Microalgal Systems, a Green Solution for Wastewater Conventional Pollutants Removal, Disinfection, and Reduction of Antibiotic Resistance Genes Prevalence?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Urban Wastewater Physicochemical Characterization
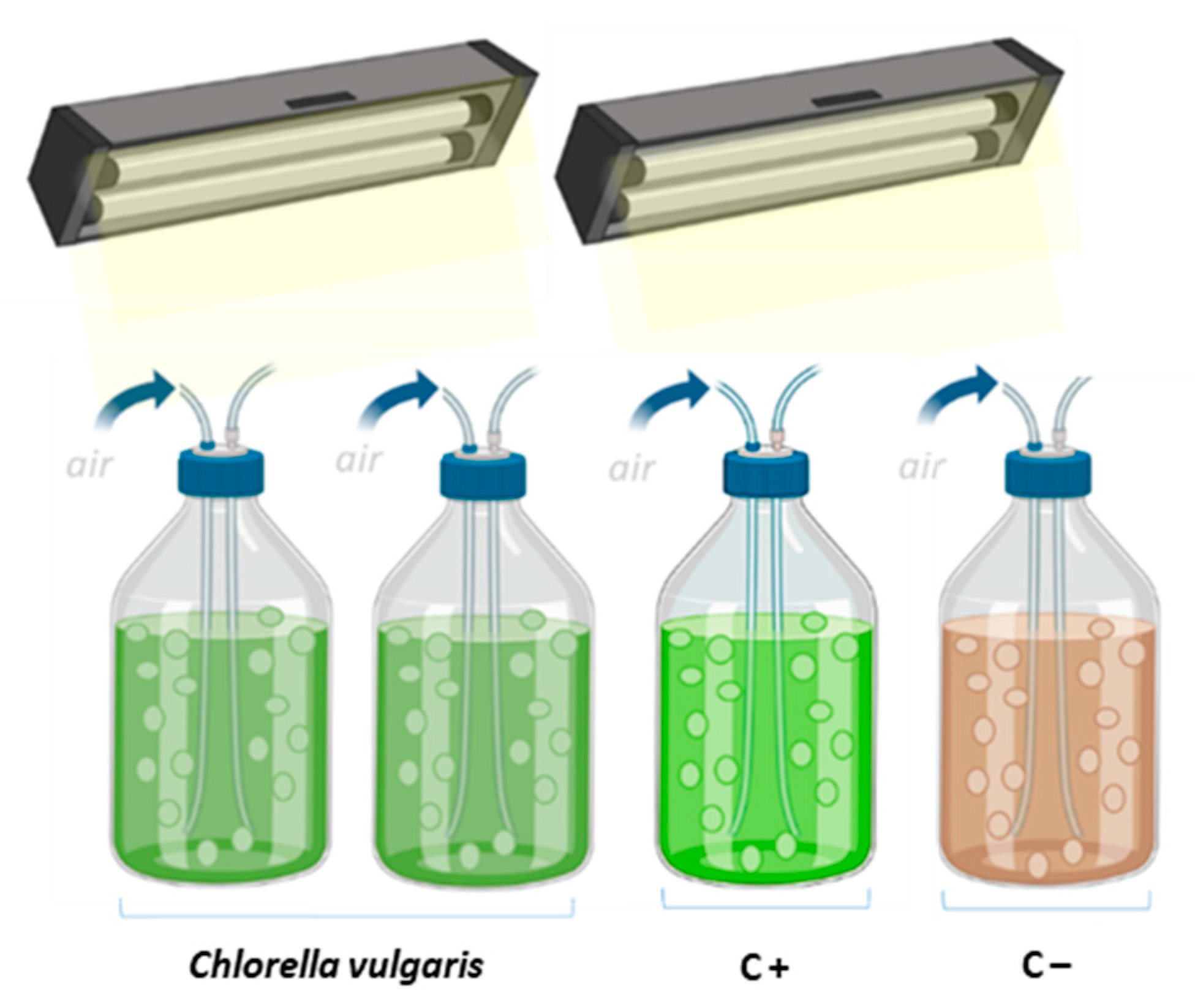
2.2. Photobioreactors Setup
2.3. Microalgal Biomass Quantification and Microalgae Identification
2.4. Microalgal Pollutants Removal
2.5. Enumeration of Culturable Microorganisms
2.6. DNA Extraction
2.7. Quantification of 16S rRNA, intl1 and Antibiotic Resistance Genes
2.8. Treated Water Storage
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
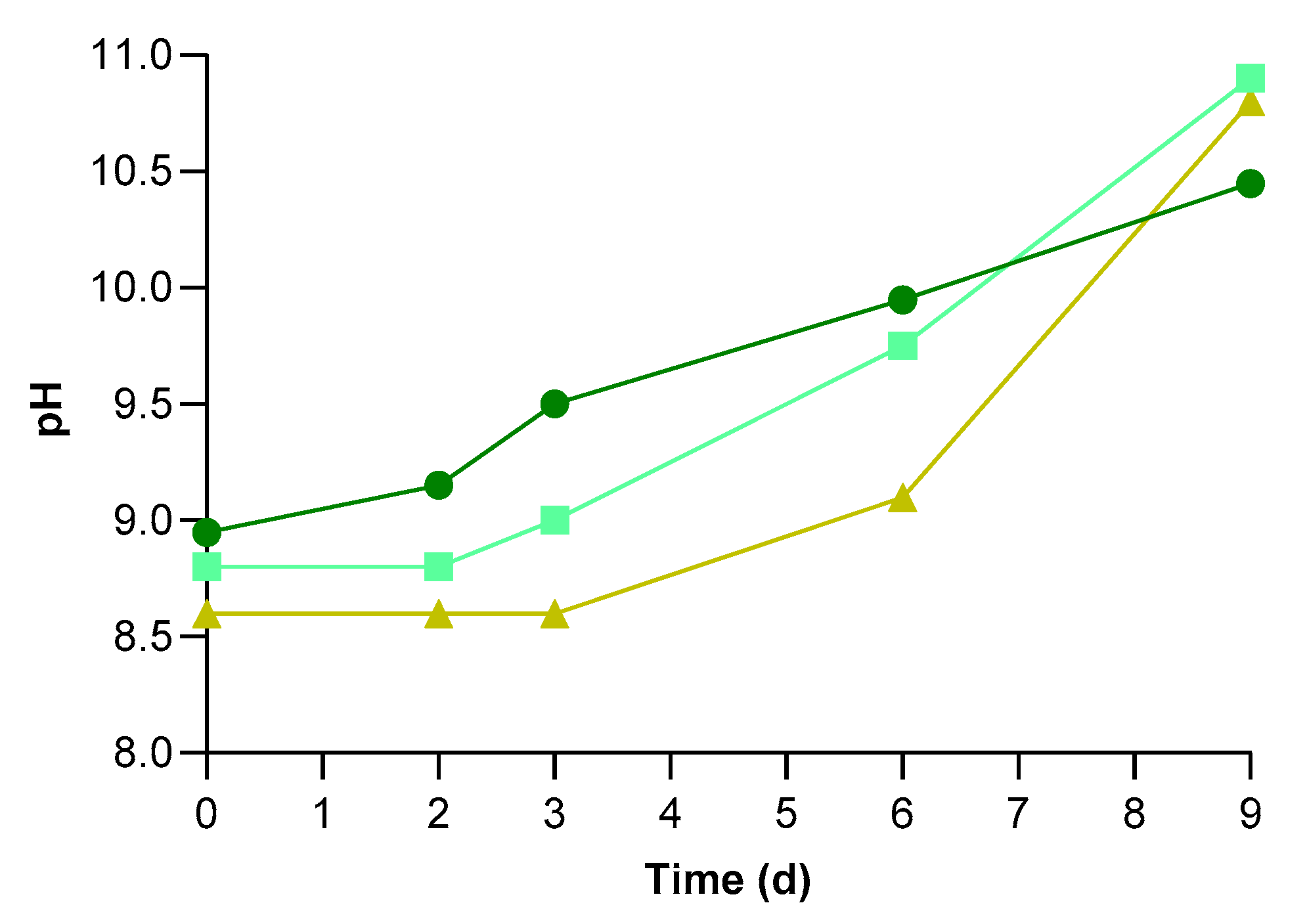
3.1. Microalgal Growth
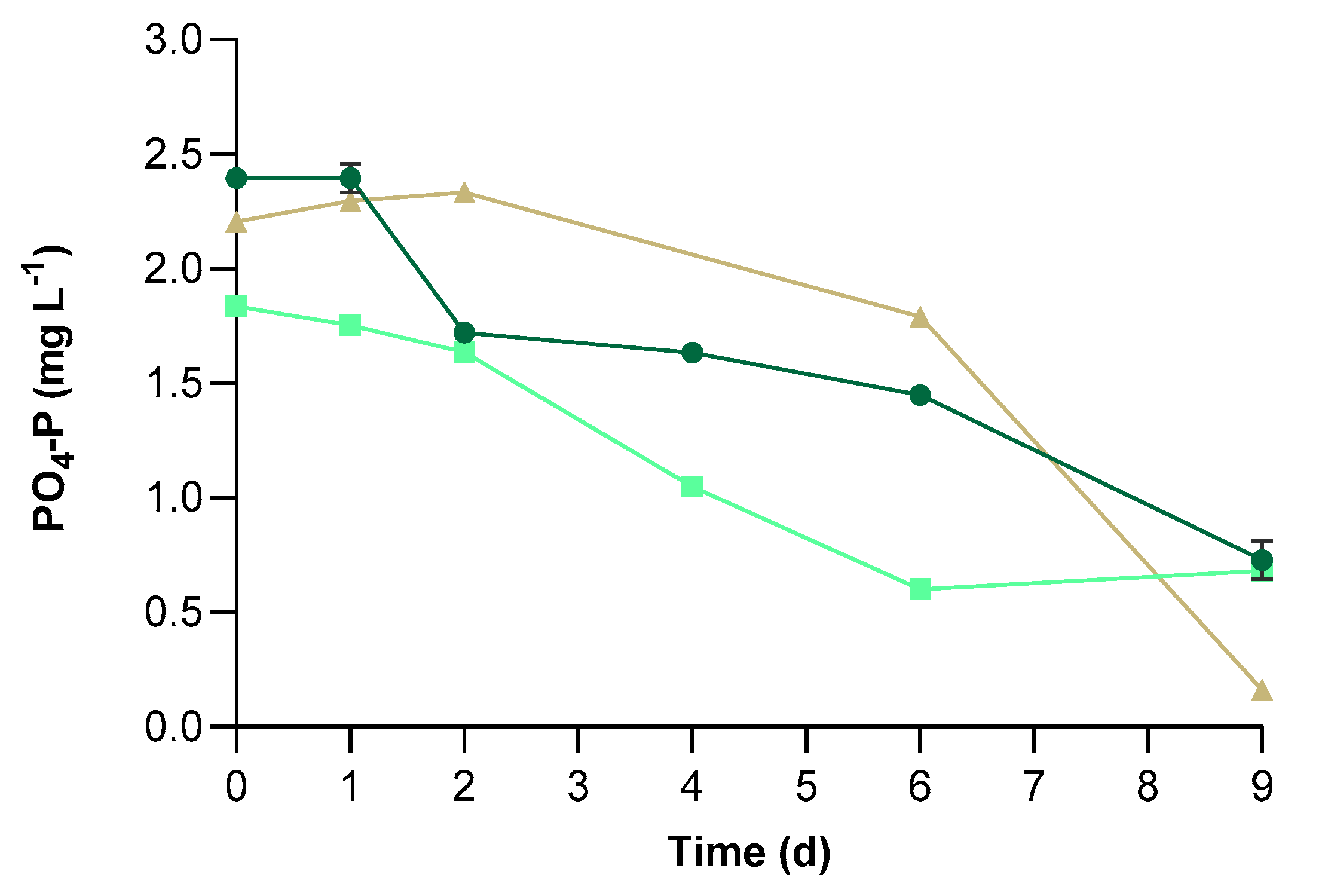
3.2. Physical-Chemical Characteristics of UWW and Conventional Pollutants Removal
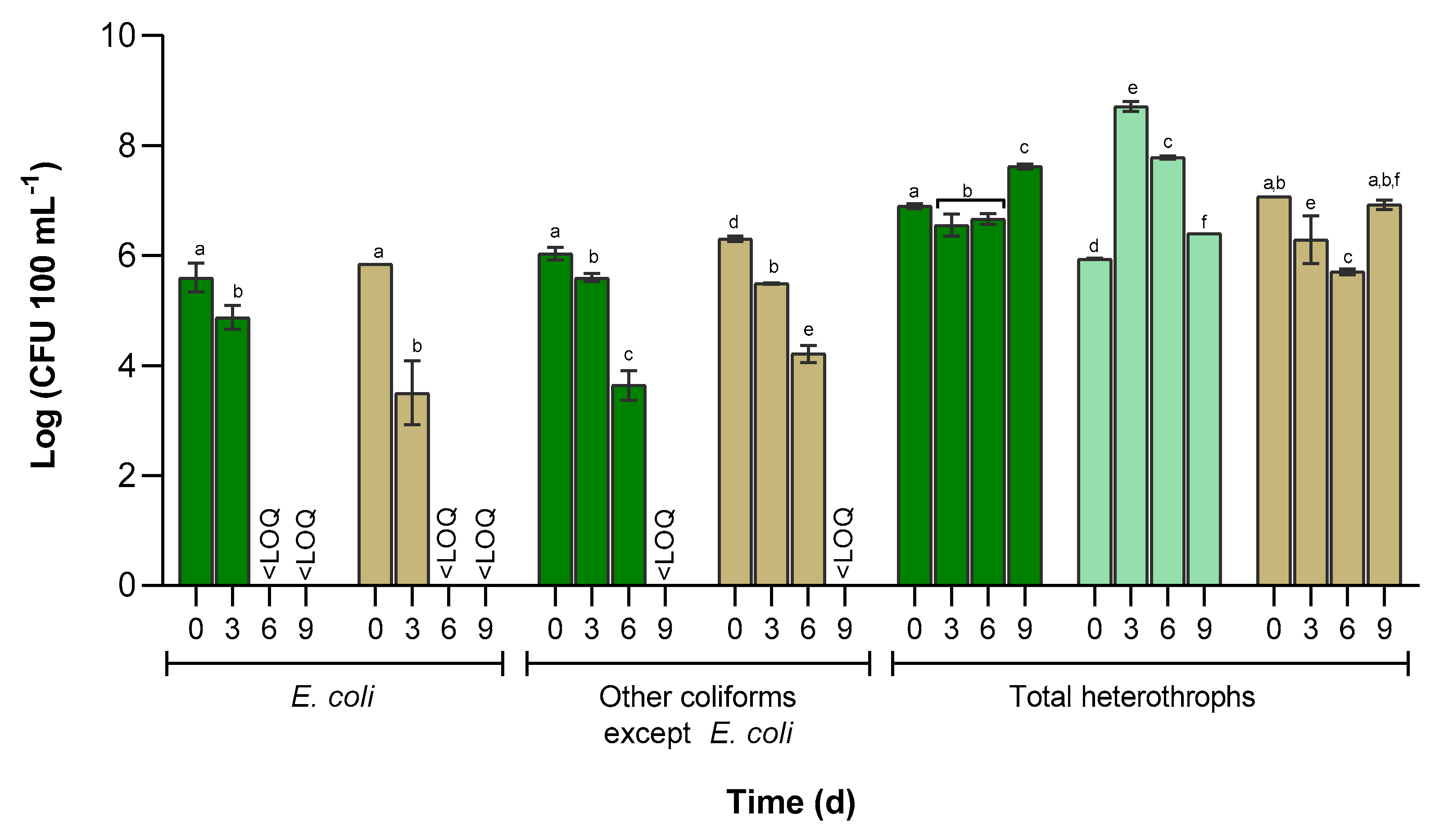
3.3. Cultivable Bacterial Abundance
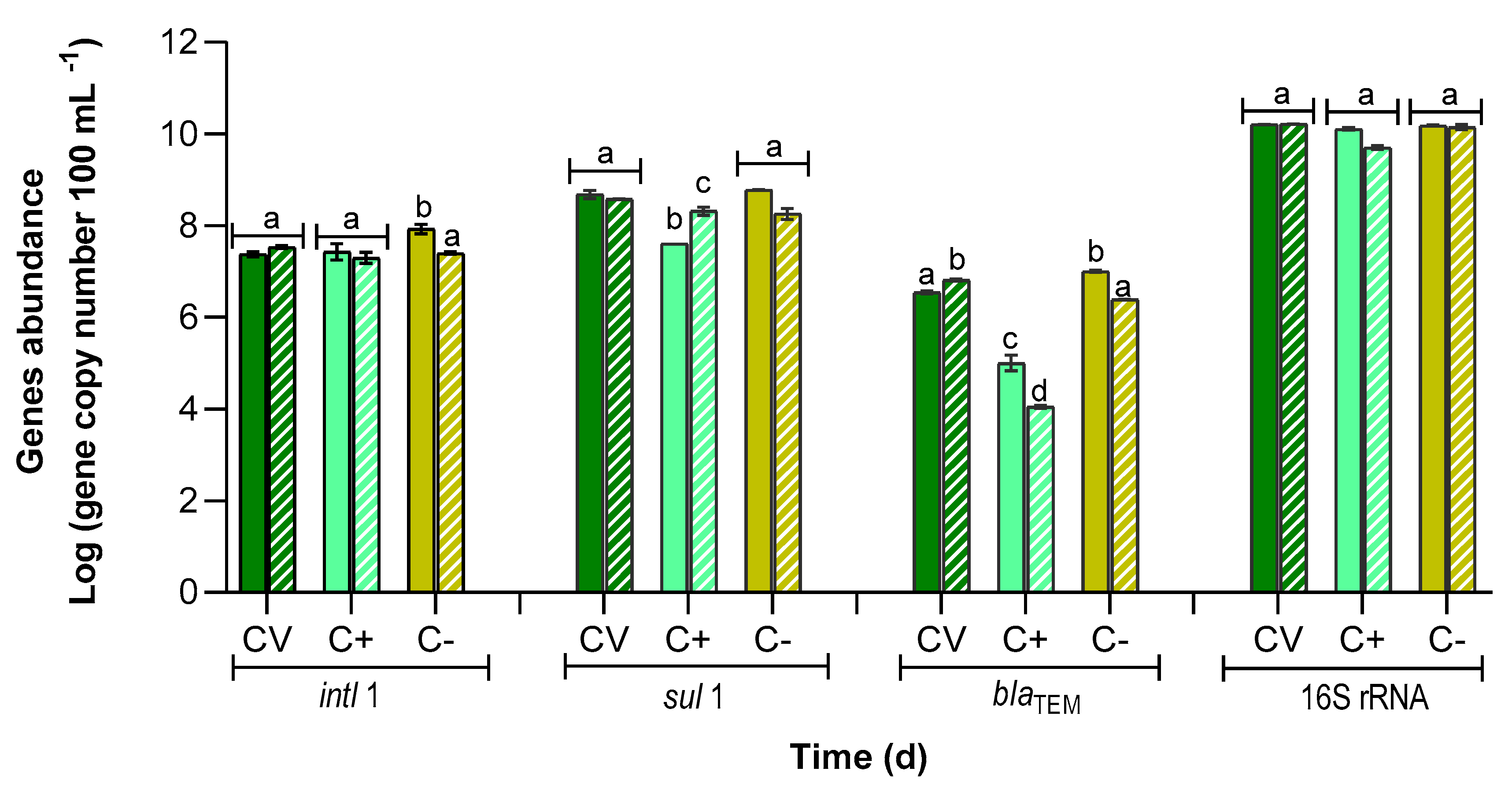
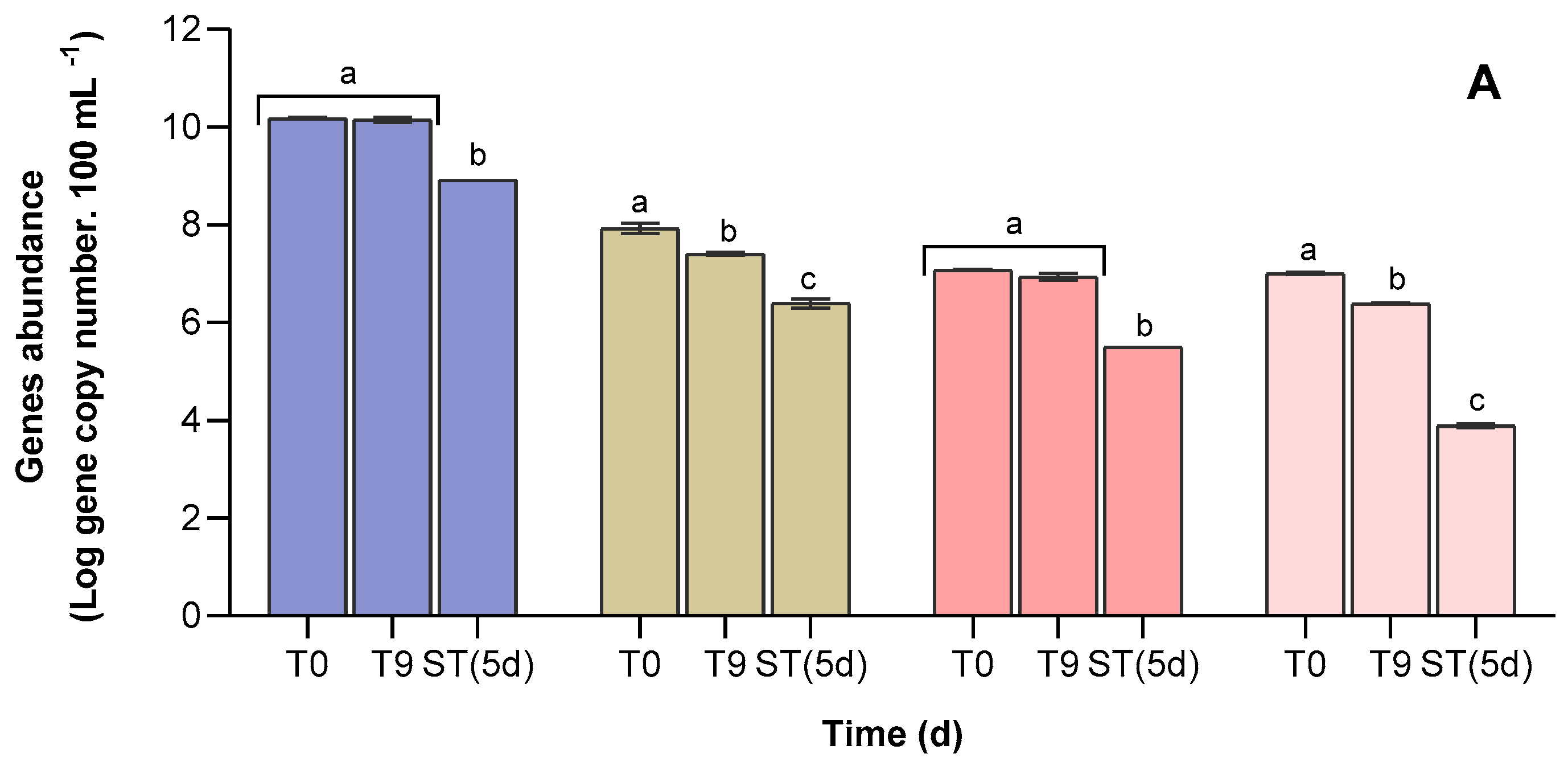
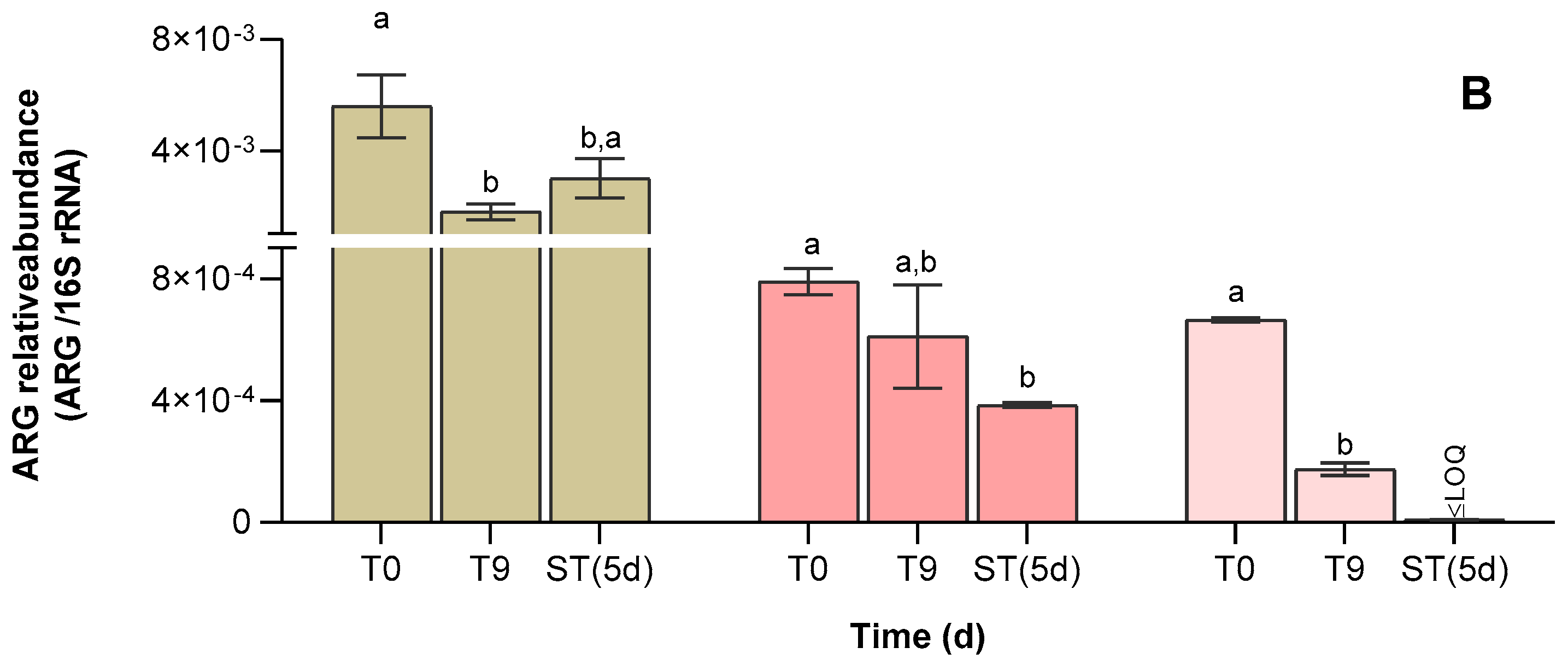
3.4. Abundance of Antibiotic Resistance Genes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, E.R.; van Vliet, M.T.H.; Qadir, M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Country-level and gridded estimates of wastewater production, collection, treatment and reuse. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Bond, P.L.; Yuan, Z. Metagenomic analysis reveals wastewater treatment plants as hotspots of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements. Water Res. 2017, 123, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Wei, L.; Xiong, Q.; Xu, S.; Li, W.; Lv, S.; Lu, Q.; Wan, L.; Wen, Z.; Zhou, W. Use of microalgae based technology for the removal of antibiotics from wastewater: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruas, G.; Serejo, M.L.; Farias, S.L.; Scarcelli, P.; Boncz, M.Á. Removal of pathogens from domestic wastewater by microalgal-bacterial systems under different cultivation conditions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 10177–10188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B. Towards environment-sustainable wastewater treatment and reclamation by the non-aerated microalgal-bacterial granular sludge process: Recent advances and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Saqib, I.; Zobia, A.; Amjad, K.; Amjad, K. Disinfection methods. In Photocatalysts; Sher Bahadar, K., Kalsoom, A., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2018; Chapter 1. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Wastewater Technology Fact Sheet: Chlorine Desinfection; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.; Shi, J.L.; von Gunten, U.; McCurry, D.L. Ozonation of organic compounds in water and wastewater: A critical review. Water Res. 2022, 213, 118053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Hashemi, H.; Mohammadi, A.; Hung, Y. A review on wastewater disinfection. Int. J. Env. Health Eng. 2013, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerkes-Medrano, D.; Leslie, H.A.; Quinn, B. Microplastics in drinking water: A review and assessment. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2019, 7, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.L.; Pires, J.C.M.; Simões, M. A review on the use of microalgal consortia for wastewater treatment. Algal Res. 2017, 24, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, J.C.G.; Ribeiro, A.R.; Barbosa, M.O.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T. A review on environmental monitoring of water organic pollutants identified by eu guidelines. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollmann, F.; Dietze, S.; Ackermann, J.-U.; Bley, T.; Walther, T.; Steingroewer, J.; Krujatz, F. Microalgae wastewater treatment: Biological and technological approaches. Eng. Life Sci. 2019, 19, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeirinho-Soares, S.; Moreira, N.F.F.; Graça, C.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Silva, A.M.T.; Nunes, O.C. Overgrowth control of potentially hazardous bacteria during storage of ozone treated wastewater through natural competition. Water Res. 2022, 209, 117932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hao, Y.; Yang, T.; Xiao, W.; Pan, M.; Huo, S.; Lyu, T. Enhancing bioenergy production from the raw and defatted microalgal biomass using wastewater as the cultivation medium. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-González, A.; Uggetti, E.; Serrano, L.; Gorchs, G.; Ferrer, I.; Díez-Montero, R. Can microalgae grown in wastewater reduce the use of inorganic fertilizers? J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouki, C.; Venieri, D.; Diamadopoulos, E. Detection and fate of antibiotic resistant bacteria in wastewater treatment plants: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 91, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hall, G.; Champagne, P. Disinfection processes and mechanisms in wastewater stabilization ponds: A review. Environ. Rev. 2018, 26, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, I.; Gómez-Ramos, M.J.; Agüera, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Chemical evaluation of contaminants in wastewater effluents and the environmental risk of reusing effluents in agriculture. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 676–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruas, G.; Serejo, M.L.; Paulo, P.L.; Boncz, M.Á. Evaluation of domestic wastewater treatment using microalgal-bacterial processes: Effect of co2 addition on pathogen removal. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadas, E.; Morales, M.d.M.; Gomez, C.; Acién, F.G.; Muñoz, R. Influence of ph and co2 source on the performance of microalgae-based secondary domestic wastewater treatment in outdoors pilot raceways. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 265, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuah, E.; Lubberding, H.J.; Asante, K.; Gijzen, H.J. The effect of ph on enterococci removal in pistia-, duckweed- and algae-based stabilization ponds for domestic wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 45, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, R.; Guieysse, B. Algal–bacterial processes for the treatment of hazardous contaminants: A review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2799–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Song, L.; Ji, X.; Huang, S.; Yu, Y.; Ye, J.; Xu, W.; Hou, M. Algal-bacterial consortium mediated system offers effective removal of nitrogen nutrients and antibiotic resistance genes. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 362, 127874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, E.M.; Gonçalves, A.L.; Sánchez-Soberón, F.; Ratola, N.; Pires, J.C.M. Microalgal cultures for the bioremediation of urban wastewaters in the presence of siloxanes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Estrada, L.; Longoria, A.; Okoye, P.U.; Sebastian, P.J. Energy and nutrients recovery from wastewater cultivated microalgae: Assessment of the impact of wastewater dilution on biogas yield. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Lei, Z. Microalgal-bacterial aggregates for wastewater treatment: A mini-review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 8, 100199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Method 352.1: Nitrogen, Nitrate (Colorimetric, Brucine) by Spectrophotometer; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, A.; Brito, A.; Janknecht, P.; Proença, M.F.; Nogueira, R. Quantification of humic acids in surface water: Effects of divalent cations, ph, and filtration. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitton, R.; Le Mével, A.; Pidou, M.; Ometto, F.; Villa, R.; Jefferson, B. Influence of microalgal n and p composition on wastewater nutrient remediation. Water Res. 2016, 91, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narciso-da-Rocha, C.; Varela, A.R.; Schwartz, T.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Blatem and vana as indicator genes of antibiotic resistance contamination in a hospital–urban wastewater treatment plant system. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2014, 2, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brankatschk, R.; Bodenhausen, N.; Zeyer, J.; Bürgmann, H. Simple absolute quantification method correcting for quantitative pcr efficiency variations for microbial community samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4481–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The miqe guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time pcr experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y. Revisiting carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus metabolisms in microalgae for wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 144590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, M.; Maia, I.B.; Cunha, P.; Guerra, I.; Magina, T.; Santos, T.; Schulze, P.S.C.; Pereira, H.; Malcata, F.X.; Navalho, J.; et al. Effects of led lighting on nannochloropsis oceanica grown in outdoor raceway ponds. Algal Res. 2022, 64, 102685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.V.; Singh, R.P. Algal consortia based metal detoxification of municipal wastewater: Implication on photosynthetic performance, lipid production, and defense responses. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 151928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wu, G.; Lu, F.; Wang, H.; Lei, A.; Wang, J. Microalgal photoautotrophic growth induces ph decrease in the aquatic environment by acidic metabolites secretion. Biotechnol. Biofuels Bioprod. 2022, 15, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; O’Fallon, J.V.; Chen, S. Bicarbonate produced from carbon capture for algae culture. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- EUR-Lex. Commission directive 98/15/ec of 27 february 1998 amending council directive 91/271/eec with respect to certain requirements established in annex i thereof. Off. J. Eur. Communities 1998, 67, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.C.; Ji, B.; Cao, L. Performance of chlorella sorokiniana-activated sludge consortium treating wastewater under light-limited heterotrophic condition. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, G.; Lee, K. Treatment of real wastewater using co-culture of immobilized chlorella vulgaris and suspended activated sludge. Water Res. 2017, 120, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, L.; Gojkovic, Z.; Munoz, R.; Funk, C. Growth performance and nutrient removal of a chlorella vulgaris-rhizobium sp. Co-culture during mixotrophic feed-batch cultivation in synthetic wastewater. Algal Res. 2019, 44, 101690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Nutrient removal and microalgal biomass production from different anaerobic digestion effluents with chlorella species. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUW Directive. Council Directive of 21 May 1991 concerning urban waste water treatment (91/271/EEC). J. Eur. Commun. 1991, 135, 40–52. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum, J.; Lee, J.; Martin, J.; Bisesi, M.S. Correlation between levels of humic acid and fecal indicator bacteria: A potential predictor of biosolids stabilization. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, S.F.; Queiroz, M.I.; Zepka, L.Q.; Jacob-Lopes, E. Microalgae biotechnology—A brief introduction. In Microalgal Biotechnology; Jacob-Lopes, E., Zepka, L.Q., Queiroz, M.I., Eds.; InTech: London, UK, 2018; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, M.; Wan, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, J.; Liao, M.; Tian, X. The humic acid-like substances released from microcystis aeruginosa contribute to defending against smaller-sized microplastics. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, F.; Liu, N.; Ge, F.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Y. Role of extracellular polymeric substances from chlorella vulgaris in the removal of ammonium and orthophosphate under the stress of cadmium. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Du, J.; Pu, L.; Chen, S. Effects of chlorella extracellular polymeric substances on the aggregation and stability of tio2 nanoparticles as electrolytes. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 209, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboríková, J.; Šutovská, M.; Kazimierová, I.; Jošková, M.; Fraňová, S.; Kopecký, J.; Capek, P. Extracellular polysaccharide produced by chlorella vulgaris—Chemical characterization and anti-asthmatic profile. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies-Colley, R.J.; Donnison, A.M.; Speed, D.J.; Ross, C.; Nagels, J.W. Inactivation of faecal indicator micro-organisms in waste stabilisation ponds: Interactions of environmental factors with sunlight. Water Res. 1999, 33, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.; Champagne, P.; Hall, G. Multivariate statistical analysis of water chemistry conditions in three wastewater stabilization ponds with algae blooms and ph fluctuations. Water Res. 2016, 96, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumacher, G.; Blume, T.; Sekoulov, I. Bacteria reduction and nutrient removal in small wastewater treatment plants by an algal biofilm. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 47, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hamouri, B.; Khallayoune, K.; Bouzoubaa, K.; Rhallabi, N.; Chalabi, M. High-rate algal pond performances in faecal coliforms and helminth egg removals. Water Res. 1994, 28, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, L.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Nguyen, L.N.; Vu, H.P.; Nghiem, L.D. Microalgae-bacteria consortium for wastewater treatment and biomass production. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, B.T.; Gennity, I.; Fitzgerald, P.S.; Ceballos, S.J.; Fiehn, O.; VanderGheynst, J.S. Algal–bacterial synergy in treatment of winery wastewater. NPJ Clean Water 2018, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Deng, L.; Qi, Z.; Wang, W. Constructed microalgal-bacterial symbiotic (mbs) system: Classification, performance, partnerships and perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.J.J.Y.; Chew, K.W.; Khoo, K.S.; Show, P.L.; Chang, J.-S. Prospects and development of algal-bacterial biotechnology in environmental management and protection. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 47, 107684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, M.R.; Gaze, W.H.; Pruden, A.; Smalla, K.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhu, Y.-G. Using the class 1 integron-integrase gene as a proxy for anthropogenic pollution. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Delanka-Pedige, H.M.K.; Munasinghe-Arachchige, S.P.; Abeysiriwardana-Arachchige, I.S.A.; Smith, G.B.; Nirmalakhandan, N.; Zhang, Y. Removal of antibiotic resistance genes in an algal-based wastewater treatment system employing galdieria sulphuraria: A comparative study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Ren, H.; Geng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K.; Ding, L. Occurrence and abundance of tetracycline, sulfonamide resistance genes, and class 1 integron in five wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7276–7284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Values | Units |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 8.6 | - |
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | 85.4 ± 4.7 | mg O2 L−1 |
| Humic Acids (HA) | 10.7 ± 0.3 | mg L−1 |
| Nitrate–nitrogen (NO3–N) | <LOD 1 | mg L−1 |
| Phosphate–phosphorus (PO4–P) | 2.2 ± 0.1 | mg L−1 |
| PBR | MCCmax (Cells mL−1) | μmax (d−1) | PX,avg (Cells mL−1 d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CV | (6.3 ± 0.4) × 105 a | 0.087 ± 0.002 a | (1.7 ± 0.6) × 104 a |
| C+ | (8.1 ± 0.2) × 105 b | 0.115 ± 0.045 a | (5.1 ± 0.2) × 104 b |
| C− | (5.5 ± 0.1) × 105 a | 0.687 ± 0.065 b | (9.0 ± 0.3) × 104 c |
| PBR | P0 (mg L−1) | MR (mg L−1) | RE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CV | 2.40 ± 0.02 a | 1.67 ± 0.09 a | 69.60 ± 3.44 a |
| C+ | 1.83 ± 0.02 c | 1.15 ± 0.03 b | 62.91 ± 0.61 b |
| C− | 2.20 ± 0.01 b | 2.04 ± 0.03 c | 92.62 ± 0.10 c |
| PBR | intl1 | sul1 | blaTEM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalence | RRG (%) | Prevalence | RRG (%) | Prevalence | RRG (%) | ||||
| T0 | T9 | T0 | T9 | T0 | T9 | ||||
| CV | (1.5 ± 0.1) × 10−3 a | (2.0 ± 0.1) × 10−3 a | −40.0 ± 6.1 a | (3.0 ± 0.1) × 10−2 a | (2.3 ± 0.1) × 10−2 a | 22.3 ± 13.9 a | (2.2 ± 0.1) × 10−4 a | (4.0 ± 0.3) × 10−4 b | −85.6 ± 4.9 a |
| C+ | (2.2 ± 1.0) × 10−3 a,b | (4.0 ± 1.5) × 10−3 a,b | 27.2 ± 54.1 b | (3.1 ± 0.1) × 10−3 a | (4.2 ± 0.1) × 10−2 a | −422.6 ± 113.5 b | (8.1 ± 2.4) × 10−6 c | (2.2 ± 0.1) × 10−6 d | 89.2 ± 5.1 b |
| C− | (5.6 ± 1.2) × 10−3 b | (1.8 ± 0.3) × 10−3 a,c | 70.4 ± 9.2 c | (3.9 ± 0.1) × 10−2 a | (1.3 ± 0.1) × 10−2 a | 69.2 ± 7.5 c | (6.6 ± 0.1) × 10−4 e | (1.7 ± 0.2) × 10−4 a | 75.7 ± 1.6 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaro, H.M.; Sousa, J.F.; Salgado, E.M.; Pires, J.C.M.; Nunes, O.C. Microalgal Systems, a Green Solution for Wastewater Conventional Pollutants Removal, Disinfection, and Reduction of Antibiotic Resistance Genes Prevalence? Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074266
Amaro HM, Sousa JF, Salgado EM, Pires JCM, Nunes OC. Microalgal Systems, a Green Solution for Wastewater Conventional Pollutants Removal, Disinfection, and Reduction of Antibiotic Resistance Genes Prevalence? Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(7):4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074266
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaro, Helena M., Joana F. Sousa, Eva M. Salgado, José C. M. Pires, and Olga C. Nunes. 2023. "Microalgal Systems, a Green Solution for Wastewater Conventional Pollutants Removal, Disinfection, and Reduction of Antibiotic Resistance Genes Prevalence?" Applied Sciences 13, no. 7: 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074266
APA StyleAmaro, H. M., Sousa, J. F., Salgado, E. M., Pires, J. C. M., & Nunes, O. C. (2023). Microalgal Systems, a Green Solution for Wastewater Conventional Pollutants Removal, Disinfection, and Reduction of Antibiotic Resistance Genes Prevalence? Applied Sciences, 13(7), 4266. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074266











