Non-Autoregressive Sparse Transformer Networks for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction
2.2. Human-Human Interactions
2.3. Transformer Networks
2.4. Non-Autoregressive Inference
3. Methods
3.1. Overview
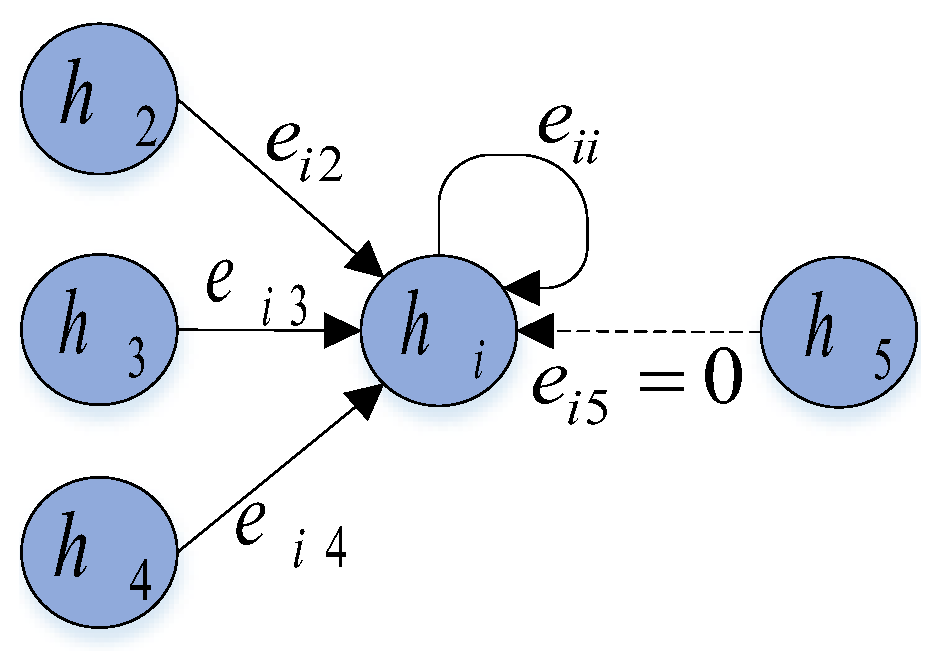
3.2. Sparse Spatial Transformer
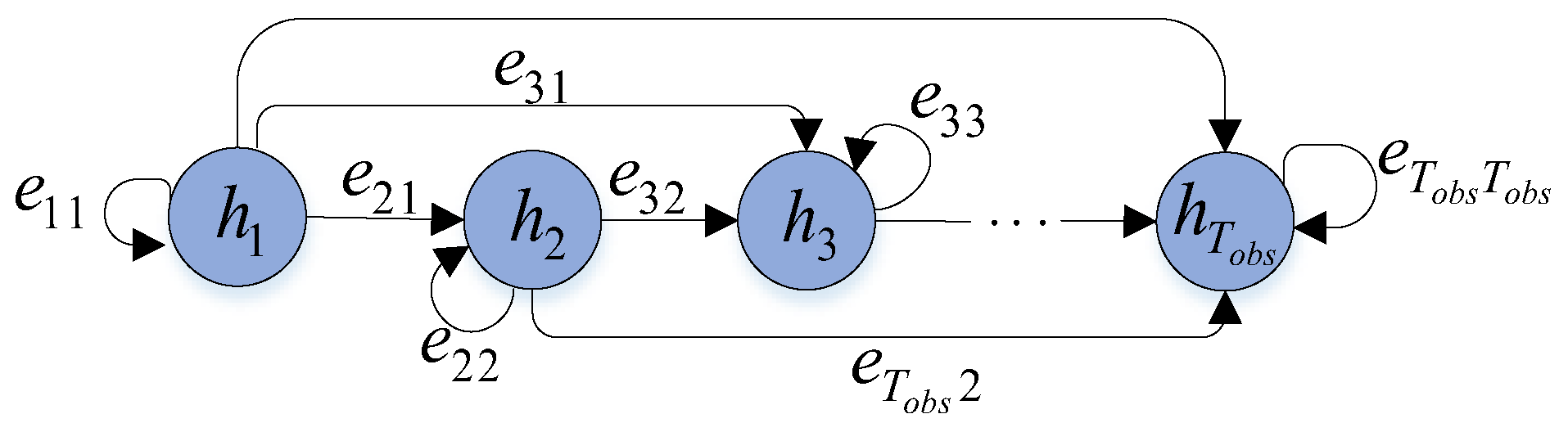
3.3. Sparse Temporal Transformer
3.4. Non-Autoregressive Transformer Decoder
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets and Metrics
4.2. Experimental Settings
4.3. Comparison with State-of-the-Arts
4.4. Ablation Study
4.4.1. The Individual Module in NaST
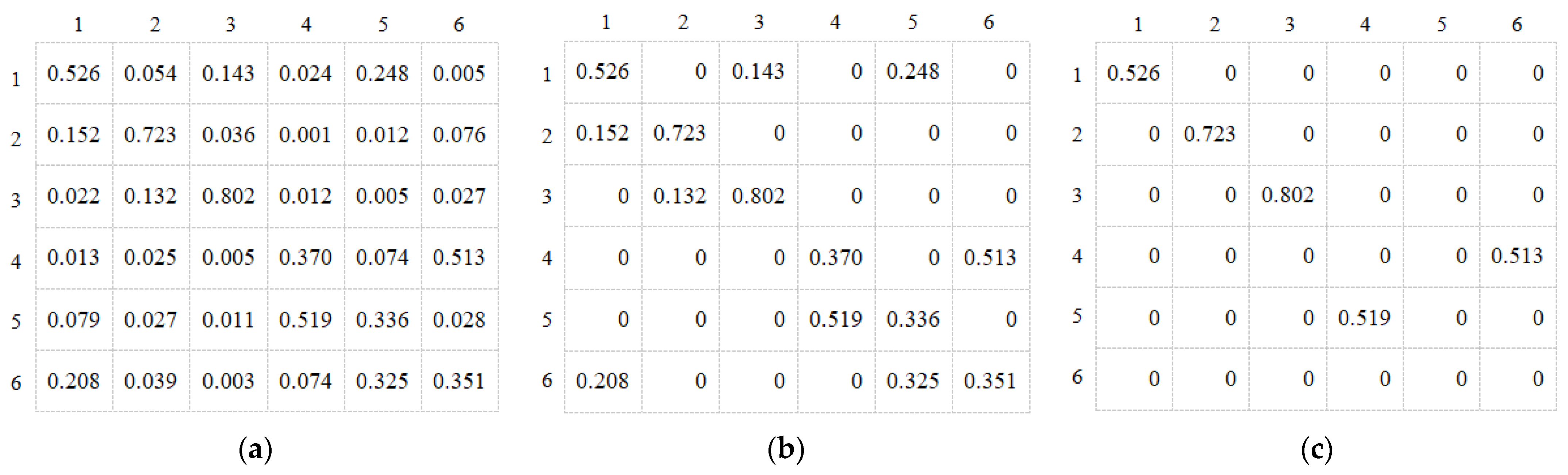
4.4.2. Contribution of Spatial and Temporal Sparsity
4.4.3. Contribution of Non-Autoregressive Prediction
4.5. Visualization
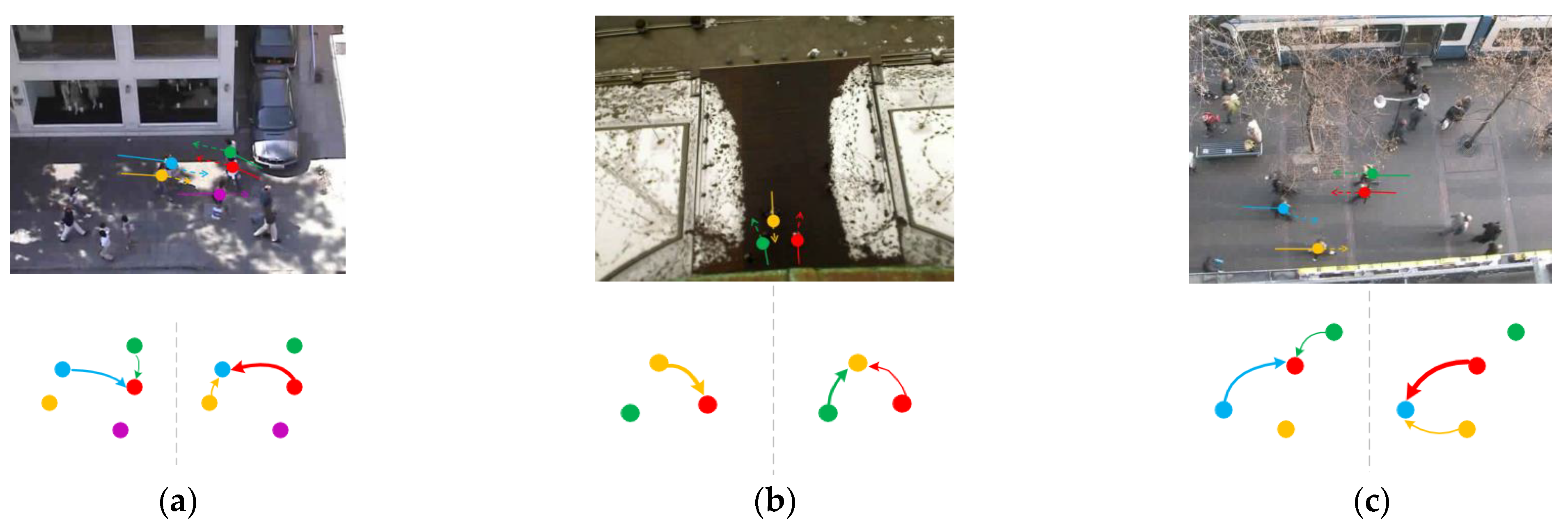
4.5.1. Trajectory Prediction Visualization
4.5.2. Sparse Directed Interaction Visualization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bai, H.; Cai, S.; Ye, N.; Hsu, D.; Lee, W.S. Intention-aware online pomdp planning for autonomous driving in a crowd. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 454–460. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Cai, P.; Bera, A.; Hsu, D.; Lee, W.S. Porca: Modeling and planning for autonomous driving among many pedestrians. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 3418–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Cai, P. Gamma: A general agent motion prediction model for autonomous driving. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.01566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luber, M.; Stork, J.A.; Tipaldi, G.D.; Arras, K.O. People tracking with human motion predictions from social forces. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 464–469. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuno, M.; Yasuda, N.; Aoki, M. Pedestrian detection and tracking in far infrared images. In Proceedings of the 2004 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop, Washington, DC, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004; p. 125. [Google Scholar]
- Alahi, A.; Goel, K.; Ramanathan, V.; Robicquet, A.; Fei-Fei, L.; Savarese, S. Social lstm: Human trajectory prediction in crowded spaces. In Proceedings of the 29th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 961–971. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Johnson, J.; Fei-Fei, L.; Savarese, S.; Alahi, A. Social gan: Socially acceptable trajectories with generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Ouyang, W.; Zhang, P.; Xue, J.; Zheng, N. Sr-lstm: State refinement for lstm towards pedestrian trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Bi, H.; Li, Z.; Mao, T.; Wang, Z. Stgat: Modeling spatial-temporal interactions for human trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanovic, B.; Pavone, M. The trajectron: Probabilistic multi-agent trajectory modeling with dynamic spatiotemporal graphs. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mehdi, M.; Niriaska, P.; Simon, G.; Helbing, D.; Theraulaz, G. The walking behavior of pedestrian social groups and its impact on crowd dynamics. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10047. [Google Scholar]
- Helbing, D.; Molnar, P. Social force model for pedestrian dynamics. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 51, 4282–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbing, D.; Buzna, L.; Johansson, A.; Werner, T. Self-organized pedestrian crowd dynamics: Experiments, simulations, and design solutions. Transp. Sci. 2005, 39, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Jiang, L.; Juan, C.N.; Hauptmann, A.G.; Li, F.F. Peeking into the future: Predicting future person activities and locations in videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5725–5734. [Google Scholar]
- Amir, S.; Vineet, K.; Ali, S.; Noriaki, H.; Hamid, R.; Silvio, S. Sophie: An attentive gan for predicting paths compliant to social and physical constraints. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1349–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, T.; Denman, S.; Sridharan, S.; Fookes, C. Soft+ hardwired attention: An lstm framework for human trajectory prediction and abnormal event detection. Neural Netw. 2018, 108, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemula, A.; Muelling, K.; Jean, O. Social attention: Modeling attention in human crowds. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kosaraju, V.; Sadeghian, A.; Roberto, M.; Reid, I.; Rezatofighi, H.; Savarese, S. Social bigat: Multimodal trajectory forecasting using bicycle-gan and graph attention networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.; Qian, K.; Elhoseiny, M.; Claudel, C. Social-stgcnn: A social spatio-temporal graph convolutional neural network for human trajectory prediction. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.11927. [Google Scholar]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Petar, V.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Pietro, L.; Bengio, Y. Graph Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z.; Chen, M.; Goodman, S.; Gimpel, K.; Sharma, P.; Soricut, R. Albert: A lite bert for self-supervised learning of language representations. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11942. [Google Scholar]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N. End-to end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vienna, Austria, 4 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Hu, H.; Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Dai, J. Learning region features for object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Ma, X.; Ren, J.; Zhao, H.; Yi, S. Spatio-temporal graph transformer networks for pedestrian trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Bradbury, J.; Xiong, C.; Victor, O.K.; Socher, R. Non-autoregressive neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini, S.; Ess, A.; Schindler, K.; Gool, L. You’ll never walk alone: Modeling social behavior for multi-target tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Kyoto, Japan, 27 September–4 October 2009; pp. 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Lerner, A.; Chrysanthou, Y.; Lischinski, D. Crowds by example. Comput. Graph. Forum 2007, 26, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yang, R.; Wang, W.; Manocha, D. Traffic predict: Trajectory prediction for heterogeneous traffic-agents. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Third AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 28–29 January 2019; pp. 6120–6127. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27 (NIPS 2014), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Lui, A.K.F.; Chan, Y.H.; Leung, M.F. Modelling of Destinations for Data-driven Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction in Public Buildings. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data, Orlando, FL, USA, 15–18 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, T.; Chen, G.; Li, J.; Lin, C.; Rao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J. Stochastic Trajectory Prediction via Motion Indeterminacy Diffusion. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Mao, W.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S. Remember Intentions: Retrospective-Memory-based Trajectory Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Löhner, R. On the modeling of pedestrian motion. Appl. Math. Model. 2010, 32, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, G.; Bierlaire, M.; Weber, M. Discrete choice models of pedestrian walking behavior. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2006, 40, 667–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Fleet, D.J.; Hertzmann, A. Gaussian process dynamical models for human motion. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 30, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Liu, J.G.; Pan, X.; Wang, B.H. A social force evacuation model with the leadership effect. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 400, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboia, P.; Goldenstein, S. Crowd simulation: Applying mobile grids to the social force model. Vis. Comput. 2012, 28, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, R.; Oyama, A.; Shah, M. Abnormal crowd behavior detection using social force model. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Berg, A.C.; Ortiz, L.E.; Berg, T.L. Who are you with and where are you going? In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 1345–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Dhariwal, P.; Nichol, A. Diffusion models beat gans on image synthesis. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Virtual, 6–14 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Nichol, A.; Dhariwal, P. Improved denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dickstein, J.S.; Weiss, E.; Maheswaranathan, N.; Ganguli, S. Deep unsupervised learning using nonequilibrium thermodynamics. In Proceedings of the The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2015), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 2256–2265. [Google Scholar]
- Jozefowicz, R.; Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I. An empirical exploration of recurrent network architectures. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2015), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 2342–2350. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Gated feedback recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2015), Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; pp. 2067–2075. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Carbonell, J.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Le, Q.V. Xlnet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. In Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 5753–5763. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Tim, S.; Sutskever, I. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training. 2018, Volume 3. Available online: https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/openai-assets/research-covers/language-unsupervised/language_understanding_paper.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Liu, J.; Lin, H.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Ren, Y.; Diao, Y.; Yang, L. Transformer-based capsule network for stock movement prediction. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Financial Technology and Natural Language Processing, Macao, China, 12 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, K.; Toshev, A.; Fei-Fei, L.; Savarese, S. Scene memory transformer for embodied agents in long-horizon tasks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zen, H.; Weiss, R.J.; Norouzi, M.; Chan, W. Wavegrad: Estimating gradients for waveform generation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vienna, Austria, 4 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhou, B. Tpnet: Trajectory proposal network for motion prediction. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Gao, J.; Lan, T.; Sun, C.; Sapp, B.; Varadarajan, B.; Shen, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chai, Y.; Schmid, C.; et al. Tnt: Target-driven trajectory prediction. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.08294. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Li, J.; Zhou, N.; Ren, L.; Lu, J. Personalized trajectory prediction via distribution discrimination. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 15580–15589. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, N.; Choi, W.; Vernaza, P.; Choy, C.B.; Torr, P.H.S.; Chandraker, M. Desire: Distant future prediction in dynamic scenes with interacting agents. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 336–345. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 9. Available online: https://d4mucfpksywv.cloudfront.net/better-language-models/language-models.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Martinez-Gonzalez, A.; Villamizar, M.; Odobez, J.-M. Pose Transformers (POTR): Human Motion Prediction with Non-Autoregressive Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Virtual, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2276–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Huynh, D.Q.; Reynolds, M. Take a NAP: Non-Autoregressive Prediction for Pedestrian Trajectories. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing (ICONIP2020), Bangkok, Thailand, 23–27 November 2020; pp. 544–556. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavian, M.; Nikdel, P.; Taherahmadi, M.; Chen, M. STPOTR: Simultaneous Human Trajectory and Pose Prediction Using a Non-Autoregressive Transformer for Robot Following Ahead. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.07600. [Google Scholar]
- Achaji, L.; Barry, T.; Fouqueray, T.; Moreau, J.; Aioun, F.; Charpillet, F. PreTR: Spatio-Temporal Non-Autoregressive Trajectory Prediction Transformer. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.09293. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, G.; Butt, A.; Curtis, K.; Lee, Y.; Fiscus, J.; Godil, A.; Joy, D.; Delgado, A.; Smeaton, A.F.; Graham, Y.; et al. Trecvid 2018: Bench marking video activity detection, video captioning and matching, video storytelling linking and video search. In Proceedings of the TREC Video Retrieval Evaluation (TRECVID), Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 13–15 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Jiang, L.; Murphy, K.; Yu, T.; Hauptmann, A. The Garden of Forking Paths: Towards multi-future trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10508–10518. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Jiang, Q.; Lu, C. Recursive social behavior graph for trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 660–669. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Cai, S.; Tan, G. GraphTCN: Spatio-Temporal Interaction Modeling for Human Trajectory Prediction. In Proceedings of the WACV 2021: Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 3449–3458. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Wang, L.; Long, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, M.; Niu, Z.; Hua, G. SGCN: Sparse Graph Convolution Network for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8994–9003. [Google Scholar]



| Models | ETH | HOTEL | UNIV | ZARA1 | ZARA2 | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social GAN [7] | 0.87/1.62 | 0.67/1.37 | 0.76/1.52 | 0.35/0.68 | 0.42/0.84 | 0.61/1.21 |
| Sophie [15] | 0.70/1.43 | 0.76/1.67 | 0.54/1.24 | 0.30/0.63 | 0.38/0.78 | 0.51/1.15 |
| Social-BIGAT [18] | 0.69/1.29 | 0.49/1.01 | 0.55/1.32 | 0.30/0.62 | 0.36/0.75 | 0.48/1.00 |
| SR-LSTM [8] | 0.63/1.25 | 0.37/0.74 | 0.51/1.10 | 0.41/0.90 | 0.32/0.70 | 0.45/0.94 |
| Social-STGCNN [19] | 0.64/1.11 | 0.49/0.85 | 0.44/0.79 | 0.34/0.53 | 0.30/0.48 | 0.44/0.75 |
| RSBG w/o context [64] | 0.80/1.53 | 0.33/0.64 | 0.80/1.53 | 0.40/0.86 | 0.30/0.65 | 0.48/0.99 |
| STAR [27] | 0.36/0.65 | 0.17/0.36 | 0.31/0.62 | 0.26/0.55 | 0.22/0.46 | 0.26/0.53 |
| SGCN [66] | 0.63/1.03 | 0.32/0.55 | 0.37/0.70 | 0.37/0.70 | 0.25/0.45 | 0.37/0.65 |
| GraphTCN [65] | 0.59/1.12 | 0.27/0.52 | 0.42/0.87 | 0.30/0.62 | 0.23/0.48 | 0.36/0.72 |
| NaST (Ours) | 0.35/0.62 | 0.15/0.35 | 0.27/0.56 | 0.25/0.56 | 0.19/0.41 | 0.24/0.50 |
| Components | Performance (ADE/FDE) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STE | TTE | TD | ETH | HOTEL | UNIV | ZARA1 | ZARA2 | AVG | |
| (a) | √ | - | √ | 0.38/0.65 | 0.26/0.42 | 0.29/0.59 | 0.38/0.67 | 0.19/0.43 | 0.30/0.55 |
| (b) | - | √ | √ | 0.37/0.64 | 0.18/0.37 | 0.35/0.67 | 0.28/0.58 | 0.20/0.44 | 0.28/0.54 |
| (c) | √ | √ | - | 0.37/0.63 | 0.16/0.35 | 0.29/0.57 | 0.27/0.58 | 0.20/0.42 | 0.26/0.51 |
| NaST | √ | √ | √ | 0.35/0.62 | 0.15/0.35 | 0.27/0.56 | 0.25/0.56 | 0.19/0.41 | 0.24/0.50 |
| Variants | ETH | HOTEL | UNIV | ZARA1 | ZARA2 | AVG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaST-sp0 | 0.39/0.65 | 0.18/0.36 | 0.36/0.67 | 0.26/0.58 | 0.23/0.44 | 0.28/0.54 |
| NaST-sp0.3 | 0.35/0.63 | 0.16/0.35 | 0.28/0.59 | 0.25/0.56 | 0.19/0.41 | 0.25/0.51 |
| NaST-sp0.5 | 0.37/0.64 | 0.17/0.36 | 0.27/0.58 | 0.26/0.56 | 0.20/0.41 | 0.25/0.51 |
| NaST-sp0.8 | 0.40/0.67 | 0.21/0.42 | 0.33/0.67 | 0.27/0.58 | 0.23/0.40 | 0.29/0.55 |
| NaST-sp1 | 0.41/0.67 | 0.21/0.42 | 0.32/0.68 | 0.27/0.60 | 0.22/0.43 | 0.29/0.56 |
| NaST-tp0 | 0.38/0.65 | 0.18/0.37 | 0.31/0.65 | 0.25/0.59 | 0.22/0.45 | 0.27/0.54 |
| NaST-tp0.2 | 0.35/0.64 | 0.16/0.37 | 0.29/0.62 | 0.26/0.57 | 0.20/0.42 | 0.25/0.52 |
| NaST-tp0.7 | 0.40/0.66 | 0.19/0.44 | 0.33/0.61 | 0.29/0.63 | 0.21/0.44 | 0.28/0.56 |
| NaST-tp1 | 0.43/0.68 | 0.20/0.44 | 0.35/0.62 | 0.29/0.64 | 0.25/0.47 | 0.30/0.57 |
| NaST | 0.35/0.62 | 0.15/0.35 | 0.27/0.56 | 0.25/0.56 | 0.19/0.41 | 0.24/0.50 |
| Variants | Performance (ADE/FDE) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETH | HOTEL | UNIV | ZARA1 | ZARA2 | AVG | |
| NaST-auto | 0.33/0.69 | 0.21/0.45 | 0.31/0.67 | 0.31/0.68 | 0.22/0.54 | 0.28/0.61 |
| NaST (ours) | 0.35/0.62 | 0.15/0.35 | 0.27/0.56 | 0.25/0.56 | 0.19/0.41 | 0.24/0.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Li, Q.; Li, S.; Kong, J.; Qi, M. Non-Autoregressive Sparse Transformer Networks for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053296
Liu D, Li Q, Li S, Kong J, Qi M. Non-Autoregressive Sparse Transformer Networks for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(5):3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053296
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Di, Qiang Li, Sen Li, Jun Kong, and Miao Qi. 2023. "Non-Autoregressive Sparse Transformer Networks for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction" Applied Sciences 13, no. 5: 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053296
APA StyleLiu, D., Li, Q., Li, S., Kong, J., & Qi, M. (2023). Non-Autoregressive Sparse Transformer Networks for Pedestrian Trajectory Prediction. Applied Sciences, 13(5), 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13053296






