Variability of Air Pollutants in the Indoor Air of a General Store
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
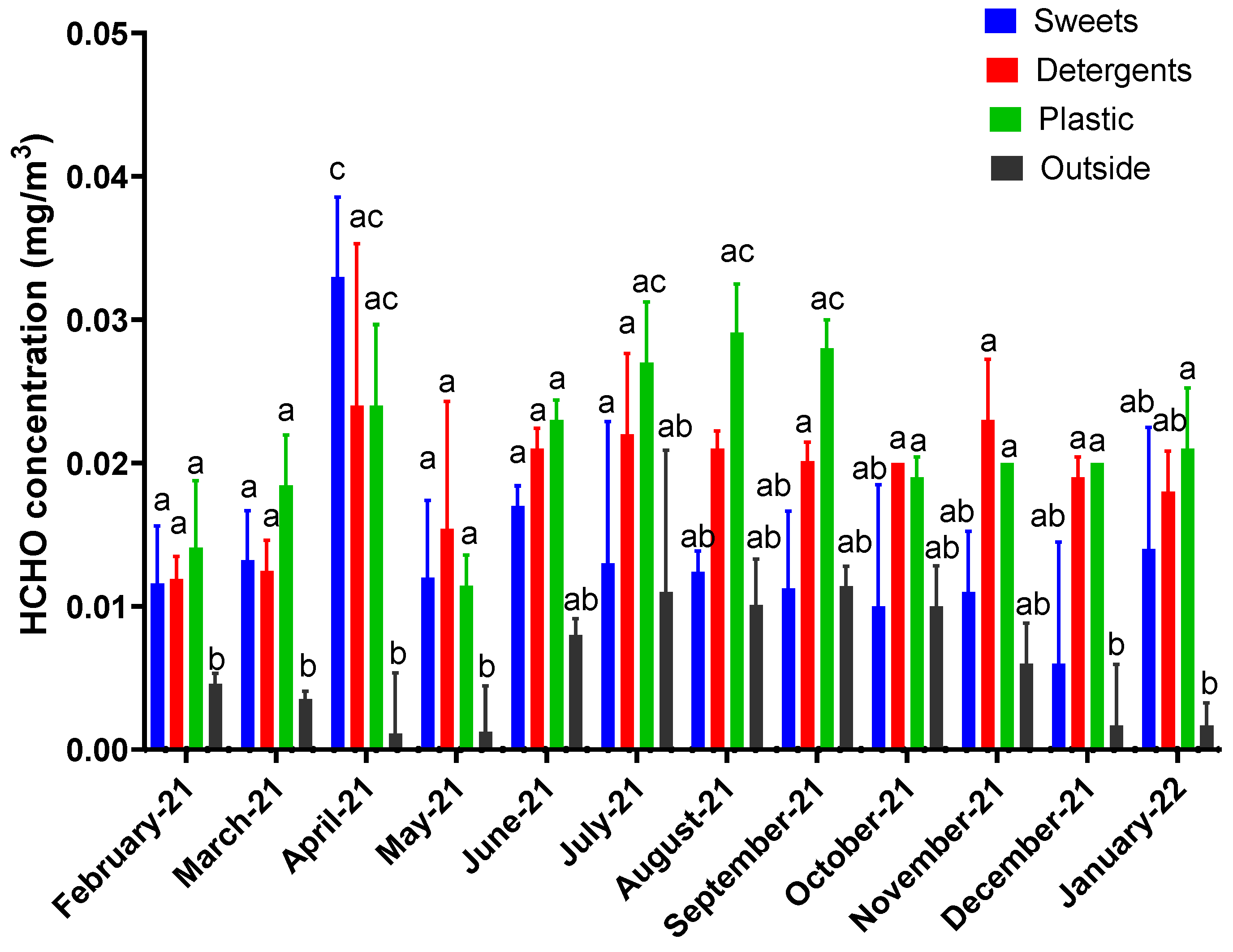
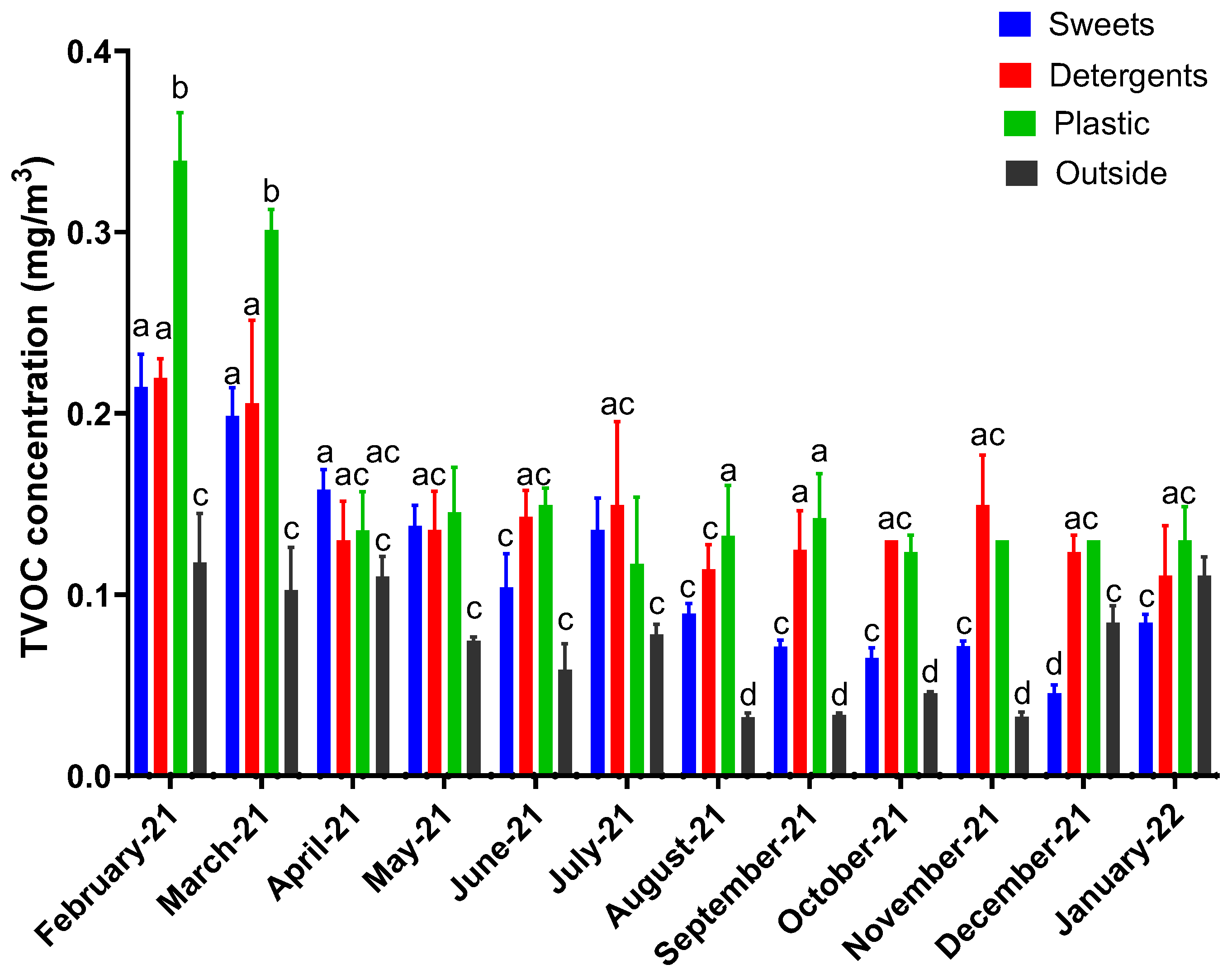
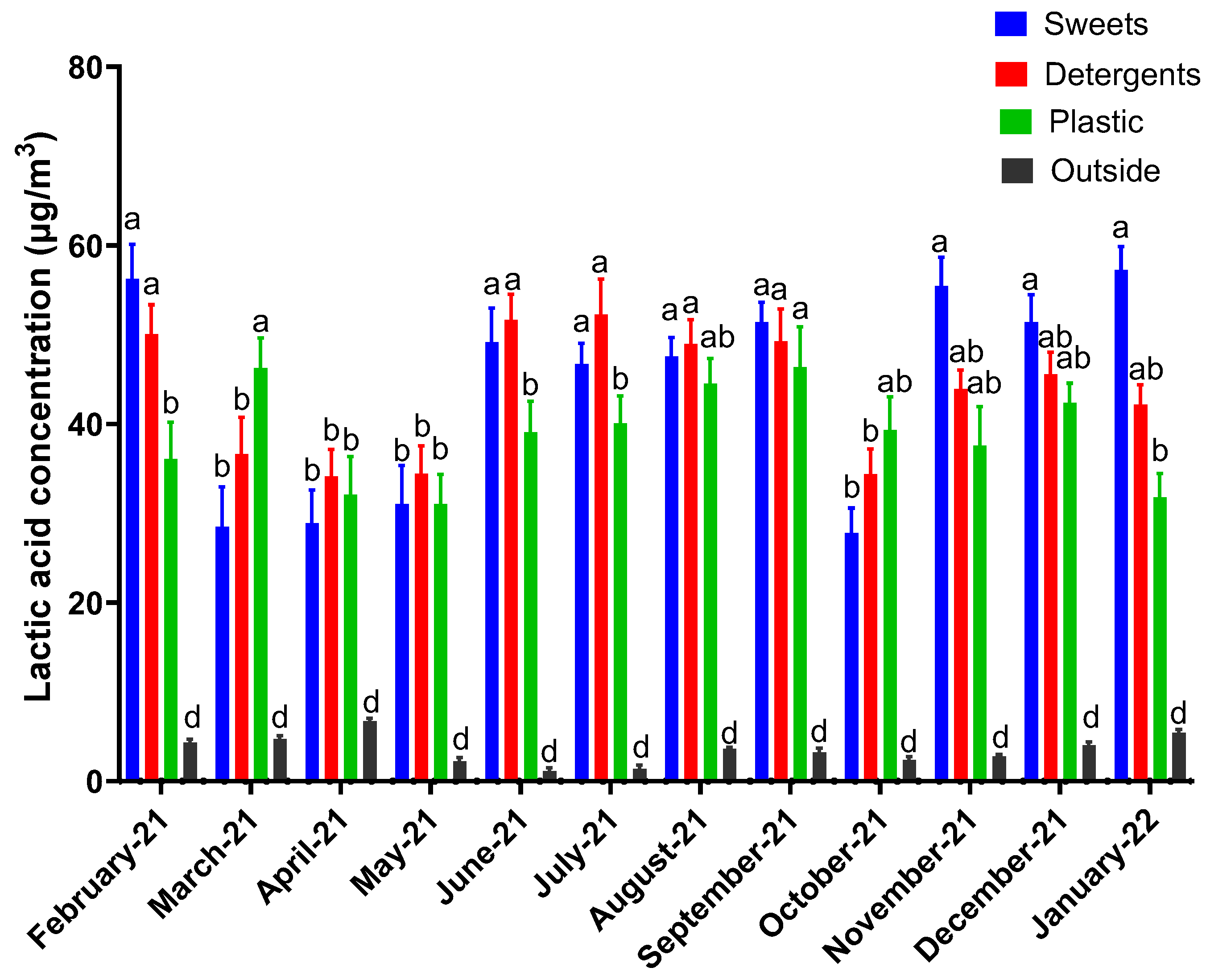
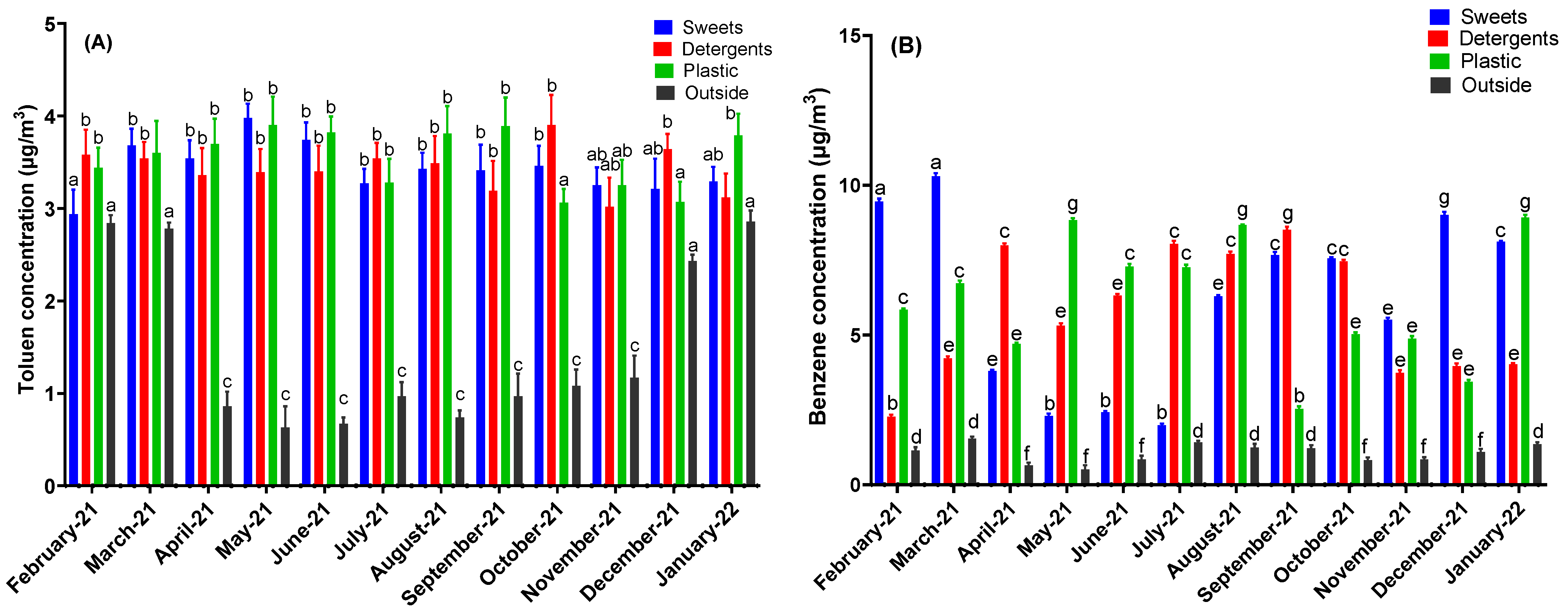
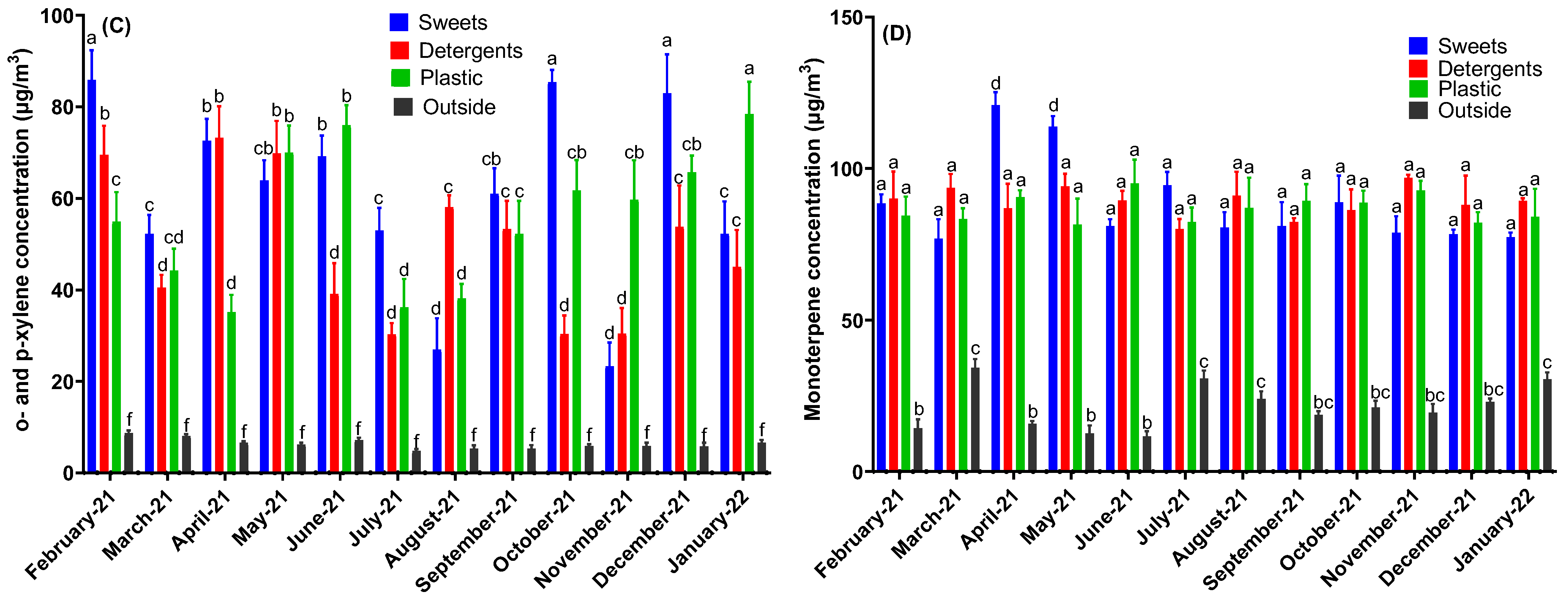
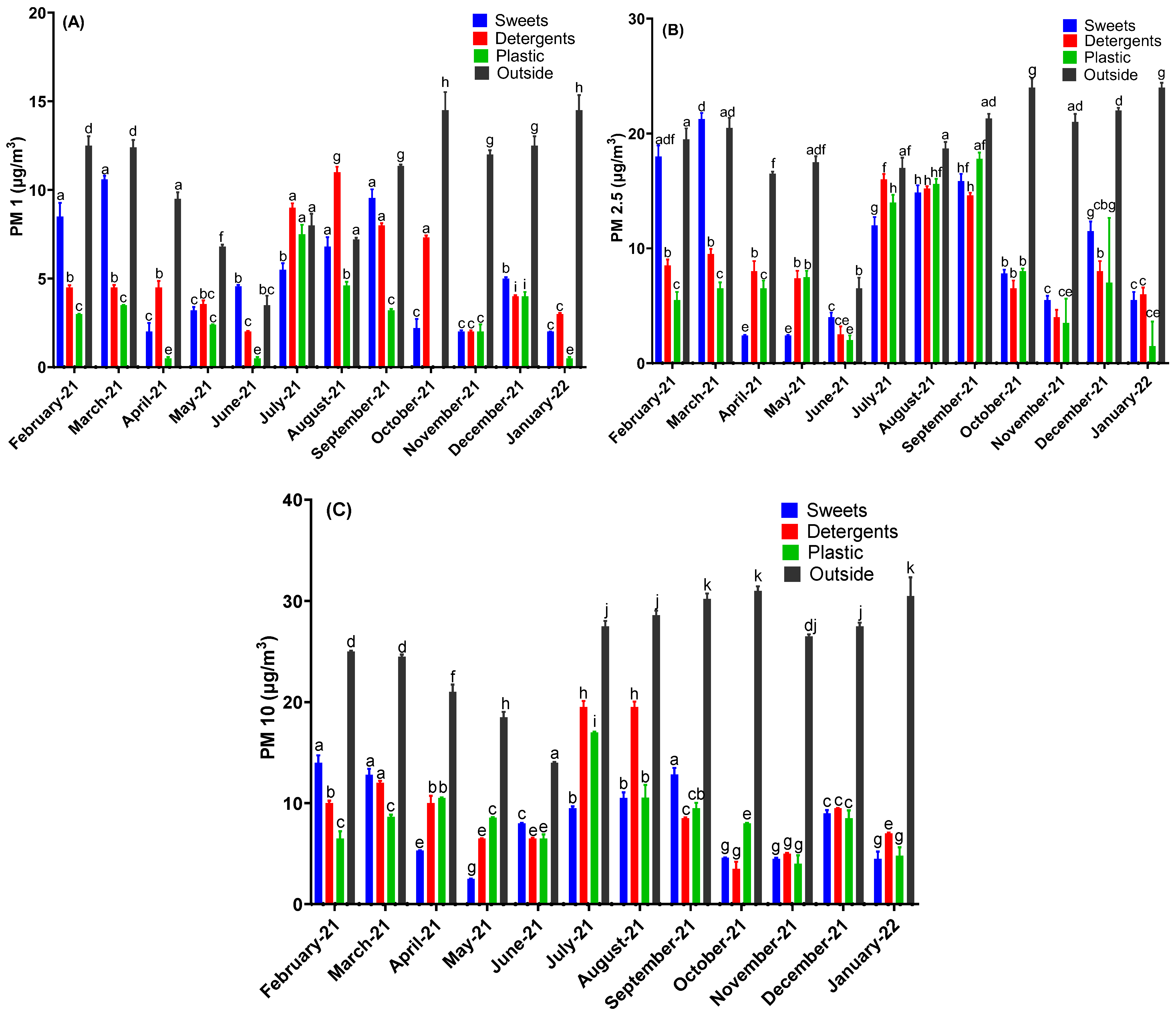
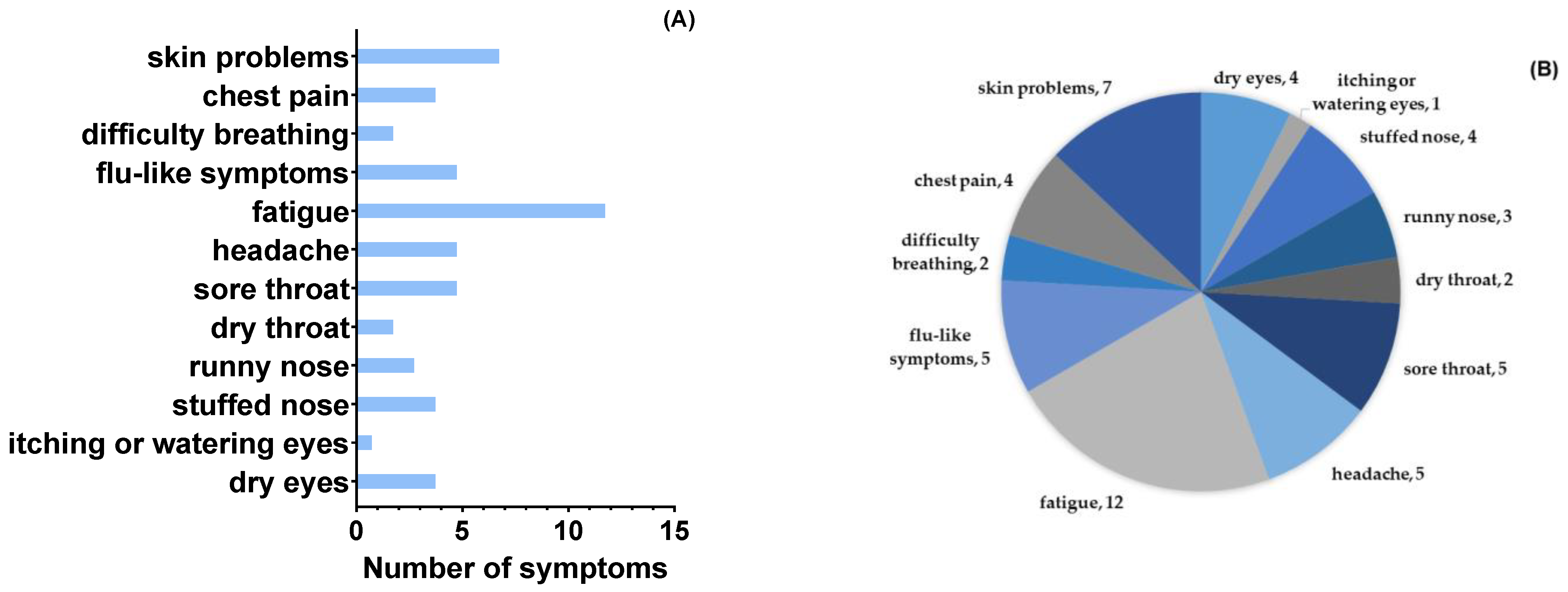
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. American Time Use Survey. Available online: https://www.bls.gov/tus/tables.htm (accessed on 11 February 2023).
- Mishra, S.; Singh, A.; Kar, S.K.; Ganesan, S. Compulsive buying behavior and its association with emotional distress, depression, and impulsivity in general population: An online survey. CNS Spectr. 2023, 28, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Johnson, K.K.J.C.; Journal, T.R. Retail therapy: Scale development. Cloth. Text. Res. J. 2011, 29, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. How Australians Use Their Time. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/statistics/people/people-and-communities/how-australians-use-their-time/latest-release (accessed on 11 February 2023).
- European Communities. How Europeans Spend Their Time Everyday Life of Women and Men; European Communities: Luxemburg, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, L.; Gao, S.; Li, M.; Yan, H.; Zhai, Y. Field investigation on the thermal environment and thermal comfort in shopping malls in the cold zone of China. Build. Environ. 2022, 214, 108892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, I.; AbdelMessih, R.N.; Steit, M.; Mina, E.M. Experimental assessment of thermal comfort and indoor air quality in worship places: The influence of occupancy level and period. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 179, 107686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Z. Predicting non-uniform indoor air quality distribution by using pulsating air supply and SVM model. Build. Environ. 2022, 219, 109171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempton, L.; Daly, D.; Kokogiannakis, G.; Dewsbury, M. A rapid review of the impact of increasing airtightness on indoor air quality. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Tu, Y.-P.; Sung, S.-Y.; Weng, W.-C.; Huang, H.-L.; Tsai, Y.I. A comprehensive analysis of the intervention of a fresh air ventilation system on indoor air quality in classrooms. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Essah, E.; Blanusa, T.; Beaman, C.P. The appearance of indoor plants and their effect on people’s perceptions of indoor air quality and subjective well-being. Build. Environ. 2022, 219, 109151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Lei, N.; Bu, Z.; Sun, H.; Li, B.; Lin, B. Investigations of indoor air quality for office buildings in different climate zones of China by subjective survey and field measurement. Build. Environ. 2022, 214, 108899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayegan, Z.; Bahri, M.; Haghighat, F. A review on an emerging solution to improve indoor air quality: Application of passive removal materials. Build. Environ. 2022, 219, 109228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Salam, M.M.M. Indoor exposure of elderly to air pollutants in residential buildings in Alexandria, Egypt. Build. Environ. 2022, 219, 109221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaniyazi, L.; Jung, C.-R.; Fook Sheng Ng, C.; Seposo, X.; Hashizume, M.; Nakayama, S.F. Early life exposure to indoor air pollutants and the risk of neurodevelopmental delays: The Japan Environment and Children’s Study. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 107004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Salam, M.M.M. Relationship between residential indoor air quality and socioeconomic factors in two urban areas in Alexandria, Egypt. Build. Environ. 2022, 207, 108425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.M.; Apte, M.G.; Maddalena, R.; Bennett, D.H. Volatile organic compounds in small- and medium-sized commercial buildings in California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9075–9083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, B.; Hermanns, K. Reducing Indoor Air Formaldehyde Concentrations. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1985, 35, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.H.; Lee, G.B.; Kim, I.S.; Park, W.M. Formaldehyde and carbon dioxide air concentrations and their relationship with indoor environmental factors in daycare centers. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovira, J.; Roig, N.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Human health risks of formaldehyde indoor levels: An issue of concern. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2016, 51, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Liu, N.; Liu, W.; Mo, J.; Zhao, Z.; Kan, H.; Deng, F.; Huang, C.; Zhao, B.; Zeng, X.; et al. Indoor formaldehyde levels in residences, schools, and offices in China in the past 30 years: A systematic review. Indoor Air 2022, 32, e13141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, L.; Barbosa, E.; Charão, M.F.; Brucker, N. Formaldehyde toxicity reports from in vitro and in vivo studies: A review and updated data. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 45, 972–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, T.; Liu, C.; Qian, H.; Li, J. Seasonal and diurnal patterns of outdoor formaldehyde and impacts on indoor environments and health. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Xia, P.; Yan, L.; Gou, X.; Giesy, J.P.; Dai, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X. Toxicological Mechanism of Individual Susceptibility to Formaldehyde-Induced Respiratory Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 6511–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, C.; Cao, K.; Valaulikar, R.; Fu, X.; Sorin, A.B. Variability of Total Volatile Organic Compounds (TVOC) in the Indoor Air of Retail Stores. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sexton, K.; Mongin, S.J.; Adgate, J.L.; Pratt, G.C.; Ramachandran, G.; Stock, T.H.; Morandi, M.T. Estimating Volatile Organic Compound Concentrations in Selected Microenvironments Using Time–Activity and Personal Exposure Data. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2007, 70, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eklund, B.M.; Burkes, S.; Morris, P.; Mosconi, L. Spatial and temporal variability in VOC levels within a commercial retail building. Indoor Air 2008, 18, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Chan, C.Y.; Wang, X.; Chan, L.Y.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Volatile organic compounds in a multi-storey shopping mall in guangzhou, South China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7374–7383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirlo, E.L.; Crain, N.; Corsi, R.L.; Siegel, J.A. Volatile organic compounds in fourteen U.S. retail stores. Indoor Air 2014, 24, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Wu, S.; Hua, Q.; Bao, C.; Liu, H. Volatile Organic Compounds in Human Exhaled Breath to Diagnose Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 606915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Singh, A.B.; Arora, T.; Singh, S.; Singh, R. Critical review on emerging health effects associated with the indoor air quality and its sustainable management. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, T.; Almeida-Silva, M.; Silva, D.; Diogo, C.; Canha, N. Indoor air quality assessment in grocery stores. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-M.; Lee, S.C.; Chan, L.Y. Indoor air quality at nine shopping malls in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 273, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanaka, R.B.; Mutlu, G.M. Particulate matter air pollution: Effects on the cardiovascular system. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karuna, S.; Dhananjay, T. Particulate Matter and Human Health. In Environmental Health; Takemi, O., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2021; Chapter 3. [Google Scholar]
- Yussuf, S.M.; Dahir, G.; Salad, A.M.; Hayir, T.M.M.; Hassan, S.A.; Gele, A. Sick building syndrome and its associated factors among adult people living in Hodan district Moqadishu Somalia. Front. Built Environ. 2023, 9, 1218659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-Y.; Tsai, M.-C.; Muo, C.-H.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Sung, F.-C.; Wu, C.-C. Personal, psychosocial and environmental factors related to sick building syndrome in official employees of Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surawattanasakul, V.; Sirikul, W.; Sapbamrer, R.; Wangsan, K.; Panumasvivat, J.; Assavanopakun, P.; Muangkaew, S. Respiratory symptoms and skin sick building syndrome among office workers at University Hospital, Chiang Mai, Thailand: Associations with indoor air quality, AIRMED Project. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jang, M.; Choi, K.; Kim, K. Perception of indoor air quality (IAQ) by workers in underground shopping centers in relation to sick-building syndrome (SBS) and store type: A cross-sectional study in Korea. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raport Privind Calitatea Aerului in Romania in Anul 2021. Available online: http://www.anpm.ro/raportare-anuala (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Raport Preliminar Privind Calitatea Aerului Inconjurator in Judetul Caras-Severin pe anul 2021. Available online: http://www.anpm.ro/documents/17201/48339360/Raport+anual+preliminar+2021_CA.pdf/254524b2-9716-45ea-a357-8be4f48b7664 (accessed on 9 November 2023).
- Popescu, L.L.; Popescu, R.S.; Catalina, T. Indoor particle’s pollution in Bucharest, Romania. Toxics 2022, 10, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noe, S.M.; Huve, K.; Niinemets, Ü.; Copolovici, L. Seasonal variation in vertical volatile compounds air concentrations within a remote hemiboreal mixed forest. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 3909–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kännaste, A.; Copolovici, L.; Niinemets, U. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Method for Determination of Biogenic Volatile Organic Compounds Emitted by Plants. In Plant Isoprenoids: Methods and Protocols; RodriguezConcepcion, M., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1153, pp. 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Popitanu, C.; Cioca, G.; Copolovici, L.; Iosif, D.; Munteanu, F.-D.; Copolovici, D. The seasonality impact of the BTEX pollution on the atmosphere of Arad City, Romania. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, M.T.; Abd Hamid, H.H.; Ahamad, F.; Khan, M.F.; Mohd Nadzir, M.S.; Othman, M.; Sahani, M.; Abdul Wahab, M.I.; Mohamad, N.; Uning, R.; et al. BTEX compositions and its potential health impacts in Malaysia. Chemosphere 2019, 237, 124451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Means, B. Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund. Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A); EPA/540/1-89/002; Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- National Research Council (US). Committee to Review EPA’s Draft IRIS Assessment of Formaldehyde. In Review of the Environmental Protection Agency’s Draft IRIS Assessment of Formaldehyde; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Raw, G.J.; Roys, M.S.; Whitehead, C.; Tong, D. Questionnaire design for sick building syndrome: An empirical comparison of options. Environ. Int. 1996, 22, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mason, M.A.; Guo, Z.; Krebs, K.A.; Roache, N.F. Source emission and model evaluation of formaldehyde from composite and solid wood furniture in a full-scale chamber. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.-Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-J. Formaldehyde and TVOC emission behavior of laminate flooring by structure of laminate flooring and heating condition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidheswaran, M.; Chen, W.; Chang, A.; Miller, R.; Cohn, S.; Sullivan, D.; Fisk, W.J.; Kumagai, K.; Destaillats, H. Formaldehyde emissions from ventilation filters under different relative humidity conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5336–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, M.; Blond, N.; Blondeau, P.; Schoemaecker, C.; Hauglustaine, D.A. Assessment of the impact of oxidation processes on indoor air pollution using the new time-resolved INCA-Indoor model. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthammer, T. Formaldehyde sources, formaldehyde concentrations and air exchange rates in European housings. Build. Environ. 2019, 150, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, J.Z.; Pati, S.; Fatchurrahman, D.; Amodio, M.L.; Colelli, G. Screening of volatile organic compounds emitted from different packaging materials: Case study on fresh-cut artichokes. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1178104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.R.; Ghim, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Ryu, J.; Shim, I.-K.; Lee, J. Volatile organic compounds in underground shopping districts in Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, M.A.; Kindzierski, W.B.; Wheeler, A.J.; Héroux, M.-È.; Wallace, L.A. Source apportionment of indoor and outdoor volatile organic compounds at homes in Edmonton, Canada. Build. Environ. 2015, 90, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, K.A.; Levin, J.O.; Sandström, T.; Lindström-Espeling, K.; Lindén, G.; Stjernberg, N.L. Terpene exposure and respiratory effects among workers in Swedish joinery shops. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 1997, 23, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settimo, G.; Manigrasso, M.; Avino, P. Indoor air quality: A focus on the European legislation and state-of-the-art research in Italy. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagonis, D.; Price, D.J.; Algrim, L.B.; Day, D.A.; Handschy, A.V.; Stark, H.; Miller, S.L.; de Gouw, J.; Jimenez, J.L.; Ziemann, P.J. Time-resolved measurements of indoor chemical emissions, deposition, and reactions in a University Art Museum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4794–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, T.; Li, T.; Shen, F.; Li, X.; Mehmood, T. The pollution characteristics of PM10 and PM2.5 during summer and winter in Beijing, Suning and Islamabad. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jin, X.; Cai, X.; Song, Y. Mechanism of haze pollution in summer and its difference with winter in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicole, W. Cannabis consumption in dispensaries: Public health implications of an emerging practice. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 084001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orru, H.; Olstrup, H.; Kukkonen, J.; López-Aparicio, S.; Segersson, D.; Geels, C.; Tamm, T.; Riikonen, K.; Maragkidou, A.; Sigsgaard, T.; et al. Health impacts of PM2.5 originating from residential wood combustion in four nordic cities. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, M.; Moghadam, S.R.; Baziar, M.; Hesam, G.; Moradpour, Z.; Zakeri, H.R. Occupational exposure to formaldehyde, lifetime cancer probability, and hazard quotient in pathology lab employees in Iran: A quantitative risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 1878–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmot, A.F.; Eley, J.; Stafford, M.; Stansfeld, S.A.; Warwick, E.; Marmot, M.G. Building health: An epidemiological study of “sick building syndrome” in the Whitehall II study. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 63, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institutul National de Statistica. Statistical Database (TEMPO), FOM105E (Number of Employees at the End of the Month in the Economy Section and Division Level). Available online: https://insse.ro/cms/ro/content/date-deschise (accessed on 10 September 2023).
| Month | CDI (mg day−1 kg−1) | HQ | LCR | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sweets | Detergents | Plastics | Outside | Sweets | Detergents | Plastics | Outside | Sweets | Detergents | Plastics | Outside | |
| February | 2.32 | 2.38 | 2.82 | 0.92 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 4.43 × 10−6 | 4.54 × 10−6 | 5.38 × 10−6 | 1.76 × 10−6 |
| March | 2.64 | 2.49 | 3.68 | 0.71 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 5.04 × 10−6 | 4.76 × 10−6 | 7.03 × 10−6 | 1.35 × 10−6 |
| April | 6.60 | 4.80 | 4.80 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.01 | 1.26 × 10−6 | 9.16 × 10−6 | 9.16 × 10−6 | 4.20 × 10−7 |
| May | 2.40 | 3.08 | 2.29 | 0.25 | 0.13 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.01 | 4.58 × 10−6 | 5.88 × 10−6 | 4.37 × 10−6 | 4.73 × 10−7 |
| June | 3.40 | 4.20 | 4.60 | 1.60 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 6.49 × 10−6 | 8.02 × 10−6 | 8.78 × 10−6 | 3.05 × 10−6 |
| July | 2.60 | 4.40 | 5.40 | 2.20 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.30 | 0.12 | 4.96 × 10−6 | 8.40 × 10−6 | 1.03 × 10−5 | 4.20 × 10−6 |
| August | 2.48 | 4.20 | 5.82 | 2.02 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.11 | 4.73 × 10−6 | 8.02 × 10−6 | 1.11 × 10−5 | 3.86 × 10−6 |
| September | 2.25 | 4.03 | 5.60 | 2.28 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.31 | 0.13 | 4.29 × 10−6 | 7.69 × 10−6 | 1.07 × 10−5 | 4.35 × 10−6 |
| October | 2.00 | 4.00 | 3.80 | 2.00 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 3.82 × 10−6 | 7.64 × 10−6 | 7.25 × 10−6 | 3.82 × 10−6 |
| November | 2.20 | 4.60 | 4.00 | 1.20 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 4.20 × 10−6 | 8.78 × 10−6 | 7.64 × 10−6 | 2.29 × 10−6 |
| December | 1.20 | 3.80 | 4.00 | 0.34 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.02 | 2.29 × 10−6 | 7.25 × 10−6 | 7.64 × 10−6 | 6.49 × 10−7 |
| January | 2.80 | 3.60 | 4.20 | 0.34 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.02 | 5.34 × 10−6 | 6.87 × 10−6 | 8.02 × 10−6 | 6.49 × 10−7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tepeneu, A.; Lupitu, A.; Surdea-Blaga, T.; Moisa, C.; Chambre, D.; Copolovici, D.M.; Copolovici, L. Variability of Air Pollutants in the Indoor Air of a General Store. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12572. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312572
Tepeneu A, Lupitu A, Surdea-Blaga T, Moisa C, Chambre D, Copolovici DM, Copolovici L. Variability of Air Pollutants in the Indoor Air of a General Store. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(23):12572. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312572
Chicago/Turabian StyleTepeneu, Andreea, Andreea Lupitu, Teodora Surdea-Blaga, Cristian Moisa, Dorina Chambre, Dana Maria Copolovici, and Lucian Copolovici. 2023. "Variability of Air Pollutants in the Indoor Air of a General Store" Applied Sciences 13, no. 23: 12572. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312572
APA StyleTepeneu, A., Lupitu, A., Surdea-Blaga, T., Moisa, C., Chambre, D., Copolovici, D. M., & Copolovici, L. (2023). Variability of Air Pollutants in the Indoor Air of a General Store. Applied Sciences, 13(23), 12572. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312572








