Comparative Study for Multi-Speaker Mongolian TTS with a New Corpus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. MnTTS2 Dataset
3.1. MnTTS
3.2. MnTTS2
3.2.1. Text Collection and Narration
3.2.2. Text Preprocessing
3.2.3. Audio Recording and Audio–Text Alignment
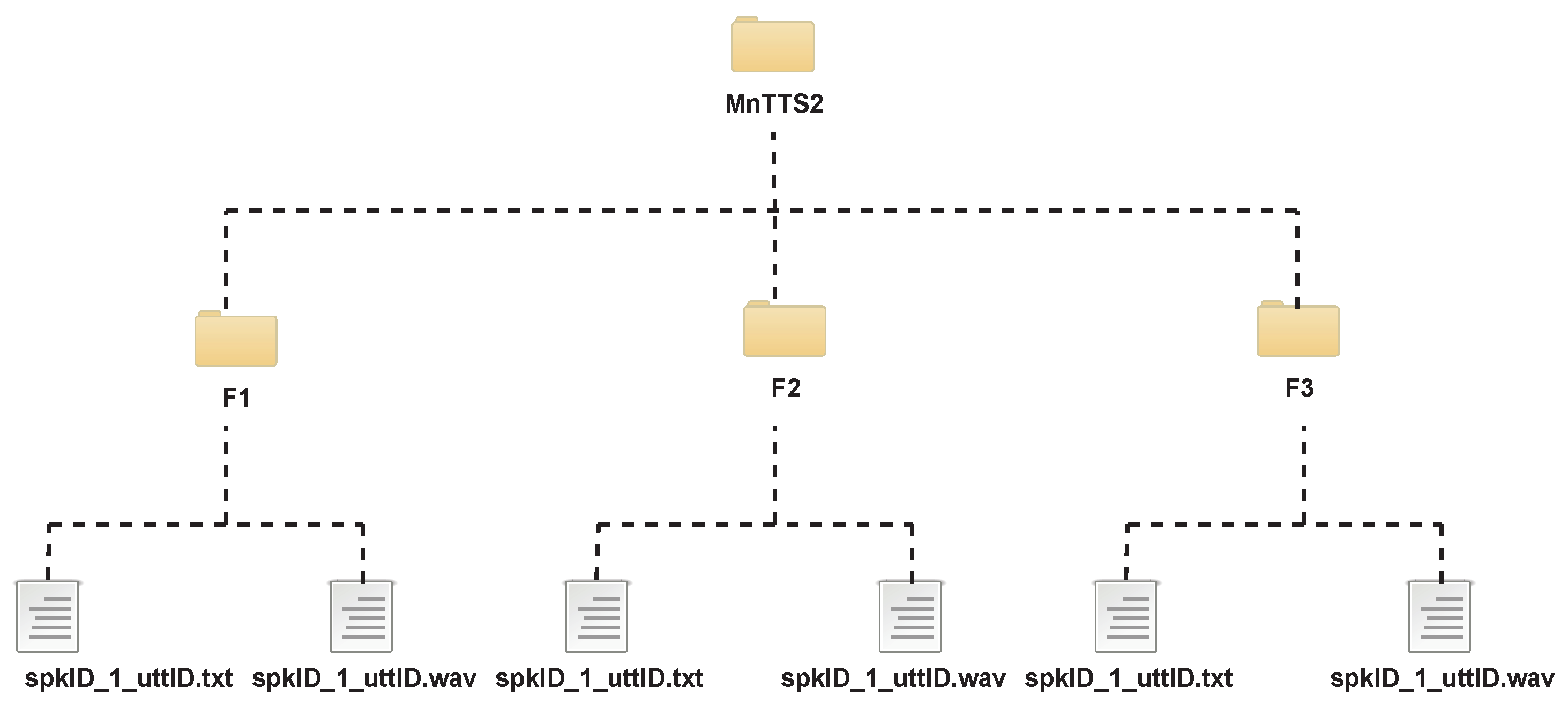
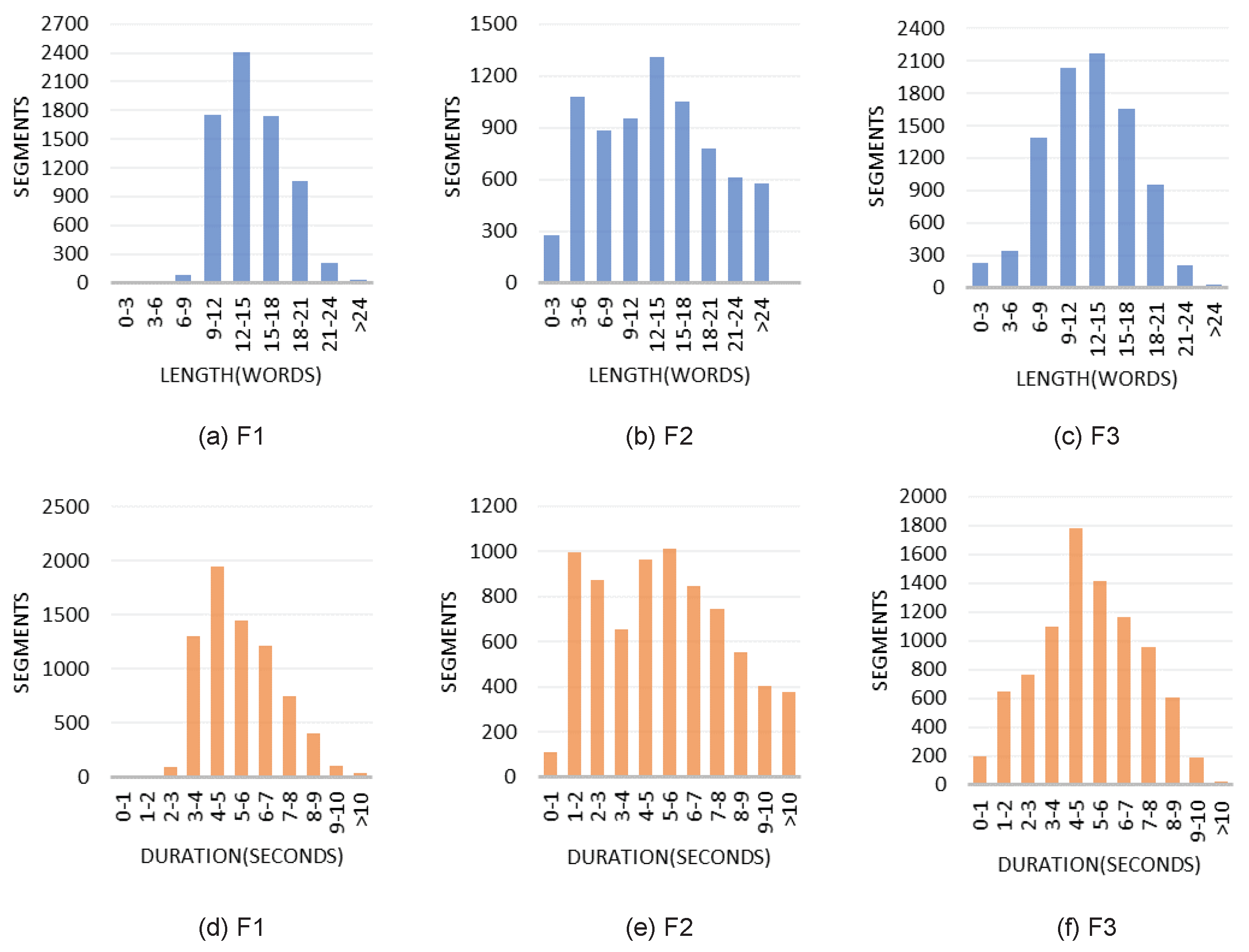
3.2.4. Corpus Structure and Statistics
4. Speech Synthesis Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
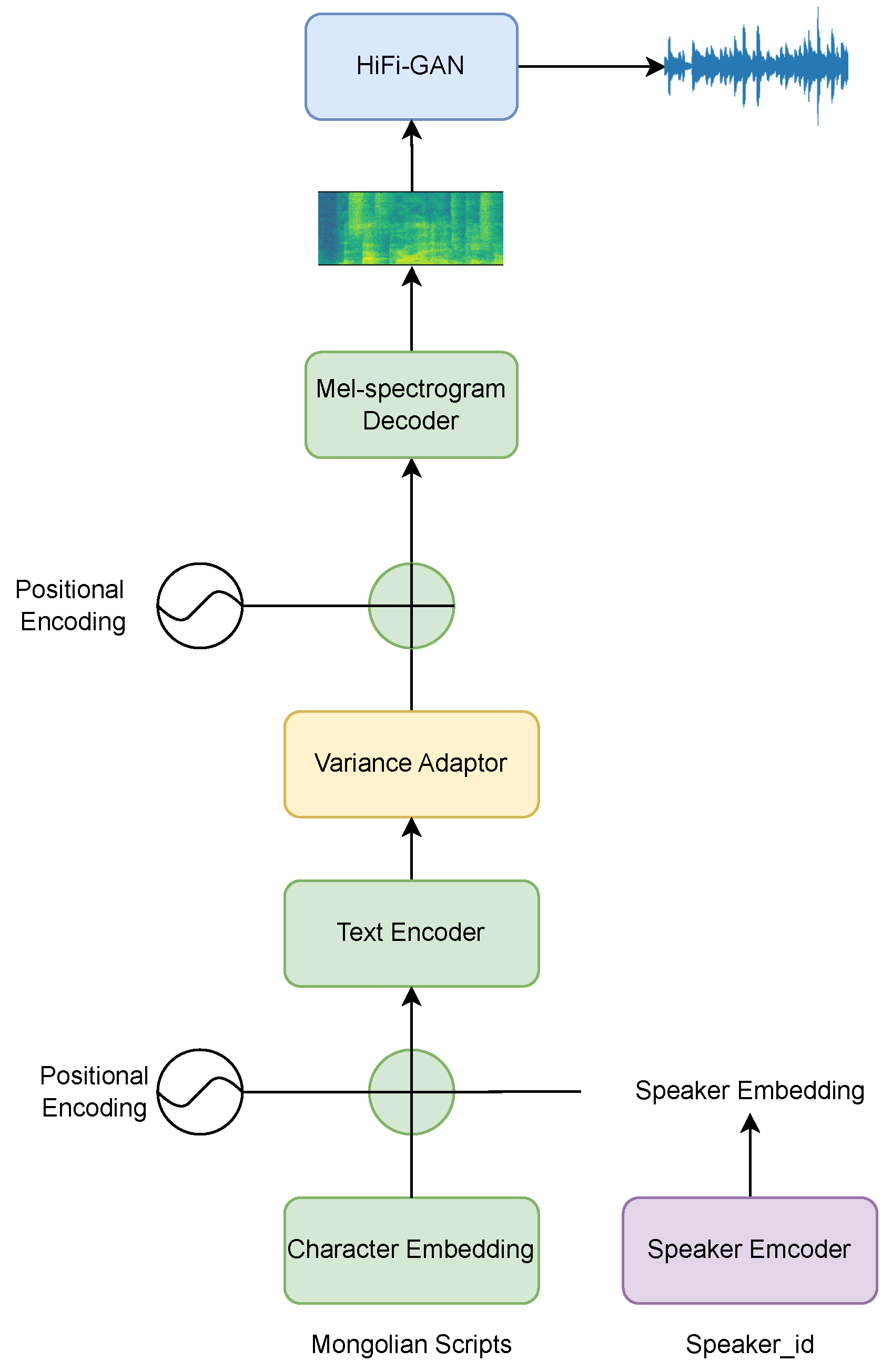
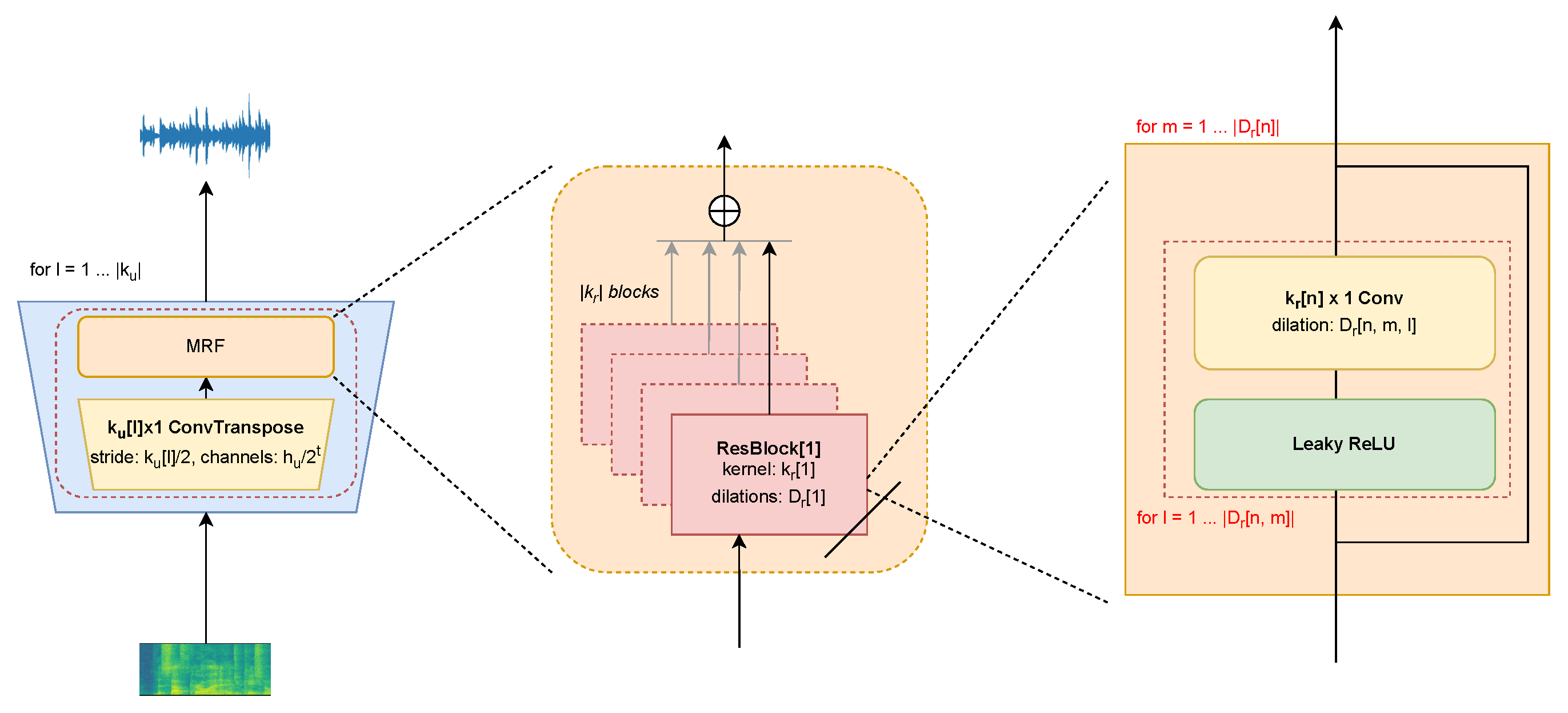
4.1.1. Experimental Steps of TTS Based on the FastSpeech2 Model and HiFi-GAN Vocoder
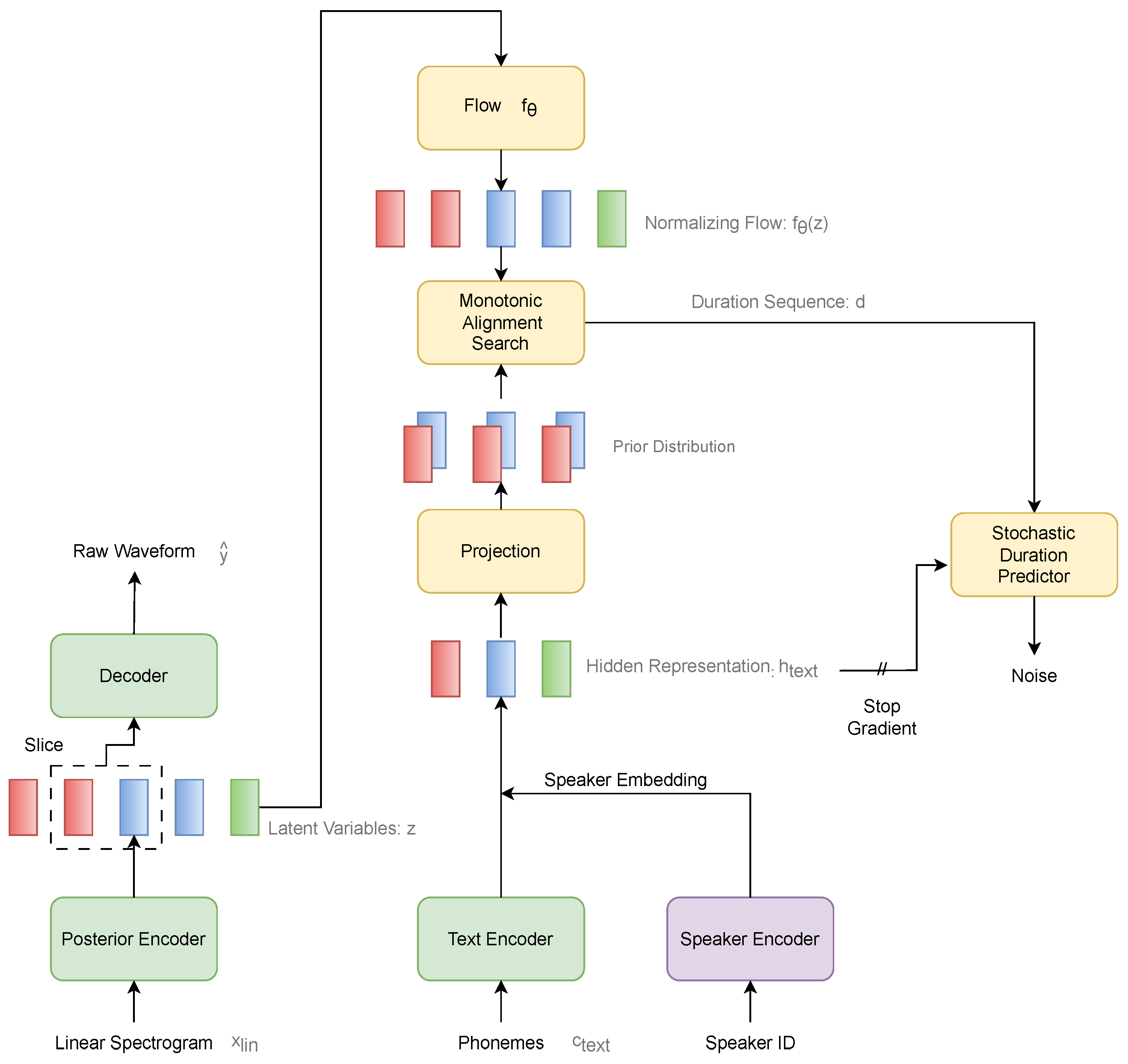
4.1.2. Experimental Steps of TTS Based on the VITS Model
4.2. Naturalness Evaluation
4.3. Speaker Similarity Evaluation
4.4. Robustness Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, J.; Pang, R.; Weiss, R.J.; Schuster, M.; Jaitly, N.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Skerrv-Ryan, R.; et al. Natural tts synthesis by conditioning wavenet on mel spectrogram predictions. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 4779–4783. [Google Scholar]
- Charpentier, F.; Stella, M. Diphone synthesis using an overlap-add technique for speech waveforms concatenation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP ’86), Tokyo, Japan, 7–11 April 1986; Volume 11, pp. 2015–2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rabiner, L.R. A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proc. IEEE 1989, 77, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, K.; Van Merriënboer, B.; Bahdanau, D.; Bengio, Y. On the properties of neural machine translation: Encoder-decoder approaches. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1259. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Skerry-Ryan, R.; Stanton, D.; Wu, Y.; Weiss, R.J.; Jaitly, N.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Bengio, S.; et al. Tacotron: Towards End-to-End Speech Synthesis. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2017, Stockholm, Sweden, 20–24 August 2017; pp. 4006–4010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, M. Neural speech synthesis with transformer network. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 29–31 January 2019; Volume 33, pp. 6706–6713. [Google Scholar]
- Arık, S.Ö.; Chrzanowski, M.; Coates, A.; Diamos, G.; Gibiansky, A.; Kang, Y.; Li, X.; Miller, J.; Ng, A.; Raiman, J.; et al. Deep voice: Real-time neural text-to-speech. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; pp. 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Bradbury, J.; Xiong, C.; Li, V.O.; Socher, R. Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Tan, X.; Qin, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, T.Y. Fastspeech: Fast, robust and controllable text to speech. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Hu, C.; Tan, X.; Qin, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, T.Y. FastSpeech 2: Fast and High-Quality End-to-End Text to Speech. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26–30 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- van den Oord, A.; Dieleman, S.; Zen, H.; Simonyan, K.; Vinyals, O.; Graves, A.; Kalchbrenner, N.; Senior, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. WaveNet: A Generative Model for Raw Audio. In Proceedings of the 9th ISCA Speech Synthesis Workshop, Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 13–15 September 2016; p. 125. [Google Scholar]
- Kalchbrenner, N.; Elsen, E.; Simonyan, K.; Noury, S.; Casagrande, N.; Lockhart, E.; Stimberg, F.; Oord, A.; Dieleman, S.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Efficient neural audio synthesis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 25–31 July 2018; pp. 2410–2419. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.; Kumar, R.; de Boissiere, T.; Gestin, L.; Teoh, W.Z.; Sotelo, J.; de Brébisson, A.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.C. Melgan: Generative adversarial networks for conditional waveform synthesis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Kim, J.; Bae, J. Hifi-gan: Generative adversarial networks for efficient and high fidelity speech synthesis. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 17022–17033. [Google Scholar]
- Bulag, U.E. Mongolian ethnicity and linguistic anxiety in China. Am. Anthropol. 2003, 105, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yin, P.; Liu, R.; Bao, F.; Gao, G. MnTTS: An Open-Source Mongolian Text-to-Speech Synthesis Dataset and Accompanied Baseline. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Asian Language Processing (IALP), Singapore, 27–28 October 2022; pp. 184–189. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Kong, J.; Son, J. Conditional variational autoencoder with adversarial learning for end-to-end text-to-speech. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 5530–5540. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, K.; Liu, B.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R.; Bao, F.; Gao, G. MnTTS2: An Open-Source Multi-Speaker Mongolian Text-to-Speech Synthesis Dataset. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2301.00657. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, K.; Johnson, L. The LJ Speech Dataset. 2017. Available online: https://keithito.com/LJ-Speech-Dataset (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Zen, H.; Dang, V.; Clark, R.; Zhang, Y.; Weiss, R.J.; Jia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y. LibriTTS: A corpus derived from LibriSpeech for text-to-speech. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.02882. [Google Scholar]
- Veaux, C.; Yamagishi, J.; MacDonald, K. CSTR VCTK Corpus: English Multi-Speaker Corpus for CSTR Voice Cloning Toolkit; The Centre for Speech Technology Research (CSTR), University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Bu, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, M. AISHELL-3: A Multi-speaker Mandarin TTS Corpus and the Baselines. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11567. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.S.; Chan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chiu, C.C.; Zoph, B.; Cubuk, E.D.; Le, Q.V. SpecAugment: A Simple Data Augmentation Method for Automatic Speech Recognition. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08779. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, P.; Yang, Z.; Hu, H.; Tan, T.; Qian, Y. Data augmentation using conditional generative adversarial networks for robust speech recognition. In Proceedings of the 2018 11th International Symposium on Chinese Spoken Language Processing (ISCSLP), Taipei City, Taiwan, 26–29 November 2018; pp. 121–125. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Tian, X.; Lee, G.; Das, R.K.; Li, H. End-to-end code-switching tts with cross-lingual language model. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 7614–7618. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, H.B. Unsupervised learning. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.J. Semi-Supervised Learning Literature Survey; Department of Computer Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Madison: Madison, WI, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, K.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M.; Wang, D. A survey of transfer learning. J. Big Data 2016, 3, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, A.; Bao, F.; Gao, G.; Shan, Y.; Liu, R. Mongolian emotional speech synthesis based on transfer learning and emotional embedding. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Asian Language Processing (IALP), Yantai, China, 23–25 October 2021; pp. 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Bao, F.; Gao, G.; Wang, W. Mongolian prosodic phrase prediction using suffix segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Asian Language Processing (IALP), Tainan, Taiwan, 21–23 November 2016; pp. 250–253. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Bao, F.; Gao, G.; Wang, Y. Mongolian text-to-speech system based on deep neural network. In Proceedings of the National Conference on Man-Machine Speech Communication, Lianyungang, China, 11–13 October 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Bao, F.; Gao, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y. Improving Mongolian Phrase Break Prediction by Using Syllable and Morphological Embeddings with BiLSTM Model. In Proceedings of the Interspeech 2018, Hyderabad, India, 2–6 September 2018; pp. 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Zhi, T.; Shi, Y.; Du, W.; Li, G.; Wang, D. M2ASR-MONGO: A Free Mongolian Speech Database and Accompanied Baselines. In Proceedings of the 24th Conference of the Oriental COCOSDA International Committee for the Co-ordination and Standardisation of Speech Databases and Assessment Techniques (O-COCOSDA 2021), Singapore, 18–20 November 2021; pp. 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streijl, R.C.; Winkler, S.; Hands, D.S. Mean opinion score (MOS) revisited: Methods and applications, limitations and alternatives. Multimed. Syst. 2016, 22, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Speaker ID | F1 | F2 | F3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistical Unit | |||||
| Character | Total | 572,016 | 459,213 | 601,366 | |
| Mean | 79 | 61 | 67 | ||
| Min | 12 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Max | 189 | 188 | 190 | ||
| Word | Total | 88,209 | 71,245 | 92,719 | |
| Mean | 12 | 9 | 10 | ||
| Min | 3 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Max | 29 | 30 | 29 | ||
| Speaker ID | F1 | F2 | F3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| System | ||||
| FastSpeech2+Griffin-Lim | 3.56 ± 0.18 | 3.59 ± 0.04 | 3.86 ± 0.12 | |
| FastSpeech2+HiFi-GAN | 4.02 ± 0.18 | 4.15 ± 0.06 | 4.29 ± 0.11 | |
| VITS | 4.60 ± 0.07 | 4.55 ± 0.08 | 4.62 ± 0.09 | |
| Ground Truth | 4.73 ± 0.08 | 4.70 ± 0.14 | 4.68 ± 0.09 | |
| Speaker ID | F1 | F2 | F3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| System | ||||
| FastSpeech2+HiFi-GAN | 4.58 ± 0.21 | 4.04 ± 0.16 | 4.12 ± 0.10 | |
| VITS | 4.56 ± 0.09 | 4.67 ± 0.08 | 4.54 ± 0.07 | |
| System | Error Types | F1 | F2 | F3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FastSpeech2+HiFi-GAN | Repeated words | 3 | 1 | 1 |
| Skipped words | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mispronounced words | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Incomplete words | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Long pauses | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
| Nonverbal sounds | 1 | 2 | 0 | |
| Total | 6 | 9 | 3 | |
| VITS | Repeated words | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| Skipped words | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mispronounced words | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Incomplete words | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Long pauses | 0 | 3 | 0 | |
| Nonverbal sounds | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
| Total | 2 | 10 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, K.; Liu, B.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R.; Bao, F.; Gao, G. Comparative Study for Multi-Speaker Mongolian TTS with a New Corpus. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4237. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074237
Liang K, Liu B, Hu Y, Liu R, Bao F, Gao G. Comparative Study for Multi-Speaker Mongolian TTS with a New Corpus. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(7):4237. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074237
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Kailin, Bin Liu, Yifan Hu, Rui Liu, Feilong Bao, and Guanglai Gao. 2023. "Comparative Study for Multi-Speaker Mongolian TTS with a New Corpus" Applied Sciences 13, no. 7: 4237. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074237
APA StyleLiang, K., Liu, B., Hu, Y., Liu, R., Bao, F., & Gao, G. (2023). Comparative Study for Multi-Speaker Mongolian TTS with a New Corpus. Applied Sciences, 13(7), 4237. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074237








