Human Pose Estimation Based on Lightweight Multi-Scale Coordinate Attention
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
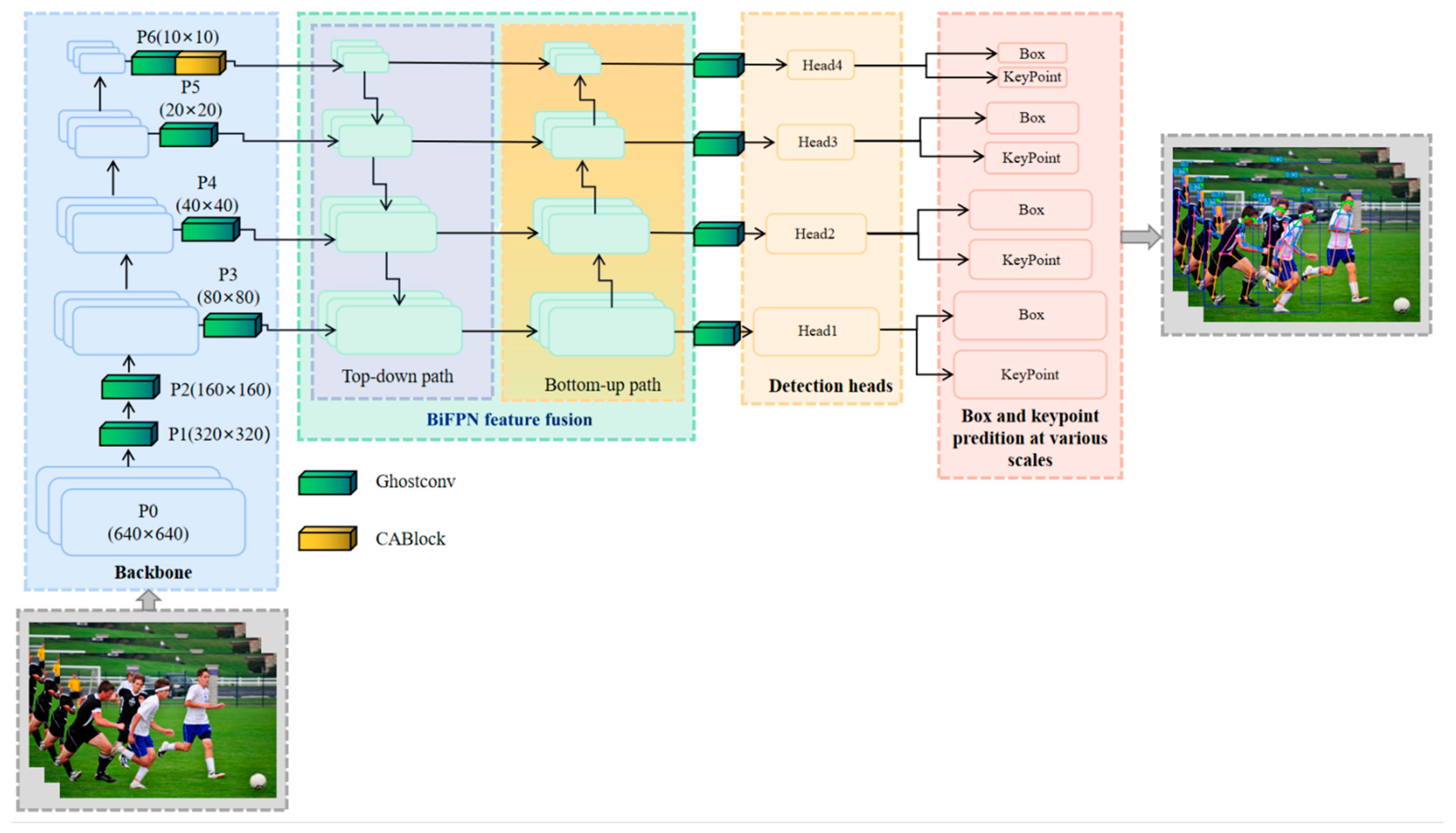
- First, the ghost bottleneck module in the lightweight network GhostNet built for tiny CNN networks was used to replace the common convolution layer in the original model in order to output more flexible and effective feature map information with fewer computing resources.
- (2)
- Second, to locate and identify the location of the human body more accurately, a coordinate attention mechanism (CA) module was integrated at the end of the backbone network. This module can obtain cross-channel, direction-aware and location-sensitive feature information, which enhances the robustness of the network in densely occluded scene tasks.
- (3)
- Finally, since the resolutions of the various input features vary and their contributions to the output features are not all equal, we attempt to add the bi-directional feature pyramid network (BiFPN) module to the feature fusing branch. For learning the significance of different input features, this module includes learnable weights that can repeatedly execute top-down and bottom-up multi-scale feature fusion.
2. Related Work
3. The Proposed Method
3.1. Overview
3.2. Lightweight Network—GhostNet
3.3. Coordinate Attention Mechanism
3.3.1. Coordinate Information Embedding
3.3.2. Coordinate Attention Generation
3.4. Bidirectional Feature Pyramid Network
3.4.1. Cross-Scale Connections
3.4.2. Weighted Feature Fusion
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Details
4.3. Validation and Analysis
4.3.1. Data Preprocessing
4.3.2. Loss
4.3.3. Evaluation Metric
4.3.4. Result Analysis
4.4. Ablation Experiment
4.5. Visual Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, B.; Wang, J. An Improved Helmet Detection Algorithm Based on YOLO V4. Int. J. Found. Comput. Sci. 2022, 33, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, X.; Gonzàlez, J.; Sobral, A.; Bouwmans, T.; Tu, C.; Zahzah, E.-h. Human pose estimation from monocular images: A comprehensive survey. Sensors 2016, 16, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadhiya, R.; Kalani, N. Analysis of deep learning based pose estimation techniques for locating landmarks on human body parts. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Circuits, Controls and Communications (CCUBE), Bangalore, India, 23–24 December 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Bao, Q.; Sun, Y.; Mei, T. Recent advances of monocular 2d and 3d human pose estimation: A deep learning perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. 2022, 55, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, S. Single-stage multi-person pose machines. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (CVPR), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019; pp. 6951–6960. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.; Wu, Y. Does learning specific features for related parts help human pose estimation? In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019; pp. 1107–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Ye, M. Fast human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019; pp. 3517–3526. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tian, Y.; He, M. Monocular human pose estimation: A survey of deep learning-based methods. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2020, 192, 102897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, G.; Du, D. AID: Pushing the Performance Boundary of Human Pose Estimation with Information Dropping Augmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Yang, W.; Xia, S.T.; Zhou, E. TokenPose: Learning Keypoint Tokens for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11293–11302. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, K.; Ren, H.; Wei, D.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J. UULPN: An ultra-lightweight network for human pose estimation based on unbiased data processing. Neurocomputing 2022, 480, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Li, D.; He, W.; Deng, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, Y.; Bao, H.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Future vehicles: Interactive wheeled robots. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2021, 64, 56101:1–156101:3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Bao, H.; Pan, W.; Pan, F. Traffic Sign Detection via Improved Sparse R-CNN for Autonomous Vehicles. J. Adv. Transp. 2022, 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Maji, D.; Nagori, S.; Mathew, M.; Poddar, D. YOLO-Pose: Enhancing YOLO for Multi Person Pose Estimation Using Object Keypoint Similarity Loss. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 2637–2646. [Google Scholar]
- Papandreou, G.; Zhu, T.; Kanazawa, N.; Toshev, A.; Tompson, J.; Bregler, C.; Murphy, K. Towards accurate multi-person pose estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4903–4911. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.S.; Xie, S.; Tai, Y.W.; Lu, C. Rmpe: Regional multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2334–2343. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Sun, J. Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7103–7112. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October 2019–02 November 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7291–7299. [Google Scholar]
- Papandreou, G.; Zhu, T.; Chen, L.C.; Gidaris, S.; Tompson, J.; Murphy, K. Personlab: Person pose estimation and instance segmentation with a bottom-up, part-based, geometric embedding model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 269–286. [Google Scholar]
- Kreiss, S.; Bertoni, L.; Alahi, A. Pifpaf: Composite fields for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019; pp. 11977–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Xiao, B.; Wang, J.; Shi, H.; Huang, T.S.; Zhang, L. Higherhrnet: Scale-aware representation learning for bottom-up human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 5386–5395. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Tan, T.; Zhou, E. Rethinking the heatmap regression for bottom-up human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 13264–13273. [Google Scholar]
- Su, K.; Yu, D.; Xu, Z.; Geng, X.; Wang, C. Multi-person pose estimation with enhanced channel-wise and spatial information. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019; pp. 5674–5682. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Shen, C. Fcpose: Fully convolutional multi-person pose estimation with dynamic instance-aware convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 9034–9043. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1580–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Wenjun, W.; Tobias, W.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, P. YOLO-G: A Lightweight Network Model for Improving the Performance of Military Targets Detection; IEEE Access: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Li, R.; Pan, C.; Bao, Y.; Zhang, H. Aircraft Targets Detection in Remote Sensing Images with Feature Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 4th Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IMCEC), Chongqing, China, 18–20 June 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; Volume 4, pp. 1542–1549. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, W.; Cheng, T.; Zhou, X.G.; Guo, W.; Yuanyuan, W.; Xuan, Z.; Hongbo, Q.; Dongyan, Z. An improved DenseNet model to classify the damage caused by cotton aphid. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. The Workpiece Sorting Method Based on Improved YOLOv5 For Vision Robotic Arm. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Guilin, China, 7–10 August 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 481–486. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, G.; Qin, J.; Xiong, N.N. Algorithm of Computer Mainboard Quality Detection for Real-Time Based on QD-YOLO. Electronics 2022, 11, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang PS, P.; Li, X.; Meng, Z. Multi-scale spatial-spectral fusion based on multi-input fusion calculation and coordinate attention for hyperspectral image classification. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 122, 108348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiahui, Y.; Yuqian, Z.; Ding, L.; Yun, F.; Thomas, S.H.; Humphrey, S. Pyramid attention networks for image restoration. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.13824. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, G.; Lin, T.Y.; Le, Q.V. Nas-fpn: Learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019; pp. 7036–7045. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Pang, R.; Le, Q.V. EfficientDet: Scalable and Efficient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10778–10787. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xia, P. Research on human-vehicle gesture interaction technology based on computer visionbility. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 6th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Beijing, China, 3–5 October 2022; pp. 1161–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, L.; Sun, J.; Chi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L. CD-TransUNet: A Hybrid Transformer Network for the Change Detection of Urban Buildings Using L-Band SAR Images. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, K.; Luo, K.; Chen, T.; Hu, R. An Improved YOLOX Model and Domain Transfer Strategy for Nighttime Pedestrian and Vehicle Detection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 12993–13000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and Efficient IOU Loss for Accurate Bounding Box Regression. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; Volume 506, pp. 146–157. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.; Liao, S.; Shao, L. Pixel-in-Pixel Net: Towards Efficient Facial Landmark Detection in the Wild. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2021, 129, 3174–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhan, Y.; Xie, W.; Zhao, T. Improved convolutional pose machines for human pose estimation using image sensor data. Sensors 2019, 19, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newell, A.; Yang, K.; Deng, J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 483–499. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, Z.; Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Bottom-up human pose estimation via disentangled keypoint regression. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14676–14686. [Google Scholar]
- Neff, C.; Sheth, A.; Furgurson, S.; Tabkhi, H. Efficienthrnet: Efficient scaling for lightweight high-resolution multi-person pose estimation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.08090. [Google Scholar]
- Osokin, D. Real-time 2d multi-person pose estimation on cpu: Lightweight openpose. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.12004. [Google Scholar]









| Parameter | Settings |
|---|---|
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Momentum | 0.937 |
| Batch size | 32 |
| Learning rate | 1 × 10−2 |
| Weight decay | 0.0005 |
| Epoch | 300 |
| Method | Backbone | Input Size | Params | GMACS | AP [0.5:0.95]% | AP50% | AR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenPose [19] | - | - | - | - | 61.8 | 84.9 | 66.5 |
| Hourglass [47] | Hourglass | 512 × 512 | 277.8 M | 413.8 | 56.6 | 81.8 | - |
| HRNet [18] | HRNet-W32 | 512 × 512 | 28.5 M | 77.8 | 64.1 | 86.3 | - |
| HigherHRNet [22] | HRNet-W48 | 640 × 640 | 63.8 M | 308.6 | 68.4 | 88.2 | - |
| DEKR [48] | HRNet-W32 | 512 × 512 | 29.6 M | 90.8 | 67.3 | 87.9 | 72.4 |
| DEKR [48] | HRNet-W48 | 640 × 640 | 65.7 M | 283.0 | 70.0 | 89.4 | 75.4 |
| YOLOv5s6-pose(baseline) [14] | Darknet_csp-d53-s | 640 × 640 | 7.2 M | 10.2 | 57.5 | 84.3 | 65.2 |
| YOLOv5s6-pose [14] | Darknet_csp-d53-s | 960 × 960 | 15.1 M | 22.9 | 62.9 | 87.6 | 69.8 |
| Ours | Darknet_csp-d53-s | 640 × 640 | 6.4 M | 7.2 | 63.2 | 90.0 | 71.9 |
| Ours | Darknet_csp-d53-m | 640 × 640 | 19.6 M | 23.5 | 67.4 | 91.0 | 74.8 |
| Method | GMACS | Input Size | AP [0.5:0.95]% | AP50% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EfficientHRNet-H-1 [49] | 28.4 | 480 | 59.2 | 82.6 |
| EfficientHRNet-H-2 [49] | 15.4 | 448 | 52.9 | 80.5 |
| EfficientHRNet-H-3 [49] | 8.4 | 416 | 44.8 | 76.7 |
| EfficientHRNet-H-4 [49] | 4.2 | 384 | 35.7 | 69.6 |
| YOLOv5-s6_960 [14] | 22.85 | 960 | 63.8 | 87.6 |
| YOLOv5-s6_640 [14] | 10.2 | 640 | 57.5 | 84.3 |
| YOLOv5-s6_576 [14] | 8.22 | 576 | 55.5 | 83.4 |
| Ours | 7.2 | 640 | 63.2 | 90.0 |
| Ours | 23.5 | 960 | 67.4 | 91.0 |
| Method | Backbone | mAP@0.5:0.95 | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| HigherHRNet [22] | HRNet-W32 | 67.1 | 6.68 |
| LightweightOpenPose [50] | - | 42.8 | 26 |
| EfficientHRNet-H-0 [49] | EfficientNetB0 | 64.8 | 22.95 |
| EfficientHRNet-H-1 [49] | EfficientNetB0 | 59.2 | 20.43 |
| EfficientHRNet-H-2 [49] | EfficientNetB0 | 52.9 | 24.53 |
| EfficientHRNet-H-3 [49] | EfficientNetB0 | 44.8 | 33.78 |
| YOLOv5-s6_960 [14] | Darknet_csp-d53-s | 63.8 | 30.8 |
| YOLOv5-s6_640 [14] | Darknet_csp-d53-s | 57.5 | 29.8 |
| YOLOv5-m6_960 [14] | Darknet_csp-d53-m | 55.5 | 27.1 |
| Ours | Darknet_csp-d53-s | 63.2 | 31.2 |
| Ours | Darknet_csp-d53-m | 67.4 | 29.5 |
| Method | GhostNet | CA | BiFPN | GMACS | mAP@0.5:0.95 | mAP@.5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | - | - | - | 10.2 | 55.1 | 84.1 |
| (2) | √ | - | - | 7.4 | 57.4 | 86.7 |
| (3) | - | √ | - | 8.4 | 56.2 | 84.9 |
| (4) | - | - | √ | 8.8 | 56.8 | 86.7 |
| (5) | √ | √ | √ | 7.2 | 57.1 | 86.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Pan, W.; Liu, H.; Xu, B. Human Pose Estimation Based on Lightweight Multi-Scale Coordinate Attention. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063614
Li X, Guo Y, Pan W, Liu H, Xu B. Human Pose Estimation Based on Lightweight Multi-Scale Coordinate Attention. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(6):3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063614
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Yuxin Guo, Weiguo Pan, Hongzhe Liu, and Bingxin Xu. 2023. "Human Pose Estimation Based on Lightweight Multi-Scale Coordinate Attention" Applied Sciences 13, no. 6: 3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063614
APA StyleLi, X., Guo, Y., Pan, W., Liu, H., & Xu, B. (2023). Human Pose Estimation Based on Lightweight Multi-Scale Coordinate Attention. Applied Sciences, 13(6), 3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13063614





