Study of Physicochemical and Gelation Properties of Fish Gelatin from Different Sources
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.1.1. Material
2.1.2. Equipment
2.2. Gelatin Protein Content and Molecular Weight Determination
2.2.1. Determination of Protein Content
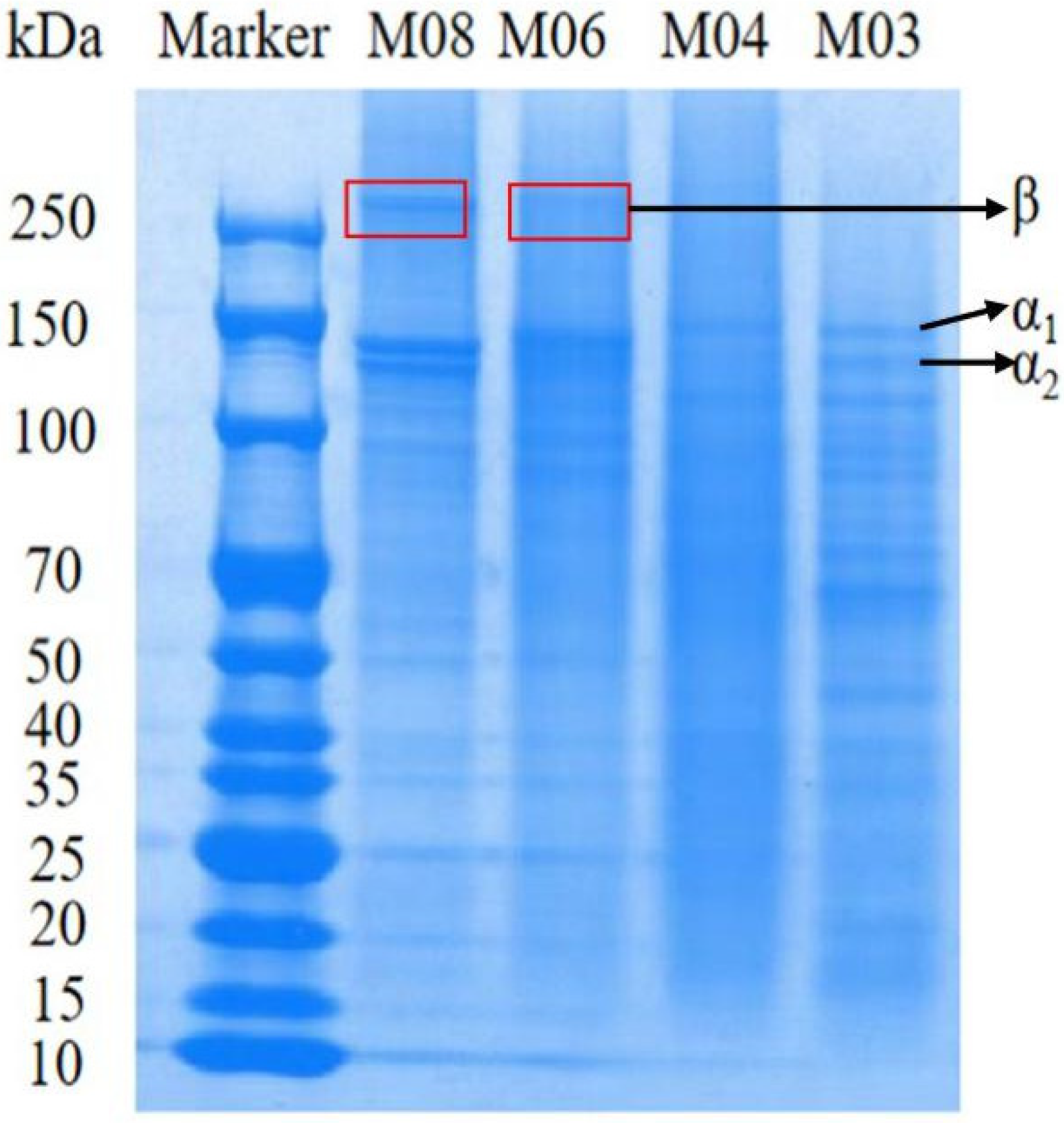
2.2.2. Gel Electrophoresis for Protein Molecular Weight Detection
2.3. Analysis of Amino Acid Composition of Gelatin
2.3.1. Sample Preparation
2.3.2. Amino Acid Analysis
2.4. Preparation of Gel
2.4.1. Gelatin Solution Preparation
2.4.2. Self-Assembly and Enzymatic Gelation
2.5. Determination of Gel Temperature and Gel Melting Point
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy Detection of Fish Gelatin
2.7. Gel Strength Assay
2.8. Water-Holding and Oil-Holding Tests of Gelatin
2.9. Detection of the Secondary Structure of Self-Assembled and Enzymatic Gels Using Fourier Infrared Spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR)
2.10. Detection of Tertiary Structure of Self-Assembled and Enzymatic Gels by X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.11. Preparation of Chicken Salt-Soluble Proteins and Gels
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Protein Content and Composition of Different Fish Gelatins
3.2. Physical and Chemical Properties of Fish Gelatin
3.3. Characteristics of Gels Derived from the 4 Fish Gelatins
3.4. Structural Detection of Self-Assembled and Enzymatic Gels
3.5. Gelatin for Low-Temperature Enzymatic Crosslinking of Chicken Salt-Soluble Proteins
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Euring, M.; Ostendorf, K.; Zhang, K. Biobased materials for food packaging. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeoka, H.C.; Ewulonu, C.M.; Nwuzor, I.C.; Obele, C.M.; Nwabanne, J.T. Packaging and degradability properties of polyvinyl alcohol/gelatin nanocomposite films filled water hyacinth cellulose nanocrystals. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 168–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Photo-crosslinkable hydrogel and its biological applications. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Ding, M.; Shi, C.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, P.; Qiao, R.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Resorbable polymer electrospun nanofibers: History, shapes and application for tissue engineering. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Mulvaney, S.J.; Regenstein, J.M. Properties of Alaska pollock skin gelatin: A comparison with tilapia and pork skin gelatins. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C313–C321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callow, M.E.; Callow, J.A.; Ista, L.K.; Coleman, S.E.; Nolasco, A.C.; López, G.P. Use of self-assembled monolayers of different wettabilities to study surface selection and primary adhesion processes of green algal (Enteromorpha) zoospores. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3249–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, S.; Liu, S.Y. Effects of gelatins on calcium phosphate precipitation: A possible application for distinguishing bovine bone gelatin from porcine skin gelatin. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2003, 16, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Zhong, J. Gelatins as emulsifiers for oil-in-water emulsions: Extraction, chemical composition, molecular structure, and molecular modification. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, E.; Sung, L.A. Interactions of recombinant mouse erythrocyte transglutaminase with membrane skeletal proteins. J. Membr. Biol. 2007, 219, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricotta, M.; Iannuzzi, M.; De Vivo, G.; Gentile, V. Physio-pathological roles of transglutaminase-catalyzed reactions. World J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 1, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, A.L.C.; de Góes-Favoni, S.P. Action of microbial transglutaminase (MTGase) in the modification of food proteins: A review. Food Chem. 2015, 171, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesiów, T.; Xiong, Y.L. Gelation properties of poultry myofibrillar proteins and comminuted poultry meat—Effect of protein concentration, pH and muscle type—A review. Fleischwirtsch. Int. 2001, 4, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Interaction of myofibrillar and preheated soy proteins. J. Food Sci. 2010, 67, 2851–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Dıaz, M.D.; Montero, P.; Gomez-Guillen, M.C. Gel properties of collagens from skins of cod (Gadus morhua) and hake (Merluccius merluccius) and their modification by the coenhancers magnesium sulphate, glycerol and transglutaminase. Food Chem. 2001, 74, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidat, O.; Belkacemi, L.; Belalia, M.; Zainol, M.K.; Barhoum, H.S. Physicochemical, rheological, and textural properties of gelatin extracted from chicken by-products (feet-heads) blend and application. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2023, 32, 100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, R.; Ding, M.; Tao, L.; Liu, L.; Tao, N.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Effect of extraction methods on the structural characteristics, functional properties, and emulsion stabilization ability of Tilapia skin gelatins. Food Chem. 2020, 328, 127114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ding, M.; Tao, L.; Liu, L.; Tao, N.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Octenyl succinic anhydride modification of bovine bone and fish skin gelatins and their application for fish oil-loaded emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- <GB6783-2013>. Available online: http://down.foodmate.net/standard/sort/3/38978.html (accessed on 20 April 2023).
- Chen, T.; Embree, H.D.; Brown, E.M.; Taylor, M.M.; Payne, G.F. Enzyme-catalyzed gel formation of gelatin and chitosan: Potential for in situ applications. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, M.; Xu, J.; Nie, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Structural and emulsion stabilization comparison of four gelatins from two freshwater and two marine fish skins. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Bi, C.; Ding, M.; Xie, J.; Xu, C.; Qiao, R.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Polymorphism and stability of nanostructures of three types of collagens from bovine flexor tendon, rat tail, and tilapia skin. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish gelatin: Properties, challenges, and prospects as an alternative to mammalian gelatins. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, X.M.; Tu, Z.C.; Liu, W.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Huang, T.; Man, Z.Z. Effect of ammonium sulfate fractional precipitation on gel strength and characteristics of gelatin from bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) scale. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 36, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, W. Testing and modeling of the state-dependent behaviors of rockfill material. Comput. Geotech. 2014, 61, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, I.J.; Draget, K.I.; Smidsrød, O. Physical and rheological properties of fish gelatin compared to mammalian gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Regenstein, J.M.; Lv, S.; Lu, J.; Jiang, S. An overview of gelatin derived from aquatic animals: Properties and modification. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soua, L.; Koubaa, M.; Barba, F.J.; Fakhfakh, J.; Ghamgui, H.K.; Chaabouni, S.E. Water-soluble Polysaccharides from Ephedra alata stems: Structural characterization, functional properties, and antioxidant activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, R.; Ding, M.; Li, L.; Tao, N.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Commercial cold-water fish skin gelatin and bovine bone gelatin: Structural, functional, and emulsion stability differences. LWT 2020, 125, 109207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilipenko, N.; Goncalves, O.H.; Bona, E.; Fernandes, I.P.; Pinto, J.A.; Sorita, G.D.; Leimann, F.V.; Barreiro, M.F. Tailoring swelling of alginate-gelatin hydrogel microspheres by crosslinking with calcium chloride combined with transglutaminase. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chiou, B.S.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; McHugh, T.H.; Zhong, F. Study of combined effects of glycerol and transglutaminase on properties of gelatin films. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Tian, Q.; Ma, Y.Q.; Wu, Y.; Miao, G.J.; Ma, Y.; Cao, D.-H.; Wang, X.-L.; Lin, C.; Pang, J.; et al. Transpositional reactivation of two LTR retrotransposons in rice-Zizania recombinant inbred lines (RILs). Hereditas 2010, 147, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.L. Structure-function relationships of muscle proteins. In Food Proteins and Their Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Chen, C.; Sun, G.; Wang, W.; Fang, H. Effects of curdlan on the color, syneresis, cooking qualities, and textural properties of potato starch noodles. Starch-Stärke 2010, 62, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| [Number] | Protein Content (%Protein) |
|---|---|
| M03 | 90.9 ± 0.3 c |
| M04 | 95.4 ± 0.5 b |
| M06 | 94.7 ± 0.3 b |
| M08 | 99.9 ± 0.1 a |
| Amino Acid Content (ug/mgCNS) | M03 | M04 | M06 | M08 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asp | 54.1922 | 58.8436 | 68.8884 | 73.336 |
| Thr | 26.355 | 24.9026 | 29.016 | 29.9064 |
| Ser | 33.177 | 36.7824 | 66.3272 | 71.7264 |
| Glu | 95.0596 | 103.5844 | 107.4772 | 112.034 |
| Ala | 99.2322 | 103.2566 | 95.828 | 100.0978 |
| Val | 22.0882 | 21.1086 | 20.2046 | 21.1596 |
| Met | 9.5148 | 9.386 | 14.965 | 18.7756 |
| Ile | 12.238 | 11.8736 | 12.9586 | 14.2264 |
| Leu | 26.4908 | 26.1532 | 25.0706 | 27.1428 |
| Tyr | 3.1944 | 3.4752 | 3.9124 | 5.4574 |
| PHe | 17.5284 | 20.2732 | 19.3872 | 19.7182 |
| Lys | 31.5506 | 32.6718 | 34.8594 | 37.0076 |
| His | 5.9378 | 6.2598 | 11.2676 | 12.8436 |
| Arg | 80.0758 | 82.4078 | 84.784 | 91.671 |
| Pro | 145.2082 | 156.3152 | 131.2282 | 140.0648 |
| Total | 661.843 | 697.294 | 726.1744 | 775.1676 |
| Percentage of hydrophobic groups | 35.22% | 35.15% | 30.82% | 31.10% |
| Gelation | Temperature °C | Melting °C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Warm water fish gelatin | M03 | 4~20 | 20~37 |
| M03+TG | - | >60 | |
| M04 | 4~23 | 25~37 | |
| M04+TG | >60 | ||
| Cold water fish gelatin | M06 | 4–10 | <17 |
| M06+TG | - | >60 | |
| M08 | 4–12 | <17 | |
| M08+TG | - | >60 | |
| Gelation | Uncrosslinked Gel Strength (g/cm) | Gel Strength after Crosslinked (g/cm) |
|---|---|---|
| M03 | 67 ± 1 c | 351 ± 2 c |
| M04 | 35 ± 1 d | 204 ± 6 d |
| M06 | 156 ± 2 b | 476 ± 6 b |
| M08 | 253 ± 1 a | 800 ± 2 a |
| Gelation | Water (%) | Oil (%) |
|---|---|---|
| M03 | 179 ± 12 f | 157 ± 5 f |
| M04 | 245 ± 15 e | 122 ± 4 g |
| M06 | 6 ± 11 g | 155 ± 6 f |
| M08 | 14 ± 13 g | 253 ± 3 c |
| M03+TG | 786 ± 13 b | 247 ± 4 d |
| M04+TG | 527 ± 11 c | 286 ± 5 b |
| M06+TG | 906 ± 14 a | 293 ± 3 a |
| M08+TG | 327 ± 12 d | 180 ± 6 e |
| Gelation | Gelatin Composite Salt Soluble Protein Gel Strength (g/cm) | Enzymatic Gel Salt Soluble Protein Gel Strength (g/cm) | Gelatin Composite Salt Soluble Protein Gel Water Holding Capacity (%) | Enzymatic Gel Salt Soluble Protein Gel Water Holding Capacity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M03 | 192.8 a | 326.3 b | 95.03 a | 91.46 a |
| M04 | 163.8 b | 209.6 c | 95.93 a | 91.45 a |
| M06 | 125.3 c | 164.9 d | 93.28 a | 90.63 a |
| M08 | 198.5 a | 416.7 a | 95.84 a | 91.53 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, M.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. Study of Physicochemical and Gelation Properties of Fish Gelatin from Different Sources. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5337. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095337
Wu J, Xiao J, Zhu M, Yang H, Liu J, Liu Y. Study of Physicochemical and Gelation Properties of Fish Gelatin from Different Sources. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(9):5337. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095337
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jintao, Jing Xiao, Mingyao Zhu, Haichuan Yang, Jingjing Liu, and Yang Liu. 2023. "Study of Physicochemical and Gelation Properties of Fish Gelatin from Different Sources" Applied Sciences 13, no. 9: 5337. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095337
APA StyleWu, J., Xiao, J., Zhu, M., Yang, H., Liu, J., & Liu, Y. (2023). Study of Physicochemical and Gelation Properties of Fish Gelatin from Different Sources. Applied Sciences, 13(9), 5337. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095337





