Extraction of Flaw Signals from the Mixed 1-D Signals by Denoising Autoencoder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
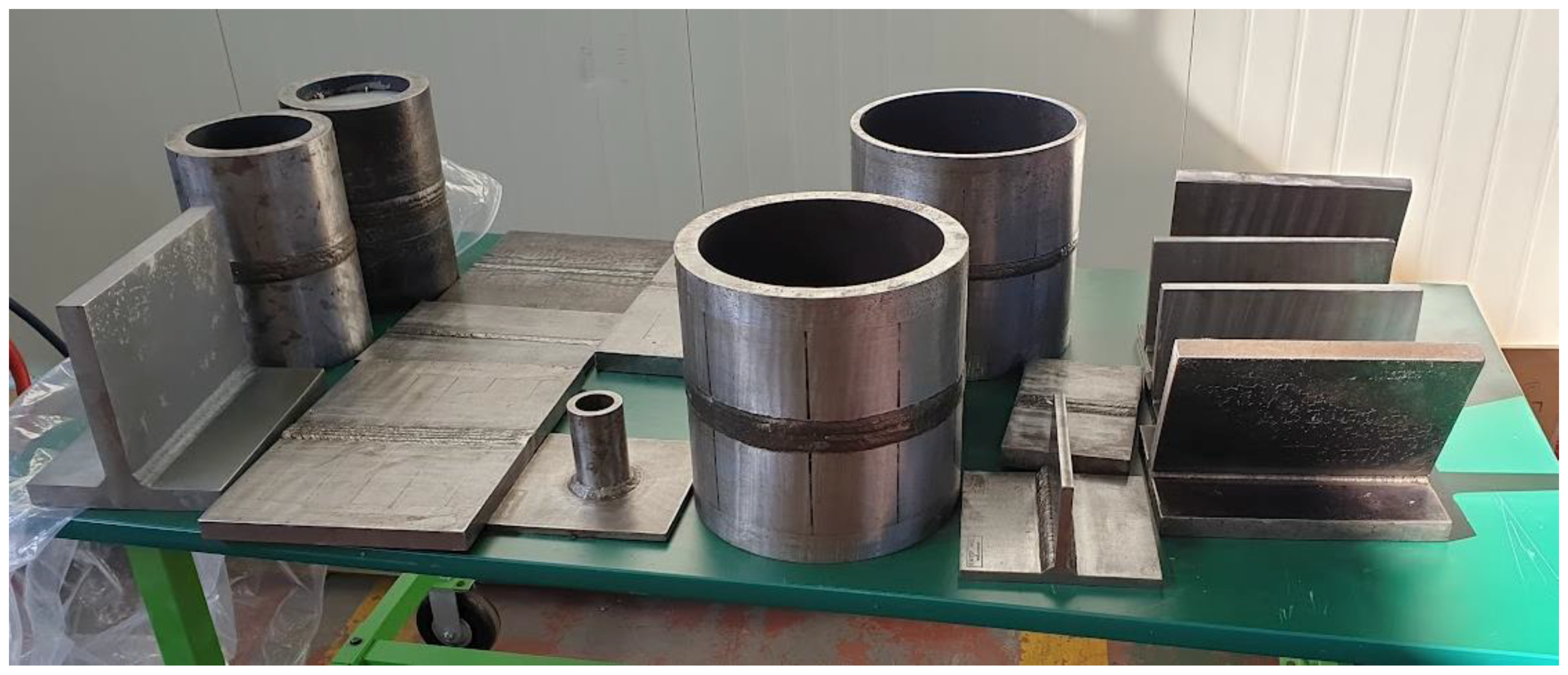
2.1. Specimen Information
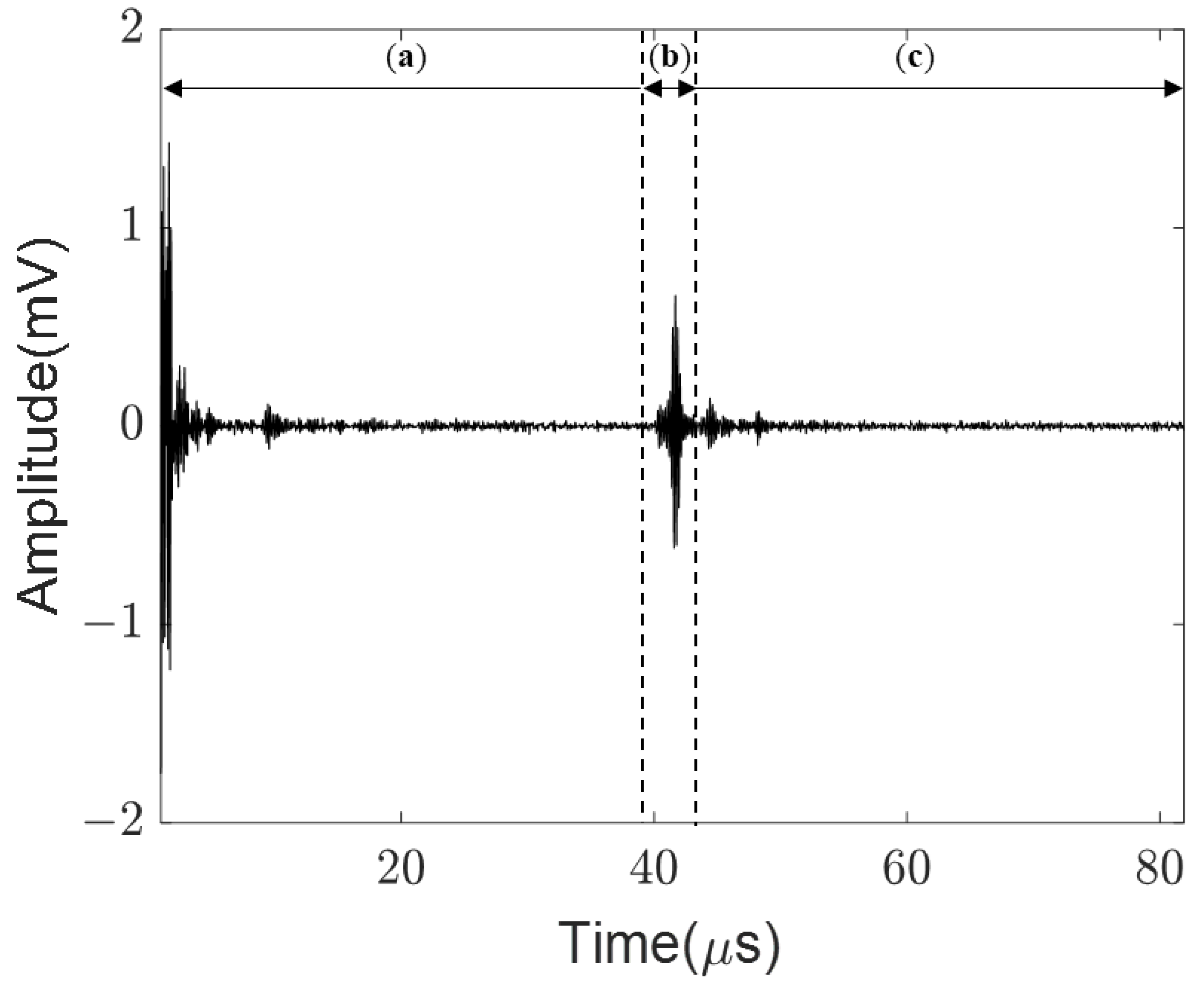
2.2. Data Acquisition
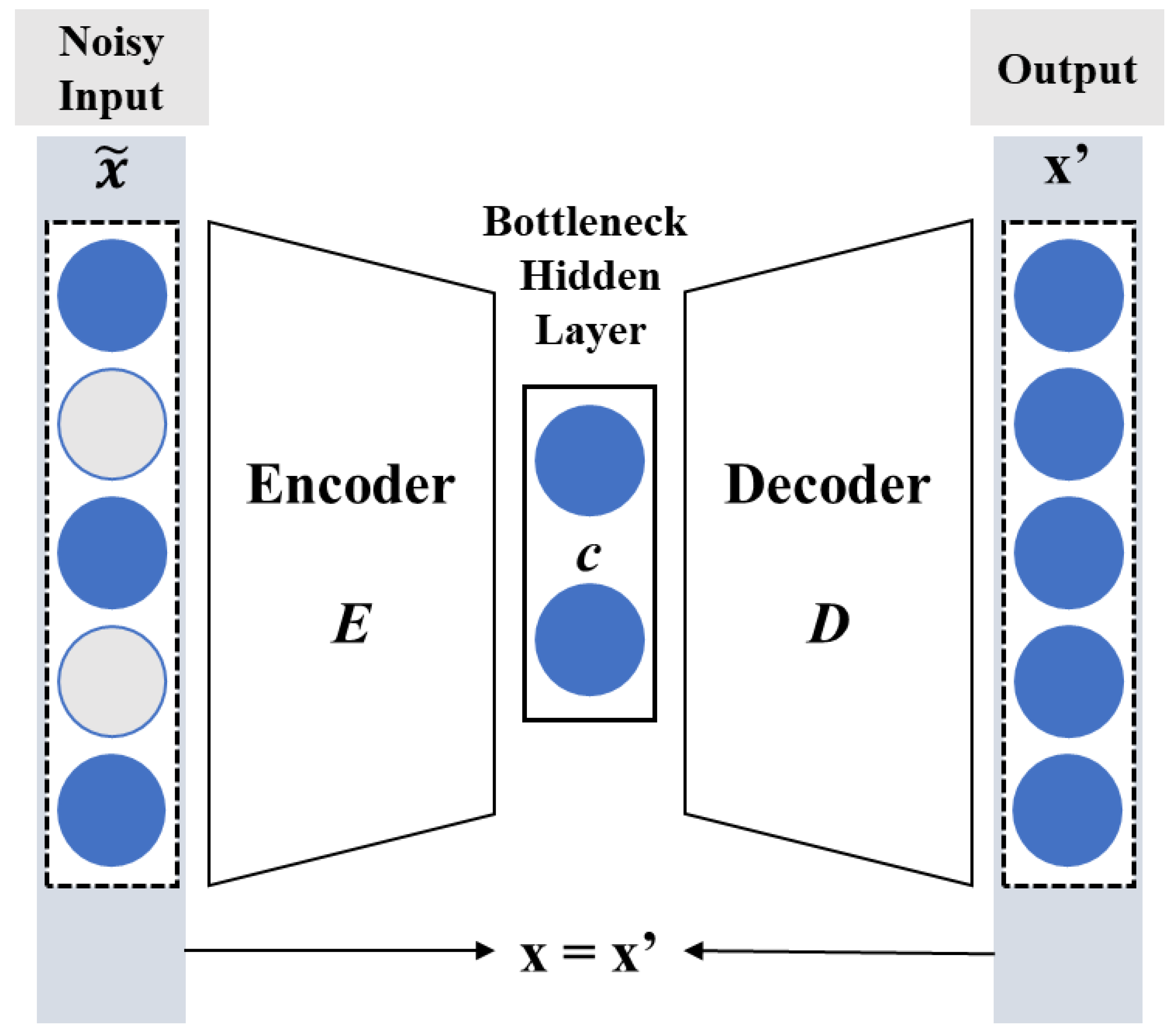
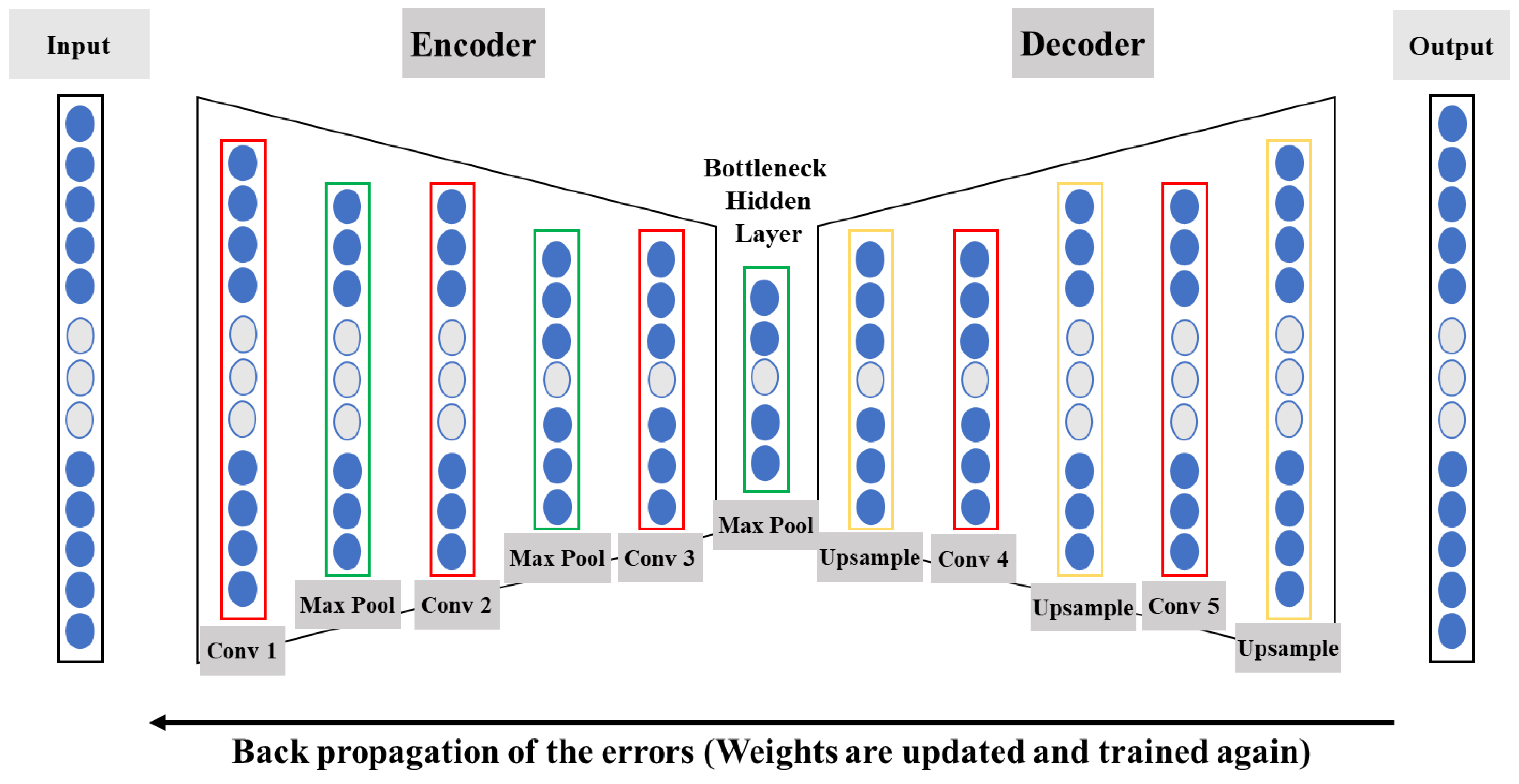
2.3. Denoising Autoencoder
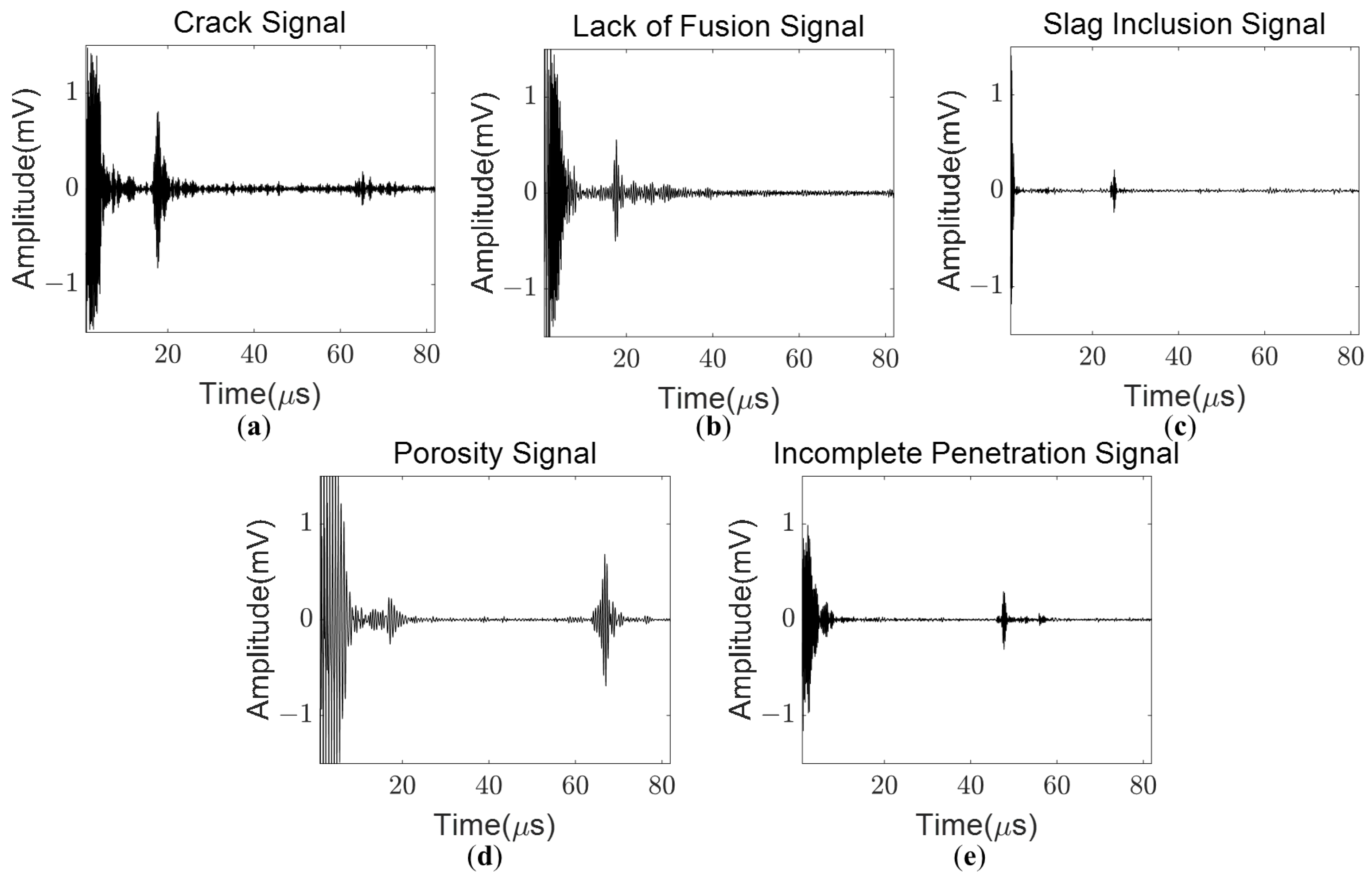
3. Ultrasonic Signal Database
3.1. Database Construction
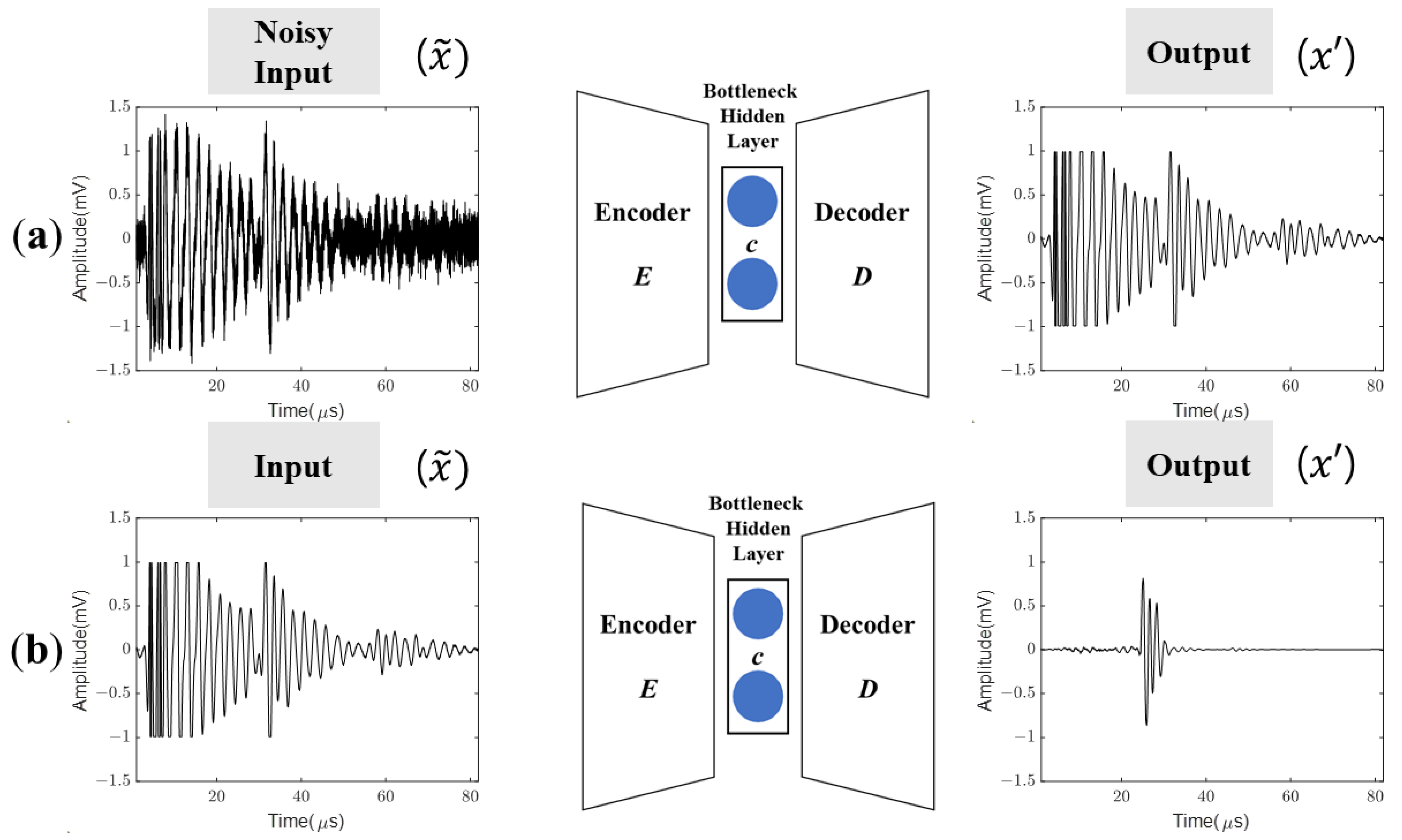
3.2. Neural Network Architecture
4. Results and Discussion
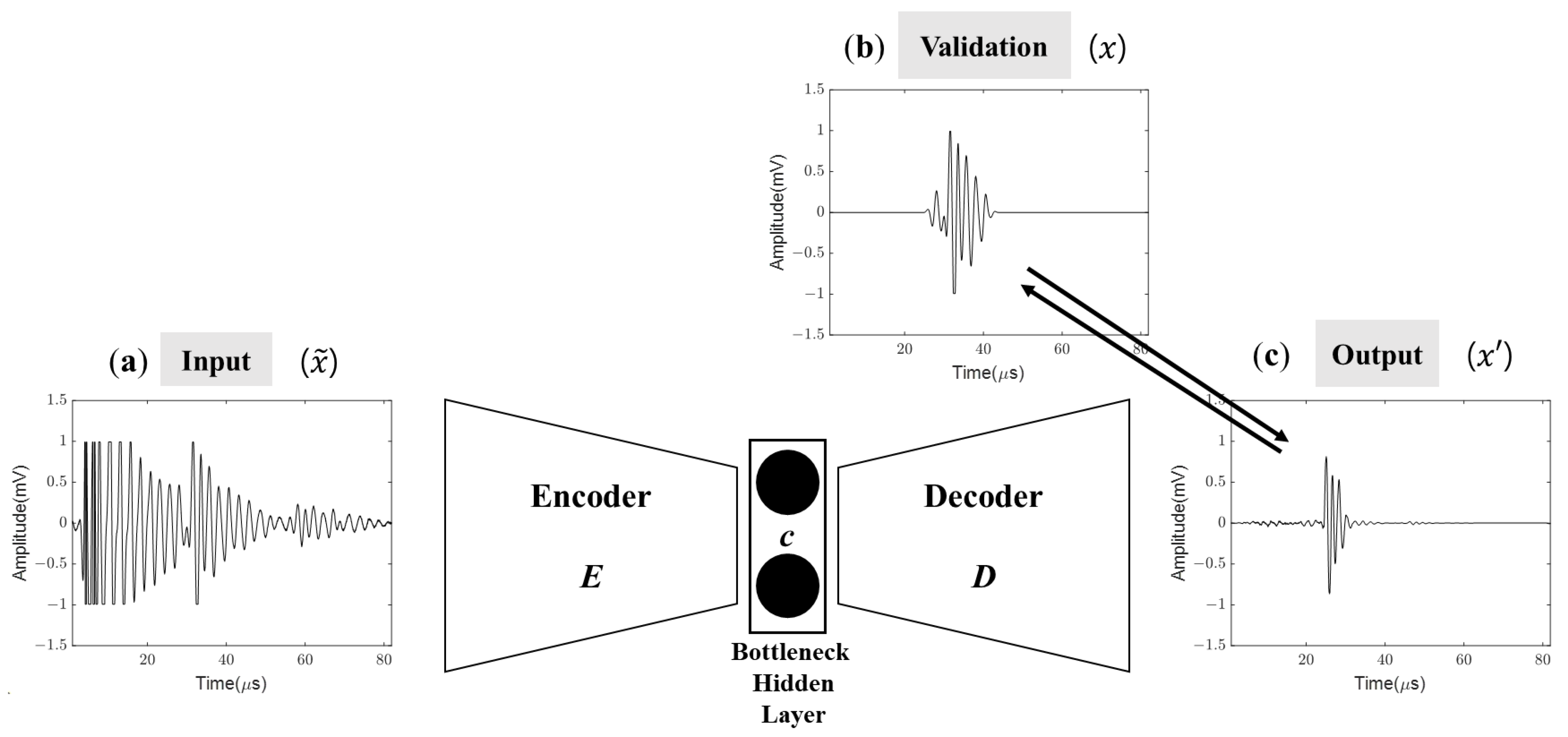
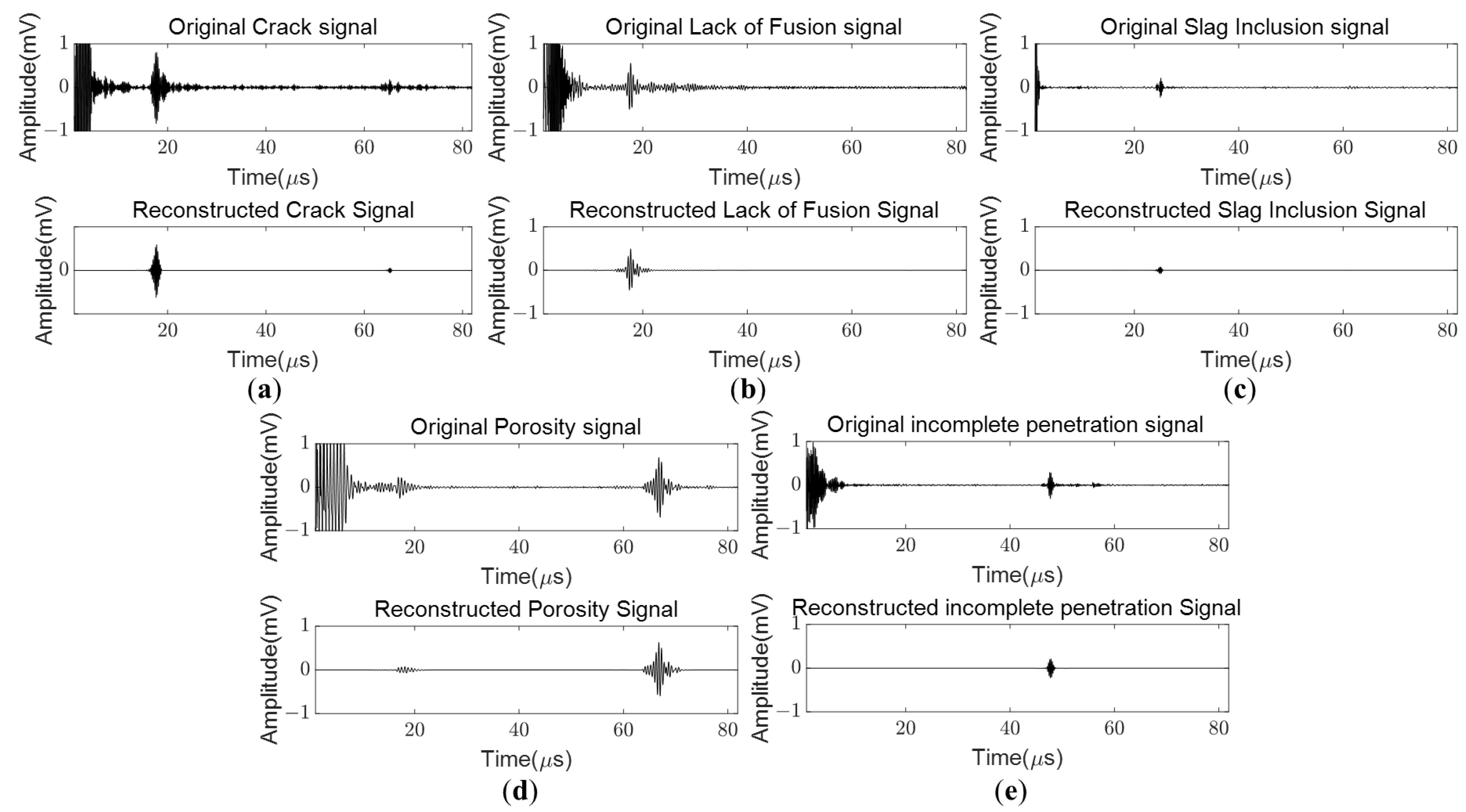
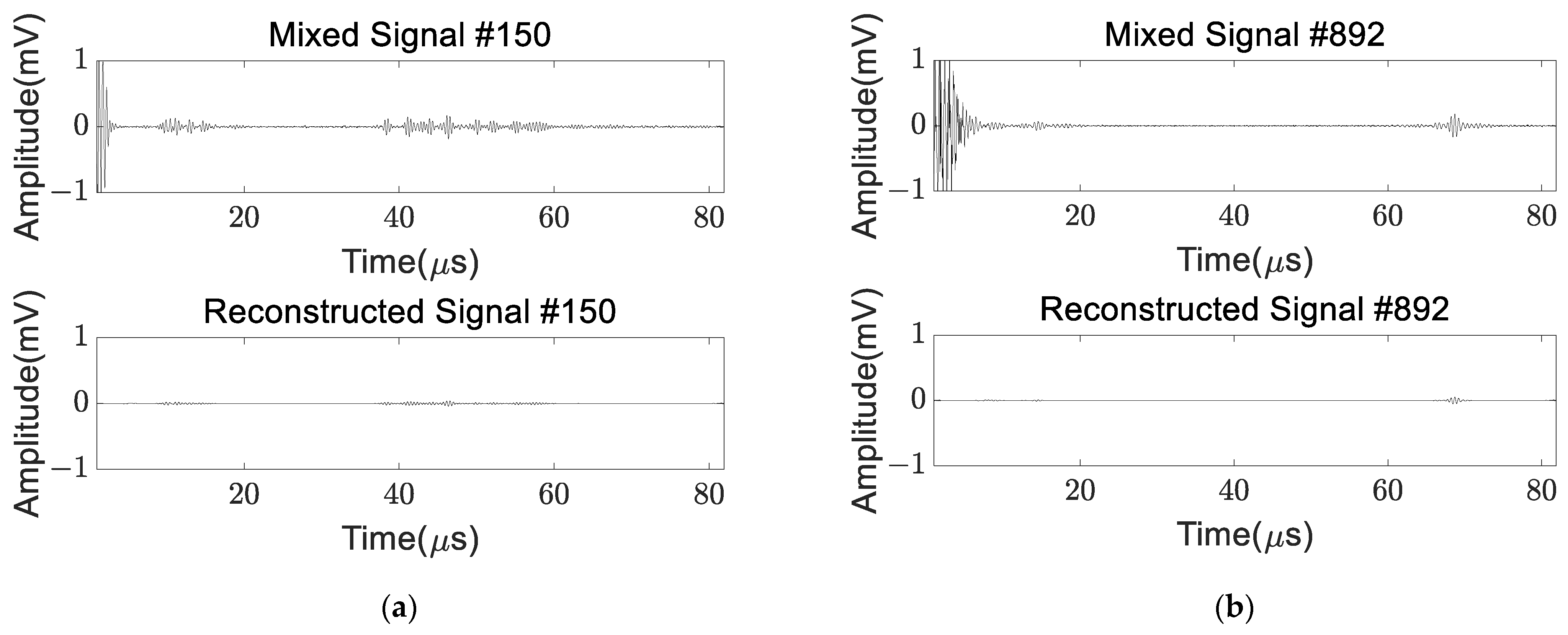
4.1. Performance of the Proposed DAE
4.2. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UT | Ultrasonic testing |
| NDE | Nondestructive evaluation |
| VT | Visual testing |
| PT | Penetration testing |
| MT | Magnetic testing |
| RT | Radiographic testing |
| ECT | Eddy current testing |
| DAE | Denoising autoencoder |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| ANN | Artificial neural networks |
| nlDAE | Learning-based denoising autoencoder |
| MSE | Mean squared error |
References
- Innopolis Foundation. Non-Destructive Testing and Inspection Market. 2019. Available online: https://innopolis.or.kr (accessed on 24 December 2022).
- Yoo, S.; Lim, I.S.; Kee-soo, E. A Study on the Capability Evaluation of an Unskilled Ultrasonic Testing Personnel after the Training Period: Carbon Steel Butt-welds Case. J. Korea Manag. Eng. Soc. 2019, 24, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, N.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.; Song, S.J.; Kang, S.S. Convolutional neural network for ultrasonic weldment flaw classification in noisy conditions. Ultrasonics 2019, 94, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondara, L. Medical image denoising using convolutional denoising autoencoders. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Data Mining Workshops (ICDMW), Barcelona, Spain, 12–15 December 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishii, T.; Komiyama, H.; Shinozaki, T.; Horiuchi, Y.; Kuroiwa, S. Reverberant speech recognition based on denoising autoencoder. In Interspeech; ISCA: Singapore, 2013; pp. 3512–3516. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.H.; Ozger, M.; Challita, U.; Sung, K.W. Noise learning-based denoising autoencoder. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2983–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, O.M.; Chen, Y. Deep denoising autoencoder for seismic random noise attenuation. Geophysics 2020, 85, V367–V376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FlawTech. Specimen Catalogue. Vol. 10-1/2020. 2020. Available online: https://www.FlawTech.com (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Sonaspection. Experts in Manufacturing Flawed Specimens and Mock-ups. 2022. Available online: https://www.sonaspection.com (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Steck, H. Autoencoders that don’t overfit towards the Identity. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 19598–19608. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, N.; Park, J.; Kim, H.J.; Song, S.J.; Kang, S.S. Performance enhancement of convolutional neural network for ultrasonic flaw classification by adopting autoencoder. NDT E Int. 2020, 111, 102218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Ahmed, A.S.; Melandsø, F.; Habib, A. Ultrasonic image denoising using machine learning in point contact excitation and detection method. Ultrasonics 2023, 127, 106834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bank, D.; Koenigstein, N.; Giryes, R. Autoencoders. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.05991. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, P.; Larochelle, H.; Lajoie, I.; Bengio, Y.; Manzagol, P.A.; Bottou, L. Stacked denoising autoencoders: Learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2010, 11, 3371–3408. [Google Scholar]



| Krautkramer | GE | Olympus | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWB 45-2 | WB 45-2 | WB 45-4 | MWB 45-2 | WB 45-2 | A430S (45°) |
| MWB 60-2 | WB 60-2 | WB 60-4 | MWB 60-2 | WB 60-2 | A430S (60°) |
| MWB 70-2 | WB 70-2 | WB 70-4 | MWB 70-2 | WB 70-2 | A430S (70°) |
| Flaw Type | Data (#) | Total (#) |
|---|---|---|
| Crack | 630 | 2463 |
| Lack of Fusion | 378 | |
| Slag Inclusion | 623 | |
| Porosity | 344 | |
| Incomplete Penetration | 488 |
| Performance | Training | Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Number of data (#) | 2463 | 1000 |
| Average of maximum amplitudes | 0.6729 | 0.6281 |
| Average difference of data points | 0.02764 | 0.03282 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-E.; Park, J.; Kim, H.-J.; Song, S.-J. Extraction of Flaw Signals from the Mixed 1-D Signals by Denoising Autoencoder. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063534
Lee S-E, Park J, Kim H-J, Song S-J. Extraction of Flaw Signals from the Mixed 1-D Signals by Denoising Autoencoder. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(6):3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063534
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seung-Eun, Jinhyun Park, Hak-Joon Kim, and Sung-Jin Song. 2023. "Extraction of Flaw Signals from the Mixed 1-D Signals by Denoising Autoencoder" Applied Sciences 13, no. 6: 3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063534
APA StyleLee, S.-E., Park, J., Kim, H.-J., & Song, S.-J. (2023). Extraction of Flaw Signals from the Mixed 1-D Signals by Denoising Autoencoder. Applied Sciences, 13(6), 3534. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063534




