Study on the Ion Mobility Spectrometry Data Classification and Application of Port Container Narcotics Using Machine Learning Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Research
Time-Series Data Classification Algorithm
3. IMS Data Characteristics
3.1. Narcotic IMS Data Types
3.2. Features of Narcotic IMS Data
3.2.1. Narcotics IMS Data Composed of RIP2RIP
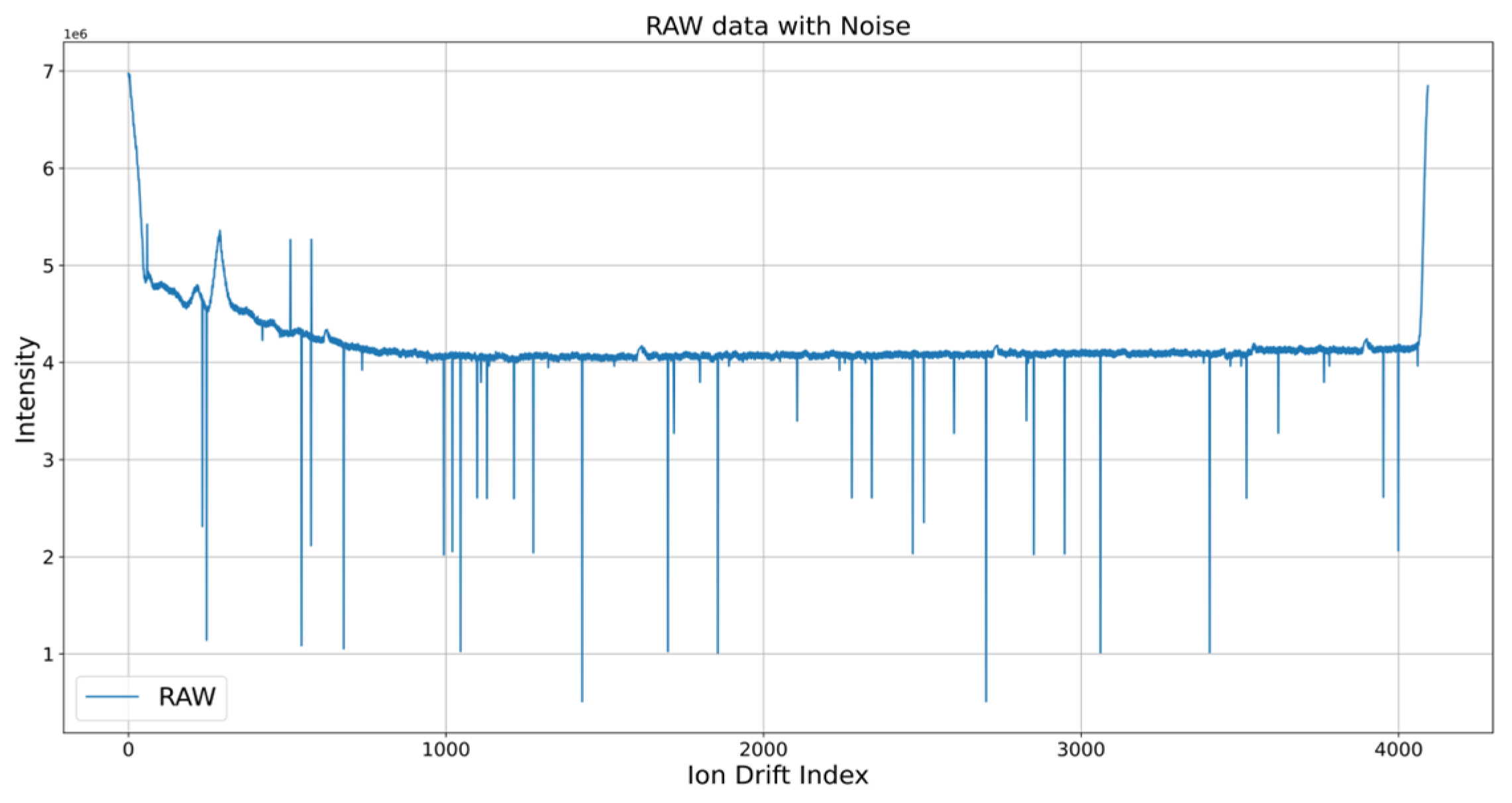
3.2.2. Narcotics IMS Data with Reduced Level of Response
3.2.3. Narcotic IMS Data Other Than the Difference between Response Sections
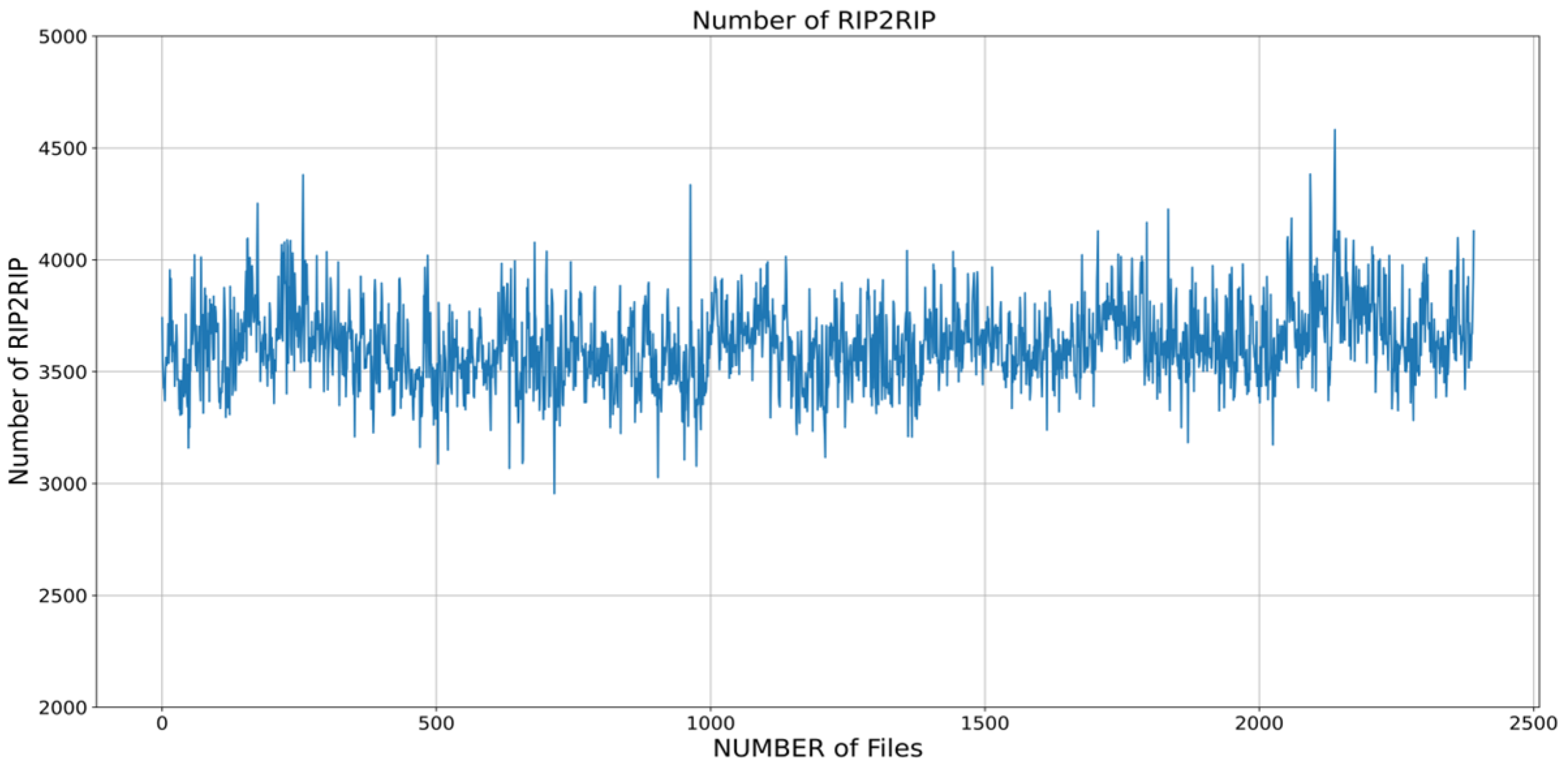
3.2.4. Diverse Data Quantity Configurations in RIP2RIP
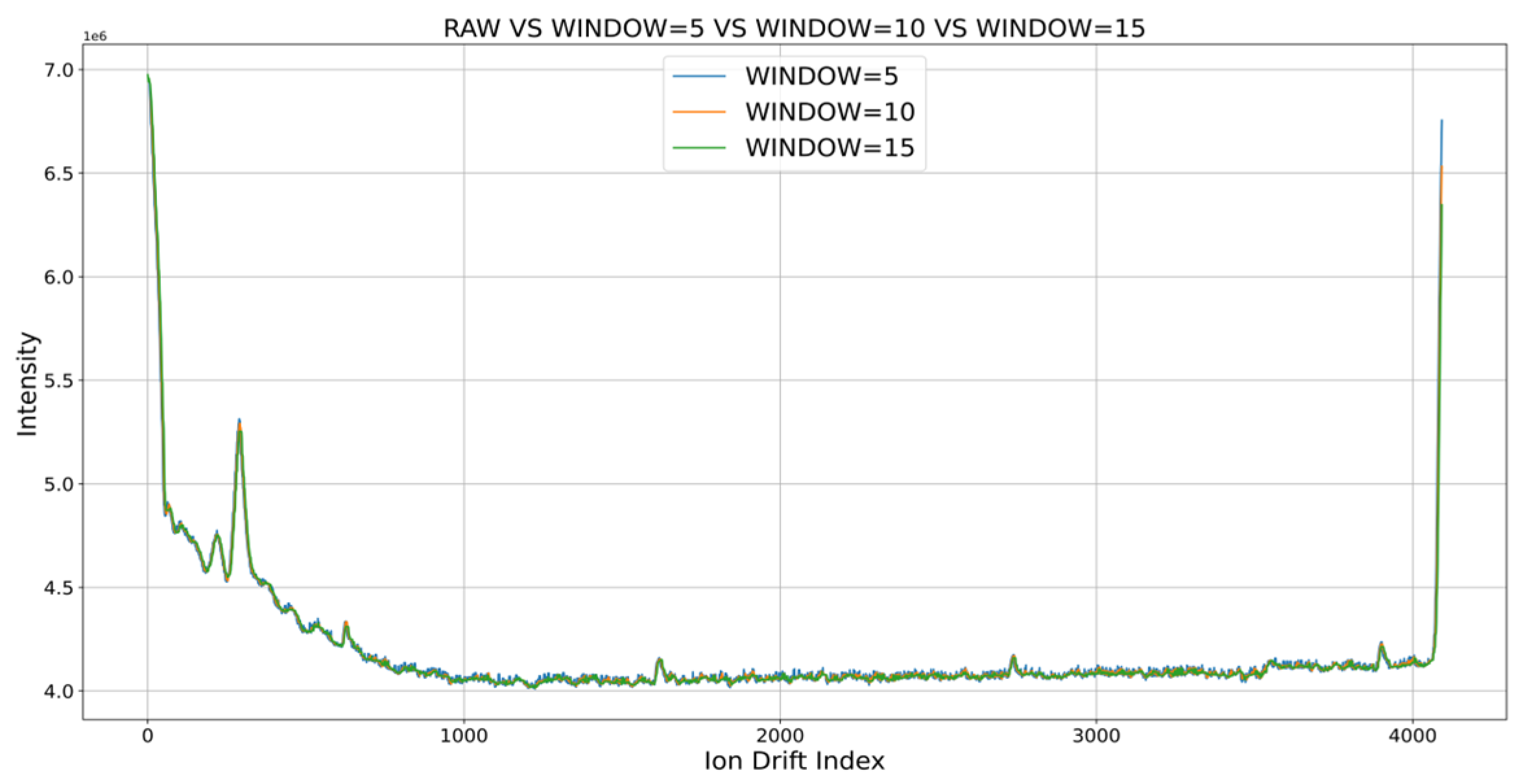
4. Narcotic IMS Data Noise Removal Algorithm
5. Narcotic IMS Data Classification Algorithm
5.1. KNN
5.2. TSF Algorithm
5.3. ROCKET Algorithm
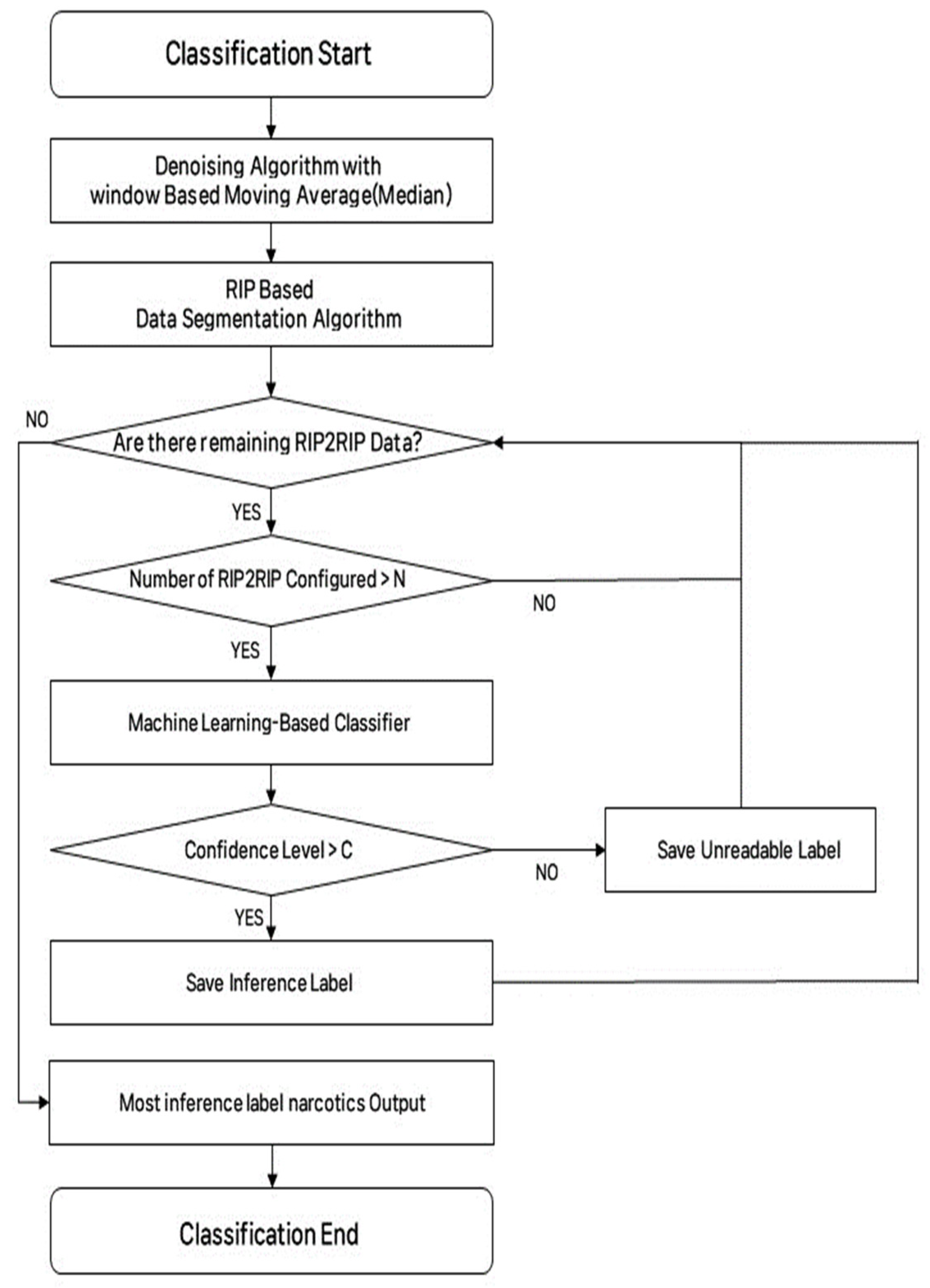
5.4. System Application Algorithm
6. Experiment Preparation and Results
6.1. Dataset Composition
6.2. Experiment Results
7. Embedded Board Application and Time Required
Embedded Board Specifications and Operating Time
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korea Prosecution Service. White Paper on Narcotic Crimes Chapter 3; Korea Prosecution Service: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2022; p. 98. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, A.Y.; Bizo, L.; Brown, W.Y. Olfactory generalization in detector dogs. Animals 2019, 9, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, W. The automatic detection of hiding narcotics in human bodies based on fractal dimension and SVM classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Applications (ICCIA), Beijing, China, 8–11 September 2017; pp. 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson, A.; Mossberg, M. Using spatial diversity to detect narcotics and explosives using NQR signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2007, 55, 4721–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goubran, R.A.; Lawrence, A.H. DSP techniques for narcotic detection using ion mobility spectrometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Sensing, Processing, Networking, IMTC Proceedings, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 19–21 May 1997; Volume 1, pp. 404–407. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, C.; Chen, N.; Hu, C.; Wang, K.; Xu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, Z.; Gong, J. A spatiotemporal deep learning model for sea surface temperature field prediction using time-series satellite data. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 120, 104502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braei, M.; Wagner, S. Anomaly detection in univariate time-series: A survey on the state-of-the-art. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.00433. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Xue, T.; Wang, D.; Qi, Y.; Su, M. Development direction of automated terminal and systematic planning of smart port. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Engineering (ICBAIE), Nanchang, China, 26–28 March 2021; pp. 708–712. [Google Scholar]
- Yau, K.-L.A.; Peng, S.; Qadir, J.; Low, Y.C.; Ling, M.H. Towards smart port infrastructures: Enhancing port activities using information and communications technology. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 83387–83404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkilä, M.; Saarni, J.; Saurama, A. Innovation in smart ports: Future directions of digitalization in container ports. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darban, Z.Z.; Webb, G.I.; Pan, S.; Aggarwal, C.C.; Salehi, M. Deep learning for time series anomaly detection: A survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.05244. [Google Scholar]
- Kostelich, E.J.; Schreiber, T. Noise reduction in chaotic time-series data: A survey of common methods. Phys. Rev. E 1993, 48, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanopoulos, A.; Alcock, R.; Manolopoulos, Y. Feature-based classification of time-series data. In Information Processing and Technology; Nikos, M., Stavros, D.N., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, U.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zaidi, N.; Ranaweera, C.; Li, G.; Zhu, Q. Kernel-based feature extraction for time series clustering. Knowledge science, engineering and management. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference, KSEM 2023, Guangzhou, China, 16–18 August 2023; pp. 276–283. [Google Scholar]
- Cover, T.M.; Hart, P.E. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 1967, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowalski, J.M.; Chady, T. Rapid identification of material defects based on pulsed multifrequency eddy current testing and the k-nearest neighbor method. Materials 2023, 16, 6650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappa, V.; Bogani, G.; Interlenghi, M.; Vittori Antisari, G.; Salvatore, C.; Zanchi, L.; Ludovisi, M.; Leone Roberti Maggiore, U.; Calareso, G.; Haeusler, E.; et al. Using radiomics and machine learning applied to MRI to predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced cervical cancer. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Runger, G.; Tuv, E.; Vladimir, M. A time series forest for classification and feature extraction. Inf. Sci. 2013, 239, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.; Petitjean, F.; Webb, G.I. ROCKET: Exceptionally fast and accurate time series classification using random convolutional kernels. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2019, 34, 1454–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS’17, Red Hook, NY, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 6000–6010. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Powell, A.; Ersoy, I.; Poostchi, M.; Silamut, K.; Palaniappan, K.; Guo, P.; Hossain, M.A.; Sameer, A.; Maude, R.J.; et al. Cnn-based image analysis for malaria diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Shenzhen, China, 15–18 December 2016; pp. 493–496. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Oates, T. Encoding time series as images for visual inspection and classification using tiled convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Workshops at the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 January 2015; AAAI Publications: Austin, TX, USA, 2015; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Eckmann, J.P.; Kamphorst, S.O.; Ruelle, D. Recurrence plots of dynamical systems. Europhys. Lett. 1987, 4, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Sampath, V.; May, M.C.; Shan, S.; Jorg, O.J.; Aguilar Martín, J.J.; Stamer, F.; Fantoni, G.; Tosello, G.; Calaon, M. Machine learning in manufacturing towards industry 4.0: From ‘for now’ to ‘four-know’. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Chow, M.Y.; Li, X.; Tian, J.; Luo, H.; Yin, S. A Data-model Interactive Remaining Useful Life Prediction Approach of Lithium-ion Batteries Based on PF-BiGRU-TSAM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 2023, 3266403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Byun, Y.-C. A CNN-GRU Approach to the Accurate Prediction of Batteries’ Remaining Useful Life from Charging Profiles. Computers 2023, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Park, K.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Jeon, W.K.; Kwon, K.W. Adaptive window-based detection of narcotics and explosives using IMS signals in cargo containers. J. Internet Comput. Serv. 2022, 23, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C. Time series data cleaning: A survey. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 1866–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhang, A.; Wang, J.; Yu, P.S. SCREEN: Stream data cleaning under speed constraints. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Melbourne, Australia, 31 May–4 June 2015; pp. 827–841. [Google Scholar]
- Berndt, D.J.; Clifford, J. Using dynamic time warping to find patterns in time series. In Proceedings of the KDD Workshop, Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 359–370. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, G.; Silva, D.F. How k-nearest neighbor parameters affect its performance. In Proceedings of the Argentine Symposium on Artificial Intelligence (ASAI), Mar del Plata, Argentina, 24–28 August 2009; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Faouzi, J.; Janati, H. pyts: A python package for time series classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Löning, M.; Bagnall, A.; Ganesh, S.; Kazakov, V.; Lines, J.; Király, F.J. sktime: A unified interface for machine learning with timeseries. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.07872. [Google Scholar]
- Tai, C.-Y.; Wang, W.-J.; Huang, Y.-M. Using Time-Series Generative Adversarial Networks to Synthesize Sensing Data for Pest Incidence Forecasting on Sustainable Agriculture. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |




| Illicit Manufacture | Smuggling | Illicit Trade | Illicit Cultivating | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of occurrences | 4 | 1392 | 3492 | 1714 |
| Occupation rate (%) | 0 | 7.6 | 19 | 9.3 |
| Injection | Possession | Others | Sum | |
| Number of occurrences | 8489 | 1032 | 2272 | 18,395 |
| Occupation rate (%) | 46.1 | 5.6 | 12.4 | 100 |
| Target Sample | Concentration (ng) | Number (Times) | Reference Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamine | 100 | 50 |  |
| Morphine hydrochloride hydrate | 100 | 35 | |
| Fentanyl | 100 | 57 | |
| Alfentanil HCI | 300 | 55 | |
| MDMA HCI | 100 | 55 | 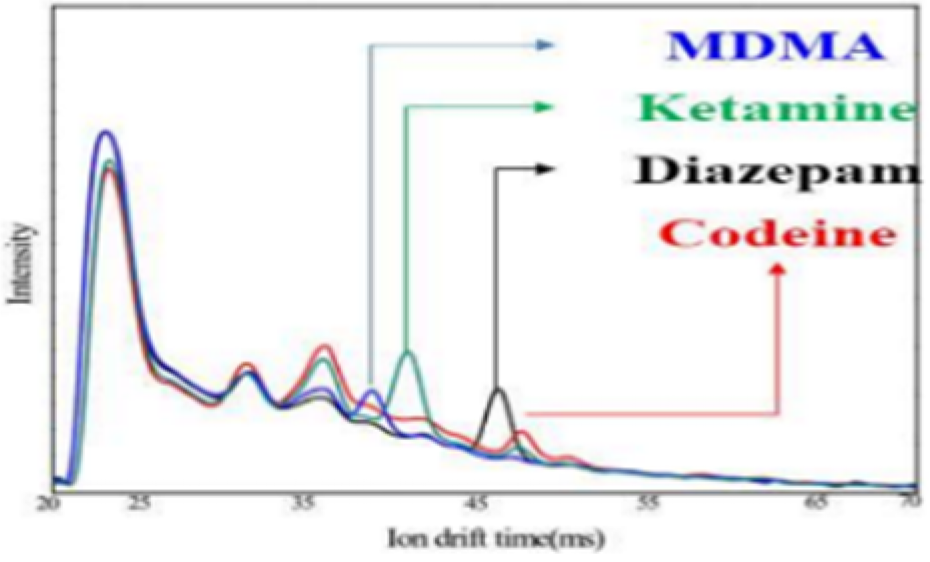 |
| Ketamine HCI | 100 | 52 | |
| Diazepam | 100 | 74 | |
| Codeine phosphate hydrate | 100 | 45 | |
| Normal state | — | 52 |
| Alf | Amp | Cod | Dia | Fen | Ket | MDMA | Mor | Normal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of testing CSV (times) | 35 | 30 | 25 | 54 | 37 | 32 | 35 | 15 | 32 |
| Alf | Amp | Cod | Dia | Fen | Ket | MDMA | Mor | Normal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of testing RIP2RIP | 1538 | 1255 | 1123 | 2308 | 1604 | 1424 | 1505 | 653 | 1467 |
| ALF | COD | FEN | KET | MDMA | Normal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data index | 800–950 | 575–625 | 625–800 | 425–525 | 350–425 | — |
| Threshold | 4,050,000 | 4,400,000 | 4,400,000 | 4,700,000 | 4,600,000 | — |
| Classifier | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1_score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Threshold | 0.362 | 0.667 | 0.362 | 0.415 (8) |
| KNN (k = 1) | 0.881 | 1 | 0.881 | 0.936 (2) |
| KNN (k = 2) | 0.813 | 1 | 0.813 | 0.896 (3) |
| KNN (k = 3) | 0.754 | 1 | 0.754 | 0.858 (4) |
| KNN (k = 4) | 0.713 | 1 | 0.713 | 0.831 (5) |
| TSF (c = 0.9) | 0.41 | 1 | 0.41 | 0.572 (7) |
| TSF (c = 0.8) | 0.56 | 1 | 0.56 | 0.731 (6) |
| ROCKET | 0.953 | 1 | 0.953 | 0.974 (1) |
| Classifier | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1_score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAA(KNN (k = 1)) | 0.970 | 1 | 0.970 | 0.989 (3) |
| SAA(KNN (k = 2)) | 0.975 | 1 | 0.975 | 0.986 (5) |
| SAA(KNN (k = 3)) | 0.970 | 1 | 0.970 | 0.988 (4) |
| SAA(KNN (k = 4)) | 0.984 | 1 | 0.984 | 0.991 (2) |
| SAA(TSF (c = 0.9)) | 0.913 | 1 | 0.913 | 0.953 (7) |
| SAA(TSF (c = 0.8)) | 0.972 | 1 | 0.972 | 0.985 (6) |
| SAA (ROCKET) | 0.993 | 1 | 0.993 | 0.996 (1) |
| Algorithm | Max (s) | Min (s) | Average (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| KNN (k = 1) | 2.2 | 1.8 | 2.17 (4) |
| KNN (k = 2) | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.09 (1) |
| KNN (k = 3) | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.12 (3) |
| KNN (k = 4) | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.10 (2) |
| TSF | 9.5 | 4.3 | 4.98 (5) |
| ROCKET | 33 | 31 | 31.7 (6) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Kemelbekova, G.; Cho, S.; Kwon, K.; Im, T. Study on the Ion Mobility Spectrometry Data Classification and Application of Port Container Narcotics Using Machine Learning Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312769
Park S, Kemelbekova G, Cho S, Kwon K, Im T. Study on the Ion Mobility Spectrometry Data Classification and Application of Port Container Narcotics Using Machine Learning Algorithm. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(23):12769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312769
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Saeyong, Gualnaz Kemelbekova, Sungyoon Cho, Kiwon Kwon, and Taeho Im. 2023. "Study on the Ion Mobility Spectrometry Data Classification and Application of Port Container Narcotics Using Machine Learning Algorithm" Applied Sciences 13, no. 23: 12769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312769
APA StylePark, S., Kemelbekova, G., Cho, S., Kwon, K., & Im, T. (2023). Study on the Ion Mobility Spectrometry Data Classification and Application of Port Container Narcotics Using Machine Learning Algorithm. Applied Sciences, 13(23), 12769. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312769









