayaram, V.; Curless, B.; Seitz, S.M.; Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I. Background matting: The world is your green screen. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 2291–2300. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Ryabtsev, A.; Sengupta, S.; Curless, B.L.; Seitz, S.M.; Kemelmacher-Shlizerman, I. Real-time high-resolution background matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8762–8771. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Price, B.; Cohen, S.; Huang, T. Deep image matting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2970–2979. [Google Scholar]
- Forte, M.; Pitié, F. F, B, Alpha Matting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.07711. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.; Lam, T.L.; Xu, Y. Semantic-guided Automatic Natural Image Matting with Trimap Generation Network and Light-weight Non-local Attention. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.17020. [Google Scholar]
- Siam, M.; Mahgoub, H.; Zahran, M.; Yogamani, S.; Jagersand, M.; El-Sallab, A. Modnet: Motion and appearance based moving object detection network for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 2859–2864. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.; Wang, L.; Luo, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M.T. Cross-domain complementary learning using pose for multi-person part segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 31, 1066–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BodyPix: Real-Time Person Segmentation in the Browser with TensorFlow.js. Available online: https://blog.tensorflow.org/2019/11/updated-bodypix-2.html (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Lin, S.; Yang, L.; Saleemi, I.; Sengupta, S. Robust High-Resolution Video Matting with Temporal Guidance. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 4–8 January 2022; pp. 238–247. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K. Fast end-to-end trainable guided filter. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1838–1847. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Liu, H.; Ding, R.; Liu, M.; Wang, P.; Yang, W. Exploiting temporal contexts with strided transformer for 3d human pose estimation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Li, F.; Weng, R.; Choi, W. Ray3D: Ray-based 3D human pose estimation for monocular absolute 3D localization. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.11471. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, C.; Papava, D.; Olaru, V.; Sminchisescu, C. Human3. 6m: Large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3d human sensing in natural environments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 36, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugaresi, C.; Tang, J.; Nash, H.; McClanahan, C.; Uboweja, E.; Hays, M.; Zhang, F.; Chang, C.L.; Yong, M.G.; Lee, J.; et al. Mediapipe: A framework for building perception pipelines. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.08172. [Google Scholar]
- MediaPipe Pose. Available online: https://google.github.io/mediapipe/solutions/pose.html (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Bazarevsky, V.; Grishchenko, I.; Raveendran, K.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, F.; Grundmann, M. Blazepose: On-device real-time body pose tracking. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.10204. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Bazavan, E.G.; Zanfir, A.; Freeman, W.T.; Sukthankar, R.; Sminchisescu, C. Ghum & ghuml: Generative 3d human shape and articulated pose models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 6184–6193. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J. DepthFormer: Exploiting Long-Range Correlation and Local Information for Accurate Monocular Depth Estimation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.14211. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Han, M.K.; Ko, D.W.; Suh, I.H. From big to small: Multi-scale local planar guidance for monocular depth estimation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.10326. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, A.; Arora, C. Attention Attention Everywhere: Monocular Depth Prediction with Skip Attention. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.09071. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yeung, D.Y.; Chen, Q. 3D-Aware Indoor Scene Synthesis with Depth Priors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.08553. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Lin, S.Y.; Xie, Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Fan, W.; Xie, X. DGGAN: Depth-image guided generative adversarial networks for disentangling RGB and depth images in 3D hand pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 411–419. [Google Scholar]
- Intel® Core™ i7 Processors. Available online: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/details/processors/core/i7.html (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- NVIDIA Graphic Card. Available online: https://www.nvidia.com/en-gb/geforce/graphics-cards/30-series/rtx-3080-3080ti/ (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- New Life Platform—ABKO. Available online: https://abkoglobal.com/ (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Bangor, A.; Kortum, P.; Miller, J. The system usability scale (SUS): An empirical evaluation. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2008, 24, 574–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Card, S.K.; Moran, T.P.; Newell, A. The Psychology of Human-Computer Interaction; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.Y.; Thropp, J.E. Review of low frame rate effects on human performance. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A Syst. Humans 2007, 37, 1063–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, B.; Walker, N.; Ribarsky, W.; Spaulding, V. Effects of variation in system responsiveness on user performance in virtual environments. Hum. Factors 1998, 40, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, H.; Kim, C.-H. Real-Time Interaction for 3D Pixel Human in Virtual Environment. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020966
Deng H, Zhang Q, Jin H, Kim C-H. Real-Time Interaction for 3D Pixel Human in Virtual Environment. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(2):966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020966
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Haoke, Qimeng Zhang, Hongyu Jin, and Chang-Hun Kim. 2023. "Real-Time Interaction for 3D Pixel Human in Virtual Environment" Applied Sciences 13, no. 2: 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020966
APA StyleDeng, H., Zhang, Q., Jin, H., & Kim, C.-H. (2023). Real-Time Interaction for 3D Pixel Human in Virtual Environment. Applied Sciences, 13(2), 966. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13020966






