Frequency and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Foodborne Pathogens in Ready-to-Eat Foods: An Evolving Public Health Challenge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Total Bacterial Count
2.3. Pathogenic Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.4. MALDI-TOF Spectrometry Based Screening of Foodborne Pathogens
2.5. Susceptibility Test for Antimicrobials
2.6. Molecular Detection of Antibiotic Resistance Genes for Foodborne Pathogens
2.6.1. Extraction of Nucleic Acid
2.6.2. Primers and Standards for Real Time PCR
3. Results
3.1. Total Bacterial Count
3.2. Different Types of Foodborne Pathogens and Their Prevalence
3.3. Identification of Foodborne Pathogens Using Protein Fingerprinting
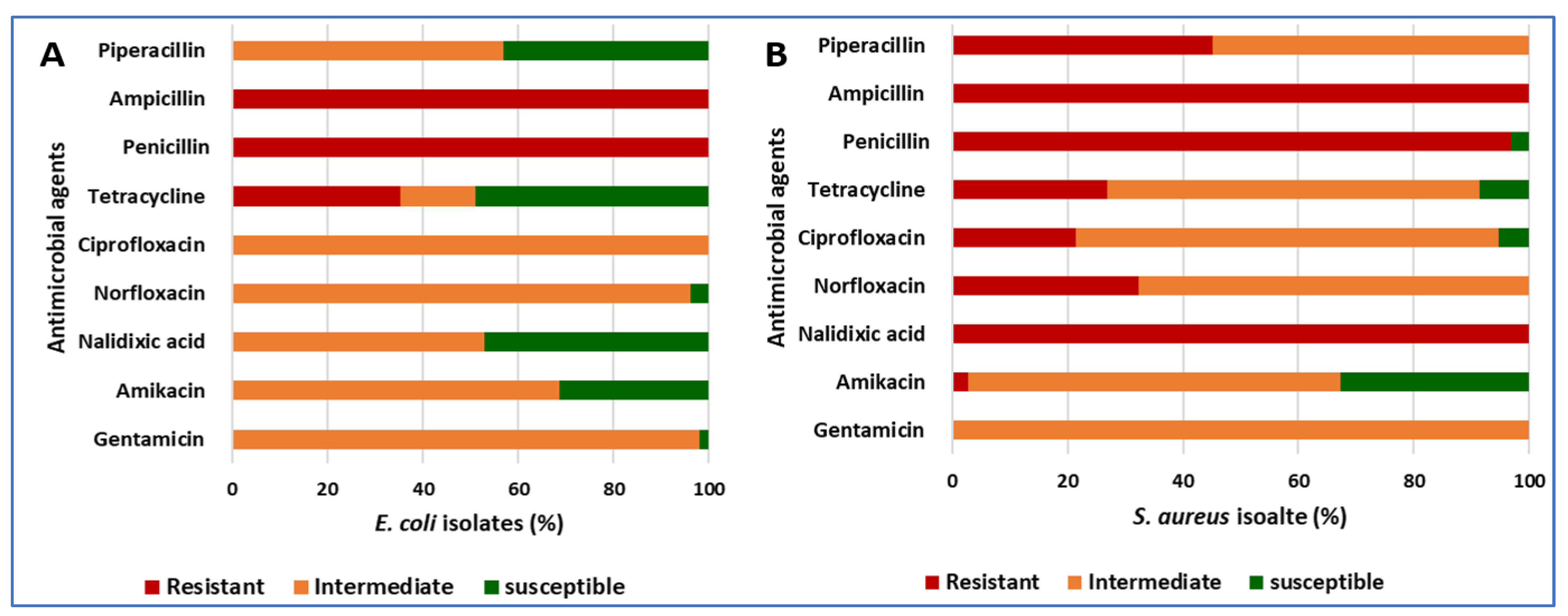
3.4. The Antibiotic Resistance Patterns of E. coli and S. aureus Isolates
3.5. The Frequency of Antibiotic Resistance Genes among E. coli and S. aureus Isolates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bintsis, T. Foodborne pathogens. AIMS Microbiol. 2017, 3, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aworh, O.C. Food safety issues in fresh produce supply chain with particular reference to sub-Saharan Africa. Food Control 2021, 123, 107737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Moussa, I.M.; Dawoud, T.M.; Mubarak, A.S.; Al-Sarar, D.; Alsubki, R.A.; Alhaji, J.H.; Hamada, M.; Abalkhail, A. Acinetobacter baumannii as a community foodborne pathogen: Peptide mass fingerprinting analysis, genotypic of biofilm formation and phenotypic pattern of antimicrobial resistance. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzaben, F.; Fat’hi, S.; Elbehiry, A.; Alsugair, M.; Marzouk, E.; Abalkhail, A.; Almuzaini, A.M.; Rawway, M.; Ibrahem, M.; Sindi, W. Laboratory diagnostic methods and antibiotic resistance patterns of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli strains: An Evolving Human Health Challenge. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeen, E.E.; Mousa, W.S.; Salam, S.Y.A.; Al-Maary, K.S.; Mubarak, A.S.; Moussa, I.M.; Hemeg, H.A.; Almuzaini, A.M.; Alajaji, A.I.; Alsubki, R.A. Antibiogram and phylogenetic diversity of enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus strains from milk products and public health implications. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1968–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, K.M.; Pires, Á.d.S.; Franco, O.L.; Orabi, A.; Hanafy, M.H.; Marzouk, E.; Hussien, H.; Alzaben, F.A.; Almuzaini, A.M.; Elbehiry, A. Enterotoxigenicity and antibiotic resistance of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from raw buffalo and cow milk. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Abdeen, E.; Al-Dubaib, M.; Alsayeqh, A.; Ibrahem, M.; Hamada, M.; Alenzi, A.; Moussa, I.; Hemeg, H.A. Proteomic characterization and discrimination of Aeromonas species recovered from meat and water samples with a spotlight on the antimicrobial resistance of Aeromonas hydrophila. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbehiry, A.; Abalkhail, A.; Marzouk, E.; Elmanssury, A.E.; Almuzaini, A.M.; Alfheeaid, H.; Alshahrani, M.T.; Huraysh, N.; Ibrahem, M.; Alzaben, F. An Overview of the Public Health Challenges in Diagnosing and Controlling Human Foodborne Pathogens. Vaccines 2023, 11, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebelo, K.; Malebo, N.; Mochane, M.J.; Masinde, M. Chemical contamination pathways and the food safety implications along the various stages of food production: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamala, K.; Kumar, V.P. Food products and food contamination. In Microbial Contamination and Food Degradation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoso, M.J.; Ferreira, V.; Truninger, M.; Maia, R.; Teixeira, P. Cross-contamination events of Campylobacter spp. in domestic kitchens associated with consumer handling practices of raw poultry. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 338, 108984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaary, K.S. Food-Borne Diseases and their Impact on Health. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2023, 20, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Qi, X.; He, Y.; Chen, J. An 11-year analysis of bacterial foodborne disease outbreaks in Zhejiang Province, China. Foods 2022, 11, 2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Alifu, X.; Chen, J.; Luo, W.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, R. Descriptive study of foodborne disease using disease monitoring data in Zhejiang Province, China, 2016–2020. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffee, S.; Henson, S.; Unnevehr, L.; Grace, D.; Cassou, E. The Safe Food Imperative: Accelerating Progress in Low-and Middle-Income Countries; World Bank Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Alhashim, L.A.; Alshahrani, N.Z.; Alshahrani, A.M.; Khalil, S.N.; Alrubayii, M.A.; Alateeq, S.K.; Zakaria, O.M. Food safety knowledge and attitudes: A cross-sectional study among Saudi consumers from food trucks owned by productive families. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzitey, F. Incidence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Escherichia coli isolated from beef (meat muscle, liver and kidney) samples in Wa Abattoir, Ghana. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1718269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatibi, S.A.; Hamidi, S.; Siahi-Shadbad, M.R. Current trends in sample preparation by solid-phase extraction techniques for the determination of antibiotic residues in foodstuffs: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3361–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatibi, S.A.; Hamidi, S.; Siahi-Shadbad, M.R. Application of liquid-liquid extraction for the determination of antibiotics in the foodstuff: Recent trends and developments. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 52, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaei, M.; Moosavy, M.-H.; Gharajalar, S.N.; Khatibi, S.A. Antibiotic resistance in the pathogenic foodborne bacteria isolated from raw kebab and hamburger: Phenotypic and genotypic study. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.Y.K.; Nang, S.C.; Chan, H.-K.; Li, J. Novel antimicrobial agents for combating antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022, 187, 114378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makabenta, J.M.V.; Nabawy, A.; Li, C.-H.; Schmidt-Malan, S.; Patel, R.; Rotello, V.M. Nanomaterial-based therapeutics for antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Om, C.; McLaws, M.-L. Antibiotics: Practice and opinions of Cambodian commercial farmers, animal feed retailers and veterinarians. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2016, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebi Bezmin Abadi, A.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Haertlé, T.; Blatt, N.L. World Health Organization report: Current crisis of antibiotic resistance. BioNanoScience 2019, 9, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Al-Amin, M.Y.; Salam, M.T.; Pawar, J.S.; Akhter, N.; Rabaan, A.A.; Alqumber, M.A. Antimicrobial Resistance: A Growing Serious Threat for Global Public Health. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacanlı, M.; Başaran, N. Importance of antibiotic residues in animal food. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsène, M.M.J.; Davares, A.K.L.; Viktorovna, P.I.; Andreevna, S.L.; Sarra, S.; Khelifi, I.; Sergueïevna, D.M. The public health issue of antibiotic residues in food and feed: Causes, consequences, and potential solutions. Vet. World 2022, 15, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addis, M. A review on antibiotic resistant and implication on food chain. J. Food Sci. 2015, 42, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bastam, M.M.; Jalili, M.; Pakzad, I.; Maleki, A.; Ghafourian, S. Pathogenic bacteria in cheese, raw and pasteurised milk. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 2445–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gutiérrez, M.; García-Fernández, C.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Capita, R. Microbial load and antibiotic resistance in raw beef preparations from northwest Spain. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, A.; Khatibi, S.A. Effect of commercial probiotic (Protexin®) on growth, survival and microbial quality of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). BMC Microbiol. 2017, 47, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crits-Christoph, A.; Hallowell, H.A.; Koutouvalis, K.; Suez, J. Good microbes, bad genes? The dissemination of antimicrobial resistance in the human microbiome. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2055944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serwecińska, L. Antimicrobials and antibiotic-resistant bacteria: A risk to the environment and to public health. Water 2020, 12, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.; Algammal, A.; Abouel-Atta, M.; Mabrok, M.; Emam, A. Pathogenicity, genetic typing, and antibiotic sensitivity of Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from Oreochromis niloticus and Tilapia zillii. Rev. Med. Vet. 2019, 170, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Algammal, A.M.; Mabrok, M.; Sivaramasamy, E.; Youssef, F.M.; Atwa, M.H.; El-Kholy, A.W.; Hetta, H.F.; Hozzein, W.N. Emerging MDR-Pseudomonas aeruginosa in fish commonly harbor opr L and tox A virulence genes and bla TEM, bla CTX-M, and tet A antibiotic-resistance genes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enany, M.E.; Algammal, A.M.; Nasef, S.A.; Abo-Eillil, S.A.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Taha, A.E.; Allam, A.A. The occurrence of the multidrug resistance (MDR) and the prevalence of virulence genes and QACs resistance genes in E. coli isolated from environmental and avian sources. AMB Express 2019, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Webster, T.J. Bacteria antibiotic resistance: New challenges and opportunities for implant-associated orthopedic infections. J. Orthop. Res. 2018, 36, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novovic, K.; Mihajlovic, S.; Vasiljevic, Z.; Filipic, B.; Begovic, J.; Jovcic, B. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii from Serbia: Revision of CarO classification. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelalcha, B.D.; Kerro Dego, O. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases Producing Enterobacteriaceae in the USA Dairy Cattle Farms and Implications for Public Health. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamma, P.D.; Aitken, S.L.; Bonomo, R.A.; Mathers, A.J.; Van Duin, D.; Clancy, C.J. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidance on the treatment of extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Enterobacterales (ESBL-E), carbapenem-resistant Enterobacterales (CRE), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa with difficult-to-treat resistance (DTR-P. aeruginosa). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 72, e169–e183. [Google Scholar]
- Newell, D.G.; Koopmans, M.; Verhoef, L.; Duizer, E.; Aidara-Kane, A.; Sprong, H.; Opsteegh, M.; Langelaar, M.; Threfall, J.; Scheutz, F. Food-borne diseases—The challenges of 20 years ago still persist while new ones continue to emerge. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, A.; Razavilar, V.; Rokni, N.; Rahimi, E. VacA and cagA genotypes status and antimicrobial resistance properties of Helicobacter pylori strains isolated from meat products in Isfahan province, Iran. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 18, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, J.; Gil, J.; Mourao, J.; Peixe, L.; Antunes, P. Ready-to-eat street-vended food as a potential vehicle of bacterial pathogens and antimicrobial resistance: An exploratory study in Porto region, Portugal. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 206, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeid, R.; Heil, S.; Verhoeven, M.; van den Heuvel, E.; de Groot LCPGM, E.S. Vitamin B12 intake from animal foods, biomarkers, and health aspects. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaf Hussain, M.; Wang, W.; Sun, C.; Gu, L.; Liu, Z.; Yu, T.; Ahmad, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, J. Molecular Characterization Of Pathogenic Salmonella Spp From Raw Beef In Karachi, Pakistan. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latha, C.; Anu, C.; Ajaykumar, V.; Sunil, B. Prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes, Yersinia enterocolitica, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella enterica Typhimurium in meat and meat products using multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Vet. World 2017, 10, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abebe, E.; Gugsa, G.; Ahmed, M. Review on major food-borne zoonotic bacterial pathogens. J. Trop. Med. 2020, 2020, 4674235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Moosavy, M.H.; Khatibi, S.A.; Barabadi, Z.; Hajibemani, A. A comparative study of the antibacterial properties of milk from different domestic animals. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2021, 74, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeżak, K.; Kozajda, A. Occurrence and spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria on animal farms and in their vicinity in Poland and Ukraine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 9533–9559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, M.E. Multidrug-resistant pathogens in the food supply. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokshi, A.; Sifri, Z.; Cennimo, D.; Horng, H. Global contributors to antibiotic resistance. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2019, 11, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, N.; Islam, N.F.; Sonowal, S.; Prasad, R.; Sarma, H. Environmental antibiotics and resistance genes as emerging contaminants: Methods of detection and bioremediation. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2021, 2, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchins, A.D.; Jinneman, K.; Chen, Y. BAM Chapter 10: Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in foods and environmental samples, and enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes in foods. In Bacteriological Analytical Manual; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2017; pp. 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Maharjan, S.; Rayamajhee, B.; Chhetri, V.S.; Sherchan, S.P.; Panta, O.P.; Karki, T.B. Microbial quality of poultry meat in an ISO 22000: 2005 certified poultry processing plant of Kathmandu valley. Int. J. Food Contam. 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Weagant, S.D.; Grant, M.A.; Burkhardt, W.; Shellfish, M.; Water, B. BAM: Enumeration of Escherichia coli and the Coliform Bacteria. In Bacteriological Analytical Manual; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2002; Volume 13, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lartigue, M.-F. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for bacterial strain characterization. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 13, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, A.; Kirby, W.; Sherris, J.C.; Turck, M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1966, 45, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.; Cockerill, F., III; Alder, J.; Bradford, P.; Eliopoulos, G.; Hardy, D. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twenty-fourth informational supplement. CLSI Stand. Antimicrob. Susceptibility Test. 2014, 34, 1–226. [Google Scholar]
- Dewey-Mattia, D.; Manikonda, K.; Hall, A.J.; Wise, M.E.; Crowe, S.J. Surveillance for foodborne disease outbreaks—United States, 2009–2015. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2018, 67, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yemmireddy, V.K.; Hung, Y.C. Using photocatalyst metal oxides as antimicrobial surface coatings to ensure food safety—Opportunities and challenges. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, J.-C.; Kooh, P.; Bayeux, T.; Guillier, L.; Meyer, T.; Jourdan-Da Silva, N.; Villena, I.; Sanaa, M.; Cerf, O. Contribution of foods and poor food-handling practices to the burden of foodborne infectious diseases in France. Foods 2020, 9, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbehiry, A.; Marzouk, E.; Hamada, M.; Al-Dubaib, M.; Alyamani, E.; Moussa, I.M.; AlRowaidhan, A.; Hemeg, H.A. Application of MALDI-TOF MS fingerprinting as a quick tool for identification and clustering of foodborne pathogens isolated from food products. New Microbiol. 2017, 40, 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Strange, E.; Benedict, R.; Smith, J.; Swift, C. Evaluation of rapid tests for monitoring alterations in meat quality during storage. J. Food Prot. 1977, 40, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, A.; Mittler, M.; Hebel, M.; Waldhans, C.; Herbert, U.; Kreyenschmidt, J. A Multi-Model Approach to Implement a Dynamic Shelf Life Criterion in Meat Supply Chains. Foods 2021, 10, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møretrø, T.; Langsrud, S. Residential bacteria on surfaces in the food industry and their implications for food safety and quality. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 1022–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrah, S.R. Bacterial indicators of viruses. In Viruses in Foods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 189–204. [Google Scholar]
- Grassi, T.; Bagordo, F.; Idolo, A.; Lugoli, F.; Gabutti, G.; De Donno, A. Rotavirus detection in environmental water samples by tangential flow ultrafiltration and RT-nested PCR. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 164, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogorzaly, L.; Tissier, A.; Bertrand, I.; Maul, A.; Gantzer, C. Relationship between F-specific RNA phage genogroups, faecal pollution indicators and human adenoviruses in river water. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Giglio, O.; Caggiano, G.; Bagordo, F.; Barbuti, G.; Brigida, S.; Lugoli, F.; Grassi, T.; La Rosa, G.; Lucentini, L.; Uricchio, V.F. Enteric viruses and fecal bacteria indicators to assess groundwater quality and suitability for irrigation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgir, A.; Khan, M.A.; Schilling, J.; Shaukat, S.S.; Shahab, S. Assessment of groundwater quality in the coastal area of Sindh province, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, W.; Woudstra, S.; Müller, A.; Grabowski, N.; Schoo, G.; Gerulat, B.; Klein, G.; Kehrenberg, C. The safety and quality of pork and poultry meat imports for the common European market received at border inspection post Hamburg Harbour between 2014 and 2015. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parafati, L.; Palmeri, R.; Trippa, D.; Restuccia, C.; Fallico, B. Quality maintenance of beef burger patties by direct addiction or encapsulation of a prickly pear fruit extract. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andritsos, N.D.; Mataragas, M.; Mavrou, E.; Stamatiou, A.; Drosinos, E.H. The microbiological condition of minced pork prepared at retail stores in Athens, Greece. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easa, S.M.H. The microbial quality of fast food and traditional fast food. Nat. Sci. 2010, 8, 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Bereda, T.W.; Emerie, Y.M.; Reta, M.A.; Asfaw, H.S. Microbiological safety of street vended foods in Jigjiga City, Eastern Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2016, 26, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahne, J.; Isele, D.; Berning, J.; Lipski, A. The contribution of fast growing, psychrotrophic microorganisms on biodiversity of refrigerated raw cow’s milk with high bacterial counts and their food spoilage potential. Food Microbiol. 2019, 79, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Alegbeleye, O.O.; Strateva, M.; Stratev, D. Understanding spoilage microbial community and spoilage mechanisms in foods of animal origin. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nethathe, B.; Matsheketsheke, P.A.; Mashau, M.E.; Ramashia, S.E. Microbial safety of ready-to-eat food sold by retailers in Thohoyandou, Limpopo province, South Africa. Cogent Food Agric. 2023, 9, 2185965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, Z.M.; Mustafa, S.I.; Ahmed, C.J.; Mikaeel, F.B.; Ali, M.M.; Khudr, A.I.; Ali, S.Z.; Haji, M.L. Multidrug-resistant and clonal dispersion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli from ready-to-eat meat products in Duhok province, Iraq. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 37, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, A.G.; El Naghy, W.S.; Shahbab, A.A.; Hassan, A.M. Evaluation of antagonistic activity of an Egyptian probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum against bacteria isolated from ready-to-eat meat products. Tanta Med. J. 2023, 51, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, J.; Asmat, T.M.; Mustafa, M.Z.; Ishtiaq, H.; Mumtaz, K.; Jalees, M.M.; Samad, A.; Shah, A.; Khalid, S.; ur Rehman, H. Contamination of ready-to-eat street food in Pakistan with Salmonella spp.: Implications for consumers and food safety. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 106, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemeg, H. Molecular characterization of antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli isolates recovered from food samples and outpatient clinics, KSA. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 928–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelalem, A.; Sisay, M.; Vipham, J.L.; Abegaz, K.; Kebede, A.; Terefe, Y. The prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profiles of bacterial isolates from meat and meat products in Ethiopia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Food Contam. 2019, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunabe, T.; Honma, Y. Relationship between O-Serogroup and presence of pathogenic factor genes in Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Immunol. 1998, 42, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, G.; Dümen, E. Escherichia coli and food safety. In The Universe of Escherichia coli; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tebbutt, G.; Southwell, J. Comparative study of visual inspections and microbiological sampling in premises manufacturing and selling high-risk foods. Epidemiol. Infect. 1989, 103, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltout, F.A.E.; Farouk, M.; Ibrahim, H.A.; Afifi, M.E. Incidence of E. coli and Salmonellae in ready to eat fast foods. Benha Vet. Med. J. 2017, 32, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-C.; Lin, C.-H.; Aljuffali, I.A.; Fang, J.-Y. Current pathogenic Escherichia coli foodborne outbreak cases and therapy development. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Synge, B. Verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli: A veterinary view. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 31S–37S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Koster, C.G.; Brul, S. MALDI-TOF MS identification and tracking of food spoilers and food-borne pathogens. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 10, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimowicz, M.; Bucka-Kolendo, J. MALDI-TOF MS–application in food microbiology. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2020, 67, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feucherolles, M.; Nennig, M.; Becker, S.L.; Martiny, D.; Losch, S.; Penny, C.; Cauchie, H.-M.; Ragimbeau, C. Combination of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and machine learning for rapid antimicrobial resistance screening: The case of Campylobacter spp. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 804484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagao, M.; Tanaka, M.; Machida, K.; Ito, Y.; Takakura, S.; Ichiyama, S. Detection of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli ST131 and ST405 clonal groups by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos-Garzón, A.; Cortes, G.; Morio, F.; Zamora-Cruz, E.L.; Linares, M.Y.; Ariza, B.E.; Valderrama, S.L.; Garzón, J.R.; Alvarez-Moreno, C.A.; Le Pape, P. Comparison between MALDI-TOF MS and MicroScan in the identification of emerging and multidrug resistant yeasts in a fourth-level hospital in Bogotá, Colombia. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.Y.; Da’na, D.A.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Application of MALDI-TOF MS for identification of environmental bacteria: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailasa, S.K.; Koduru, J.R.; Baek, S.H.; Wu, H.-F.; Hussain, C.M.; Park, T.J. Review on matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the rapid screening of microbial species: A promising bioanalytical tool. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkaoui, A.; Hibbs, J.; Emonet, S.; Tangomo, M.; Girard, M.; Francois, P.; Schrenzel, J. Comparison of two matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry methods with conventional phenotypic identification for routine identification of bacteria to the species level. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlovic, M.; Huber, I.; Konrad, R.; Busch, U. Application of MALDI-TOF MS for the identification of food borne bacteria. Open Microbiol. J. 2013, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valilis, E.; Ramsey, A.; Sidiq, S.; DuPont, H.L. Non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli—A poorly appreciated enteric pathogen: Systematic review. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 76, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrine, M.; Matambisso, G.; Nobela, N.; Vubil, D.; Massora, S.; Acácio, S.; Nhampossa, T.; Alonso, P.; Mandomando, I. Low frequency of enterohemorrhagic, enteroinvasive and diffusely adherent Escherichia coli in children under 5 years in rural Mozambique: A case-control study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Dudeja, P.K. Pathophysiology of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli-induced Diarrhea. Pathophysiology 2023, 2, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, F.M.; Grigura, V.; Vickers, T.J.; Prouty, M.G.; Iannotti, L.L.; Dulience, S.J.L.; Fleckenstein, J.M. Seroprevalence Study of Conserved Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Antigens in Globally Diverse Populations. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Aila, N.A.; Al Laham, N.A.; Ayesh, B.M. Prevalence of extended spectrum beta lactamase and molecular detection of blaTEM, blaSHV and blaCTX-M genotypes among Gram negative bacilli isolates from pediatric patient population in Gaza strip. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, I.d.A.; Ferrari, R.G.; Panzenhagen, P.; Pereira dos Santos, A.M.; Rodrigues, G.L.; Junior, C.A.C.; Mano, S.B. The antibiotic resistome in Escherichia coli isolated from human, food, and animal sources. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134, lxac059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria: A challenge for the food industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegría, Á.; Arias-Temprano, M.; Fernández-Natal, I.; Rodríguez-Calleja, J.M.; García-López, M.-L.; Santos, J.A. Molecular diversity of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli from foods of animal origin and human patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, H.; Jackson, C.R.; Frye, J.G.; Hiott, L.M.; Samir, M.; Awad, A.; Woodley, T.A. Antimicrobial resistance, genetic diversity and multilocus sequence typing of Escherichia coli from humans, retail chicken and ground beef in Egypt. Pathogens 2020, 9, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W.; Zadernowska, A.; Łaniewska-Trokenheim, Ł. Staphylococcus aureus from ready-to-eat food as a source of multiple antibiotic resistance genes. In Proceedings of the CBU International Conference Proceedings, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–24 March 2017; pp. 1108–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Shahraz, F.; Dadkhah, H.; Khaksar, R.; Mahmoudzadeh, M.; Hosseini, H.; Kamran, M.; Bourke, P. Analysis of antibiotic resistance patterns and detection of mecA gene in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from packaged hamburger. Meat Sci. 2012, 90, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aa, A.; Ibrahim, E.; Fouad, E.; Gaber, E. Antibiotic resistance of staphylococci concerning strains included in food industry in Egypt. Int. J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2016, 8, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Mahros, M.A.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Sallam, K.I. Multidrug-, methicillin-, and vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from ready-to-eat meat sandwiches: An ongoing food and public health concern. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 346, 109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamebo, T.; Bacha, K.; Ketema, T. The growth potential and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Salmonella species and Staphylococcus aureus isolated from mobile phones of food handlers and health care workers in Jimma Town, Southwest Ethiopia. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 10, 254–259. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, G.M.; HAFEZ, T.A.; ELDahshan, H.A. prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of staphylococcus aureus isolated from meat and some meat products with detection of resistant genes using PCR. Egypt. J. Agric. Res 2015, 93, 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Çetinkaya, F.; Tülay, E. Detection of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from various foods. Uludağ Üniv. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2012, 31, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Torki Baghbaderani, Z.; Shakerian, A.; Rahimi, E. Phenotypic and genotypic assessment of antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria isolated from retail meat. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu-Wu, J.W.F.; Guadamuz-Mayorga, C.; Oviedo-Cerdas, D.; Zamora, W.J. Antibiotic resistance and food safety: Perspectives on new technologies and molecules for microbial control in the food industry. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoletti, O.; Budka, H.; Buncic, S.; Colin, P.; Collins, J.D.; De, A.; Koeijer, J.G.; Havelaar, A.; Hope, J.; Klein, G. Foodborne antimicrobial resistance as a biological hazard Draft Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Biological Hazards 2. EFSA J. 2008, 341, 1–131. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, S. Understanding the contribution of environmental factors in the spread of antimicrobial resistance. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2015, 20, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.J. Environmental factors influencing the development and spread of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, fux053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzidic, S.; Bedeković, V. Horizontal gene transfer-emerging multidrug resistance in hospital bacteria. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2003, 24, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Djordjevic, S.P.; Stokes, H.W.; Chowdhury, P.R. Mobile elements, zoonotic pathogens and commensal bacteria: Conduits for the delivery of resistance genes into humans, production animals and soil microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanton, I.C.; Bethel, A.; Leonard, A.F.C.; Gaze, W.H.; Garside, R. Existing evidence on antibiotic resistance exposure and transmission to humans from the environment: A systematic map. Environ. Evid. 2022, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Costa, V.M.; King, C.E.; Kalan, L.; Morar, M.; Sung, W.W.; Schwarz, C.; Froese, D.; Zazula, G.; Calmels, F.; Debruyne, R. Antibiotic resistance is ancient. Nature 2011, 477, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Feng, J.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Li, B. Reponses of microbial community and antibiotic resistance genes to the selection pressures of ampicillin, cephalexin and chloramphenicol in activated sludge reactors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazeena, S.H.; Chen, X.-H.; Yeh, C.-S.; Hsieh, C.-W.; Chen, M.-H.; Huang, P.-H.; Hou, C.-Y.; Shih, M.-K. The relationship among knowledge, attitude, and behavior of workers on food safety in Taiwan’s Company A. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 60, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayuti, Y.; Albattat, A.; Ariffin, A.; Nazrin, N.; Silahudeen, T. Food safety knowledge, attitude and practices among management and science university students, Shah Alam. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2020, 10, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okojie, O.; Wagbatsoma, V.; Ighoroge, A. An assessment of food hygiene among food handlers in a Nigerian university campus. Niger. Postgrad. Med. J. 2005, 12, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, İ.; Lekesiz, Ö. Hygiene, Control and Contamination in Foods: A Review. Eurasian J. Med. Biol. Sci. 2022, 2, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ayad, A.A.; Abdulsalam, N.M.; Khateeb, N.A.; Hijazi, M.A.; Williams, L.L. Saudi Arabia household awareness and knowledge of food safety. Foods 2022, 11, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Target | Oligonucleotide Sequence | Base Pair (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| blaTEM | F: ATC AGC AAT AAA CCA GC | 516 |
| R: CCC CGA AGA ACG TTT TC | ||
| tet(A) | F: GGTTCACTCGAACGACGTCA | 577 |
| R: CTGTCCGACAAGTTGCATGA | ||
| blaz | F: TGA CCA CTT TTA TCA GCA ACC | 700 |
| R: GCC ATT TCA ACA CCT TCT TTC | ||
| mecA | F: AAA ATC GAT GGT AAA GGT TGG C | 532 |
| R: AGT TCT GCA GTA CCG GAT TTG C |
| Foodborne Pathogen | Positive Shawarma Samples | Positive Chicken Burger Samples | Total (n = 300) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| E. coli | 58 | 38.67 | 44 | 29.33 | 102 | 34.00 |
| S. aureus | 48 | 32.00 | 45 | 30.00 | 93 | 31.00 |
| Salmonella | 19 | 12.67 | 13 | 8.67 | 32 | 10.67 |
| L. monocytogenes | 13 | 8.67 | 9 | 6.00 | 22 | 7.33 |
| A. baumannii | 12 | 8.00 | 8 | 5.33 | 20 | 6.67 |
| Hafnia alevei | 7 | 4.67 | 5 | 3.33 | 12 | 4.00 |
| Antibiotic Class | Conc. | E. coli (n = 102) | S. aureus (n = 93) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibition Zone Breakpoints (mm) | % of Isolates/Total Isolates | Inhibition Zone Breakpoints (mm) | % of Isolates/Total Isolates | ||||||||||
| S | I | R | R | I | S | S | I | R | R | I | S | ||
| Aminoglycoside | |||||||||||||
| Gentamicin | 10 µg | ≥27 | 19–26 | ≤18 | 0 | 98.04 | 1.96 | ≥28 | 19–27 | ≤17 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Amikacin | 30 µg | ≥27 | 19–26 | ≤18 | 0 | 68.63 | 31.37 | ≥27 | 20–26 | ≤19 | 2.76 | 64.52 | 32.72 |
| Quinolones | |||||||||||||
| Nalidixic acid | 30 µg | ≥29 | 22–28 | ≤21 | 0 | 52.94 | 47.06 | ≥29 | 22–28 | ≤21 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Fluoroquinolone | |||||||||||||
| Norfloxacin | 10 µg | ≥36 | 28–35 | ≤27 | 0 | 96.08 | 3.92 | ≥29 | 17–28 | ≤16 | 32.26 | 67.74 | 0 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 5 µg | ≥41 | 30–40 | ≤29 | 0 | 100 | 0 | ≥31 | 22–30 | ≤21 | 21.51 | 73.12 | 5.38 |
| Tetracyclines | |||||||||||||
| Tetracycline | 30 µg | ≥26 | 18–25 | ≤17 | 35.29 | 15.69 | 49.02 | ≥31 | 24–30 | ≤23 | 26.88 | 64.52 | 8.60 |
| Β-lactam penicillins | |||||||||||||
| Penicillin | 10 IU | ≥15 | - | ≤14 | 100 | 0 | 0 | ≥15 | - | ≤14 | 96.77 | 0 | 3.23 |
| Ampicillin | 10 µg | ≥15 | 16–22 | ≤15 | 100 | 0 | 0 | ≥36 | 27–35 | ≤26 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Piperacillin | 100 µg | ≥31 | 24–30 | ≤23 | 0 | 56.86 | 43.14 | ≥31 | 24–30 | ≤23 | 45.16 | 54.84 | 0 |
| Foodborne Pathogen | Antibiotic Resistance Genes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| blaTEM | tet(A) | blaz | mecA | ||||||
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | ||
| E. coli | Total (N = 102) | 57 | 55.89 | 46 | 45.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Shawarma (N = 58) | 33 | 56.9 | 27 | 46.55 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Chicken burger (N = 44) | 24 | 54.55 | 19 | 43.18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| S. aureus | Total (N = 93) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 21.5 | 44 | 47.31 |
| Shawarma (N = 48) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 18.75 | 23 | 47.92 | |
| Chicken burger (N = 45) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 22.92 | 21 | 43.75 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abalkhail, A. Frequency and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Foodborne Pathogens in Ready-to-Eat Foods: An Evolving Public Health Challenge. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12846. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312846
Abalkhail A. Frequency and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Foodborne Pathogens in Ready-to-Eat Foods: An Evolving Public Health Challenge. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(23):12846. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312846
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbalkhail, Adil. 2023. "Frequency and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Foodborne Pathogens in Ready-to-Eat Foods: An Evolving Public Health Challenge" Applied Sciences 13, no. 23: 12846. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312846
APA StyleAbalkhail, A. (2023). Frequency and Antimicrobial Resistance Patterns of Foodborne Pathogens in Ready-to-Eat Foods: An Evolving Public Health Challenge. Applied Sciences, 13(23), 12846. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132312846







