Impact of Intracavity Power Variations toward Ultrashort Pulse Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
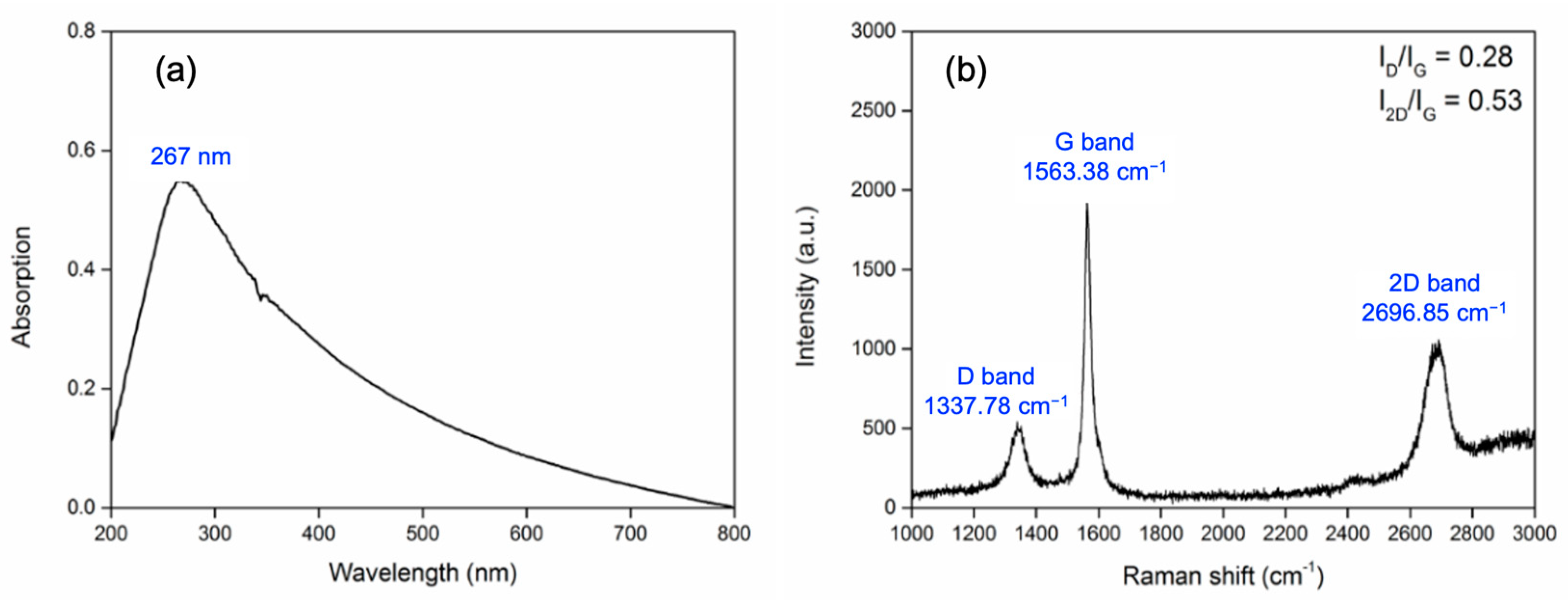
2. Graphene Nanoplatelet Powder
3. Saturable Absorber Characteristics
4. Experimental Setup
5. Pulse Laser Performance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mears, R.J.; Reekie, L.; Jauncey, I.M. High-power tunable erbium-doped fiber laser operating at 1.55 μm. In Proceedings of the Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics, Baltimore, MD, USA, 26 April–1 May 1987; pp. 122–123. Available online: https://opg.optica.org/abstract.cfm?uri=cleo-1987-WD3 (accessed on 16 February 2023).
- Furusawa, K.; Malinowski, A.; Price, J.H.V.; Monro, T.M.; Sahu, J.K.; Nilsson, J.; Richardson, D.J. Cladding pumped Ytterbium-doped fiber laser with holey inner and outer cladding. Opt. Express 2001, 9, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán-Sánchez, M.; Reyes-Mora, A.; Pottiez, O.; Rodríguez-Morales, L.A.; Armas-Rivera, I.; Bello-Jiménez, M.; Alaniz-Baylón, J.; Ibarra-Escamilla, B. Dark rectangular pulses from a dumbbell-shaped mode-locked double-clad Er:Yb laser. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2022, 34, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Yang, H.; Xi, X.; Ye, Y.; Huang, L.; Yang, B.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Z.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.; et al. Optimization and demonstration of 6 kW oscillating-amplifying integrated fiber laser employing spindle-shaped fiber to suppress SRS and TMI. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 159, 108903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klenke, A.; Jauregui, C.; Steinkopff, A.; Aleshire, C.; Limpert, J. High-power multicore fiber laser systems. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2022, 84, 100412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChmielowskI, P.; Nikodem, M. Widely tunable continuous-wave fiber laser in the 1.55–1.8 µm wavelength region. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 42300–42307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, J.; Ghafoor, S.; Kousar, A.; Kanwal, B.; Qureshi, K.K. Design of a continuous-wave ytterbium-doped tunable fiber laser pump for thulium-doped fiber amplifiers. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 3541–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Ramirez, L.G.; Silva-Alvarado, E.C.; Gallegos-Arellano, E.; Fernandez-Jaramillo, A.A.; Estudillo-Ayala, J.M.; Jauregui-Vazquez, D.; Rojas-Laguna, R.; Sierra-Hernandez, J.M. Select-cutoff Mach-Zehnder interferometer based on waist-enlarged technique and its multi-wavelength fiber laser application. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 128, 104508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, J.; Ghafoor, S.; Atieh, A.; Kanwal, B.; Qureshi, K.K. Widely tunable and switchable multiwavelength erbium-doped fiber laser based on a single ring cavity. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2022, 39, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinnecker, V.; Madden, S.; Stokes-Griffin, C.; Compston, P.; Rode, A.V.; Rapp, L. Ultrashort pulse laser ablation of steel in ambient air. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 148, 107757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ito, Y.; Sun, H.; Sugita, N. Investigation of multi-timescale processing phenomena in femtosecond laser drilling of zirconia ceramics. Opt. Express 2022, 31, 37394–37406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, F.A.; Paula, K.T.; Santos, M.V.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Mendonça, C.R. Direct femtosecond laser printing of silk fibroin periodic structure with lower mid-infrared reflectivity. Opt. Mater. 2022, 135, 113335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flamm, D.; Kaiser, M.; Fell, M.; Kahmann, M.; Lang, M.; Kleiner, J.; Hesse, T. Protecting the edge: Ultrafast laser modified C-shaped glass edges. J. Laser Appl. 2022, 34, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Gao, X.; Cong, Z. High repetition rate actively mode-locked Er:fiber laser with tunable pulse duration. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2022, 20, 071402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.Y.; Perros, A.P.; Li, D.; Kim, M.; Sun, Z. Scalable graphene electro–optical modulators for all-fibre pulsed lasers. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 9873–9880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Set, S.Y.; Yaguchi, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Jablonski, M. Laser mode locking using a saturable absorber incorporating carbon nanotubes. J. Light. Technol. 2004, 22, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, Y.; Rozhin, A.G.; Kataura, H.; Achiba, Y.; Takumoto, M. Carbon nanotube-poly(vinylalcohol) nanocomposite film devices: Applications for femtosecond fiber laser mode lockers and optical amplifier noise suppressors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 44, 1621–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Tang, D.Y.; Jose, R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C.T.; Loh, K.P. Graphene-polymer nanofiber membrane for ultrafast photonics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hasan, T.; Torrisi, F.; Popa, D.; Privitera, G.; Wang, F.; Bonaccorso, F.; Basko, D.M.; Ferrari, A.C. Graphene mode-locked ultrafast laser. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, F.; Gong, M.-M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, Z.-W.; Shen, H.-B.; Chen, S.-C. Generation of Q-switched and mode-locked pulses based on PbS/CdS saturable absorbers in an Er-doped fiber laser. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 5956–5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Z.; Yang, F.; Han, Y.; Fan, W.; Li, S.; Bai, C.; Lu, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, G.; Fu, S.; et al. Large energy mode-locked phenomenon based on ZrS2 in Er-doped fiber laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 157, 108725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Zhang, C.; Ahmed, R.; Asghar, H.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, N.Z.; Chen, T.; Baig, M.A.; Wang, Z. Carbon nanoparticles (CNPs) as a saturable absorber for a passively Q-switched erbium (Er3+) doped fiber laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 160, 109046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawliszewska, M.; Tomaszewska, D.; Soboń, G.; Dużyńska, A.; Zdrojek, M.; Sotor, J. Broadband metallic carbon nanotube saturable absorber for ultrashort pulse generation in the 1500–2100 nm spectral range. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soboh, R.S.M.; Al-Masoodi, A.H.H.; Erman, F.N.A.; Al-Masoodi, A.H.H.; Nizamani, B.; Arof, H.; Apsari, R.; Harun, S.W. Mode-locked ytterbium-doped fiber laser with zinc phthalocyanine thin film saturable absorber. Front. Optoelectron. 2022, 15, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahib, M.A.A.B.; Zulkipli, N.F.; Rosol, A.H.A.; Yasin, M.; Harun, S.W. Titanium carbide MXene as a mode locker in erbium-doped fiber laser cavity. J. Russ. Laser Res. 2022, 43, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, R.; Wu, R.; Lv, Y.; Liu, W. GaSb film is a saturable absorber for dissipative soliton generation in a fiber laser. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 55971–55978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, Y. Mode-locked fiber laser based on α-Fe2O3 nanosheets as saturable absorbers. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 144, 107417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.; Zulkipli, N.F.; Ahmed, N.; Jusoh, Z.; Musa, B.; Apsari, R.; Harun, S.W. Lanthanum hexaboride for Q-switching and mode-locking applications. Opt. Commun. 2022, 502, 127396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.; Fuse, K.; Xu, B.; Yamashita, S. Optical deposition of graphene and carbon nanotubes in a fiber ferrule for passive mode- locked lasing. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 23054–23061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.W.; Windeler, R.S.; DiGiovanni, D.J. Optically driven deposition of single-walled carbon-nanotube saturable absorbers on optical fiber end-faces. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 9176–9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, K.; Yamashita, S. Optically manipulated deposition of carbon nanotubes onto optical fiber end. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, L988–L990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geim, A.K.; Novoselov, K.S. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.M.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Song, Y.W. Multilayered graphene efficiently formed by mechanical exfoliation for nonlinear saturable absorbers in fiber mode-locked lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 211102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, G.; Chen, S.; Guo, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Bao, Q.; Wen, S.; Tang, D.; et al. Mechanically exfoliated black phosphorus as a new saturable absorber for both Q-switching and mode-locking laser operation. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 12823–12833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotor, J.; Sobon, G.; Kowalczyk, M.; Mzcherzynski, W.; Paletko, P.; Abramski, K.M. Ultrafast thulium-doped fiber laser mode locked with black phosphorus. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 3885–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yu, P.; Wu, D.; Singh, B.; Zeng, Q.; Lin, H.; Zhou, W.; Lin, J.; Suenaga, K.; Liu, Z.; et al. Atomically thin noble metal dichalcogenide: A broadband mid-infrared semiconductor. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, D.; Zapata, J.D.; Nascimento, R.; Rosa, H.G.; Saito, L.A.M.; Thoroh de Souza, E.A. Mode-locked erbium-doped fiber laser based on a mechanically exfoliated ReS2 saturable absorber onto D-shaped optical fiber. Opt. Express 2022, 12, 4506–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, S.I.; Ahmad, H. Thermal release tape assisted mechanical exfoliation of pristine TMD and the performance of the exfoliated TMD saturable absorbers for Q-switched laser generation. Opt. Mater. 2022, 128, 112363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Tong, L. Interfacial charge transfer and ultrafast photonics application of 2D graphene/InSe heterostructure. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G. Graphene mode-locked fiber laser at 2.8 μm. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2016, 28, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, T.; Xie, G.; Qiao, Z.; Qin, Z.; Ma, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F.; Yuan, P.; Ma, J.; Qian, L. Indium selenide film: A promising saturable absorber in 3- to 4-μm band for mid-infrared pulsed laser. Nanophotonics 2020, 9, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Hai, T.; Xie, G.; Ma, J.; Yuan, P.; Qian, L.; Li, L.; Zhao, L.; Shen, D. Black phosphorus Q-switched and mode-locked mid-infrared Er:ZBLAN fiber laser at 3.5 μm wavelength. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 8224–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Li, P.; Yu, L.; Ruan, S.; Li, K.; Yan, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, C.; Liu, W.; et al. Mode-locked fiber laser of 3.5 µm using a single-walled carbon nanotube saturable absorber mirror. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2022, 20, 011404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.Y.; Latif, A.A.; Abu Bakar, M.H.; Muhammad, F.D.; Huang, N.M.; Omar, M.F.; Mahdi, M.A. Passively mode-locked ultrashort pulsed fiber laser incorporating multi-layered graphene nanoplatelet saturable absorber. J. Phys. Commun. 2018, 2, 075005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abas, A.F.; Lau, K.Y.; Muhammad, F.D.; Abdulkawi, W.M.; Al-Moliki, Y.M.; Alresheedi, M.T.; Mahdi, M.A. Dual-wavelength mode-locked oscillation with graphene nanoplatelet saturable absorber in erbium-doped fiber laser. Electronics 2022, 11, 2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamra, A.A.B.; Lim, H.N.; Chee, W.K.; Huang, N.M. Electro-exfoliating graphene from graphite for direct fabrication of supercapacitor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 360, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.X.; Feng, D.J.; Zhang, M.S.; Jiang, S.Z.; Zhang, C. Mode-locked erbium-doped all fiber laser using few-layer graphene as a saturable absorber. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 72, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wan, X.; Ruan, Q.; Yang, R.; Du, T.; Chen, N.; Cai, Z.; Luo, Z. Effects of nanomaterial saturable absorption on passively mode-locked fiber lasers in an anomalous dispersion regime: Simulations and experiments. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2018, 24, 1100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, C.R.; Desurvire, E. Modeling of erbium-doped fiber amplifier. J. Light. Technol. 1991, 9, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abas, A.F.; Lau, K.Y.; Al-Moliki, Y.M.; Aladadi, Y.T.; Alresheedi, M.T.; Mahdi, M.A. Impact of Intracavity Power Variations toward Ultrashort Pulse Generation. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074087
Abas AF, Lau KY, Al-Moliki YM, Aladadi YT, Alresheedi MT, Mahdi MA. Impact of Intracavity Power Variations toward Ultrashort Pulse Generation. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(7):4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074087
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbas, Ahmad Fauzi, Kuen Yao Lau, Yahya Mohammed Al-Moliki, Yosef Taher Aladadi, Mohammed Thamer Alresheedi, and Mohd Adzir Mahdi. 2023. "Impact of Intracavity Power Variations toward Ultrashort Pulse Generation" Applied Sciences 13, no. 7: 4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074087
APA StyleAbas, A. F., Lau, K. Y., Al-Moliki, Y. M., Aladadi, Y. T., Alresheedi, M. T., & Mahdi, M. A. (2023). Impact of Intracavity Power Variations toward Ultrashort Pulse Generation. Applied Sciences, 13(7), 4087. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074087





