A Screening Model of Antibacterial Agents Based on Escherichia coli Cell-Division Protein
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains, Plasmids, and Reagents
2.2. Cloning of the ftsZ Gene and Construction of the Recombinant Plasmids
2.3. Recombinant Expression of FtsZ Protein
2.4. Isolation and Purification of the Recombinant FtsZ Protein
2.5. Determination of the GTPase Activity of the Recombinant FtsZ Protein
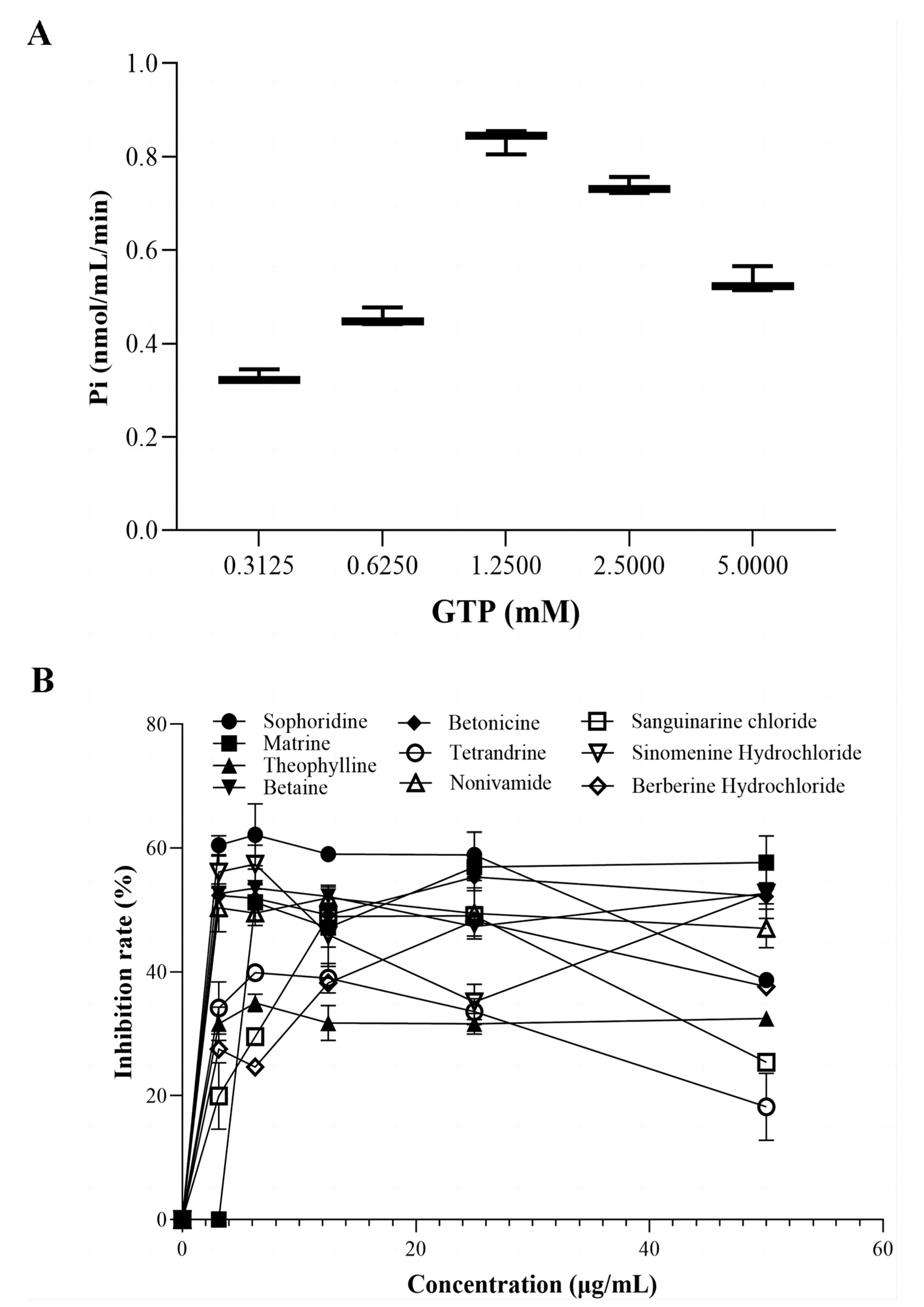
2.6. Screening of Alkaloids Based on FtsZ GTPase Activity
2.7. Antibacterial Activity of Alkaloids
2.8. Cytotoxicity of Alkaloids
2.9. Interaction of Berberine Hydrochloride and the Recombinant FtsZ Protein
3. Results
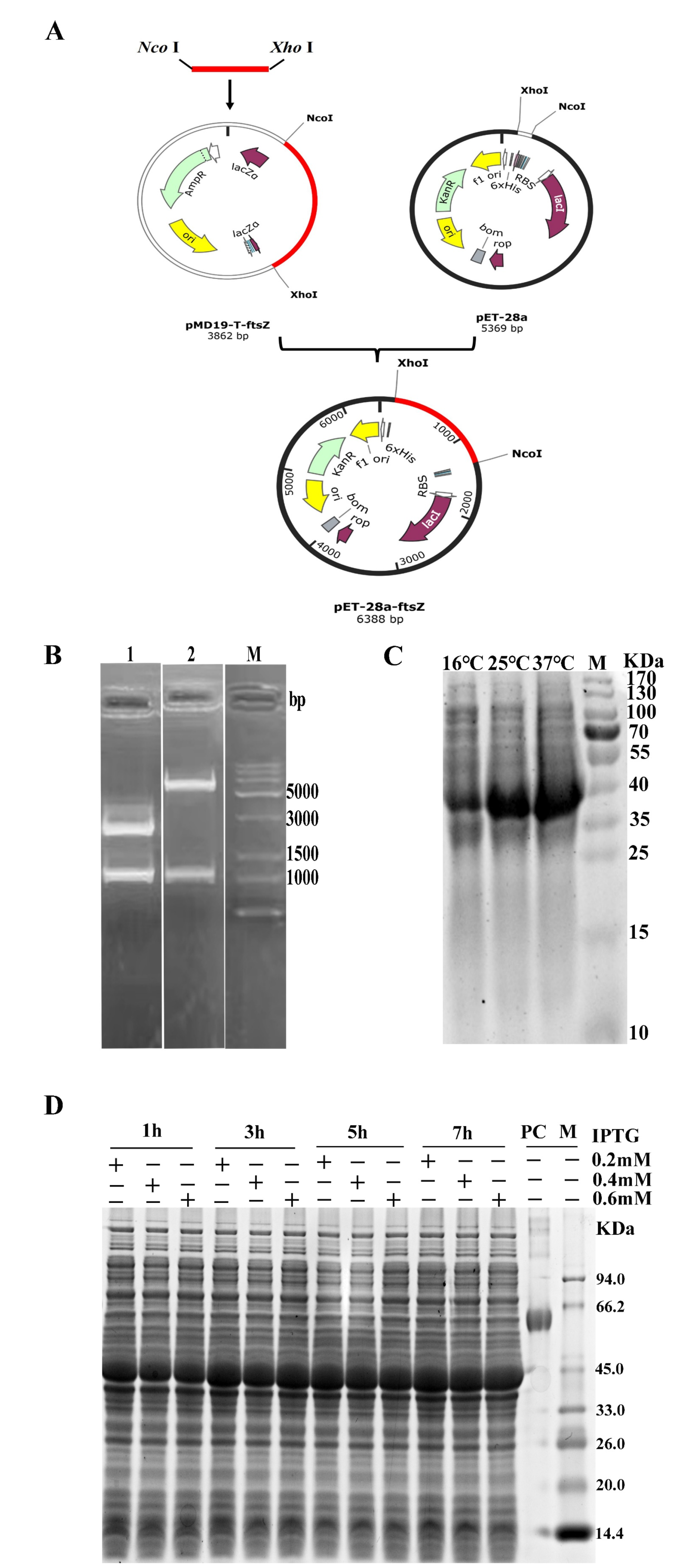
3.1. Construction of Recombinant Plasmids
3.2. Optimization of FtsZ Expression
3.3. Isolation and Purification of the Recombinant FtsZ Protein
3.4. The GTPase Activity of the Recombinant FtsZ Protein
3.5. A Screening Model of Antibacterial Agents Based on FtsZ GTPase Activity
3.6. Antibacterial Activity of Alkaloids
3.7. Cytotoxicity of Alkaloids
3.8. Interaction of Berberine Hydrochloride and the Recombinant FtsZ Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Croxen, M.A.; Law, R.J.; Scholz, R.; Keeney, K.M.; Wlodarska, M.; Finlay, B.B. Recent advances in understanding enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 822–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, M.C.; McEwen, S.A.; Pearl, D.L.; Lyytikäinen, O.; Jacobsson, G.; Collignon, P.; Gregson, D.B.; Valiquette, L.; Laupland, K.B. Mortality in Escherichia coli bloodstream infections: A multinational population-based cohort study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokhn, E.S.; Salami, A.; El Roz, A.; Salloum, L.; Bahmad, H.F.; Ghssein, G. Antimicrobial susceptibilities and laboratory profiles of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis isolates as agents of urinary tract infection in Lebanon: Paving the way for better diagnostics. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, F.; Khan, I.A.; Patel, S.; Siddiq, A.U.; Saha, N.C.; Khan, A.I.; Saha, A.; Cravioto, A.; Clemens, J.; Qadri, F.; et al. Diarrheal illness and healthcare seeking behavior among a population at high risk for diarrhea in Dhaka, Bangladesh. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Lutkenhaus, J. At the heart of bacterial cytokinesis: The Z ring. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.A.; Whatley, Z.N.; Joshi, C.P.; Osawa, M.; Erickson, H.P. Probing for binding regions of the FtsZ protein surface through site-directed insertions: Discovery of fully functional FtsZ-fluorescent proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 199, e00553-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Sahu, S.K. FtsZ inhibitors as a new genera of antibacterial agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 91, 103169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchino, K.; Chan, H.; Hwang, L.C.; Bruheim, P. The ethanologenic bacterium Zymomonas mobilis divides asymmetrically and exhibits heterogeneity in DNA content. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02441-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, E.; Lutkenhaus, J. FtsZ regulates frequency of cell division in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 2765–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, T.; Ploeger, G.E.J.; Verheul, J.; Comvalius, A.D.; Martos, A.; Alfonso, C.; van Marle, J.; Rivas, G.; Blaauwen, T.D. The GTPase activity of Escherichia coli FtsZ determines the magnitude of the FtsZ polymer bundling by ZapA in Vitro. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 11056–11066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Blaauwen, T.; Luirink, J. Checks and balances in bacterial cell division. mBio 2019, 10, e00149-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.K.; Makde, R.D.; Kumar, V.; Panda, D. SepF increases the assembly and bundling of FtsZ polymers and stabilizes FtsZ protofilaments by binding along its length. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 31116–31124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Addinall, S.G.; Small, E.; Whitaker, D.; Sturrock, S.; Donachie, W.D.; Khattar, M.M. New temperature-sensitive alleles of ftsZ in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Teng, D.; Mao, R.; Hao, Y.; Yang, N.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Recent progress of bacterial FtsZ inhibitors with a focus on peptides. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 1091–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.; Lim, Y.H. Resveratrol antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli is mediated by Z-ring formation inhibition via suppression of FtsZ expression. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, D.; Singh, J.K.; Roy, N.; Panda, D. Curcumin inhibits FtsZ assembly: An attractive mechanism for its antibacterial activity. Biochem. J. 2008, 410, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Galgoci, A.; Kodali, S.; Herath, K.B.; Jayasuriya, H.; Dorso, K.; Vicente, F.; González, A.; Cully, D.; Bramhill, D.; et al. Discovery of a small molecule that inhibits cell division by blocking FtsZ, a novel therapeutic target of antibiotics. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 44424–44428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domadia, P.; Swarup, S.; Bhunia, A.; Sivaraman, J.; Dasgupta, D. Inhibition of bacterial cell division protein FtsZ by cinnamaldehyde. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domadia, P.N.; Bhunia, A.; Sivaraman, J.; Swarup, S.; Dasgupta, D. Berberine targets assembly of Escherichia coli cell division protein FtsZ. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 3225–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.L.; Sun, N.; Fung, Y.H.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Chan, P.H.; Wong, W.L.; Wong, K.Y. Discovery of FtsZ inhibitors by virtual screening as antibacterial agents and study of the inhibition mechanism. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 13, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Yu, Z.; Song, W.; Li, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Hong, W.; Sun, N. Indole-core-based novel antibacterial agent targeting FtsZ. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Hobrath, J.V.; Ross, L.; Connelly, M.C.; Lofton, H.; Rajagopalan, M.; Guy, R.K.; Reynolds, R.C. Screening and development of new inhibitors of FtsZ from M. tuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, F.; Kumar, M.; Koley, T.; Sharma, P.; Haque, M.A.; Kapil, A.; Kumar, M.; Kaur, P.; Ethayathulla, A.S. Screening of plant-based natural compounds as an inhibitor of FtsZ from Salmonella Typhi using the computational, biochemical and in vitro cell-based studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, H.; Zhuang, X.; Zang, Y.; Chen, J. First report of Vicia cryptic virus M infecting cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 105, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, R.; Huang, S.; Song, D.; Liu, R. Prokaryotic expression, protein purification and functional verification of human homotypic fusion and vacuole protein sorting complex subunit. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Veloria, J.; Shin, M.; Devkota, A.K.; Payne, S.M.; Cho, E.J.; Dalby, K.N. Developing colorimetric and luminescence-based high-throughput screening platforms for monitoring the GTPase activity of ferrous iron transport protein B (FeoB). SLAS Discov. Adv. Sci. Drug Discov. 2019, 24, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachem, C.Y.; Clarridge, J.E.; Reddy, R.; Flamm, R.; Evans, D.G.; Tanaka, S.; Graham, D.Y. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Helicobacter pylori comparison of E-test, broth microdilution, and disk diffusion for ampicillin, clarithromycin, and metronidazole. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1996, 24, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Chan, F.-Y.; Lu, Y.-J.; Neves, M.A.C.; Lui, H.-K.; Wang, Y.; Chow, K.-Y.; Chan, K.-F.; Yan, S.-C.; Leung, Y.-C.; et al. Rational design of berberine-based FtsZ inhibitors with broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jin, B.; Cornelius, L.A.; Zhou, B.; Fu, X.; Shang, D.; Zheng, H. Inhibitory effects of Rap1GAP overexpression on proliferation and migration of endothelial cells via ERK and Akt pathways. Cur Med Sci. 2011, 31, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, M.; Lau, K.T.; Shepherd, R.; Slater, C.; Diamond, D. Determination of phosphate using a highly sensitive paired emitter–detector diode photometric flow detector. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 597, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisson-Filho, A.W.; Hsu, Y.P.; Squyres, G.R.; Kuru, E.; Wu, F.; Jukes, C.; Sun, Y.; Dekker, C.; Holden, S.; VanNieuwenhze, M.S.; et al. Treadmilling by FtsZ filaments drives peptidoglycan synthesis and bacterial cell division. Science 2017, 355, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casiraghi, A.; Suigo, L.; Valoti, E.; Straniero, V. Targeting bacterial cell division: A binding site-centered approach to the most promising inhibitors of the essential protein FtsZ. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahanty, S.; Rathinasamy, K. The natural anthraquinone dye purpurin exerts antibacterial activity by perturbing the FtsZ assembly. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 50, 116463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honrubia-Marcos, M.P.; Ramos, A.; Gil, J.A. Overexpression of the ftsZ gene from Corynebacterium glutamicum (Brevibacterium lactofermentum) in Escherichia coli. Can. J. Microbiol. 2005, 51, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, R.; Babaeipour, V.; Mohammadpour Aghdarm, M.; Deldar, A.A. Overexpression, overproduction, purification, and characterization of rhGH in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2021, 68, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, T.; Leimkühler, S. TusA is a versatile protein that links translation efficiency to cell division in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, e00659-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez Cruz, N.A.; Caspeta, L.; Pérez, N.O.; Ramírez, O.T.; Trujillo Roldán, M.A. Production of recombinant proteins in E. coli by the heat inducible expression system based on the phage lambda pL and/or pR promoters. Microb. Cell Factories 2010, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaneophytou, C.P.; Kontopidis, G. Statistical approaches to maximize recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: A general review. Protein Expr. Purif. 2014, 94, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.M.; Zhang, G.Y.; Ji, X.D.; Cao, L.; Shu, L.; Hua, Z.C. Expression of soluble, biologically active recombinant human endostatin in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 41, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yari, K.; Afzali, S.; Mozafari, H.; Mansouri, K.; Mostafaie, A. Molecular cloning, expression and purification of recombinant soluble mouse endostatin as an anti-angiogenic protein in Escherichia coli. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X.; Selvaraj, J.N.; Zhang, G. Genetic engineering modification and fermentation optimization for extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gräslund, S.; Nordlund, P.; Weigelt, J.; Hallberg, B.M.; Bray, J.; Gileadi, O.; Knapp, S.; Oppermann, U.; Arrowsmith, C.; Hui, R.; et al. Protein production and purification. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swalley, S.E.; Fulghum, J.R.; Chambers, S.P. Screening factors effecting a response in soluble protein expression: Formalized approach using design of experiments. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 351, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Shi, H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, K. Cloning and purification of recombinant silkworm dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase expressed in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2010, 72, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeze, R.J.; Solomon, C.J.; Pope, D.H. Effects of low temperature on in vivo and in vitro protein synthesis in Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas fluorescens. J. Bacteriol. 1978, 134, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedwell, D.B. Effect of low temperature on microbial growth: Lowered affinity for substrates limits growth at low temperature. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 30, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, L.; Guan, C.; Xun, M.; Wu, F.; Lei, Y. Establishment of purification method for prokaryotic expression of Serpin gene for Dermatophagoides farinae. Protein Expr. Purif. 2022, 195–196, 106080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sousa, R. Expression and purification of E. coli BirA biotin ligase for in vitro biotinylation. Protein Expr. Purif. 2012, 82, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, Y.Y.; Zhang, W. Downstream processing of recombinant human insulin and its analogues production from E. coli inclusion bodies. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Jindal, B.; Singh, P.; Datta, A.; Panda, D. Plumbagin inhibits cytokinesis in Bacillus subtilis by inhibiting FtsZ assembly—a mechanistic study of its antibacterial activity. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 4585–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalit, D.N.; Romberg, L.; Mets, R.B.; Hebert, A.M.; Mitchison, T.J.; Kirschner, M.W.; RayChaudhuri, D. Targeting cell division: Small-molecule inhibitors of FtsZ GTPase perturb cytokinetic ring assembly and induce bacterial lethality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11821–11826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osawa, M.; Erickson, H.P. FtsZ from divergent foreign bacteria can function for cell division in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 7132–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sanguinarine Chloride | Tetrandrine | Berberine Hydrochloride | Theophylline | Sophoridine | Matrine | Sinomenine Hydrochloride | Betaine | Betonicine | Nonivamide | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg/mL) | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC |
| E. coli CVCC1515 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 2.56 | >5.12 | 5.12 | 10.24 | 5.12 | >5.12 | 8.88 | 5.12 | >10.24 | - | >10.24 | - | >5.12 | - |
| E. coli CVCC195 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.64 | >0.64 | 2.56 | >5.12 | 5.12 | 10.24 | 5.12 | >5.12 | >5.12 | >5.12 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| S. enteritidis CVCC3377 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.64 | 2.56 | >5.12 | 10.24 | >10.24 | >5.12 | >5.12 | >5.12 | >5.12 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| S. enteritidis ATCC14028 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | >0.64 | - | 2.56 | >5.12 | 5.12 | 10.24 | 5.12 | >5.12 | >8.88 | 8.88 | >10.24 | - | >10.24 | - | >5.12 | - |
| S. aureus ATCC43300 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.64 | 2.56 | >5.12 | 10.24 | >10.24 | >5.12 | >5.12 | >8.88 | >8.88 | >10.24 | - | >10.24 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Q.; Wu, J.; Xi, B.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Li, H. A Screening Model of Antibacterial Agents Based on Escherichia coli Cell-Division Protein. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074493
Fan Q, Wu J, Xi B, Li C, Wang X, Li H. A Screening Model of Antibacterial Agents Based on Escherichia coli Cell-Division Protein. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(7):4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074493
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Qiuyu, Jianwen Wu, Bolin Xi, Chunxiao Li, Xiumin Wang, and Huanrong Li. 2023. "A Screening Model of Antibacterial Agents Based on Escherichia coli Cell-Division Protein" Applied Sciences 13, no. 7: 4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074493
APA StyleFan, Q., Wu, J., Xi, B., Li, C., Wang, X., & Li, H. (2023). A Screening Model of Antibacterial Agents Based on Escherichia coli Cell-Division Protein. Applied Sciences, 13(7), 4493. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13074493







