Gaussian Mixture Model for Marine Reverberations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
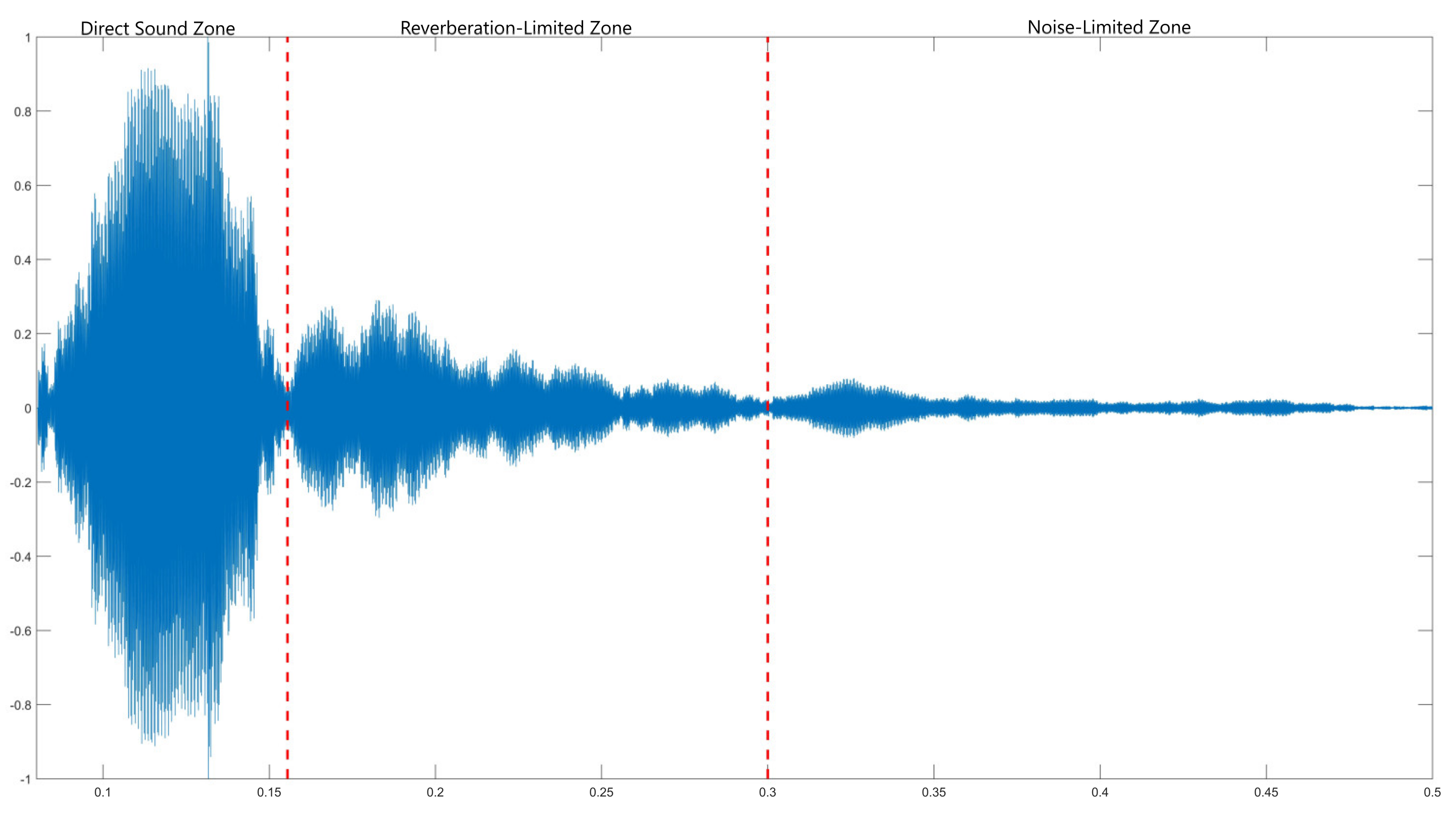
2. Theoretical and Statistical Distribution Characteristics of Reverberation
3. Statistical Modeling of Ocean Reverberation Data Based on the Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) Method
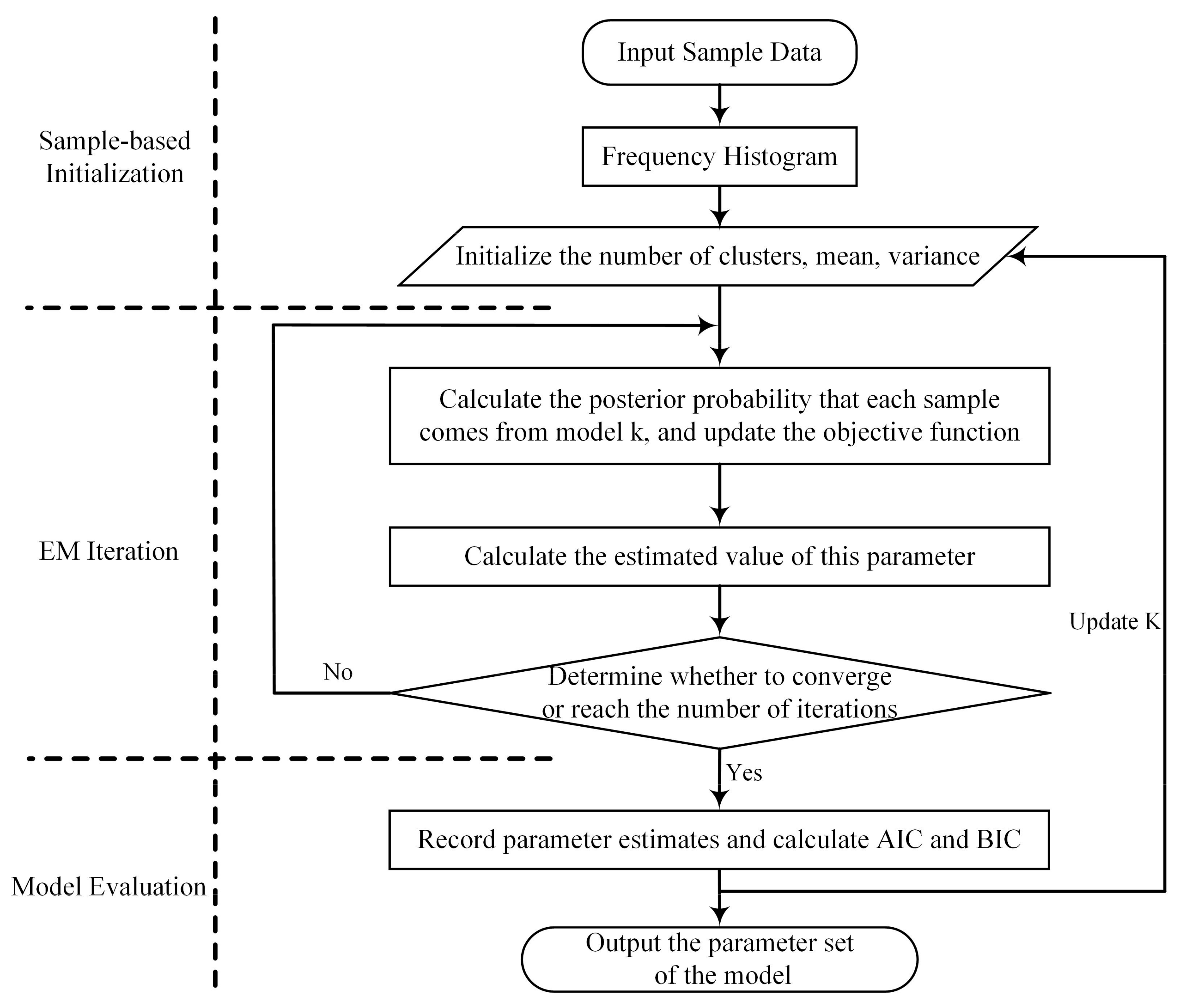
3.1. Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) and Its Parameter Estimation Method (EM Algorithm)
3.2. Improved EM Parameter Estimation Method
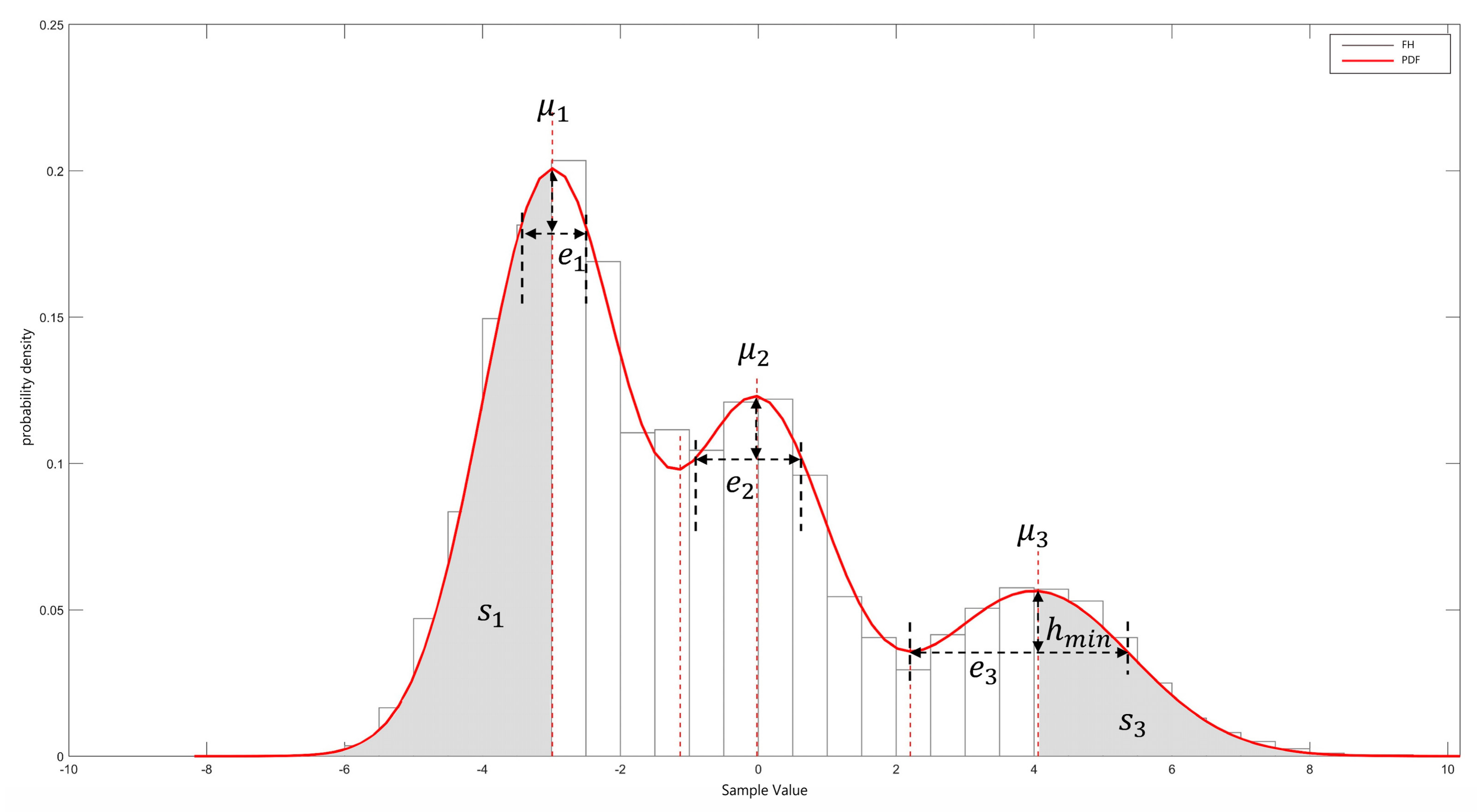
3.2.1. Parameter Initialization Based on Reverberation Data
3.2.2. GMM Parameter Estimation Based on EM Algorithm
3.2.3. Model Evaluation
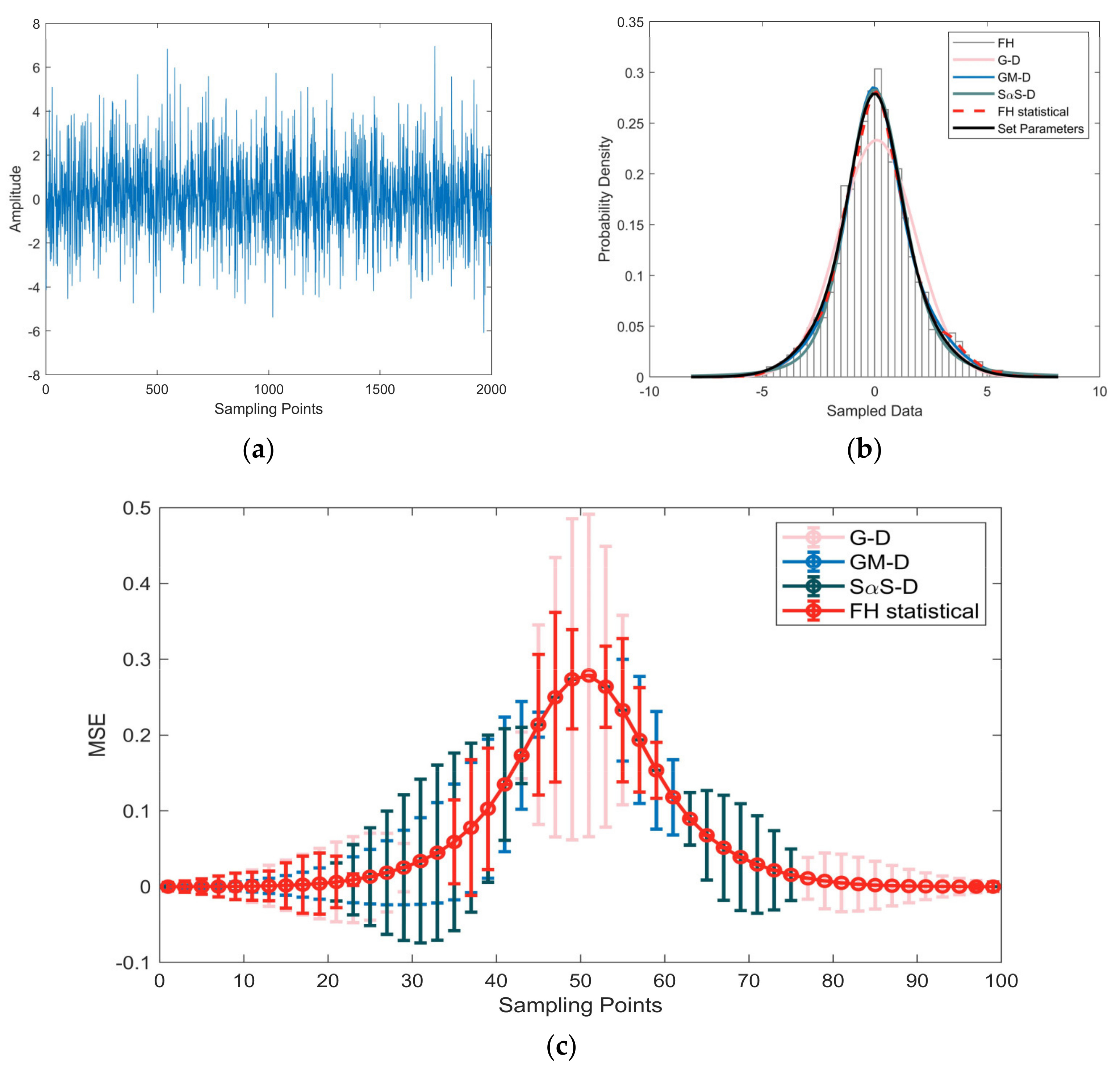
4. Simulation and Experiments Analysis
5. Verification Based on the Measured Data
5.1. Method Validation
5.2. Analysis of Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| EM | Expectation–maximization |
| FOA | First Order Ambisonics |
| GMM | Gaussian Mixture Model |
| SαS | Symmetric Alpha–Stable |
| GGMM | Generalized Gaussian Mixture Model |
| BGMM | Bounded Gaussian Mixture Model |
| BGGMM | Bounded Generalized Gaussian Mixture Model |
| Probability density function | |
| FH | Frequency histogram |
| LFM | Linear Frequency Modulation |
| CW | Continuous wave |
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
References
- Wang, L.; Wang, Q. The influence of marine biological noise on sonar detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/OES China Ocean Acoustics (COA), Harbin, China, 9–11 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, T. Shengna Jishu, 2nd ed.; Harbin Engineering University Press: Harbin, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, P. Theoretical Model of Reverberation Noise. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1964, 36, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olishevski, B. Statistical Characteristics of Sea Reverberation, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Middleton, D. New physical–statistical methods and models for clutter and reverberation: The ka–distribution and related probability structures. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1999, 24, 261–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernkopf, F.; Bouchaffra, D. Genetic–based EM algorithm for learning gaussian mixture models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, P. Gaussian mixture model for reverberation. Tech. Acoust. 2007, 26, 514–518. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Wei, H.; Lou, L. Oceanic reverberation probability density modeling based on symmetric alpha–stable distribution. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2021, 42, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Wang, P.; Gu, X. Comparison of two EM algorithms for gaussian mixture parameter estimation. Tech. Acoust. 2014, 33, 539–543. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Yu, Z. An improved expectation–maximum algorithm. J. Jilin Univ. (Sci. Ed.) 2022, 60, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Najar, F.; Bourouis, S.; Bouguila, N. A comparison between different gaussian–based mixture models. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACS 14th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Hammamet, Tunisia, 30 October–3 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Yu, R.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, T. Image denoising using asymmetric gaussian mixture models. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Symposium in Sensing and Instrumentation in IoT Era (ISSI), Shanghai, China, 6–7 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Przyborowski, M.; Ślęzak, D. Approximation of the expectation–maximization algorithm for gaussian mixture models on big data. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Kyoto, Japan, 13–16 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Gong, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, G. Study of characteristics of acoustic intensity in acoustic vector ocean reverberation based on CW pulse. J. Nav. Univ. Eng. 2022, 34, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Ivakin, A.N.; Williams, K.L. Midfrequency acoustic propagation and reverberation in a deep ice–covered arctic ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2022, 152, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, F.; Zhang, X.; Han, J. Experimental analysis of statistical property of low frequency reverberation envelope in shallow water. In Proceedings of the 2021 OES China Ocean Acoustics, Heilongjiang, China, 14–17 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Cheng, T. Active sonar reverberation suppression based on beam space data normalization. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Xiamen, China, 22–25 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q. Introduction to Sonar Signal Processing, 2nd ed.; Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Glodek, M.; Schels, M.; Schwenker, F. Ensemble gaussian mixture models for probability density estimation. Comput. Stat. 2013, 28, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chu, F.; Zhu, D. Research on gaussian mixture auto–regressive reverberation modeling and whitening algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing, Xi’an, China, 17–20 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanović, A.; Perić, Z.; Nikolić, J. The effect of uniform data quantization on GMM–based clustering by means of EM algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 20th International Symposium INFOTEH–JAHORINA, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, 17–19 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kasim, F.A.B.; Pheng, H.S.; Nordin, S.Z.B. Gaussian mixture modelexpectation maximization algorithm for brain images. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Sciences (AiDAS), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–9 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Stepashko, V. Asymptotic properties of a class of criteria for best model selection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 15th International Conference on Computer Sciences and Information Technologies, Zbarazh, Ukraine, 23–26 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Zhou, L. Model selection using modified AIC and BIC in joint modeling of paired functional data. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2010, 80, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Tarokh, V.; Yang, Y. Bridging AIC and BIC: A new criterion for autoregression. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2017, 64, 4024–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Wen, H.; Yang, Y. A parameter estimation method of α stable distribution and its application in the statistical modeling of ice–generated noise. Acta Acust. 2023, 48, 319–326. [Google Scholar]

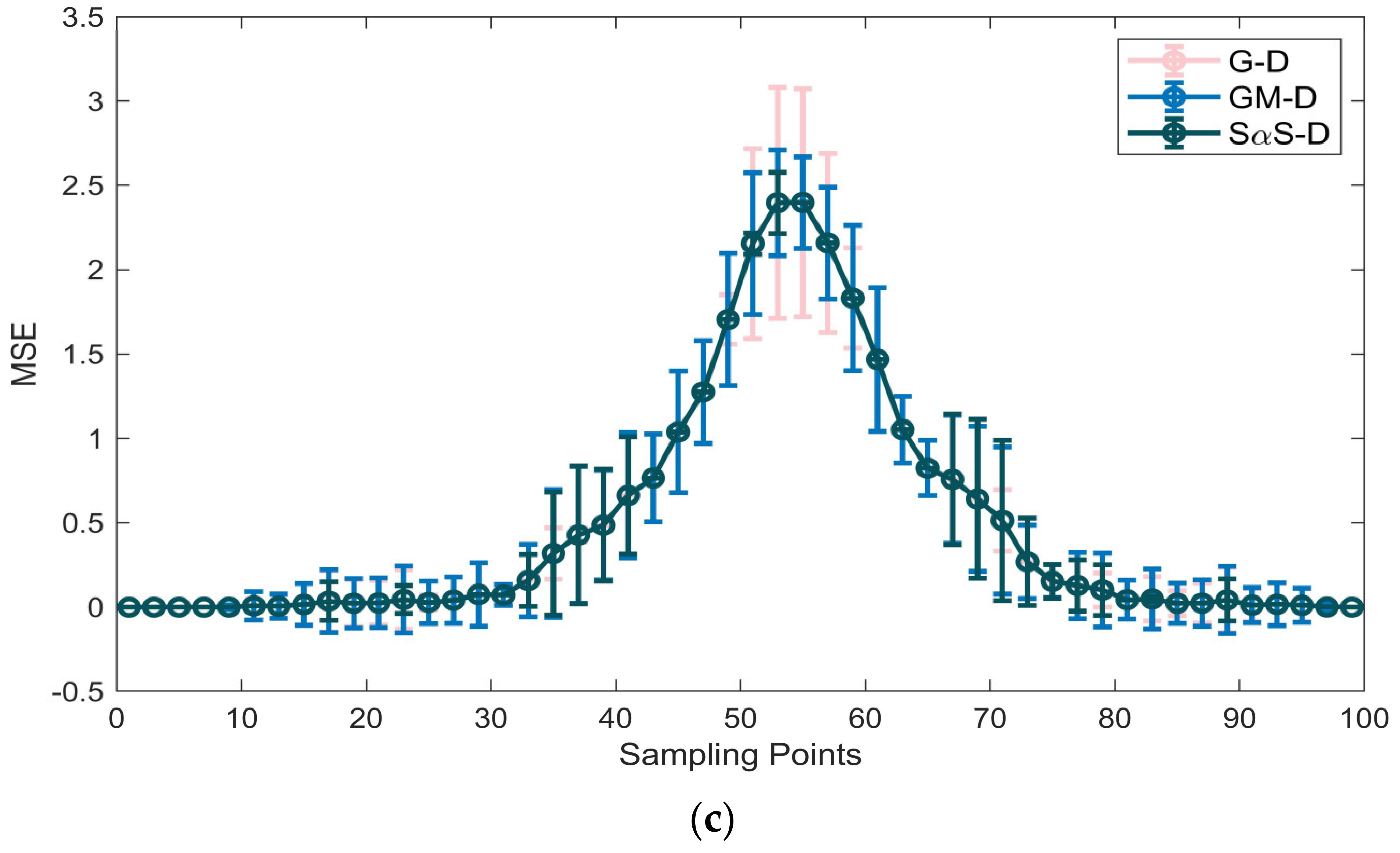
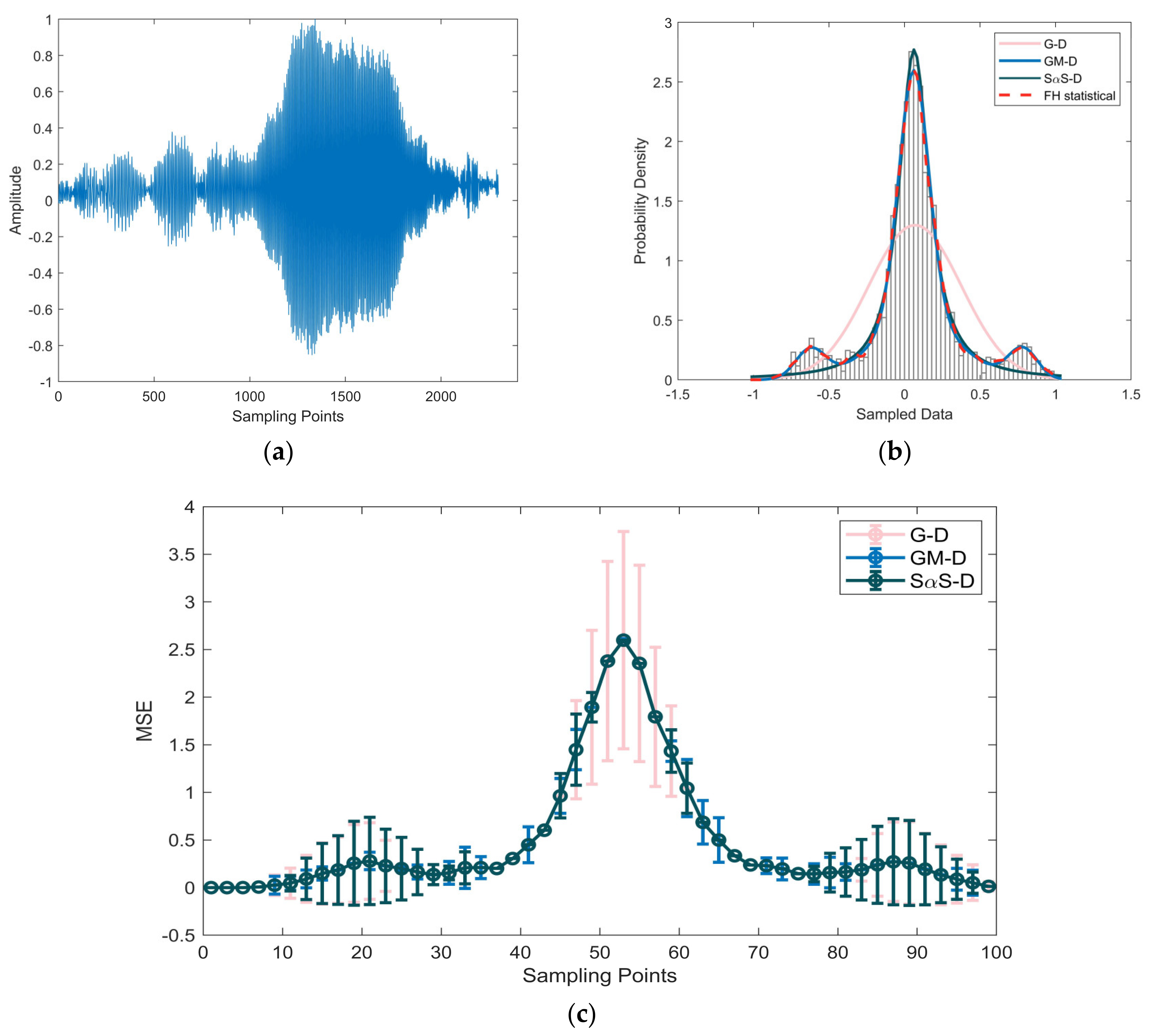
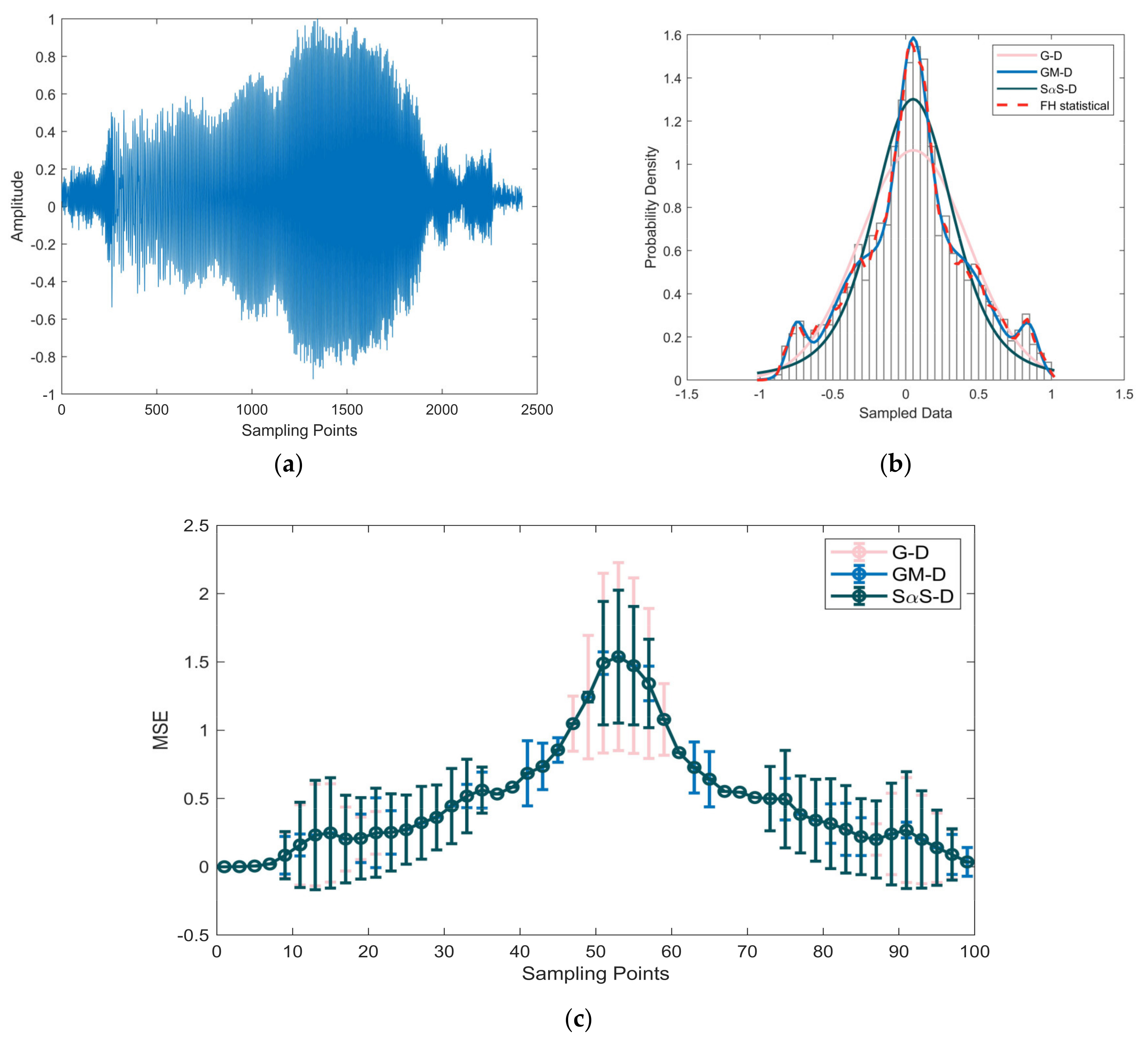
| Distribution | G–D | SαS–D | GM–D | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | |||||||||
| Estimation | 0.096 | 1.710 | 1.579 | 0.149 | 1.011 | 0.141 | 0.648 | 0.185 | 2.015 |
| 0.352 | −0.068 | 0.881 | |||||||
| MSE | 2.2 × 10−4 | 2.4 × 10−5 | 1.8 × 10−5 | ||||||
| Distribution | G–D | SαS–D | GM–D | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | |||||||||
| Estimation | −0.144 | 0.271 | 1.430 | 0.112 | −0.148 | −0.123 | 0.385 | −0.123 | 2.091 |
| 0.615 | −0.158 | 0.267 | |||||||
| MSE | 0.0420 | 0.0062 | 0.0009 | ||||||
| Distribution | G–D | SαS–D | GM–D | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | |||||||||
| Estimation | −0.144 | 0.271 | 1.430 | 0.112 | −0.148 | −0.123 | 0.248 | 0.004 | 0.013 |
| 0.692 | 0.692 | 0.037 | |||||||
| 0.060 | 0.031 | 0.051 | |||||||
| MSE | 0.5546 | 0.0550 | 0.0139 | ||||||
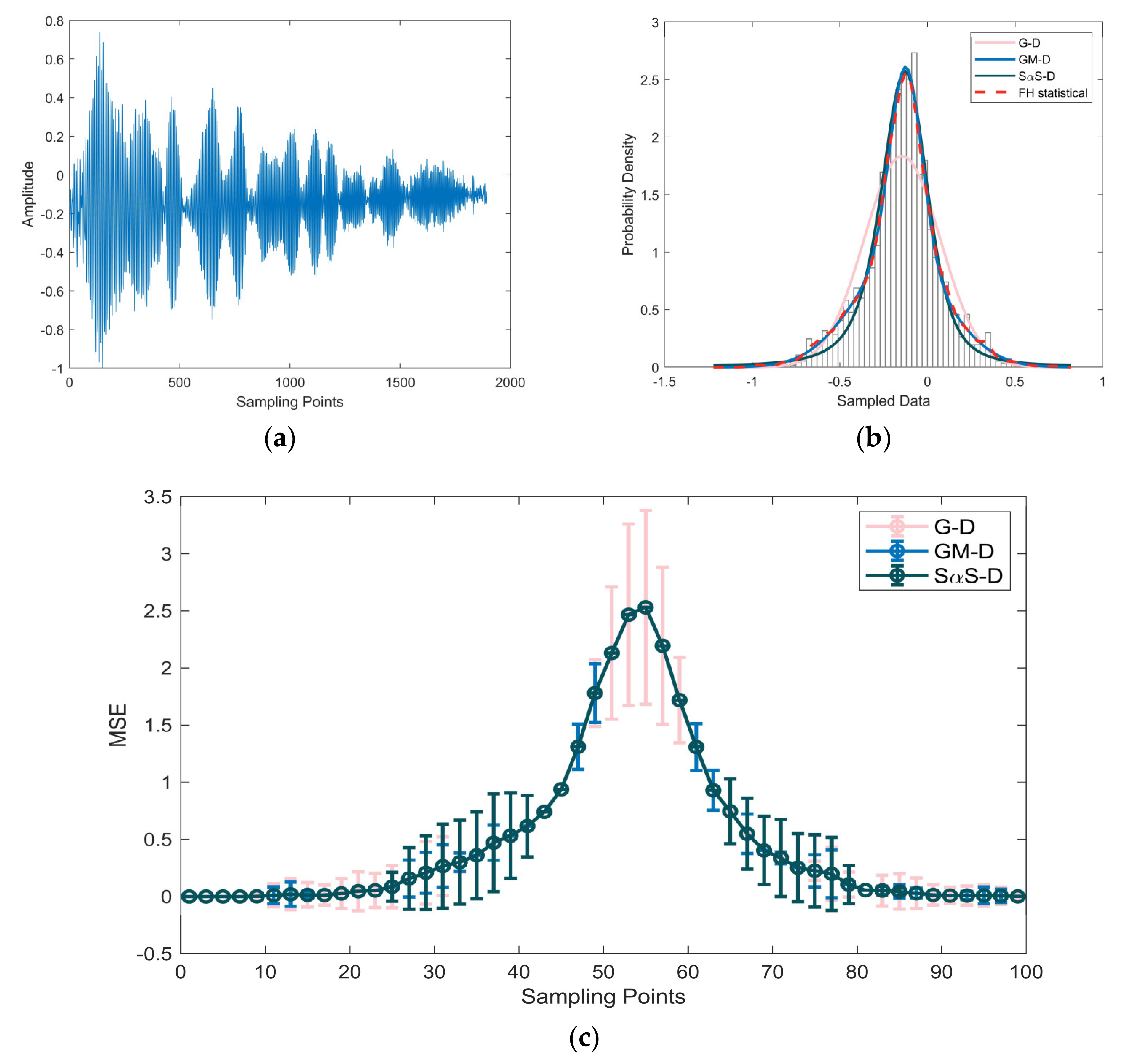
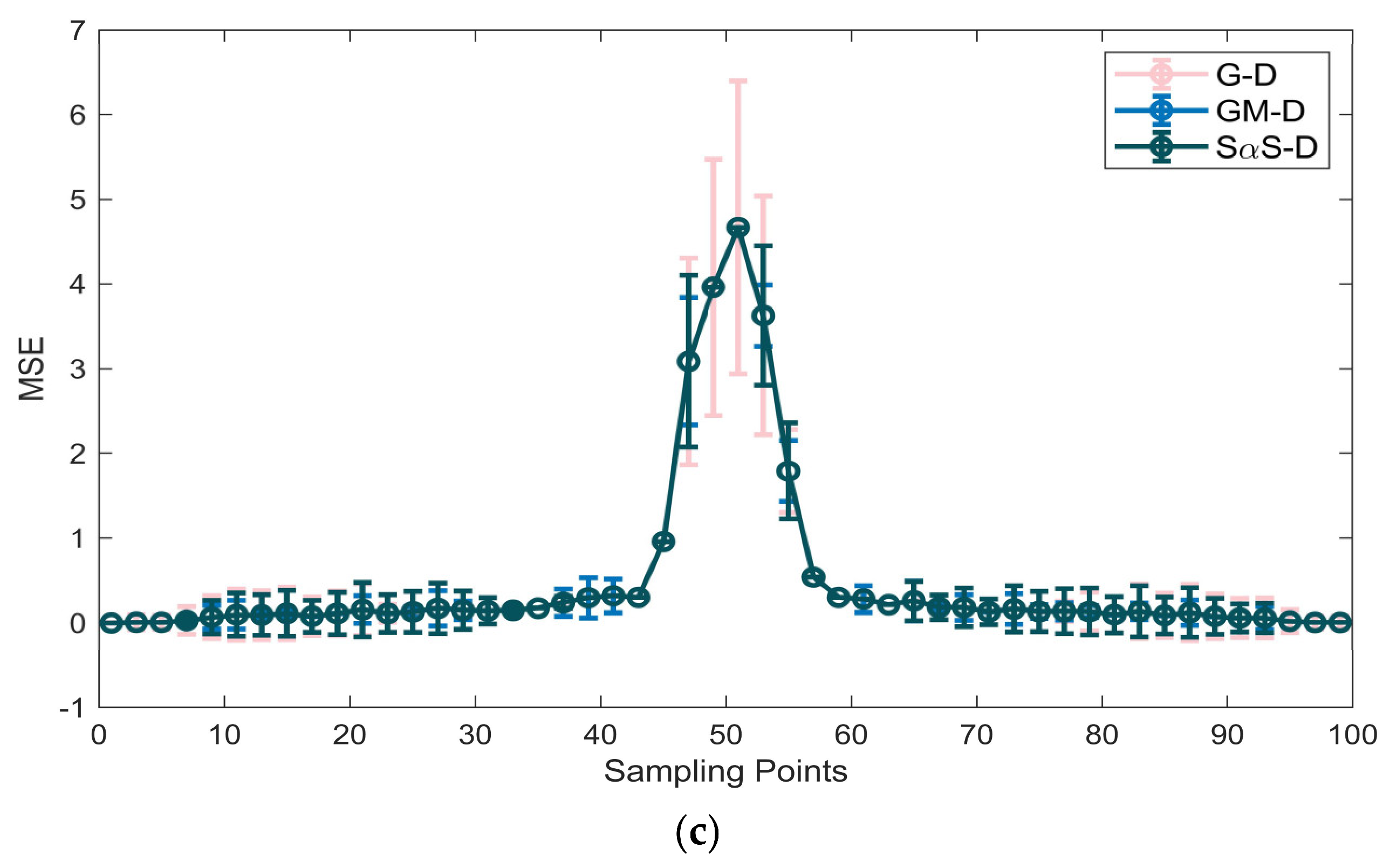
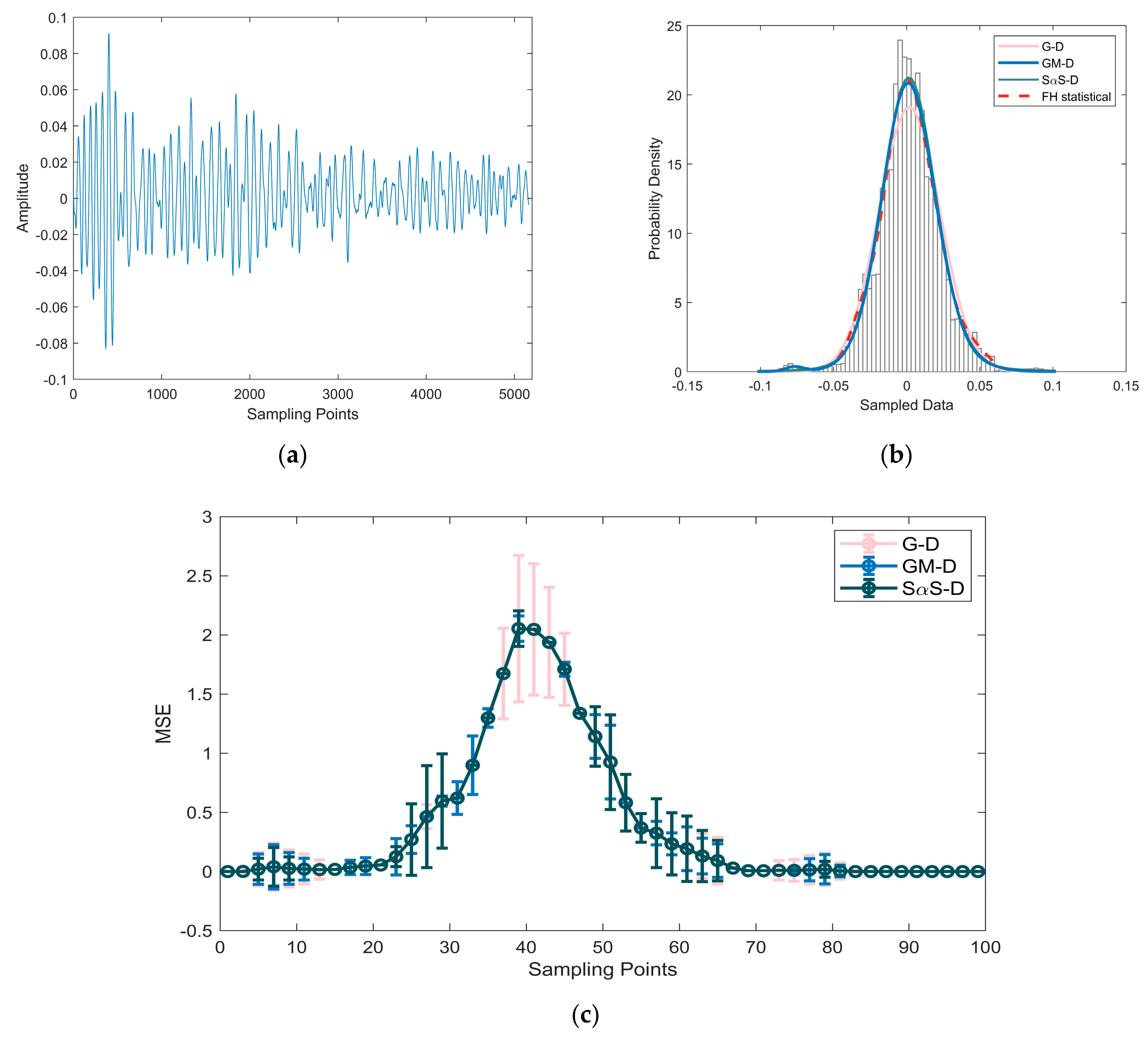
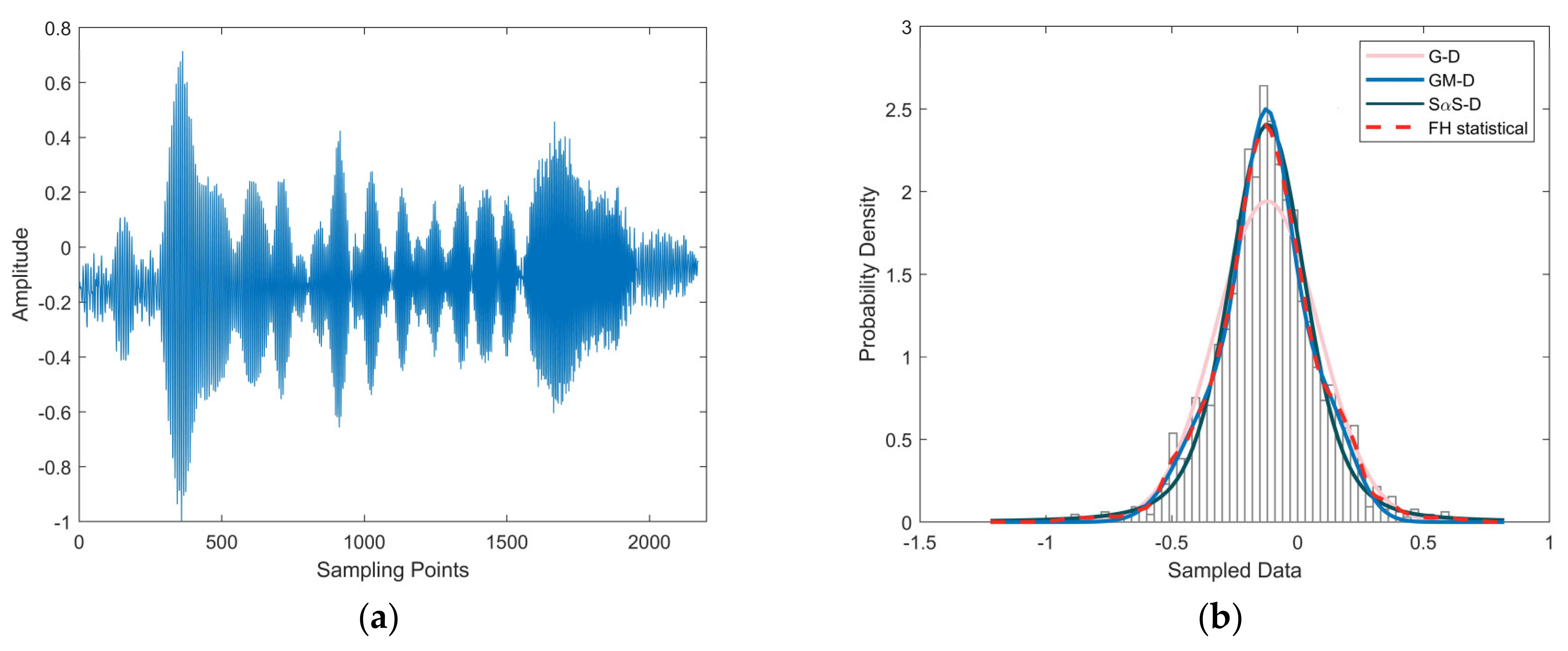
| Data | Figure 6a | Figure 7a | Figure 8a | Figure 9a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | |
| 0.0107 | 0.0170 | 0.0189 | 0.0230 | |
| 6 | 5 | 4 | 6 | |
| 0.0015 | 0.0015 | 0.0013 | 0.0006 | |
| 6 | 5 | 4 | 6 | |
| 0.0031 | 0.0015 | 0.0013 | 0.0006 | |
| 3 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| 0.0031 | 0.0027 | 0.0013 | 0.0013 |
| Parameter | SαS–D [] | GM–D [] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data | |||||||
| Figure 6a | 1.627 | 0.151 | 0.133 | 0.024 | 0.767 | 0 | 0.023 |
| 0.206 | 0.0138 | 0.015 | |||||
| 0.027 | −0.037 | 0.100 | |||||
| Figure 7b | 1.077 | 0.030 | 0.112 | 0.093 | 0.741 | −0.087 | 0.149 |
| 0.254 | −0.096 | 0.057 | |||||
| 0.005 | −0.656 | 0.253 | |||||
| Figure 8b | 1.606 | −0.028 | 0.09 | −0.09 | 0.514 | 0.062 | 0.098 |
| 0.061 | −0.062 | 0.281 | |||||
| 0.354 | 0.077 | 0.253 | |||||
| 0.061 | 0.782 | 0.096 | |||||
| Figure 9b | 1.537 | 0.010 | 0.220 | 0.053 | 0.255 | 0.420 | 0.196 |
| 0.036 | 0.847 | 0.068 | |||||
| 0.032 | −0.752 | 0.059 | |||||
| 0.372 | 0.060 | 0.115 | |||||
| 0.305 | −0.272 | 0.221 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, T.; Wen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, B.; Zhou, M. Gaussian Mixture Model for Marine Reverberations. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12063. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132112063
Sun T, Wen Y, Zhang X, Jia B, Zhou M. Gaussian Mixture Model for Marine Reverberations. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(21):12063. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132112063
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Tongjing, Yabin Wen, Xuegang Zhang, Bing Jia, and Mengwei Zhou. 2023. "Gaussian Mixture Model for Marine Reverberations" Applied Sciences 13, no. 21: 12063. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132112063
APA StyleSun, T., Wen, Y., Zhang, X., Jia, B., & Zhou, M. (2023). Gaussian Mixture Model for Marine Reverberations. Applied Sciences, 13(21), 12063. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132112063





