Efficient Data Preprocessing with Ensemble Machine Learning Technique for the Early Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
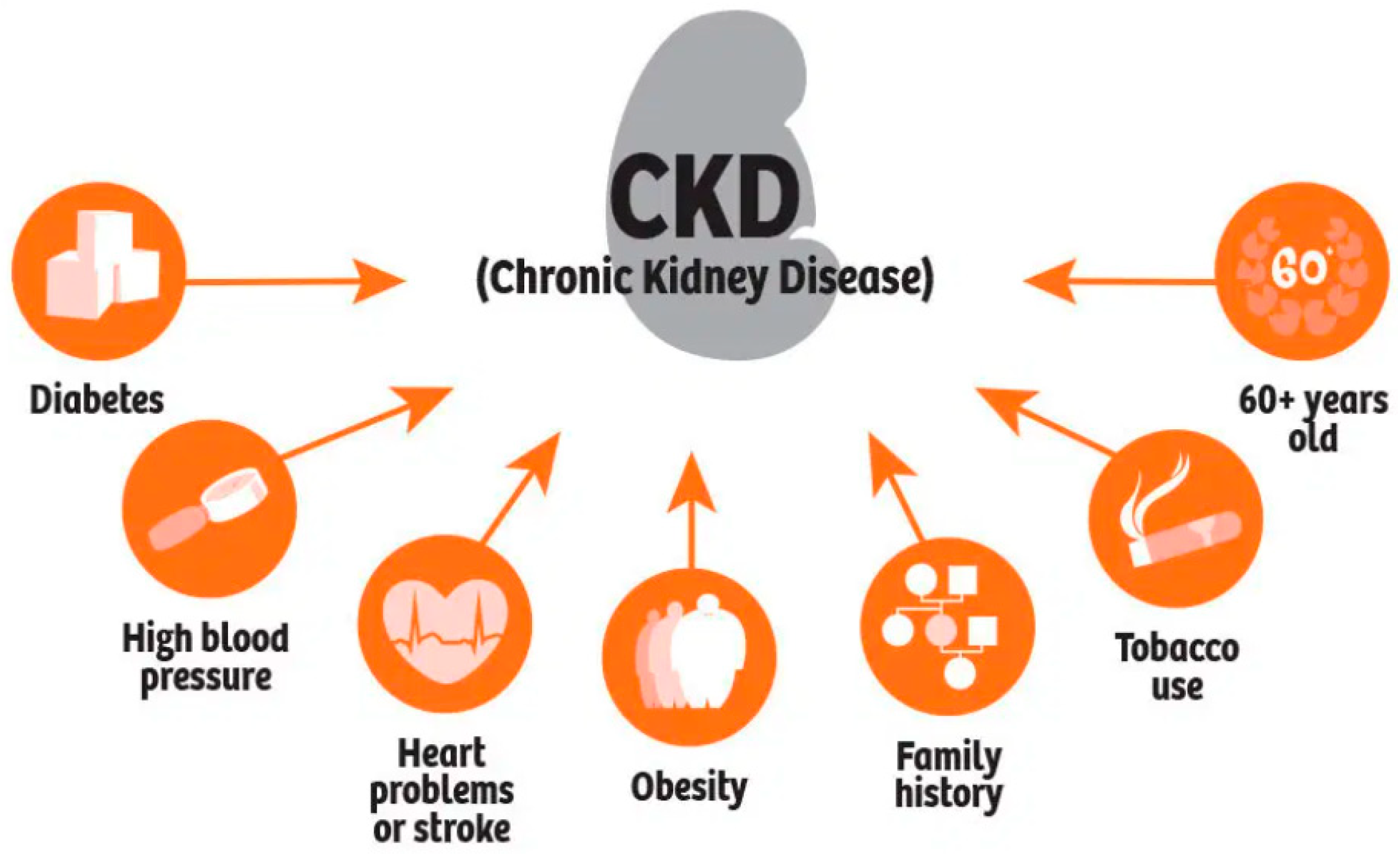
:1. Introduction
- Detection of chronic kidney disease in the early stages to avoid critical health issues.
- Early detection of chronic kidney disease will be helpful for low-income people so that they can take prior precautions as they cannot undergo or afford major surgery.
2. Related Works
3. Proposed Methodology
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Preprocessing
3.3. Feature Selection
3.4. Classification
3.4.1. Regression Analysis (RA)
3.4.2. K-Nearest-Neighbors (k-NN)
3.4.3. Decision Tree (DT) Classifier
3.4.4. Random Forest (RF) Classifier
3.4.5. Support Vector Classifiers (SVM)
3.4.6. XGBoost
| Algorithm 1: Overall functioning of XGBoost |
A: booster:
|
B. silent:
|
C. nthread
|
| If one wishes to run on all cores, leave the value blank and the algorithm will figure it out. |
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Im, C.-G.; Son, D.-M.; Kwon, H.-J.; Lee, S.-H. Tone Image Classification and Weighted Learning for Visible and NIR Image Fusion. Entropy 2022, 24, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, K.K.; Jha, R.; Jha, A.K.; Hassan, A.M.; Yadav, S.K.; Mahesh, T. A Brief Comparison On Machine Learning Algorithms Based On Various Applications: A Comprehensive Survey. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Computation System and Information Technology for Sustainable Solutions (CSITSS), Bangalore, India, 16–18 December 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopashree, S.; Anitha, J.; Mahesh, T.; Kumar, V.V.; Viriyasitavat, W.; Kaur, A. An IoT based authentication system for therapeutic herbs measured by local descriptors using machine learning approach. Measurement 2022, 200, 111484, ISSN 0263-2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, X.; Wu, L.; Ji, Q. Multi-Task Transformer with Adaptive Cross-Entropy Loss for Multi-Dialect Speech Recognition. Entropy 2022, 24, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Song, M.; Ma, C.; Ge, Z.; Li, P. Detecting the Critical States of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Degree Matrix Network Entropy by Cross-Tissue Analysis. Entropy 2022, 24, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- “UCI Machine Learning Repository” [Online]. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Chronic_Kidney_Disease (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Chronic Kidney Disease Overview. Available online: https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/tc/chronickidney-disease-topic-overview (accessed on 24 February 2018).
- Mahesh, T.R.; Vinoth Kumar, V.; Muthukumaran, V.; Shashikala, H.K.; Swapna, B.; Guluwadi, S. Performance Analysis of XGBoost Ensemble Methods for Survivability with the Classification of Breast Cancer. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunarathne, W.H.S.D.; Perera, K.D.M.; Kahandawaarachchi, K.A.D.C.P. Performance Evaluation on Machine Learning Classification Techniques for Disease Classification and Forecasting through Data Analytics for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 17th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering, Washington, DC, USA, 23–25 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gowramma, G.S.; Mahesh, T.R.; Gowda, G. An automatic system for IVF data classification by utilizing multilayer perceptron algorithm. ICCTEST-2017 2017, 2, 667–672. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-H.; Ye, S.-Y. Classification of chronic kidney disease in sonography using the GLCM and artificial neural network. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramya, S.; Radha, N. Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Proc. Int. J. Innov. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 2016, 4, 812–820. [Google Scholar]
- Mahesh, T.R.; Kaladevi, A.C.; Balajee, J.M.; Vivek, V.; Prabu, M.; Muthukumaran, V. An Efficient Ensemble Method Using K-Fold Cross Validation for the Early Detection of Benign and Malignant Breast Cancer. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2022, 14, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Kabir, M.T.; Mahmood, N.T.; Rahman, R.M. Diagnosis of kidney disease using fuzzy expert system. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Software, Knowledge, Information Management and Applications Journal of Healthcare Engineering (SKIMA 2014), IEEE, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 18–20 December 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Khamparia, A.; Saini, G.; Pandey, B.; Tiwari, S.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A. KDSAE: Chronic kidney disease classification with multimedia data learning using deep stacked auto encoder network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 79, 35425–35440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, T.R.; Vivek, V.; Kumar, V.V.; Natarajan, R.; Sathya, S.; Kanimozhi, S. A Comparative Performance Analysis of Machine Learning Approaches for the Early Prediction of Diabetes Disease. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Applied Informatics (ACCAI), Chennai, India, 28–29 January 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, P. Chronic Kidney Disease Prediction on Imbalanced Data by Multilayer Perceptron: Chronic Kidney Disease Prediction. In Proceedings of the 41st IEEE International Conference on Computer Software and Applications (COMPSAC), IEEE, Turin, Italy, 4–8 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarveshvar, M.R.; Gogoi, A.; Chaubey, A.K.; Rohit, S.; Mahesh, T.R. Performance of different Machine Learning Techniques for the Prediction of Heart Diseases. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Forensics, Analytics, Big Data, Security (FABS), Bengaluru, India, 21–22 December 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, M.T.; Venkatesan, V.K.; Izonin, I.; Havryliuk, M.; Bhat, C.R. Homogeneous Adaboost Ensemble Machine Learning Algorithms with Reduced Entropy on Balanced Data. Entropy 2023, 25, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Chen, X. Estimation of Chronic Illness Severity Based on Machine Learning Methods. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, V.D. Chronic disease detection model using machine learning techniques. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2020, 9, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, A.; Garg, P. Detecting and Diagnosing a Disease by Patient Monitoring System. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2014, 2, 493–499. [Google Scholar]
- Mahesh, T.R.; Sivakami, R.; Manimozhi, I.; Krishnamoorthy, N.; Swapna, B. Early Predictive Model for Detection of Plant Leaf Diseases Using MobileNetV2 Architecture. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 2023, 11, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Mahesh, T.R.; Kumar, V.V.; Vivek, V.; Raghunath, K.M.K.; Madhuri, G.S. Early predictive model for breast cancer classification using blended ensemble learning. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, V.K.; Ramakrishna, M.T.; Batyuk, A.; Barna, A.; Havrysh, B. High-Performance Artificial Intelligence Recommendation of Quality Research Papers Using Effective Collaborative Approach. Systems 2023, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22Nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, KDD’16, New York, NY, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Mahesh, T.R.; Kumar, D.; Vinoth Kumar, V.; Asghar, J.; Mekcha Bazezew, B.; Natarajan, R.; Vivek, V. Blended Ensemble Learning Prediction Model for Strengthening Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Diabetes Disease. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, H.; Ali, S.; Ponum, M.; Hasan, O.; Mahmood, M.T.; Iftikhar, M.; Malik, M.H. Chronic kidney disease diagnosis using decision tree algorithms. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabanayagam, C.; Xu, D.; Ting, D.S.W.; Nusinovici, S.; Banu, R.; Hamzah, H.; Lim, C.; Tham, Y.-C.; Cheung, C.Y.; Tai, E.S.; et al. A deep learning algorithm to detect chronic kidney disease from retinal photographs in community-based populations. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e295–e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonia, R.C.; Gupta, M.K.; Abunadi, I.; Albraikan, A.A.; Al-Wesabi, F.N.; Hamza, M.A. Intelligent Diagnostic Prediction and Classification Models for Detection of Kidney Disease. Healthcare 2022, 10, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhoseny, M.; Shankar, K.; Uthayakumar, J. Intelligent Diagnostic Prediction and Classification System for Chronic Kidney Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ifraz, G.M.; Rashid, M.H.; Tazin, T.; Bourouis, S.; Khan, M.M. Comparative Analysis for Prediction of Kidney Disease Using Intelligent Machine Learning Methods. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2021, 2021, 6141470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yashfi, S.Y.; Islam, A.; Pritilata; Sakib, N.; Islam, T.; Shahbaaz, M.; Pantho, S.S. Risk Prediction of Chronic Kidney Disease Using Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2020 11th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kharagpur, India, 1–3 July 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.S.; Lin, Y.J.; Lin, C.H.; Wang, S.T.; Lin, S.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Wu, J.L.; Chang, S.S. Predicting metabolic syndrome with machine learning models using a decision tree algorithm: Retrospective cohort study. JMIR Public Heal. Surveill. 2020, 8, e17110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Matsushita, K.; Sang, Y.; Brunskill, N.J.; Carrero, J.J.; Chodick, G.; Hasegawa, T.; Heerspink, H.L.; Hirayama, A.; Landman, G.W.; et al. Serum potassium and adverse outcomes across the range of kidney function: A CKD Prognosis Consortium meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










| Stage | Description | GFR (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|
| I | Kidney function is normal | ≥90 |
| II | Mild increase in GFR | 60–89 |
| III | Moderate increase in GFR | 30–59 |
| IV | Severe increase in GFR | 15–29 |
| V | Kidney failure | 15 or dialysis |
| Study and Year | ML Techniques | Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Ilyas, H. et al. (2019) [28] | Random forest and J48 algorithms | Random forest accuracy—78.25% and J48 accuracy—85% |
| Sabanayagam et al. (2020) [29] | Deep Learning Algorithm (DLA) | DLA accuracy—95% |
| Poonia, R.C. et al. (2022) [30] | LR model + chi-square feature selection (K > 14), where K is number of features | Accuracy—97.5% |
| Elhoseny, M. et al. (2019) [31] | Ant Colony-based Optimization (D-ACO) algorithm | D-ACO accuracy—95% |
| Components | Before SMOTE | After Smote | (Mean ± SD) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall (N = 400) | Overall (N = 750) | |||
| Age (Mean ± SD) | 38.52 ± 16.49 | 38.40 ± 16.53 | - | |
| Gender, [N (%)] | Male | 280 (70) | 375 (50) | 38.13 ± 16.51 |
| Female | 120 (30) | 375 (50) | ||
| CKD | 250 (62.5) | 300 (40) | 38.25 ± 16.55 | |
| Non-CKD | 150 (37.5) | 300 (40) | ||
| Testing Samples | - | 150 (20) | 38.29 ± 16.49 | |
| Attributes/Features | Values Used |
|---|---|
| Age (A) | Discrete integer values |
| Blood pressure (BP) | Discrete integer values |
| Specific gravity (sg) | Nominal values |
| Albumin (Al) | Nominal values |
| Sugar(su) | Nominal values |
| Blood glucose random (bgr) | Numerical value |
| Blood urea (bu) | Numerical value |
| Serum creatinine (sc) | Numerical value |
| Sodium (sod) | Numerical value |
| Potassium (pot) | Numerical value |
| Haemoglobin (haem) | Numerical value |
| Packed cell volume | Numerical value |
| White blood cell count | Numerical value |
| Red blood cell count | Numerical value |
| ML Techniques | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | 95.00 | 96.30 | 97.56 | 96.93 |
| KNN | 91.00 | 91.18 | 96.47 | 94.75 |
| RF | 90.00 | 93.10 | 96.42 | 94.73 |
| DT | 88.00 | 91.95 | 94.11 | 93.01 |
| SVM | 94.00 | 95.69 | 97.80 | 96.73 |
| XGBoost (EL Method) | 98.00 | 98.90 | 98.90 | 98.90 |
| ML Techniques | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boosting | 95.44 | 94.22 | 96.66 | 98.01 |
| Bagging | 93.62 | 91.22 | 92.55 | 94.44 |
| Voting | 94.66 | 94.70 | 96.77 | 95.34 |
| Rotation Forest | 91.20 | 91.88 | 92.24 | 90.40 |
| XGBoost (EL Method) | 98.00 | 98.90 | 98.90 | 98.90 |
| Study and Year | Sampling Strategy | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Ifraz et al. (2021) [32] | 70–30% training-testing | 97.00% |
| S. Y. Yashfi et al. (2020) [33] | 10-fold cross-validation | 97.12% |
| Cheng-Sheng Yu et al. (2020) [34] | 10-fold cross-validation | 90.40% |
| Kovesdy et al. (2018) [35] | 70–30% training-testing | 95.0% |
| Proposed model | 75–25% training-testing | 98.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venkatesan, V.K.; Ramakrishna, M.T.; Izonin, I.; Tkachenko, R.; Havryliuk, M. Efficient Data Preprocessing with Ensemble Machine Learning Technique for the Early Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13052885
Venkatesan VK, Ramakrishna MT, Izonin I, Tkachenko R, Havryliuk M. Efficient Data Preprocessing with Ensemble Machine Learning Technique for the Early Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(5):2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13052885
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenkatesan, Vinoth Kumar, Mahesh Thyluru Ramakrishna, Ivan Izonin, Roman Tkachenko, and Myroslav Havryliuk. 2023. "Efficient Data Preprocessing with Ensemble Machine Learning Technique for the Early Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease" Applied Sciences 13, no. 5: 2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13052885
APA StyleVenkatesan, V. K., Ramakrishna, M. T., Izonin, I., Tkachenko, R., & Havryliuk, M. (2023). Efficient Data Preprocessing with Ensemble Machine Learning Technique for the Early Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease. Applied Sciences, 13(5), 2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13052885









