Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Neonatology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Applications of Artificial Intelligence
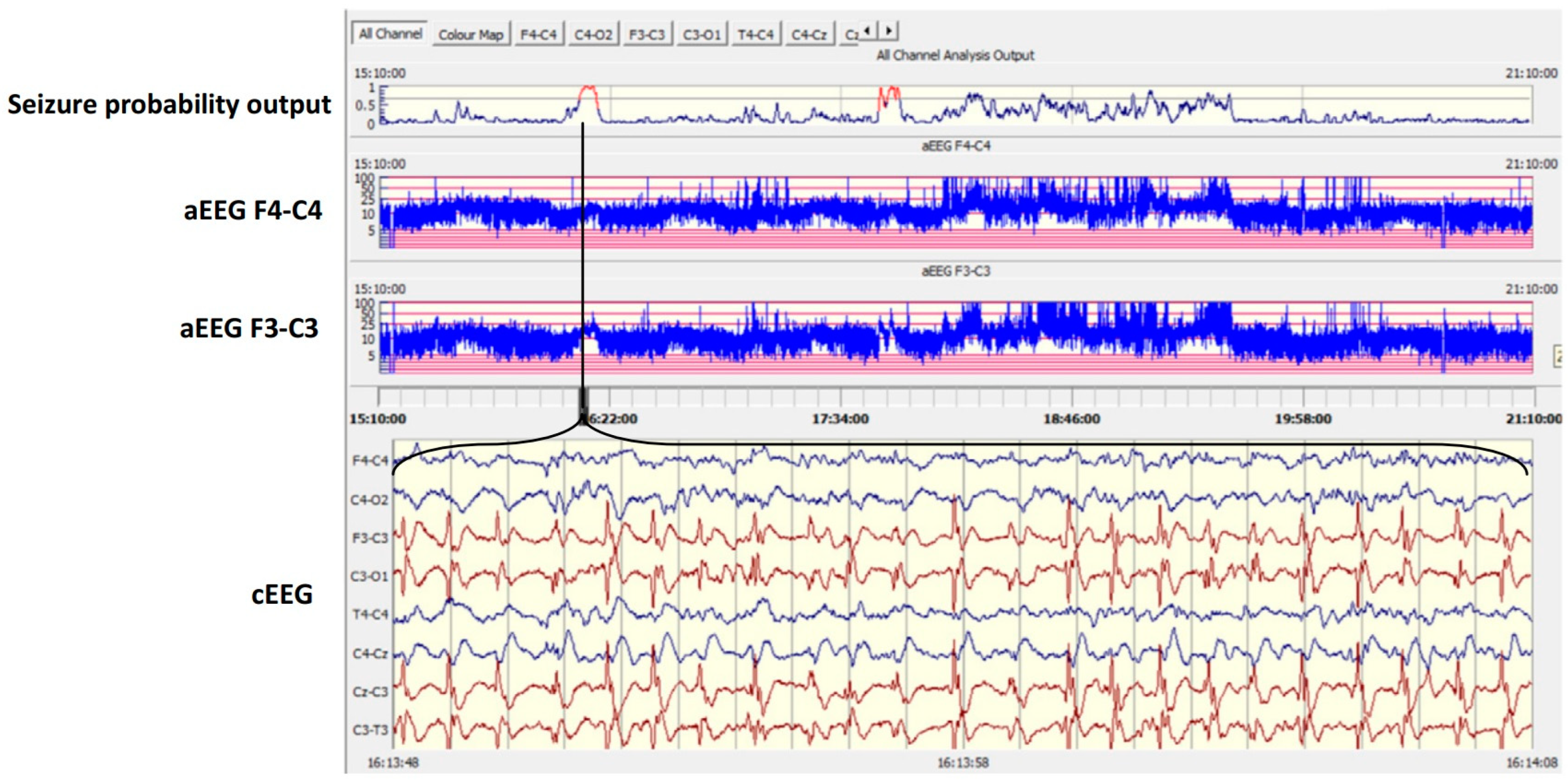
2.1. AI and Neuromonitoring
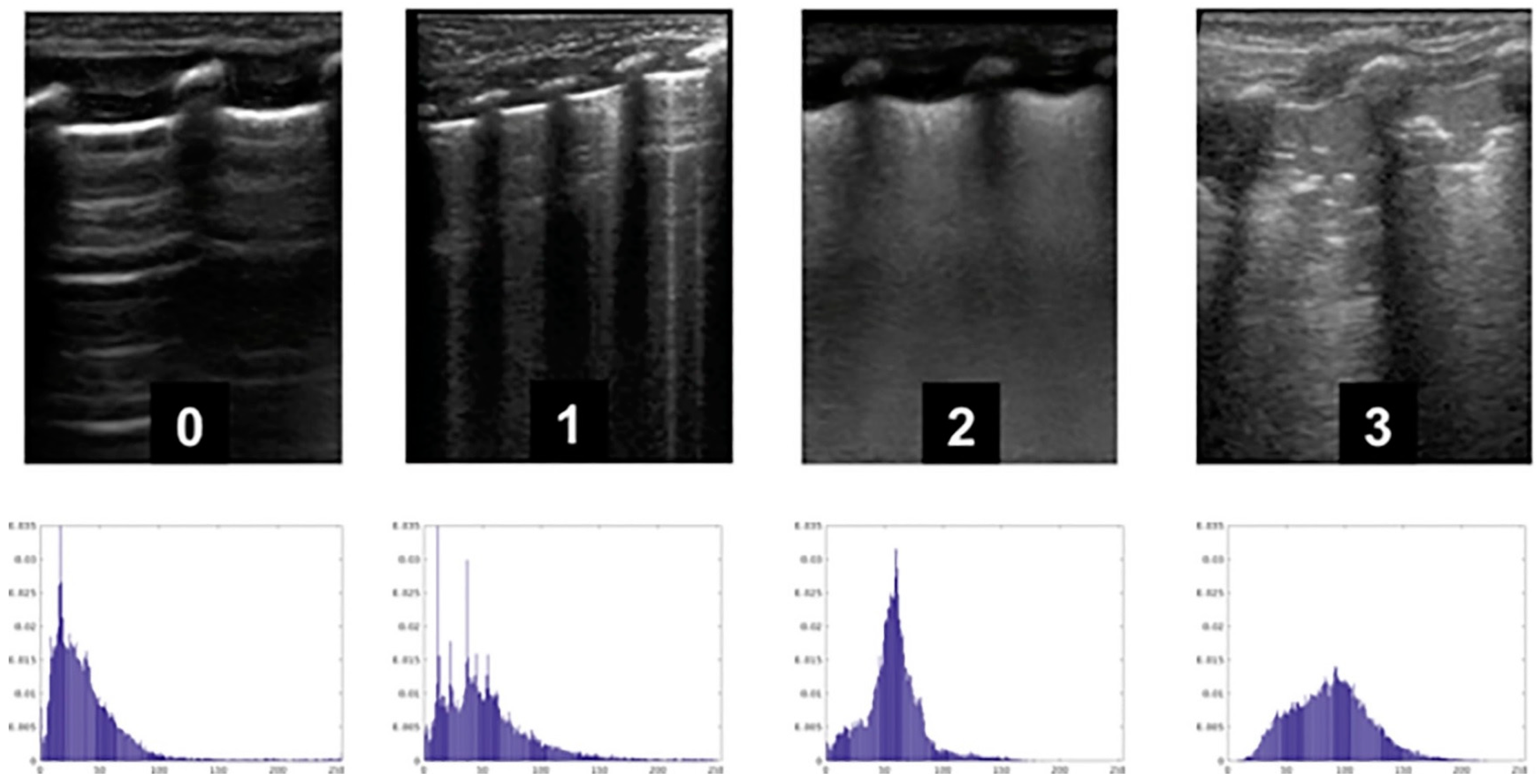
2.2. AI and the Respiratory System
2.3. AI and the Eye
2.4. AI and Vital Signs Monitoring
2.5. AI and the Gastrointestinal System
2.6. AI and Neonatal Jaundice
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helm, J.M.; Swiergosz, A.M.; Haeberle, H.S.; Karnuta, J.M.; Schaffer, J.L.; Krebs, V.E.; Spitzer, A.I.; Ramkumar, P.N. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: Definitions, Applications, and Future Directions. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2020, 13, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, G. Artificial Intelligence in the Intensive Care Unit. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, N.; Arshad, A.; Mazer, M.B.; Carroll, C.L.; Shein, S.L.; Remy, K.E. The use of machine learning and artificial intelligence within pediatric critical care. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 93, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramgopal, S.; Sanchez-Pinto, L.N.; Horvat, C.M.; Carroll, M.S.; Luo, Y.; Florin, T.A. Artificial intelligence-based clinical decision support in pediatrics. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 93, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, B.H.; Bower, M.R.; Stengel, K.A.; Worrell, G.A.; Stead, M. Large-scale electrophysiology: Acquisition, compression, encryption, and storage of big data. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 180, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shellhaas, R.A.; Clancy, R.R. Characterization of neonatal seizures by conventional EEG and single-channel EEG. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2007, 118, 2156–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, B.; Hahn, C.D. Continuous EEG monitoring in the neonatal intensive care unit. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2013, 30, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.; Oozeer, R.; de Vries, L.; Dubowitz, L.M.; Dubowitz, V. Continuous EEG monitoring of neonatal seizures: Diagnostic and prognostic considerations. Arch. Dis. Child. 1989, 64, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matic, V.; Cherian, P.J.; Koolen, N.; Naulaers, G.; Swarte, R.M.; Govaert, P.; Van Huffel, S.; De Vos, M. Holistic approach for automated background EEG assessment in asphyxiated full-term infants. J. Neural. Eng. 2014, 11, 066007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, S.M.; Pinchefsky, E.; Tse, I.; Marchi, V.; Kohonen, J.; Kauppila, M.; Airaksinen, M.; Tapani, K.; Nevalainen, P.; Hahn, C.; et al. Building an Open Source Classifier for the Neonatal EEG Background: A Systematic Feature-Based Approach From Expert Scoring to Clinical Visualization. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 675154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, N.J.; Korotchikova, I.; Temko, A.; Lightbody, G.; Marnane, W.P.; Boylan, G.B. An automated system for grading EEG abnormality in term neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raurale, S.A.; Boylan, G.B.; Mathieson, S.R.; Marnane, W.P.; Lightbody, G.; O’Toole, J.M. Grading hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonatal EEG with convolutional neural networks and quadratic time-frequency distributions. J. Neural. Eng. 2021, 18, 046007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, M.E.; Lightbody, G.; Mathieson, S.R.; Marnane, W.P.; Boylan, G.B.; O’Toole, J.M. Development of an EEG artefact detection algorithm and its application in grading neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 118917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, A.M.; O’Toole, J.M.; Proietti, J.; Livingstone, V.; Mitra, S.; Marnane, W.P.; Finder, M.; Dempsey, E.M.; Murray, D.M.; Boylan, G.B. Machine learning for the early prediction of infants with electrographic seizures in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolen, N.; Oberdorfer, L.; Rona, Z.; Giordano, V.; Werther, T.; Klebermass-Schrehof, K.; Stevenson, N.; Vanhatalo, S. Automated classification of neonatal sleep states using EEG. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 128, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghimatgar, H.; Kazemi, K.; Helfroush, M.S.; Pillay, K.; Dereymaker, A.; Jansen, K.; Vos, M.; Aarabi, A. Neonatal EEG sleep stage classification based on deep learning and HMM. J. Neural. Eng. 2020, 17, 036031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natalucci, G.; Rousson, V.; Bucher, H.U.; Bernet, V.; Hagmann, C.; Latal, B. Delayed cyclic activity development on early amplitude-integrated EEG in the preterm infant with brain lesions. Neonatology 2013, 103, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klebermass, K.; Olischar, M.; Waldhoer, T.; Fuiko, R.; Pollak, A.; Weninger, M. Amplitude-integrated EEG pattern predicts further outcome in preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 70, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheth, R.D.; Hobbs, G.R.; Mullett, M. Neonatal seizures: Incidence, onset, and etiology by gestational age. J. Perinatol. 1999, 19, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasudevan, C.; Levene, M. Epidemiology and aetiology of neonatal seizures. Semin. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 2013, 18, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, H.C.; Shellhaas, R.A.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Chang, T.; Abend, N.S.; Chu, C.J.; Cilio, M.R.; Glidden, D.V.; Bonifacio, S.L.; Massey, S.; et al. Contemporary Profile of Seizures in Neonates: A Prospective Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2016, 174, 98–103.e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, R.P.; Banwell, B.; Berg, R.A.; Dlugos, D.J.; Donnelly, M.; Ichord, R.; Kessler, S.K.; Lavelle, J.; Massey, S.L.; Hewlett, J.; et al. Impact of an ICU EEG monitoring pathway on timeliness of therapeutic intervention and electrographic seizure termination. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glass, H.C.; Glidden, D.; Jeremy, R.J.; Barkovich, A.J.; Ferriero, D.M.; Miller, S.P. Clinical Neonatal Seizures are Independently Associated with Outcome in Infants at Risk for Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury. J. Pediatr. 2009, 155, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Payne, E.T.; Zhao, X.Y.; Frndova, H.; McBain, K.; Sharma, R.; Hutchison, J.S.; Hahn, C.D. Seizure burden is independently associated with short term outcome in critically ill children. Brain 2014, 137 Pt 5, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivasakumar, P.; Zempel, J.; Trivedi, S.; Wallendorf, M.; Rao, R.; Smith, B.; Inder, T.; Mathur, A.M. Treating EEG Seizures in Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pediatrics 2015, 136, e1302–e1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chapman, K.E.; Specchio, N.; Shinnar, S.; Holmes, G.L. Seizing control of epileptic activity can improve outcome. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1482–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slaughter, L.A.; Patel, A.D.; Slaughter, J.L. Pharmacological treatment of neonatal seizures: A systematic review. J. Child. Neurol. 2013, 28, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, D.M.; Boylan, G.B.; Ali, I.; Ryan, C.A.; Murphy, B.P.; Connolly, S. Defining the gap between electrographic seizure burden, clinical expression and staff recognition of neonatal seizures. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal. Neonatal. Ed. 2008, 93, F187–F191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shellhaas, R.A.; Chang, T.; Tsuchida, T.; Scher, M.S.; Riviello, J.J.; Abend, N.S.; Nguyen, S.; Wusthoff, C.J.; Clancy, R.R. The American Clinical Neurophysiology Society’s Guideline on Continuous Electroencephalography Monitoring in Neonates. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2011, 28, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tagin, M.A.; Woolcott, C.G.; Vincer, M.J.; Whyte, R.K.; Stinson, D.A. Hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2012, 166, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Vries, L.S.; Toet, M.C. Amplitude integrated electroencephalography in the full-term newborn. Clin. Perinatol. 2006, 33, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, L.S.; Hellström-Westas, L. Role of cerebral function monitoring in the newborn. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal. Neonatal. Ed. 2005, 90, F201–F207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rakshasbhuvankar, A.; Rao, S.; Palumbo, L.; Ghosh, S.; Nagarajan, L. Amplitude Integrated Electroencephalography Compared With Conventional Video EEG for Neonatal Seizure Detection: A Diagnostic Accuracy Study. J. Child. Neurol. 2017, 32, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennie, J.M.; Chorley, G.; Boylan, G.B.; Pressler, R.; Nguyen, Y.; Hooper, R. Non-expert use of the cerebral function monitor for neonatal seizure detection. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal. Neonatal. Ed. 2004, 89, F37–F40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Appendino, J.P.; McNamara, P.J.; Keyzers, M.; Stephens, D.; Hahn, C.D. The impact of amplitude-integrated electroencephalography on NICU practice. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 39, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Temko, A.; Lightbody, G. Detecting Neonatal Seizures With Computer Algorithms. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 33, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Hahn, J.S.; Heldt, G.P.; Coen, R.W. Detection of neonatal seizures through computerized EEG analysis. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1992, 82, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotman, J.; Flanagan, D.; Zhang, J.; Rosenblatt, B. Automatic seizure detection in the newborn: Methods and initial evaluation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1997, 103, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieson, S.R.; Stevenson, N.J.; Low, E.; Marnane, W.P.; Rennie, J.M.; Temko, A.; Lightbody, G.; Boylan, G.B. Validation of an automated seizure detection algorithm for term neonates. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Temko, A.; Boylan, G.; Marnane, W.; Lightbody, G. Robust neonatal EEG seizure detection through adaptive background modeling. Int. J. Neural. Syst. 2013, 23, 1350018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevenson, N.J.; Clancy, R.R.; Vanhatalo, S.; Rosén, I.; Rennie, J.M.; Boylan, G.B. Interobserver agreement for neonatal seizure detection using multichannel EEG. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharpe, C.; Davis, S.L.; Reiner, G.E.; Lee, L.I.; Gold, J.J.; Nespeca, M.; Wang, S.G.; Joe, P.; Kuperman, R.; Gardner, M.; et al. Assessing the Feasibility of Providing a Real-Time Response to Seizures Detected With Continuous Long-Term Neonatal Electroencephalography Monitoring. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 36, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, A.M.; Rennie, J.M.; de Vries, L.S.; Blennow, M.; Foran, A.; Shah, D.K.; Pressler, R.M.; Kapellou, O.; Dempsey, E.M.; Mathieson, S.R.; et al. A machine-learning algorithm for neonatal seizure recognition: A multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet. Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, L.S.; Groenendaal, F.; van Haastert, I.C.; Eken, P.; Rademaker, K.J.; Meiners, L.C. Asymmetrical myelination of the posterior limb of the internal capsule in infants with periventricular haemorrhagic infarction: An early predictor of hemiplegia. Neuropediatrics 1999, 30, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, E.A.; De Luca, C.R.; Doyle, L.W.; Roberts, G.; Anderson, P.J. School-age outcomes of extremely preterm or extremely low birth weight children. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e1053–e1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Odding, E.; Roebroeck, M.E.; Stam, H.J. The epidemiology of cerebral palsy: Incidence, impairments and risk factors. Disabil. Rehabil. 2006, 28, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drougia, A.; Giapros, V.; Krallis, N.; Theocharis, P.; Nikaki, A.; Tzoufi, M.; Andronikou, S. Incidence and risk factors for cerebral palsy in infants with perinatal problems: A 15-year review. Early Hum. Dev. 2007, 83, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, N.; Galijasevic, M.; Regodic, M.; Grams, A.E.; Siedentopf, C.; Steiger, R.; Hammerl, M.; Haltmeier, M.; Gizewski, E.R.; Janjic, T. A deep learning pipeline for the automated segmentation of posterior limb of internal capsule in preterm neonates. Artif. Intell. Med. 2022, 132, 102384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valavani, E.; Blesa, M.; Galdi, P.; Sullivan, G.; Dean, B.; Cruickshank, H.; Sitko-Rudnicka, M.; Bastin, M.E.; Chin, R.F.M.; MacIntyre, D.J.; et al. Language function following preterm birth: Prediction using machine learning. Pediatr. Res. 2022, 92, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Li, H.; Dillman, J.R.; Altaye, M.; Wang, H.; Parikh, N.A.; He, L. A self-training deep neural network for early prediction of cognitive deficits in very preterm infants using brain functional connectome data. Pediatr. Radiol. 2022, 52, 2227–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balta, D.; Kuo, H.; Wang, J.; Porco, I.G.; Morozova, O.; Schladen, M.M.; Cereatti, A.; Lum, P.S.; Della Croce, U. Characterization of Infants’ General Movements Using a Commercial RGB-Depth Sensor and a Deep Neural Network Tracking Processing Tool: An Exploratory Study. Sensors 2022, 22, 7426. [Google Scholar]
- Dell’Orto, V.; Nobile, S.; Correani, A.; Marchionni, P.; Giretti, I.; Rondina, C.; Burattini, I.; Palazzi, M.L.; Carnielli, V.P. Early nasal continuous positive airway pressure failure prediction in preterm infants less than 32 weeks gestational age suffering from respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2021, 56, 3879–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, D.G.; Carnielli, V.; Greisen, G.; Hallman, M.; Ozek, E.; Te Pas, A.; Plavka, R.; Roehr, C.C.; Saugstad, O.D.; Simeoni, U.; et al. European Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Respiratory Distress Syndrome—2019 Update. Neonatology 2019, 115, 432–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.M.; Sie, L.; Liu, J.; Profit, J.; Lee, H.C. Evaluation of Trends in Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Respiratory Support Practice for Very Low Birth Weight Infants: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2022, 243, 47–52.e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz-Salamon, M.; Gerner, E.M.; Jonsson, B.; Lagercrantz, H. Early motor and mental development in very preterm infants with chronic lung disease. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal. Neonatal. Ed. 2000, 83, F1–F6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotten, C.M.; Oh, W.; McDonald, S.; Carlo, W.; Fanaroff, A.A.; Duara, S.; Stoll, B.; Laptook, A.; Poole, K.; Wright, L.L.; et al. Prolonged hospital stay for extremely premature infants: Risk factors, center differences, and the impact of mortality on selecting a best-performing center. J. Perinatol. 2005, 25, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McAleese, K.A.; Knapp, M.A.; Rhodes, T.T. Financial and emotional cost of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Clin. Pediatr. 1993, 32, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, J.M.; Zhang, H.; Kirpalani, H.; DeMauro, S.B. Living with Severe Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia-Parental Views of Their Child’s Quality of Life. J. Pediatr. 2019, 207, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobile, S.; Marchionni, P.; Vento, G.; Vendettuoli, V.; Marabini, C.; Lio, A.; Ricci, C.; Mercadante, D.; Colnaghi, M.; Mosca, F.; et al. New Insights on Early Patterns of Respiratory Disease among Extremely Low Gestational Age Newborns. Neonatology 2017, 112, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vento, G.; Ventura, M.L.; Pastorino, R.; van Kaam, A.H.; Carnielli, V.; Cools, F.; Dani, C.; Mosca, F.; Polglase, G.; Tagliabue, P.; et al. Lung recruitment before surfactant administration in extremely preterm neonates with respiratory distress syndrome (IN-REC-SUR-E): A randomised, unblinded, controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Veluthandath, A.V.; Rowe, D.J.; Madsen, J.; Clark, H.W.; Postle, A.D.; Wilkinson, J.S.; Murugan, G.S. Prediction of Neonatal Respiratory Distress Biomarker Concentration by Application of Machine Learning to Mid-Infrared Spectra. Sensors 2022, 22, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, F.; Migliaro, F.; Verdoliva, L.; Gragnaniello, D.; Poggi, G.; Kosova, R.; Sansone, C.; Vallone, G.; Capasso, L. Visual assessment versus computer-assisted gray scale analysis in the ultrasound evaluation of neonatal respiratory status. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laughon, M.M.; Langer, J.C.; Bose, C.L.; Smith, P.B.; Ambalavanan, N.; Kennedy, K.A.; Stoll, B.J.; Buchter, S.; Laptook, A.R.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; et al. Prediction of bronchopulmonary dysplasia by postnatal age in extremely premature infants. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1715–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, M.; Sandhu, J.; Chou, F.S. Developing a machine learning-based tool to extend the usability of the NICHD BPD Outcome Estimator to the Asian population. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, W.; He, W.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ta, D. Early severity prediction of BPD for premature infants from chest X-ray images using deep learning: A study at the 28th day of oxygen inhalation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 221, 106869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, D.; Chen, H.; Dong, X.; Chen, J.; Mei, M.; Lu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, B.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Predicted by Developing a Machine Learning Model of Genetic and Clinical Information. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 689071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, R.M.; Pham, A.; Rao, S.S.; Vora, F.M.; Hou, G.; Kent, C.; Rodriguez, A.; Narang, A.; Tan, J.B.C.; Chou, F.S. Machine learning for prediction of bronchopulmonary dysplasia-free survival among very preterm infants. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, S.; Marchionni, P.; Noviello, C.; Carnielli, V.P. Correlation between cardiorespiratory events and gastro-esophageal reflux in preterm and term infants: Analysis of predisposing factors. Early Hum. Dev. 2019, 134, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finer, N.N.; Higgins, R.; Kattwinkel, J.; Martin, R.J. Summary Proceedings From the Apnea-of-Prematurity Group. Pediatrics 2006, 117 (Suppl. S1), S47–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eichenwald, E.C. Apnea of Prematurity. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20153757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, S.B.; Burnell, E. Monitoring apnea of prematurity: Validity of nursing documentation and bedside cardiorespiratory monitor. Am. J. Perinatol. 2013, 30, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varisco, G.; Peng, Z.; Kommers, D.; Zhan, Z.; Cottaar, W.; Andriessen, P.; Long, X.; van Pul, C. Central apnea detection in premature infants using machine learning. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 226, 107155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobile, S.; Gnocchini, F.; Pantanetti, M.; Battistini, P.; Carnielli, V.P. The importance of oxygen control reaffirmed: Experience of ROP reduction at a single tertiary care center. J. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus. 2014, 51, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Mo, Z.; Wu, R.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xiao, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lin, Z.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Model to Predict the Occurrence and Severity of Retinopathy of Prematurity. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2217447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redd, T.K.; Campbell, J.P.; Brown, J.M.; Kim, S.J.; Ostmo, S.; Chan, R.V.P.; Dy, J.; Erdogmus, D.; Ioannidis, S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; et al. Evaluation of a deep learning image assessment system for detecting severe retinopathy of prematurity. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antognoli, L.; Marchionni, P.; Nobile, S.; Carnielli, V.; Scalise, L. Assessment of cardio-respiratory rates by non-invasive measurement methods in hospitalized preterm neonates. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), Rome, Italy, 11–13 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Vats, V.; Nagori, A.; Singh, P.; Dutt, R.; Bandhey, H.; Wason, M.; Lodha, R.; Sethi, T. Early Prediction of Hemodynamic Shock in Pediatric Intensive Care Units With Deep Learning on Thermal Videos. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 862411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyra, S.; Rixen, J.; Heimann, K.; Karthik, S.; Joseph, J.; Jayaraman, K.; Orlikowsky, T.; Sivaprakasam, M.; Leonhardt, S.; Hoog Antink, C. Camera fusion for real-time temperature monitoring of neonates using deep learning. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2022, 60, 1787–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.; Kim, D.; Na, J.Y.; Jung, D.; Ahn, J.-H.; Kim, T.H.; Park, H.-K. Development of artificial neural networks for early prediction of intestinal perforation in preterm infants. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, H.S.; Park, G.; Lim, J.; Shin, J.E.; Eun, H.S.; Park, M.S.; Lee, S.M. Application of Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Postnatal Growth Failure in Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Yonsei Med. J. 2022, 63, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althnian, A.; Almanea, N.; Aloboud, N. Neonatal Jaundice Diagnosis Using a Smartphone Camera Based on Eye, Skin, and Fused Features with Transfer Learning. Sensors 2021, 21, 7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedalia, J.; Farkash, R.; Wasserteil, N.; Kasirer, Y.; Rottenstreich, M.; Unger, R.; Grisaru Granovsky, S. Primary risk stratification for neonatal jaundice among term neonates using machine learning algorithm. Early Hum. Dev. 2022, 165, 105538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, V.; Oddie, S.; McGuire, W. Ethical Issues in Perinatal Clinical Research. Neonatology 2019, 116, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Fuente, M.; Arruza, L.; Muro, M.; Zozaya, C.; Avila, A.; López-Ortego, P.; González-Armengod, G.; Torrent, A.; Luis Gavilán, J.; del Cerro, M.J. The economic impact of prematurity and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2017, 176, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, F.; Fernandes, E.; Virella, D.; Abrantes, A.; Neto, M.T. Born Preterm: A Public Health Issue. Port. J. Public Health 2019, 37, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zejin Ou, Z.; Yu, D.; Liang, Y.; He, H.; He, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gao, Y.; Wu, F.; Chen, Q. Yongzhi LiGlobal trends in incidence and death of neonatal disorders and its specific causes in 204 countries/territories during 1990–2019. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 360. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chioma, R.; Sbordone, A.; Patti, M.L.; Perri, A.; Vento, G.; Nobile, S. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Neonatology. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053211
Chioma R, Sbordone A, Patti ML, Perri A, Vento G, Nobile S. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Neonatology. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(5):3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053211
Chicago/Turabian StyleChioma, Roberto, Annamaria Sbordone, Maria Letizia Patti, Alessandro Perri, Giovanni Vento, and Stefano Nobile. 2023. "Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Neonatology" Applied Sciences 13, no. 5: 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053211
APA StyleChioma, R., Sbordone, A., Patti, M. L., Perri, A., Vento, G., & Nobile, S. (2023). Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Neonatology. Applied Sciences, 13(5), 3211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053211






