Physical, Mechanical, and Thermal Properties of Natural Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites for Construction and Automotive Applications
Abstract
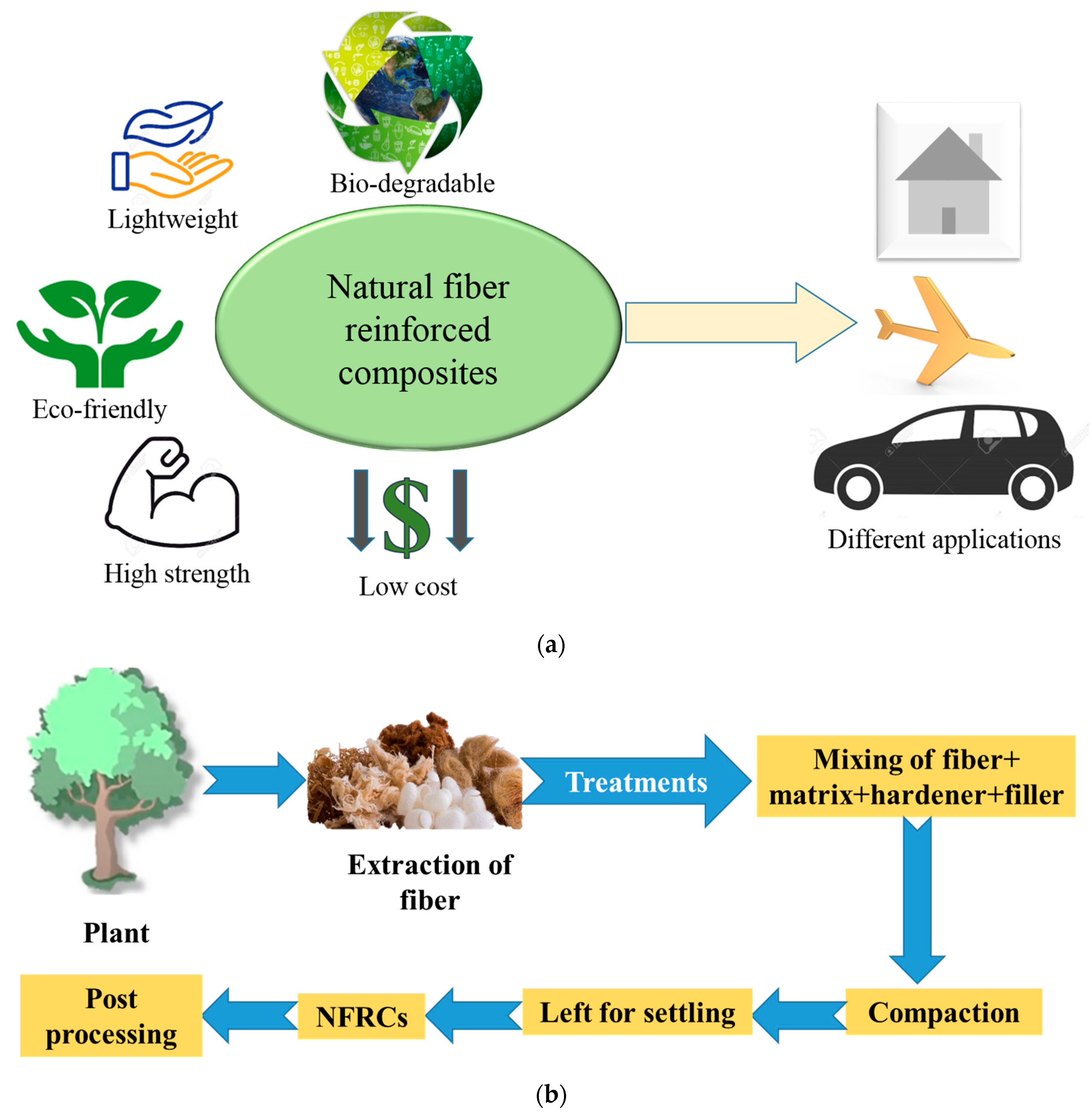
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Epoxy-based composites based on reinforcement;
- (2)
- Physical and mechanical properties of natural fibers;
- (3)
- Physical properties of the natural fiber-reinforced epoxy composites;
- (4)
- Mechanical properties of the natural fiber-reinforced epoxy composites;
- (5)
- Thermal behaviour of the natural fibers reinforced epoxy composites;
- (6)
- Physico-chemical treatment of the natural fibers;
- (7)
- Applications of natural fiber-reinforced epoxy-based composites;
- (8)
- Summary and future perspectives.
2. Epoxy-Based Composites
2.1. Epoxy-Based Composites Reinforced with Recycled Aggregates
2.2. Epoxy-Based Composites Reinforced with Natural Fibers
3. Physical and Mechanical Properties of the Natural Fibers
4. Physical Properties of the Natural Fibers Reinforced Epoxy Composites
4.1. Wear Behaviour
4.2. Porosity
4.3. Water Adsorption
5. Mechanical Properties of the Natural Fibers Reinforced Epoxy Composites
5.1. Tensile Behaviour
5.2. Impact Strength/Toughness
5.3. Flexural Behaviour
5.4. Hardness
5.5. Damping
6. Thermal Behaviour of Epoxy-Based NFRCs
7. Physico-Chemical Treatment of the Natural Fibers
7.1. Physical Treatment of Natural Fibers
7.2. Chemical Treatment of Natural Fibers

| Treatments | Chemical Used | Effects | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alkali, mercerization (physical treatment) | Sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide | Reduces lignin content, moisture absorption ability, wax, and oil covering; improves thermal stability, tensile strength, flexural strength, and fiber–matrix adhesion | [42,139,153] |
| Enzyme (chemical treatment) | Hydrolases and oxidoreductases | Reduces hydrophilic pectin, lignin, and hemi cellulosic components | [154] |
| Acetylation (chemical treatment) | Acetic anhydride, silane toluene, and a small amount of catalyst perchloric acid | Improves dimensional stability, hydrophobicity, interfacial properties and mechanical properties | [143,144,147] |
| Ozone (chemical treatment) | Ozone gas | Improves surface energy and contact angle | [155] |
| Grafting (chemical treatment) | Acrylonitrile, methyl methacrylate, Maleic anhydride grafted polypropylene, and polystyrene | Improves UV-protective properties, hydrophobicity, and mechanical characteristics and interfacial adhesion | [18,24,156] |
| Isocyanate (chemical treatment) | Carbon tetrachloride and dibutyl tin dilaurate, toluene diisocyanate, isocyanate acetone | Improves mechanical properties, reduce hydrophilicity | [149,150] |
| Benzoylation (chemical treatment) | Benzoyl chloride | Improve hydrophobicity | [150,157] |
| Peroxide (chemical treatment) | Benzoyl peroxide or dicumyle peroxide | Reduces moisture absorption, improves mechanical properties. | [148] |
| Graphene coating | Graphene oxide | Improves mechanical and thermal properties | [151,158] |
| Plasma (physical treatment) | Argon cold, low frequency, and radio frequency oxygen plasma | Improves hydrophobicity and mechanical properties | [106,133] |
| Corona (physical treatment) | - | Improves surface energy | [132] |
| Sodium chlorite (chemical treatment) | - | Improves tensile strength, tensile modulus/modulus of elasticity | [152,159] |
| Duralin (physical treatment) | - | Reduces moisture absorption and biological degradation | [17,136,160] |
8. Applications of Natural Fibers Reinforced Epoxy-Based Composites
8.1. Automobile Applications
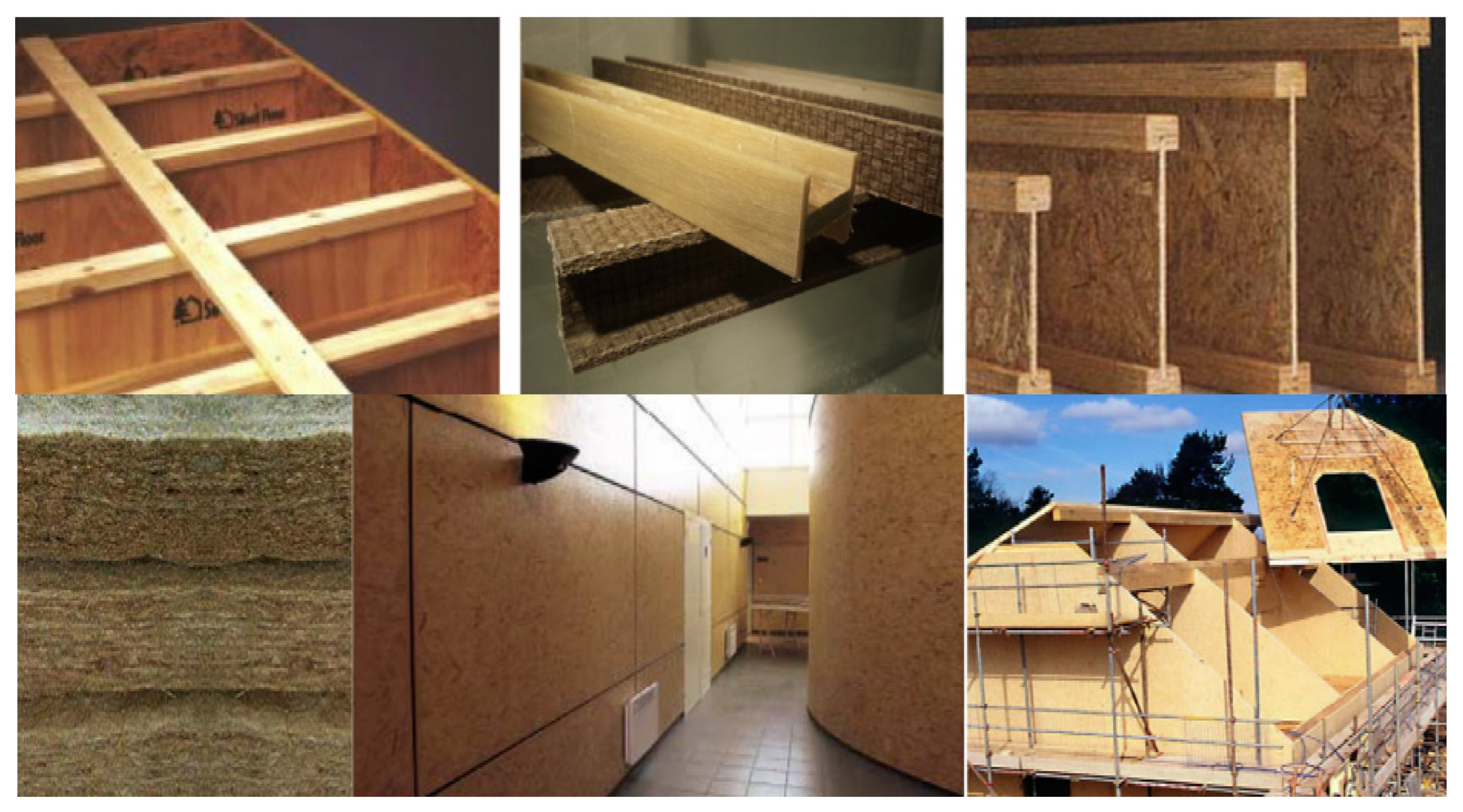
8.2. Construction Applications
9. Summary and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sałasińska, K.; Cabulis, P.; Kirpluks, M.; Kovalovs, A.; Kozikowski, P.; Barczewski, M.; Celiński, M.; Mizera, K.; Gałecka, M.; Skukis, E.; et al. The Effect of Manufacture Process on Mechanical Properties and Burning Behavior of Epoxy-Based Hybrid Composites. Materials 2022, 15, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.O.; Akpan, E.; Dhakal, H.N. Review on natural plant fibres and their hybrid composites for structural applications: Recent trends and future perspectives. Compos. Part C 2022, 9, 100322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boey, J.Y.; Lee, C.K.; Tay, G.S. Factors Affecting Mechanical Properties of Reinforced Bioplastics: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Prasad, L.; Bijlwan, P.P.; Yadav, A. Thermogravimetric analysis of lignocellulosic leaf-based fiber-reinforced thermosets polymer composites: An overview. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Khorshidi, H.; Najafi, E.; Ghasemi, M. Fresh, mechanical and microstructural properties of alkali-activated composites incorporating nanomaterials: A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordon, H.C.F.; Cagnoni, F.C.; Ferreira, F.F. Comparison of physical and mechanical properties of civil construction plaster and recycled waste gypsum from São Paulo, Brazil. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 22, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuganti, S.; Chennareddy, R.; Riad, A.; Taha, M. Pultruded GFRP Reinforcing Bars Using Nanomodified Vinyl Ester. Materials 2020, 13, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.L.; Li, X.; Park, S.J. Synthesis and application of epoxy resins: A review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.H. Epoxies in the construction industry. In Chemistry and Technology of Thermosetting Polymers in Construction Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 78–122. [Google Scholar]
- Belaadi, A.; Bezazi, A.; Bourchak, M.; Scarpa, F.; Zhu, C. Thermochemical and statistical mechanical properties of natural sisal fibres. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 67, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borri, A.; Corradi, M.; Speranzini, E. Reinforcement of wood with natural fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesoro, G. Epoxy Resins-Chemistry and Technology, 2nd ed.; Clayton, A.M., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-T.; Huang, P.; Li, Y.-Q.; Hu, N.; Fu, S.-Y. Epoxy nanocomposites significantly toughened by both poly(sulfone) and graphene oxide. Compos. Commun. 2019, 14, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, U.; Teuwen, J.; Dransfeld, C. Toughening of Epoxy Systems with Interpenetrating Polymer Network (IPN): A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, S.; Banthia, A.K. Use of acrylate-based liquid rubbers as toughening agents and adhesive property modifiers of epoxy resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 3814–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Xu, L.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tusiime, R.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Zhang, H. Enhancing the Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Epoxy Resin via Blending with Thermoplastic Polysulfone. Polymers 2019, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramon, E.; Sguazzo, C.; Moreira, P. A Review of Recent Research on Bio-Based Epoxy Systems for Engineering Applications and Potentialities in the Aviation Sector. Aerospace 2018, 5, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.D.; Jamiru, T.; Sadiku, E.R.; Kupolati, W.K.; Agwuncha, S.C. Impact of Surface Modification and Nanoparticle on Sisal Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Nanocomposites. J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 2016, 4235975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Reis, J.M.L. Effect of temperature on the mechanical properties of polymer mortars. Mater. Res. 2012, 15, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, V.; Saini, R.; Sinha, S. Natural fiber-mediated epoxy composites—A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 99, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.; Low, I.M. Mechanical properties and water absorption behaviour of recycled cellulose fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Polym. Test. 2012, 31, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, L.; Singh, G.; Yadav, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A. Properties of functionally gradient composites reinforced with waste natural fillers. Acta Period. Technol. 2019, 50, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beluns, S.; Gaidukovs, S.; Platnieks, O.; Barkane, A.; Gaidukova, G.; Grase, L.; Nabels-Sneiders, M.; Kovalovs, A.; Thakur, V.K. Clean manufacturing of cellulose nanopapers by incorporating lignin and xylan as sustainable additives. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2022, 3, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, L.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Pua, G.; Jawaid, M.; Islam, M.S. A Review on Natural Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composite and Its Applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 243947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticoalu, A.; Aravinthan, T.; Cardona, F. A review of current development in natural fiber composites for structural and infrastructure applications. In Proceedings of the Southern Region Engineering Conference 2010, SREC 2010—Incorporating the 17th Annual International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice, M2VIP 2010, Toowoomba, Australia, 11–12 November 2010; pp. 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, L.; Kumar, S.; Patel, R.V.; Yadav, A.; Kumar, V.; Winczek, J. Physical and Mechanical Behaviour of Sugarcane Bagasse Fibre-Reinforced Epoxy Bio-Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, M.; Saba, N.; Jawaid, M.; Nasir, M. Potential of natural fiber/biomass filler-reinforced polymer composites in aerospace applications. In Sustainable Composites for Aerospace Applications; Jawaid, M., Thariq MBTSC for AA, Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 253–268. ISBN 978-0-08-102131-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mansor, M.R.; Nurfaizey, A.H.; Tamaldin, N.; Nordin, M.N.A. 11—Natural fiber polymer composites: Utilization in aerospace engineering. In Woodhead Publishing Series in Composites Science and Engineering; Verma, D., Fortunati, E., Jain, S., Zhang, X., Eds.; Woodhead: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 203–224. ISBN 978-0-08-102426-3. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, V.; Bajpai, P.K.; Maheshwari, S. An investigation on wear and dynamic mechanical behavior of jute/hemp/flax reinforced composites and its hybrids for tribological applications. Fibers Polym. 2018, 19, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeroual, M.; Bouguettaia, H.; Bechki, D.; Boughali, S.; Bouchekima, B.; Mahcene, H. Experimental investigation on a double-slope solar still with partially cooled condenser in the region of Ouargla (Algeria). Energy Procedia 2011, 6, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Bajpai, P.K.; Maheshwari, S. Studies on Mechanical and Morphological Characterization of Developed Jute/Hemp/Flax Reinforced Hybrid Composites for Structural Applications. J. Nat. Fibers 2018, 15, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuganti, S.; Soliman, E.; Reda Taha, M. 3D-Printed Pseudo Ductile Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Composite Using Discrete Fiber Orientations. Fibers 2020, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, L.; Kumain, A.; Patel, R.V.; Yadav, A.; Winczek, J. Physical and Mechanical Behavior of Hemp and Nettle Fiber-Reinforced Polyester Resin-based Hybrid Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 19, 2632–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F. Chemical treatments on plant-based natural fibre reinforced polymer composites: An overview. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2883–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Mechanical properties of surface-treated ramie fiber fabric/epoxy resin composite fabricated by vacuum-assisted resin infusion molding with hot compaction. J. Compos. Mater. 2016, 50, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.J.D.; Marques, M.L.; Velasco, F.G.; Fornari Junior, C.; Luzardo, F.M.; Tashima, M.M. A new treatment for coconut fibers to improve the properties of cement-based composites—Combined effect of natural latex/pozzolanic materials. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2017, 12, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnudu, D.M.; Sreeramulu, D.; Reddy, P.V.; Rao, H.R. Effect of alkali treatment on mechanical properties of Prosopis Juliflora hybrid composites. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2018, 13, 2933–2935. [Google Scholar]
- Agunsoye, J.O.; Aigbodion, V.S. Bagasse filled recycled polyethylene bio-composites: Morphological and mechanical properties study. Results Phys. 2013, 3, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-López, E.O.; Pérez-Fonseca, A.A.; Fuentes-Talavera, F.J.; Anzaldo, J.; González-Núñez, R.; Rodrigue, D.; Robledo-Ortíz, J.R. Rotomolded polyethylene-agave fiber composites: Effect of fiber surface treatment on the mechanical properties. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrakhiz, F.Z.; Malha, M.; Bouhfid, R.; Benmoussa, K.; Qaiss, A. Tensile, flexural and torsional properties of chemically treated alfa, coir and bagasse reinforced polypropylene. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 47, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, F.; Liang, W.; Wang, Z.; Duan, Z.; Yang, B. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Polymers 2018, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Mohanty, A.K.; Askeland, P.; Drzal, L.T.; Misra, M. Influence of fiber surface treatment on properties of Indian grass fiber reinforced soy protein based biocomposites. Polymer 2004, 45, 7589–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branciforti, M.C.; Marinelli, A.L.; Kobayashi, M.; Ambrosio, J.D.; Monteiro, M.R.; Nobre, A.D. Wood polymer composites technology supporting the recovery and protection of tropical forests: The amazonian phoenix project. Sustainability 2009, 1, 1431–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledzki, A.K.; Gassan, J. Composites reinforced with cellulose based fibres. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1999, 24, 221–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, A. Hemp fiber and its composites—A review. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 46, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckermann, G.W.; Pickering, K.L. Engineering and evaluation of hemp fibre reinforced polypropylene composites: Fibre treatment and matrix modification. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agus Suryawan, I.G.P.; Suardana, N.P.G.; Suprapta Winaya, I.N.; Budiarsa Suyasa, I.W.; Tirta Nindhia, T.G. Study of stinging nettle (urtica dioica l.) Fibers reinforced green composite materials: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 201, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.P.; Patel, R.V.; Hasan, M.F.; Yadav, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A. Fabrication and evaluation of physical and mechanical properties of jute and coconut coir reinforced polymer matrix composite. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 2572–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticoalu, A.; Aravinthan, T.; Cardona, F. A review on the characteristics of gomuti fibre and its composites with thermoset resins. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2013, 32, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Adeyanju, C.A.; Ogunniyi, S.; Adeniyi, A.G.; Abdulkareem, S.A. An empirical review of the recent advances in treatment of natural fibers for reinforced plastic composites. Compos. Interfaces 2021, 28, 925–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodros, E.; Baley, C. Study of the tensile properties of stinging nettle fibres (Urtica dioica). Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2143–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoko, G.R.; Honest, B.K. Stabilization of Nigerian Deltaic Laterites with Saw Dust Ash. Int. J. Sci. Res. Manag. 2014, 2, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Hillig, É.; Freire, E.; Zattera, A.J.; Zanoto, G.; Grison, K.; Zeni, M. Use of sawdust in polyethylene composites. Prog. Rubber, Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2008, 24, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, M.; Molenda, M.; Bańda, M.; Gondek, E. Mechanical properties of sawdust and woodchips. Fuel 2015, 159, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.; Hameed Sultan, M.T.B.; Ariffin, A.H. The challenges of natural fiber in manufacturing, material selection, and technology application: A review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2018, 37, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, T.P.; Navaneethakrishnan, P.; Shankar, S.; Rajasekar, R.; Rajini, N. Characterization of natural fiber and composites—A review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2013, 32, 1457–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, S. Mechanical properties of kenaf fibers and kenaf/PLA composites. Mech. Mater. 2008, 40, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, S.; Cao, Y.; Fukumoto, I. Press forming of short natural fiber-reinforced biodegradable resin: Effects of fiber volume and length on flexural properties. Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.H. Preparation and properties of multi-functional cotton fabric treated by gallnut extract. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerbu, C. Practical solution for improving the mechanical behaviour of the composite materials reinforced with flax woven fabric. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía Osorio, J.C.; Rodríguez Baracaldo, R.; Olaya Florez, J.J. The influence of alkali treatment on banana fibre’s mechanical properties. Ing. eInvestig. 2012, 32, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, S.; Wickramasinghe, G.D.; Wijayapala, U.S. Study on dyeing behavior of banana fiber with reactive dyes. J. Eng. Fiber. Fabr. 2019, 14, 1558925019884478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, Y.O.; Jimoh, A.A. Microstructural characterisation, physical and chemical properties of rice husk ash as viable Pozzolan in building material: A case study of some Nigerian grown rice varieties. Niger. J. Technol. 2018, 37, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugochukwu, S.; Ridzuan, M.J.M.; Majid, M.S.A.; Cheng, E.M.; Firdaus, A.Z.A.; Marsi, N. Influence of distilled water and alkaline solution on the scratch resistance properties of Napier fibre filled epoxy (NFFE) composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 14412–14424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitria; Ermawar, R.A.; Fatriasari, W.; Fajriutami, T.; Yanto, D.H.Y.Y.; Falah, F.; Hermiati, E. Biopulping of bamboo using white-rot fungi Schizophyllum Commune. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium for Sustainable Humanosphere, Bandung, Indonesia, 29 August 2012; pp. 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.K.; Jodhani, A.; Singh, A.P. Bamboo as construction material and bamboo reinforcement. Int. J. Civ. Struct. Eng. Res. 2016, 4, 312–323. [Google Scholar]
- Nath, S.; Jena, H.; Priyanka; Sahini, D. Analysis of Mechanical Properties of Jute Epoxy Composite with Cenosphere Filler. Silicon 2019, 11, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.V.; Reddy, R.V.S.; Rajendra Prasad, P.; Mohana Krishnudu, D.; Reddy, R.M.; Rao, H.R. Evaluation of Mechanical and Wear Performances of Natural Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 2218–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.K.; Narang, H.K.; Bhattacharya, S. Mechanical properties of natural fibre polymer composites. J. Polym. Eng. 2017, 37, 879–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharana, S.M.; Samal, P.; Dehury, J.; Mohanty, P.P. Effect of fiber content and orientation on mechanical properties of epoxy composites reinforced with jute and Kevlar. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylsamy, K.; Rajendran, I. Investigation on physio-chemical and mechanical properties of raw and alkali-treated Agave americana fiber. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2010, 29, 2925–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.W.; Yousif, B.F. Potential of kenaf fibres as reinforcement for tribological applications. Wear 2009, 267, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, B.; Leong, O.; Ong, L.; Jye, W. The Effect of Treatment on Tribo-Performance of CFRP Composites. Recent Patents Mater. Sci. 2009, 2, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Prasad, L.; Patel, V.K.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, A. Physico-Mechanical Properties and Taguchi Optimized Abrasive Wear of Alkali Treated and Fly Ash Reinforced Himalayan Agave Fiber Polyester Composite. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 9269–9282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Prasad, L.; Patel, V.K.; Kumain, A.; Yadav, A. Experimental and numerical study on physico-mechanical properties and Taguchi’s designed abrasive wear behavior of hemp/nettle-polyester hybrid composite. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 6912–6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivamurthy, B.; Thimmappa, B.H.S.; Monteiro, J. Sliding wear, mechanical, flammability, and water intake properties of banana short fiber/Al(OH)3/epoxy composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2020, 17, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, L.; Bairwan, R.; Yadav, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, V.; Winczek, J. Evaluation of Physical, Mechanical, and Wear Properties of Jatropha Shell Powder Reinforced Epoxy Glass Fiber Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 12195–12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylsamy, K.; Rajendran, I. Influence of Fibre Length on the Wear Behaviour of Chopped Agave americana Fibre Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 44, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridzuan, M.J.M.; Abdul Majid, M.S.; Khasri, A.; Gan, E.H.D.; Razlan, Z.M.; Syahrullail, S. Effect of pineapple leaf (PALF), napier, and hemp fibres as filler on the scratch resistance of epoxy composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5384–5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, T.P.; Kanny, K. Water barrier properties of nanoclay filled sisal fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesh, P.; Puttegowda, M.; Mavinkere Rangappa, S.; Siengchin, S. A review on extraction, chemical treatment, characterization of natural fibers and its composites for potential applications. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 6239–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, V.; Kumar, M.; Kaup, V. A Review on Natural Fiber Composite Material in Automotive Applications. Eng. Sci. 2021, 18, es8d589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladele, I.O.; Ibrahim, I.O.; Adediran, A.A.; Akinwekomi, A.D.; Adetula, Y.V.; Olayanju, T.M.A. Modified palm kernel shell fiber/particulate cassava peel hybrid reinforced epoxy composites. Results Mater. 2020, 5, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieparda, W.; Rojewski, S.; Wüstenhagen, S.; Kicinska-Jakubowska, A.; Krombholz, A. Chemical modification of natural fibres to epoxy laminate for lightweight constructions. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 140, 106171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthiveettil Ramakrishnan, S.; Vijayananth, K.; Pudhupalayam Muthukutti, G.; Spatenka, P.; Arivendan, A.; Ganesan, S.P. The effect of various composite and operating parameters in wear properties of epoxy-based natural fiber composites. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2022, 24, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laraba, S.R.; Rezzoug, A.; Halimi, R.; Wei, L.; Yang, Y.; Abdi, S.; Li, Y.; Jie, W. Development of sandwich using low-cost natural fibers: Alfa-Epoxy composite core and jute/metallic mesh-Epoxy hybrid skin composite. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 184, 115093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshwaran, N.; Elaya Perumal, A.; Arunsundaranayagam, D. Fiber surface treatment and its effect on mechanical and visco-elastic behaviour of banana/epoxy composite. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, H.A.; Tanni, T.R.; Shahid, M.A. Analysis of Water Absorption of Different Natural Fibers. J. Text. Sci. Technol. 2021, 7, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, L.; Singh, V.; Patel, R.V.; Yadav, A.; Kumar, V.; Winczek, J. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Rambans (Agave) Fiber Reinforced with Polyester Composite Materials. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 6104–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Prasad, L.; Patel, V.K.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, A.; Winczek, J. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Natural Leaf Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Polyester Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyapragash, R.; Srinivasan, V.; Sathiyamurthy, S. Mechanical properties of natural fiber/particulate reinforced epoxy composites—A review of the literature. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 1223–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Kindo, S.; Patnaik, A. Effect of fiber length on mechanical behavior of coir fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Fibers Polym. 2011, 12, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Srivastava, R.K. Tensile and Flexural Properties of Sisal Fibre Reinforced Epoxy Composite: A Comparison between Unidirectional and Mat form of Fibres. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 2434–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, A.; Purushothaman, R.; Udhayasankar, R.; Vijayaraj, S.; Karthikeyan, B. Study on Mechanical, Thermal and Morphological Properties of Banana Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites. J. Bio Tribo-Corrosion 2020, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Jamwal, A.; Gupta, P.; Thakur, S.; Gupta, S. Processing and characterization of pine epoxy based composites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2148, 030017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidhar, B.A. Tensile and compressive behaviour of multilayer flax-rib knitted preform reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylsamy, K.; Rajendran, I. Influence of alkali treatment and fibre length on mechanical properties of short Agave fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4629–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshappa, S.C.; Jayadevappa, S.Y.; Puttiah, P.K.W. Mechanical behavior of areca fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2012, 31, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, A.P.; Soemardi, T.P.; Widjajalaksmi, K.; Reksoprodjo, A.H.S. Tensile and flexural strength of ramie fiber reinforced epoxy composites for socket prosthesis application. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2011, 6, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Maleque, M.A.; Belal, F.Y.; Sapuan, S.M. Mechanical properties study of pseudo-stem banana fiber reinforced epoxy composite. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2007, 32, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Olaitan, A.; Terhemen, A.; King, G.; Oluwatoyin, O. Comparative Assessment of Mechanical Properties of Groundnut Shell and Rice Husk Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Am. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 5, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshwaran, N.; ElayaPerumal, A.; Alavudeen, A.; Thiruchitrambalam, M. Mechanical and water absorption behaviour of banana/sisal reinforced hybrid composites. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4017–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerdhass, R.; Gnanavelbabu, A.; Rajkumar, K. Mechanical Properties of Luffa Fiber and Ground nut Reinforced Epoxy Polymer Hybrid Composites. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 2042–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djafari Petroudy, S.R.R. Physical and mechanical properties of natural fibers. In Advanced High Strength Natural Fibre Composites in Construction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 59–83. ISBN 9780081004302. [Google Scholar]
- Balaji, A.; Karthikeyan, B.; Swaminathan, J. Comparative mechanical, thermal, and morphological study of untreated and NaOH-treated bagasse fiber-reinforced cardanol green composites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2019, 2, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, E.; Panigrahi, S. Effect of Plasma Treatment on Structure, Wettability of Jute Fiber and Flexural Strength of its Composite. J. Compos. Mater. 2009, 43, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Paiva, F.F.G.; de Maria, V.P.K.; Torres, G.B.; Dognani, G.; dos Santos, R.J.; Cabrera, F.C.; Job, A.E. Sugarcane bagasse fiber as semi-reinforcement filler in natural rubber composite sandals. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 21, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Verpoest, J.; Ivens, I. Mechanical properties of flax fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Die Angew. Makromol. Chemie 1999, 272, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopalan, M.; Niranjanaa, M.; Umapathy, M.J. Study on the mechanical properties and thermal properties of jute and banana fiber reinforced epoxy hybrid composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 51, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punyamurthy, R.; Sampathkumar, D.; Bennehalli, B.; Patel, R.; Venkateshappa, S.C. Abaca Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites: Evaluation of Impact Strength. Int. J. Sci. Basic Appl. Res. 2014, 4531, 305–317. [Google Scholar]
- Srisuwan, S.; Prasoetsopha, N.; Suppakarn, N.; Chumsamrong, P. The Effects of Alkalized and Silanized Woven Sisal Fibers on Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber Modified Epoxy Resin. Energy Procedia 2014, 56, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh Kumar, C.; Arumugam, V.; Dhakal, H.N.; John, R. Effect of temperature and hybridisation on the low velocity impact behavior of hemp-basalt/epoxy composites. Compos. Struct. 2015, 125, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, F.; Antunes, F. Novel ranking framework for retrospective simultaneous assessment of fire and mechanical performances of natural fiber-reinforced polymeric composites: Literature update from the previous decade. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2022, 28, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, K.Z.; Johari, M.A.M.; Demirboğa, R. Impact of fiber reinforcements on properties of geopolymer composites: A review. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawaid, M.; Abdul Khalil, H.P.S.; Abu Bakar, A. Woven hybrid composites: Tensile and flexural properties of oil palm-woven jute fibres based epoxy composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 5190–5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potluri, R.; James Paul, K.; Abdul Kalam, S.; Prasanthi, P. Mechanical Properties Characterization of Okra Fiber Based Green Composites; Hybrid Laminates. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 2893–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, K.; Sahoo, P.; Bhowmik, S. Study of Mechanical Properties of Wood Dust Reinforced Epoxy Composite. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, K.; Bhowmik, S. Optimization of Mechanical Properties of Epoxy based Wood Dust Reinforced Green Composite Using Taguchi Method. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugochukwu, S.; Ridzuan, M.J.M.; Abdul Majid, M.S.; Cheng, E.M.; Razlan, Z.M.; Marsi, N. Effect of thermal ageing on the scratch resistance of natural-fibre-reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Struct. 2021, 261, 113586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanavel, V.; Raja, T.; Yadav, A.; Ravichandran, M.; Winczek, J. Evaluation of Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Jute and Ramie Reinforced Epoxy-based Hybrid Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 8022–8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shesan, O.J.; Stephen, A.C.; Chioma, A.G.; Neerish, R.; Rotimi, S.E. Improving the Mechanical Properties of Natural Fiber Composites for Structural and Biomedical Applications. In Renewable and Sustainable Composites; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Asim, M.; Paridah, M.T.; Chandrasekar, M.; Shahroze, R.M.; Jawaid, M.; Nasir, M.; Siakeng, R. Thermal stability of natural fibers and their polymer composites. Iran. Polym. J. 2020, 29, 625–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnet, S.; Otsuka, M.; Sasaki, C.; Asada, C.; Nakamura, Y. Functionalization of the active ingredients of Japanese green tea (Camellia sinensis) for the synthesis of bio-based epoxy resin. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 73, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, M.; Júnior, H.L.O.; Zattera, A.J. Thermal Decomposition of Natural Fibers: Kinetics and Degradation Mechanisms. In Reactions and Mechanisms in Thermal Analysis of Advanced Materials; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 515–545. ISBN 9781119117711. [Google Scholar]
- Balaji, A.; Karthikeyan, B.; Swaminathan, J.; Sundar Raj, C. Thermal behavior of cardanol resin reinforced 20 mm long untreated bagasse fiber composites. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2018, 23, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norul Izani, M.A.; Paridah, M.T.; Anwar, U.M.K.; Mohd Nor, M.Y.; H’ng, P.S. Effects of fiber treatment on morphology, tensile and thermogravimetric analysis of oil palm empty fruit bunches fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 45, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, H.; Low, I.M.; Alothman, Z. Mechanical, thermal and microstructural characteristics of cellulose fibre reinforced epoxy/organoclay nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2762–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.S.S.; de Queiroz, H.F.M.; Aguiar, R.A.A.; Banea, M.D. A Review on the Thermal Characterisation of Natural and Hybrid Fiber Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, P.; Prasad, B.D.; Narayana, K.L. Influence of Montmorillonite Clay Content on Thermal, Mechanical, Water Absorption and Biodegradability Properties of Treated Kenaf Fiber/PLA-Hybrid Biocomposites. Silicon 2021, 13, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanimozhi, T.; Sundara Pandian, S.; Gokulkumar, S.; Sathish, S. Influence of Acacia concinna and Vachellia nilotica seed nanopowder on the properties of short Turkish hemp–reinforced epoxy composites. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2022, 146442072211454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippon, J.A.; Evans, D.J. Improving the properties of natural fibres by chemical treatments. In Handbook of Natural Fibres; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 63–140. [Google Scholar]
- Gassan, J.; Gutowski, V.S. Effects of corona discharge and UV treatment on the properties of jute-fibre expoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2000, 60, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Nguyen, M.H.; Hwang, B.S.; Lee, S. Effect of plasma treatment on the mechanical properties of natural fiber/PP composites. WIT Trans Built Env. 2008, 97, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Gibeop, N.; Lee, D.W.; Prasad, C.V.; Toru, F.; Kim, B.S.; Song, J., II. Effect of plasma treatment on mechanical properties of jute fiber/poly(lactic acid) biodegradable composites. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2013, 22, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Fangueiro, R. Physical Modification of Natural Fibers and Thermoplastic Films for Composites—A Review. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2009, 22, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwawi, M. A Review on Natural Fiber Bio-Composites, Surface Modifications and Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, A.; Ashour, F.H.; Hakim, A.A.A.; Bassyouni, M. Recent advances in biodegradable polymers for sustainable applications. NPJ Mater. Degrad. 2022, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.M.; Wang, H.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F.; Aravinthan, T. Mechanical properties of chemically-treated hemp fibre reinforced sandwich composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Gupta, M. A review on the properties of natural fibres and its bio-composites: Effect of alkali treatment. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2020, 234, 198–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.M.F.; Horváth, P.G.; Alpár, T. Potential Natural Fiber Polymeric Nanobiocomposites: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Goh, K.L. Effect of Mercerization/Alkali Surface Treatment of Natural Fibres and Their Utilization in Polymer Composites: Mechanical and Morphological Studies. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilay, V.; Mariatti, M.; Mat Taib, R.; Todo, M. Effect of fiber surface treatment and fiber loading on the properties of bagasse fiber-reinforced unsaturated polyester composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, C.; Yu, Y. Interfacial studies of sisal fiber reinforced high density polyethylene (HDPE) composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouarhim, W.; Zari, N.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A. el kacem Mechanical performance of natural fibers–based thermosetting composites. In Mechanical and Physical Testing of Biocomposites, Fibre-Reinforced Composites and Hybrid Composites; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 43–60. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.A.; Pandit, P. Chemical processing of knitted fabrics. In Advanced Knitting Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 503–536. [Google Scholar]
- Arya, P.; Ghosh, S. Non-Formaldehyde Wrinkle Resistant Finish for Linen. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 9719–9728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Tabil, Æ.L.G.; Panigrahi, Æ.S. Chemical Treatments of Natural Fiber for Use in Natural Fiber-Reinforced Composites: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczewski, M.; Matykiewicz, D.; Szostak, M. The effect of two-step surface treatment by hydrogen peroxide and silanization of flax/cotton fabrics on epoxy-based laminates thermomechanical properties and structure. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 13813–13824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fu, R.; Deng, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xian, G. Surface Modification of Flax Fibers with Isocyanate and Its Effects on Fiber/Epoxy Interfacial Properties. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 2888–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenned, J.J.; Sankaranarayanasamy, K.; Kumar, C.S. Chemical, biological, and nanoclay treatments for natural plant fiber-reinforced polymer composites: A review. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2021, 29, 1011–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, F.; Karim, N.; Afroj, S.; Koncherry, V.; Novoselov, K.S.; Potluri, P. High-Performance Graphene-Based Natural Fiber Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 34502–34512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyayunita, T.; Widyorini, R.; Marsoem, S.N.; Irawati, D. Effect of Different Conditions of Sodium Chloride Treatment on the Characteristics of Kenaf Fiber-Epoxy Composite Board. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2022, 50, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, R.S.; Prasad, L.; Yadav, A.; Winczek, J. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Pinecone Scale Fiber/Vigna Mungo Powder Reinforced Polypropylene Based Hybrid Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 11458–11468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.P.; Cruz, J.; Fangueiro, R. Surface modification of natural fibers in polymer composites. In Green Composites for Automotive Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 3–41. [Google Scholar]
- Maqsood, H.S.; Bashir, U.; Wiener, J.; Puchalski, M.; Sztajnowski, S.; Militky, J. Ozone treatment of jute fibers. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; McDonald, A. A Review on Grafting of Biofibers for Biocomposites. Materials 2016, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safri, S.N.A.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shah, A.U.M. Characterization of benzoyl treated sugar palm/glass fibre hybrid composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 11563–11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanshour, F.; Ramakrishnan, K.; Layek, R.K.; Laurikainen, P.; Prapavesis, A.; Kanerva, M.; Kallio, P.; Van Vuure, A.W.; Sarlin, E. Effect of graphene oxide surface treatment on the interfacial adhesion and the tensile performance of flax epoxy composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 142, 106270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setyayunita, T.; Widyorini, R.; Marsoem, S.N.; Irawati, D. Study on The Characteristics of NaCl Treated Kenaf Fiber Epoxy Composite Board. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 891, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puglia, D.; Biagiotti, J.; Kenny, J.M. A Review on Natural Fibre-Based Composites—Part II. J. Nat. Fibers 2005, 1, 23–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyavihalli Girijappa, Y.G.; Mavinkere Rangappa, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. Natural Fibers as Sustainable and Renewable Resource for Development of Eco-Friendly Composites: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateshwar Reddy, P.; Saikumar Reddy, R.V.; Lakshmana Rao, J.; Mohana Krishnudu, D.; Rajendra Prasad, P. An overview on natural fiber reinforced composites for structural and non-structural applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 6210–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, F.; He, G.; Sheng, C.; He, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, R.; Ning, X. Yarn on yarn abrasion performance of high modulus polyethylene fiber improved by graphene/polyurethane composites coating. J. Eng. Fiber. Fabr. 2021, 16, 1558925020983563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, S.; Hossain, M.S. Natural Fibre Composite (NFC): New Gateway for Jute, Kenaf and Allied Fibres in Automobiles and Infrastructure Sector. World J. Res. Rev. 2017, 5, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Khondker, O.A.; Ishiaku, U.S.; Nakai, A.; Hamada, H. Fabrication Mechanical Properties of Unidirectional Jute/PP Composites Using Jute Yarns by Film Stacking Method. J. Polym. Environ. 2005, 13, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.; He, G.; Hu, Z.; Chou, C.; Shi, J.; Li, J.; Meng, Q.; Ning, X.; Wang, L.; Ning, F. Yarn on yarn abrasion failure mechanism of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber. J. Eng. Fiber. Fabr. 2021, 16, 15589250211052766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Takagi, H.; Nakagaito, A.N.; Li, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N. Effect of alkali treatment on interfacial bonding in abaca fiber-reinforced composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 90, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Banana/Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polypropylene Hybrid Composites: Fabrication and Performance Evaluation. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2009, 48, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandramohan, D. Natural Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites for Automobile Accessories. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 9, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaker, K.; Nawab, Y.; Jabbar, M. Bio-composites: Eco-friendly Substitute of Glass Fiber Composites. In Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–25. ISBN 9783030111557. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, E.; Schartel, B.; Acierno, D.; Cimino, F.; Russo, P. Tailoring the flame retardant and mechanical performances of natural fiber-reinforced biopolymer by multi-component laminate. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 44, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graupner, N.; Herrmann, A.S.; Müssig, J. Natural and man-made cellulose fibre-reinforced poly(lactic acid) (PLA) composites: An overview about mechanical characteristics and application areas. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2009, 40, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cao, S.; Yilmaz, E. Influence of 3D-printed polymer structures on dynamic splitting and crack propagation behavior of cementitious tailings backfill. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 343, 128137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascano, D.; Balart, R.; Garcia-Sanoguera, D.; Agüero, A.; Boronat, T.; Montanes, N. Manufacturing and Characterization of Hybrid Composites with Basalt and Flax Fabrics and a Partially Bio-based Epoxy Resin. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorseng, K.; Mavinkere Rangappa, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Siengchin, S. Towards green composites: Bioepoxy composites reinforced with bamboo/basalt/carbon fabrics. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, M.C.A.; Glória, G.O.; Altoé, G.R.; Amoy Netto, P.; Margem, F.M.; Braga, F.O.; Monteiro, S.N. Evaluation of the Diameter Influence on the Tensile Strength of Pineapple Leaf Fibers (PALF) by Weibull Method. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, M.R.; Arpitha, G.R.; Naik, L.L.; Gopalakrishna, K.; Yogesha, B. Applications of Natural Fibers and Its Composites: An Overview. Nat. Resour. 2016, 7, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugu Nachippan, N.; Alphonse, M.; Bupesh Raja, V.; Shasidhar, S.; Varun Teja, G.; Harinath Reddy, R. Experimental investigation of hemp fiber hybrid composite material for automotive application. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 3666–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, J.; Queiroz, H.; Aguiar, R.; Lima, R.; Cavalcanti, D.; Doina Banea, M. A Review of Recent Advances in Hybrid Natural Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composites. J. Renew. Mater. 2022, 10, 561–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneshwaran, S.; John, K.; Deepak Joel Johnson, R.; Uthayakumar, M.; Arumugaprabu, V.; Kumaran, S.T. Conventional and unconventional machining performance of natural fibre-reinforced polymer composites: A review. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2021, 40, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potluri, R.; Chaitanya Krishna, N. Potential and Applications of Green Composites in Industrial Space. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 22, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Kumar, U.; Pal, A. Status and Scope of the Jute Industry in India in Comparison to other World Producers. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2016, 24, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Yilmaz, E. Strength, acoustic, and fractal behavior of fiber reinforced cemented tailings backfill subjected to triaxial compression loads. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 338, 127667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potluri, R. Natural Fiber-Based Hybrid Bio-composites: Processing, Characterization, and Applications. In Green Composites; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, L.; Krishnaraj, V.; Sathish, S.; Gokulkumar, S.; Karthi, N.; Rajeshkumar, L.; Balaji, D.; Vigneshkumar, N.; Elango, K.S. A review on natural fiber reinforced hybrid composites: Chemical treatments, manufacturing methods and potential applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 8080–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lila, M.K.; Singh, B.; Pabla, B.S.; Singh, I. Effect of environmental conditioning on natural fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 17006–17011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alms, J.B.; Yonko, P.J.; McDowell, R.C.; Advani, S.G. Design and Development of an I-Beam from Natural Composites. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2009, 3, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweib, M.A.; Hu, B.; O’Donnell, A.; Shenton, H.W.; Wool, R.P. All natural composite sandwich beams for structural applications. Compos. Struct. 2004, 63, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisanda, E.T.N. The manufacture of roofing panels from sisal fibre reinforced composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1993, 38, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, K.; Tronchin, L.; Barbieri, F. Coconut fibre insulators: The hygrothermal behaviour in the case of green roofs. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 266, 121026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Appearance | Colourless to Pale Yellow Liquid |
|---|---|
| Flexural strength (MPa) | 40–67 |
| Specific gravity (kg/m3) | 1120–1210 |
| Viscosity at 25 °C (kg/m s) | 0.25–0.75 |
| Heat distortion temperature (°C) | 50 |
| Solid content (%) | 84 |
| Modulus of elasticity (MPa) | 3100 to 3800 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 90 to 120 |
| Max percentage elongation (%) | 4 |
| Impact strength (kg/m2) | 9 |
| Glass transition temperatures | 150 to 220 °C |
| Natural Fiber | Physical Appearance and Texture | Density (g/cm3) | Diameter (µm) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jute | Light brown, fine | 1.3–1.45 | 25–200 | 393–773 | 13–26.5 | 1.5–1.8 | [43,44] |
| Sisal | White, coarse-stiff | 1.45 | 50–200 | 468–640 | 9.4–22 | 3–6 | [43,44] |
| Hemp | White to light brown, silky-fine | 1.48 | 26.5 | 514 | 24.8 | 1.5–4 | [45,46,47] |
| Coir | White to brown, coarse | 1.15 | 100–450 | 131–175 | 4–6 | 4–6 | [43,48] |
| Sugar palm | Brown to black, coarse-stiff | 1.29 | 50–800 | 190.29 | 3.69 | – | [49] |
| Sugarcane bagasse | - | 0.33 | 67–312 | 222 | 27.1 | – | [50] |
| Nettle | - | 0.72 | 15.5–24.3 | 1594 | 59–115 | – | [18,51] |
| Saw dust | Generally light yellow to brown (varies from trees to trees), particles | 2.05 (SG) 0.31–0.32 | 75–600 | 16–24 | 0.2 × 10−3–0.36 × 10−3 | – | [52,53,54] |
| Wood chips | Generally light yellow to brown (varies from trees to trees) | 0.28–0.32 | 3000–16000 | – | 0.25 × 10−3–0.33 × 10−3 | – | [54] |
| Softwood | - | 1.5 | – | 1000 | 0.04 | 4.4 | [55] |
| Flax Agatha | - | 1.50–1.53 | 14.4–15.6 | 962–1800 | 46–96 | – | [47] |
| Ramie | - | 1.51 | 34 | 400–968 | 60–128 | 3.6–3.8 | [43,47] |
| Okra | - | – | 61–93 | 184–557.3 | 8.9–11.8 | 4–8 | [56] |
| Agave | - | 1.20 | 126–344 | – | – | 7.07 | [56] |
| Banana | - | 1.35 | 50–250 | 600 | 17.85 | 3.36 | [56] |
| Sea grass | - | 1.50 | 5 | 453–692 | 3.1–3.7 | 13–26.3 | [56] |
| Kenaf | 1.3 | – | 233 | 40–53 | 1.8 | [50,57,58] | |
| Cotton | White, creamy white, yellowish white, fine | 1.51–1.6 | 2–7 | 287–597 | 5.5–12.6 | 3–10 | [43,59] |
| Luffa | - | 0.82 | 25–60 | 385 | 12.2 | – | [50] |
| Banana | - | 1.35 | 70–210 | 198.9–780.3 | 6.6–25.6 | – | [60,61,62] |
| Rice husk | Fine, grey | 2.30–2.36 | 45 Particle size | – | – | – | [63] |
| Coconut coir | - | 1.15 | 100–450 | 500 | 2.5 | 3.36 | [55] |
| Napier | - | 0.36 | – | 73 | 5.68 | 1.4 | [64] |
| Bamboo | White yellow | 0.51–0.72 | 21–26 | 225 | 17.2 | 3 | [65,66] |
| Abaca | - | 0.83 | 1.5 | 900 | 12–13.8 | 3–12 | [55] |
| Flax ariane | - | 1.53 | 12–23.6 | 853–1825 | 43–73 | 1.2–3.2 | [44,47] |
| Date | - | 0.99 | – | 309 | 11.32 | 2.73 | [56] |
| Palmyrah | - | 1.09 | 8 | 180–215 | 4.4–6.1 | – | [49] |
| Pineapple leaf | - | 1.07–1.50 | 20–80 | 413–1627 | 34.5–82.5 | 1.6 | [50] |
| Henequen | - | 1.4 | – | 430–580 | – | – | [24] |
| Ramie | - | 1.50 | 50 | 220–938 | 44–128 | 2–3.8 | [56] |
| Composites | Density (g/cm3) | Porosity/Volume of Void Fraction | Water Absorption % (Till Steady State) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jute/epoxy (25/75) | 1.08 | 7.50 | - | [31] |
| Jute/epoxy (35/65) | 1.276 | 1.09 | 10 | [67] |
| Bagasse/epoxy (3/97), 5 mm fiber length | 1.14 | 1.02 | 7.12 | [26] |
| Bagasse/epoxy (3/97), 10 mm fiber length | 1.13 | 1.94 | 8.11 | [26] |
| Bagasse/epoxy (3/97), 15 mm fiber length | 1.12 | 2.62 | 16 | [26] |
| Hemp/epoxy (9/91) | 1.275 | 3.40 | 0.7 | [18] |
| Hemp/epoxy (25/75) | 1.10 | 6.12 | - | [31] |
| Nettle/epoxy (9/91) | 1.283 | 5.17 | 1 | [18] |
| Hemp + nettle/epoxy (18/82) | 1.35 | 2.46 | 1.2 | [18] |
| Prosopis juliflora/epoxy (20/80) | 1.14 | - | - | [68] |
| Abutilon indicum/epoxy (20/80) | 1.12 | - | - | [68] |
| Tapsi/epoxy (20/80) | 1.31 | - | - | [68] |
| Coir/epoxy (30/70) | 1.28 | - | 0.09 | [69] |
| Banana/epoxy(30/70) | 1.10 | - | 0.1 | [69] |
| Sisal/epoxy (30/70) | 1.16 | - | 0.05 | [69] |
| Flax/epoxy (25/75) | 1.07 | 8.09 | - | [31] |
| Jute + hemp/epoxy (25/75) | 1.09 | 6.89 | - | [31] |
| Flax + hemp/epoxy (25/75) | 1.08 | 7.52 | - | [31] |
| Jute + hemp + flax/epoxy (25/75) | 1.10 | 6.30 | - | [31] |
| (Kevlar + Jute)/epoxy ((20 + 20)/60 0° fiber orientation | 1.23 | 4.27 | - | [70] |
| (Kevlar + Jute)/epoxy ((20 + 20)/60 30° fiber orientation | 1.22 | 5.20 | - | [70] |
| (Kevlar + Jute)/epoxy ((20 + 20)/60 45° fiber orientation | 1.20 | 6.75 | - | [70] |
| (Kevlar + Jute)/epoxy ((20 + 20)/60 60° fiber orientation | 1.20 | 6.75 | - | [70] |
| Agave raw fiber | 1.20 | - | 7.69 | [71] |
| Agave fiber with 5% NaOH | 1.30 | - | 8.74 | [71] |
| Agave fiber with 10% NaOH | 13.2 | - | 8.64 | [71] |
| Composites (wt%/wt%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Impact Strength (J/m) | Impact Energy (kJ/m2) | Hardness | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coir/epoxy (30/70), 5 mm fiber length | 3.208 | 25.41 | - | 16.0 | 15 HV | [92] |
| Coir/epoxy (30/70) 20 mm fiber length | 9.15 | 31.28 | - | 16.5 | 12.6 HV | [92] |
| Coir/epoxy (30/70) 30 mm fiber length | 13.05 | 35.42 | - | 17.5 | 16.9 HV | [92] |
| (Kevlar+ Jute)/epoxy (20 + 20)/60 0° fiber orientation | 75 | 42 | - | - | - | [70] |
| (Kevlar+ Jute)/epoxy (20 + 20)/60 30° fiber orientation | 94 | 33 | - | - | - | [70] |
| (Kevlar+ Jute)/epoxy (20 + 20)/60 45° fiber orientation | 71 | 45 | - | - | - | [70] |
| (Kevlar+ Jute)/epoxy (20 + 20)/60 60° fiber orientation | 68 | 35 | - | - | - | [70] |
| Sisal/epoxy (15/85) | 66.74 | 204.3 | - | - | - | [93] |
| Sisal/epoxy (20/85) | 87.54 | 167.7 | - | - | - | [93] |
| Sisal/epoxy (25/85) | 74.89 | 235.3 | - | - | - | [93] |
| Sisal/epoxy (30/85) | 132.73 | 288.6 | - | - | - | [93] |
| Sisal/epoxy (30/85), mat form | 89.30 | 152.12 | - | - | - | [93] |
| Jute/epoxy (35/65) | 38.00 | 10 | - | 10.2 | [67] | |
| Banana/epoxy (5/95) | 26.3 | 46.2 | - | 220 | 54.5 HRB | [94] |
| Banana/epoxy (10/90) | 27.2 | 52.5 | - | 2400 | 60.8 HRB | [94] |
| Banana/epoxy (15/85) | 30.4 | 56.3 | - | 2700 | 65.4 HRB | [94] |
| Banana/epoxy (20/80) | 29.4 | 54.3 | - | 2600 | 68 HRB | [94] |
| Coir/epoxy (30/70) | - | 4 J | 36 HRC | [69] | ||
| Banana/epoxy (30/70) | - | 5 J | 63 HRC | [69] | ||
| Sisal/epoxy (30/70) | - | 4 J | 54 HRC | [69] | ||
| Pine/epoxy (10/90) | 53 | 61 | - | 18 | - | [95] |
| Pine/epoxy (20/80) | 50 | 57 | - | 16 | - | [95] |
| Pine/epoxy (30/70) | 39 | 43 | - | 14 | - | [95] |
| Pine/epoxy (40/60) | 36 | 38 | - | 11 | - | [95] |
| Bagasse/epoxy (3/97), 5 mm fiber length | 26.36 | - | - | 2.4 | 25 HV | [26] |
| Bagasse/epoxy (3/97), 10 mm fiber length | 29.23 | - | - | 2.5 | 39 HV | [26] |
| Bagasse/epoxy (3/97), 15 mm fiber length | 23.57 | - | - | 3.7 | 32 HV | [26] |
| Flax fabric/epoxy (26.64/73.36), 2 mm laminate thickness | 35.59 | - | - | - | - | [96] |
| Flax fabric/epoxy (21.17/78.83), 4 mm laminate thickness | 29.74 | - | - | - | - | [96] |
| Agave/epoxy (30/70), untreated, 3 mm fiber length | - | 55 | 120 | - | - | [97] |
| Agave/epoxy (30/70), NaOH treated, 3 mm fiber length | - | 60 | 140 | - | - | [97] |
| Agave/epoxy (30/70), untreated, 7 mm fiber length | - | 41 | 100 | - | - | [97] |
| Agave/epoxy (30/70), NaOH treated, 7 mm fiber length | - | 48 | 115 | - | - | [97] |
| Agave/epoxy (30/70), untreated, 10 mm fiber length | - | 41.5 | 55 | - | - | [97] |
| Agave/epoxy (30/70), NaOH treated, 10 mm fiber length | 39 | 63 | - | - | [97] | |
| Areca/epoxy (50/50) | 27.50 | 25.00 | 93.33 | - | - | [98] |
| Ramie/epoxy (40/60) | 86 | 103 | - | - | [99] | |
| Pseudo stem Banana-epoxy | 45.57 | 73.58 | 92.66 | - | - | [100] |
| Ground nuts shell/epoxy (12.5/87.5) | 36.66 | 43.43 | 7.91 | - | 6.8 HRF | [101] |
| Rice husk/epoxy (12.5/87.5) | 12.71 | 22.72 | 4.27 | - | 6.9 HRF | [101] |
| Coir pith-epoxy | 9.00 | 23.00 | 18.67 | - | - | |
| Banana + sisal/epoxy (8/92), 5 mm fiber length | 9.48 | 28.43 | 2.15 | - | - | [102] |
| Banana + sisal/epoxy (12/88), 5 mm fiber length, 5 mm fiber length | 16.39 | 26.15 | 2.37 | - | - | [102] |
| Banana + sisal/epoxy (16/84), 5 mm fiber length, 5 mm fiber length | 12.74 | 37.56 | 2.62 | - | - | [102] |
| Banana + sisal/epoxy (8/92), 10 mm fiber length | 8.54 | 22.22 | 5.21 | - | - | [102] |
| Banana + sisal/epoxy (12/88), 5 mm fiber length, 10 mm fiber length | 15.52 | 31.4 | 8.33 | - | - | [102] |
| Banana + sisal/epoxy (16/84), 5 mm fiber length, 10 mm fiber length | 10.3 | 25.56 | 11.56 | - | - | [102] |
| Luffa + groundnut- epoxy (40/60) | 20 | 53 | - | 1.1 | - | [103] |
| Hemp/epoxy (9/91) | 69.85 | 10.15 | - | 5.7 | 50.1 HV | [18] |
| Nettle/epoxy (9/91) | 66.9 | 16 | - | 6.7 | 52.0 HV | [18] |
| Hemp + nettle/Epoxy (18/82) | 71.72 | 14.21 | - | 6.2 | 59.1 HV | [18] |
| Prosopis Juliflora/epoxy (20/80) | 72 | 254 | 74 | - | - | [68] |
| Abutilon Indicum/epoxy (20/80) | 67 | 216 | 92 | - | - | [68] |
| Tapsi/epoxy (20/80) | 49 | 225 | 45 | - | - | [68] |
| Natural Fibers | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Hemp fiber | Rope, paper and packaging, furniture, electrical, banknotes, and pipes manufacturing. | [24] |
| Oil palm fiber | Structural insulated panels, windows, door frames, fencing, roofing, decking, and siding materials | [24] |
| Wood fiber | Window frames, railing systems, door shutters, decking, panels, and fencing | [24] |
| Flax fiber | Window frames, panels, decking, railing systems, fencing, bicycle frame, fork, seat post, snowboards, and tennis rackets | [24] |
| Rice husk fiber | Building panels, bricks, frame of the window, decking, and railing systems | [24] |
| Sisal fiber | Core in elevator steel wire cables, agricultural twine or baler twine, and freight handling | [161] |
| Stalk fiber | Panels in building, furniture, as bricks, constructing drains and in pipelines | [24] |
| Kenaf fiber | Packing material, mobile case, bags, insulating material, clothing-grade cloth, soilless potting mixes, and animal bedding | [162] |
| Cotton fiber | Furniture, textile composites yarn, goods, and cordage | [24] |
| Coir fibers | Paper weight, filling material for seat upholstery, seat cushions, cover, brush, brooms, ropes, yarns for nets, bags, mats, and padding for the mattress | [24,163] |
| Coconut fiber | Seat bottoms, back cushions and head, rope, mats, mattress, brush, and upholstery | [161] |
| Ramie fiber | Sewing thread, packaging material, fishing net, filter cloths, upholstery, canvas, and clothes | [24] |
| Bagasse fiber | Fencing the frame of the window, panels, decking, and railing systems | |
| Jute fiber | Building panels, roofing sheets, door frames, door shutters, transport, packaging, geotextiles, mobile casing, indoor elements in housing, and chipboards | [162,164,165,166] |
| Abaca fiber | Under floor body panels | [167] |
| Pineapple leaf | Automobile componentss, textile, and mats | [161] |
| Date palm | Textile for the indoor house, mats | [161] |
| Banana fiber | Floor protection for passenger cars | [168] |
| Roselle fibers | Automobile seat cover, visor in a two-wheeler, name plate, and indicator cover | [169] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patel, R.V.; Yadav, A.; Winczek, J. Physical, Mechanical, and Thermal Properties of Natural Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites for Construction and Automotive Applications. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5126. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085126
Patel RV, Yadav A, Winczek J. Physical, Mechanical, and Thermal Properties of Natural Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites for Construction and Automotive Applications. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(8):5126. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085126
Chicago/Turabian StylePatel, Raj Vardhan, Anshul Yadav, and Jerzy Winczek. 2023. "Physical, Mechanical, and Thermal Properties of Natural Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites for Construction and Automotive Applications" Applied Sciences 13, no. 8: 5126. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085126
APA StylePatel, R. V., Yadav, A., & Winczek, J. (2023). Physical, Mechanical, and Thermal Properties of Natural Fiber-Reinforced Epoxy Composites for Construction and Automotive Applications. Applied Sciences, 13(8), 5126. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085126










