A Focused Event Crawler with Temporal Intent
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We propose a new automated method for detecting temporal intent on events. This method uses Google Trends data to automatically and quantitatively estimate the start time and the temporal distribution of events, in contrast to previous manual judgements based on expert experience.
- We propose a new focused crawling framework that incorporates the temporal intent of events. In particular, the framework integrates the start time of the temporal intent into the process of topic representation and similarity computation, and its overall temporal distribution into the URL (Uniform Resource Locator) priority assignment. In addition, a new URL priority assignment method is proposed, in which the quantified temporal distribution is used as the independent variable of a natural exponential function.
2. Related Work
2.1. URL Priority Assignment
2.2. Temporal Focused Crawlers
3. Mathematical Proof and Identification of Temporal Intent
3.1. Mathematical Proof of Temporal Intent Using Bayes Formula
3.2. Identification of Temporal Intent by Google Trends
4. Temporal Intent-Based Focused Crawler
4.1. Topical Representation with Temporal Intent
4.2. Relevance Calculation with Start Time
4.3. URL Priority Assignment with Quantified Temporal Distribution
5. Experiments and Discussion
5.1. Experimental Setup
5.1.1. Effectiveness Metrics
5.1.2. Data Preparation
5.2. Experiment 1: Temporal Intent Identification
5.3. Experiment 2: Effectiveness of Our Focused Crawler
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franceschini, R.; Rosi, A.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Exploring a landslide inventory created by automated web data mining: The case of Italy. Landslides 2022, 19, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufi, F.K.; Khalil, I. Automated Disaster Monitoring from Social Media Posts Using AI-Based Location Intelligence and Sentiment Analysis. IEEE Trans. Comput. Social Syst. 2022; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jin, H.D.; Zhang, Y. Risk assessment of earthquake network public opinion based on global search BP neural network. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiresmaili, M.; Talebian, A.; Miraki, S. Pre-hospital emergency response to terrorist attacks: A scoping review. Hong Kong J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 29, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.; Dias, G.; Jorge, A.M.; Jatowt, A. Survey of temporal information retrieval and related applications. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2014, 47, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Hu, H.; Zeng, D.D.; Wu, W. Emergency Event Web Information Acquisition using Crowd Web Sensors. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 95, 2393–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakandan, S.; Arun, A.; Bhukya, R.R.; Hardas, B.M.; Kumar, T.C.A.; Ashok, M. An Automated Word Embedding with Parameter Tuned Model for Web Crawling. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2022, 32, 1617–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Li, R. A Focused Crawler for Borderlands Situation Information with Geographical Properties of Place Names. Sustainability 2014, 6, 6529–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Q.; Shi, Z.; Xiao, Y. VSEC: A Vertical Search Engine for E-commerce. In Recent Progress in Data Engineering and Internet Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Lupiani-Ruiz, E.; García-Manotas, I.; Valencia-García, R.; García-Sánchez, F.; Castellanos-Nieves, D.; Fernández-Breis, J.T.; Camón-Herrero, J.B. Financial news semantic search engine. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 15565–15572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.S.; Zhong, G. A novel focused crawler combining Web space evolution and domain ontology. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 243, 108495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchakounte, F.; Ngnintedem, J.C.T.; Damakoa, I.; Ahmadou, F.; Fotso, F.A.K. Crawl-shing: A focused crawler for fetching phishing contents based on graph isomorphism. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 8888–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dang, D.; Zhou, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, X.; Huang, S. Crawling Strategy Based on Domain Ontology of Emergency Plans. In Proceedings of the 2013 the International Conference on Education Technology and Information System (ICETIS 2013), Sanya, China, 21–22 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, H.M.; Chang, C.H.; Kao, T.Y.; Cheng, C.T.; Huang, Y.Y.; Cheong, K.P. Enabling maps/location searches on mobile devices: Constructing a POI database via focused crawling and information extraction. Int. J. Geog. Inf. Sci. 2016, 30, 1405–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.J. Towards open decision support systems based on semantic focused crawling. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 3914–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Chen, J.; Wu, H. Discovering Land Cover Web Map Services from the Deep Web with JavaScript Invocation Rules. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2016, 5, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva, A.S.; Lisboa-Filho, J. A Focused Crawler for Web Feature Service and Web Map Service Discovering. In Proceedings of the Web and Wireless Geographical Information Systems: 18th International Symposium, W2GIS 2020, Wuhan, China, 13–14 November 2020; p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- Capuano, A.; Rinaldi, A.M.; Russo, C. An ontology-driven multimedia focused crawler based on linked open data and deep learning techniques. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 7577–7598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.K.N.; Bucur, D.; Atil, B.; Pitel, G.; Ruis, F.; Kadkhodaei, H.; Litvak, N. Look back, look around: A systematic analysis of effective predictors for new outlinks in focused Web crawling. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 260, 110126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talvensaari, T.; Pirkola, A.; Järvelin, K.; Juhola, M.; Laurikkala, J. Focused web crawling in the acquisition of comparable corpora. Inf. Retr. 2008, 11, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, M.H.; Ha, J.; Lee, S. Novel approaches to crawling important pages early. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2012, 33, 707–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukadil, K.; Rekik, M.; Rekik, M.; Ben-Abdallah, H. FC4CD: A new SOA-based Focused Crawler for Cloud service Discovery. Computing 2018, 100, 1081–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajiv, S.; Navaneethan, C. A Supervised Learning-Based Approach for Focused Web Crawling for IoMT Using Global Co-Occurrence Matrix. Expert Syst. 2022; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gan, Z.; Xi, T.; Du, Y.; Wu, J.; He, Y.; Jiang, P.; Liu, X.; Lai, X. A semantic and intelligent focused crawler based on semantic vector space model and membrane computing optimization algorithm. Appl. Intell. 2022, 53, 7390–7407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Du, Y.J. A novel focused crawler based on cell-like membrane computing optimization algorithm. Neurocomputing 2014, 123, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Bhatia, R.; Garg, S.; Aujla, G.S.; Mann, R.S. Fuzzy Based Efficient Mechanism for URL Assignment in Dynamic Web Crawler. In Advanced Informatics for Computing Research: First International Conference, ICAICR 2017, Jalandhar, India, 17–18 March 2017, Revised Selected Papers; Singh, D., Raman, B., Luhach, A.K., Lingras, P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, G.K.; Pateriya, R.K.; Kaushik, P. An efficient focused crawler using LSTM-CNN based deep learning. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2023, 14, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.M.; Lee, S.; Fox, E.A. Focused crawler for events. Int. J. Digit. Libr. 2018, 19, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, M.; Balakireva, L.; Van de Sompel, H. Focused crawl of web archives to build event collections. In Proceedings of the 10th ACM Conference on Web Science, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 27–30 May 2018; pp. 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, P.; Macedo, J.; Craveiro, O.; Madeira, H. Time-Aware Focused Web Crawling. In Advances in Information Retrieval; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 534–539. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Hauff, C. Temporal Query Intent Disambiguation using Time-Series Data. In Proceedings of the 39th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Pisa, Italy, 17–21 July 2016; pp. 1017–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, R.; Jorge Alípio, M.; Dias, G. Using Web Snippets and Web Query-logs to Measure Implicit Temporal Intents in Queries. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Query Representation and Understanding of the 34th ACM Annual SIGIR Conference (SIGIR 2011), Beijing, China, 24–28 July 2011. 4p. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, S.P.; Yoo, H.S.; Choi, S. Ten years of research change using Google Trends: From the perspective of big data utilizations and applications. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 130, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.W.; Margolin, D. Collective Information Seeking during a Health Crisis: Predictors of Google Trends during COVID-19. Health Commun. 2023; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, V.S.; McKee, M.; Stuckler, D. Google Trends: Opportunities and limitations in health and health policy research. Health Policy 2019, 123, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simionescu, M.; Cifuentes-Faura, J. Can unemployment forecasts based on Google Trends help government design better policies? An investigation based on Spain and Portugal. J. Policy Model. 2022, 44, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simionescu, M.; Cifuentes-Faura, J. Forecasting National and Regional Youth Unemployment in Spain Using Google Trends. Soc. Indic. Res. 2022, 164, 1187–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Using Google Trends to Track the Global Interest in International Financial Reporting Standards: Evidence from Big Data. Intell. Syst. Account. Financ. Manag. 2023; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Perucich, F. Assessing the Accuracy of Google Trends for Predicting Presidential Elections: The Case of Chile, 2006–2021. Data 2022, 7, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, R.A.; Ladle, R.; Jaric, I.; Malhado, A.C.M.; Mittermeier, J.C.; Roll, U.; Soriano-Redondo, A.; Verissimo, D.; Fink, C.; Hausmann, A.; et al. Digital data sources and methods for conservation culturomics. Conserv. Biol. 2021, 35, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Lin, J. Comparative Analysis of Temporal-Spatial Evolution of Online Public Opinion Based on Search Engine Attention:Cases of Google Trends and Baidu Index. J. Intell. 2013, 32, 7–10+16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B. Web Data Mining: Exploring Hyperlinks, Contents, and Usage Data, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 217–218. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Philip, S.Y. Time sensitive ranking with application to publication search. In Link Mining: Models, Algorithms, and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 187–209. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, R.M.; Premkumar, M.; Jangir, P.; Elkotb, M.A.; Elavarasan, R.M.; Nisar, K.S. IRKO: An Improved Runge-Kutta Optimization Algorithm for Global Optimization Problems. CMC-Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 70, 4803–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Dhar, A.R.; Roy, S.S. A partition cum unification based genetic- firefly algorithm for single objective optimization. Sadhana 2021, 46, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Akbari, M.A.; Jun, C.Y.; Bateni, S.M.; Zare, M.; Zahedi, A.; Pai, H.T.; Band, S.S.; Moslehpour, M.; Chau, K.W. Circulatory System Based Optimization (CSBO): An expert multilevel biologically inspired meta-heuristic algorithm. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2022, 16, 1483–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
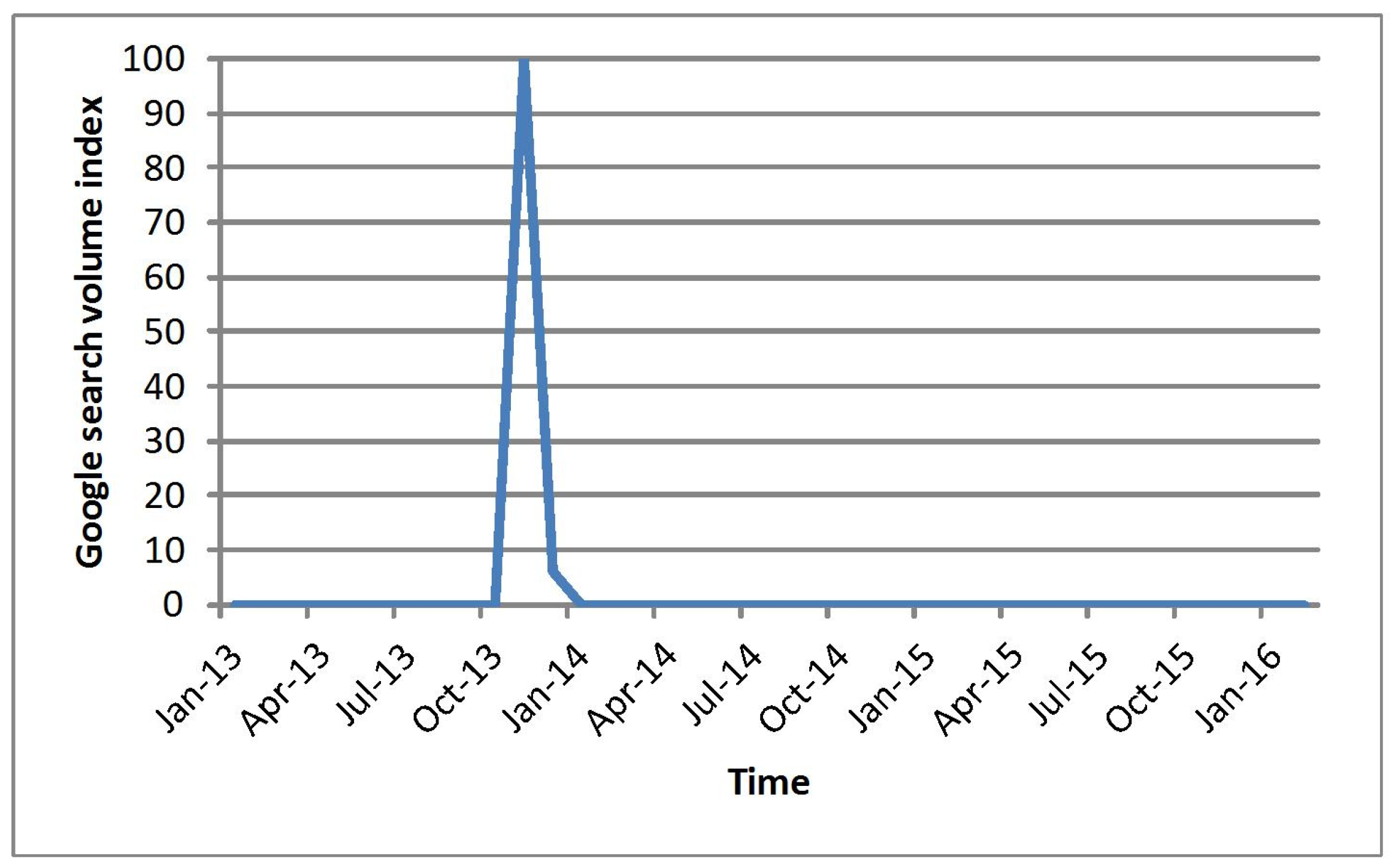



| Event Name | Time Interval When the Initial Search Volume Index Is Zero | Time When the Initial Search Volume Index Is Greater than Zero | Detected Start Time | Actual Start Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WenChuan earthquake | [2004-01, 2008-04] | 2008-05 | 2008-05 | 2008-05-21 |
| YuShu earthquake | [2004-01, 2010-03] | 2010-04 | 2010-04 | 2010-04-14 |
| Typhoon HaiYan | [2004-01, 2013-10] | 2013-11 | 2013-11 | 2013-11-03 |
| Haiti earthquake | [2004-01, 2009-12] | 2010-01 | 2010-01 | 2010-01-12 |
| Indian Ocean Tsunami | [2004-01, 2004-11] | 2004-12 | 2004-12 | 2004-12-26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Hou, D. A Focused Event Crawler with Temporal Intent. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074149
Wu H, Hou D. A Focused Event Crawler with Temporal Intent. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(7):4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074149
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Hao, and Dongyang Hou. 2023. "A Focused Event Crawler with Temporal Intent" Applied Sciences 13, no. 7: 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074149
APA StyleWu, H., & Hou, D. (2023). A Focused Event Crawler with Temporal Intent. Applied Sciences, 13(7), 4149. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074149






