Glass-Forming Ability and Magnetic Properties of Al82Fe16Ce2 and Al82Fe14Mn2Ce2 Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stachurski; Zbigniew, H.; Wang, G.; Tan, X. An Introduction to Metallic Glasses and Amorphous Metals; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Inoue, A. Metallic Glasses. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Suryanarayana, C. Bulk Metallic Glasses, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; p. 565. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, A.; Takeuchi, A. Bulk Metallic Glasses: Formation and Applications. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology; Buschow, K.H.J., Cahn, R.W., Flemings, M.C., Ilschner, B., Kramer, E.J., Mahajan, S., Veyssière, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, K.M.; Liaw, P. Bulk Metallic Glasses; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.J.; Yao, J.H.; Chao, Y.S.; Wang, J.Q.; Ma, E. Developing Aluminum-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses. Philos. Mag. 2010, 90, 3215–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, J.; Ranganathan, S. Bulk metallic glasses: A new class of engineering materials. Sadhana 2003, 28, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Takeuchi, A. Recent Progress in Bulk Glassy Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 1892–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perepezko, J.H.; Hebert, R.J. Amorphous aluminum alloys—Synthesis and stability. JOM 2002, 54, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Kimura, H. Fabrications and mechanical properties of bulk amorphous, nanocrystalline, nanoquasicrystalline alloys in aluminum-based system. J. Light Met. 2001, 1, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A. Amorphous, nanoquasicrystalline and nanocrystalline alloys in Al-based systems. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1998, 43, 365–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Yue, X.; Inoue, A.; Liu, C.-T.; Shen, X.; Liaw, P.K. Recent Topics on the Structure and Crystallization of Al-based Glassy Alloys. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, e20180619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Kimura, H.; Inoue, A. Amorphous forming ability and mechanical properties of rapidly solidified Al–Zr–LTM (LTM = Fe, Co, Ni and Cu) alloys. Mater. Lett. 2002, 52, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzola-Quiquia, J.; Osmic, E.; Häussler, P. The magnetic properties of amorphous AlxFe100−x alloys investigated by the atomic structure, magnetoresistance and anomalous Hall effect. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 526, 167624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical alloying: A critical review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2022, 10, 619–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eskandarany, M.S. Mechanical Alloying: Energy Storage, Protective Coatings, and Medical Applications, 3rd ed.; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2020; p. 484. [Google Scholar]
- Schroers, J. Bulk Metallic Glasses. Phys. Today 2013, 66, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayati, M.H.; Mohamed, F.A. Application of mechanical alloying/milling for synthesis of nanocrystalline and amorphous materials. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 394–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, P.; Chang, A.; Zhao, T.; Li, W.; Chang, C.; Jia, J.; Wang, Q.; You, F.; Feng, D.; et al. Glass-forming ability, thermal stability, mechanical and electrochemical behavior of Al-Ce-TM (TM = Ti, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni and Cu) amorphous alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids X 2019, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqida, S.N.; Shah, L.H.; Naher, S.; Brabazon, D. 5.04—Rapid Solidification Processing and Bulk Metallic Glass Casting. In Comprehensive Materials Processing; Hashmi, S., Batalha, G.F., Van Tyne, C.J., Yilbas, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabiałek, M. Influence of the Quenching Rate on the Structure and Magnetic Properties of the Fe-Based Amorphous Alloy. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2016, 61, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabiałek, M. Fabrication Methods for Bulk Amorphous Alloys. In Alloy Materials and Their Allied Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoa, H.X.; Tuan, N.Q.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, B.H.; Viet, N.H.; Kim, J.S. Fabrication of Fe-TiB2 Composite Powder by High-Energy Milling and Subsequent Reaction Synthesis. J. Korean Powder Metall. Inst. 2013, 20, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.V.; Do, N.B.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Nguyen, C.S.; Trinh, V.T.; Le, H.T.; Jorge Junior, A.M. Synthesis and magnetic properties of Al–Cu–Fe quasicrystals prepared by mechanical alloying and heat treatment. J. Mater. Res. 2023, 38, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, N.H.; Oanh, N.T. Microstructure and Electrical Property of Ex-Situ and In-Situ Copper Titanium Carbide Nanocomposites. Metals 2020, 10, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendrachari, S. An Overview of High-Entropy Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying Followed by the Characterization of Their Microstructure and Various Properties. Alloys 2022, 1, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suñol, J.-J. Mechanical Alloying: Processing and Materials. Metals 2021, 11, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, S.; Ammar, H.R.; Almangour, B.; Elborolosy, S.A.; Mekky, A.-b.H.; Alaboodi, A.S. Influence of Milling Time and Ball-to-Powder Ratio on Mechanical Behavior of FeMn30Cu5 Biodegradable Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying and Hot-Forging. Crystals 2022, 12, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Ruiz, M.; Rivera Olvera, J.N.; Morales Davila, R.; González Reyes, L.; Garibay Febles, V.; Garcia Martinez, J.; Diaz Barriga Arceo, L.G. Synthesis and Characterization of Mechanically Alloyed, Nanostructured Cubic MoW Carbide. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosviryakov, A.; Bazlov, A. The Study of Thermal Stability of Mechanically Alloyed Al-5 wt.% TiO2 Composites with Cu and Stearic Acid Additives. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Kong, F.; Zhu, S.; Liu, C.T.; Al-Marzouki, F. Development and Applications of Highly Functional Al-based Materials by Use of Metastable Phases. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 1414–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, Q.; Wei, J.; Liang, C.; Yang, T.; Wang, G.; Xia, C. Effects of Al-based alloy powders on the mechanical behavior, corrosion resistance and infrared emissivity of polyurethane composite coatings. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 624, 126782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnowski, M.; Kulik, T. Nanocrystalline and amorphous Al–Fe alloys containing 60–85% of Al synthesised by mechanical alloying and phase transformations induced by heating of milling products. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 116, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, D.N.; Oanh, N.T.H.; Viet, N.H. Al-Fe-Ni Metallic Glasses via Mechanical Alloying and Its Consolidation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, P.; Cuevas, F.G.; Montes, J.M.; Cintas, J. Solid state amorphization in the Al-Fe binary system during high energy milling. AIP Conf. Proc. 2013, 1569, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binh, D.N.; Oanh, N.T.H.; Viet, N.H. The effect of Ni and Ti additions on the glass forming ability and magnetic properties of Al-Fe-Y alloy prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2022, 583, 121478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Nguyen, O.T.H.; Dudina, D.V.; Le, V.V.; Kim, J.-S. Crystallization Kinetics of Al-Fe and Al-Fe-Y Amorphous Alloys Produced by Mechanical Milling. J. Nanomater. 2016, 2016, 1909108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, A.I.; Zaitseva, N.E.; Shakhpazov, E.K.; Arutyunyan, N.A.; Dunaev, S.F. Association in liquid Al-Fe alloys and its relation to quasicrystal formation. Dokl. Phys. Chem. 2006, 408, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet, N.H.; Oanh, N.T.H.; Quynh, P.N.D.; Lap, T.Q.; Kim, J.S. Thermal Stability of Amorphous Al-Fe-Y Prepared by Mechanical Alloying. Mater. Sci. Forum 2015, 804, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oanh, N.T.H.; Binh, D.N.; Dang Duc, D.; Hoang Thi Ngoc, Q.; Viet, N.H. Effect of Transition Elements on the Thermal Stability of Glassy Alloys 82Al–16Fe–2TM (TM: Ti, Ni, Cu) Prepared by Mechanical Alloying. Materials 2021, 14, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viet, N.H.; Oanh, N.T.; Kim, J.-S.; Jorge, A.M. Crystallization Kinetics and Consolidation of Al82La10Fe4Ni4 Glassy Alloy Powder by Spark Plasma Sintering. Metals 2018, 8, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Han, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wen, C.e. Fabrication of Al-based bulk metallic glass by mechanical alloying and vacuum hot consolidation. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 501, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oanh, N.T.H.; Viet, N.H.; Dudina, D.V.; Jorge, A.M.; Kim, J.-S. Structural characterization and magnetic properties of Al82Fe16TM2 (TM: Ti, Ni, Cu) alloys prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2017, 468, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GÖĞEbakan, M.; Avar, B. Structural evolutions of the mechanically alloyed Al70Cu20Fe10 powders. Pramana 2011, 77, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, U. Hume-Rothery Rules for Structurally Complex Alloy Phases; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiong, X.Z.; Zhou, W.; Li, J.F. Influence of substitution of La by Ce on the glass forming ability and crystallization behavior of Al–Ni–La alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 576, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Classification of Bulk Metallic Glasses by Atomic Size Difference, Heat of Mixing and Period of Constituent Elements and Its Application to Characterization of the Main Alloying Element. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2817–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Dong, C.; Shek, C.H. Bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2004, 44, 45–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.-b.; Du, J.; Huang, Z.-h. Design and preparation of Al-Fe-Ce ternary aluminum alloys with high thermal conductivity. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 1781–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, J.; Ranganathan, S. Crystallisation in Al–ETM–LTM–La metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2004, 12, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.; Bhatt, J.; Biswas, K.; Gurao, N.P. A new perspective to thermodynamical designing of high entropy bulk metallic glasses (HE-BMGs). Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 595, 412350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleg, S.; Bekhouche, A.; Hachache, H.; Sunol, J.J. Effect of Aluminum Addition on the Microstructure, Magnetic, and Mechanical Properties of FeCrCoNiMn High-Entropy Alloy. Crystals 2023, 13, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Mauger, L.; Muñoz, J.A.; Xiao, Y.; Sheets, A.O.; Semiatin, S.L.; Horwath, J.; Turgut, Z. Magnetic and vibrational properties of high-entropy alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 07E307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervens, W.; Wilmesmeier, H. Magnetic Materials. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jeż, B.; Wysłocki, J.; Walters, S.; Postawa, P.; Nabiałek, M. The Process of Magnetizing FeNbYHfB Bulk Amorphous Alloys in Strong Magnetic Fields. Materials 2020, 13, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boll, R. (Ed.) Soft Magnetic Materials: Fundamentals, Alloys, Properties, Products, Applications; Siemens AG, Berlin and Miinchen: Munich, Germany, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Kronmüller, H.; Fähnle, M.; Domann, M.; Grimm, H.; Grimm, R.; Gröger, B. Magnetic properties of amorphous ferromagnetic alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1979, 13, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

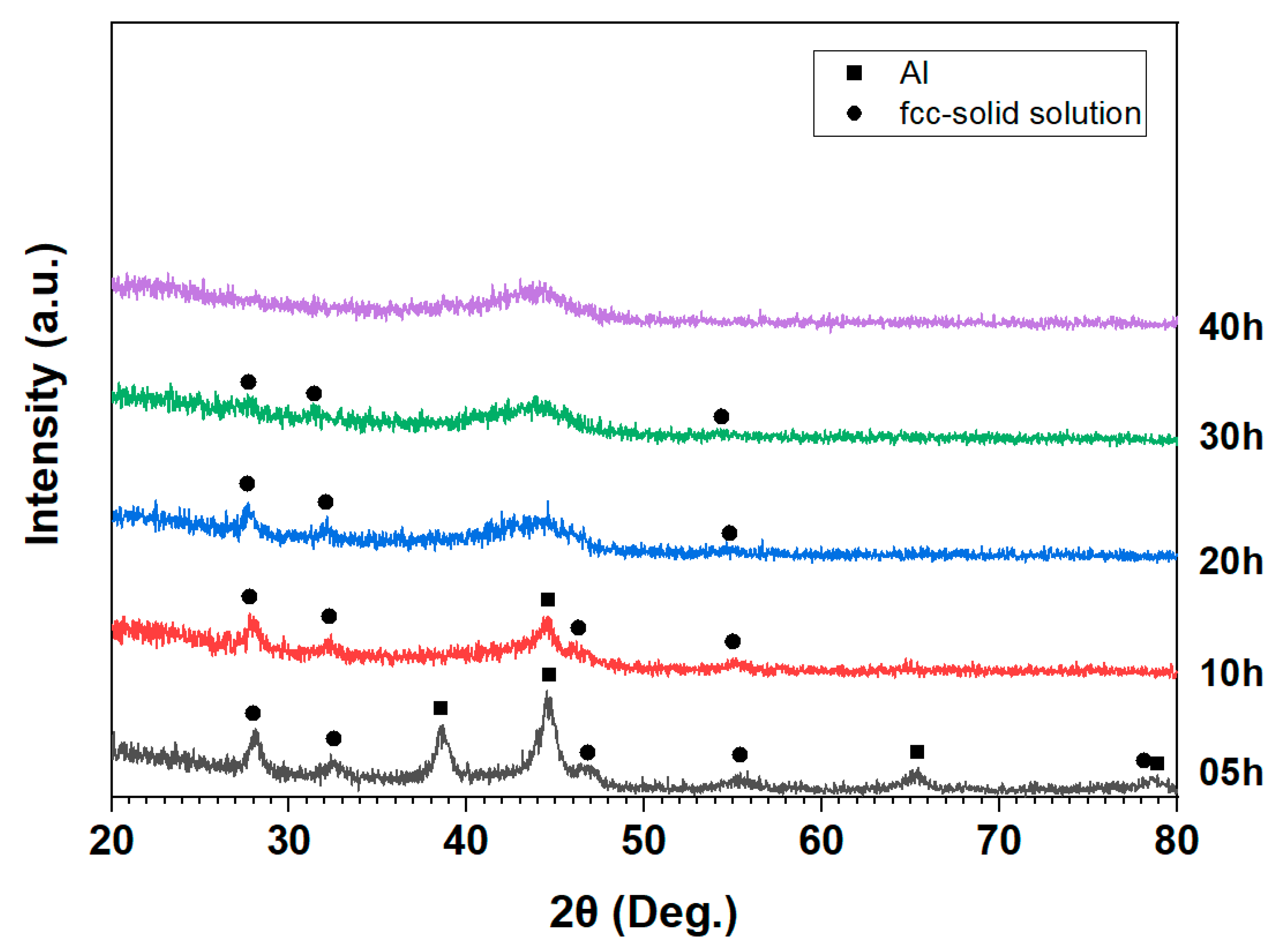
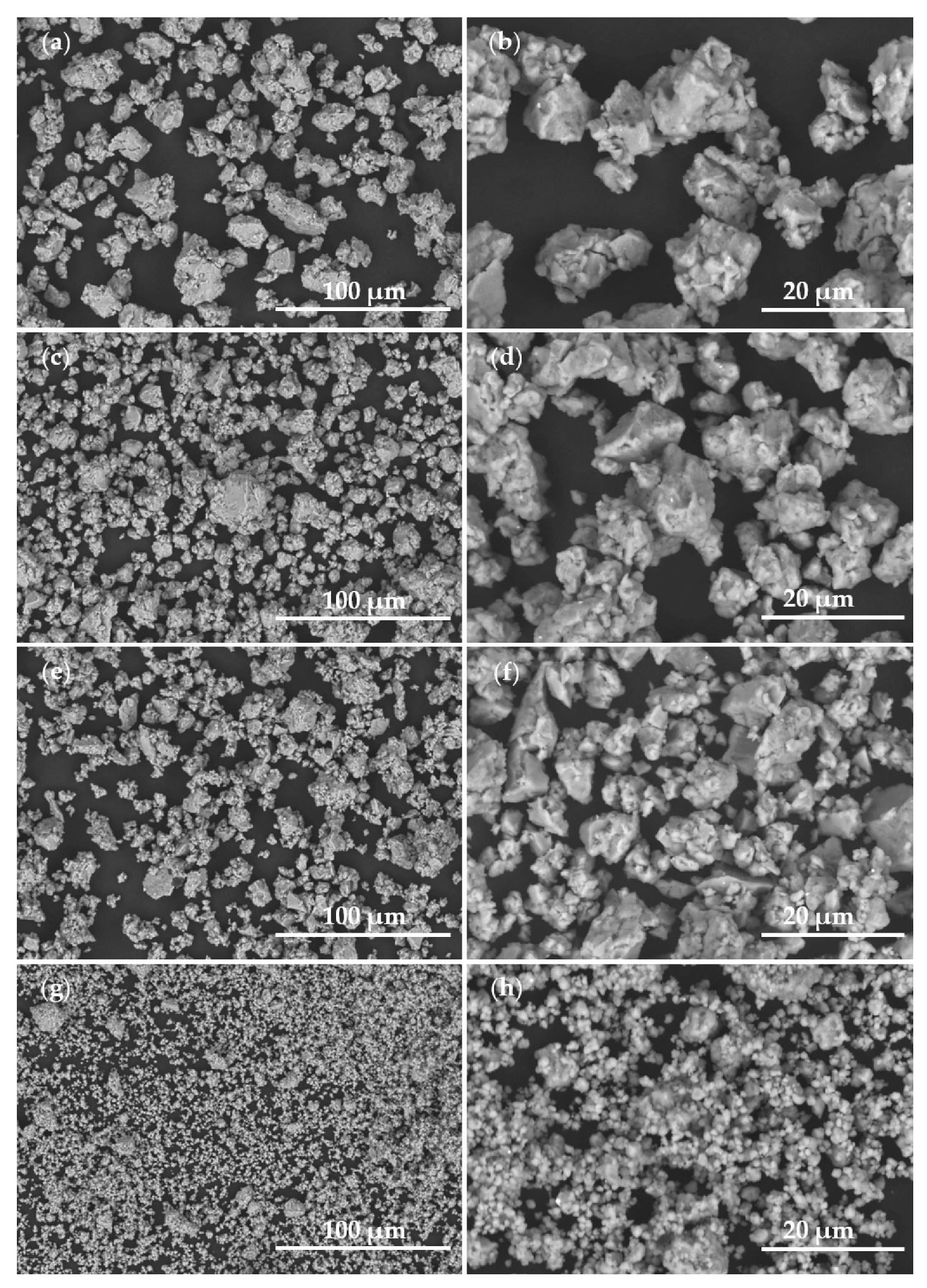
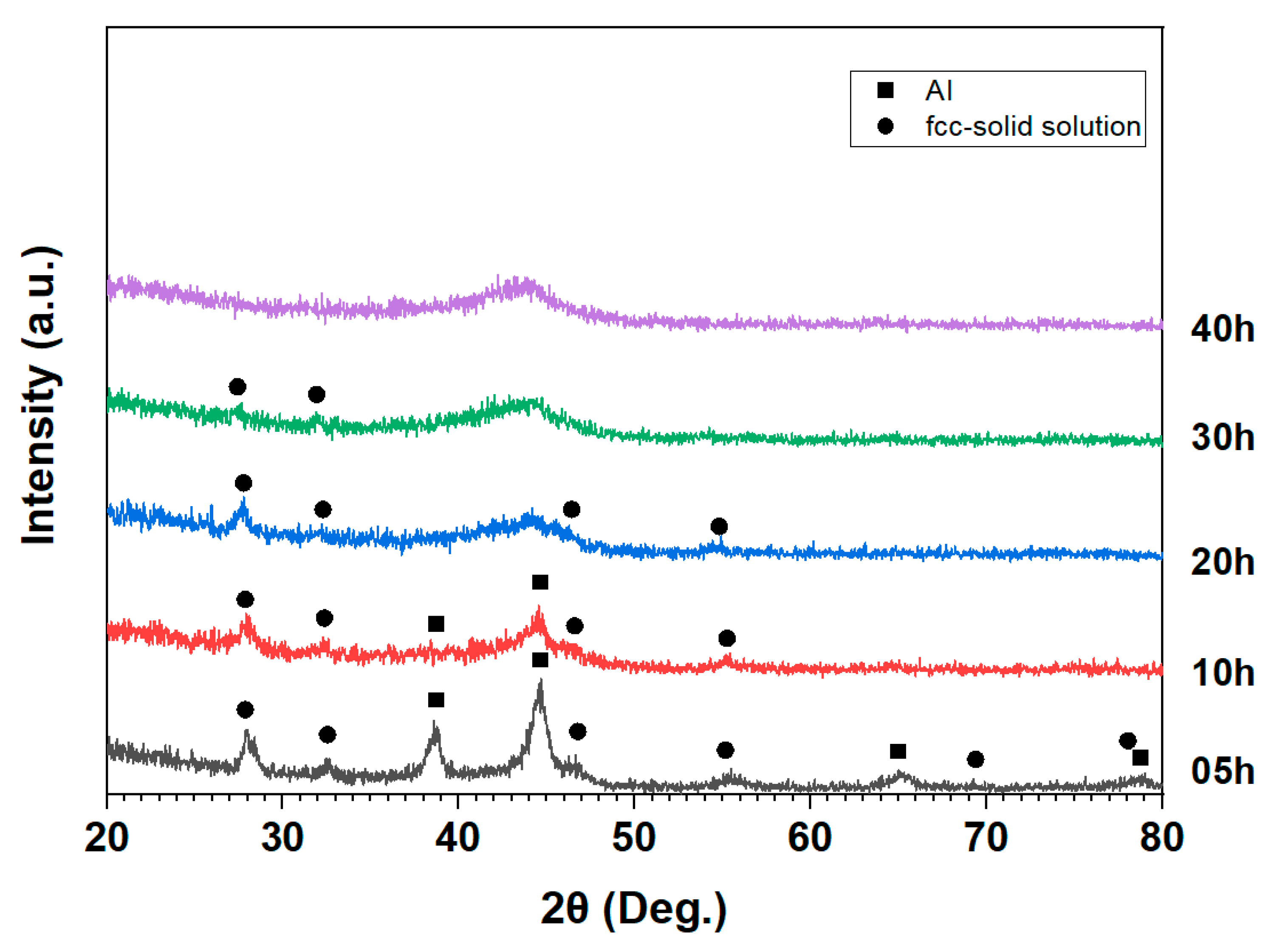

| Al | Fe | Ti | Ni | Cu | Mn | Y | Ce | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | - | 13 [%] | 2.7 [%] | 12.5 [%] | 10 [%] | 5.5 [%] | 21.4 [%] | 21.8 [%] |
| Fe | −11 [kJ/mole] | - | 15.6 [%] | 0.8 [%] | 3.1 [%] | 8.1 [%] | 31.8 [%] | 32.2 [%] |
| Ti | −30 [kJ/mole] | −17 [kJ/mole] | - | 14.9 [%] | 12.9 [%] | 8.1 [%] | 19.2 [%] | 19.6 [%] |
| Ni | −22 [kJ/mole] | −2 [kJ/mole] | −35 [kJ/mole] | - | 2.3 [%] | 7.4 [%] | 31.3 [%] | 31.6 [%] |
| Cu | −1 [kJ/mole] | +13 [kJ/mole] | −8 [kJ/mole] | −8 [kJ/mole] | - | +5.1 [%] | 29.6 [%] | 30 [%] |
| Mn | −19 [kJ/mole] | 0 [kJ/mole] | −8 [kJ/mole] | −8 [kJ/mole] | +4 [kJ/mole] | - | 25.8 [%] | 26 [%] |
| Y | −38 [kJ/mole] | −1 [kJ/mole] | +15 [kJ/mole] | −31 [kJ/mole] | −22 [kJ/mole] | −1 [kJ/mole] | - | 0.5 [%] |
| Ce | −38 [kJ/mole] | +3 [kJ/mole] | +18 [kJ/mole] | −28 [kJ/mole] | −21 [kJ/mole] | +1 [kJ/mole] | 0 [kJ/mole] | - |
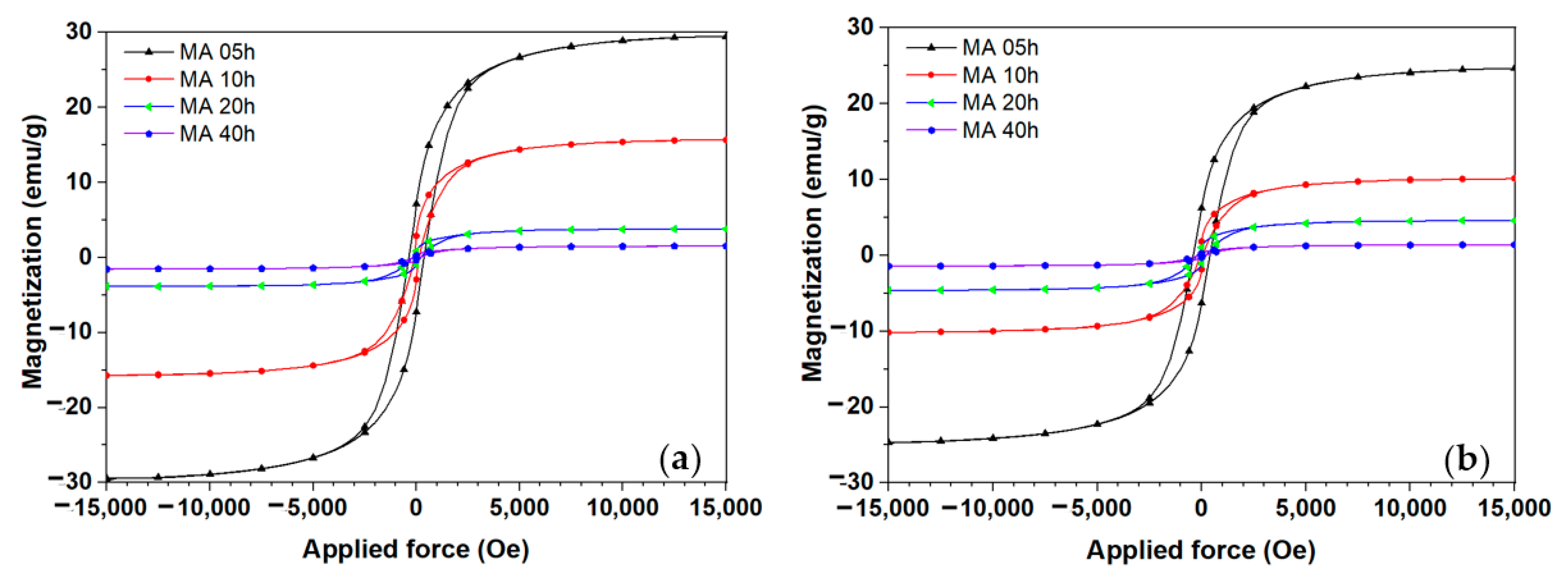
| Al82Fe16Ce2 | 5 h | 10 h | 20 h | 40 h | ||
| Hc, Oe | 366.45 | 118.49 | 207.20 | 156.69 | ||
| Ms, emu/g | 29.5 | 15.70 | 3.84 | 1.53 | ||
| Al82Fe14Mn2Ce2 | 5 h | 10 h | 20 h | 40 h | ||
| Hc, Oe | 398.99 | 81.02 | 218.36 | 158.45 | ||
| Ms, emu/g | 24.69 | 10.17 | 4.62 | 1.41 | ||
| Al82Fe14Ni2Y2 | 5 h | 10 h | 20 h | 40 h | 60 h | |
| Hc, Oe | - | 340.8 | - | 282.1 | 186.5 | |
| Ms, emu/g | - | 13.0 | - | 2.7 | 0.8 | |
| Al82Fe14Ti2Y2 | 5 h | 10 h | 20 h | 40 h | 60 h | 100 h |
| Hc, Oe | - | 256.4 | - | 299.9 | 281.0 | 198.9 |
| Ms, emu/g | - | 14 | - | 2.8 | 1.2 | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hai, N.H.; Viet, N.H.; Oanh, N.T.H. Glass-Forming Ability and Magnetic Properties of Al82Fe16Ce2 and Al82Fe14Mn2Ce2 Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010152
Hai NH, Viet NH, Oanh NTH. Glass-Forming Ability and Magnetic Properties of Al82Fe16Ce2 and Al82Fe14Mn2Ce2 Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(1):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010152
Chicago/Turabian StyleHai, Nguyen Hong, Nguyen Hoang Viet, and Nguyen Thi Hoang Oanh. 2024. "Glass-Forming Ability and Magnetic Properties of Al82Fe16Ce2 and Al82Fe14Mn2Ce2 Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying" Applied Sciences 14, no. 1: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010152
APA StyleHai, N. H., Viet, N. H., & Oanh, N. T. H. (2024). Glass-Forming Ability and Magnetic Properties of Al82Fe16Ce2 and Al82Fe14Mn2Ce2 Alloys Prepared by Mechanical Alloying. Applied Sciences, 14(1), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14010152







