Construction of an Online Cloud Platform for Zhuang Speech Recognition and Translation with Edge-Computing-Based Deep Learning Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A method for automatic construction method of a large-scale Zhuang speech annotation database is proposed, which allows for acquisition of deep learning data in a short timeframe.
- SAformerNet, a more efficient and accurate transformer-based automatic speech recognition (ASR) network is achieved by inserting additional downsampling modules. This model has speedy training and decoding processes, and equivalent recognition performance to the existing ASR model under certain computational resources.
- A neural machine translation model for Zhuang and other languages using a deep learning architecture is presented.
- A natural language processing system based on edge computing is proposed for the efficient and accurate multilingual translation of Zhuang’s output, thus completing the cycle from theory to practice and efficiently serving the cause of village revitalization.
2. Previous Work
3. System Design
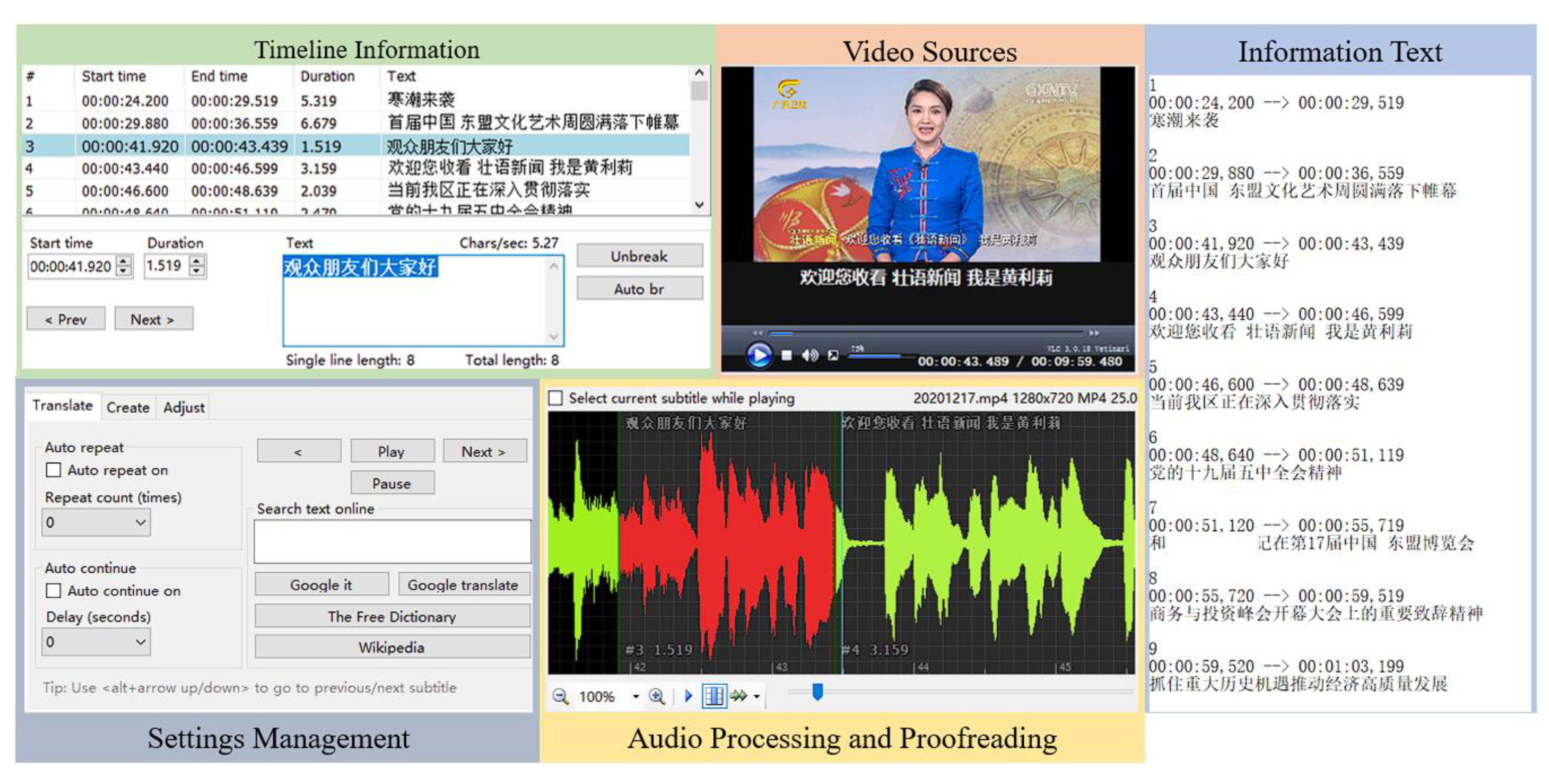
3.1. Establishment of Zhuang Language Speech Database
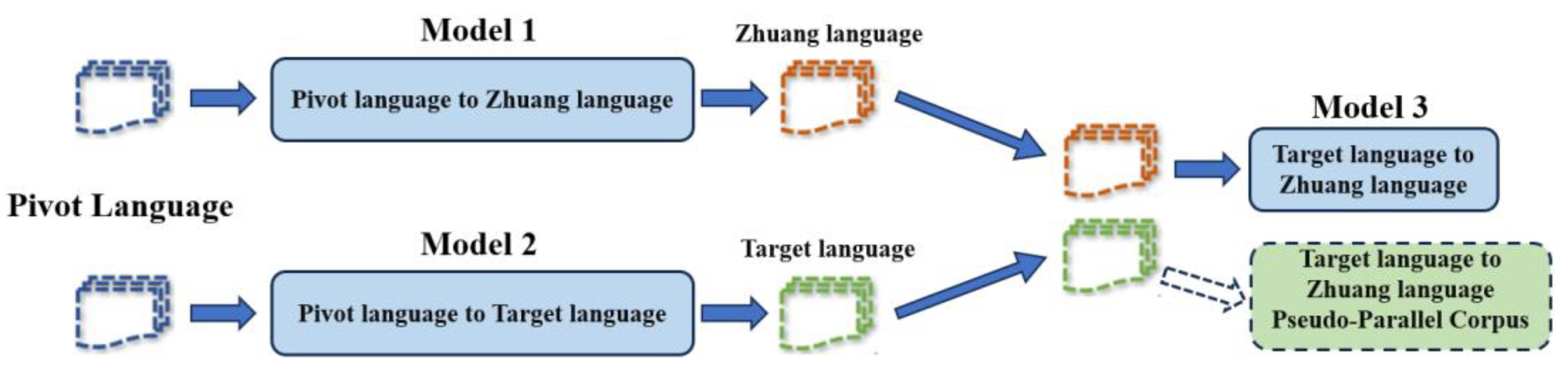
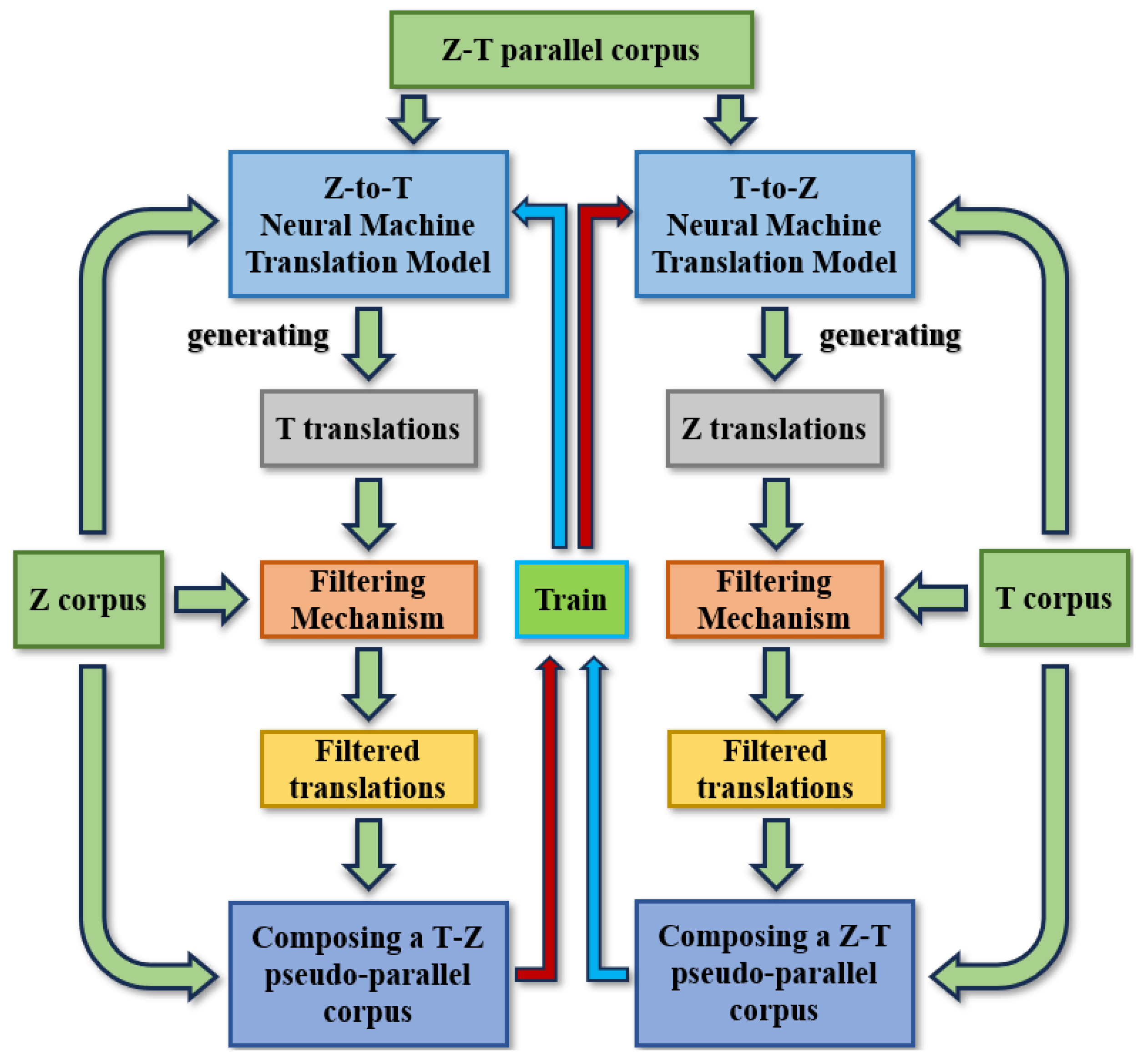
3.2. Multi Language Neural Machine Translation Model Based on BART
3.3. An End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition Algorithm Based on Conformer
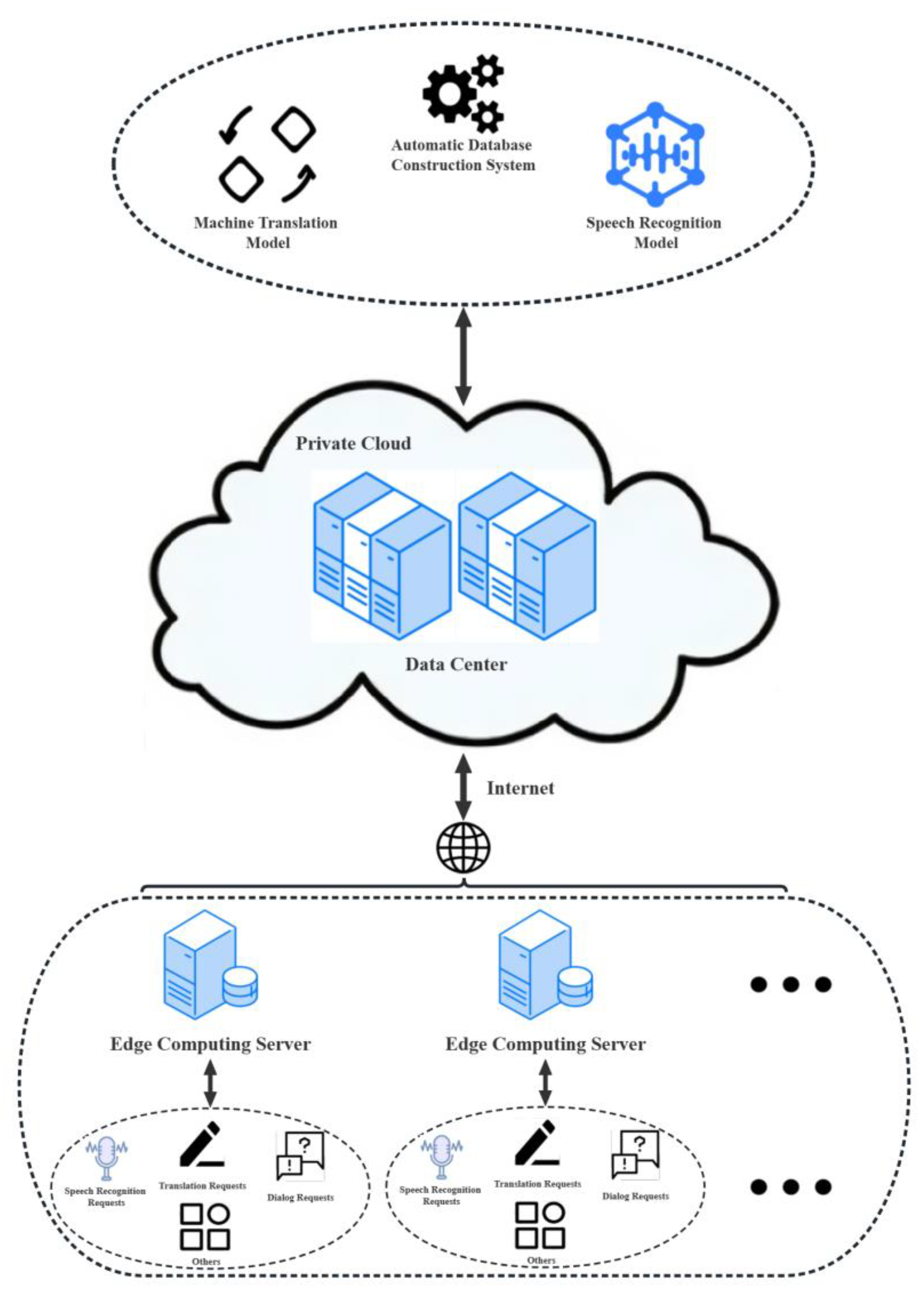
3.4. Acceleration Method of Edge Computing for Multimodal Cooperative Operation Based on Cloud Platform
4. Results
4.1. Mini-Terminal Platform
4.2. Experiment Setup
4.3. Parallel Corpus Selection and Retranslation Results
4.4. Speech Recognition Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grey, A. Language Rights in a Changing China: A National Overview and Zhuang Case Study; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Berlin, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- A Review of the Relationship and Comparative Research between Zhuang and Chinese Language—Part 7 of the Zhuang Language Research Series. Inheritance 2014, 3, 124–125.
- Min, L. Brief Records of Dong Language; Ethnic Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Analysis of the Current Situation of Translation Studies in Minority language in China. Foreign Lang. Teach. Res. 2015, 1, 130–140.
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Kolesnikov, A.; Houlsby, N.; Beyer, L. Scaling vision transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 12104–12113. [Google Scholar]
- Gulati, A.; Qin, J.; Chiu, C.C.; Parmar, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Han, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. Conformer: Convolution-augmented transformer for speech recognition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.08100. [Google Scholar]
- Irshad, I.; Yasmin, M. Feminism and literary translation: A systematic review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comelles, E.; Atserias, J. VERTa: A linguistic approach to automatic machine translation evaluation. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2019, 53, 57–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Daniel, P. A comprehensive survey on various fully automatic machine translation evaluation metrics. Neural Process. Lett. 2022, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, E. A structured review of the validity of BLEU. Comput. Linguist. 2018, 44, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, F.; Joty, S.; Màrquez, L.; Nakov, P. Machine translation evaluation with neural networks. Comput. Speech Lang. 2017, 45, 180–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Gholami, A.; Yao, Z.; Mahoney, M.; Keutzer, K. I-bert: Integer-only bert quantization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 5506–5518. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Park, J.; Park, S.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.; Choi, J. Nn-lut: Neural approximation of non-linear operations for efficient transformer inference. In Proceedings of the 59th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–14 July 2022; pp. 577–582. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.; Wang, M.; Liang, S.; Lin, J.; Wang, Z. Hardware accelerator for multi-head attention and position-wise feed-forward in the transformer. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International System-on-Chip Conference (SOCC), Virtual, 8–11 September 2020; pp. 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, J.T.; Chen, C.; Li, K. Accelerating attention mechanism on fpgas based on efficient reconfigurable systolic array. In ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems (TECS); Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Han, S. Spatten: Efficient sparse attention architecture with cascade token and head pruning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 February–3 March 2021; pp. 97–110. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, P.; Tang, X.; Hu, J. Algorithm-Hardware Co-Design of Attention Mechanism on Fpga Devices. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems (TECS); Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 20, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Burchi, M.; Vielzeuf, V. Efficient conformer: Progressive downsampling and grouped attention for automatic speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), Cartagena, Colombia, 13–17 December 2021; pp. 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Gholami, A.; Shaw, A.; Lee, N.; Mangalam, K.; Malik, J.; Mahoney, M.; Keutzer, K. Squeezeformer: An efficient transformer for automatic speech recognition. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 9361–9373. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Perslev, M.; Jensen, M.; Darkner, S.; Jennum, P.; Igel, C. U-time: A fully convolutional network for time series segmentation applied to sleep staging. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Yu, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y. Nextformer: A convnext augmented conformer for end-to-end speech recognition. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.14747. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Tan, X.; Qin, T.; Lu, J.; Liu, T. Mass: Masked sequence to sequence pre-training for language generation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.02450. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, M.; Liu, Y.; Goyal, N.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Mohamed, A.; Levy, O.; Stoyanov, V.; Zettlemoyer, L. Bart: Denoising sequence-to-sequence pre-training for natural language generation, translation, and comprehension. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.13461. [Google Scholar]
- Sennrich, R.; Birch, A.; Currey, A.; Germann, U.; Haddow, B.; Heafield, K.; Barone, A.; Williams, P. The University of Edinburgh’s neural MT systems for WMT17. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.00726. [Google Scholar]
- Currey, A.; Miceli-Barone, A.V.; Heafield, K. Copied monolingual data improves low-resource neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the Second Conference on Machine Translation, Copenhagen, Denmark, 7–8 September 2017; pp. 148–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ham, T.J.; Jung, S.J.; Kim, S.; Oh, Y.; Park, Y.; Song, Y.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Park, K.; Lee, J.; et al. A^3: Accelerating attention mechanisms in neural networks with approximation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on High Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2020; pp. 328–341. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Pandey, S.; Fang, H.; Lyu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Xie, M.; Wan, L.; Liu, H.; Ding, C. Ftrans: Energy-efficient acceleration of transformers using fpga. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design, Boston, MA, USA, 10–12 August 2020; pp. 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, P.F.; Cocke, J.; Della Pietra, S.A.; Della Pietra, V.J.; Jelinek, F.; Lafferty, J.D.; Mercer, R.L.; Roosin, P.S. A statistical approach to machine translation. Comput. Linguist. 1990, 16, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 3104–3112. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, ICIR 2015, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Meng, F.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J. Retrieving sequential information for non-autoregressive neural machine translation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.09444. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training. 2018. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/ (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Libovický, J.; Helcl, J. End-to-end non-autoregressive neural machine translation with connectionist temporal classification. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.04719. [Google Scholar]
- Fadaee, M.; Bisazza, A.; Monz, C. Data augmentation for low-resource neural machine translation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.00440. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Pham, H.; Dai, Z.; Neubig, G. SwitchOut: An efficient data augmentation algorithm for neural machine translation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.07512. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Keung, P. Improving non-autoregressive neural machine translation with monolingual data. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.00932. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, M.; Kong, X.; Anastasopoulos, A.; Neubig, G. Generalized data augmentation for low-resource translation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.03785. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.G.; Navab, N.; Wachinger, C. Concurrent spatial and channel ‘squeeze & excitation’ in fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2018: 21st International Conference, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; pp. 421–429. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ning, Z.; Guo, L.; Guo, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, G. Online learning for distributed computation offloading in wireless powered mobile edge computing networks. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2021, 33, 1841–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premsankar, G.; Di Francesco, M.; Taleb, T. Edge computing for the Internet of Things: A case study. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.S.; Zhang, Y.; Chiu, C.C.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Chan, W.; Le, Q.V.; Wu, Y. Specaugment on large scale datasets. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 6879–6883. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.S.; Chan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chiu, C.C.; Zoph, B.; Cubuk, E.D.; Le, Q.V. Specaugment: A simple data augmentation method for automatic speech recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08779. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, H.; Du, J.; Na, X.; Wu, B.; Zheng, H. Aishell-1: An open-source mandarin speech corpus and a speech recognition baseline. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th Conference of the Oriental Chapter of the International Coordinating Committee on Speech Databases and Speech I/O Systems and Assessment (O-COCOSDA), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1–3 November 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa, T.; Yaguchi, M.; Uchimoto, K.; Utiyama, M.; Sumita, E.; Kurohashi, S.; Isahara, H. ASPEC: Asian scientific paper excerpt corpus. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC′16), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; pp. 2204–2208. [Google Scholar]

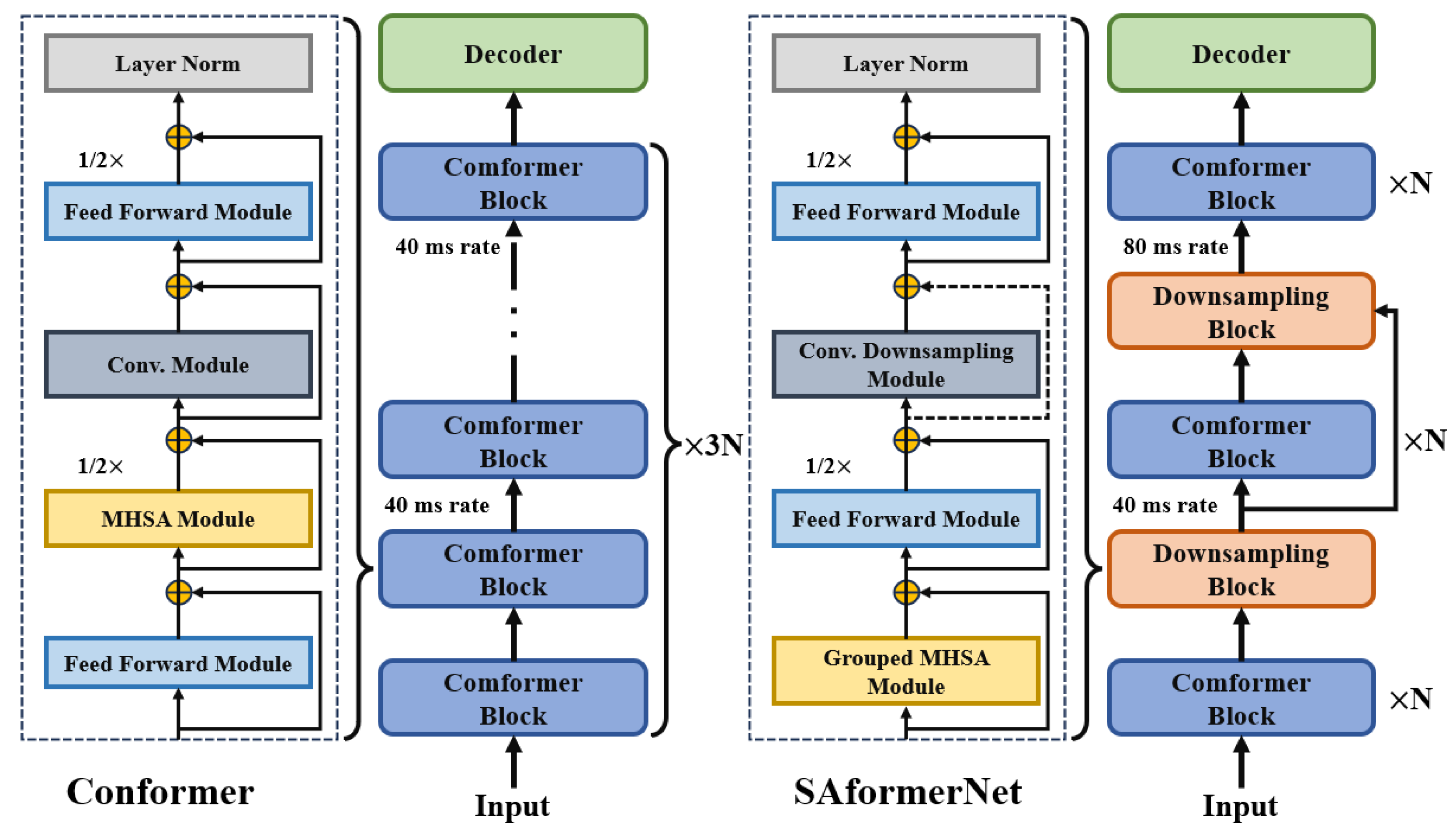
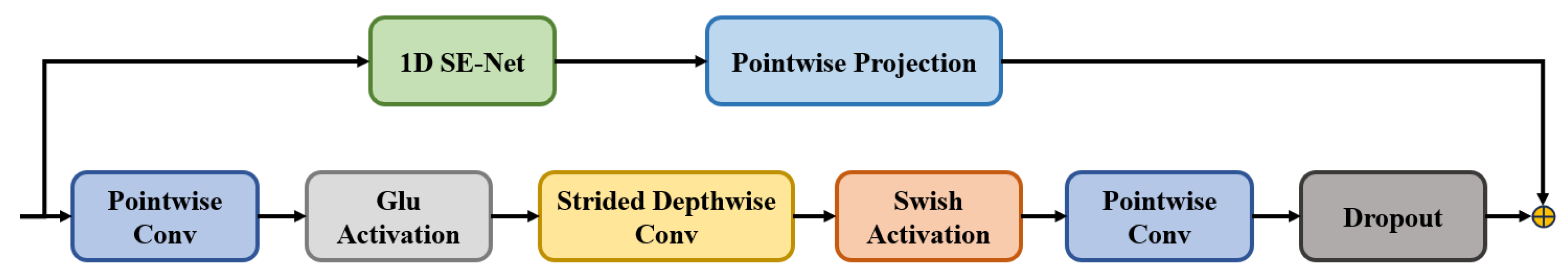



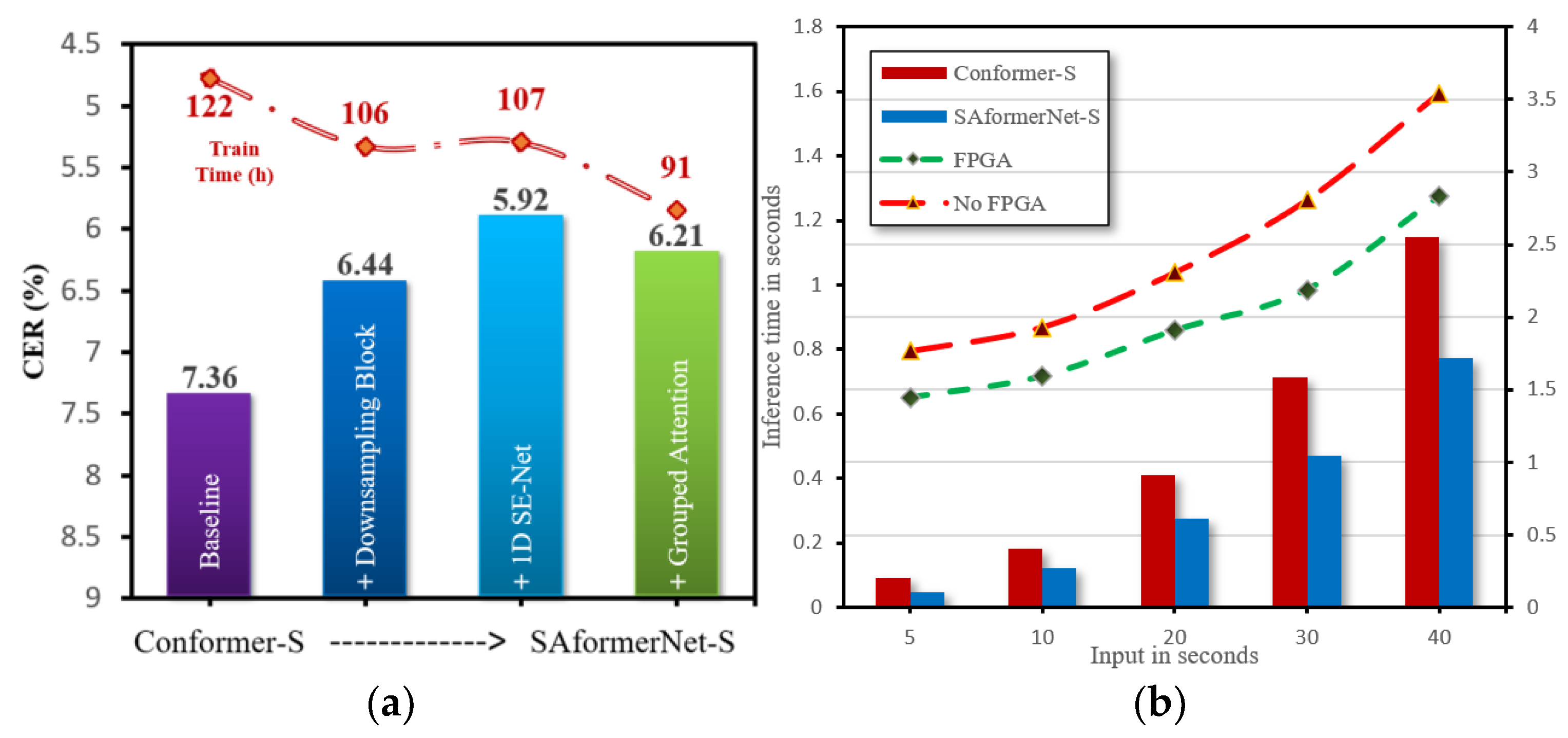
| Model | Encoder Blocks | Encoder Dims | Attention Heads | Group Size | Params (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conformer-S | 16 | 176 | 4 | - | 13.0 |
| SAformerNet-S | 15 | 120,168,240 | 4 | 3 | 13.4 |
| Conformer-M | 18 | 256 | 4 | - | 30.6 |
| SAformerNet-M | 16 | 180,256,360 | 4 | 3 | 33.4 |
| Translation Model | Data Types | ASPEC-JC BLEU Scores | OPUS JA-ZH BLEU Scores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese-to-Japanese | Original data | 34.24 | 34.20 |
| Japanese-to-Chinese | Original data | 32.19 | 33.41 |
| Chinese-to-Japanese | Processed data | 35.16 | 35.45 |
| Japanese-to-Chinese | Processed data | 33.02 | 33.10 |
| Translation Model | Retranslation Strategies | ASPEC-JC BLEU Scores | OPUS JA-ZH BLEU Scores |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese-to-Japanese | No filtering mechanism | 35.97 | 36.12 |
| Japanese-to-Chinese | No filtering mechanism | 34.31 | 34.36 |
| Chinese-to-Japanese | With filtering mechanism | 37.51 | 37.74 |
| Japanese-to-Chinese | With filtering mechanism | 35.82 | 35.92 |
| Model Architecture | Model Type | CER (%) | Params (M) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISHELL-1 | Zhuang Language Dataset | ||||
| Dev | Test | Test | |||
| LAS + SpecAugm | Seq2Seq | 8.63 | 11.32 | 13.2 | - |
| Conformer-S | CTC | 5.62 | 5.95 | 7.36 | 13.0 |
| Eff. Conformer-S | RNN-T | 5.68 | 6.03 | 7.49 | 10.3 |
| SAformerNet-S (ours) | CTC | 5.69 | 6.13 | 6.21 | 13.4 |
| w/o grouped Att | CTC | 5.50 | 5.76 | 5.92 | 13.4 |
| Conformer-M | CTC | 5.40 | 5.67 | 6.99 | 30.5 |
| Eff. Conformer-M | RNN-T | 5.43 | 5.81 | 7.11 | 30.7 |
| SAformerNet m (ours) | CTC | 5.52 | 6.01 | 6.11 | 33.4 |
| w/o grouped Att | CTC | 5.36 | 5.58 | 5.67 | 33.4 |
| Modules | Hardware Accelerator Modules | Average Resource Usage | GPU Latency | FPGA Latency | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Available Resources | BRAM | CLBs | LUT | DSP | ||||
| 912 | 548,160 | 274,080 | 2520 | |||||
| MHSA | Matrix Operation | 0 | 192,110 | 215,464 | 0 | 28.50% | 1935.8 us | 269.7 us |
| Softmax | 0 | 37,847 | 32,560 | 0 | 4.75% | |||
| FFN | Layer-Norm | 55 | 8475 | 14,230 | 209 | 5.25% | 864.3 us | 438.3 us |
| Weight Memory | 720 | 240 | 4696 | 0 | 20.19% | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Z.; Huang, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, R.; Lyu, X.; Duan, T.; Bu, Z.; Liang, J. Construction of an Online Cloud Platform for Zhuang Speech Recognition and Translation with Edge-Computing-Based Deep Learning Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212184
Fan Z, Huang M, Zhang X, Liu R, Lyu X, Duan T, Bu Z, Liang J. Construction of an Online Cloud Platform for Zhuang Speech Recognition and Translation with Edge-Computing-Based Deep Learning Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(22):12184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212184
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Zeping, Min Huang, Xuejun Zhang, Rongqi Liu, Xinyi Lyu, Taisen Duan, Zhaohui Bu, and Jianghua Liang. 2023. "Construction of an Online Cloud Platform for Zhuang Speech Recognition and Translation with Edge-Computing-Based Deep Learning Algorithm" Applied Sciences 13, no. 22: 12184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212184
APA StyleFan, Z., Huang, M., Zhang, X., Liu, R., Lyu, X., Duan, T., Bu, Z., & Liang, J. (2023). Construction of an Online Cloud Platform for Zhuang Speech Recognition and Translation with Edge-Computing-Based Deep Learning Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 13(22), 12184. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212184







