Abstract
The present study evaluates the antimicrobial potential of non-equilibrium plasma against microorganisms isolated from diatomaceous earth, which is a waste product from the beer filtration process. For evaluation, waste diatomaceous earth from an industrial brewery was treated with non-equilibrium plasma using a glidearc reactor. The temperature of the treated samples was monitored. The effect of plasma on the morphology of the treated material was investigated microscopically. Plasma can affect the treated material in various ways and change its physicochemical properties. Consequently, the scope of potential plasma applications is constantly expanding from material technologies to decontamination applications in the food industry, environmental protection and medicine and stimulates activities in, for example, agriculture and medicine. At the same time, microbiological analyzes were carried out to determine the presence of selected groups of microorganisms on diatomaceous earth before and after plasma treatment. The study revealed that the porous structure of diatomaceous earth is not an obstacle to the effective removal of microorganisms from it using plasma. A significant decrease in the amount of both bacteria and yeast relative to the control (non-plasma samples) was observed with the increasing contact time of the diatomaceous earth with the plasma. The numbers of bacteria and yeast decreased by a maximum of 2.2 log10 CFU∙g−1 and 1.72 log10 CFU∙g−1 (30 min of plasma contact), respectively. The obtained results are extremely promising and encourage further, in-depth research to optimize the plasma process and its effect on microorganisms.
1. Introduction
The use of diatomaceous earth in beer filtration is considered one of the fifty most important technological achievements in brewing of past years [1]. This is because diatomaceous earth is characterized by a unique porosity and high adsorption capacity, as well as a low density [2]. Thanks to that, it possible to achieve high beer clarity with relatively low auxiliary material costs. After properly conducted cold conditioning, lager beer is clear; however, to ensure a higher level of clarity and stability, filtration is necessary. Diatomaceous earth deposits were formed by the deposition of ancient marine algae (diatoms), mainly in the present-day USA and China. Its global production in 2013 was 2.3 Mt, of which more than 30% was extracted in the USA, about 20% was in China and 14% was in Denmark; the rest was extracted in 26 other countries [3]. It is thought that about two-thirds of its total extraction is used for beverage (mainly beer) filtration purposes [4].
In order to obtain a clear beer, it is recommended to use 1 to 2 g of this rock per liter of clear product. However, after the filtration stage, the mass of spent diatomaceous earth is significantly higher than the original mass. This is because some of the water and other organic components (yeast, proteins, and polyphenols) are retained with it on the filter barrier [4,5]. For a medium-sized brewery, the amount of spent diatomaceous earth with sludge generated annually is around 100 tones [6]. As a result, along with spent grains, residual yeasts and trub, it represents the main brewing waste. Its consumption could be reduced by using other, often expensive, filtration materials or by promoting the consumption of cloudy, unfiltered beer. Such a procedure would be uneconomical or difficult to implement, especially for large beer producers whose consumers expect beer with very high clarity [5].
The environmental consequences of producing such large quantities of spent diatomaceous earth are not yet well understood. The main part of the diatomaceous earth used for filtration is still stored or used as fertilizer [2,7].
The current trend of reducing generated waste and finding alternative ways to manage it is one of the priorities for food production plants. In addition, some scientific centers work on finding alternative ways to use diatomaceous earth. Preliminary research aimed at using diatomaceous earth in the production of cost-effective biosorbents [7], storage pest control agents [8], brick production [9,10,11] and silver nanocomposites [6] seem to be interesting solutions in this regard.
The multiple possibilities of using plasma result from the fact that numerous active agents are generated during its operation, which can affect the treated material in different ways and change its physicochemical properties. Consequently, the scope of potential applications of plasma in material technologies is constantly expanding: from cleaning and simple changes in wettability and surface micro-roughness to chemical and structural modifications, removal or deposition of layers and the formation of anti-corrosion coatings or coatings with other specific properties that protect against gas diffusion, high temperatures, excessive wear, etc. [12,13,14]. Other possible applications are based on the strong antimicrobial effect of plasma, as it generates reactive oxygen and nitrogen forms, i.e., hydrogen peroxide, OH, OH2, NO, O3 radicals, etc. A very important, additional antimicrobial factor is UV radiation, which is generated during plasma treatment [15,16,17]. The effect of plasma on microorganisms is multistage. The most common are: irreversible damage to the cell wall, disruption of the function of the cytoplasmic membrane and cell organelles, and damage to the genetic material [15]. In general, medical technologies use plasma, e.g., for disinfection and stimulation and in anti-cancer therapies, wound healing and theranostics [18,19,20].
The antimicrobial properties of plasma are used wherever the use of high temperatures for decontamination is not advisable due to the thermolability of sterilized materials. In low-temperature applications, non-equilibrium plasmas can be used, where the local electron temperatures are much higher than the temperatures of the ions and neutral particles. Therefore, non-equilibrium plasma is successfully applied in the medical field to sterilize surgical and dental instruments and also as an aid in the treatment of hard-to-heal wounds [21]. Plasma has also been used for many years in environmental protection for the treatment of water, wastewater, production liquids and soil [22,23,24], neutralization and stabilization of municipal waste, and for the removal of waste gases [17,25]. Non-equilibrium plasma is used in the food industry when it is necessary to remove or eliminate microorganisms from packaging or preserved foods and to extend the shelf life of foods such as juices and meat [17,26]. Its decontaminating and stimulating properties have been reflected in various studies in the field of agriculture, e.g., for accelerating seed germination or plant conditioning [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34].
In order to lower the temperature of the process, systems operating under reduced pressure can be used, allowing for the generation of plasma with a relatively large volume and a uniform shape of the discharge [35,36,37,38,39]. The main disadvantage of these solutions are the limitations related to the vacuum chamber, in which the treated object must be placed—it is very difficult to process large-sized or complex-shaped materials here. The use of a vacuum is also associated with additional costs and a larger size for the entire system. In the case of atmospheric plasma, temperature reduction is possible, for example through the use of noble gases in combination with a dielectric barrier or indirect plasma treatment. In the latter case, the workpiece is not in direct contact with the plasma but with the active particles generated in it, which reach its surface with a stream of gas or another medium (e.g., water—so-called plasma-activated water). An example of an indirect plasma treatment system is a gliding arc discharge (GAD) reactor. The discharge created is in the form of an arc, that, as a result of gas-dynamic forces, moves along outwardly curved electrodes. The discharge is extinguished when the electrical energy supplied from the power source is unable to compensate for the energy losses of the elongated arc column. Once the discharge is extinguished, it is almost immediately restored in the ignition zone and the reactor cycle repeats. One of the greatest advantages of reactors of this design is the ability to operate them using atmospheric air as the working gas, which significantly reduces the cost of treatment. For example, Ashtiani et al. used a glide arc reactor as a pretreatment to the hot-air-drying of grapes, obtaining samples with better color as well as decreased total phenol content, antioxidant activity and vitamin C losses in the dried grapes [40]. In the work of Šerá et al. [41], the reactor was used to treat wheat, which allowed increased germination. In the work of Šerá et al. [41], the reactor was used to treat of Maize (Zea mays L.), which allowed stimulation of seed germination (to 141%), root length (to 221%), shoot length (to 298%) and root weight (to 122%). The influence of the treatment on maize physiology was strictly dependent on its time, which could either decrease or increase such parameters as abscisic acid, jasmonic acid, jasmonate isoleucine and active cytokinins [41]. The reactor was also used in PAW processing, e.g., to remove Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Candida albicans in tap water [42], as well as remove Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Proteus mirabilis inoculated to shrimp (in vivo condition) and shrimp agar (in vitro condition) [43]. The reactor that is the subject of the current research has been used to, among other things, improve Lavatera thuringiaca L. seeds’ germination [44], extending the shelf-life of tomato juice with preserving of selected bioactive compounds by removing E. coli while retaining the total carotenoid (+13%), lycopene (+11%) and vitamin C (−5%) [45] or PAW generation for improved germination of beetroot (Beta vulgaris) and carrot (Daucus carota) seeds [27].
Therefore, considering the above, analyzes were performed to determine whether non-equilibrium plasma effectively eliminates the microorganisms from the porous structure of the beer production waste—diatomaceous earth.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Material
According to the manufacturer’s declaration, diatomaceous earth before the beer filtration process is microbiologically clean and safe from a physicochemical point of view. The test material was spent diatomaceous earth after beer filtration. Prior to filtration, Becogur 200, 1200 and 3500 diatomaceous earth (Eaton, Bonn, Germany) was dosed at a temperature of 2 °C into beer with an alcoholic strength by volume of 6% in a total amount of 150 g/hL of beer. The beer was then pumped to a plate filter whose plates retained diatomaceous earth together with absorbed suspended solids and yeast cells. The optimum beer flow rate during filtration was 80–100 hL/h, and the operating pressure was 1.5 bar. The filtration was followed by removal of spent diatomaceous earth from the plates into suitable containers. The spent earth was averaged for consistency and then taken into 30 L unit containers for further analysis.
2.2. Glidearc Reactor
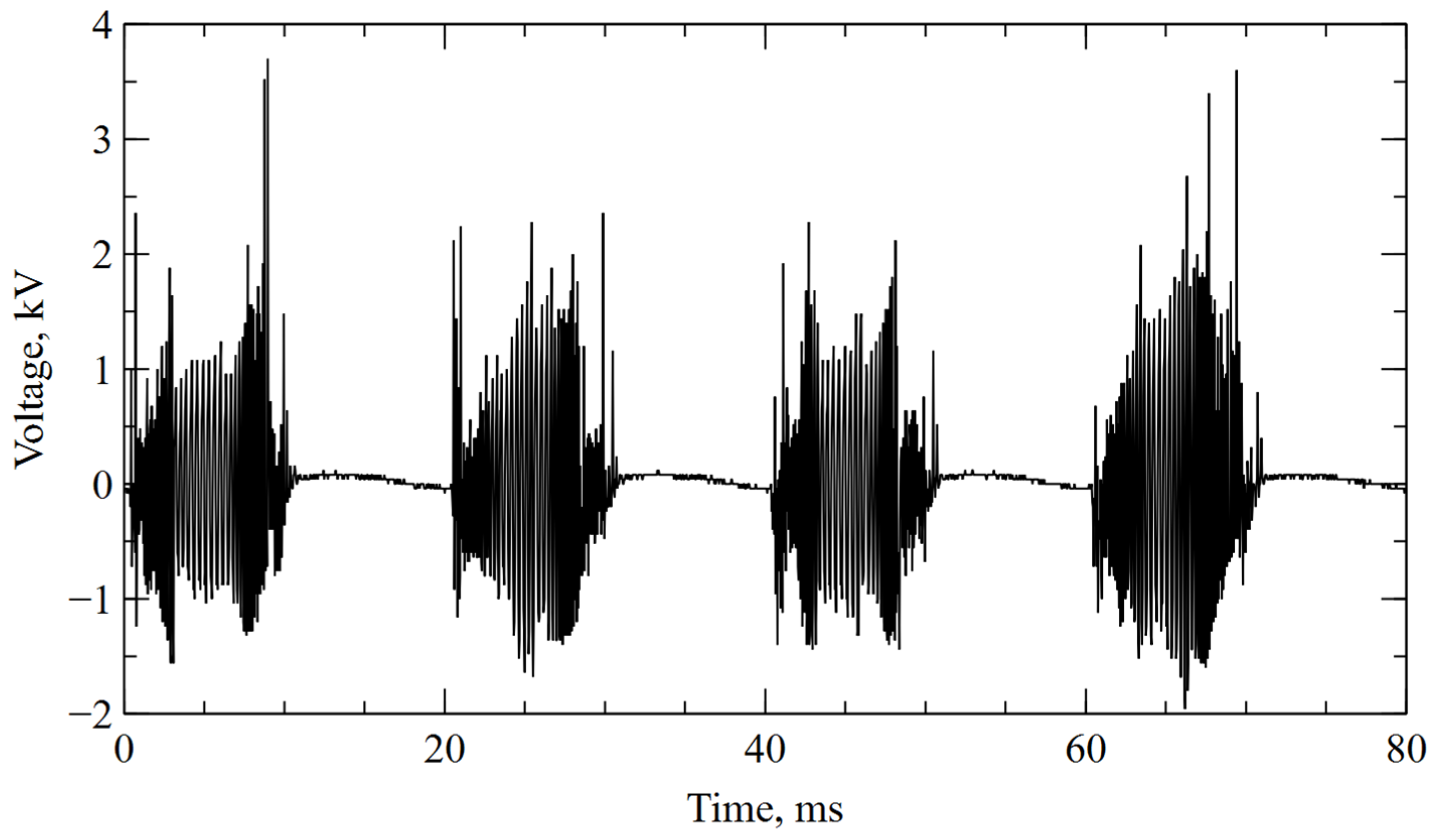
Two diverging copper electrodes (⌀ = 2 mm, L = 80 mm) of a GAD reactor operated at atmospheric pressure. The electrodes were placed in a glass tube of ⌀ = 50 mm. Air was selected as the substrate gas, and the flow rate of 440 L/h was maintained with a glass tube variable area flow meter (Zakłady Automatyki “ROTAMETR”, Gliwice, Poland). The power supply was based on an electronic high-voltage transformer of 50 Hz operation cycle. It consists of converter giving a series of high-voltage microimpulses in a 10 ms time span so the transformer works in a cut-off state for the next 10 ms. The frequency of the pulses (from 5 to 20 kHz) and their amplitude are variable, which is mainly due to the high irregularity of the electricity caused by the influence of gas dynamic forces (Figure 1). The apparent power of the reactor was 40 VA at an RMS (root-mean-square) voltage of 680 V (3.7 kV peak voltage). Previous studies, which were performed using time-integrated optical emission spectroscopy, have shown that the reactor is a source of non-equilibrium plasma in which the dominant gas products are nitrogen oxides [46].
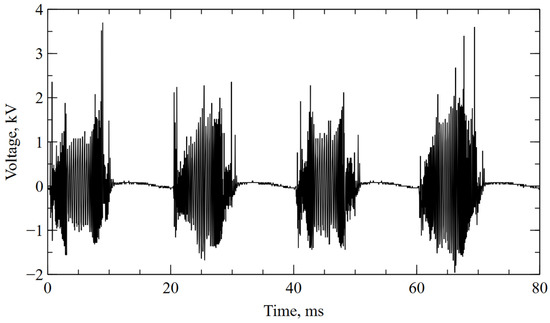
Figure 1.
Voltage between electrodes during plasma treatment.
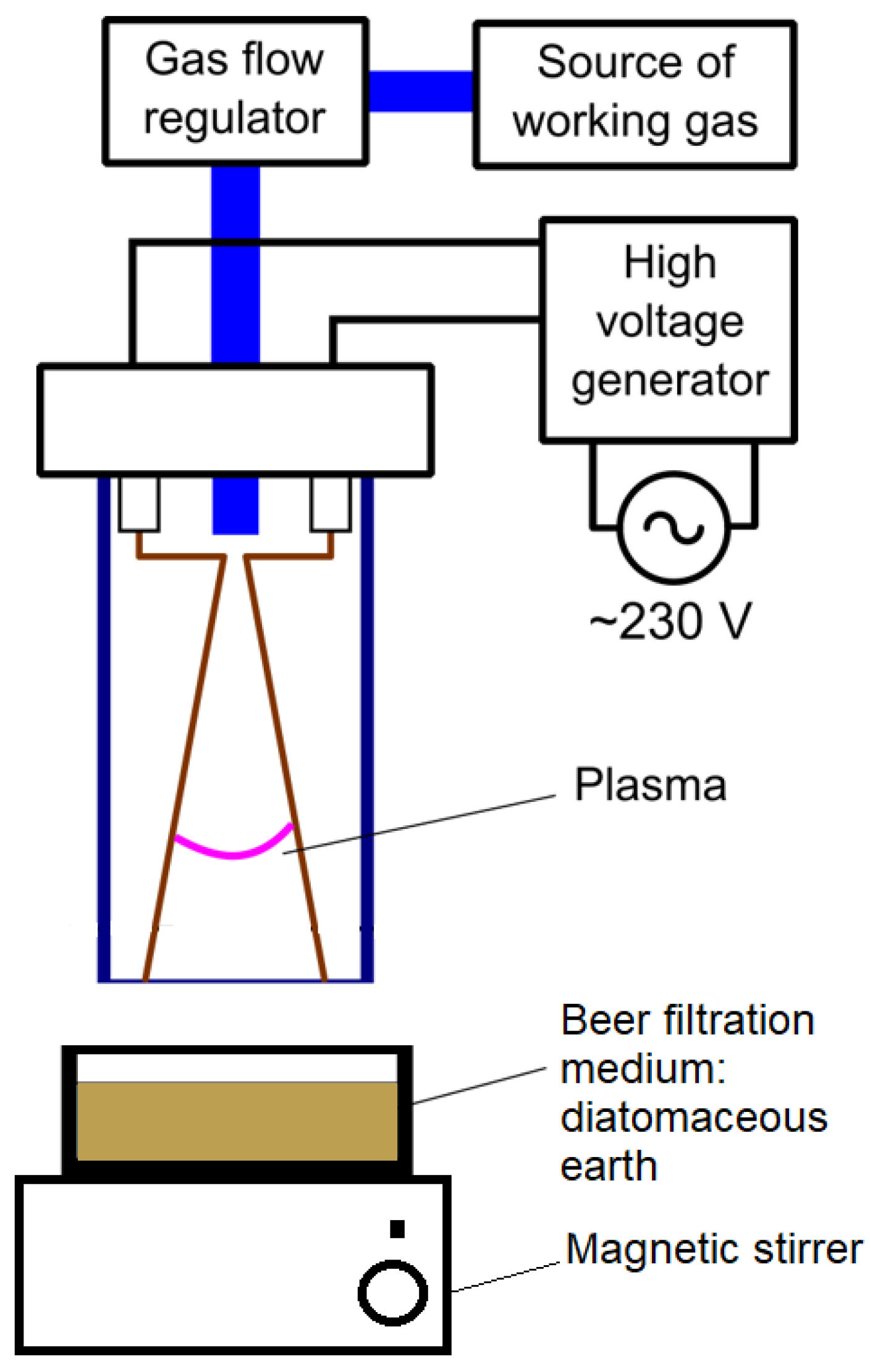
The sample was 25 g of spent beer filtration medium—diatomaceous earth. The sample was placed in a Petri dish, which was located on the magnetic stirrer (AREX, VELP Scientifica, Usmate, Italy) operating at 200 RPM and in the zone of operation of the plasma reactor with a distance of 10 mm between the sample’s surface and the electrodes. The experimental set-up scheme is shown in Figure 2. Plasma treatment times were 5, 10, 20, 25, and 30 min (P5, P10, P20, P25, and P30). The temperature of the sample was measured after the set treatment time with a K-type thermocouple connected to a DT-847U (Maxtech, Taipei, Taiwan) meter. The initial temperature of the sample was 21.2 °C, equal to the ambient temperature. After 30 min, the plasma treatment temperature was 29.2 °C.
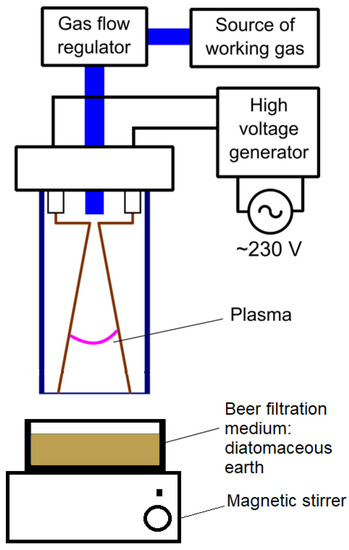
Figure 2.
Scheme of the experiment.
Morphology of the plasma-treated material was further examined using a KEYENCE VHX-5000 optical microscope and VH-Z100R lenses. Spectroscopic analysis was performed with a Jasco FT-IR-4200 type A spectrophotometer (Jasco, Tokyo, Japan) and the attenuated total reflection technique performed using a Jasco ATR PRO ONE single reflection (Jasco, Tokyo, Japan) and a ZnSe crystal. Immediately after plasma treatment, the diatomaceous earth was mixed, then applied to the crystal and pressed down with a screw. Measurements were taken between 4000 cm−1 and 1000 cm−1 with averaging from 30 scans.
2.3. Microbiological Analyzes
All plasma-treated and control (non-treated) samples were analyzed in triplicate using the serial dilution method by Koch [17]. The purpose of the analysis was to determine the number of epidemiologically relevant microbial groups (listed in Table 1). In addition, since diatomaceous earth was used in the beer filtration process, yeast colonies were also expected to be detected. A pH meter (Elmetron, Zabrze, Poland) was used to measure pH of all samples [47]. After the incubation period, the grown colonies were counted, with the results given in colony-forming units per gram of sample dry matter (CFU g−1 D.M.).

Table 1.
Microorganism development conditions.
Microorganisms that grew on the plates were identified using the MALDI-TOF MS technique (Bruker Daltonik, Bremen, Germany) in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommended methodology and the guidelines in the studies of other authors [48,49,50]. Scores ≥1.7 and <2.0 indicated identification to the genus level, whereas scores ≥2.0 indicated identification to the species level.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis of the obtained results was made with the use of Statistica v.13.0 software (StatSoft, Tulsa, OK, USA). Pearson’s correlation coefficient r was calculated between the abundance of microorganisms and plasma exposure time. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was also performed to test the significance of differences in the number of bacteria and yeast subjected to different plasma treatment times.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Microscope
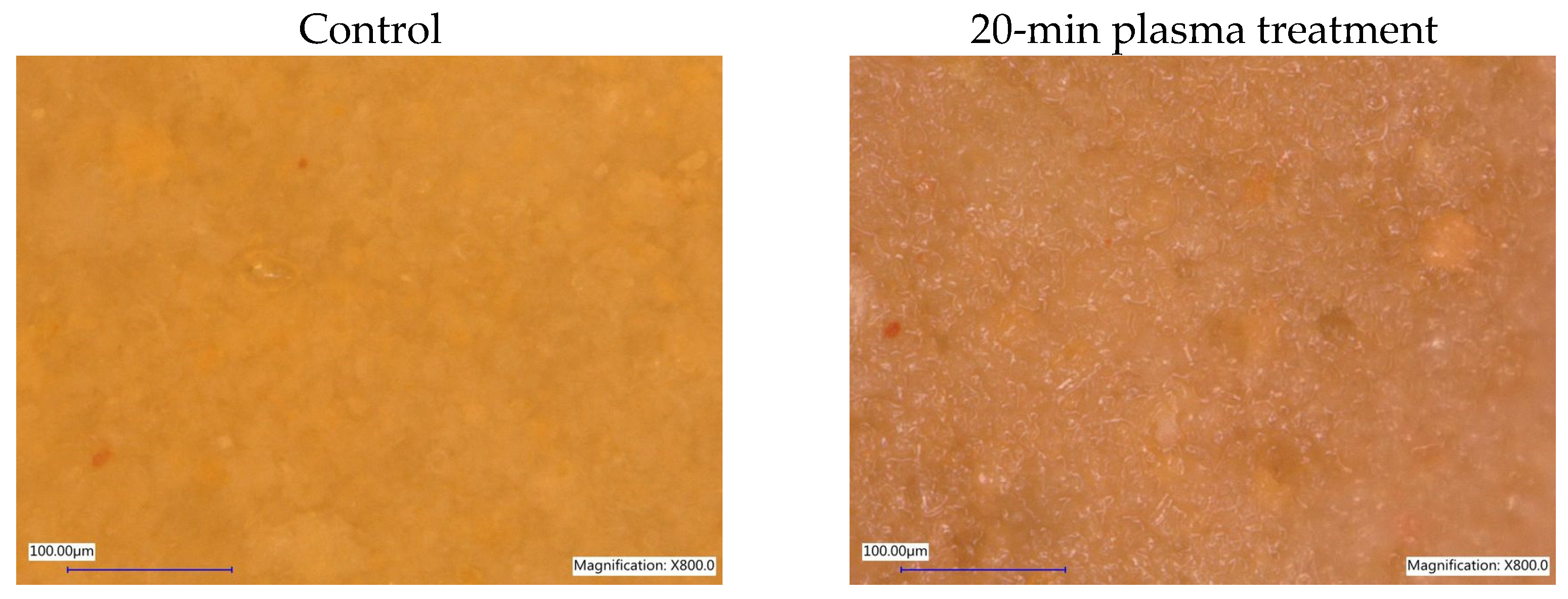
Microscopic observations made using an optical microscope and the applied magnifications indicate that plasma treatment does not significantly affect the morphology of diatomaceous earth, which is mainly SiO2 amorphous silica with minor admixtures of crystalline silica, calcium, sodium, iron, magnesium, copper, zirconium, titanium, boron, manganese, and other compounds. As expected, drying of the samples was observed with longer processing times, making the grains more visible. Despite the relatively low processing temperature, drying resulted from the working gas flow. Figure 3 shows a comparison of imaging diatomaceous earth with variable grain size in the control sample and the sample treated with plasma for 20 min.
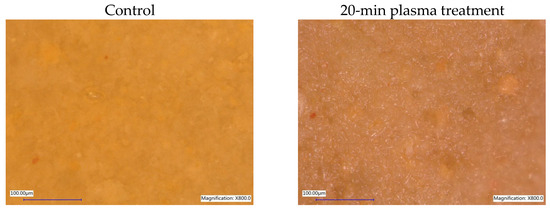
Figure 3.
Microscopic imaging of diatomaceous earth before and after non-equilibrium plasma treatment—KEYENCE VHX-5000 optical microscope, magnification 800×.
Diatomaceous earth, whose origin is natural sedimentary rock based on silica, underwent extensive, long-lasting geological processes, sometimes related to the high pressure and elevated temperatures. According to the literature [51,52], high-temperature calcination tests were conducted and SEM examination revealed that temperatures up to 900 °C did not significantly change pore forms, sizes, surface texture and morphology in diatomites forming tested substrate. Structure changes in higher temperatures or in high pressure conditions led to the fragmentation and densification of the sample. Conditions applied in this experiment did not change sample’s morphology and structure.
3.2. FTIR Spectra
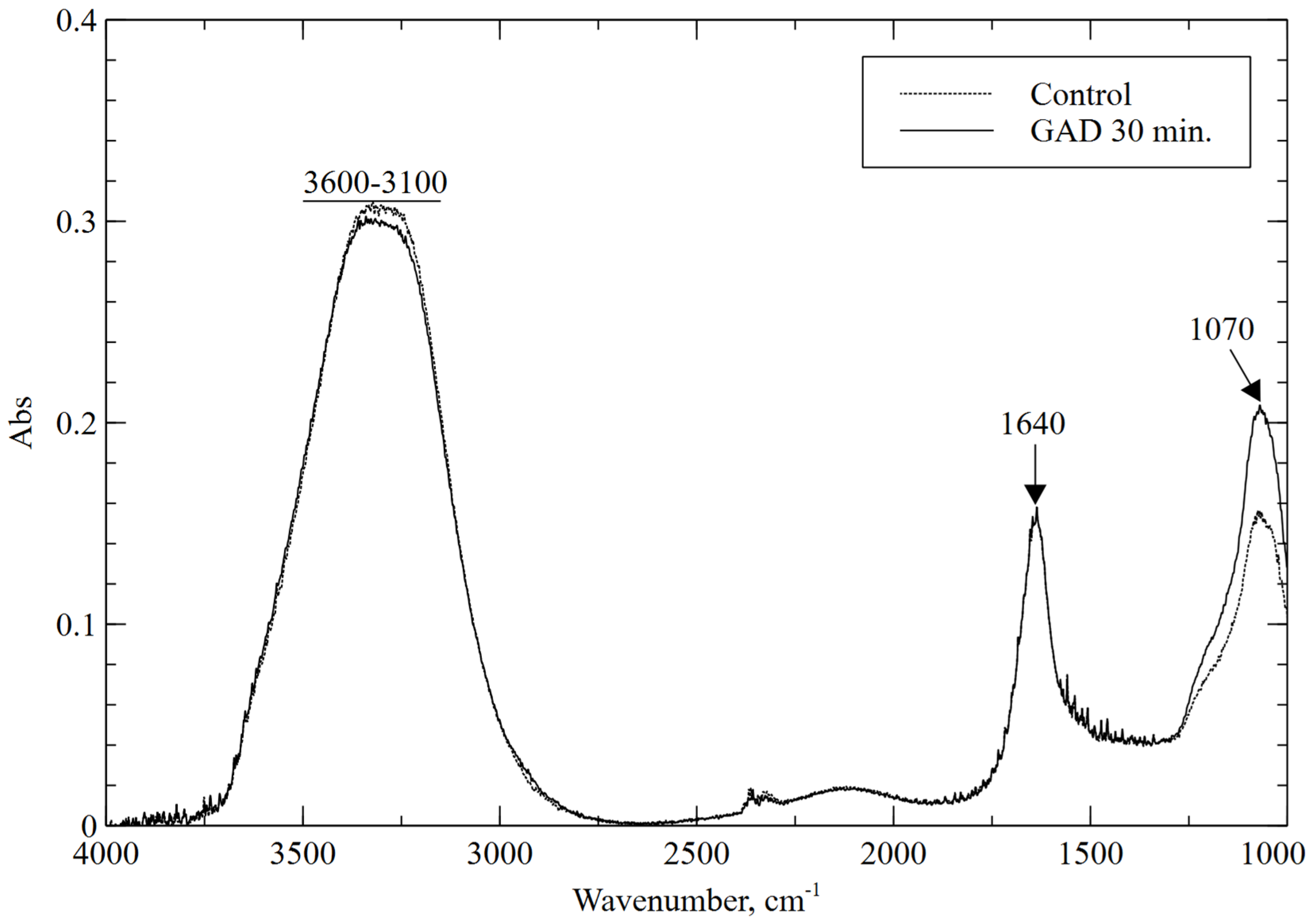
For all tested treatment times, the obtained FTIR spectrum does not differ significantly from the spectrum for the control sample, as shown in the example in Figure 4 for a treatment time of 30 min. The spectrum shows peaks characteristic of diatomaceous earth. The broad band between 3100 and 3600 cm−1 is due to H-O-H stretching vibrations of absorbed water, whereas the band at 1640 cm−1 may be related to the presence of water H-O-H bending vibrations from the absorbed water in opal present in the sample [51]. The very strong absorption peak at 1070 could be related to Si-O stretching vibrations from Si-O-Si [53]. For all treatment times, slightly reduced absorbances were observed for the H-O-H band with a slight increase in the Si-O band, which may be related to the evaporation of water during treatment. The obtained spectra were consistent with those reported in the literature; no formation of new functional groups was observed for any of the conditions.
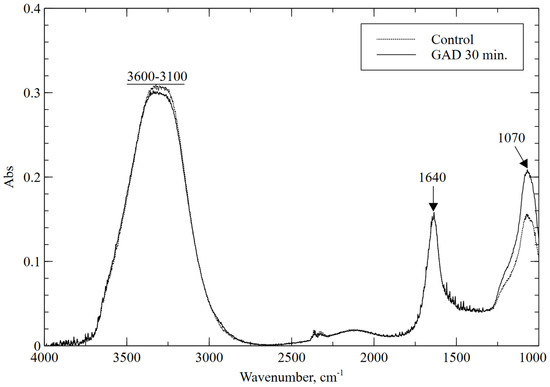
Figure 4.
FTIR spectra for the control sample and the 30 min plasma treatment.
3.3. Microbiological Analysis
Microbiological analysis revealed that spent diatomaceous earth after beer filtration was populated by two groups of microorganisms: bacteria and yeast. The obtained results are consistent with the available literature data, stating that, due to its porous structure, during the filtration process diatomaceous earth retains the yeast used in beer production on its surface, as well as a few bacteria that get into the solution during routine technological work [54,55]. No other groups of analyzed microorganisms were found in spent diatomaceous earth. Species identification of the isolated bacteria and yeasts using the MALDI-TOF MS technique allowed us to determine the following three bacterial species (n = 155): Citrobacter freundii (n = 90), Citrobacter braakii (n = 55) and Hafnia alvei (n = 10) and three species of yeast (n = 320): Saccharomyces cerevisiae (n = 300), Candida spherica (n = 10) and Rhodotorula glutinis (n = 10).
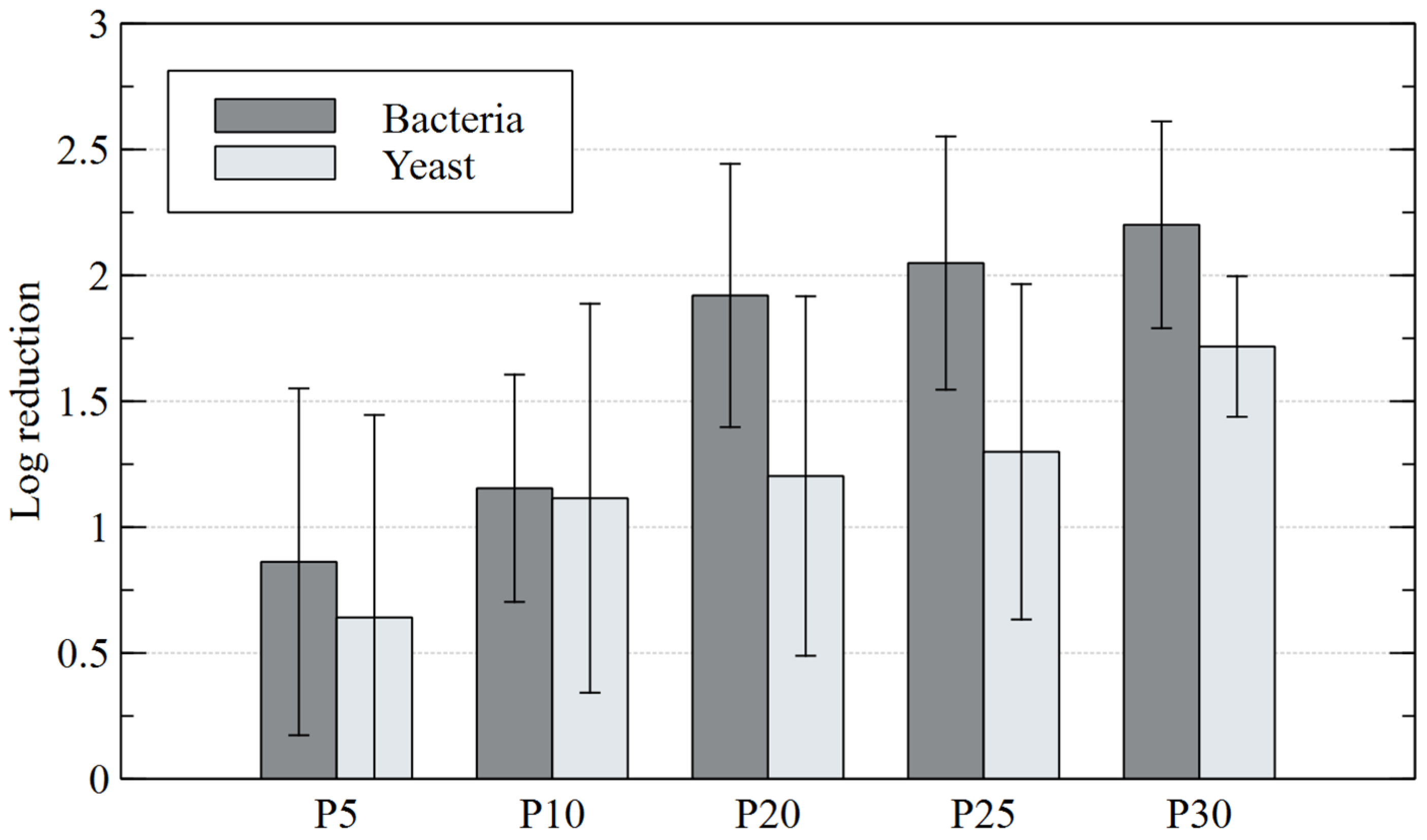
Based on the test results shown in Figure 5, it should be concluded that the non-equilibrium plasma has a strong lethal property against the tested bacteria and yeast. In the control sample, not subjected to plasma treatment, the following levels of bacteria and yeasts were found: 635,760 (CFU∙g−1 D.M.) and 1,046,722 (CFU∙g−1 D.M.), respectively. It was clearly visible in the plasma-treated samples that the number of microorganisms decreased with the increasing contact time of diatomaceous earth with plasma. The best results were obtained after 30 min of plasma treatment, as bacterial and yeast counts dropped to 2461 and 42,033 (CFU∙g−1 D.M.), respectively. However, even at shorter contact times the plasma worked effectively. A large decrease in the number of bacteria was observed after 10 min of plasma treatment of diatomaceous earth and amounted to 120,707 (CFU∙g−1 D.M.). In the case of yeast, successive count decreases were more evenly distributed and proportional to the plasma treatment time. Analysis of the obtained results showed that the log10 reduction of bacteria relative to the control was as follows: 0.86 (P5), 1.15 (P10), 1.92 (P20), 2.05 (P25) and 2.20 (P30). In contrast, the log10 reduction of yeasts was: 0.64 (P5), 1.11 (P10), 1.2 (P20), 1.3 (P25) and 1.72 (P30). The lethal properties of non-equilibrium plasma against bacteria and yeasts were also confirmed by other authors [56,57,58]. Prehn et al. [56] found a 31–89% decrease in E. coli (depending on the strain) in plasma-treated air. Maeda et al. [57] observed 100% elimination of multidrug-resistant strains of Salmonella enterica after just 5 min of plasma treatment. On the other hand, Ryu et al. [58] examined the effect of environmental factors on the survival of S. cerevisiae yeast cells placed in two solutions: water and saline. Their study revealed that yeast cells treated with plasma in water underwent the most severe morphological and physiological damage, including damage to membrane lipids and genomic DNA. S. cerevisiae cells treated with plasma in saline were much less damaged. The shares of yeast cells that survived plasma treatment were 80% and 40% for saline and water, respectively. Ryu et al. [58] concluded that this was due to the protective role of saline against yeast, weakening the effect of free radicals. Soušková et al. [59], during their study on plasma treatment of Candida albicans yeast in an aqueous suspension, obtained even better results because the number of cells that survived the process dropped dramatically from 5 × 104 CFU/mL to zero after just 6 min of contact with plasma. As the examples above show, it is clear that non-equilibrium plasma can be used to eliminate microorganisms from various sources.
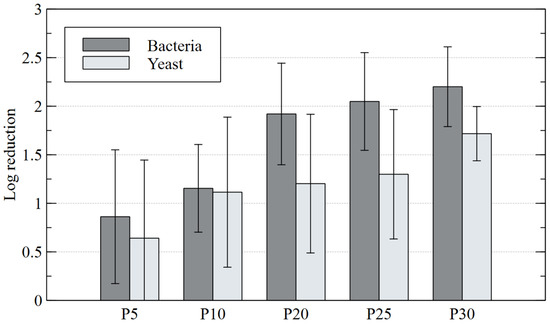
Figure 5.
Logarithmic CFU reduction of microorganisms colonizing diatomaceous earth for different plasma treatment times.
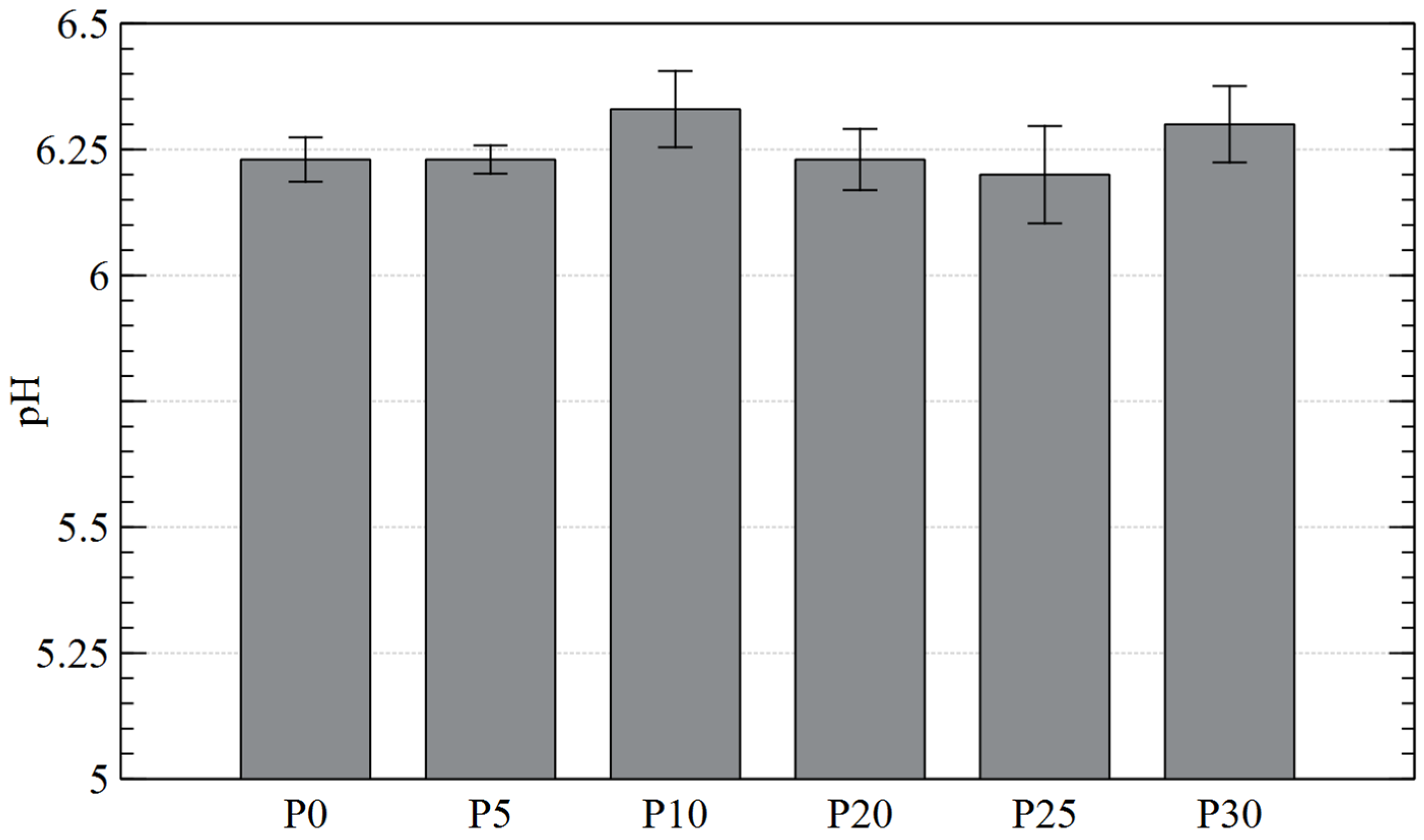
The average pH of the tested diatomaceous earth samples ranged from 6.20 to 6.33, i.e., it can be considered close to neutral and thus favorable for both groups of microorganisms [60]. Therefore, it suggests that the pH of diatomaceous earth was not a factor in the decrease in the number of the analyzed microorganisms (Figure 6).
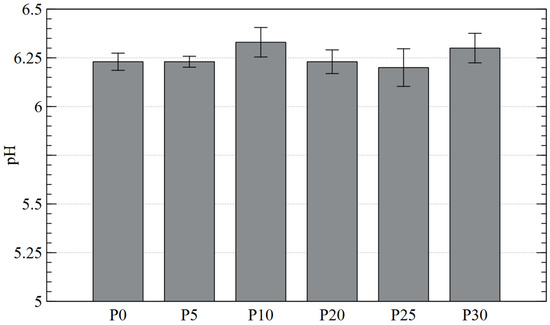
Figure 6.
pH of diatomaceous earth before and after contact with plasma.
Statistical analysis confirmed the results obtained in this study. The differences in microbial abundance between the proposed variants of the plasma treatment process were found to be statistically significant. Additionally, statistical analysis of the dependence of the average microbial abundance in the tested samples on the plasma exposure time confirmed a high negative correlation between these values. The correlation coefficient for bacteria was r = −0.89 and for yeast it was r = −0.98 (p < 0.05).
To the best of our knowledge, there are currently no published study results on using non-equilibrium plasma to remove microbial contaminants from the porous surface of diatomaceous earth. Therefore, our analyzes fill that gap and allow us to expand the possibilities of plasma application to new areas. Our previous study, related to the removal of microorganisms from the porous surface of mixed municipal waste for alternative fuel production, has also given promising results in the context of plasma applications in this area [17]. Non-equilibrium plasma helped to reduce the abundance of bacteria, mold and pathogenic microorganisms, i.e., Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp. and Staphylococcus spp. in municipal waste. Nevertheless, this method also had its limitations resulting from the porous structure of the mixed municipal waste, its heterogeneity, higher moisture content and the presence of organic substances [17].
The exact effects of non-equilibrium plasma on microorganisms are not yet fully understood [61]. With regard to bacteria, non-equilibrium plasma most often induces morphological changes, i.e., modification of the shape of the bacterial cell. In addition, it contributes to structural disorders within the bacterial surface, as well as changes in the arrangement of organelles. Non-equilibrium plasma enhances the formation of perforations in the cell wall and thus promotes the release of cell contents to the outside, which directly leads to cell death [62,63]. Yeast, including the Saccharomyces cerevisiae species that predominates in our studies, is a traditional model eukaryotic organism used in many studies that asses cellular processes [61]. Treating yeast cells with non-equilibrium plasma induces several types of stress, resulting mainly from the presence of free radicals reacting with yeast cellular components, i.e., proteins, enzymes, genetic material and lipids. The kind of disorder caused by plasma in yeast cells impairs their basic functions, leads to disturbances of physiological and biochemical nature and eventually causes death [64]. Therefore, although the aim of the present study was to quantitatively assess the antimicrobial properties of non-equilibrium plasma, having obtained promising results in this aspect it was reasonable, as a next step, to deepen the analysis towards characterization of the mechanisms behind this process. Such a comprehensive procedure will make it possible to determine the most optimal conditions for the plasma treatment of diatomaceous earth and, ultimately, to approximate the obtained results to other microbiologically contaminated porous materials.
4. Summary
The conducted research confirms the possibility of using non-equilibrium plasma produced in a glide arc reactor for decontamination of microorganisms colonizing diatomaceous earth after the beer filtration process. Analysis of the material’s porous surface with an optical microscope with 800× magnification did not reveal any destruction of the material as a result of plasma treatment, other than its drying due to the flow of working gas. Additionally, the FTIR spectra obtained show no change in the chemical composition of the material for all treatment times (5, 10, 20, 25 and 30 min). Microbiological tests identified three types of bacteria (Citrobacter freundii, Citrobacter braakii and Hafnia alvei) and three types of yeasts (Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Candida spherica and Rhodotorula glutinis) present in the tested material, which are associated with beer production. The effect of plasma treatment on reducing the number of listed organisms is already evident for the shortest time (5 min), and its effect increases with time. Compared with control samples, a reduction of 2.2 log10 CFU∙g−1 in the total number of bacteria and 1.72 log10 CFU∙g−1 in contaminants was observed for a time of 30 min. Although the results obtained seem very promising, more research is needed to explain the mechanisms behind the removal of microorganisms from the tested porous material. Due to the low operating costs of the system (only electricity and widely available air as a working gas are needed for operation), the authors believe that the studied system is likely to someday have practical applications in removing microorganisms colonizing diatomaceous earth after the beer filtration process by scaling up the system to a larger number of reactors operating in parallel and may also have a chance to be used with other surfaces with irregular shape and structure.
On the basis of the performed research, the following final conclusions can be drawn:
- The non-equilibrium plasma generated in the mini glidearc reactor has a lethality potential against bacteria and yeast.
- Bacteria and yeast can be effectively removed from the porous surface of diatomaceous earth using non-equilibrium plasma.
- It is reasonable to conduct further studies to determine the possibility of removing other types of microorganisms from surfaces with irregular shape and structure.
- Further research involving the optimization of the diatomaceous earth plasma process that leads to the complete elimination of microorganisms from its surface will contribute to its reuse in the beer filtration process as well as in other industries, i.e., cosmetology, agriculture or chemical technology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.W.-K. and J.P.; methodology, K.W.-K. and J.P.; validation, K.W.-K.; formal analysis, K.W.-K., J.P., P.T., M.K. and D.Z.; investigation, K.W.-K. and J.P.; resources, K.W.-K., M.Z. and J.P.; data curation, K.W.-K. and J.P.; writing—original draft preparation, K.W.-K., P.T., S.B. and J.P.; writing—review and editing, K.W.-K., M.Z., P.T., S.B. and J.P.; visualization, K.W.-K. and J.P.; supervision, K.W.-K. and J.P.; project administration, K.W.-K. and J.P.; funding acquisition, K.W.-K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the statutory measures of the University of Agriculture in Krakow and granted for the Department of Microbiology and Biomonitoring.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kristiansen, A.G.; Director, S. 50 Achievements in Brewing Science and Technology in 350 Years—Part 2. Brauwelt Int. 2014, 32, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, X.; Tian, W.; Wang, L.; Bai, J.; Qiao, K.; Zhao, J. Biological Regeneration of Brewery Spent Diatomite and Its Reuse in Basic Dye and Chromium (III) Ions Removal. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 128, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, R.; Gunathilake, C.; Dassanayake, R. Suitability of Reusing the Spent Diatomaceous Earth in Brick Production: A Review. Adv. Technol. 2022, 2022, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillaudeau, L.; Blanpain-Avet, P.; Daufin, G. Water, Wastewater and Waste Management in Brewing Industries. J. Clean. Prod. 2006, 14, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, T.R.S.; De Mello, P.P.M.; Sérvulo, E.F.C. Solid Wastes in Brewing Process: A Review. J. Brew. Distill. 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rangam, N.V.; Sudagar, A.J.; Ruszczak, A.; Borowicz, P.; Tóth, J.; Kövér, L.; Michałowska, D.; Roszko, M.Ł.; Noworyta, K.R.; Lesiak, B. Valorizing the Unexplored Filtration Waste of Brewing Industry for Green Silver Nanocomposite Synthesis. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semião, M.A.; Haminiuk, C.W.I.; Maciel, G.M. Residual Diatomaceous Earth as a Potential and Cost Effective Biosorbent of the Azo Textile Dye Reactive Blue 160. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wille, C.L.; Wille, P.E.; da Rosa, J.M.; Boff, M.I.C.; Franco, C.R. Efficacy of Recovered Diatomaceous Earth from Brewery to Control Sitophilus Zeamais and Acanthoscelides Obtectus. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2019, 83, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotes-Palomino, M.T.; Martínez-García, C.; Eliche-Quesada, D.; Pérez-Villarejo, L. Production of Ceramic Material Using Wastes from Brewing Industry. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 663, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, S.; Cuevas, M.; La Rubia, M.D.; Eliche-Quesada, D. Preliminary Study of the Use of Spent Diatomaceous Earth from the Brewing Industry in Clay Matrix Bricks. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2017, 116, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, R.; Gunathilake, C. Development of Environmentally Friendly Bricks Using Spent Diatomaceous Earth. Sri Lankan J. Appl. Sci. 2022, 1, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Hegemann, D.; Brunner, H.; Oehr, C. Plasma Treatment of Polymers for Surface and Adhesion Improvement. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2003, 208, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesel, A.; Junkar, I.; Cvelbar, U.; Kovac, J.; Mozetic, M. Surface Modification of Polyester by Oxygen- and Nitrogen-Plasma Treatment. Surf. Interface Anal. 2008, 40, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłat, J.; Terebun, P.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Diatczyk, J. RF Atmospheric Plasma Jet Surface Treatment of Paper. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 374001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisan, M.; Barbeau, J.; Crevier, M.-C.; Pelletier, J.; Philip, N.; Saoudi, B. Plasma Sterilization. Methods and Mechanisms. Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisset, J.-L.; Pawłat, J. Chemical Effects of Air Plasma Species on Aqueous Solutes in Direct and Delayed Exposure Modes: Discharge, Post-Discharge and Plasma Activated Water. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2016, 36, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłat, J.; Terebun, P.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Wolny-Koładka, K. Possibility of Humid Municipal Wastes Hygienisation Using Gliding Arc Plasma Reactor. Water 2021, 13, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miebach, L.; Freund, E.; Clemen, R.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Metelmann, H.-R.; von Woedtke, T.; Gerling, T.; Wende, K.; Bekeschus, S. Conductivity Augments ROS and RNS Delivery and Tumor Toxicity of an Argon Plasma Jet. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 180, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maho, T.; Binois, R.; Brulé-Morabito, F.; Demasure, M.; Douat, C.; Dozias, S.; Escot Bocanegra, P.; Goard, I.; Hocqueloux, L.; Le Helloco, C.; et al. Anti-Bacterial Action of Plasma Multi-Jets in the Context of Chronic Wound Healing. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przekora, A.; Audemar, M.; Pawłat, J.; Canal, C.; Thomann, J.-S.; Labay, C.; Wojcik, M.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Terebun, P.; Ginalska, G.; et al. Positive Effect of Cold Atmospheric Nitrogen Plasma on the Behavior of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cultured on a Bone Scaffold Containing Iron Oxide-Loaded Silica Nanoparticles Catalyst. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggeman, P.J.; Kushner, M.J.; Locke, B.R.; Gardeniers, J.G.E.; Graham, W.G.; Graves, D.B.; Hofman-Caris, R.C.H.M.; Maric, D.; Reid, J.P.; Ceriani, E.; et al. Plasma–Liquid Interactions: A Review and Roadmap. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2016, 25, 053002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młotek, M.; Ulejczyk, B.; Woroszył, J.; Walerczak, I.; Krawczyk, K. Purification of the Gas after Pyrolysis in Coupled Plasma-Catalytic System. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2017, 19, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Jõgi, I.; Hołub, M.; Brandenburg, R. Non-Thermal Plasma Based Decomposition of Volatile Organic Compounds in Industrial Exhaust Gases. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3745–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłat, J. Electrical Discharges in Humid Environments: Generators, Effects, Application; Wydawnictwo Politechniki Lubelskiej: Lublin, Poland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, E.; Rani, D.A.; Cheeseman, C.R.; Deegan, D.; Wise, M.; Boccaccini, A.R. Thermal Plasma Technology for the Treatment of Wastes: A Critical Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maćkiw, E.; Mąka, Ł.; Ścieżyńska, H.; Pawlicka, M.; Dziadczyk, P.; Rżanek-Boroch, Z. The Impact of Plasma-Modified Films with Sulfur Dioxide, Sodium Oxide on Food Pathogenic Microorganisms. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2015, 28, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terebun, P.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Hensel, K.; Kopacki, M.; Pawłat, J. Influence of Plasma Activated Water Generated in a Gliding Arc Discharge Reactor on Germination of Beetroot and Carrot Seeds. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kučerová, K.; Henselová, M.; Slováková, Ľ.; Bačovčinová, M.; Hensel, K. Effect of Plasma Activated Water, Hydrogen Peroxide, and Nitrates on Lettuce Growth and Its Physiological Parameters. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemeli, G.B.N.; Janda, M.; Machala, Z. Non-Thermal Plasma as a Priming Tool to Improve the Yield of Pea in Outdoor Conditions. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2022, 42, 1143–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, H.; Nishime, T.M.C.; Wannicke, N.; Mui, T.S.M.; Horn, S.; Quade, A.; Weltmann, K.-D. A Medium-Scale Volume Dielectric Barrier Discharge System for Short-Term Treatment of Cereal Seeds Indicates Improved Germination Performance with Long-Term Effects. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 044904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradu, C.; Kutasi, K.; Magureanu, M.; Puač, N.; Živković, S. Reactive Nitrogen Species in Plasma-Activated Water: Generation, Chemistry and Application in Agriculture. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 223001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirgedaitė-Šėžienė, V.; Lučinskaitė, I.; Mildažienė, V.; Ivankov, A.; Koga, K.; Shiratani, M.; Laužikė, K.; Baliuckas, V. Changes in Content of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity Induced in Needles of Different Half-Sib Families of Norway Spruce (Picea Abies (L.) H. Karst) by Seed Treatment with Cold Plasma. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, N.; Yamamoto, K. Variations in Plant Growth Characteristics due to Oxygen Plasma Irradiation on Leaf and Seed. Agronomy 2022, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, Y.; Contaldo, N.; Laurita, R.; Várallyay, E.; Canel, A.; Gherardi, M.; Colombo, V.; Bertaccini, A. Plasma Activated Water Triggers Plant Defence Responses. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroussi, M. Low Temperature Plasma-Based Sterilization: Overview and State-of-the-Art. Plasma Process. Polym. 2005, 2, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, S.; Feichtinger, J.; Hertel, C. Response of Deinococcus Radiodurans to Low-Pressure Low-Temperature Plasma Sterilization Processes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popelka, A.; Kronek, J.; Novák, I.; Kleinová, A.; Mičušík, M.; Špírková, M.; Omastová, M. Surface Modification of Low-Density Polyethylene with Poly(2-Ethyl-2-Oxazoline) Using a Low-Pressure Plasma Treatment. Vacuum 2014, 100, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutze, A.; Jeong, J.Y.; Babayan, S.E.; Park, J.; Selwyn, G.S.; Hicks, R.F. The Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Jet: A Review and Comparison to Other Plasma Sources. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1998, 26, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, S.; Moisan, M.; Tabrizian, M.; Barbeau, J.; Pelletier, J.; Ricard, A.; Yahia, L. Using the Flowing Afterglow of a Plasma to Inactivate Bacillus Subtilis Spores: Influence of the Operating Conditions. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 88, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraei Ashtiani, S.-H.; Rafiee, M.; Mohebi Morad, M.; Khojastehpour, M.; Khani, M.R.; Rohani, A.; Shokri, B.; Martynenko, A. Impact of Gliding Arc Plasma Pretreatment on Drying Efficiency and Physicochemical Properties of Grape. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 63, 102381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šerá, B.; Vanková, R.; Roháček, K.; Šerý, M. Gliding Arc Plasma Treatment of Maize (Zea Mays L.) Grains Promotes Seed Germination and Early Growth, Affecting Hormone Pools, but Not Significantly Photosynthetic Parameters. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappim, W.; da Sampaio, A.G.; Miranda, F.; Fraga, M.; Petraconi, G.; da Silva Sobrinho, A.; Kostov, K.; Koga-Ito, C.; Pessoa, R. Antimicrobial Effect of Plasma-Activated Tap Water on Staphylococcus Aureus, Escherichia Coli, and Candida Albicans. Water 2021, 13, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Hosseini, H.; Abedi, A.-S.; Khani, M.; Heshmati, A.; Abhari, K.; Shahraz, F.; Taghizadeh, M.; Akhavan, A. Gliding Arc Plasma Discharge Conditions on Microbial, Physicochemical, and Sensory Properties of Shrimp (Litopenaeus Vannamei): In Vivo and In Vitro Studies. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2022, 15, 2327–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłat, J.; Starek, A.; Sujak, A.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Terebun, P.; Budzeń, M. Effects of Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Generated in GlidArc Reactor on Lavatera Thuringiaca L. Seeds’ Germination. Plasma Process. Polym. 2018, 15, 1700064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starek, A.; Pawłat, J.; Chudzik, B.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Terebun, P.; Sagan, A.; Andrejko, D. Evaluation of Selected Microbial and Physicochemical Parameters of Fresh Tomato Juice after Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Treatment during Refrigerated Storage. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawłat, J.; Terebun, P.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Tarabová, B.; Kovaľová, Z.; Kučerová, K.; Machala, Z.; Janda, M.; Hensel, K. Evaluation of Oxidative Species in Gaseous and Liquid Phase Generated by Mini-Gliding Arc Discharge. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2019, 39, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolny-Koładka, K.; Żukowski, W. Mixed Municipal Solid Waste Hygienisation for Refuse-Derived Fuel Production by Ozonation in the Novel Configuration Using Fluidized Bed and Horizontal Reactor. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhme, K.; Fernández-No, I.C.; Barros-Velázquez, J.; Gallardo, J.M.; Calo-Mata, P.; Cañas, B. Species Differentiation of Seafood Spoilage and Pathogenic Gram-Negative Bacteria by MALDI-TOF Mass Fingerprinting. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3169–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxatto, A.; Prod’hom, G.; Greub, G. Applications of MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Diagnostic Microbiology. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 380–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, P.; Rolain, J.-M.; Fournier, P.E.; La Scola, B.; Drancourt, M.; Raoult, D. MALDI-TOF-Mass Spectrometry Applications in Clinical Microbiology. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1733–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reka, A.A.; Pavlovski, B.; Fazlija, E.; Berisha, A.; Pacarizi, M.; Daghmehchi, M.; Sacalis, C.; Jovanovski, G.; Makreski, P.; Oral, A. Diatomaceous Earth: Characterization, Thermal Modification, and Application. Open Chem. 2021, 19, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galotta, A.; Giust, E.; Bortolotti, M.; Sorarù, G.D.; Sglavo, V.M.; Biesuz, M. Cold Sintering of Diatomaceous Earth. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 104, 4329–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatoni, A.; Koesnarpadi, S.; Hidayati, N. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Diatomaceous Earth—4,4-Diaminodiphenylether-O-Hydroxybenzaldehyde as an Adsorbent of Ag(i) Metal Ion. Indones. J. Chem. 2010, 10, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarska, A.A.; Pilarski, K.; Adamski, M.; Zaborowicz, M.; Cais-Sokolińska, D.; Wolna-Maruwka, A.; Niewiadomska, A. Eco-Friendly and Effective Diatomaceous Earth/Peat (DEP) Microbial Carriers in the Anaerobic Biodegradation of Food Waste Products. Energies 2022, 15, 3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; De Belie, N.; Verstraete, W. Diatomaceous Earth as a Protective Vehicle for Bacteria Applied for Self-Healing Concrete. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 39, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prehn, F.; Timmermann, E.; Kettlitz, M.; Schaufler, K.; Günther, S.; Hahn, V. Inactivation of Airborne Bacteria by Plasma Treatment and Ionic Wind for Indoor Air Cleaning. Plasma Process. Polym. 2020, 17, 2000027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Toyokawa, Y.; Shimizu, N.; Imanishi, Y.; Sakudo, A. Inactivation of Salmonella by Nitrogen Gas Plasma Generated by a Static Induction Thyristor as a Pulsed Power Supply. Food Control 2015, 52, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Shim, G.-B.; Uhm, H.-S.; Park, G.; Choi, E.H. Effects of Background Fluid on the Efficiency of Inactivating Yeast with Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soušková, H.; Scholtz, V.; Julák, J.; Kommová, L.; Savická, D.; Pazlarová, J. The Survival of Micromycetes and Yeasts under the Low-Temperature Plasma Generated in Electrical Discharge. Folia Microbiol. 2011, 56, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Bååth, E. Contrasting Soil PH Effects on Fungal and Bacterial Growth Suggest Functional Redundancy in Carbon Mineralization. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1589–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polčic, P.; Machala, Z. Effects of Non-Thermal Plasma on Yeast Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkawareek, M.Y.; Algwari, Q.T.; Laverty, G.; Gorman, S.P.; Graham, W.G.; O’Connell, D.; Gilmore, B.F. Eradication of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms by Atmospheric Pressure Non-Thermal Plasma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duske, K.; Wegner, K.; Donnert, M.; Kunert, U.; Podbielski, A.; Kreikemeyer, B.; Gerling, T.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Nebe, B.; Bader, R. Comparative In Vitro Study of Different Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Jets Concerning Their Antimicrobial Potential and Cellular Reaction. Plasma Process. Polym. 2015, 12, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-N.; Paek, K.-H.; Ju, W.-T.; Lee, Y.-H. Sterilization of Bacteria, Yeast, and Bacterial Endospores by Atmospheric-Pressure Cold Plasma Using Helium and Oxygen. J. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).