Effect of Secondary Oxidation of Pre-Oxidized Coal on Early Warning Value for Spontaneous Combustion of Coal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coal Samples
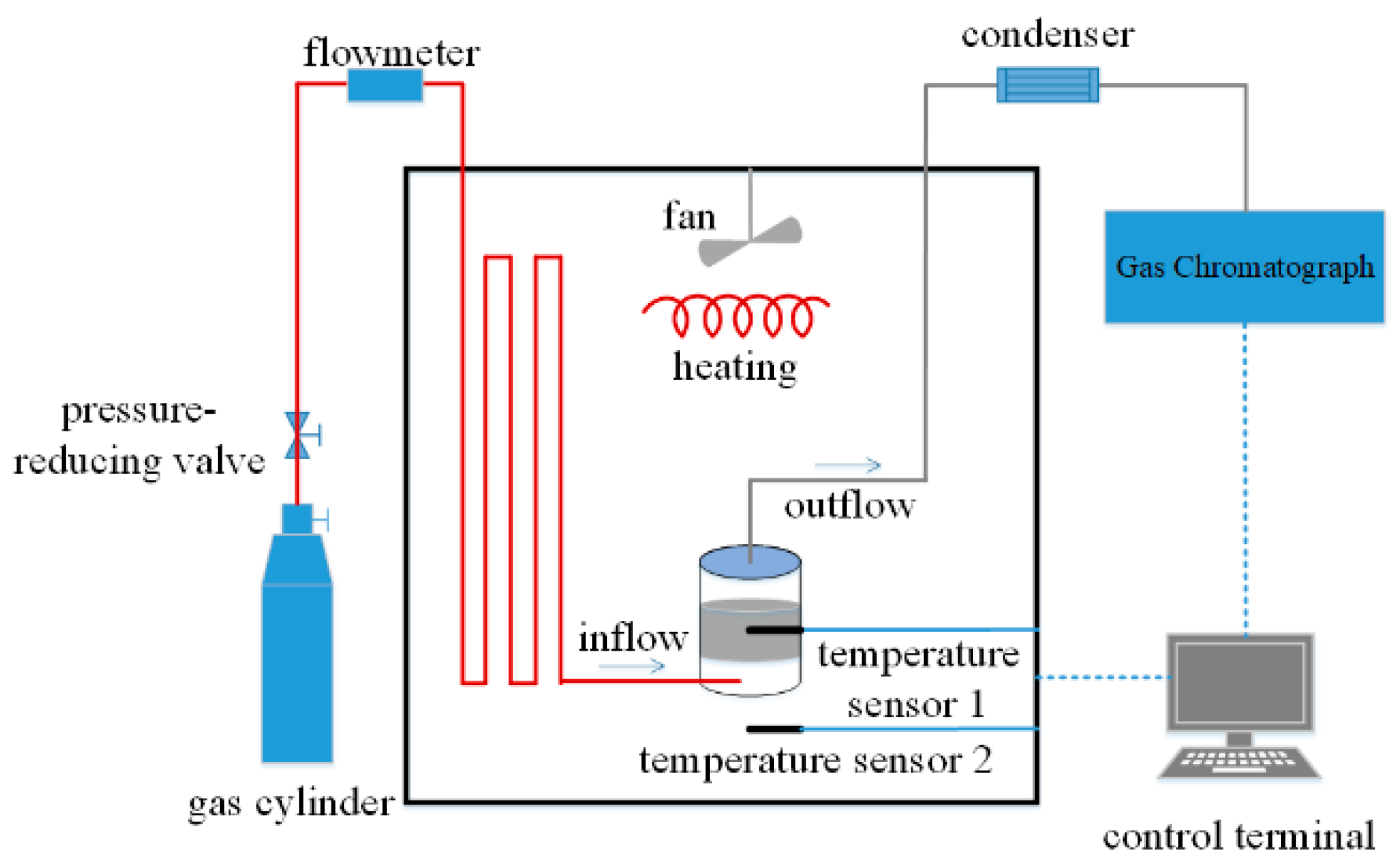
2.2. Experimental Apparatus
2.3. Experimental Process
3. Results and Discussion
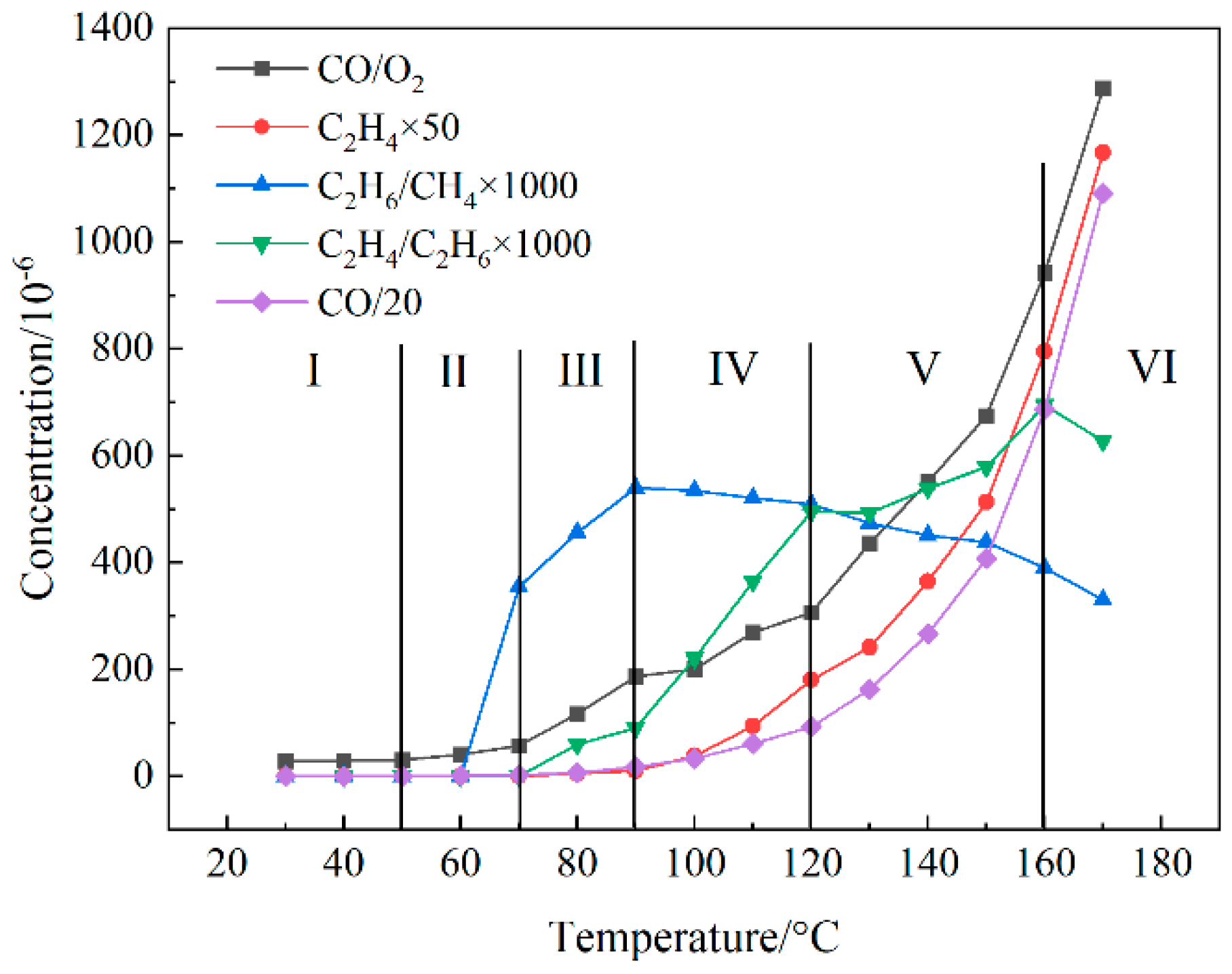
3.1. Spontaneous Combustion Stage Division and Index Selection
- Stage I: oxidation stage (t < 50 °C). At this stage, coal begins to slowly oxidize, and every forecast indicator rises slowly. This stage can be characterized by the CO concentration, which is less than 17.225 ppm, and the spontaneous combustion of coal.
- Stage II: self-heating stage (50 °C < t < 0 °C). At this stage, the increase in CO/O2 is accelerated, and the reaction rate of coal and oxygen is slowly increased. The accumulated heat can increase the temperature of coal.
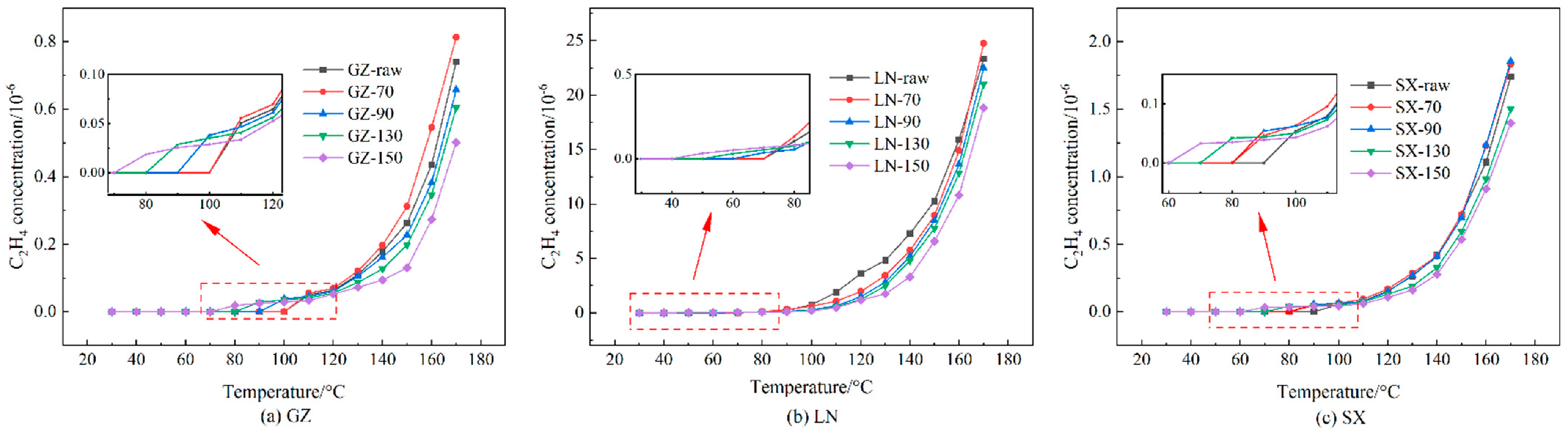
- Stage III: accelerating stage (70 °C < t < 90 °C). The main indication that this stage has been entered is the appearance of C2H4, which indicates that coal oxidation is beginning to accelerate, and the rapid increase in C2H6 and CO/O2. After this stage begins, the spontaneous combustion of coal will be difficult to control.
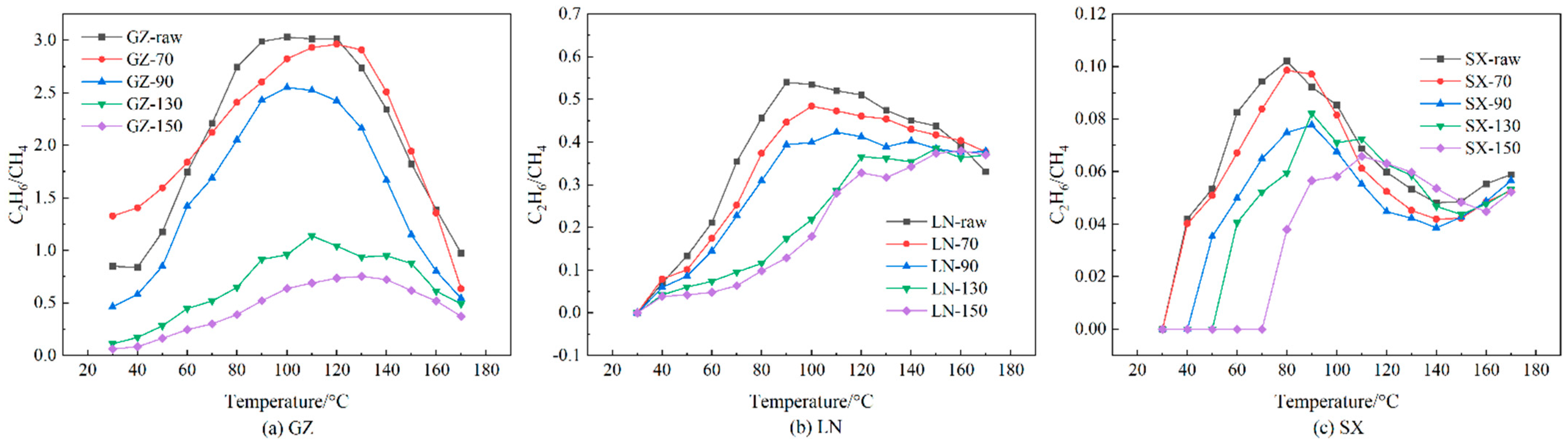
- Stage IV: intense stage (90 °C < t < 120 °C). The indication that this stage has begun is the presence of C2H6/CH4 at its maximum value. At this time, the coal sample reaction is intense, and C2H4 begins to increase rapidly.
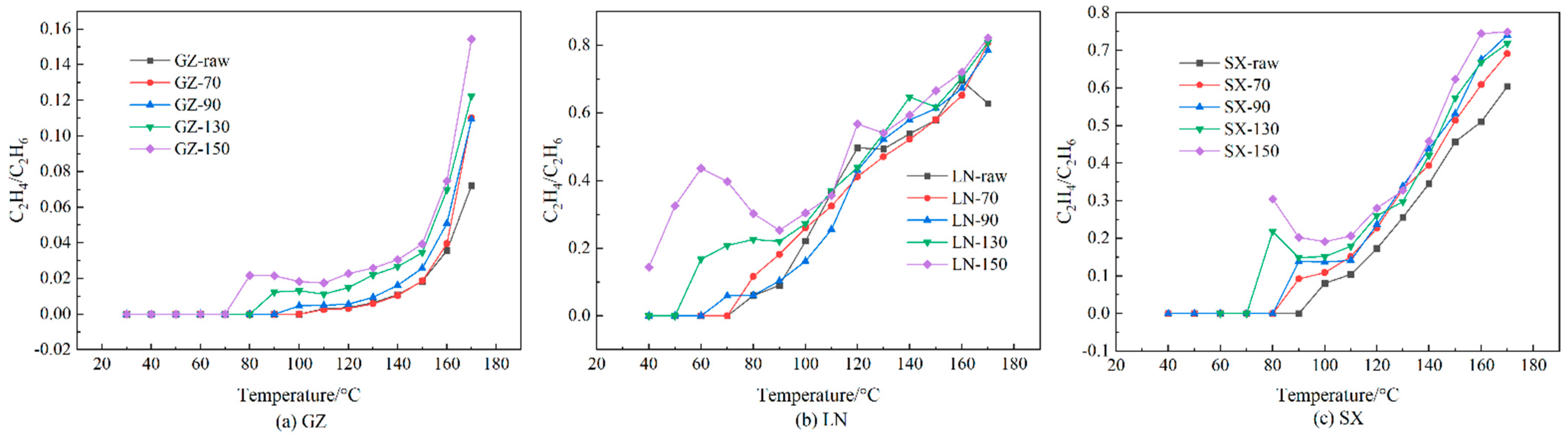
- Stage V: pyrolysis stage (120 °C < t < 160 °C). This stage is marked by the maximum amount of C2H4/C2H6, followed by a slower rate of increase.
- Stage VI: fission stage (t > 160 °C). At this stage, the formation rate of C2H4 is lower than C2H6, while the maximum C2H4/C2H6 value appears.
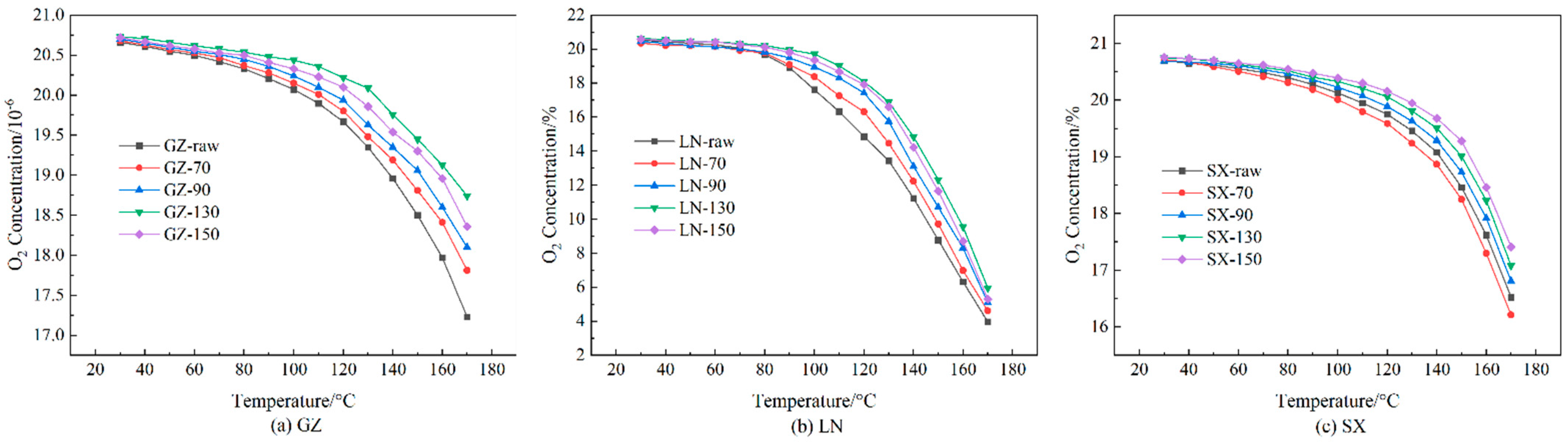
3.2. Oxygen Concentration
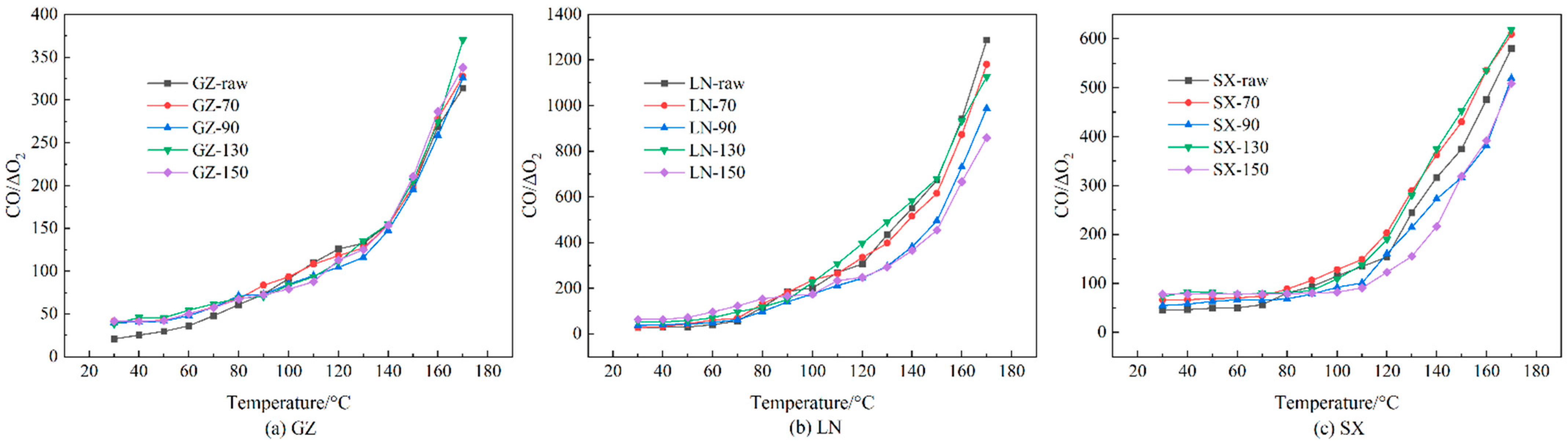
3.3. Oxidation Gas Products and Ratios
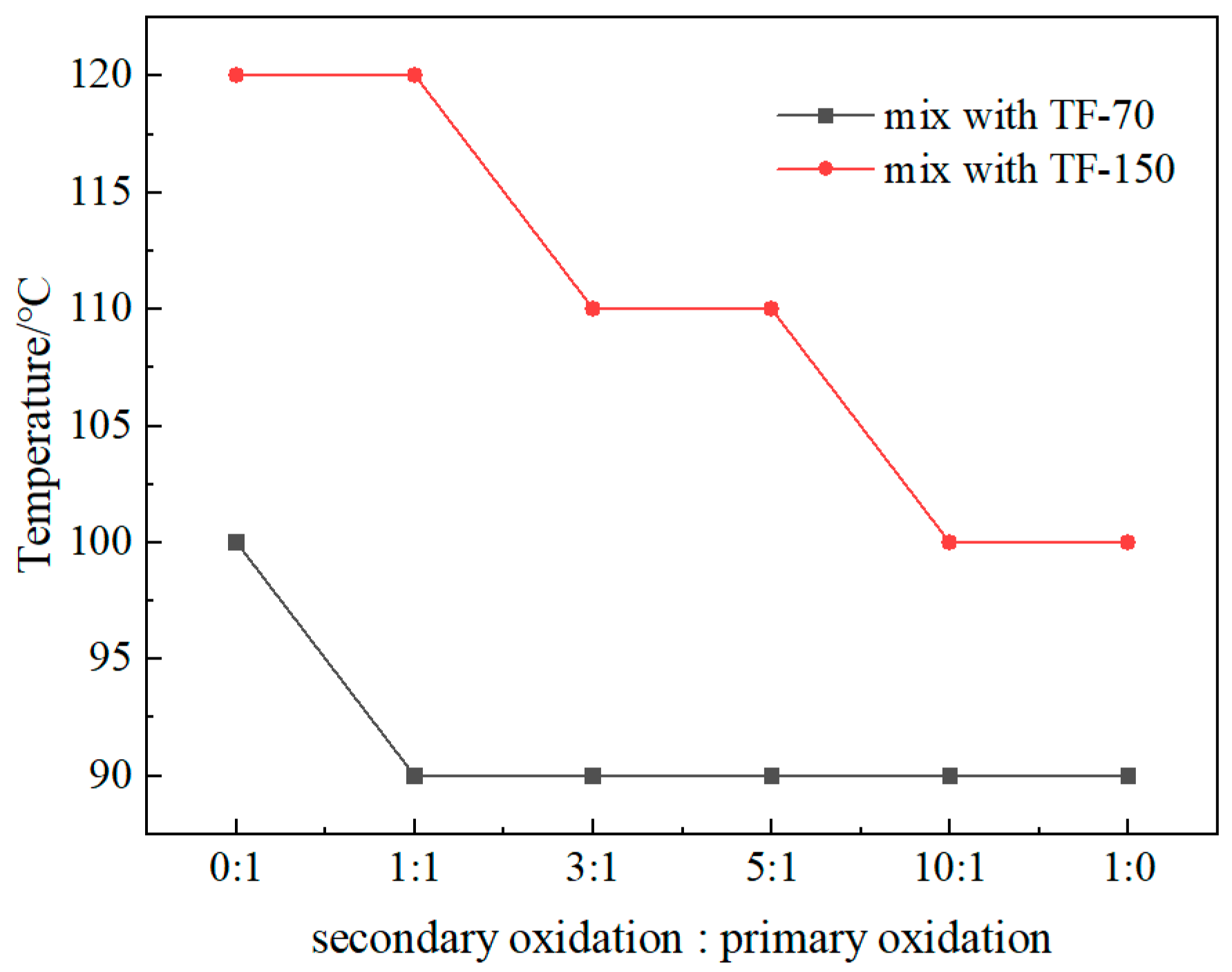
3.4. Pyrolysis Gas and Ratio
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Onifade, M.; Genc, B. A review of research on spontaneous combustion of coal. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2020, 30, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Y.; Kuenzer, C. Coal fires in China over the last decade: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 133, 72–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavialova, O.; Grygorian, M.; Kostenko, V.; Kostenko, T.; Pokaliuk, V. Theoretical basis for the formation of damaging factors during the coal aerosol explosion. Min. Miner. Depos. 2021, 15, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, X.; Deng, J.; Wen, H.; Xiao, Y.; Jia, H. Research on coal spontaneous combustion period based on pure oxygen adiabatic oxidation experiment. Fuel 2021, 288, 119651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Huang, A.C.; Liu, X.R.; Zhai, X.W.; Wang, C.P. Thermal analysis of spontaneous combustion behavior of partially oxidized coal. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 104, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Chen, X.K.; Zhai, X.W.; Bai, Y.E. Thermogravimetric and infrared spectroscopic studies of the spontaneous combustion characteristics of different pre-oxidized lignites. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 32476–32489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.K.; Wang, C.H.; Chao, J.K.; Jia, H.L.; Wang, J. Experimental research on the characteristics of the secondary oxidation heat of different unloaded coals. Fuel 2022, 307, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, H. Experimental investigation on microstructure evolution and spontaneous combustion properties of secondary oxidation of lignite. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 124, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, S.; Yang, W.; Tang, Z.; Hu, X.; Song, W.; Zhou, B.; Yang, K. Secondary oxidation of crushed coal based on free radicals and active groups. Fuel 2021, 290, 120051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, S.; Yang, W.; Tang, Z.; Song, W.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, X. Effect of particle size and low-temperature secondary oxidation on the active groups in coal structures. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 149, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pis, J.; de La Puente, G.; Fuente, E.; Morán, A.; Rubiera, F. A study of the self-heating of fresh and oxidized coals by differential thermal analysis. Thermochim. Acta 1996, 279, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Liu, Q.Q.; Sun, L.L.; Song, X.; Du, W.Z.; Yan, D.C.; Wang, Y. Secondary Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics of Coal Based on Programed Temperature Experiments. J. Energy Resour. Technol. Trans. ASME 2018, 140, 082204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worasuwannarak, N.; Nakagawa, H.; Miura, K. Effect of pre-oxidation at low temperature on the carbonization behavior of coal. Fuel 2002, 81, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S. Effects of pre-oxidation temperature on coal secondary spontaneous combustion. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gao, P.; Sun, W.L.; Fan, H.H.; He, Y.Z.; Han, T. Thermal Behavior of the Low-temperature Secondary Oxidation of Coal under Different Pre-oxidation Temperatures. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2022, 194, 1712–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, L.H.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.N. Multiscale thermal behavioral characterization of spontaneous combustion of pre-oxidized coal with different air exposure time. Energy 2023, 262, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, B.; Liu, S.-H.; Lei, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y. Thermal kinetics of nitrogen inhibiting spontaneous combustion of secondary oxidation coal and extinguishing effects. Fuel 2020, 278, 118223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascetin, A.; Brune, J.; Adiguzel, D. The study of permeability changes of a gob structure in an underground coal mine to prevent spontaneous combustion. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2021, 35, 693–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamiy, Y.; Kostenko, V.; Zavialova, O.; Kostenko, T.; Zhurbynskyi, D. Identifying sources of coal spontaneous heating in mine workings using aerogas control automatic systems. Min. Miner. Depos. 2020, 14, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.C.; Luo, H.Z.; Ren, T. Forecasting spontaneous combustion of coal in underground coal mines by index gases: A review. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2019, 57, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.X.; Bi, R.Q.; Huang, J.J.; Shan, W.X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, D.Y. Experimental study on early prediction index gas for spontaneous combustion. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Liao, G.X.; Sun, J.H.; Li, P.D. Experimental research on index gas of the coal spontaneous at low-temperature stage. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2004, 17, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.Y.; Deng, X.L.; Li, S.L.; Cai, K.X.; Zhu, H.; Li, F.; Deng, J. Experiment study of optimization on prediction index gases of coal spontaneous combustion. J. Cent. South Univ. 2016, 23, 2321–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cen, X.X.; Wang, W.F.; Deng, J.; Wen, H.; Xiao, Y.; Shu, C.M. The graded warning method of coal spontaneous combustion in Tangjiahui Mine. Fuel 2021, 288, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, R. Study on coal spontaneous combustion characteristic temperature of growth rate analysis. In Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Safety Science and Technology (ISSST), Beijing, China, 4–6 November 2014; pp. 796–805. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, H.; Guo, J.; Jin, Y.F.; Wei, G.M.; Yang, Z.W. Coal spontaneous combustion and N-2 suppression in triple goafs: A numerical simulation and experimental study. Fuel 2020, 271, 117625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.D.; Yang, Y.L.; Zheng, K.Y.; Miao, G.D.; Wang, M.H.; Li, P.R. Study on the Spontaneous Combustion Characteristics and Prevention Technology of Coal Seam in Overlying Close Goaf. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2022, 194, 2233–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Guo, R.Z.; Wu, M.M.; Wang, W.F.; Ren, L.F.; Wei, G.M. Determination on the hazard zone of spontaneous coal combustion in the adjacent gob of different mining stages. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 142, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Peiyu, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Gao, Y. Influence of coal secondary oxidation on the concentration field of composite goaf [J/OL]. J. China Coal Soc. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ren, T.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z. A review on numerical solutions to self-heating of coal stockpile: Mechanism, theoretical basis, and variable study. Fuel 2016, 182, 80–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.-W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhong, K.-Q.; Shu, C.-M.; Lü, H.-F.; Deng, J.; Wu, S. Overview of commonly used materials for coal spontaneous combustion prevention. Fuel 2020, 275, 117981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutao, Z.; Yuanbo, Z.; Yaqing, L.; Xueqiang, S.; Yujie, Z. Heat effects and kinetics of coal spontaneous combustion at various oxygen contents. Energy 2021, 234, 121299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.G.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, J.F.; Zhou, C.S. Study on the Effect of Extraneous Moisture on the Spontaneous Combustion of Coal and Its Mechanism of Action. Energies 2020, 13, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, S.; Tang, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhou, B. Free radical and functional group reaction and index gas CO emission during coal spontaneous combustion. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2018, 190, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zou, L.; Ren, L.F.; Chung, Y.H.; Zhang, P.Y.; Shu, C.M. Prediction indices and limiting parameters of coal spontaneous combustion in the Huainan mining area in China. Fuel 2020, 264, 116883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Zhang, M.Q.; Yang, Z.B.; Yu, J.X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.W. Division of coal spontaneous combustion stages and selection of indicator gases. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wen, H.; Zheng, X.Z.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.J. A method for evaluating the spontaneous combustion of coal by monitoring various gases. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Deng, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Formation law of hydrocarbon index gases during coal spontaneous combustion in an oxygen-poor environment. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2018, 41, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mad (%) | Aad (%) | Vad (%) | FCad (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GZ | 3.30 | 9.89 | 6.60 | 80.21 |
| LN | 3.55 | 20.63 | 32.65 | 41.37 |
| SX | 1.22 | 19.835 | 13.98 | 64.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, C.; Jiang, S.; Shao, H.; Wu, Z.; Bascompta, M. Effect of Secondary Oxidation of Pre-Oxidized Coal on Early Warning Value for Spontaneous Combustion of Coal. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053154
Guo C, Jiang S, Shao H, Wu Z, Bascompta M. Effect of Secondary Oxidation of Pre-Oxidized Coal on Early Warning Value for Spontaneous Combustion of Coal. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(5):3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053154
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Chaowei, Shuguang Jiang, Hao Shao, Zhengyan Wu, and Marc Bascompta. 2023. "Effect of Secondary Oxidation of Pre-Oxidized Coal on Early Warning Value for Spontaneous Combustion of Coal" Applied Sciences 13, no. 5: 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053154
APA StyleGuo, C., Jiang, S., Shao, H., Wu, Z., & Bascompta, M. (2023). Effect of Secondary Oxidation of Pre-Oxidized Coal on Early Warning Value for Spontaneous Combustion of Coal. Applied Sciences, 13(5), 3154. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053154








