Role of Technology Innovation in Telemedicine: Focus on Sport Nutrition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Current Technology
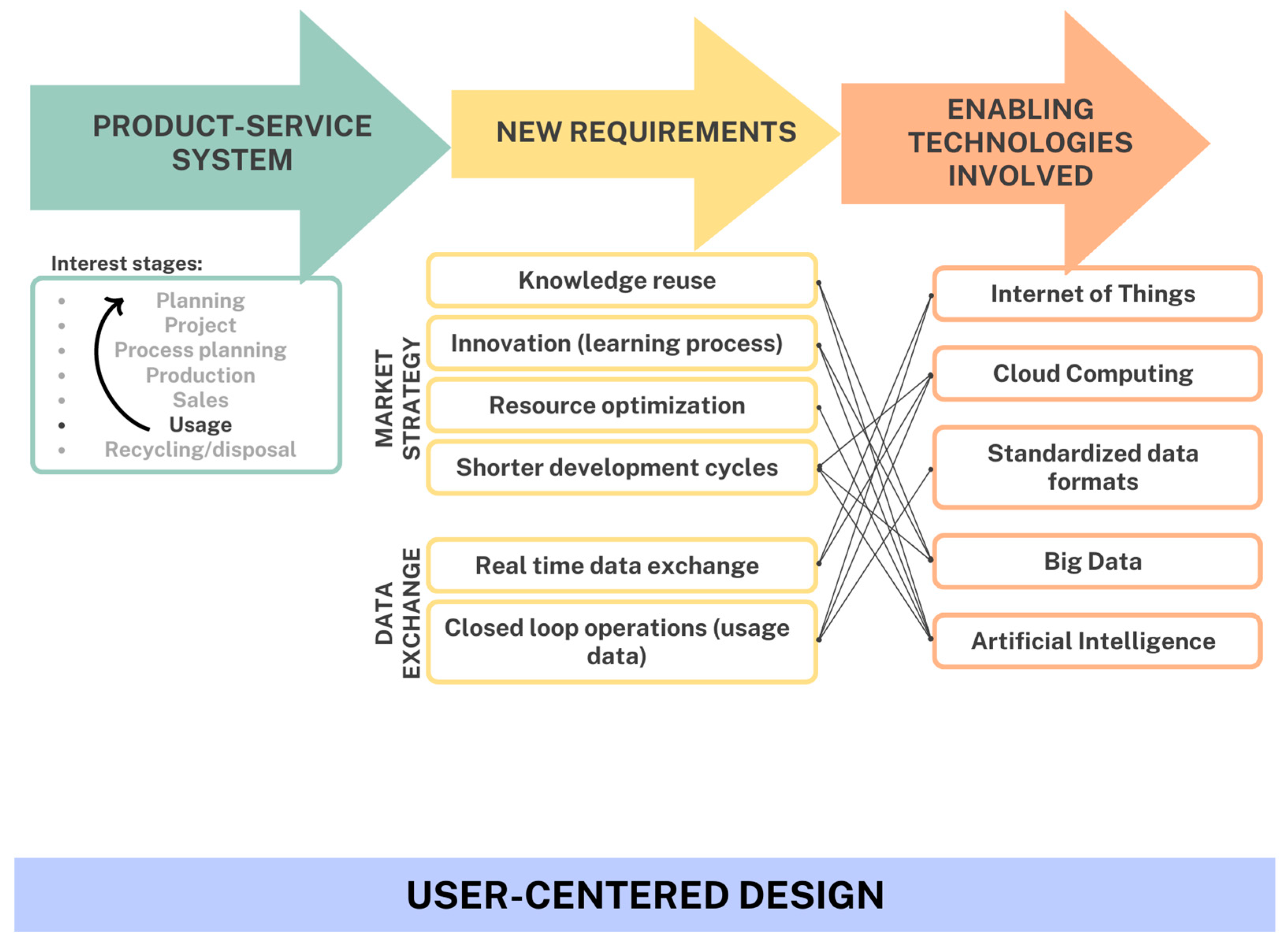
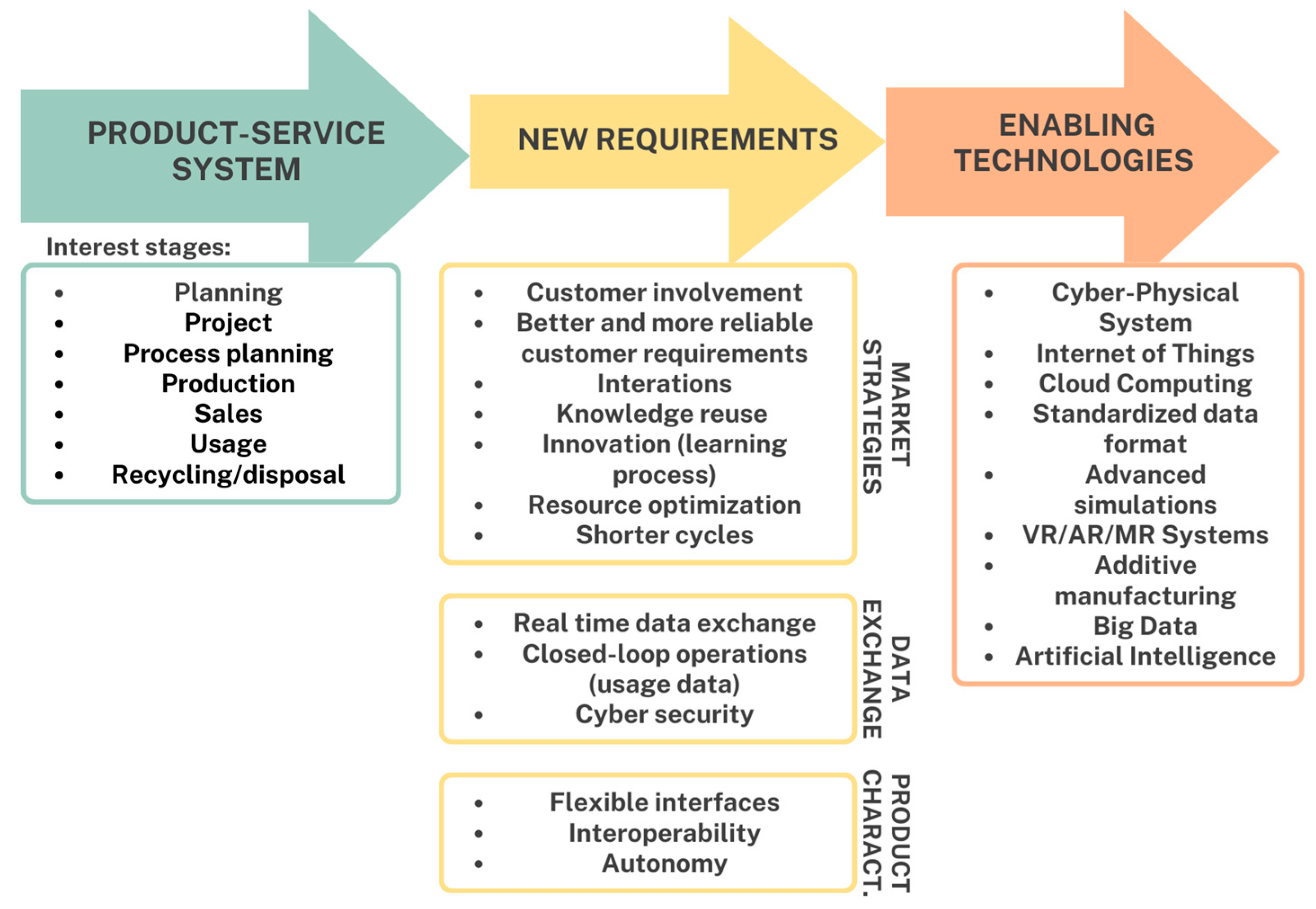
2.1. Application Framework
2.2. Enabling Technologies and eHealth
2.3. New Frontiers in Sports Technology
2.4. National Sports and Interests
2.5. System User Perception
2.6. Technological Self-Efficacy
2.7. Technological Anxiety
2.8. User Satisfaction and System Acceptance
2.9. New Modeling Approach
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions and Future Developments
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, R.; Pringle, T.; Kenneson, A. Telemedicine challenges and strategies for the medical nutrition therapy of patients with inherited metabolic disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2021, 132, S346–S347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nittari, G.; Savva, G.; Tomassoni, D.; Tayebati, S.K.; Amenta, F. Telemedicine in the COVID-19 Era: A Narrative Review Based on Current Evidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, L.E.; Bishop, C.E.; Vats, K.R.; Azzuqa, A. Meeting families where they are: Institution, evaluation, and sustainability of telemedicineprenatal neonatology consultation in the COVID-19 pandemic health emergency. Semin. Perinatol. 2021, 45, 151417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Naqvi, I.; Tom, S.; Almeida, B.; Baratt, Y.; Ulane, C.M. Integrating neurology and pharmacy through telemedicine: A novel care model. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 432, 120085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, B.; Paul, N.; Balzer, F.; Noritomi, D.T.; Spies, C. Telemedicine in the intensive care unit: A vehicle to improve quality of care? J. Crit. Care 2020, 61, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, O.H.; Taha, Z.K.; Alsabah, M.Q.; Hussein, Y.S.; Mohammed, A.S. A review on utilizing machine learning technology in the fields of electronic emergency triage and patient priority systems in telemedicine: Coherent taxonomy, motivations, open research challenges and recommendations for intelligent future work. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 209, 106357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riviera, M.; O’Neil, D.A.; Viers, B.R.; Pruthi, S.; Gardner, M.R. Are patients willing to engage in telemedicine for their care: A survey of preuse perceptions and acceptance of remote video visit in a urological patient population. Urology 2015, 85, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, N.; Schumann, M.; Kraft, K.; Hoffman, W. Telemedicine and telecare for older patients—A systematic review. Maturitas 2012, 73, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C.; Bourke, S.; Heuss, S. From testers to cocreators—The Value of and Approaches to Successful Patient Engagement in the Development of eHealth Solutions: Qualitative Expert Interview Study. JMIR Hum. Factors 2022, 9, e41481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Topol, E.J. Telemedicine 2020 and the next decade. Lancet 2020, 395, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashshur, R.L.; Shannon, G.W.; Smith, B.R.; Alverson, D.C.; Antoniotti, N.; Barsan, W.; Bashshur, N.; Brown, E.; Coye, M.; Doarn, C.; et al. The Empirical Foundations of Telemedicine Interventions for Chronic Disease Management. Telemed. J. E Health 2014, 20, 769–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roettl, J.; Bidmon, S.; Terlutter, R. What Predicts Patients’ Willingness to Undergo Online Treatment and Pay for Online Treatment? Results from a Web-Based Survey to Investigate the Changing Patient-Physician Relationship. J. Med. Internet Res. 2016, 18, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Moore, L.W. Renal Telenutrition for Kidney Health: Leveraging Telehealth and Telemedicine for Nutritional Assessment and Dietary Management of Patients with Kidney Disorders. J. Ren. Nutr. 2020, 30, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, J.E.; Zegarra-Parodi, R.; Van Dun, P.; Cerritelli, F.; Vaucher, P. Models and theoretical frameworks for osteopathic care—A critical view and call for updates and research. Int. J. Osteopath. Med. 2020, 35, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallati, C.; Schutzer, K. Development of smart products for elders within the Industry 4.0 context: A conceptual framework. Procedia CIRP 2021, 100, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.L.; Brown, M.M.; Patwa, D.; Nirmalan, A.; Edwards, P.A. Telemedicine, telementoring, and telesurgery for surgical practices. Curr. Probl. Surg. 2021, 58, 100986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robiony, M.; Bocin, E.; Sembronio, S.; Costa, F.; Arboit, L. Working in the era of COVID-19: An organization model formaxillofacial surgery based on telemedicine and video consultation. J. Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surg. 2021, 49, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reforma, L.G.; Duffy, C.R.; Collier, A.Y.; Wylie, B.J.; Shainker, S.A. A multidisciplinary telemedicine model for managementof coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in obstetricalpatients. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. MFM 2020, 2, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.Y.; Knight, S.; Guetter, C.R.; Davis, C.; Moller, M. Telemedicine and telementoring in the surgical specialties: A narrative review. Am. J. Surg. 2019, 218, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, E.F.J.; Bonfiglioli, C.; Brunner, M.; Frawley, J. Parents’ use of social media as a health information source for their children: A scoping review. Acad. Pediatr. 2021, 22, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlankha, S.; Chhabra, D.; Shukla, P. Effectiveness of gamification for the rehabilitation of neurodegenerative disorders, Chaos. Solitons Fractals. 2020, 140, 110192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandalà, M.; Laurino, C.; Malagoli, A.; Palmieri, B. La telemedicina: Ieri e oggi. Companion Ser. IHPB 2019, 9, 4–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Pham, Q.; Prabadevi, B.; Deepa, N.; Dev, K.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Ruby, R.; Liyannage, M. Industry 5.0: A survey on enabling technologies and potential applications. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2021, 26, 100257. [Google Scholar]
- Laroui, M.; Nour, B.; Moungla, H.; Cherif, M.A.; Afifi, H. Edge and fog computing for IoT: A survey on current research activities & future directions. Comput. Commun. 2021, 180, 210–231. [Google Scholar]
- Allam, Z.; Jones, D.S. Future (post-COVID) digital, smart and sustainable cities in the wake of 6G: Digital twins, immersive realities and new urban economies. Land Use Policy 2021, 101, 105201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, L.; Rochester, C. Embedded system and smart embedded wearable devices promote youth sports health. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2021, 83, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ming, H. Detection of sports energy consumption based on Iots and cloud computing. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments 2021, 46, 101224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; You, Y. Design and data analysis of wearable sports posturemeasurement system based on Internet of Things. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 60, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.T.; Burke, L.M.; Erdman, K.A. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and Athletic Performance. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 116, 501–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellingwerff, T.; Bovim, I.M.; Whitfield, J. Contemporary Nutrition Interventions to Optimize Performance in Middle-Distance Runners. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 29, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, R.; Kerksik, C.M.; Campbell, B.I.; Cribb, P.J.; Wells, S.D.; Skwiat, T.M.; Purpura, M.; Ziegenfuss, T.; Ferrando, A.; Arent, S.; et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Protein and exercise. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2017, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheuvront, S.N.; Kenefick, R.W. Personalized fluid and fuel intake for performance optimization in the heat. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2021, 24, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerksik, C.M.; Wilborn, C.D.; Roberts, M.D.; Smith-Ryan, A.; Kleiner, S.M.; Jager, R.; Collins, R.; Cooke, M.; Davis, J.; Galvan, E.; et al. ISSN exercise & sports nutrition review update: Research & recommendations. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2018, 15, 38. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J. Nano-enabled personalized nutrition: Developingmulticomponent-bioactive colloidal delivery systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 282, 102211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Han, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, T.; Guan, H.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, L.; Xue, X.; Li, P.; et al. A self-powered wearable body-detecting/brain-stimulating system for improving sports enduranceperformance. Nano Energy 2021, 93, 106851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pueo, B.; Jimenez-Olmedo, J.M. Application of motion capture technology for sport performance analysis. Retos 2017, 32, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plastoi, C. The increase sports performance skiers with modern audiovisual technology contribution, Annals of “Dunarea de Jos”. Univ. Galati 2014, 1, 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Thibault, L.; Harvey, J. Sport Policy in Canada; University of Ottawa Press: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, M.; Smith, J. The Insitutional Work of Own the Podium in Developing High Performance Sport in Canada. J. Sport Manag. 2016, 30, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, H.; Lu, M.; Gan, L. The Research on Application of Information Technology in sports Stadiums. Phys. Procedia 2011, 22, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parraga, A.G.; Ruiz-Navarro, J.J.; Cuenca-Fernandez, F.; Lopez-Belmonte, O.; Abraides, J.A.; Fernandes, R.; Aureliano, R. The Impact of Wetsuit Use on Swimming Performance, Physiology and Biomechanics: A Systematic Review. Physiologia 2022, 2, 198–230. [Google Scholar]
- Neptune, R.R.; McGowan, C.P.; Fiandt, J.M. The influence of Muscle Physiology and Advanced Technology on Sports Performance. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 11, 81–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, F.D. Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology. MIS Q. 1989, 13, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, M.; Kazala, R.; Koruba, Z.; Kozlowski, M.; Lucinska, M.; Sitek, K.; Spyrka, J. Emotion Recognition Method for Call/contact Centre Systems. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Isanejad, O. Presentation of the Extended Technology Acceptance Model in Sports Organizations. Ann. Appl. Sport Sci. 2018, 6, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, F.; Xi, L.; Yu, J.; Zhang, M. Relationship between Technology Acceptance and Self-Directed Learning: Mediation Role of Positive Emotions and Technological Self-Efficacy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.; Guzmàn, S.; Concha, C. Exploring factors that affect technological anxiety (technoanxiety) of univerity administrative staff. In Proceedings of the 17th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Madrid, Spain, 22–25 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Liu, D.; Morente-Molinera, J.; Herrera-Viedma, E. A data-driven method for user satisfaction evaluation of smart and connected products. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 210, 118392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Mazzei, D.; Mateu, A.; Reinares, M.; Murru, A.; del Mar Bonnin, C.; Martin, C.V.; Valenti, M.; Undurraga, J.; Strejilevich, S.; Sanchez-Moreno, J.; et al. Psychoeducation in bipolar disorder with a SIMPLe smartphone application: Feasibility, acceptability and satisfaction. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 200, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanova-Pavlova, M.; Andonov, V.; Stoyanov, T.; Angelova, M.; Cook, G.; Klein, B.; Vassilev, P.; Stefanova, E. Modeling Telehealth Services with Generalized Nets. In Recent Contributions in Intelligent Systems; Studies in Computational Intelligence; Sgurev, V., Yager, R., Kacprzyk, J., Atanassov, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy, C.R.; Arias, C.A.; Guerrero, Y.N. The new cloud computing paradigm: The way to IT seen as utility. Lat. Am. Caribb. J. Eng. Educ. 2012, 6, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, H.; Engstrom, J. The antecedents, forms and consequences of patient involvement: A narrative review of the literature. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2016, 53, 351–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, G.; Tekli, J. Automated and Personalized Nutrition Health Assessment, Recommendation, and Progress Evaluation using Fuzzy Reasoning. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2021, 151, 102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzetti, M.; Signoretti, I.; Salerno, L.; Marczak, S.; Bastos, R. Improving Agile Software Development using User-Centered Design and Lean Startup. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2021, 141, 106718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandra, S.; Handayani, P.W.; Azzahro, F. Indonesian Hospital Telemedicine Acceptance Model: The Influence of User Behaviorand Technological Dimensions. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, S.; Shafiq, M.; Kakria, P. Investigating acceptance of telemedicine services through an extended technology acceptance model (TAM). Technol. Soc. 2020, 60, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manafo, E.; Petermann, L.; Mason-Lai, P.; Vandall-Walker, V. Patient engagement in Canada: A scoping review od the “how” and “what” of patient engagement in health research. Health Res. Polocy Syst. 2018, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouabida, K.; Lebouche, B.; Pomey, M. Telehealth and COVID-19 Pandemic: An Overview of the Telehealth Use, Advantages, Challenges, and Opportunities during COVID-19 Pandemic. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoonakker, P.L.T.; Carayon, P.; Hundt, A.; Kelly, M. SEIPS 3.0: Human-centered design of the patient journey for patient safety. Appl. Ergon. 2020, 84, 103033. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vasco, P.; Moscatelli, F.; La Torre, M.E.; Valenzano, A.; Monda, V.; Cibelli, G.; de Stefano, M.I.; Marsala, G.; Dalia, C.; Bassi, P.; et al. Role of Technology Innovation in Telemedicine: Focus on Sport Nutrition. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13084837
Vasco P, Moscatelli F, La Torre ME, Valenzano A, Monda V, Cibelli G, de Stefano MI, Marsala G, Dalia C, Bassi P, et al. Role of Technology Innovation in Telemedicine: Focus on Sport Nutrition. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(8):4837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13084837
Chicago/Turabian StyleVasco, Paride, Fiorenzo Moscatelli, Maria Ester La Torre, Anna Valenzano, Vincenzo Monda, Giuseppe Cibelli, Maria Ida de Stefano, Gabriella Marsala, Carmine Dalia, Paola Bassi, and et al. 2023. "Role of Technology Innovation in Telemedicine: Focus on Sport Nutrition" Applied Sciences 13, no. 8: 4837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13084837
APA StyleVasco, P., Moscatelli, F., La Torre, M. E., Valenzano, A., Monda, V., Cibelli, G., de Stefano, M. I., Marsala, G., Dalia, C., Bassi, P., Porro, C., Toto, G., Limone, P., Messina, G., & Polito, R. (2023). Role of Technology Innovation in Telemedicine: Focus on Sport Nutrition. Applied Sciences, 13(8), 4837. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13084837









