Experimental Investigation of Lanthanum-Modified Reinforced Composite Material for Phosphorus Removal
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of La-EPRC Particles
2.2. Optimizing Adsorption Substrate Preparation for La-EPRC Particles
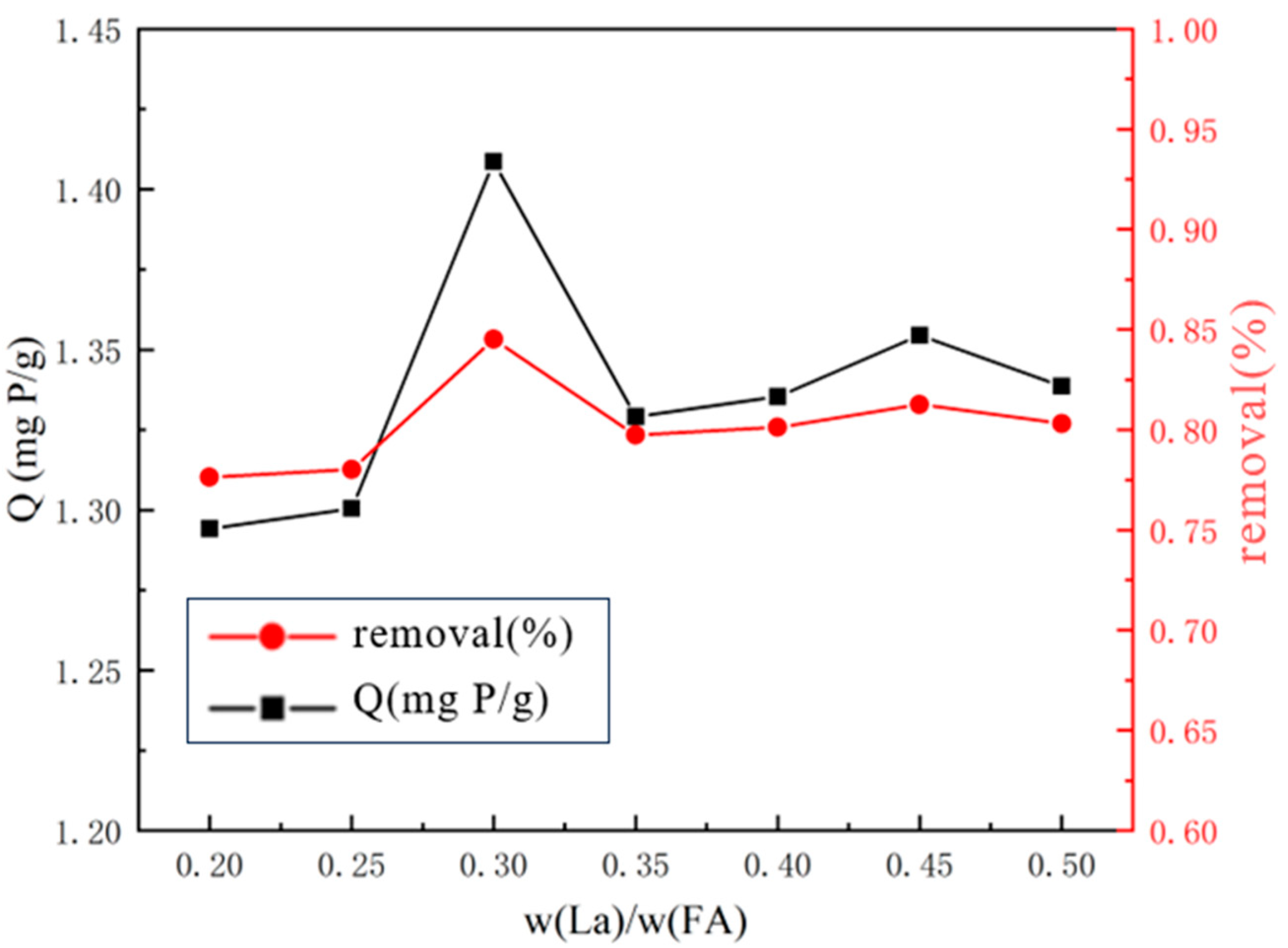
2.2.1. Optimal Lanthanum-to-Substrate Mass Ratio
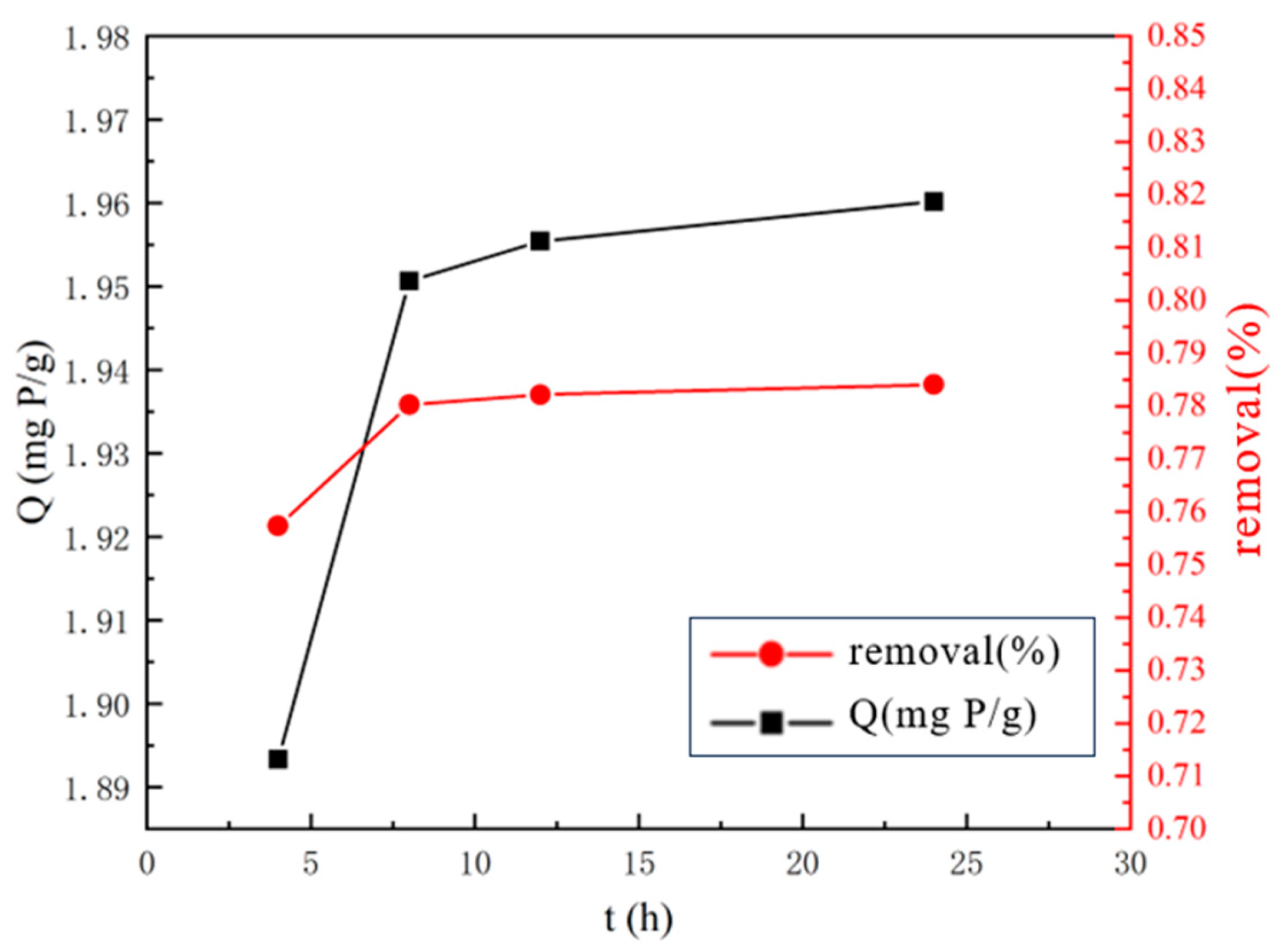
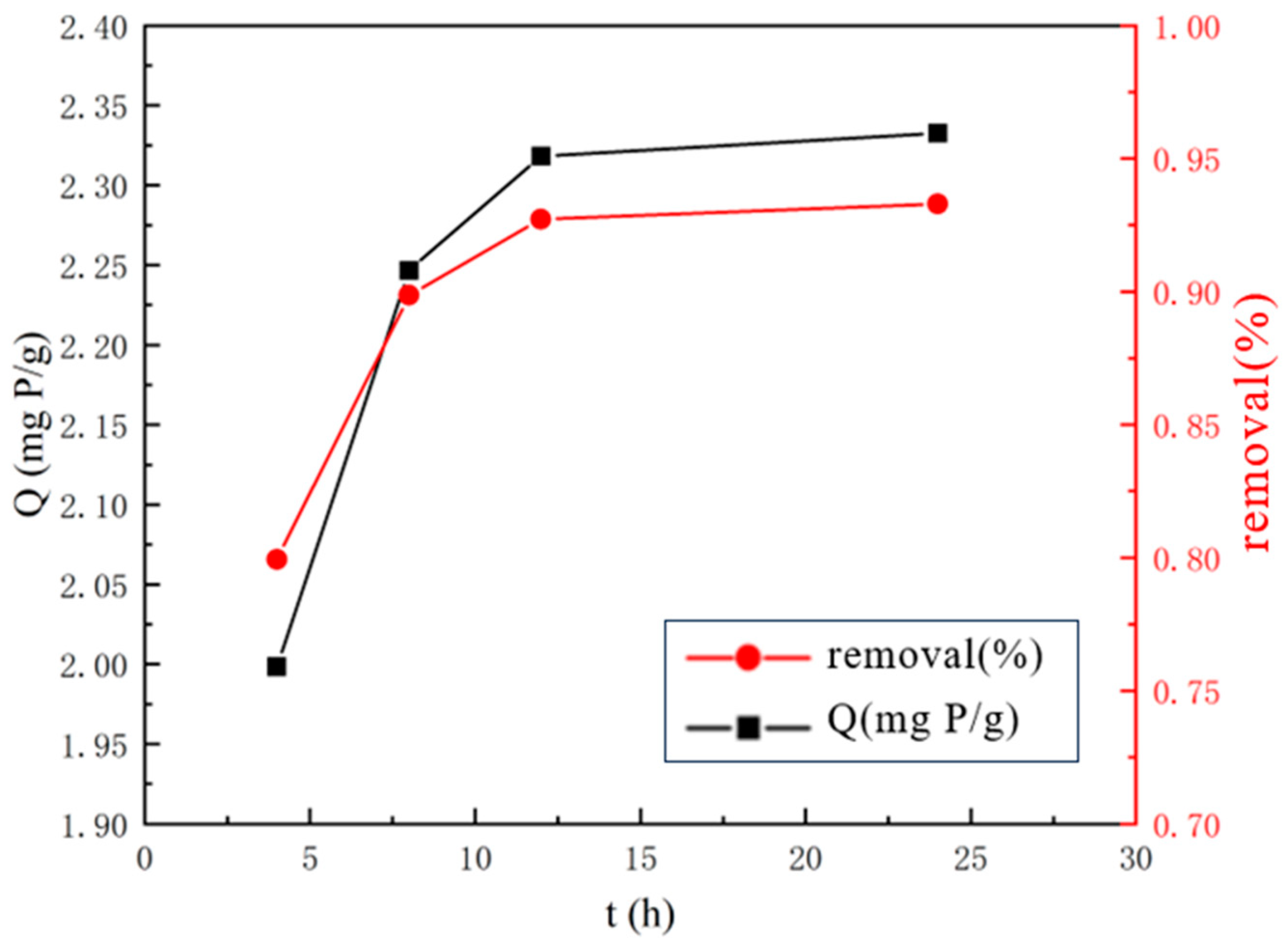
2.2.2. Optimal Lanthanum Nitrate Solution Impregnation Time
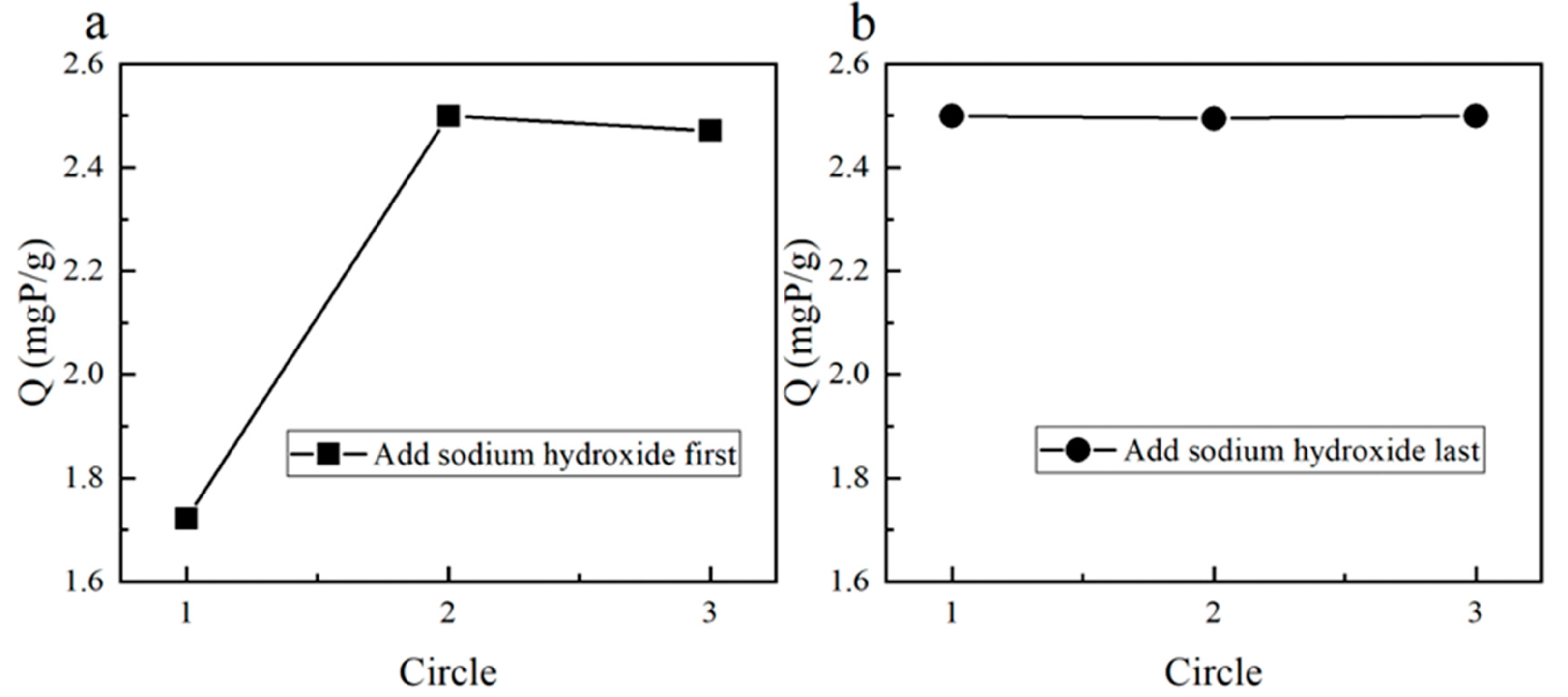
2.2.3. Optimal Lanthanide Fixation Scheme
2.3. Characterization of La-EPRC Particles for Static Adsorption of Phosphorus Removal
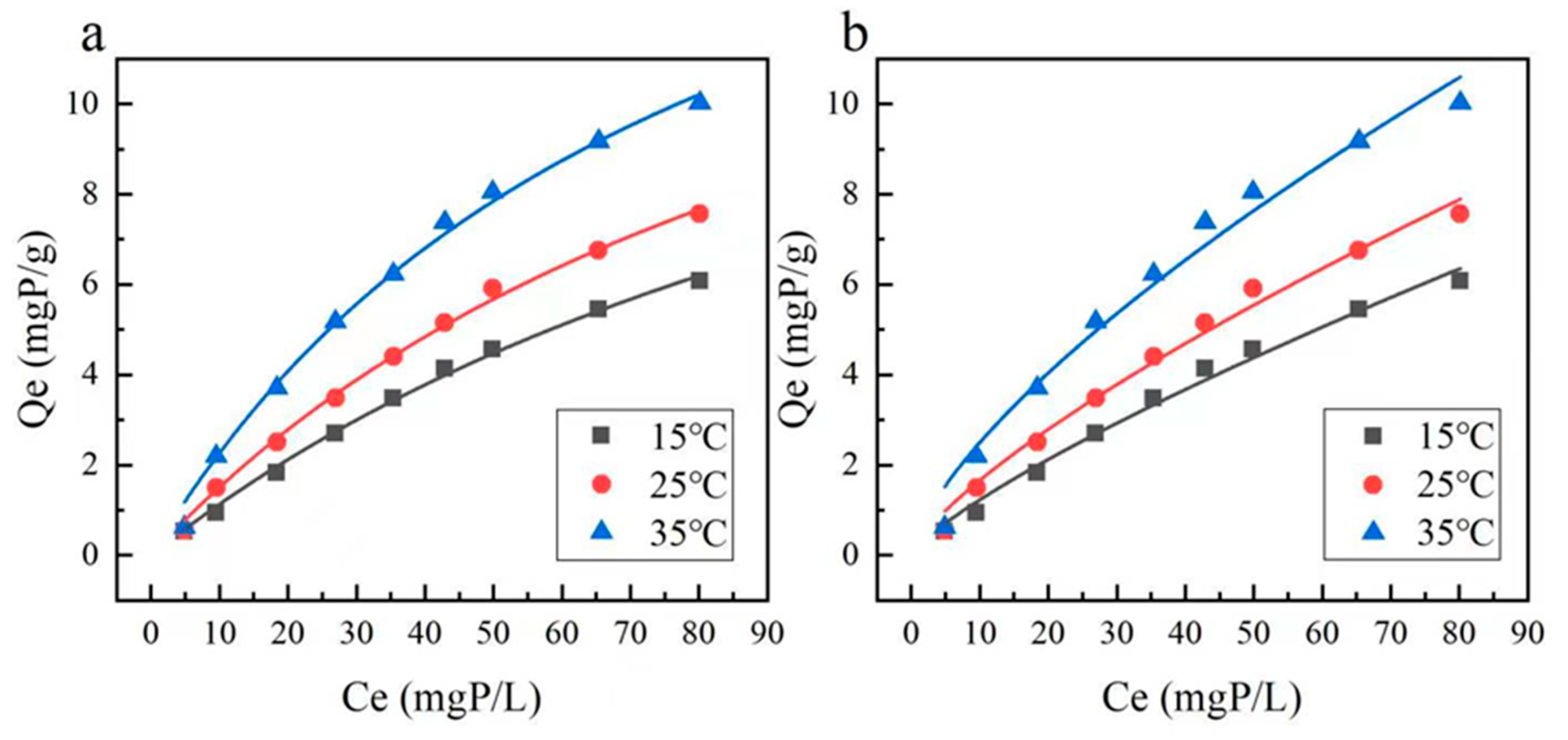
2.3.1. Adsorption Isotherm Experiments
- Langmuir adsorption isotherm modeling
- Freundlich adsorption isotherm model
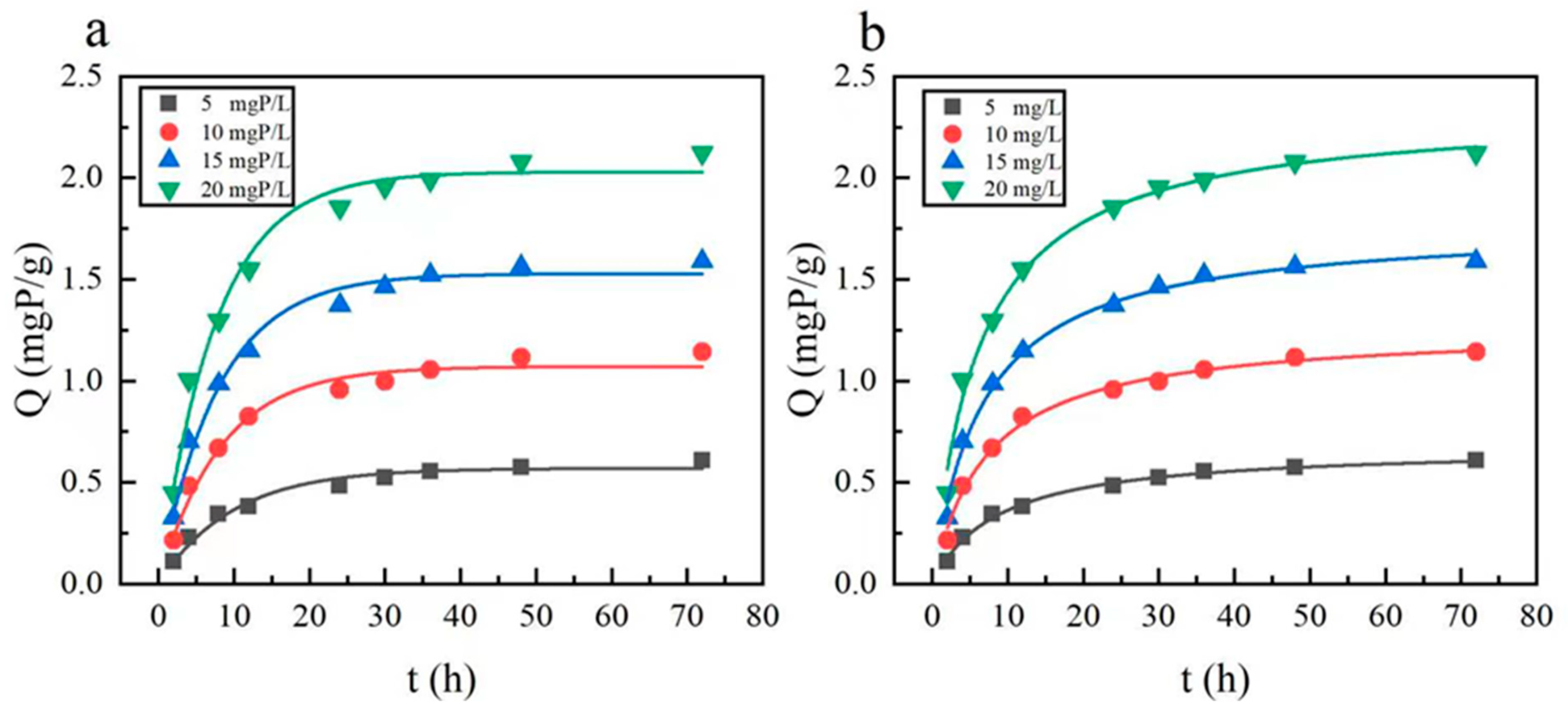
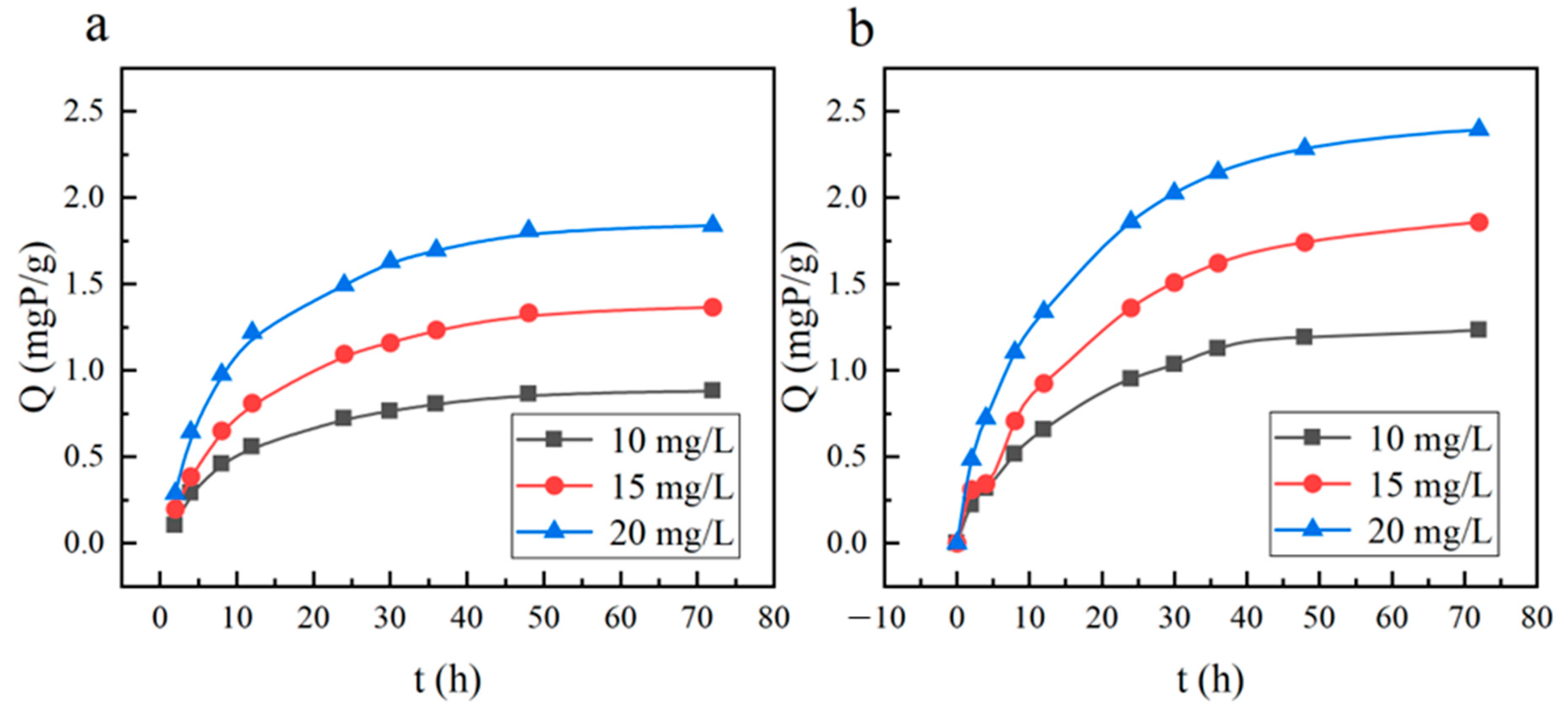
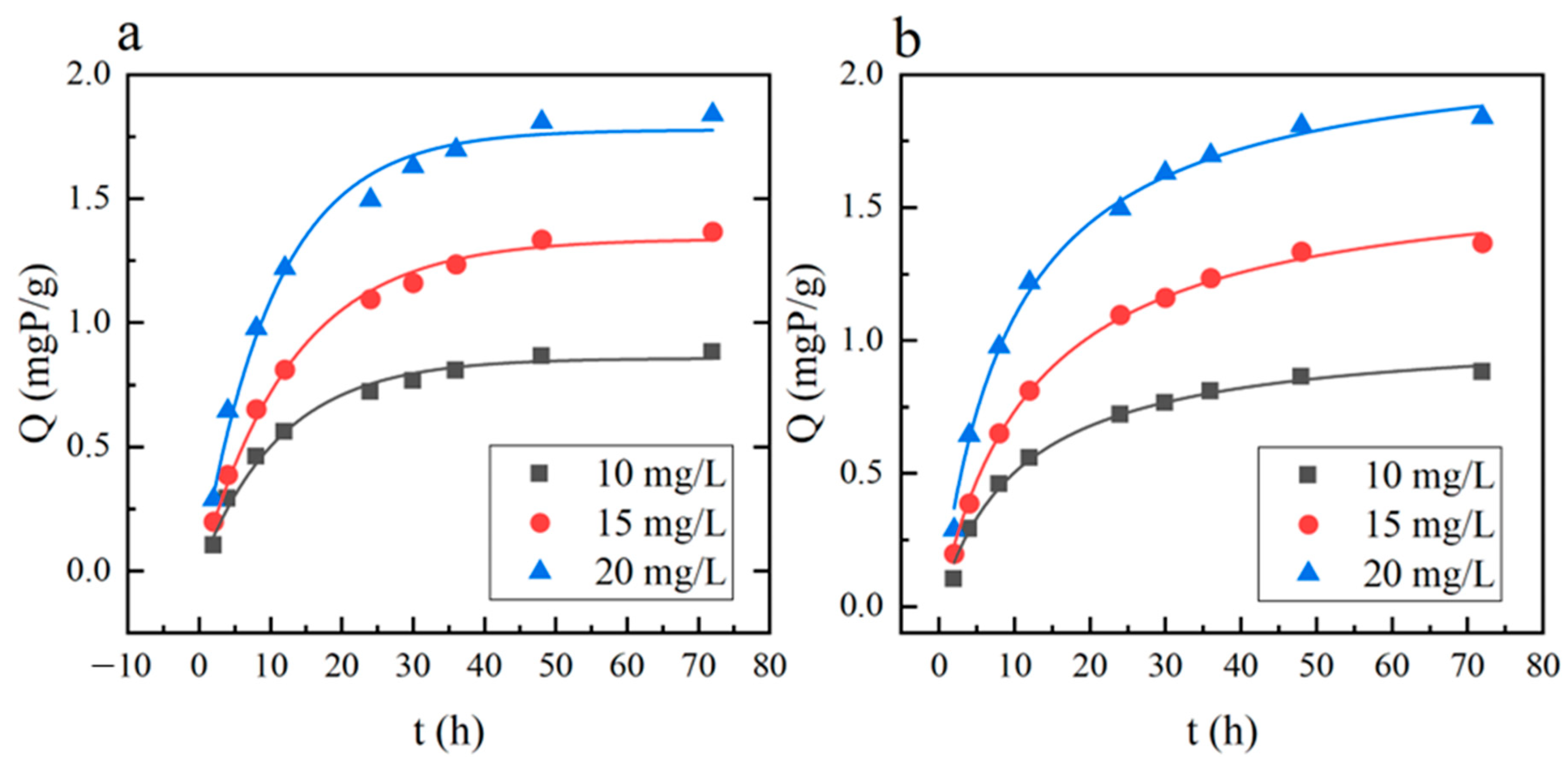
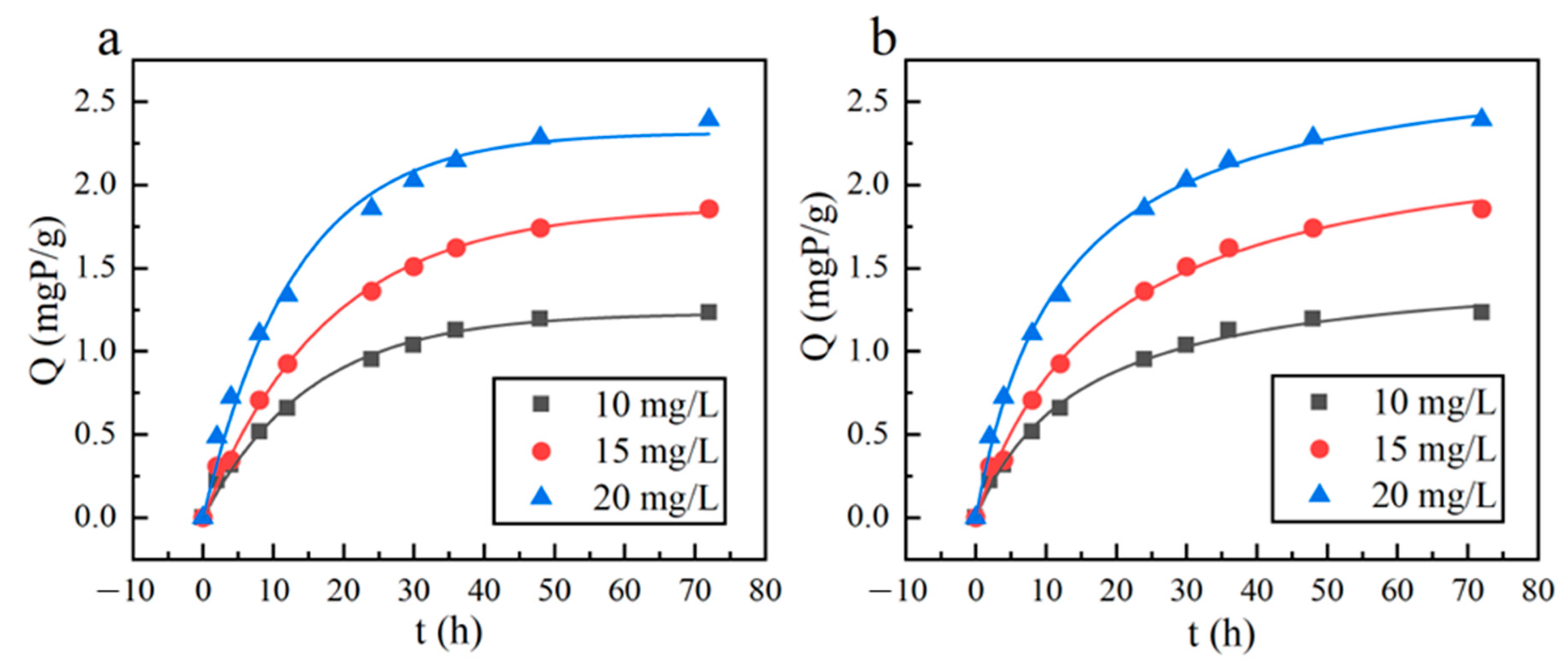
2.3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
- PFO adsorption kinetic model
- PSO adsorption kinetic model
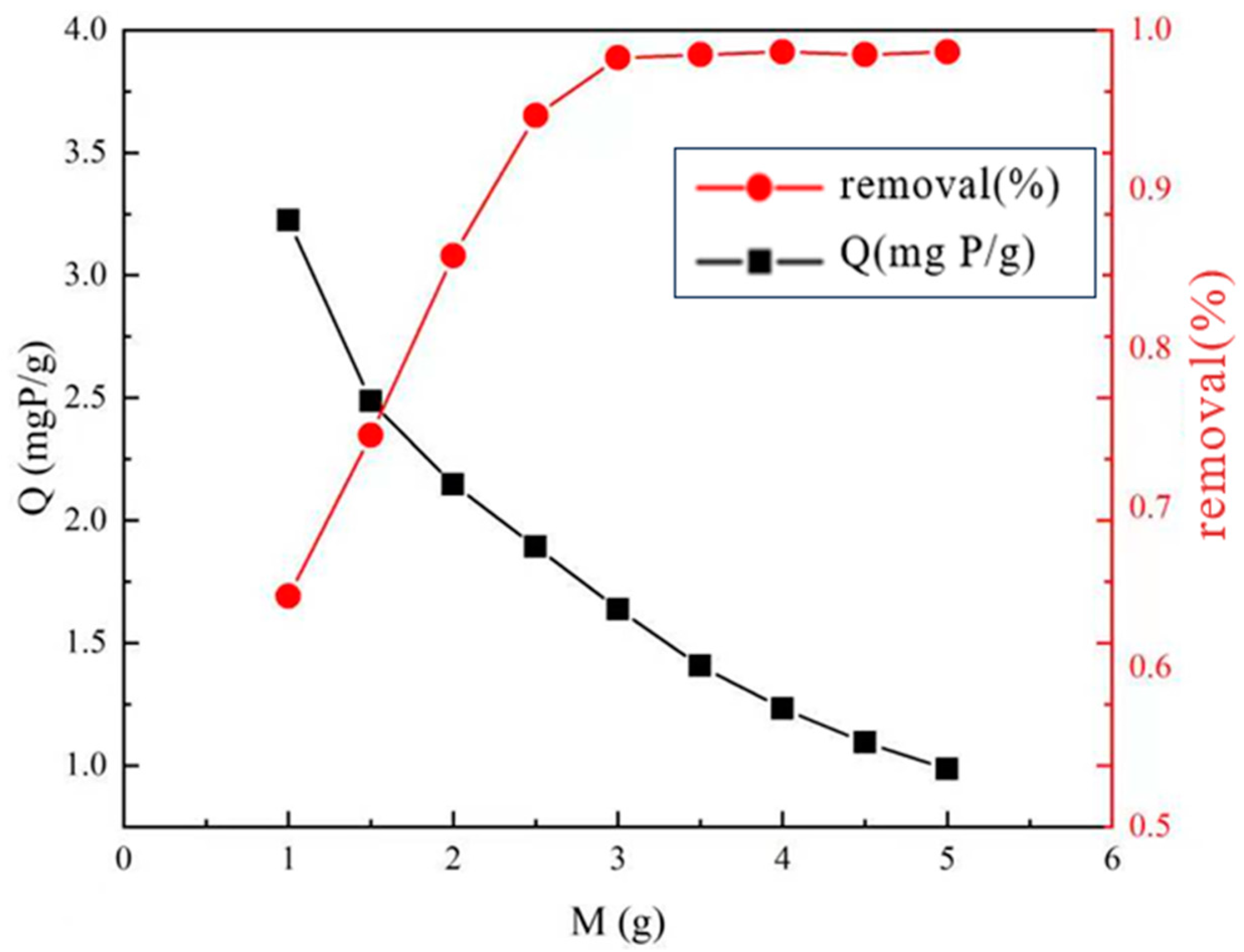
2.3.3. Adsorbent Dosage Experiment
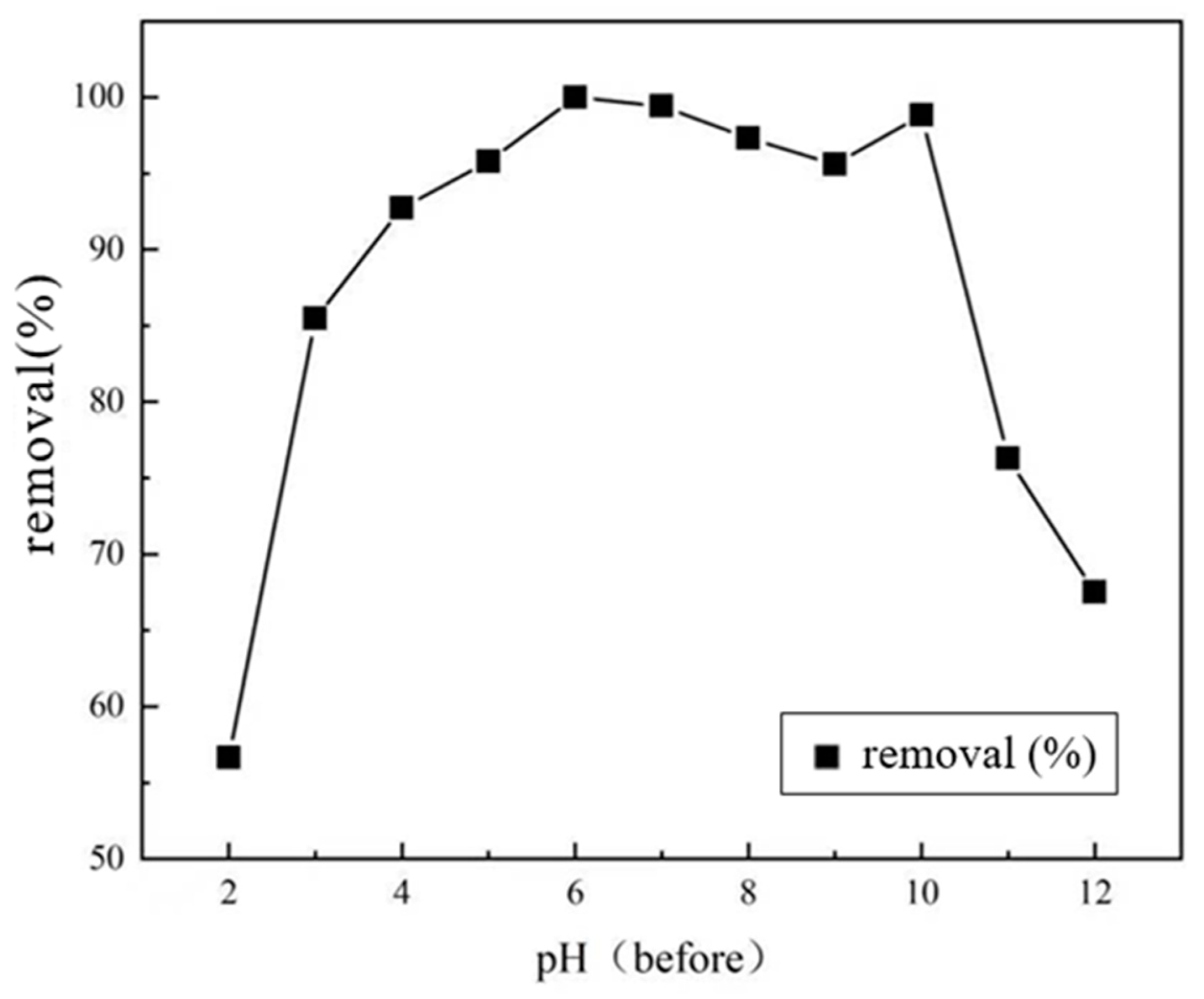
2.3.4. Solution pH Experiments
2.3.5. Coexisting Anion Experiments
2.4. Stability Analysis and Regeneration Studies of La-EPRC Particles
2.4.1. Material Adsorption Stability
- 1.
- Room Temperature Water Desorption
- 2.
- Desorption in High-Temperature Water
- 3.
- Desorption in Sulfuric Acid Solution
2.4.2. Adsorbent Regeneration Experiment
- NaOH Concentration
- 2.
- Desorption Time
- 3.
- Three Successive Adsorption–Desorption Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of Preparation Conditions for Adsorption Substrates of La-EPRC Particles
3.1.1. Optimal Lanthanum-to-Substrate Mass Ratio
3.1.2. Optimal Lanthanum Nitrate Solution Impregnation Time
3.1.3. Optimal Lanthanide Immobilization Procedure
3.2. Characterization of La-EPRC Particles for Static Adsorption of Phosphorus Removal
3.2.1. Adsorption Isotherms
3.2.2. Adsorption Kinetics
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage on Phosphorus Removal
3.2.4. Effect of Solution pH on Adsorption Effect
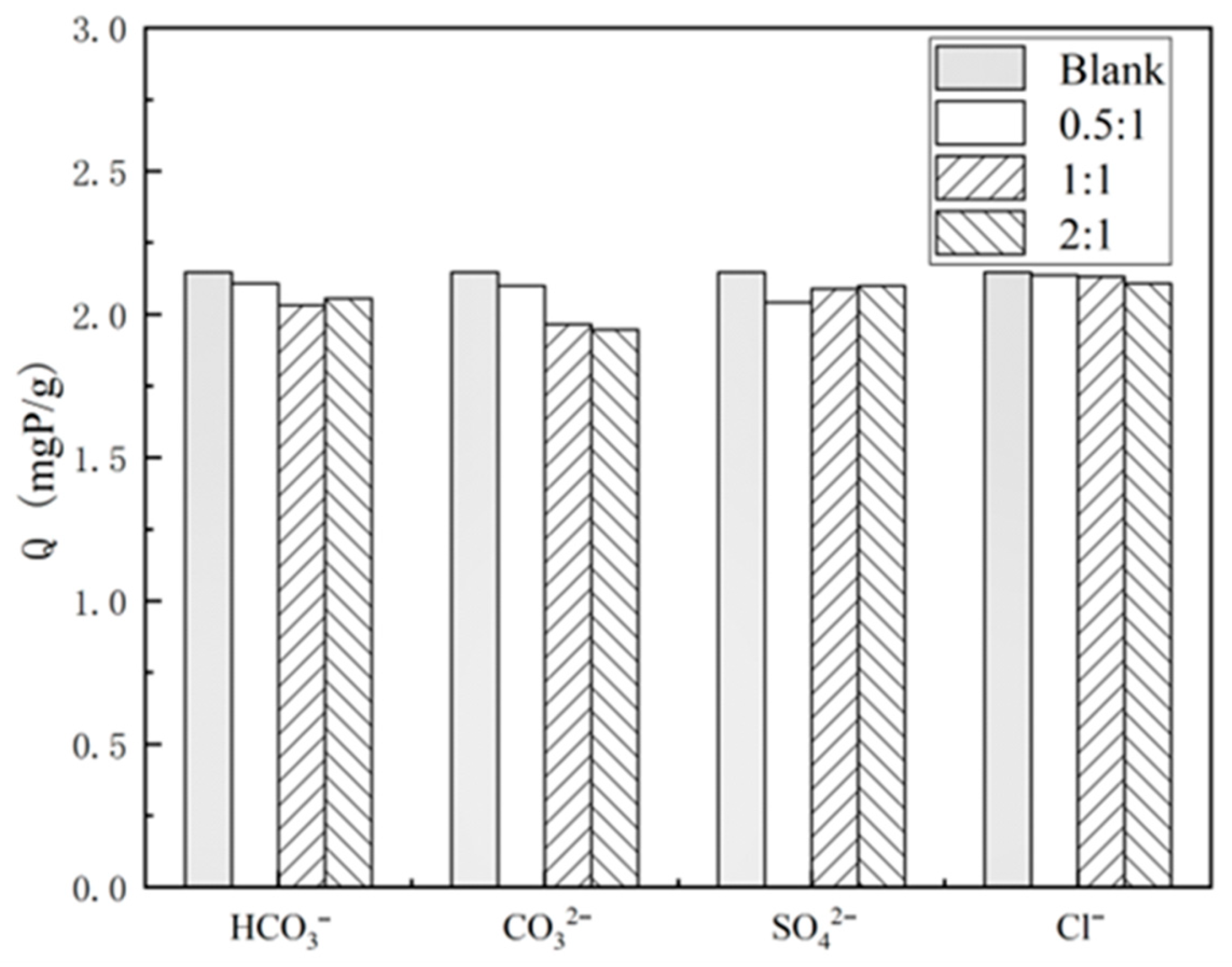
3.2.5. Influence of Coexisting Anions on the Effectiveness of Phosphorus Removal
3.3. Safety Analysis and Regeneration Study of La-EPRC Particles
3.3.1. Desorption Experiments
- Desorption in Water at Room Temperature
- 2.
- Desorption in Hot Water at High Temperature
- 3.
- Desorption in Sulfuric Acid Solution
3.3.2. Adsorbent Regeneration Experiment
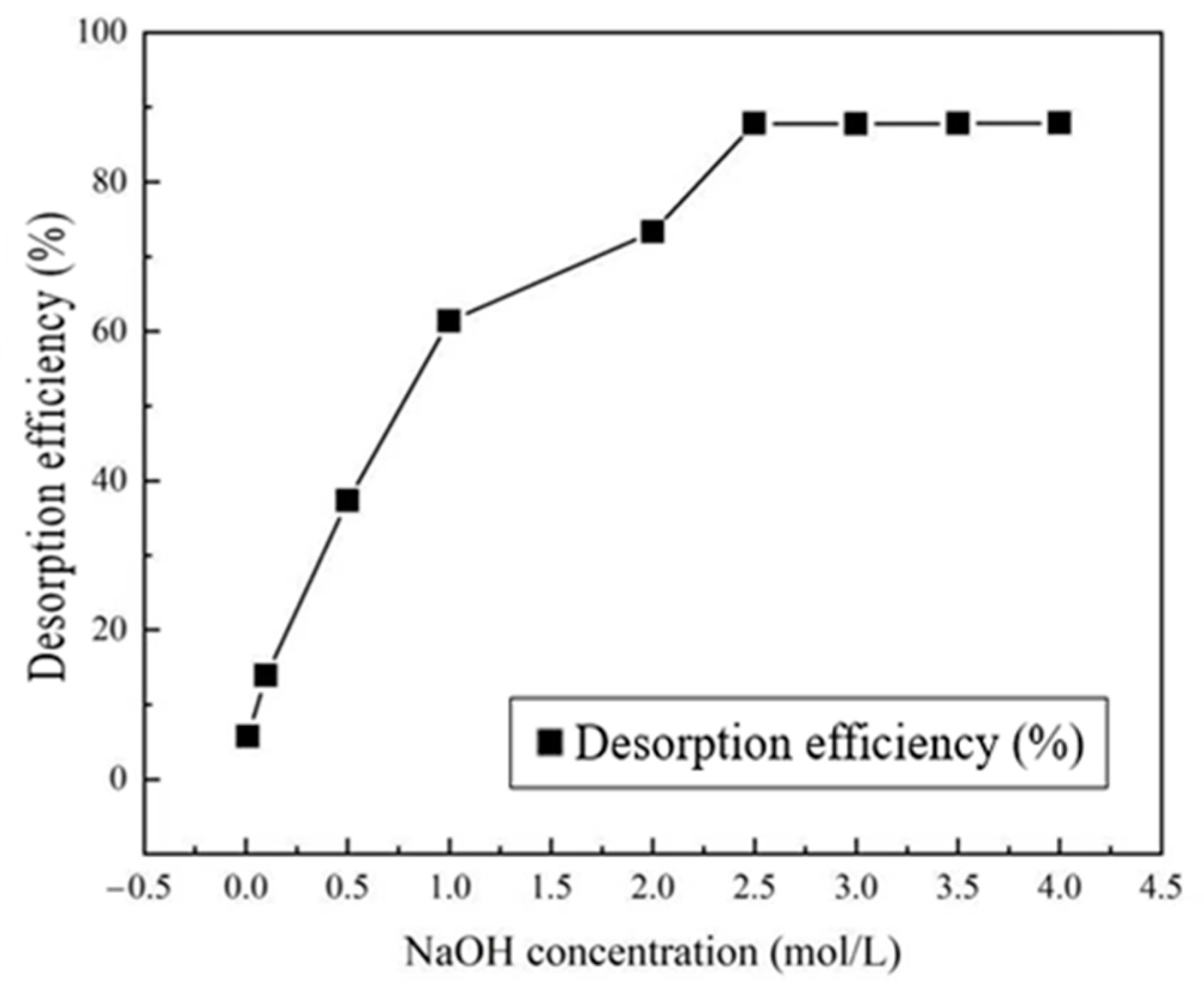
- Effect of NaOH Concentration on The Regeneration Effect of Adsorbent
- 2.
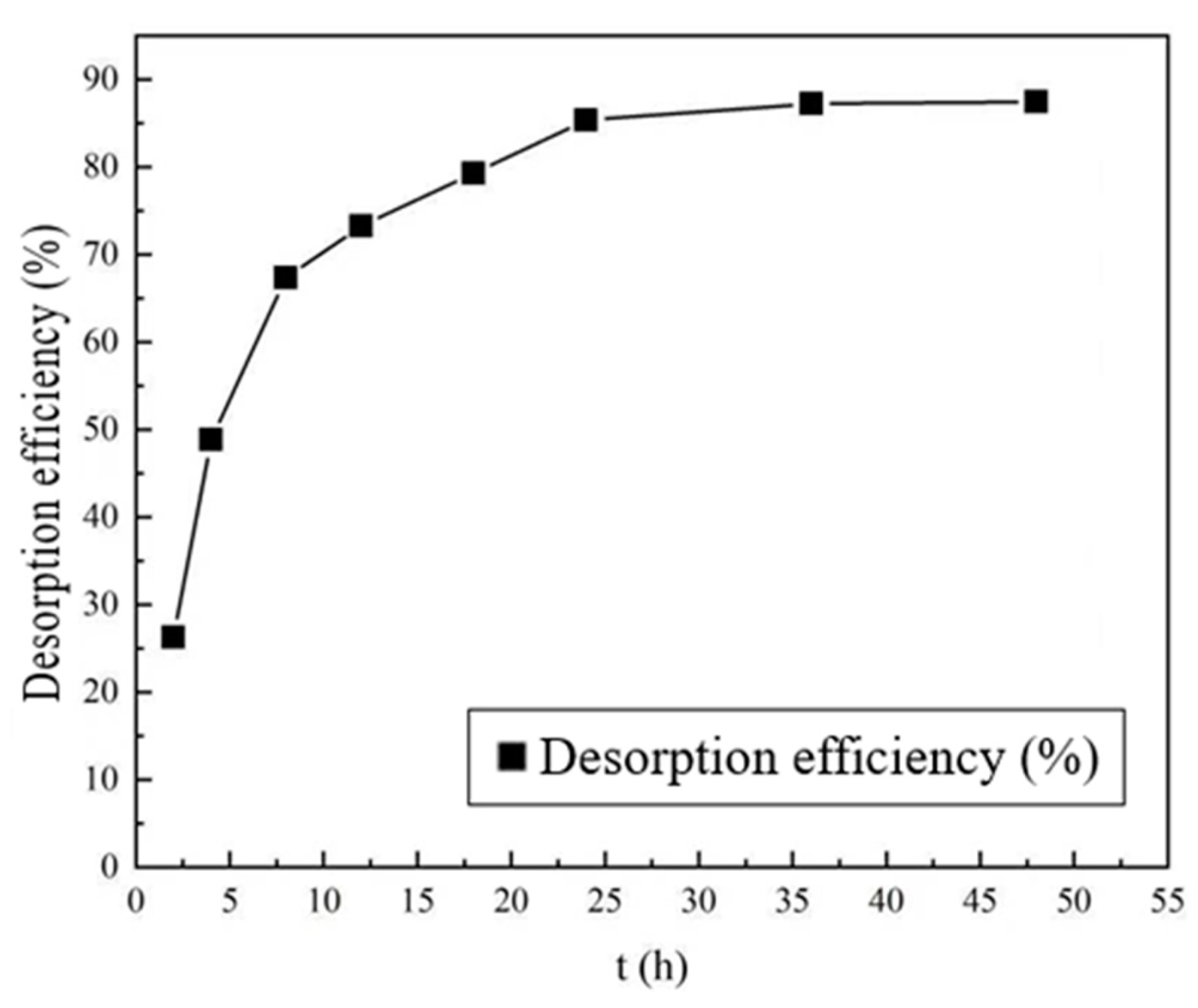
- Effect of Desorption Time on Regeneration of Adsorbent
- 3.
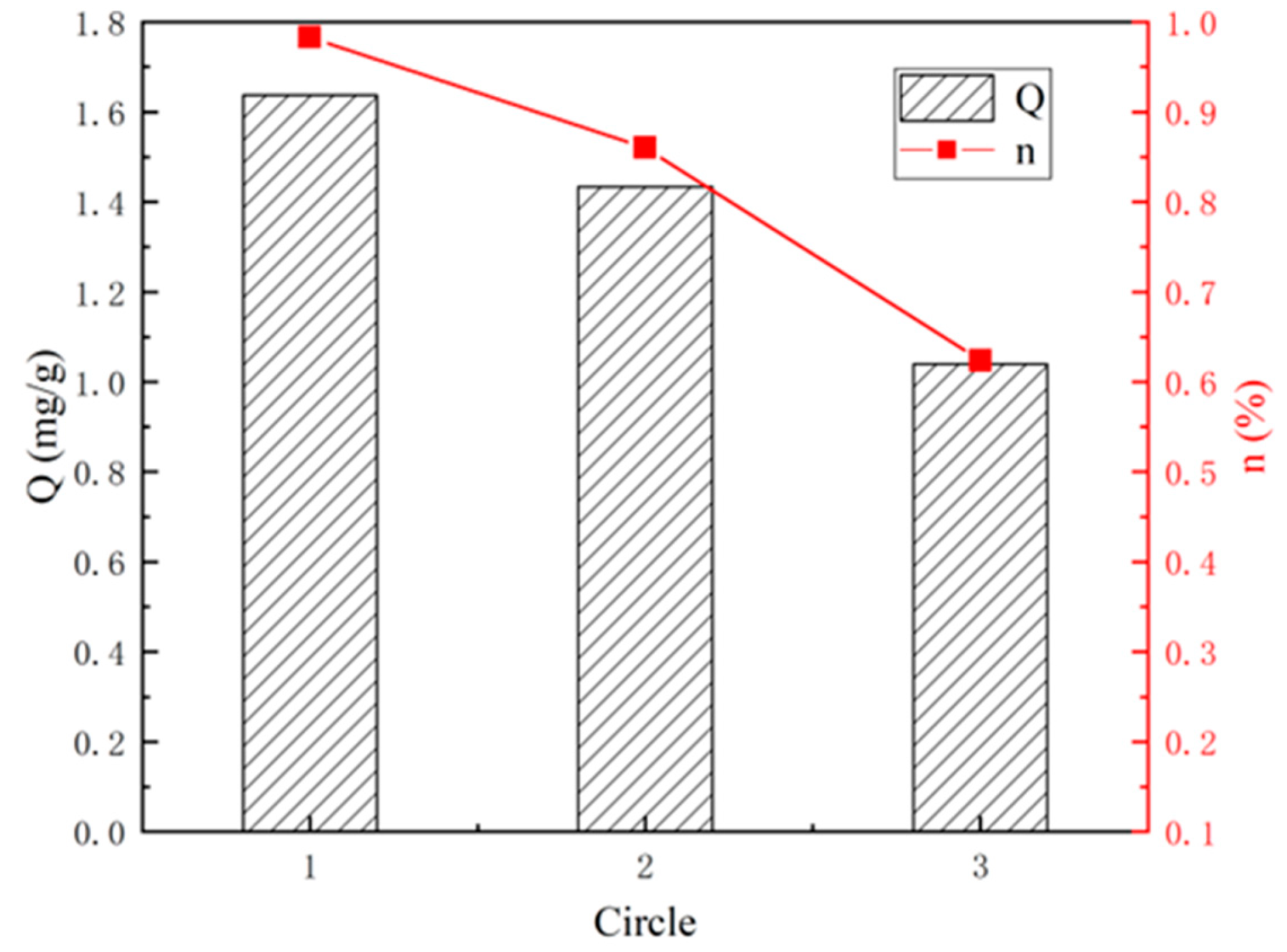
- Three successive adsorption–desorption experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daneshgar, S.; Callegari, A.; Capodaglio, A.G.; Vaccari, D. The Potential Phosphorus Crisis: Resource Conservation and Possible Escape Technologies: A Review. Resources 2018, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, D.L.; Corman, J.; Edwards, M.; Elser, J.J. Sustainability Challenges of Phosphorus and Food: Solutions from Closing the Human Phosphorus Cycle. Bioscience 2011, 61, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benammar, L.; Menasria, T.; Ayachi, A.; Benounis, M. Phosphate removal using aerobic bacterial consortium and pure cultures isolated from activated sludge. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 95, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.C.; Yuan, L.J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, W.W. The mechanism of biological phosphorus removal under anoxic-aerobic alternation condition with starch as sole carbon source and its biochemical pathway. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 132, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; He, X.M.; Hu, H.M.; Zhang, T.T.; Qu, J.; Zhang, Q.W. Enhanced phosphate removal from wastewater by using in situ generated fresh trivalent Fe composition through the interaction of Fe(II) on CaCO3. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 221, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.L.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Pan, B.C.; Lo, I.M.C. Selective Phosphate Removal from Water and Wastewater using Sorption: Process Fundamentals and Removal Mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, C.Z.; Liu, S.; Hanigan, D.; Liu, S.T.; Zhao, H.Z. Ultrafiltration membrane microreactor (MMR) for simultaneous removal of nitrate and phosphate from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.G.; Shi, J.; Xu, Z.W.; Zhu, S.Y.; Cui, Y.X. Phosphorus removal and recovery from fosfomycin pharmaceutical wastewater by the induced crystallization process. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.; Bandosz, T.J. Analysis of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim adsorption on sewage sludge and fish waste derived adsorbents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 220, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purbasari, A.; Ariyanti, D.; Fitriani, E. Adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solutions on fly ash-based porous geopolymer. Glob. Nest J. 2023, 25, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J.; Bolan, N.S. Removal and Recovery of Phosphate From Water Using Sorption. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 847–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copetti, D.; Finsterle, K.; Marziali, L.; Stefani, F.; Tartari, G.; Douglas, G.; Reitzel, K.; Spears, B.M.; Winfield, I.J.; Crosa, G.; et al. Eutrophication management in surface waters using lanthanum modified bentonite: A review. Water Res. 2016, 97, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, I.; Iucolano, F. Production of lightweight gypsum using a vegetal protein as foaming agent. Mater. Struct. 2020, 53, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.A.Q.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.P.; Zhang, Z.Y. Adsorption for phosphate by crosslinked/non-crosslinked-chitosan-Fe(III) complex sorbents: Characteristic and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.L.; Lan, R.; He, L.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Pei, X.J. A critical review of adsorption isotherm models for aqueous contaminants: Curve characteristics, site energy distribution and common controversies. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, Z. A spectrophotometric method for captopril determination by using fluorescein natrium-bromine system. Rev. Roum. De Chim. 2012, 57, 721–727. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Niu, X.; Zhao, B. Study on Adsorption Mechanism for Phosphorus Removal with Spongy Iron. China Water Wastewater 2003, 19, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Yang, Y.; Ping, H.B. Removal of Phosphorus in Water by Modified Red Earth. Chin. J. Spectrosc. Lab. 2011, 28, 1483–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Eris, S.; Bashiri, H. Kinetic study of the adsorption of dyes onto activated carbon. Prog. React. Kinet. Mech. 2016, 41, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.V. Pseudo-second order models for the adsorption of safranin onto activated carbon: Comparison of linear and non-linear regression methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 142, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, S.J.; Wang, S.H. Kinetics and thermodynamics of efficient phosphorus removal by a complex material. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 56, 1949–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.J.; Han, M.N.; Shih, K.M.; Su, M.H.; Diao, Z.H.; Long, J.Y.; Chen, D.Y.; Hou, L.A.; Peng, Y. Nano-rod Ca-decorated sludge derived carbon for removal of phosphorus. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmanuelawati, I.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.W.; Zhou, L.; Yu, C.Z. Low-cost and large-scale synthesis of functional porous materials for phosphate removal with high performance. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 6173–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Lai, L.; Lin, L.D.; Wu, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; Kong, H.N. Phosphate removal from water by a novel zeolite/lanthanum hydroxide hybrid material prepared from coal fly ash. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2015, 50, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
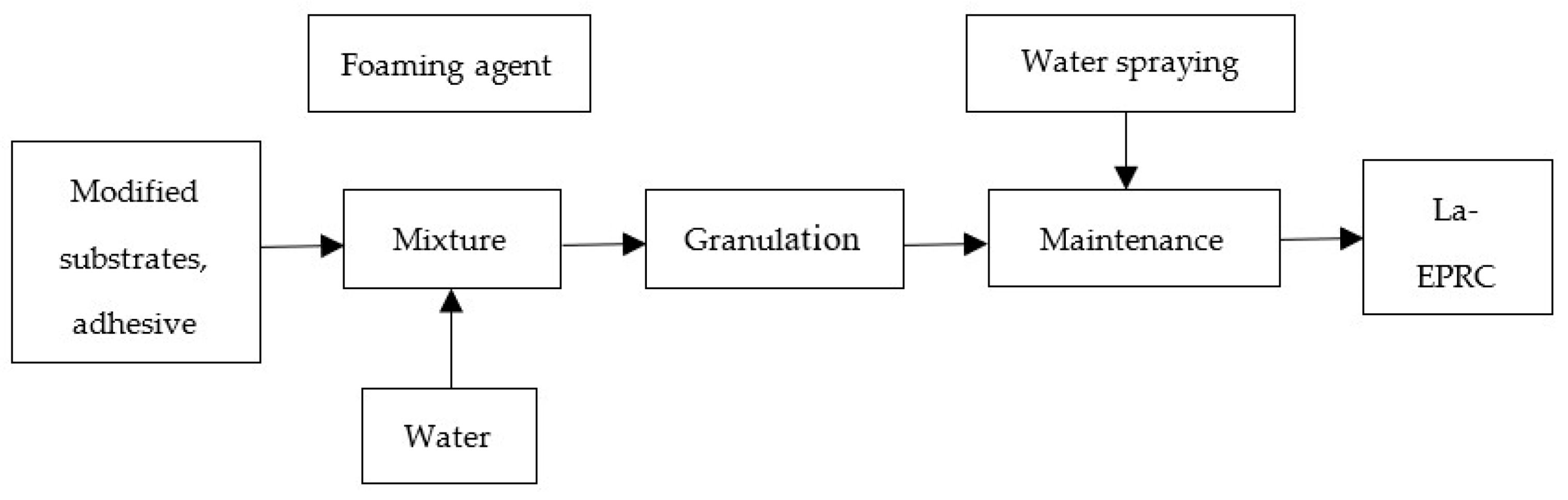


| Adsorption Substrates | Density (g/cm3) | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Color |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Slag | 3.10 | 0.3653 | Sepia |
| Coal Ash | 2.34 | 0.0580 | Grizzly |
| Chemical Composition | Steel Slag | Coal Ash |
|---|---|---|
| CaO | 55.0 | 1.31 |
| Fe2O3 | 21.5 | 4.39 |
| Al2O3 | 1.51 | 45.9 |
| SiO2 | 13.4 | 44.4 |
| MgO | 3.65 | 0.261 |
| MnO | 1.75 | 0.026 |
| SO3 | 0.512 | 0.666 |
| V2O5 | 0.417 | 0.038 |
| TiO2 | 1.26 | 0.296 |
| Na2O | 0.077 | 0.094 |
| ZnO | - | 0.021 |
| CuO | - | 0.02 |
| Ingredient | CaO | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | MgO | SO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity Contained | 63.5 | 4.52 | 5.15 | 21.32 | 1.46 | 2.25 |
| Temperature (°C) | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (L/mg) | QM (mg/g) | R2 | KF | 1/n | R2 | |
| 15 | 0.00705 | 17.16754 | 0.99653 | 0.19981 | 0.7892 | 0.9882 |
| 25 | 0.00895 | 18.36118 | 0.99637 | 0.29693 | 0.7481 | 0.98699 |
| 35 | 0.01251 | 20.39518 | 0.99338 | 0.50447 | 0.6946 | 0.97572 |
| PFO Adsorption Kinetics | PSO Adsorption Kinetics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Phosphorus Concentration (mg P/L) | qe (mg/g) | K1 | R2 | Initial Phosphorus Concentration (mg P/L) | qe (mg/g) | K2 | R2 |
| 5 | 0.56935 | 0.1028 | 0.9706 | 5 | 0.67577 | 0.17179 | 0.99366 |
| 10 | 1.07083 | 0.12135 | 0.96394 | 10 | 1.26282 | 0.11048 | 0.99021 |
| 15 | 1.52834 | 0.12648 | 0.98207 | 15 | 1.77373 | 0.08435 | 0.99186 |
| 20 | 2.02956 | 0.13264 | 0.97696 | 20 | 2.3399 | 0.06823 | 0.99038 |
| Temperature | PFO Adsorption Kinetics | PSO Adsorption Kinetics | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Phosphorus (Chemistry) | qe | K1 | R2 | Initial Phosphorus (Chemistry) | qe | K2 | R2 | |
| 15 °C | 10 | 0.8561 | 0.0882 | 0.9875 | 10 | 1.0389 | 0.09038 | 0.9908 |
| 15 | 1.3376 | 0.0772 | 0.9939 | 15 | 1.6457 | 0.04879 | 0.9972 | |
| 20 | 1.7768 | 0.0954 | 0.9870 | 20 | 2.1316 | 0.04902 | 0.9945 | |
| 35 °C | 10 | 1.2312 | 0.0662 | 0.9947 | 10 | 1.5382 | 0.00455 | 0.9957 |
| 15 | 1.8674 | 0.0567 | 0.9957 | 15 | 2.3984 | 0.02247 | 0.9951 | |
| 20 | 2.3163 | 0.0768 | 0.9889 | 20 | 2.8273 | 0.02914 | 0.9972 | |
| Adsorption (mg/g) | Desorption (mg/g) | Desorption Rate (%) | Particle Surface State |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.606 | 0.0007 | 0.115 | No change |
| 1.142 | 0.001 | 0.087 | No change |
| 2.113 | 0.003 | 0.142 | No change |
| 2.563 | 0.005 | 0.195 | No change |
| 2.798 | 0.009 | 0.321 | No change |
| 3.124 | 0.012 | 0.384 | No change |
| 3.434 | 0.018 | 0.524 | No change |
| Adsorption (mg/g) | Desorption (mg/g) | Desorption Rate (%) | Particle Surface State |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.612 | 0.001 | 0.163 | No change |
| 1.135 | 0.003 | 0.264 | No change |
| 2.342 | 0.005 | 0.213 | No change |
| 2.534 | 0.009 | 0.355 | No change |
| 2.857 | 0.013 | 0.455 | No change |
| 3.215 | 0.018 | 0.559 | No change |
| 3.445 | 0.021 | 0.609 | No change |
| Sulfuric Acid Concentration (mol/L) | Adsorption (mg/g) | Desorption (mg/g) | Desorption Rate (%) | Particle Surface State |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 2.160 | 0.123 | 5.694 | No change |
| 0.5 | 2.142 | 0.201 | 9.383 | Small portion of surface material peeling off |
| 1 | 2.133 | 0.436 | 20.44 | Further increase in solution turbidity |
| 5 | 2.204 | 0.875 | 39.70 | The particles are eroded to a greater extent |
| 10 | 2.198 | 1.329 | 60.46 | Pellets fall apart |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhu, L. Experimental Investigation of Lanthanum-Modified Reinforced Composite Material for Phosphorus Removal. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010135
Liu Y, Zhu L. Experimental Investigation of Lanthanum-Modified Reinforced Composite Material for Phosphorus Removal. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(1):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010135
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yan, and Lingfeng Zhu. 2024. "Experimental Investigation of Lanthanum-Modified Reinforced Composite Material for Phosphorus Removal" Applied Sciences 14, no. 1: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010135
APA StyleLiu, Y., & Zhu, L. (2024). Experimental Investigation of Lanthanum-Modified Reinforced Composite Material for Phosphorus Removal. Applied Sciences, 14(1), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010135





