Balance Control of Brushless Direct Current Motor Driven Two-Rotor UAV
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Brushless Direct Current Motor
2.1. Mathematical Model of the BLDCM
2.2. Matlab/Simulink Model of the BLDCM
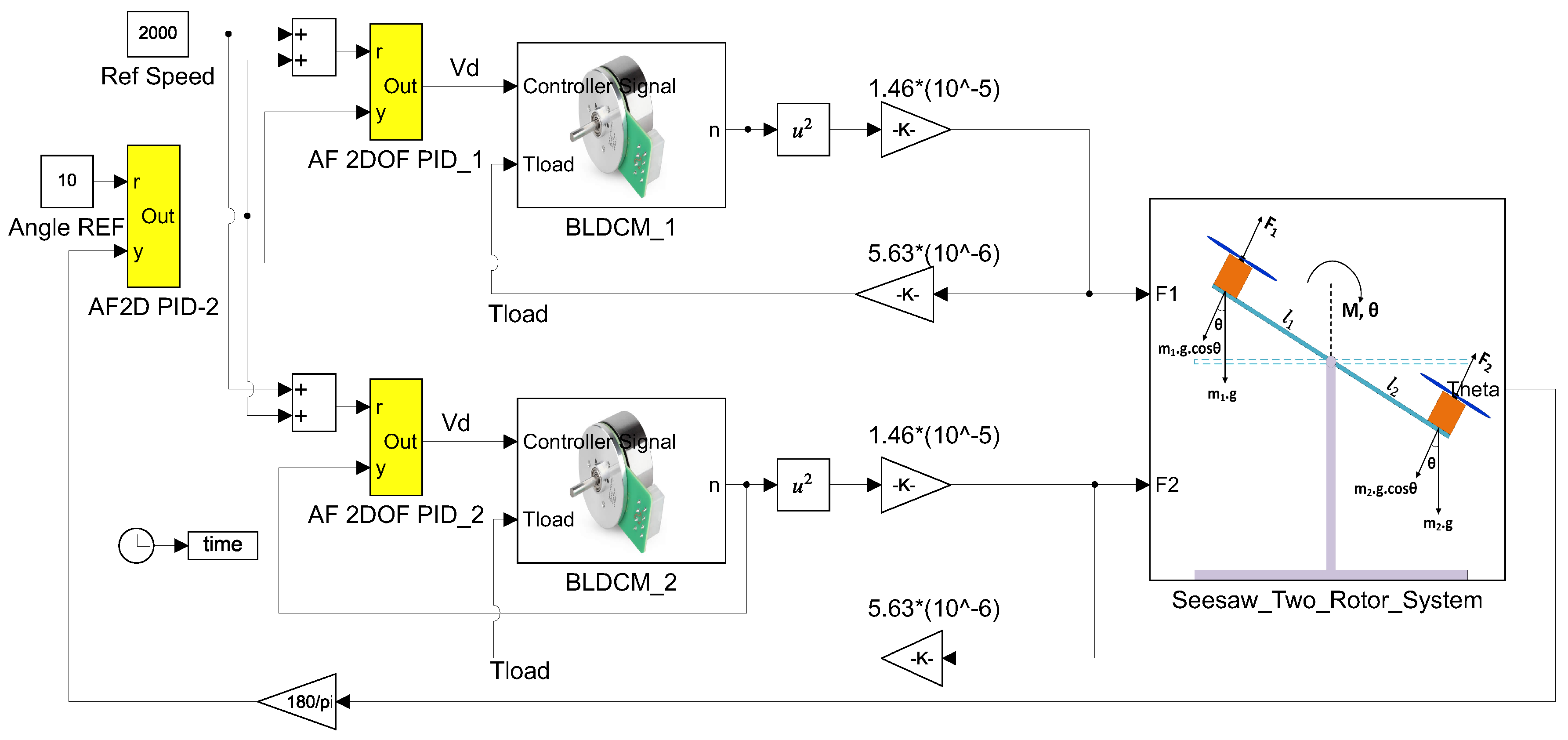
3. Mathematical Model and Control of the Two-Rotor UAV System
3.1. Control of 2R-UAV Balance System Using Both Classical PID and 2-DOF PID Controllers
Determining the Parameters of the Classical PID and 2-DOF PID Controllers Using the PSO
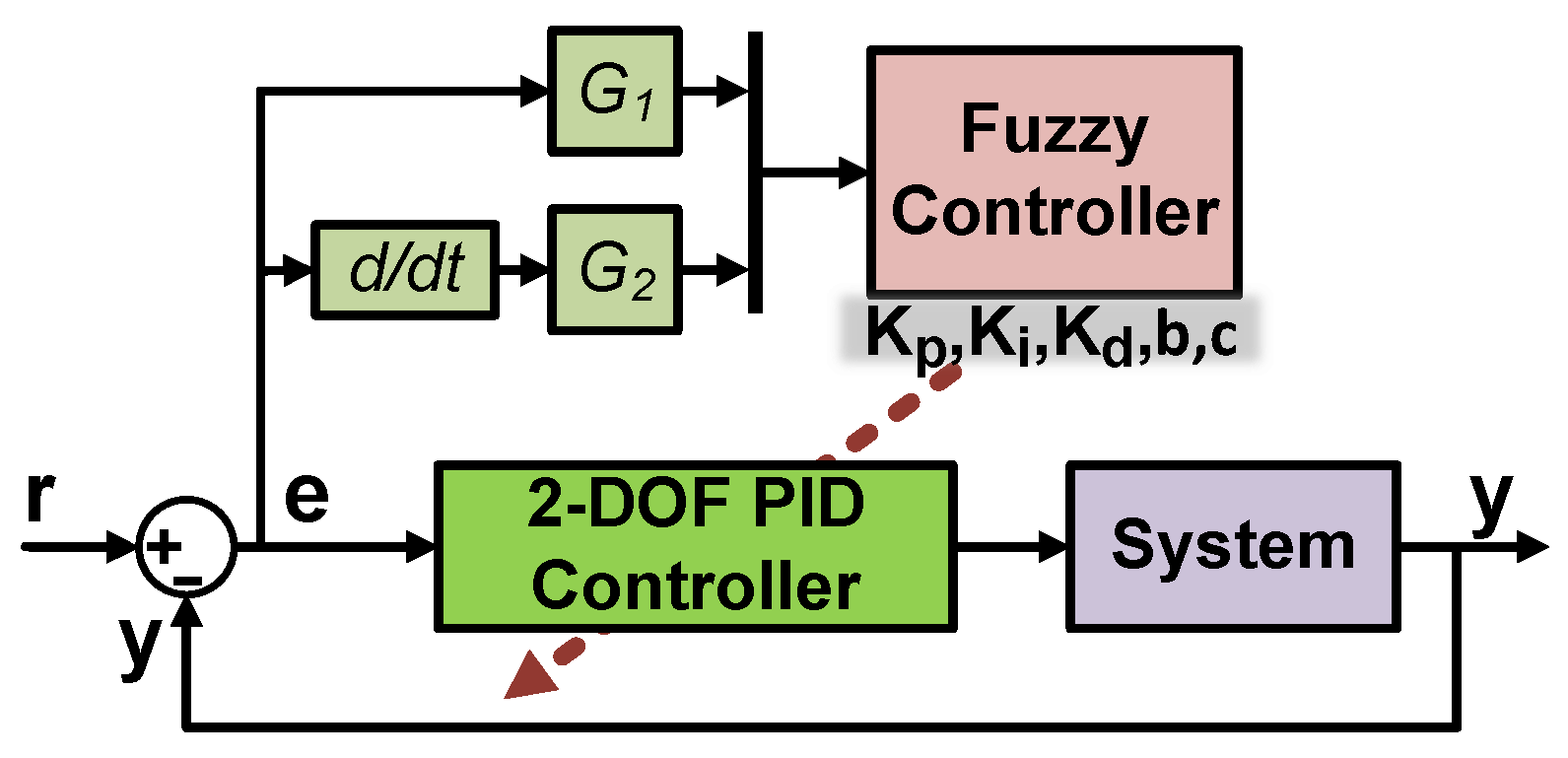
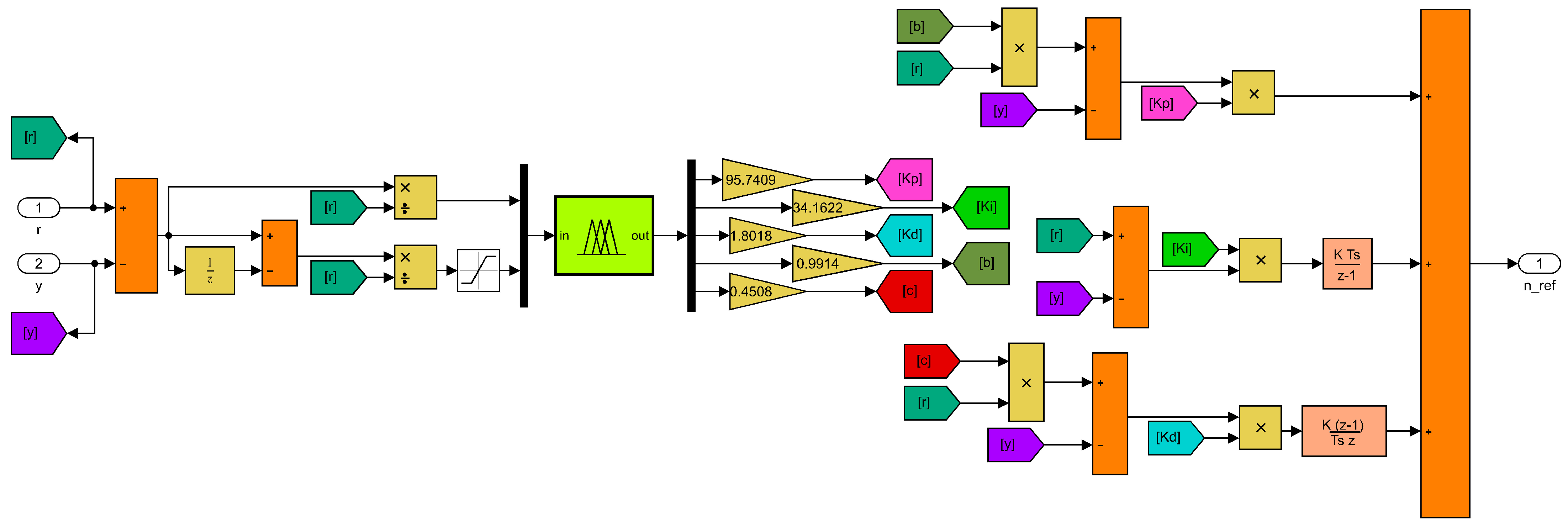
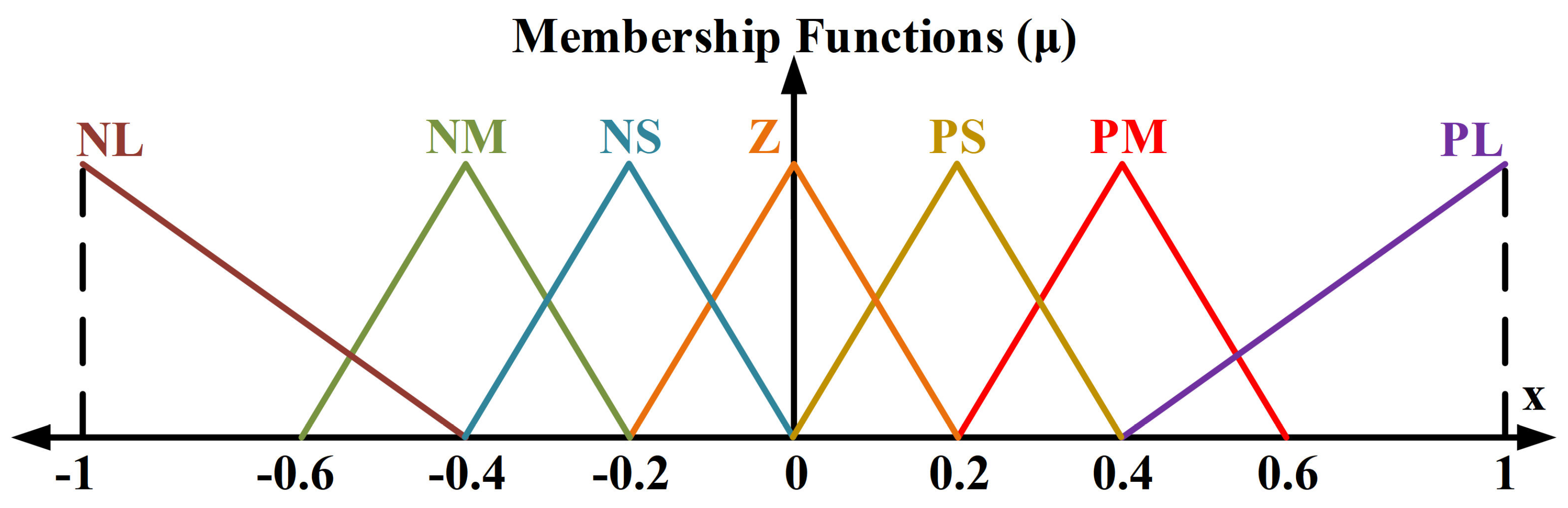
3.2. Control of 2R-UAV Balance System Using Offered Adaptive Fuzzy 2-DOF PID
- Fuzzification: Converts digital inputs into fuzzy data.
- Rule Base: Contains rule tables prepared by an expert opinion.
- Inference Mechanism: A fuzzy set is created for the output using membership functions and rule base.
- Defuzzification: Converts fuzzy data into digital outputs.
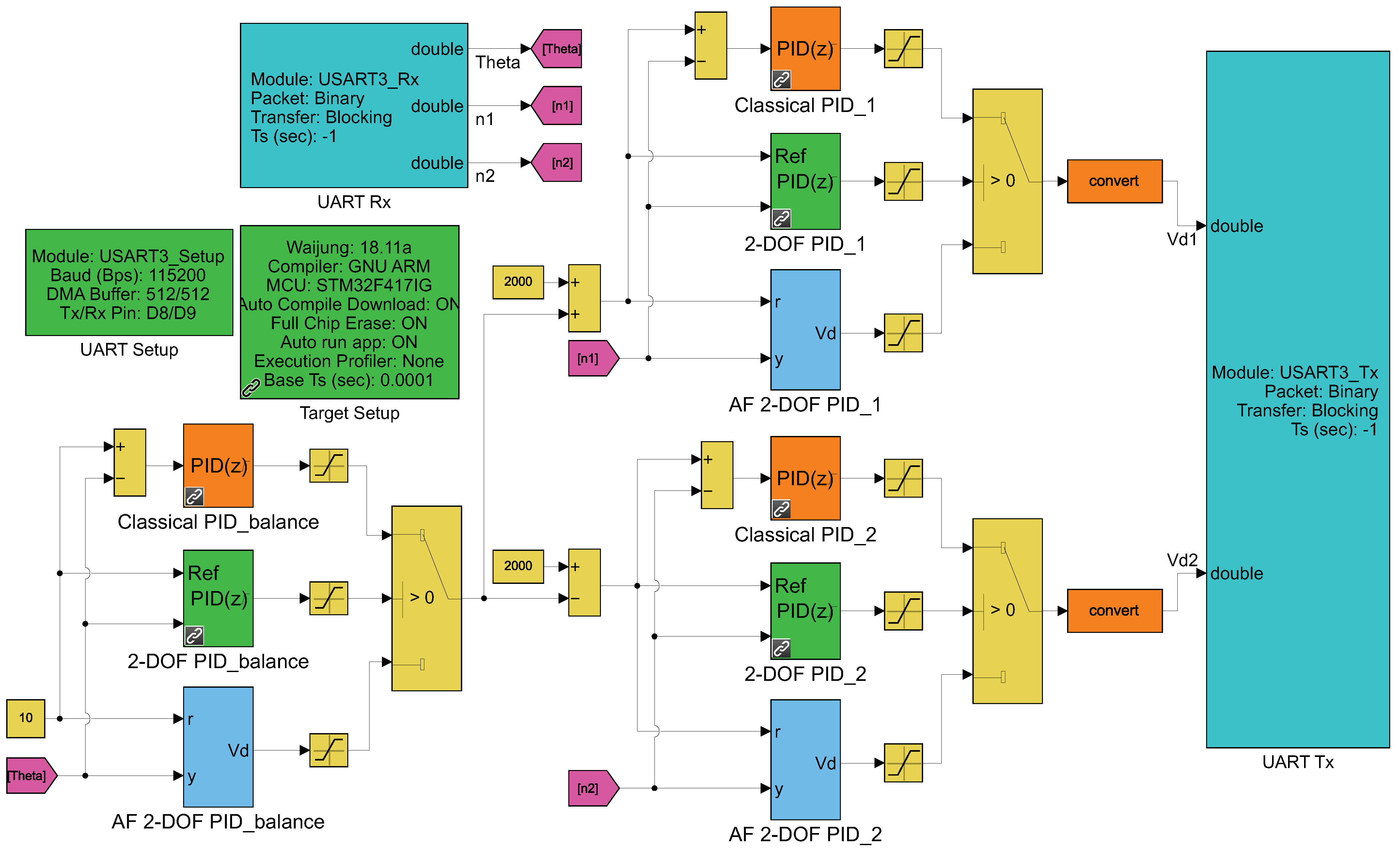
4. Co-Simulation of BLDCM Driven Two-Rotor UAV Balance System
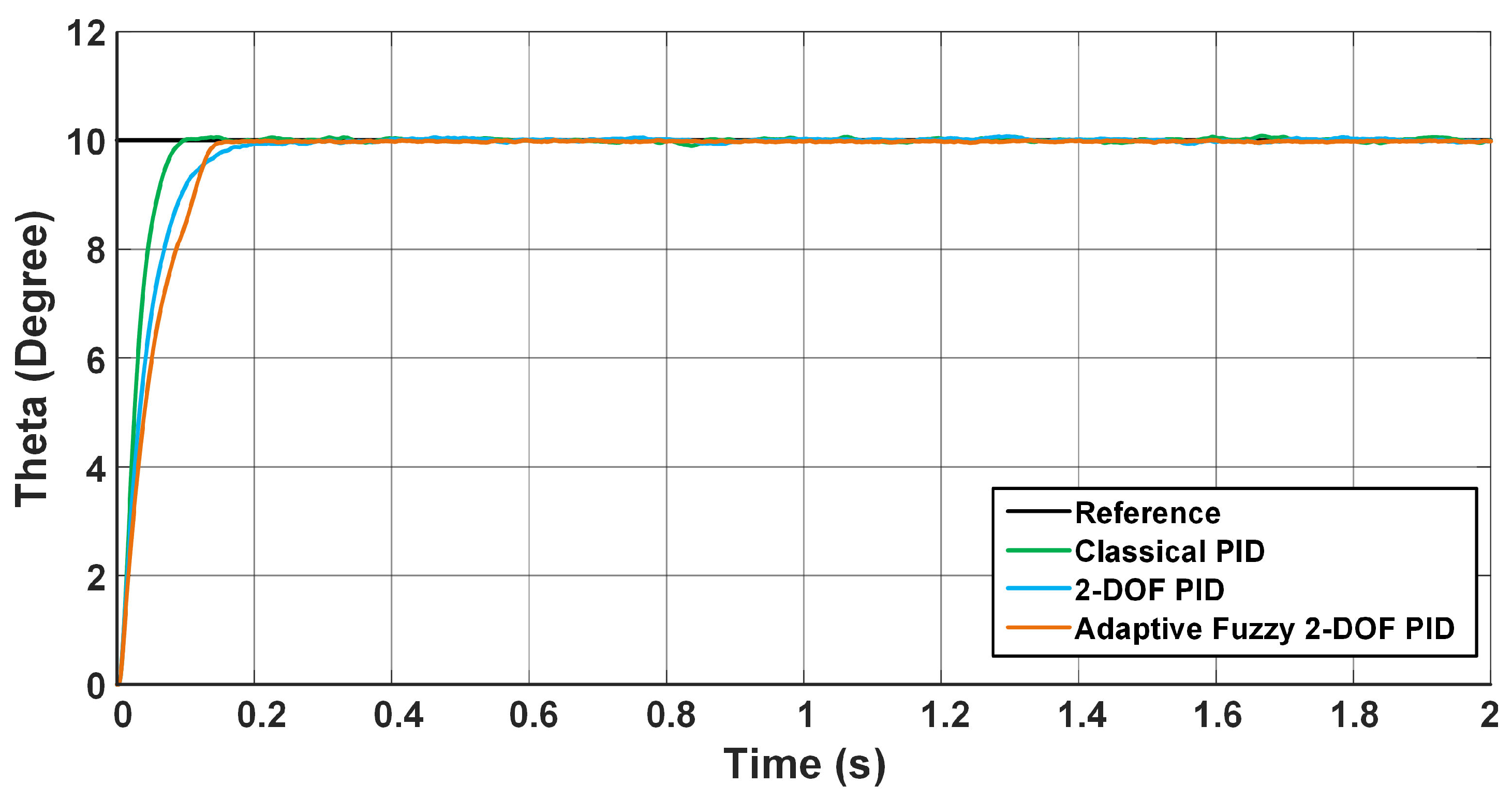
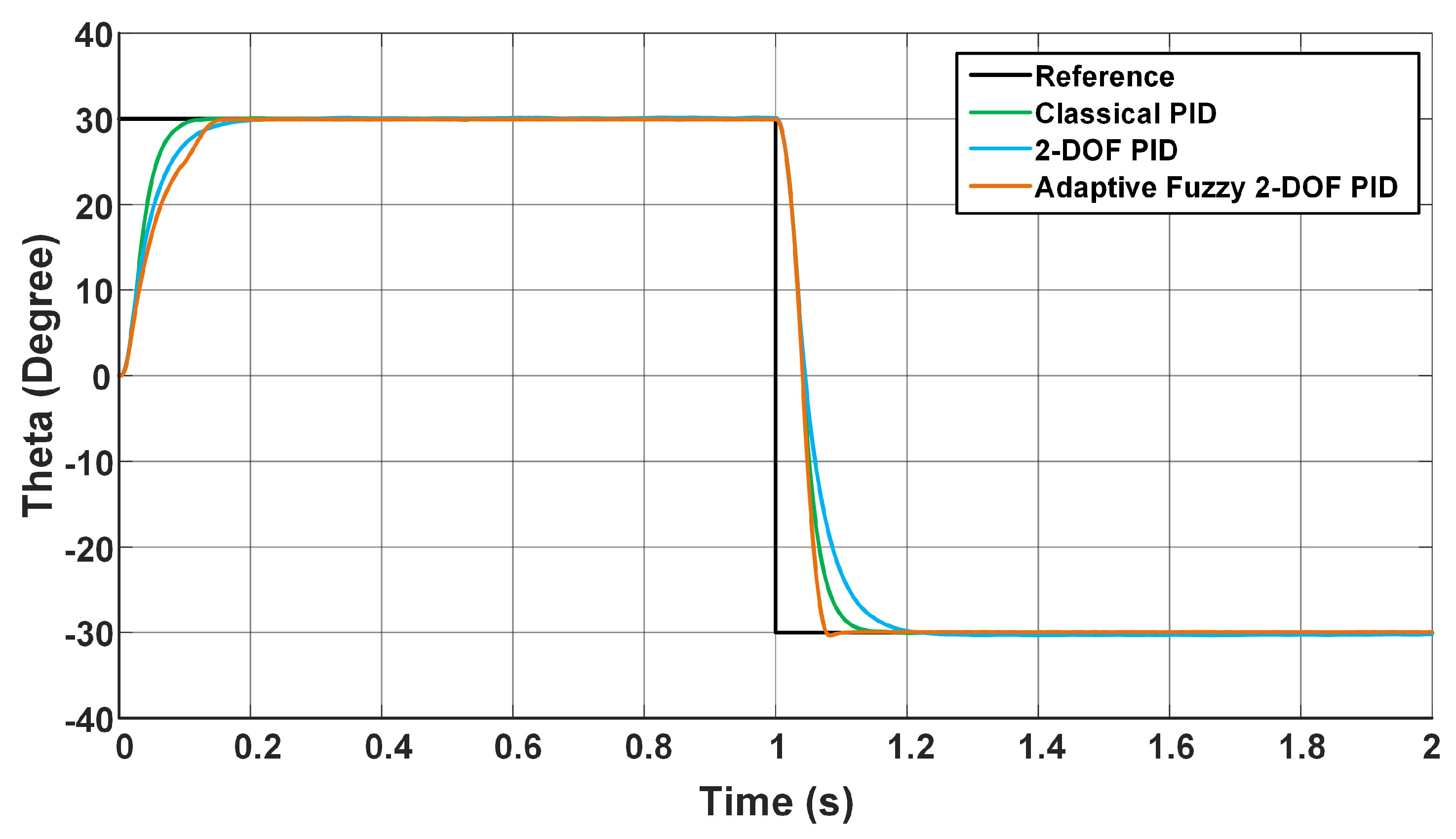
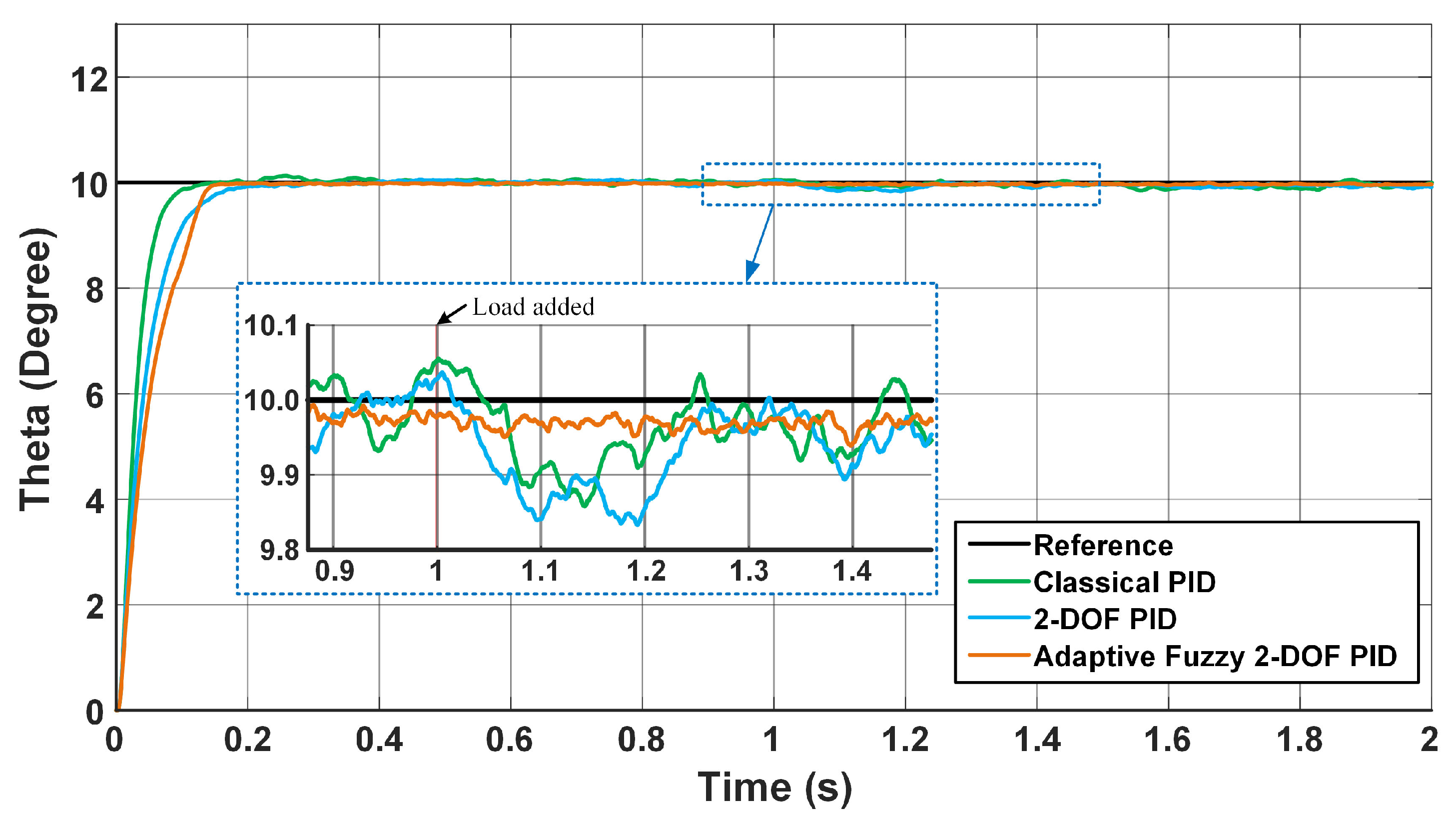
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BLDCM | Brushless Direct Current Motor |
| DOF | Degree of Freedom |
| PID | Proportional Integral Derivative Controller |
| UAV | Unmanned Areal Vehicle |
| rpm | Revolutions per Minute |
References
- Belge, E.; Hızır, K.; Parlak, A.; Altan, A.; Hacıoğlu, R. Estimation of small unmanned aerial vehicle lateral dynamic model with system identification approaches. Balk. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 8, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukdar, I.; Yigit, T.; Celik, H. BLDC Motor Driven, PSO Optimized 2-DOF PID Control of the Seesaw Balance System. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey, 25–27 November 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, Z.A.; Wang, D.; Aamir, M. Fuzzy-based hybrid control algorithm for the stabilization of a tri-rotor UAV. Sensors 2016, 16, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harun-Or-Rashid, M.; Wahid, N.B. Seesaw dynamics and control-experimental study. J. Mech. Robot. 2019, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.N.; Roh, M.S.; Song, J.B.; Song, W.J.; Kang, B.S.; Kim, J. An Experimental Study of a Single Axis Seesaw Attitude Control Consisting of Motor and Propeller. J. Adv. Navig. Technol. 2012, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayadi, A.; Adhinata, F.D.; Sembiring, J.P.; Putri, N.U.; Pranita, E.; Setiawan, A. Implementation of PID Control as a One Axis Balancing Control System on the Bicopter Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Converging Technology in Electrical and Information Engineering (ICCTEIE), Bandar Lampung, Indonesia, 25–26 October 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, P.; Hrishikeshavan, V.; Rand, O.; Chopra, I. Design and development of a scaled quadrotor biplane with variable pitch proprotors for rapid payload delivery. In Proceedings of the American Helicopter Society 72nd Annual Forum, West Palm Beach, FL, USA, 17–19 May 2016; pp. 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tashakori, A.; Ektesabi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, N. Modeling of BLDC motor with ideal back-EMF for automotive applications. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–21 October 2011; Volume 2, pp. 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kroičs, K.; Būmanis, A. BLDC Motor Speed Control with Digital Adaptive PID-Fuzzy Controller and Reduced Harmonic Content. Energies 2024, 17, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüzgeç, U.; Ökten, İ.; Üçgün, H.; Gün, A.R.; Türkyilmaz, T.; Kesler, M.; Karakuzu, C.; Gökhan, U. Development of the test platform for rotary wing unmanned air vehicle. Bilecik Seyh Edebali Univ. J. Sci. 2016, 3, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Can, K.; Orman, K.; Başçi, A.; Derdiyok, A. Trajectory tracking control of a four rotor unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) using two degree of freedom PI controller. In Proceedings of the 2016 National Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Biomedical Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey, 1–3 December 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 682–686. [Google Scholar]
- Eltayeb, A.; Rahmat, M.F.; Eltoum, M.M.; Ibrahim, M.S.; Basri, M.A.M. Trajectory tracking for the quadcopter uav utilizing fuzzy PID control approach. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computer, Control, Electrical, and Electronics Engineering (ICCCEEE), Khartoum, Sudan, 26 February–1 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rabah, M.; Rohan, A.; Han, Y.J.; Kim, S.H. Design of fuzzy-PID controller for quadcopter trajectory-tracking. Int. J. Fuzzy Log. Intell. Syst. 2018, 18, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inayathullaah, M.; Sivakumar, N.; Balasundaram, A.; Arul, R.; Angalaeswari, S. Time Domain Investigation of Hybrid Intelligent Controllers Fed Five-Phase PMBLDC Motor Drive. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, H.; Yigit, T. Field-oriented control of the PMSM with 2-DOF PI controller tuned by using PSO. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Processing (IDAP), Malatya, Turkey, 28–30 September 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Özdemir, M.T. A novel optimum PI controller design based on stability boundary locussupported particle swarm optimization in AVR system. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2021, 29, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Saidon, W.S.; Razak, M.A.A.; Samat, A.A.A. Optimization of PI Parameters for Speed Controller of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor by using Particle Swarm Optimization Technique. Int. J. Simul. Syst. Sci. Technol. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. An AEFA-Based optimum design of fuzzy PID controller for attitude control flywheel with BLDC motor. Aerospace 2022, 9, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Gao, L. The Brushless DC motor control system Based on neural network fuzzy PID control of power electronics technology. Optik 2022, 271, 169879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzaldean, M.M. Design of speed-controller for brushless dc-motor based on grey predictor-PID controller. Eng. Technol. J. 2018, 36, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunkas, M.; Aydoğdu, O. Realization of fuzzy logic controlled brushless dc motor drives using Matlab/Simulink. Math. Comput. Appl. 2010, 15, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uurtsaikh, L.; Tengis, T.; Batmunkh, A. Control of Seesaw balancing using decision boundary based on classification method. Int. J. Internet Broadcast. Commun. 2019, 11, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Usha, S.; Dubey, P.M.; Ramya, R.; Suganyadevi, M. Performance enhancement of BLDC motor using PID controller. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2021, 12, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preitl, S.; Stînean, A.I.; Precup, R.E.; Preitl, Z.; Petriu, E.M.; Dragoş, C.A.; Rădac, M.B. Controller design methods for driving systems based on extensions of symmetrical optimum method with DC and BLDC Motor Applications. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2012, 45, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couceiro, M.; Ghamisi, P.; Couceiro, M.; Ghamisi, P. Particle Swarm Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bunday, B.D.; Kiri, V.A. Maximum likelihood estimation—Practical merits of variable metric optimisation methods. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. Stat. 1987, 36, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Huseyin Bilgic, H.; Conker, C.; Yavuz, H. Fuzzy logic–based decision support system for selection of optimum input shaping techniques in point-to-point motion systems. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I J. Syst. Control Eng. 2021, 235, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, S.; Gunduz, H.; Yildirim, B.; Özdemir, M.T. An innovative LFC scheme for multi-area microgrid incorporating with hydrogen-based demand response mechanism. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 39425–39441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelebi, M. Genetic Algorithm Based Optimal Adaptive Fuzzy PID Controller Synthesis. Master’s Thesis, Yildiz Technical University, Istanbul, Turkey, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Asadi, F.; Pongswatd, S. Programming the ARM® Cortex®-M4-based STM32F4 Microcontrollers with Simulink®; Morgan & Claypool Publishers: San Rafael, CA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]



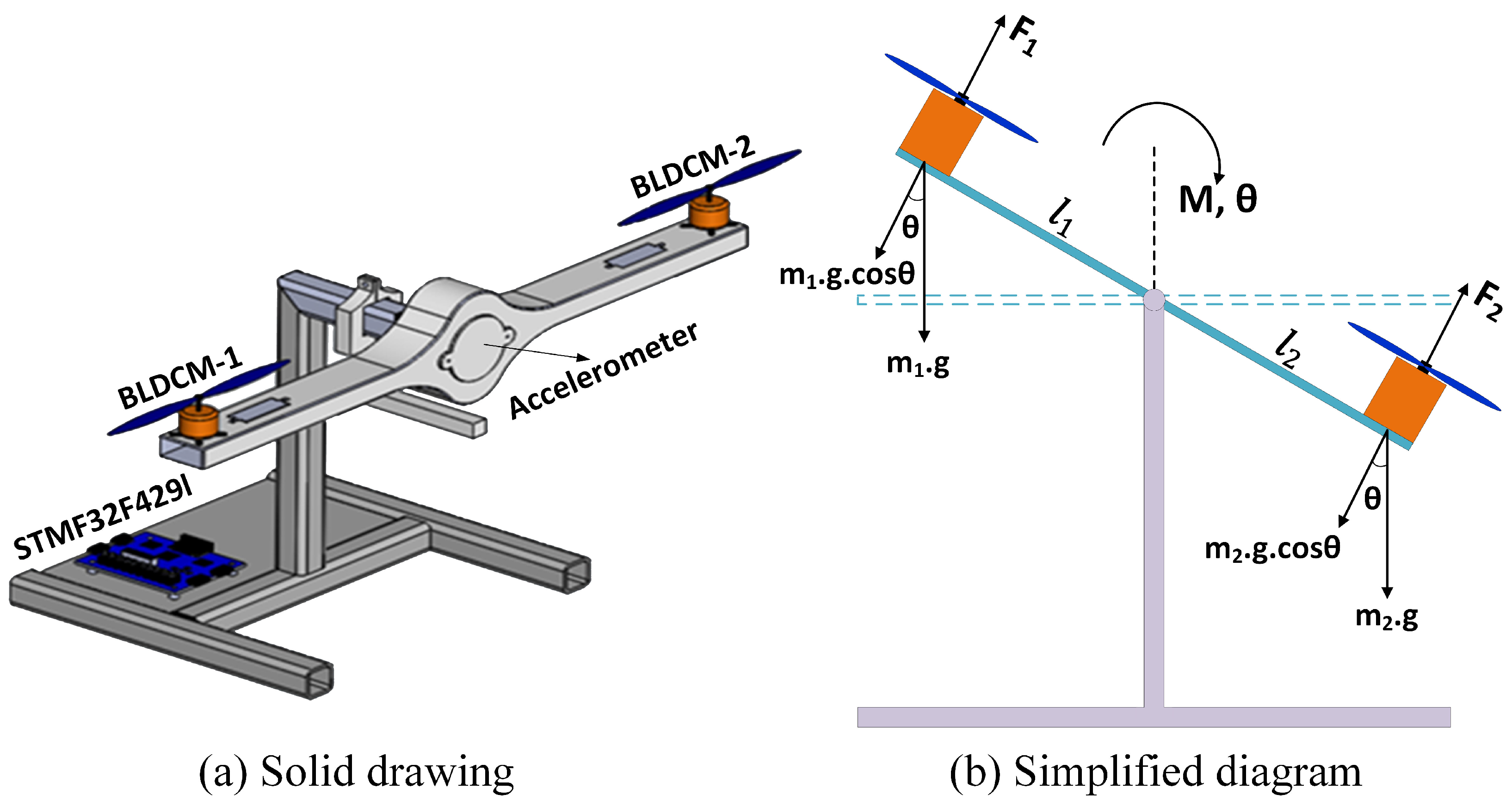
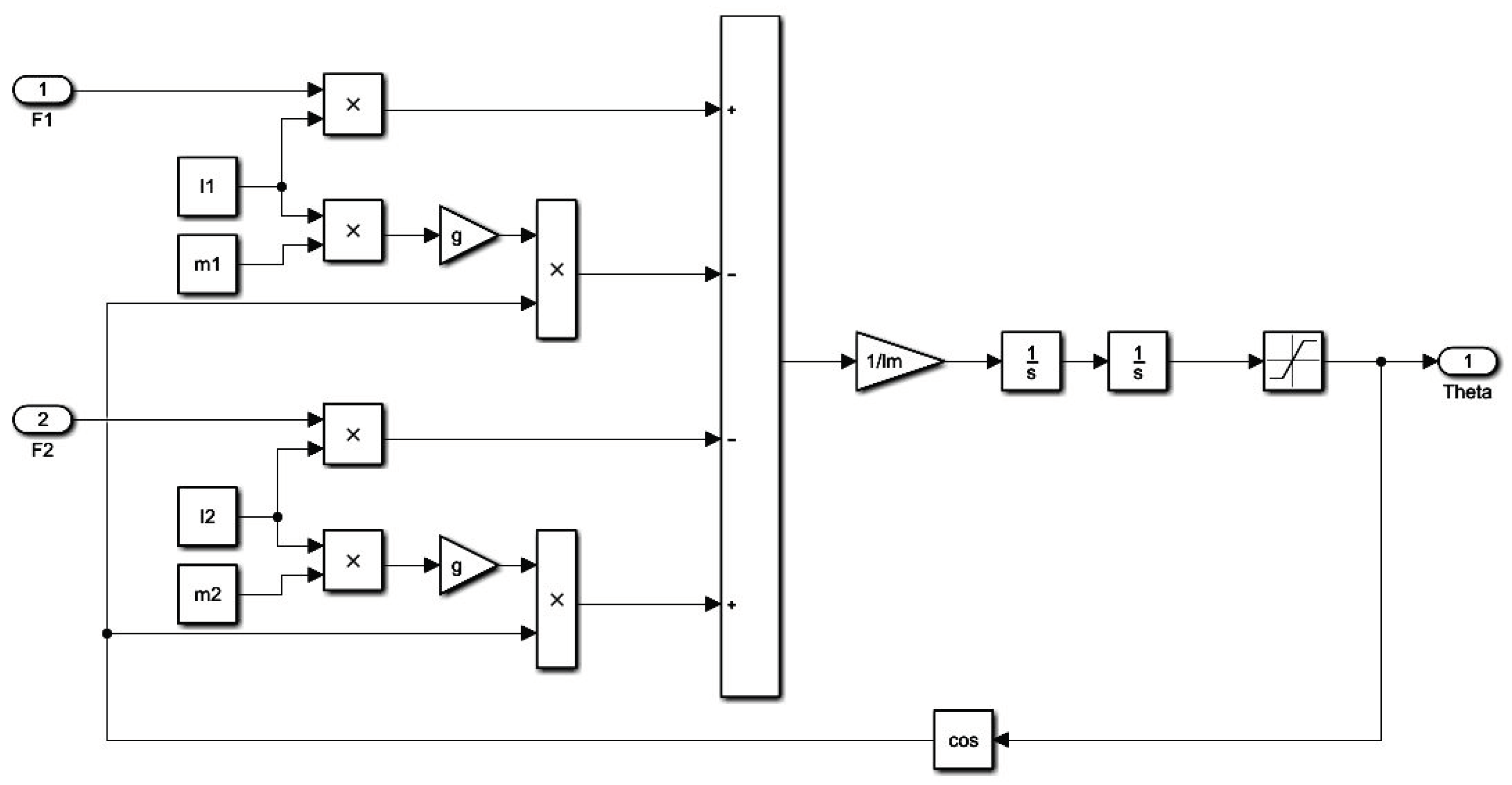


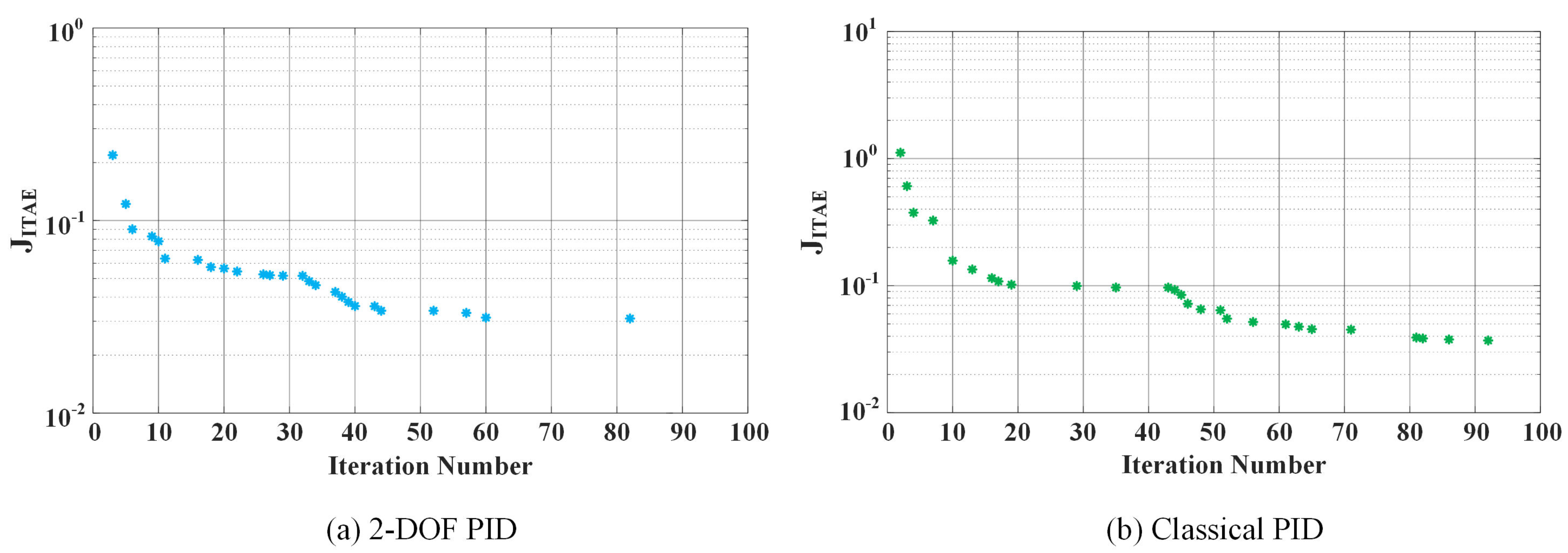
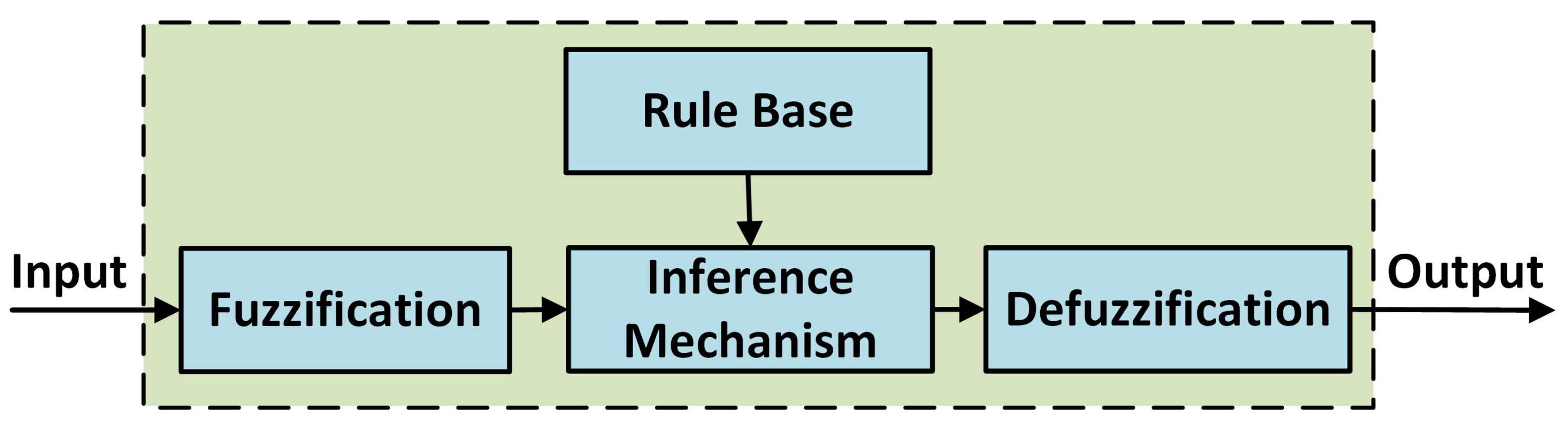
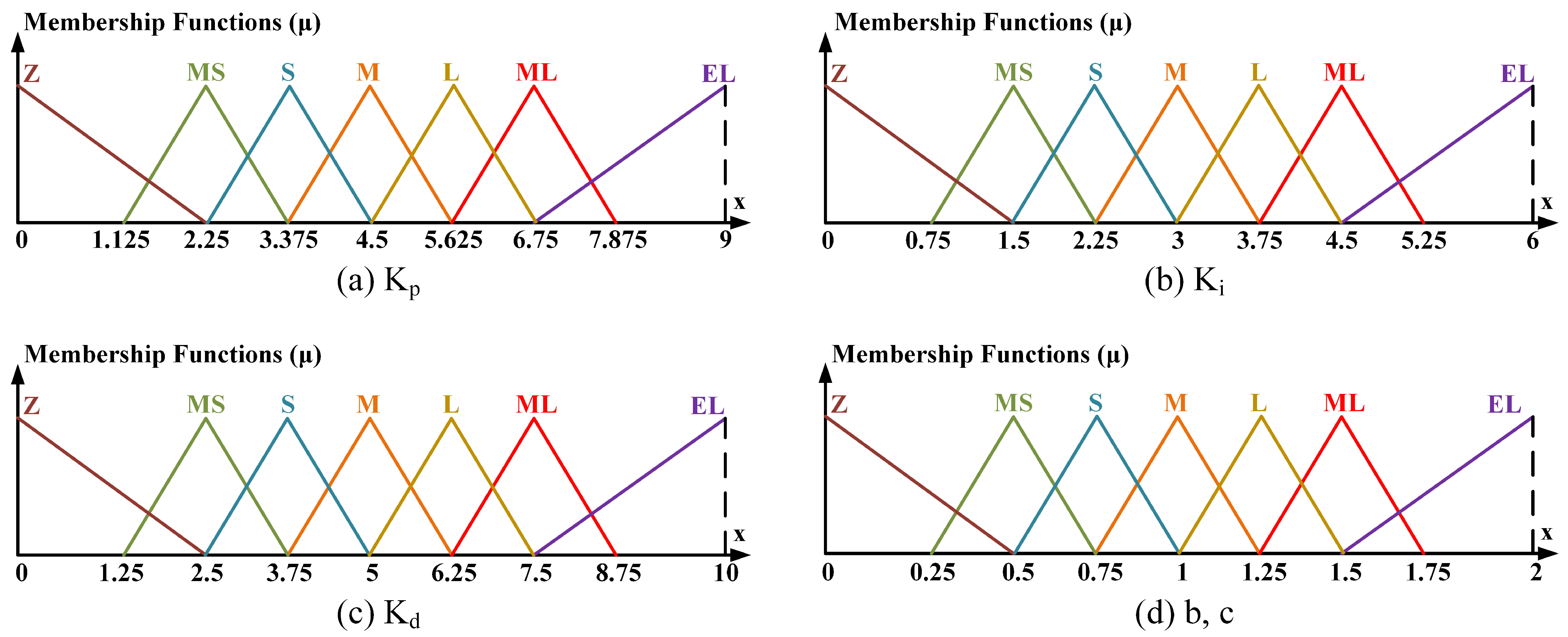

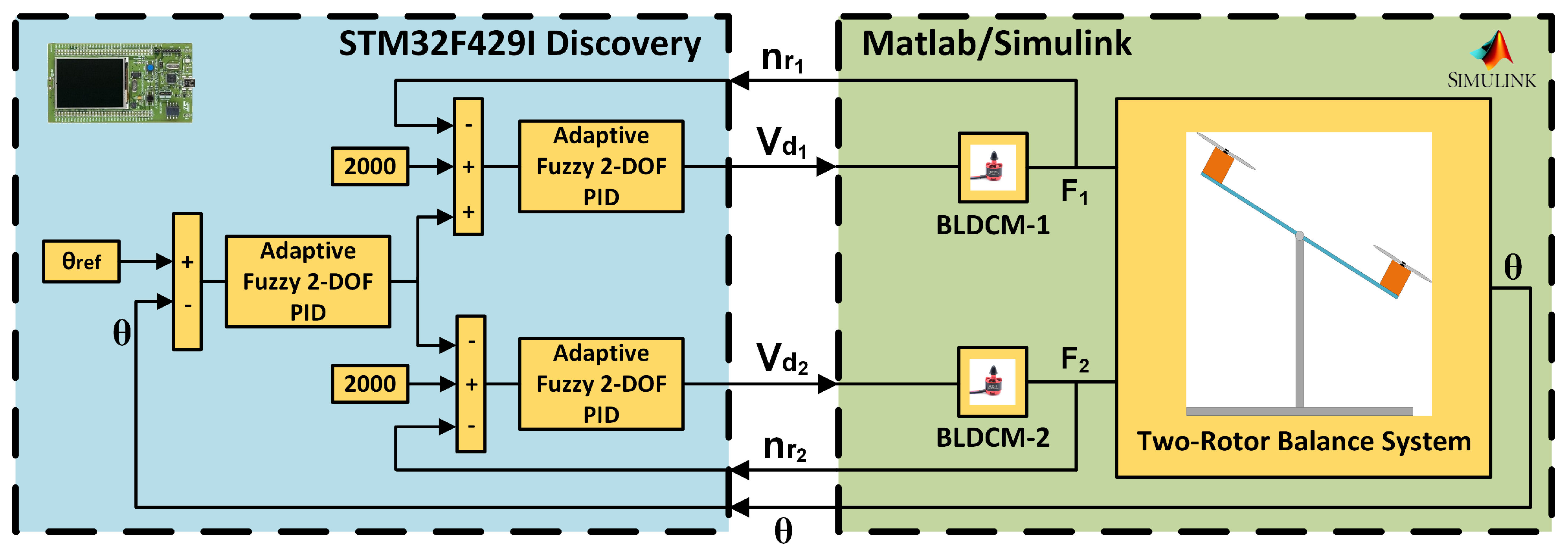
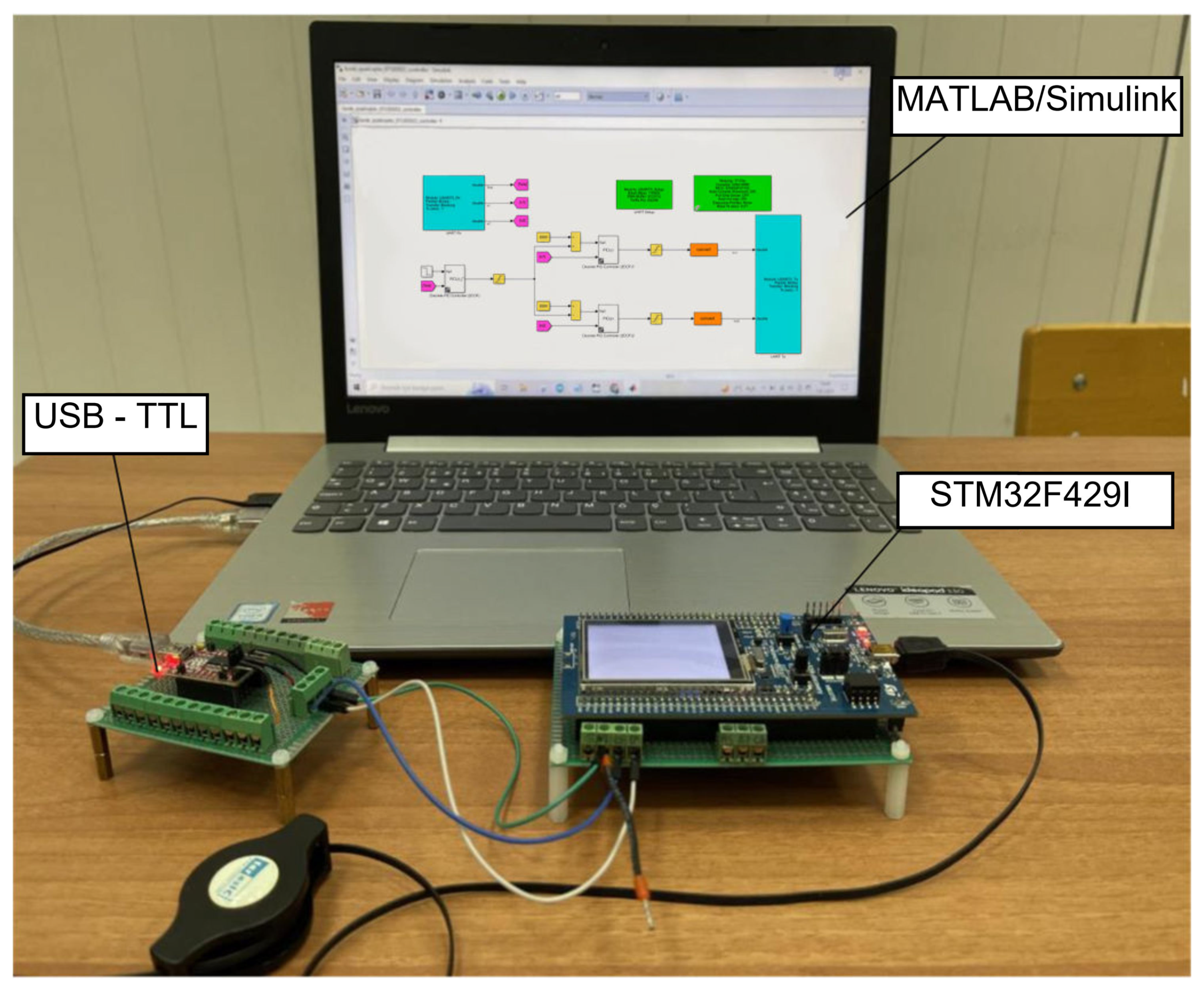
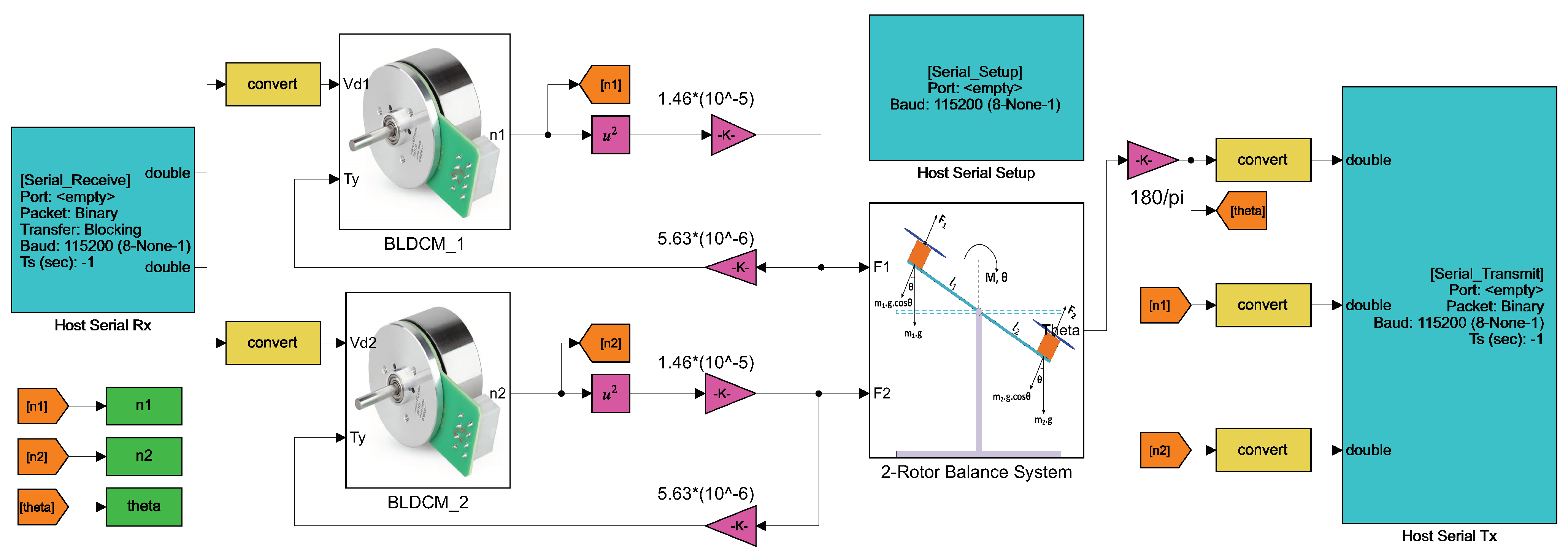



| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| R | 0.304 |
| L | 0.2135 mH |
| P | 16 Poles |
| B | 0 |
| 24 V | |
| J | kg· |
| 0.0369 V·s/rad | |
| 0.0369 Nm/A |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Mass of the motor 1 () | kg |
| Length of the link 1 () | m |
| Mass of the motor 2 () | kg |
| Length of the link 2 () | m |
| Gravity (g) | m/ |
| Parameters | Classical PID | 2-DOF PID |
|---|---|---|
| Number of individuals | 100 | 100 |
| Number of iterations | 100 | 100 |
| Number of parameters searched | 6 | 10 |
| Search space | ||
| w | ||
| Balance System Angle Control | BLDCM Speed Control | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 83.1974 | 56.6088 | ||
| 0.8507 | 53.6323 | ||
| 2.3771 | 0.0097 | ||
| Balance System Angle Control | BLDCM Speed Control | ||
| 95.7409 | 64.4943 | ||
| 34.1622 | 8.8104 | ||
| 1.8018 | 0.0190 | ||
| b | 0.9914 | b | 1.0806 |
| c | 0.4508 | c | 0.9884 |
| NL | NS | Z | PS | PL | ||
| NL | ML/L/Z/S/Z | L/M/MS/MS/MS | MS/S/S/ML/S | L/M/M/MS/M | ML/L/ML/S/ML | |
| NS | ML/L/MS/S/MS | L/M/M/MS/M | S/S/L/M/L | L/M/ML/MS/ML | ML/L/ML/S/ML | |
| e | Z | ML/L/S/S/S | S/M/L/L/L | M/S/L/M/M | L/M/ML/M/ML | ML/L/ML/S/ML |
| PS | ML/L/L/S/L | S/M/ML/L/ML | S/S/ML/ML/ML | ML/M/EL/MS/ML | ML/L/ML/S/ML | |
| PL | ML/EL/EL/Z/ML | M/M/EL/M/EL | S/S/EL/M/ML | ML/M/EL/S/ML | EL/L/EL/Z/ML | |
| NL | NS | Z | PS | PL | ||
| NL | ML/L/Z/MS/Z | L/M/MS/MS/MS | MS/MS/S/ML/S | L/M/M/S/M | ML/L/ML/MS/ML | |
| NS | ML/L/MS/MS/MS | L/M/M/S/M | M/M/L/M/L | L/M/ML/S/ML | ML/L/ML/MS/ML | |
| e | Z | ML/L/S/MS/S | S/M/L/L/L | M/S/L/M/L | M/M/ML/M/ML | ML/L/ML/MS/ML |
| PS | ML/L/L/MS/L | S/M/ML/L/ML | MS/M/ML/ML/ML | L/M/EL/S/ML | ML/L/EL/MS/ML | |
| PL | EL/L/EL/Z/ML | M/M/EL/M/ML | M/S/EL/M/ML | ML/M/EL/MS/ML | EL/L/EL/Z/ML | |
| Reference (Degree) | Performance Criteria | Classical PID Controller | 2-DOF PID Controller | AF 2-DOF PID Controller | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Scenario | 0 to 10 | Rising Time (s) | 0.0496 | 0.0301 | 0.0605 |
| Settling Time (s) | 0.0817 | 0.0536 | 0.0808 | ||
| Overshoot (%) | 0.8372 | 1.0363 | 0 | ||
| Steady State Error | 0.055 | 0.06 | 0.02 | ||
| 2. Scenario | 0 to 30 | Rising Time (s) | 0.0529 | 0.0339 | 0.0619 |
| Settling Time (s) | 0.0984 | 0.0590 | 0.0867 | ||
| Overshoot (%) | 0.2392 | 0.7373 | 0 | ||
| Steady State Error | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.05 | ||
| 30 to −30 | Rising Time (s) | 0.0471 | 0.0199 | 0.0283 | |
| Settling Time (s) | 0.1097 | 0.1120 | 0.0772 | ||
| Overshoot (%) | 0.3139 | 5.6182 | 0 | ||
| Steady State Error | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.06 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cukdar, I.; Yigit, T.; Celik, H. Balance Control of Brushless Direct Current Motor Driven Two-Rotor UAV. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104059
Cukdar I, Yigit T, Celik H. Balance Control of Brushless Direct Current Motor Driven Two-Rotor UAV. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(10):4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104059
Chicago/Turabian StyleCukdar, Ibrahim, Tevfik Yigit, and Hakan Celik. 2024. "Balance Control of Brushless Direct Current Motor Driven Two-Rotor UAV" Applied Sciences 14, no. 10: 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104059
APA StyleCukdar, I., Yigit, T., & Celik, H. (2024). Balance Control of Brushless Direct Current Motor Driven Two-Rotor UAV. Applied Sciences, 14(10), 4059. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14104059






