The Effect of a Static Magnetic Field on microRNA in Relation to the Regulation of the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in a Fibroblast Cell Line That Had Been Treated with Fluoride Ions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture Conditions
2.2. Molecular Analyses
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
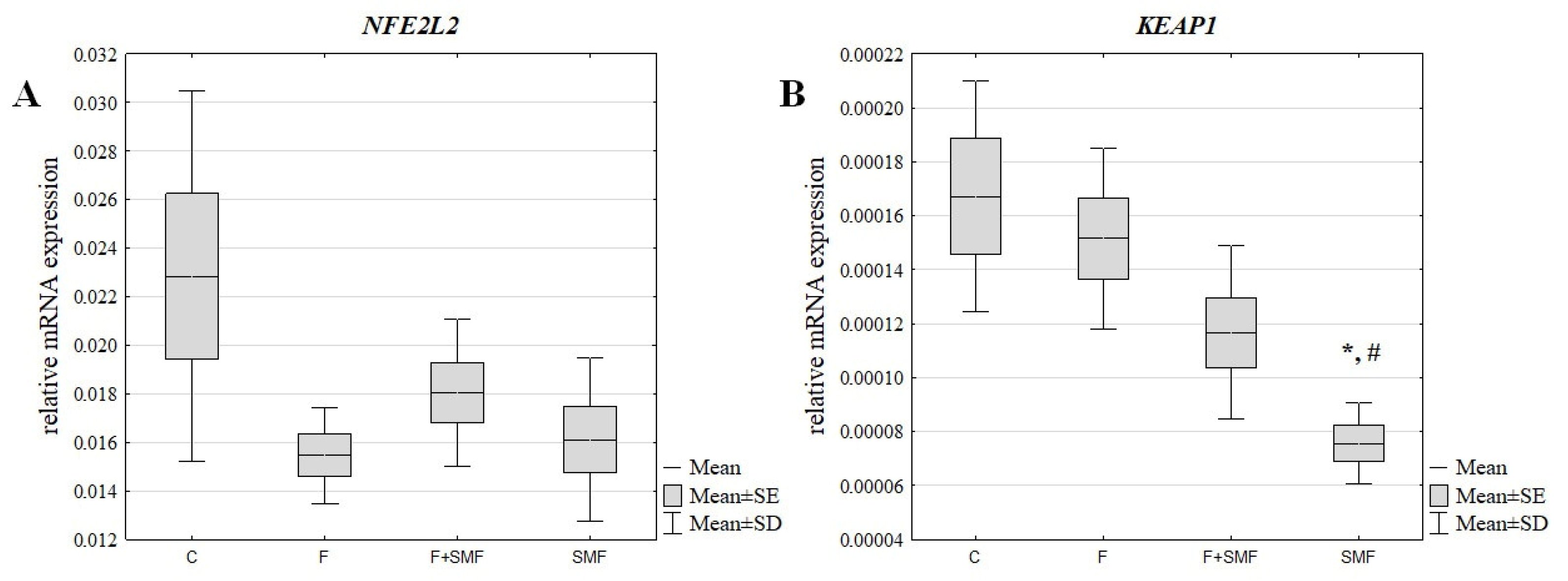
3.1. The mRNA Expression Level of NFE2L2 and KEAP1 in the NHDF Cells after Treatment with Fluoride Ions and an SMF
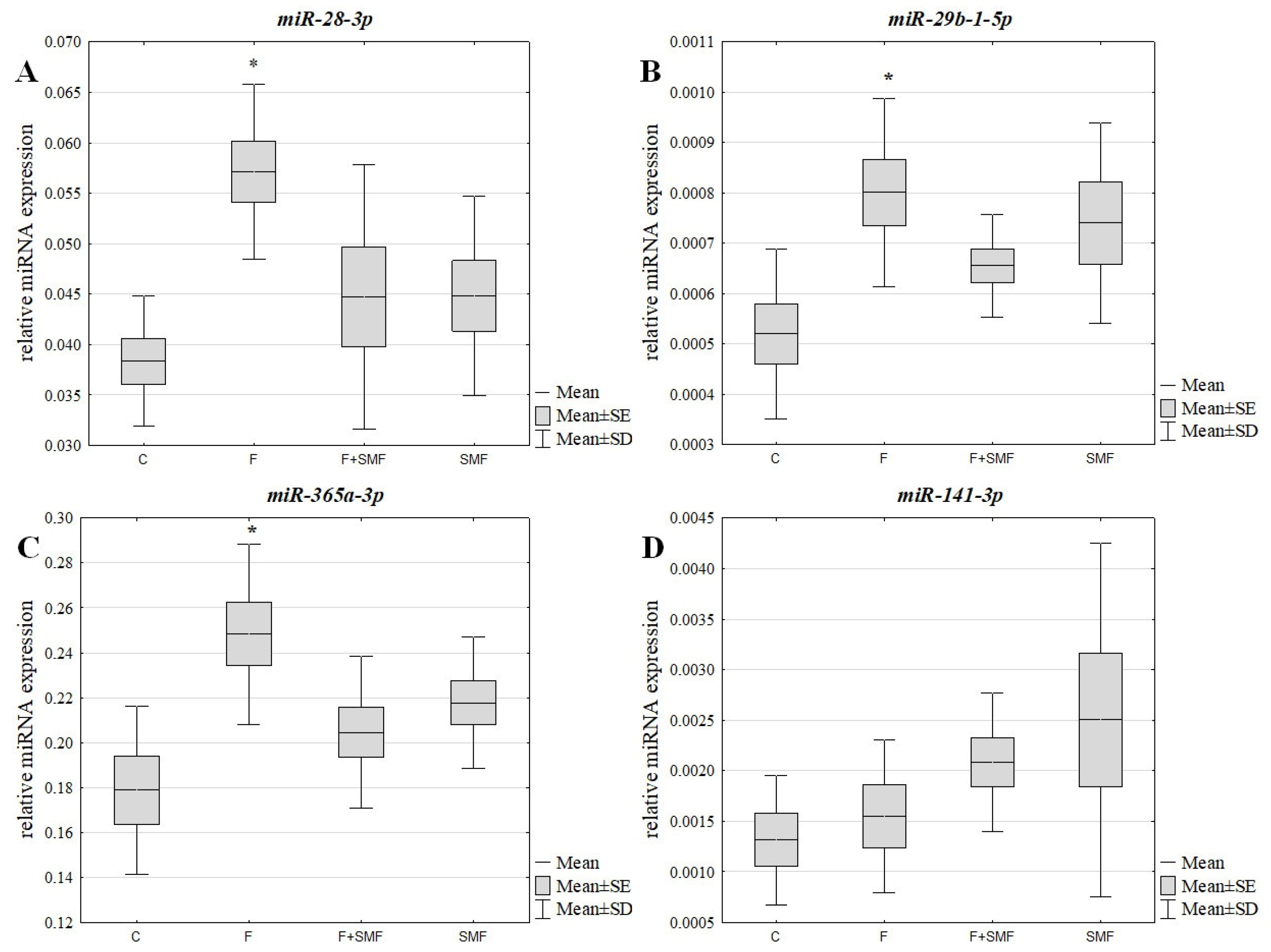
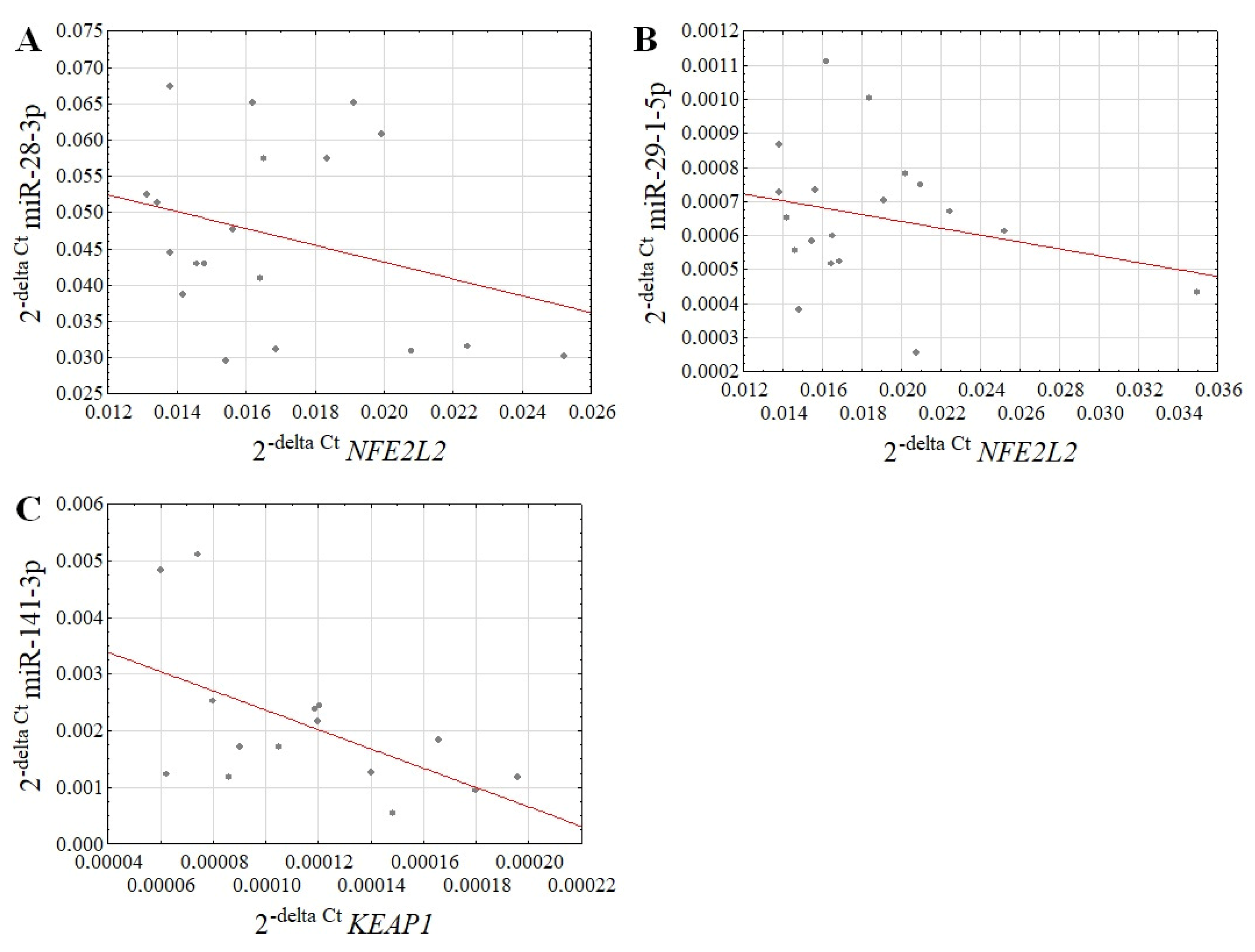
3.2. The miRNA Expression Level in the NHDF Cells after Treatment with Fluoride Ions and an SMF
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Correia de Sousa, M.; Gjorgjieva, M.; Dolicka, D.; Sobolewski, C.; Foti, M. Deciphering miRNAs’ Action through miRNA Editing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hill, M.; Tran, N. miRNA interplay: Mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Dis. Model. Mech. 2021, 14, dmm047662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali Syeda, Z.; Langden, S.S.S.; Munkhzul, C.; Lee, M.; Song, S.J. Regulatory Mechanism of MicroRNA Expression in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kura, B.; Szeiffova Bacova, B.; Kalocayova, B.; Sykora, M.; Slezak, J. Oxidative Stress-Responsive MicroRNAs in Heart Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, Q.; Ping, D.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Lin, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, A. The Role of Exosomal microRNAs and Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 3232869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellezza, I.; Giambanco, I.; Minelli, A.; Donato, R. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moi, P.; Chan, K.; Asunis, I.; Cao, A.; Kan, Y.W. Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 9926–9930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, F.; Antonucci, L.; Karin, M. NRF2 as a regulator of cell metabolism and inflammation in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saenen, N.D.; Martens, D.S.; Neven, K.Y.; Alfano, R.; Bové, H.; Janssen, B.G.; Roels, H.A.; Plusquin, M.; Vrijens, K.; Nawrot, T.S. Air pollution-induced placental alterations: An interplay of oxidative stress, epigenetics, and the aging phenotype? Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.J.; Husen, A.Z.; Khoshnaw, N.; Getta, H.A.; Hussein, Z.S.; Yassin, A.K.; Jalal, S.D.; Mohammed, R.N.; Alwan, A.F. The Effects of Smoking on IgE, Oxidative Stress and Haemoglobin Concentration. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S.; Jung, S.; Müller, R.; Lademann, J.; Zuberbier, T.; Zastrow, L.; Reble, C.; Beckers, I.; Meinke, M.C. Skin type differences in solar-simulated radiation-induced oxidative stress. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Flora, S.J.S. Fluoride in Drinking Water and Skeletal Fluorosis: A Review of the Global Impact. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2020, 7, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaee, T.; Bouxsein, M.L.; Karim, L. Increasing fluoride content deteriorates rat bone mechanical properties. Bone 2020, 136, 115369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, H.A.B.D.S.; Dionizio, A.S.; Araujo, T.T.; Fernandes, M.D.S.; Iano, F.G.; Buzalaf, M.A.R. Proposed mechanism for understanding the dose- and time-dependency of the effects of fluoride in the liver. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2018, 358, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhong, N.; Angwa, L.M.; Pei, J. The dose-time effects of fluoride on the expression and DNA methylation level of the promoter region of BMP-2 and BMP-7 in rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 75, 103331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, H.; Badr, A.M.; Abdelgwad, M.; Abd El-Galil, T.I. Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in sodium fluoride-induced cardiac toxicity and the prophylactic role of vitamin C versus platelet-rich plasma. Folia Morphol. 2022, 81, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, T.; Selvaraj, M.; Poomalai, S. Epigallocatechin gallate potentially abrogates fluoride induced lung oxidative stress, inflammation via Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway in rats: An in-vivo and in-silico study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 39, 128–139, Erratum in Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, D.; Srivastava, R.; Chattopadhyay, A. Sodium fluoride generates ROS and alters transcription of genes for xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) liver: Expression pattern of Nrf2/Keap1 (INrf2). Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2015, 25, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Cao, J.; Xie, L. Fluoride exposure changed the expression of microRNAs in gills of male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 233, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Ommati, M.M.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Z.; Niu, R.; Wang, J. Multiomics Analysis Revealed the Molecular Mechanism of miRNAs in Fluoride-Induced Hepatic Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disorders. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 14284–14295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzo, L.; Tunesi, M.; Boeri, L.; Laganà, M.; Giordano, C.; Raimondi, M.T. Influence of the static magnetic field on cell response in a miniaturized optically accessible bioreactor for 3D cell culture. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chekhun, V.F.; Demash, D.V.; Nalieskina, L.A. Evaluation of biological effects and possible mechanisms of action of static magnetic field. Fiziol. Zh. 2012, 58, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimsa-Dudek, M.; Synowiec-Wojtarowicz, A.; Derewniuk, M.; Gawron, S.; Paul-Samojedny, M.; Kruszniewska-Rajs, C.; Pawłowska-Góral, K. Impact of fluoride and a static magnetic field on the gene expression that is associated with the antioxidant defense system of human fibroblasts. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 287, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamkowski, A.; Kreitlow, M.; Radunz, J.; Willenbockel, M.; Stiemer, M.; Fichte, L.O.; Rädel, C.F.; Majewski, M.; Ostheim, P.; Port, M.; et al. Analyzing the impact of 900 MHz EMF short-term exposure to the expression of 667 miRNAs in human peripheral blood cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawron, S.; Glinka, M.; Wolnik, T. Magnetyczna komora badawcza dedykowana do hodowli komórek. Zesz. Probl. Masz. Elektr. 2012, 4, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Glinka, M.; Gawron, S.; Sieroń, A.; Pawłowska-Góral, K.; Cieślar, G.; Sieroń-Stołtny, K. Test chambers for cell culture in static magnetic field. J. Magn. Mater. 2013, 331, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, L.; Abbro, L. Bioeffects of moderate-intensity static magnetic fields on cell cultures. Micron 2005, 36, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.J.; Docherty, P.D.; Pons, D.; Chase, J.G. Serum fluoride levels in ambulance staff after commencement of methoxyflurane administration compared to meta-analysis results for the general public. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2021, 34, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.B.; Chiu, C.M.; Hsu, S.D.; Huang, W.Y.; Chien, C.H.; Lee, T.Y.; Huang, H.D. miRTar: An integrated system for identifying miRNA-target interactions in human. BMC. Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayers, D.; Baron, B.; Hunter, T. miRNA Influences in NRF2 Pathway Interactions within Cancer Models. J. Nucleic Acids 2015, 2015, 143636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, P.D.; Huang, B.W.; Tsuji, Y. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhan, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, T. Targeting Nrf2-Mediated Oxidative Stress Response Signaling Pathways as New Therapeutic Strategy for Pituitary Adenomas. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 565748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cheng, S.Q.; Guo, W.; Cai, Z.Y.; Sun, Y.Q.; Huang, X.X.; Yang, J.; Ji, J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Dong, Y.F.; et al. Oridonin prevents oxidative stress-induced endothelial injury via promoting Nrf-2 pathway in ischaemic stroke. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 9753–9766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.M.; Maltagliati, A.J. Nrf2 at the heart of oxidative stress and cardiac protection. Physiol. Genom. 2018, 50, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.; Xiao, J.H. The Keap1-Nrf2 System: A Mediator between Oxidative Stress and Aging. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6635460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Hu, B.; Zang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H. Nrf2 drives oxidative stress-induced autophagy in nucleus pulposus cells via a Keap1/Nrf2/p62 feedback loop to protect intervertebral disc from degeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimsa-Dudek, M.; Krawczyk, A.; Synowiec-Wojtarowicz, A. The Protective Effect of Static Magnetic Fields with Different Magnetic Inductions against Fluoride Toxicity Is Related to the NRF2 Signaling Pathway. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimsa-Dudek, M.; Synowiec-Wojtarowicz, A.; Derewniuk, M.; Paul-Samojedny, M.; Pawłowska-Góral, K. The effect of simultaneous exposure of human fibroblasts to fluoride and moderate intensity static magnetic fields. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Qi, J.; Bai, C.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S. Glycine alleviates fluoride-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis and senescence in a porcine testicular Sertoli cell line. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2021, 56, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Cui, H.; Deng, H.; Kuang, P.; Liu, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Sodium fluoride causes oxidative stress and apoptosis in the mouse liver. Aging 2017, 9, 1623–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, W.; Yu, R.; He, L. Effect of fluoride on PERK-Nrf2 signaling pathway in mouse ameloblasts. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipour, M.; Hajipour-Verdom, B.; Javan, M.; Abdolmaleki, P. Static and Electromagnetic Fields Differently Affect Proliferation and Cell Death through Acid Enhancement of ROS Generation in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Radiat. Res. 2022, 198, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Yu, B.; Song, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Ji, X.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Wei, M.; et al. Static Magnetic Fields Reduce Oxidative Stress to Improve Wound Healing and Alleviate Diabetic Complications. Cells 2022, 11, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, Q.; Dai, J.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Mou, T.; Pu, J.; Yang, H.; Wei, X.; Wu, Z. MicroRNA-141-3p attenuates oxidative stress-induced hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury via Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 7575–7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Blasio, A.; di Fiore, R.; Pratelli, G.; Drago-Ferrante, R.; Saliba, C.; Baldacchino, S.; Grech, G.; Scerri, C.; Vento, R.; Tesoriere, G. A loop involving NRF2, miR-29b-1-5p and AKT, regulates cell fate of MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Yao, Y.; Eades, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q. MiR-28 regulates Nrf2 expression through a Keap1-independent mechanism. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 129, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dongoran, R.A.; Wu, T.Y. Cryptotanshinone activate Nrf2 expression through microRNA regulations. Cancer Res. 2017, 77 (Suppl. 13), 5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, C.; Liu, C.; Wu, X.; Yu, M.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, W.; Lv, S.; Li, W. MT1DP loaded by folate-modified liposomes sensitizes erastin-induced ferroptosis via regulating miR-365a-3p/NRF2 axis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Name | Oligo Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| NFE2-like bZIP transcription factor 2 (NFE2L2) | FH1_NFE2L2 | Forward: CGTTTGTAGATGACAATGAGG |
| BH1_NFE2L2 | Reverse: AGAAGTTTCAGGTGACTGAG | |
| Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) | FH1_KEAP1 | Forward: CGTTTGTAGATGACAATGAGG |
| BH1_KEAP1 | Reverse: CTCCAAGGACGTAGATTCTC | |
| β-actin (ACTB) | FH1_ACTB | Forward: GACGACATGGAGAAAATCTG |
| BH1_ACTB | Reverse: ATGATCTGGGTCATCTTCTC |
| Groups | mRNA Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NFE2L2 | KEAP1 | |||
| FC vs. C | FC vs. F | FC vs. C | FC vs. F | |
| F | −1.48 | - | −1.10 | - |
| F + SMF | −1.27 | 1.17 | −1.43 | −1.30 |
| SMF | −1.42 | 1.04 | −2.21 | −2.00 |
| Groups | miRNA Level | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-28-3p | miR-29b-1-5p | miR-365a-3p | miR-141-3p | |||||
| FC vs. C | FC vs. F | FC vs. C | FC vs. F | FC vs. C | FC vs. F | FC vs. C | FC vs. F | |
| F | 1.49 | - | 1.54 | - | 1.39 | - | 1.18 | - |
| F + SMF | 1.17 | −1.28 | 1.26 | −1.22 | 1.14 | −1.21 | 1.58 | 1.34 |
| SMF | 1.17 | −1.27 | 1.42 | −1.08 | 1.22 | −1.14 | 1.90 | 1.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kimsa-Dudek, M.; Krawczyk, A.; Synowiec-Wojtarowicz, A. The Effect of a Static Magnetic Field on microRNA in Relation to the Regulation of the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in a Fibroblast Cell Line That Had Been Treated with Fluoride Ions. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031470
Kimsa-Dudek M, Krawczyk A, Synowiec-Wojtarowicz A. The Effect of a Static Magnetic Field on microRNA in Relation to the Regulation of the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in a Fibroblast Cell Line That Had Been Treated with Fluoride Ions. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(3):1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031470
Chicago/Turabian StyleKimsa-Dudek, Magdalena, Agata Krawczyk, and Agnieszka Synowiec-Wojtarowicz. 2023. "The Effect of a Static Magnetic Field on microRNA in Relation to the Regulation of the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in a Fibroblast Cell Line That Had Been Treated with Fluoride Ions" Applied Sciences 13, no. 3: 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031470
APA StyleKimsa-Dudek, M., Krawczyk, A., & Synowiec-Wojtarowicz, A. (2023). The Effect of a Static Magnetic Field on microRNA in Relation to the Regulation of the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in a Fibroblast Cell Line That Had Been Treated with Fluoride Ions. Applied Sciences, 13(3), 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13031470






