Complimentary Staining of Caries Detector Dyes in Primary Teeth with or without the Application of a Dentine Bonding Agent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Randomization and Blinding
2.2. Sample Preparation
- Group I: dye application without a dentine bonding agent;
- Group II: dye application after being smeared with a dentine bonding agent.
Bonding Agent Application
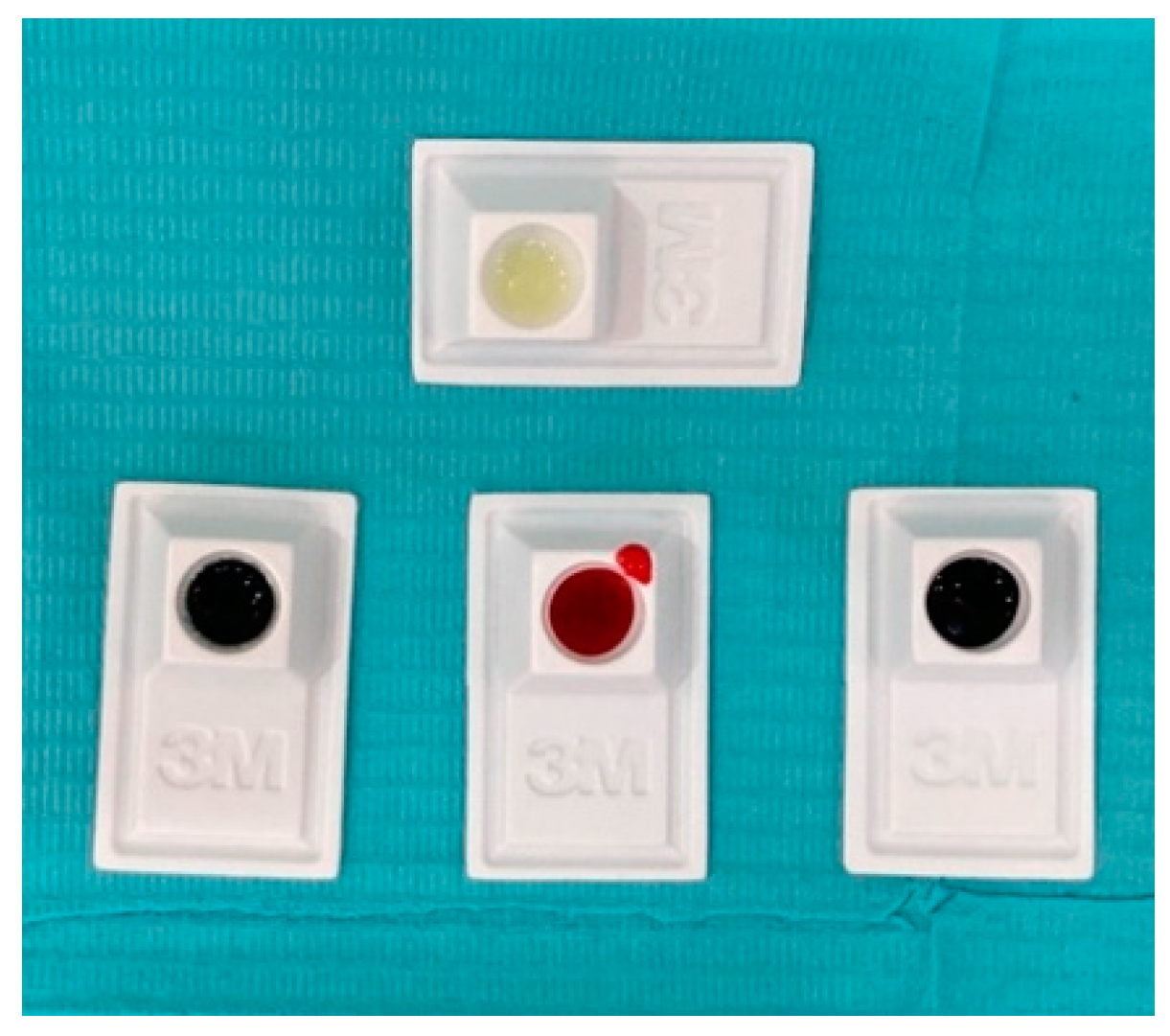
2.3. Caries Indicator Dye Application and Staining Assessment
- Group A Snoop—blue color (SNOOP Caries Detecting Dye—Pulpdent Corporation, Watertown, MA, USA).
- Group B Sable seek—black color (Ultradent Sable™ Seek™ Caries Indicator, Aam Westhover Berg, Germany).
- Group C Elements—pink color (Elements, Caries Indicator, Industrial Estate, Digiana, Jammu, India).
2.4. Removal of Staining
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iwami, Y.; Hayashi, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Hayashi, M.; Takeshige, F.; Ebisu, S. Evaluating the objectivity of caries removal with a caries detector dye using color evaluation and PCR. J. Dent. 2007, 35, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberson, M.; Heymann, O. Sturdevant’s Art and Science of Operative Dentistry, 5th ed.; Mosby: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2006; pp. 308–311. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, V.; Craig, R.G.; Curro, F.A.; Green, W.S.; Ship, J.A. Treatment of deep carious lesions by complete excavation or partial removal: A critical review. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2008, 139, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyas, M.J.; Anusavice, K.J.; Frencken, F.E.; Mount, G.J. Minimal intervention dentistry—A review. FDI Commission Project 1-97. Int. Dent. J. 2000, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch-Kinch, C.A.; McLean, M.E. Minimally invasive dentistry. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2003, 134, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mount, G.J.; Ngo, H. Minimal intervention; a new concept for operative dentistry. Quintessence Int. 2000, 31, 527–533. [Google Scholar]
- FDI. FDI Policy Statement: Minimal Intervention in the Management of Dental Caries; Adopted by the FDI General Assembly: 1 October 2002-Vienna; FDI: Vienna, Austria, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fusayama, T.; Terashima, S. Differentiation of two layers of carious dentin by staining. J. Dent. Res. 1972, 51, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusayama, T. Two layers of carious dentin; diagnosis and treatment. Oper. Dent. 1979, 4, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ohgushi, K.; Fusayama, T. Electron microscopic structure of the two layers of carious dentin. J. Dent. Res. 1975, 54, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuboki, Y.; Ohgushi, K.; Fusayama, T. Collagen biochemistry of two layers of carious dentin. J. Dent. Res. 1977, 56, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyauchi, H.; Iwaku, M.; Fusayama, T. Physiological recalcification of carious dentin. Bull. Tokyo Med. Dent. Univ. 1978, 25, 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Watson, T.F.; Kidd, E.A. Dentine caries: Take it or leave it? Dent. Update 2000, 27, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, E.; Toyston-Bechal, S.; Beighton, D. Microbiological validation of assessments of caries activity during cavity preparation. Caries Res. 1993, 27, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weerheijm, K.L.; de Soet, J.J.; van Amirongen, W.E.; de Graaff, J. The effect of grass-ionomer cement on caries dentin: An in vivo study. Caries Res. 1993, 27, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, E.A.; Fejerskov, O.; Mjor, I. Caries removal and the pulpo-dentinal complex. In Dental Caries: The Disease and Its Clinical Management, 1st ed.; Fejerskov, O., Kidd, E., Eds.; Blackwell Munksgaard: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 267–274. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.H.; Charbeneau, G.T. A comparison of digital and optical criteria for detecting carious dentin. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1985, 53, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, E.A.; Joyston-Bechal, S.; Beighton, D. The use of a caries detector dye during cavity preparation: A microbiological assessment. Br. Dent. J. 1993, 174, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusayama, T. Clinical guide removing caries using a caries-detecting solution. Quintessence Int. 1988, 19, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zacharia, M.A.; Munshi, A.K. Microbiological assessment of dentin stained with a caries detector dye. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 1995, 19, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Itoh, K.; Kusunoki, M.; Oikawa, M.; Tani, C.; Hisamitsu, H. In vitro comparison of three caries dyes. Am. J. Dent. 2009, 22, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Javaheri, M.; Maleki-Kambakhsh, S.; Etemad-Moghadam, S. Efficacy of two caries detector dyes in the diagnosis of dental caries. J. Dent. 2010, 7, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, A.; Kidd, E.A.; Watson, T.F. In vitro validation of carious dentin removed using different excavation criteria. Am. J. Dent. 2003, 16, 228–230. [Google Scholar]
- McComb, D. Caries-detector dyes—How accurate and useful are they? J. Can. Dent. Assoc. 2000, 66, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yip, H.K.; Stevenson, A.G.; Beeley, J.A. The specificity of caries detector dyes in cavity preparation. Br. Dent. J. 1994, 176, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boston, D.W.; Liao, J. Staining of non-carious human coronal dentin by caries dyes. Oper. Dent. 2004, 29, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franco, S.J.; Kelsey, W.P. Caries removal with and without a disclosing solution of basic fuchsin. Oper. Dent. 1981, 6, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Boston, D.W.; Graver, H.T. Histologicial study of an acid red caries-disclosing dye. Oper. Dent. 1989, 14, 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- Akbari, M.; Rouhani, A.; Samiee, S.; Jafarzadeh, H. Effect of dentin bonding agent on the prevention of tooth discoloration produced by mineral trioxide aggregate. Int. J. Dent. 2012, 2012, 563203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.L.; Jang, Y.E.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, Y. Pre-application of dentin bonding agent prevents discoloration caused by mineral trioxide aggregate. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, A.M.D.S.; Santos, T.J.S.D.; Tertulino, M.D.; dos Medeiros, M.C.S.; da Silva, A.O.; Borges, B.C.D. Degree of conversion, translucency and intrinsic color stability of composites during surface modeling with lubricants. Braz. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 17, e18325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, F.S.; Barros, M.C.R.; Santana, M.L.C.; de Jesus Oliveira, L.S.; Silva, P.F.D.; Lima, G.D.S.; Faria-E-Silva, A.L. Effects of adhesive used as modeling liquid on the stability of the color and opacity of composites. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2018, 30, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demacro, F.F.; Matos, A.B.; Matson, E.; Powers, J.M. Dyes for caries detection influence sound dentin bond strength. Oper. Dent. 1998, 23, 294–298. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, L.E.; Thomas, M.S.; Jathanna, V.; Lewis, A.J.; Srikant, N. Effect of Caries Detecting Dye on Microleakage of Composite Resin Restorations Bonded with Total-etch and Self-etch Adhesive Systems. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2019, 13, ZC01–ZC03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, T.; Pandit, I.K.; Srivastava, N.; Gugnani, N.; Gupta, M. An evaluation of microleakage of various glass ionomer based restorative materials in deciduous and permanent teeth: An in vitro study. Saudi Dent. J. 2012, 24, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravichandran, N.K.; Tumkur Lakshmikantha, H.; Park, H.S.; Jeon, M.; Kim, J. Analysis of Enamel Loss by Prophylaxis and Etching Treatment in Human Tooth Using Optical Coherence Tomography: An In Vitro Study. J. Healthc. Eng. 2019, 8973825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, U.P.; Tikku, A.P.; Chandra, A.; Loomba, K.; Boruah, L.C. Influence of caries detection dye on bond strength of sound and carious affected dentin: An in-vitro study. J. Conserv. Dent. 2011, 14, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marya, C.M.; Taneja, P.; Ahuja, T.K.; Nagpal, R.; Kataria, S. Modified extrinsic tooth stain index and its clinical applicability. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2023, 27, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Tunc, E.S.; Sahin, Z.; Guler, E.; Bayrak, S.; Tuloglu, N. Effectiveness of different cleaning solutions in removing residual caries detector dyes. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2018, 31, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostona, D.W.; Jefferiesb, S.R.; Gaughanc, J.P. The Relative Location of the Dye Staining Endpoint Indicated With Polypropylene Glycol-Based Caries Dye versus Conventional Propylene Glycol-Based Caries Dye. Eur. J. Dent. 2008, 2, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjanic, V.; Mirjanić, Đ.; Arbutina, A. Changes on dental enamel on acid etching. Contemp. Mater. 2016, 2, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govind, S.; Jena, A.; Kamilla, S.K.; Mohanty, N.; Mallikarjuna, R.M.; Nalawade, T.; Saraf, S.; Khaldi, N.A.; Jahdhami, S.A.; Shivagange, V. Diagnosis and Assessment of Dental Caries Using Novel Bioactive Caries Detecting Dye Solution. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashirekha, G.; Jena, A.; Mohanty, N.; Kamilla, S.K. Novel bioactive caries-detecting dye solution: Cytotoxicity, antimicrobial activity, scanning electron microscope, and stereomicroscopic analysis in diagnosis of dental caries. J. Conserv. Dent. 2020, 23, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zampetti, P.; Scribante, A. Historical and bibliometric notes on the use of fluoride in caries prevention. Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2020, 21, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fallahzadeh, F.; Heidari, S.; Najafi, F.; Hajihasani, M.; Noshiri, N.; Nazari, N.F. Efficacy of a Novel Bioactive Glass-Polymer Composite for Enamel Remineralization following Erosive Challenge. Int. J. Dent. 2022, 2022, 6539671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butera, A.; Pascadopoli, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Trapani, B.; Gallo, S.; Radu, M.; Scribante, A. Biomimetic hydroxyapatite paste for molar-incisor hypomineralization: A randomized clinical trial. Oral Dis. 2023, 29, 2789–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Caries Detector Dyes | Without Dentine Bonding Agent (Group I) | With Dentine Bonding Agent (Group II) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group A | Snoop | 5 (33.3%) | 0 (0%) |
| Group B | Sable seek | 4 (26.6%) | 0 (0%) |
| Group C | Elements | 15 (100%) | 4 (26.6%) |
| Groups | Subgroups | Mean Rank | Sum of Ranks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without bonding agent | 13.00 | 195 | Mann–Whitney U = 270.00 p value = 0.016 | |
| Snoop | ||||
| With bonding agent | 18.00 | 270 | ||
| Without bonding agent | 17.50 | 210 | Mann–Whitney U = 82.50 p value = 0.035 | |
| Sable seek | ||||
| With bonding agent | 13.50 | 255 | ||
| Without bonding agent | 17.50 | 210 | Mann–Whitney U = 82.50 p value = 0.035 | |
| Elements | ||||
| With bonding agent | 13.50 | 255 |
| Caries Detector Dyes | With Distilled Water | With Sodium Hypochlorite 3.25% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group A-15 | Snoop | 10 (66.6%) | 15 (100%) |
| Group B-15 | Sable seek | 11 (73%) | 15 (100%) |
| Group C-15 | Elements | 0 (0%) | 4 (26%) |
| Groups | Mean Rank | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Distilled water | Snoop | 15.50 | Chi Square = 44.00 p < 0.001 |
| Sable seek | 15.50 | ||
| Elements | 38.00 | ||
| Sodium hypochlorite | Snoop | 15.00 | Chi Square = 17.25 p < 0.001 |
| Sable seek | 22.50 | ||
| Elements | 31.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abushanan, A.; Sharanesha, R.B.; Alazmah, A.; Algahtani, M. Complimentary Staining of Caries Detector Dyes in Primary Teeth with or without the Application of a Dentine Bonding Agent. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212124
Abushanan A, Sharanesha RB, Alazmah A, Algahtani M. Complimentary Staining of Caries Detector Dyes in Primary Teeth with or without the Application of a Dentine Bonding Agent. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(22):12124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212124
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbushanan, AlWaleed, Rajashekhara B. Sharanesha, Abdulfatah Alazmah, and Mazin Algahtani. 2023. "Complimentary Staining of Caries Detector Dyes in Primary Teeth with or without the Application of a Dentine Bonding Agent" Applied Sciences 13, no. 22: 12124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212124
APA StyleAbushanan, A., Sharanesha, R. B., Alazmah, A., & Algahtani, M. (2023). Complimentary Staining of Caries Detector Dyes in Primary Teeth with or without the Application of a Dentine Bonding Agent. Applied Sciences, 13(22), 12124. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212124






