The Two-Parameter Bifurcation and Evolution of Hunting Motion for a Bogie System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
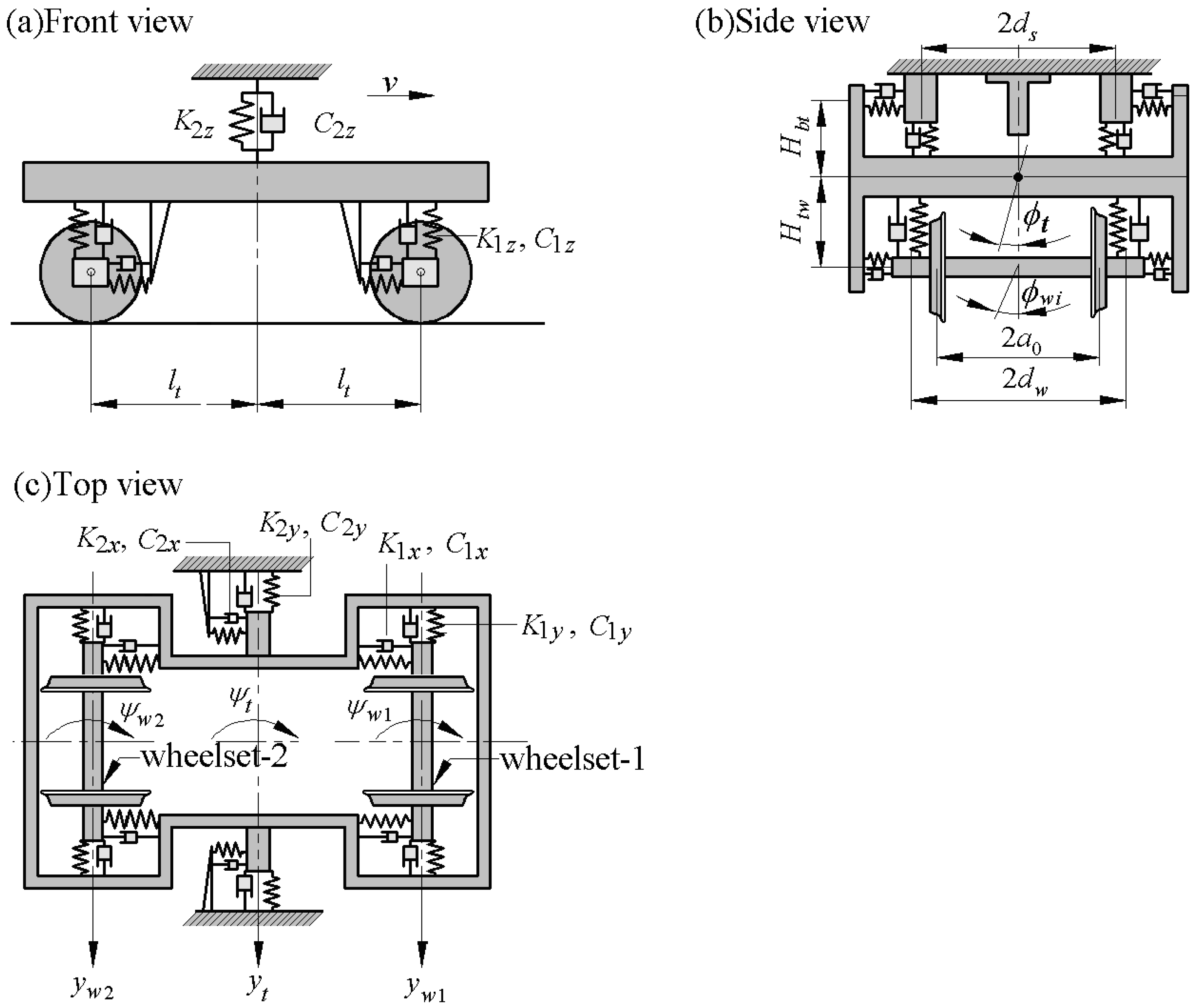
2. Dynamic Model
2.1. Wheel–Rail Interaction Force
2.1.1. Nonlinear, Non-Smooth Wheel–Rail Contact Relation
- The CHN60 rail and LMA wheel profile (extensively adopted in Chinese railways) are obtained and imported into the software.
- The parameters required for calculating the wheel–rail contact relationship are entered, as shown in Table 2.
- The calculated wheel–rail contact geometry parameters are compiled into data tables about the lateral displacement of the wheelset, as shown in Table 3.
2.1.2. The Creep Forces
2.1.3. The Normal Contact Forces
2.1.4. The Flange Force
2.2. Subsection
2.3. Ordinary Differential Equations of the System
3. Method of Investigation
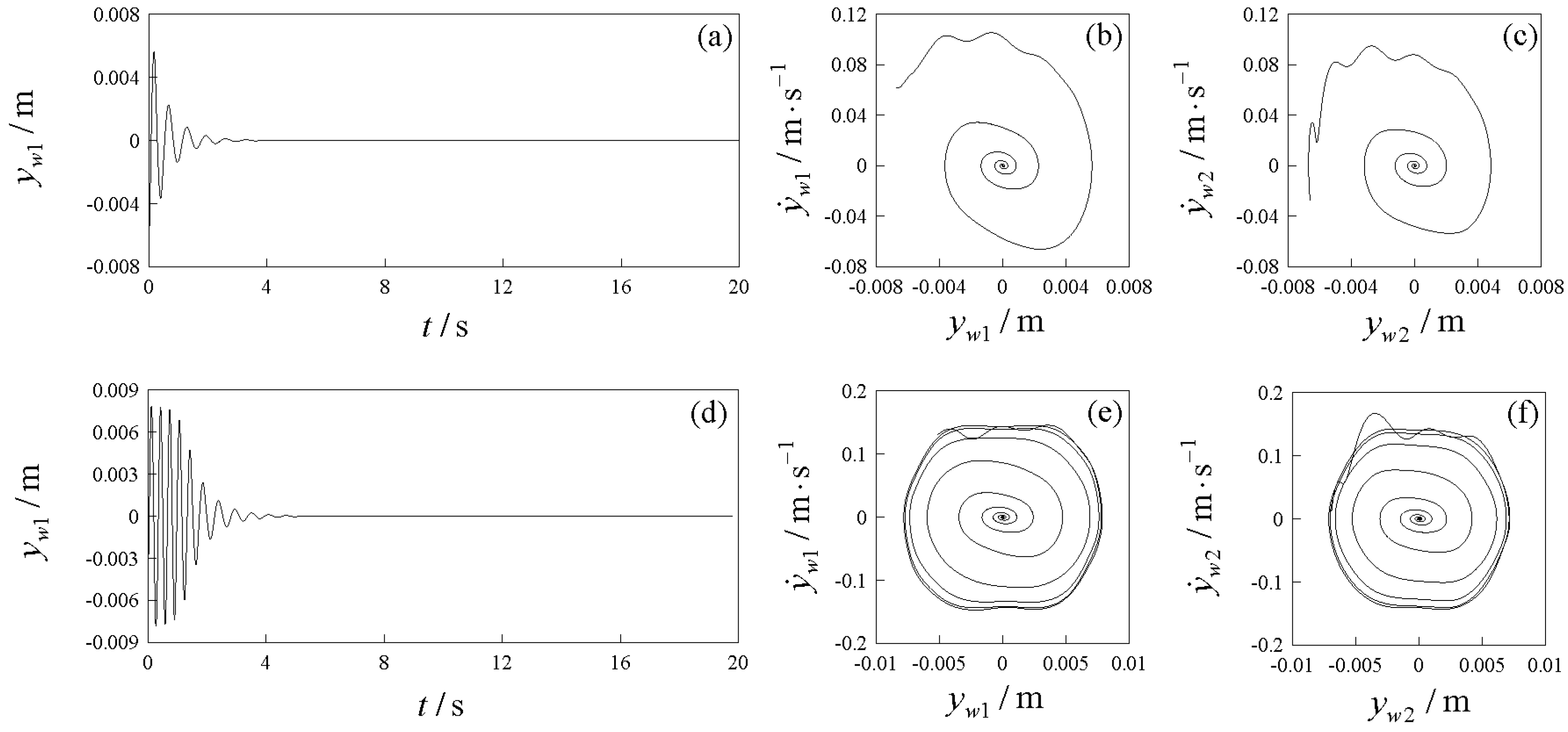
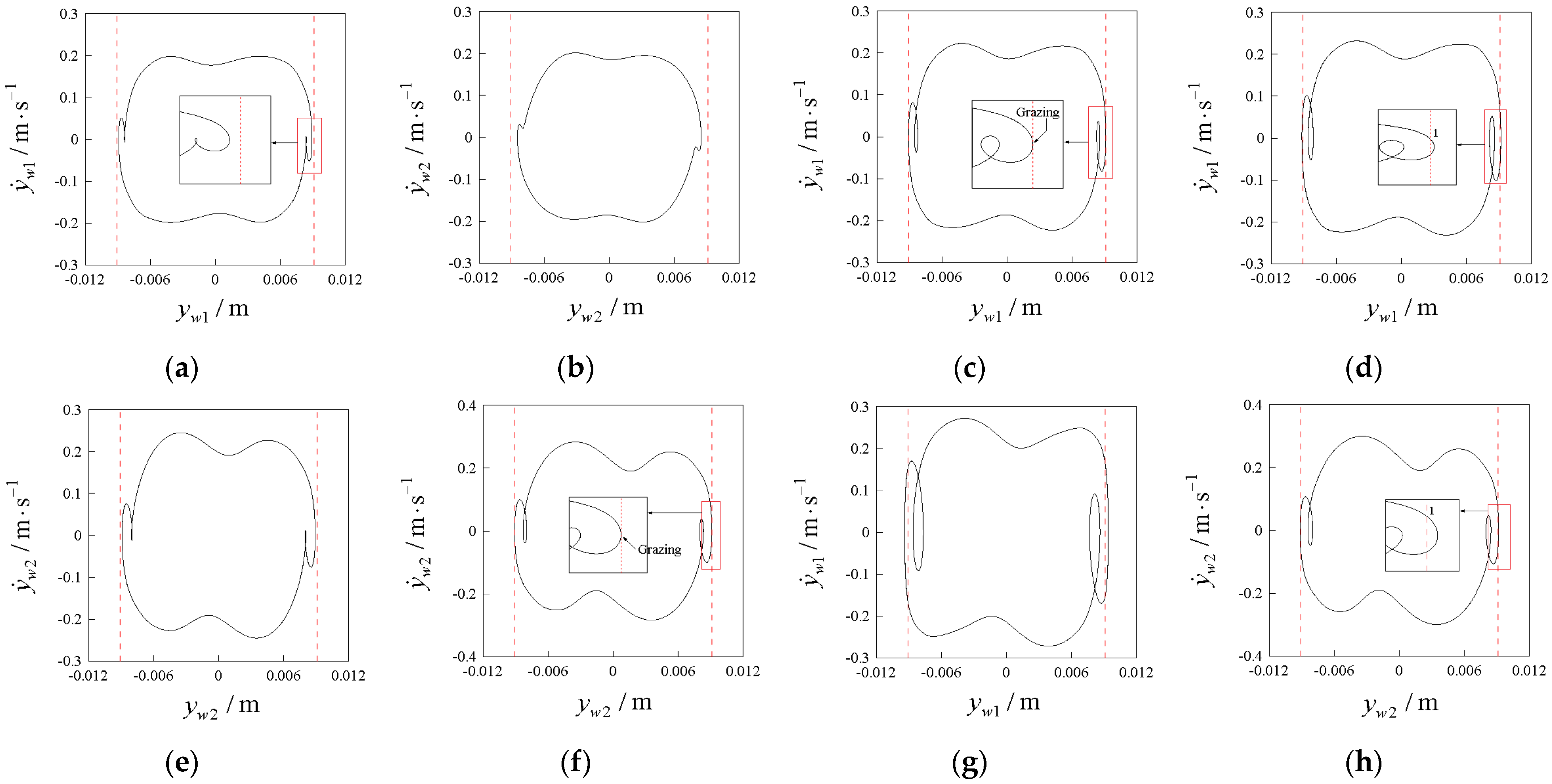
3.1. Poincaré Sections
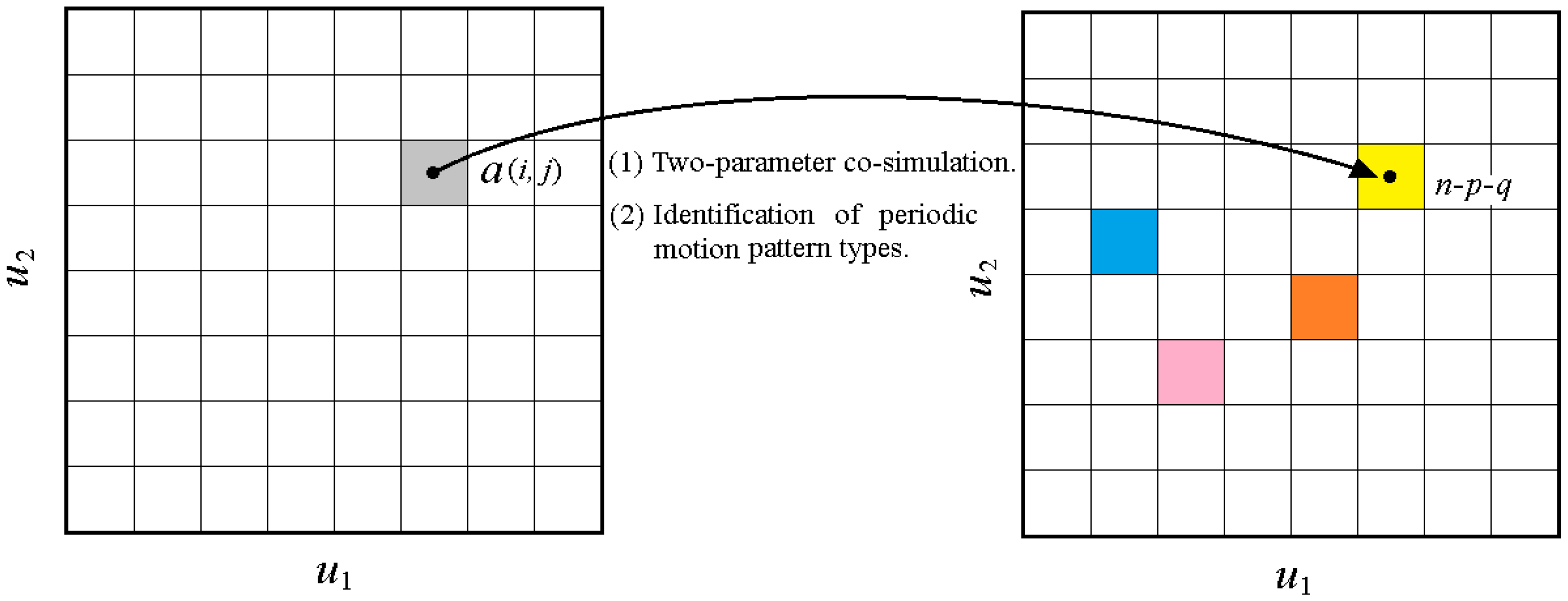
3.2. Two-Parameter Co-Simulation Theory
4. Numerical Results and Discussions
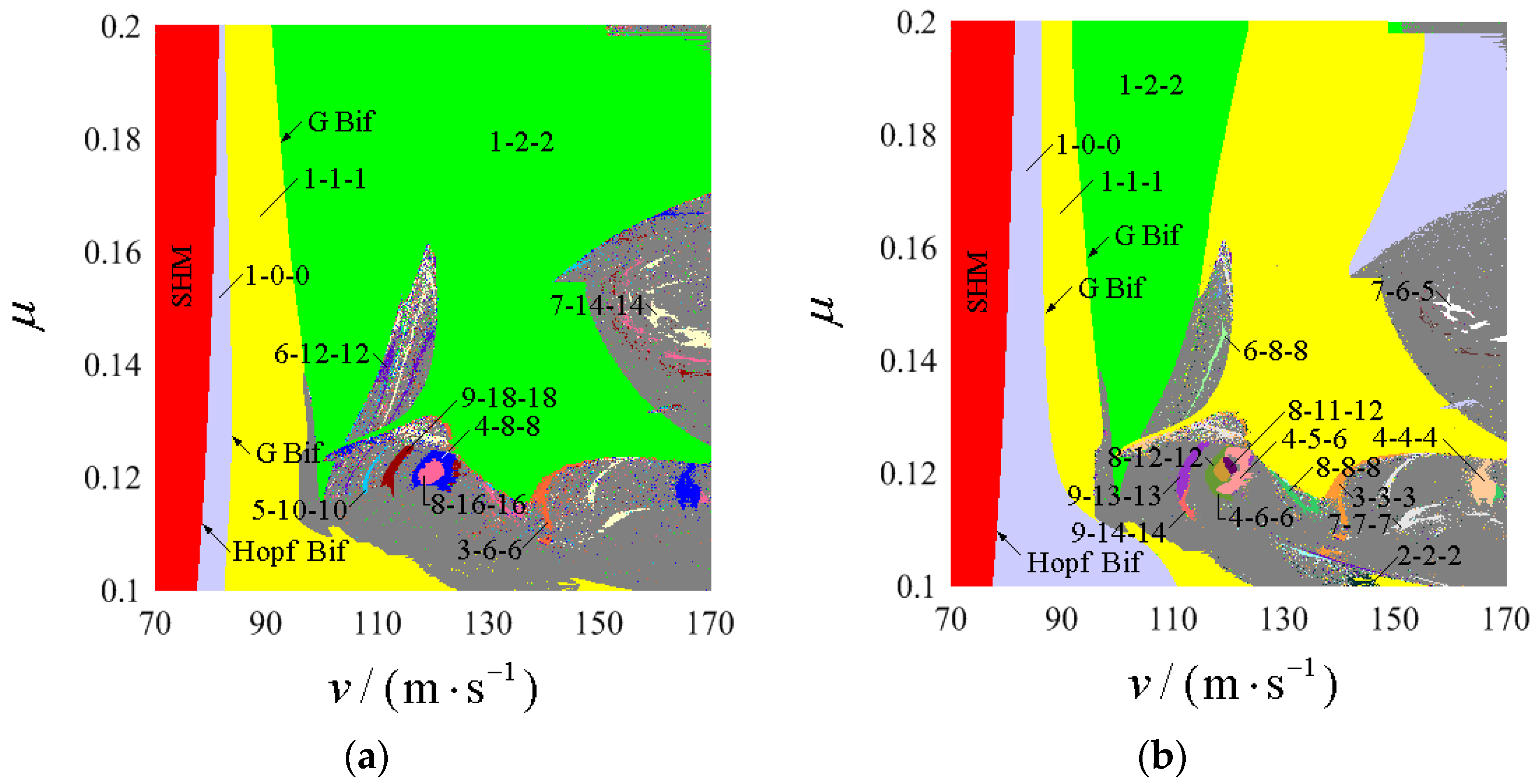
4.1. Hunting Motion Patterns and Distribution Regions in the Two-Parameter Plane and Wheel–Rail Impact Characteristics
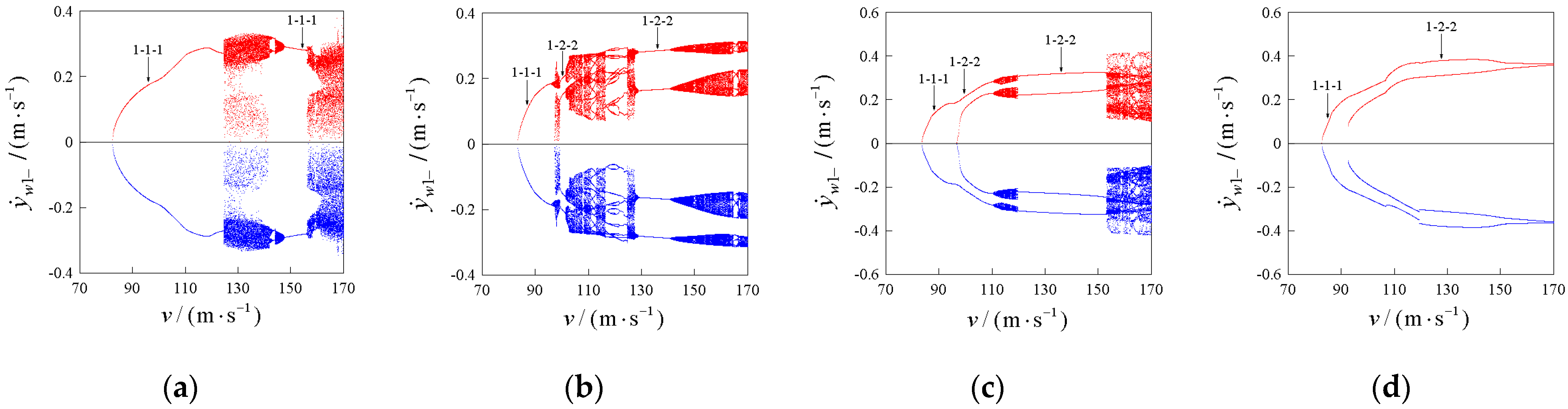
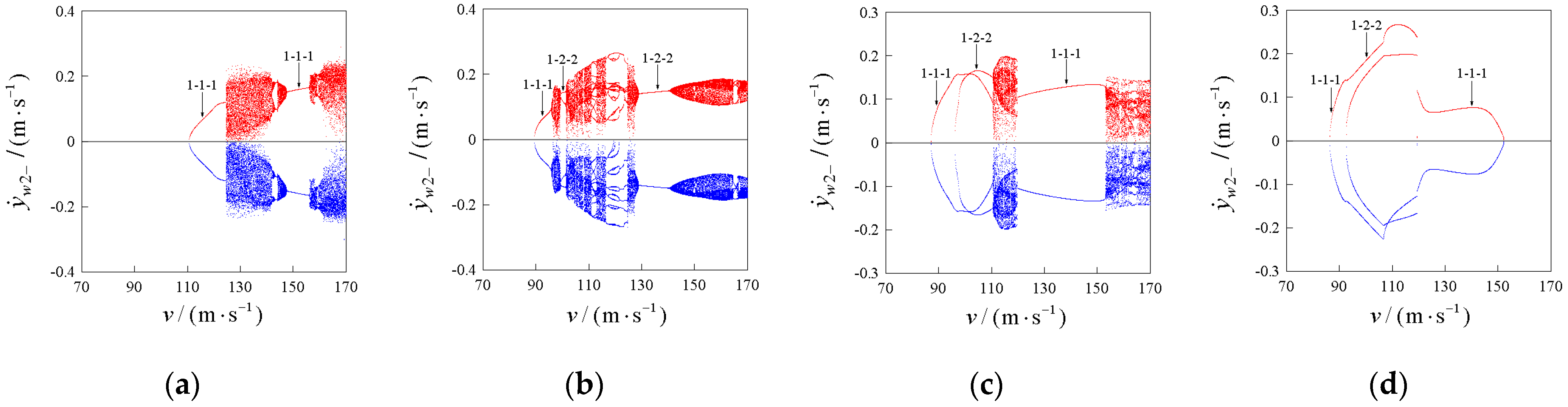
4.2. Bifurcation and Evolution of Periodic Hunting Motion
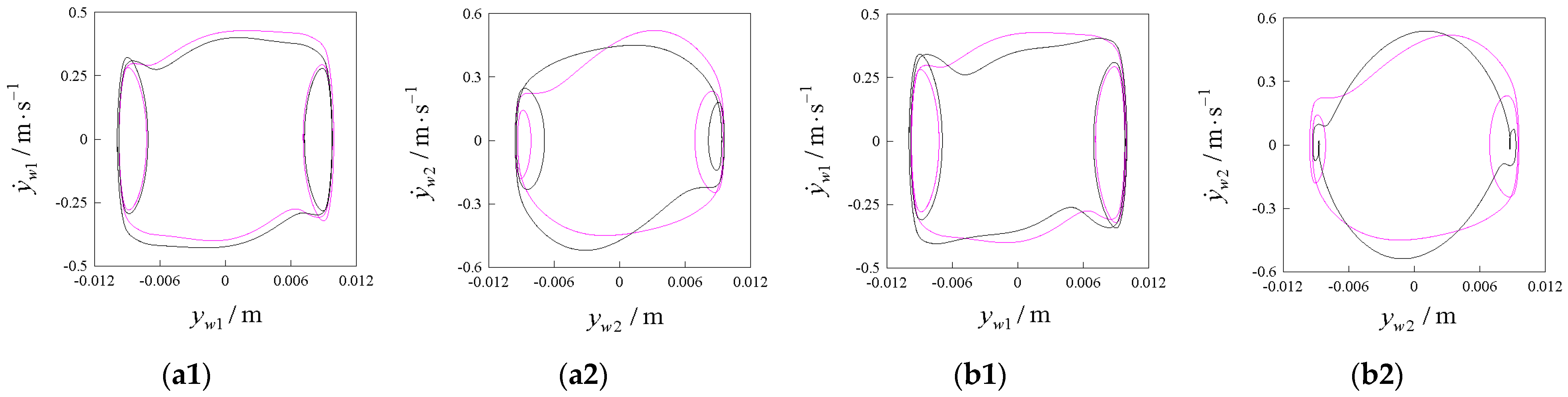
4.2.1. Select μ = 0.12
4.2.2. Select μ = 0.18
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.; Sandu, C.; Holton, C. Dynamic Model for the Wheel–Rail Contact Friction. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2012, 50, 299–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knothe, K.; Böhm, F. History of Stability of Railway and Road Vehicles. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1999, 31, 283–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, N. A Practical Calculation Method of Quasi-Static Curving Performance of Railway Bogie Vehicles. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1979, 8, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffel, H. The Influence of the Suspension on the Hunting Stability of Railways. Rail Int. 1979, 10, 662–696. [Google Scholar]
- Wickens, A.H. The Dynamic Stability of Railway Vehicle Wheelsets and Bogies Having Profiled Wheels. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1965, 1, 319–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickens, A.H. Paper 1: The Dynamics of Railway Vehicles on Straight Track: Fundamental Considerations of Lateral Stability. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Conf. Proc. 1965, 180, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperrider, N.K. The Hunting Behavior of Conventional Railway Trucks. J. Eng. Ind. 1972, 94, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huilgol, R.R. Hopf-Friedrichs Bifurcation and the Hunting of a Railway Axle. Quart. Appl. Math. 1978, 36, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Steindl, A.; Troger, H. Nonlinear Stability Analysis of a Bogie of a Low-platform Wagon. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1992, 20, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Yang, S.P. Hopf Bifurcation and Hunting Behavior in a Rail Wheelset with Flange Contact. Nonlinear Dyn. 1997, 15, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, W.H.; Dai, H.Y. Hunting Instability Analysis and H ∞ Controlled Stabilizer Design for High Speed Railway Passenger Car. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1998, 29, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Z.Y. Hopf Bifurcation and Nonlinear Oscillations in Railway Vehicle Systems. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1999, 33, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, U. Nonlinear dynamic behaviour of a railway wheelset. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2009, 47, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhao, B.; Deng, Y. Instability Phenomenon Associated with Two Typical High Speed Railway Vehicles. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 2018, 105, 130–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zeng, J. Hopf Bifurcation Analysis of Railway Bogie. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 92, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Huang, C.; Zeng, J.; Cao, H. Hopf–Hopf Bifurcation Analysis Based on Resonance and Non-Resonance in a Simplified Railway Wheelset Model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2022, 108, 1197–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas-Petersen, C.; True, H. Periodic, Biperiodic and Chaotic Dynamical Behaviour of Railway Vehicles. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1986, 15, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- True, H. Railway Vehicle Chaos and Asymmetric Hunting. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1992, 20, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- True, H.; Jensen, J.C. Parameter Study of Hunting and Chaos in Railway Vehicle Dynamics. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1994, 23, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaksen, P.; True, H. On the Ultimate Transition to Chaos in the Dynamics of Cooperrider’s Bogie. Chaos Solitons Fractals 1997, 8, 559–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- True, H. On the Theory of Nonlinear Dynamics and Its Applications in Vehicle Systems Dynamics. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1999, 31, 393–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J.; Li, Y.H.; Gao, Q. Lateral Bifurcation Behavior of a Four-Axle Railway Passenger Car. J. Appl. Mech. 2010, 77, 061001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J.; Li, Y.H.; Yue, Y. The “Resultant Bifurcation Diagram” Method and Its Application to Bifurcation Behaviors of a Symmetric Railway Bogie System. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 70, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J. Symmetric/Asymmetric Bifurcation Analysis of Railway Bogie System under Complex Nonlinear Wheel-rail Contact Relation. JME 2013, 49, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J.; Li, Y.H.; Yue, Y.; True, H. Symmetric/Asymmetric Bifurcation Behaviours of a Bogie System. J. Sound Vib. 2013, 332, 936–951. [Google Scholar]
- Bustos, A.; Tomas-Rodriguez, M.; Rubio, H.; Castejon, C. On the Nonlinear Hunting Stability of a High-Speed Train Bogie. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 2059–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zboinski, K.; Dusza, M. Self-Exciting Vibrations and Hopf’s Bifurcation in Nonlinear Stability Analysis of Rail Vehicles in a Curved Track. Eur. J. Mech.—A/Solids 2010, 29, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zboinski, K.; Dusza, M. Extended Study of Railway Vehicle Lateral Stability in a Curved Track. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2011, 49, 789–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zeng, J.; Chi, M.R.; Wang, J.B. Carbody Elastic Vibrations of High-Speed Vehicles Caused by Bogie Hunting Instability. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2017, 55, 1321–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Guan, Q.; Chi, M.; Wen, Z.F.; Sun, J.F. An Investigation into the Influence of Wheel–Rail Contact Relationships on the Carbody Hunting Stability of an Electric Locomotive. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2022, 236, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Ding, X.; Ling, L.; Li, F.S.; Liu, T.; Wang, K.Y.; Zhai, W.M. Mechanism of High-Speed Train Carbody Shaking Due to Degradation of Wheel-Rail Contact Geometry. Int. J. Rail Transp. 2023, 11, 289–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, C.N.; True, H. On a New Route to Chaos in Railway Dynamics. Nonlinear Dyn. 1997, 13, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Berg, M. Challenges in Simulation of Rail Vehicle Dynamics. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2009, 47, 1023–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Seok, J. Bifurcation Analysis on the Hunting Behavior of a Dual-Bogie Railway Vehicle Using the Method of Multiple Scales. J. Sound Vib. 2010, 329, 4017–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, P.C.; Li, D.H.; Chen, H.B.; Yue, Y.; Xie, J.H. Generalized Hopf Bifurcation of a Non-Smooth Railway Wheelset System. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 100, 3277–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Cui, N. Bifurcation, Geometric Constraint, Chaos, and Its Control in a Railway Wheelset System. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2023, 46, 7311–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.H.; Wei, X.K.; Liu, J.Z.; Cao, H.J. Bifurcation of a Modified Railway Wheelset Model with Nonlinear Equivalent Conicity and Wheel–Rail Force. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 102, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Shi, H.L.; Luo, R.; Zeng, J. Bifurcation Analysis of a Railway Wheelset with Nonlinear Wheel–Rail Contact. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 104, 989–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, G.; Dixon, R.; Goodall, R. Least Squares Method Applied to Rail Vehicle Contact Condition Monitoring. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2008, 41, 7451–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- True, H.; Engsig-Karup, A.P.; Bigoni, D. On the Numerical and Computational Aspects of Non-Smoothnesses That Occur in Railway Vehicle Dynamics. Math. Comput. Simul. 2014, 95, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J.; True, H.; Li, Y.H. Lateral Dynamic Features of a Railway Vehicle. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part F J. Rail Rapid Transit 2016, 230, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Dai, H.Y. On the Nonlinear Dynamics of a High-Speed Railway Vehicle with Non-smooth Elements. Appl. Math. Model. 2019, 76, 526–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; True, H.; Dai, H.Y. A Codimension Two Bifurcation in a Railway Bogie System. Arch. Appl. Mech. 2018, 88, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.W.; Shi, Y.Q.; Zhu, X.F.; Du, S.S. Hunting Patterns and Bifurcation Characteristics of a Three-Axle Locomotive Bogie System in the Presence of the Flange Contact Nonlinearity. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 136, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zeng, J.; Xie, J.H.; Jia, L. Bifurcation/instability Forms of High Speed Railway Vehicles. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2013, 56, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.T.; Dai, H.Y. Loss of Stability of a Railway Wheelset, Subcritical or Supercritical. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2017, 55, 1731–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yang, S.P.; Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, P.F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.W. Research on Hunting Stability and Bifurcation Characteristics of Nonlinear Stochastic Wheelset System. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 2023, 44, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kik, W. Comparison of the behaviour of different wheelset-track models. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1992, 20, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Petersen, D.E. Curving Dynamics of Railway Vehicles; Technical Report; Department of Mathematical Modelling, Technical University of Denmark: Kongens Lyngby, Denmark, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kalker, J.J. A fast algorithm for the simplified theory of rolling contact. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1982, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Hedrick, J.K.; Elkins, J.A. A comparison of alternative creep force models for rail vehicle dynamic analysis. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 1983, 12, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




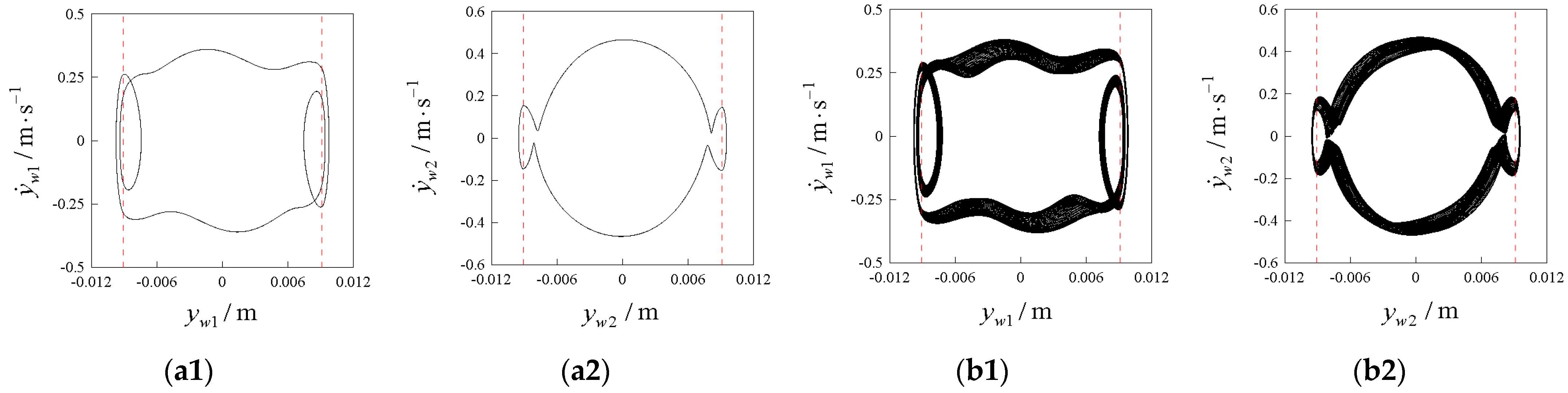
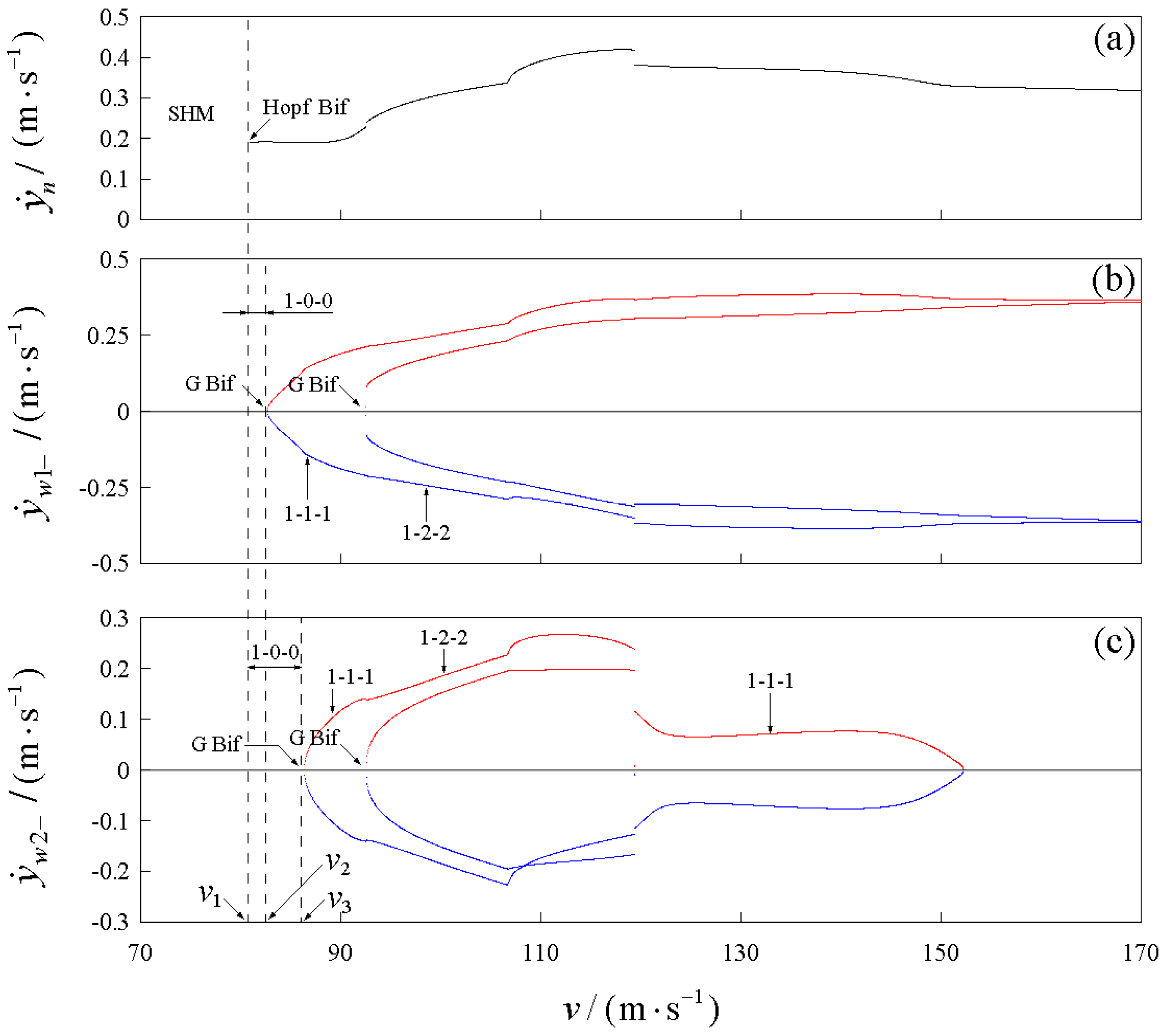
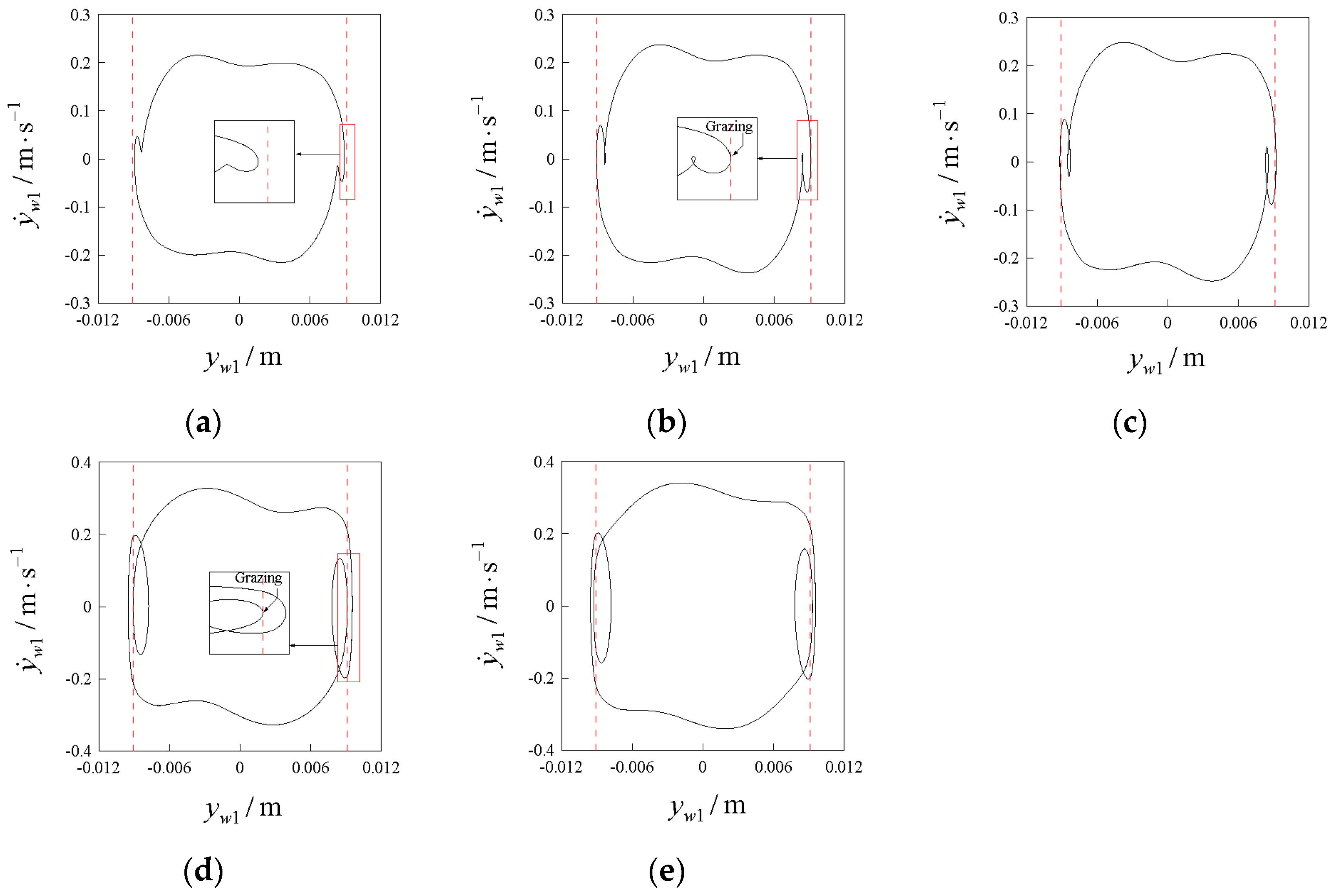
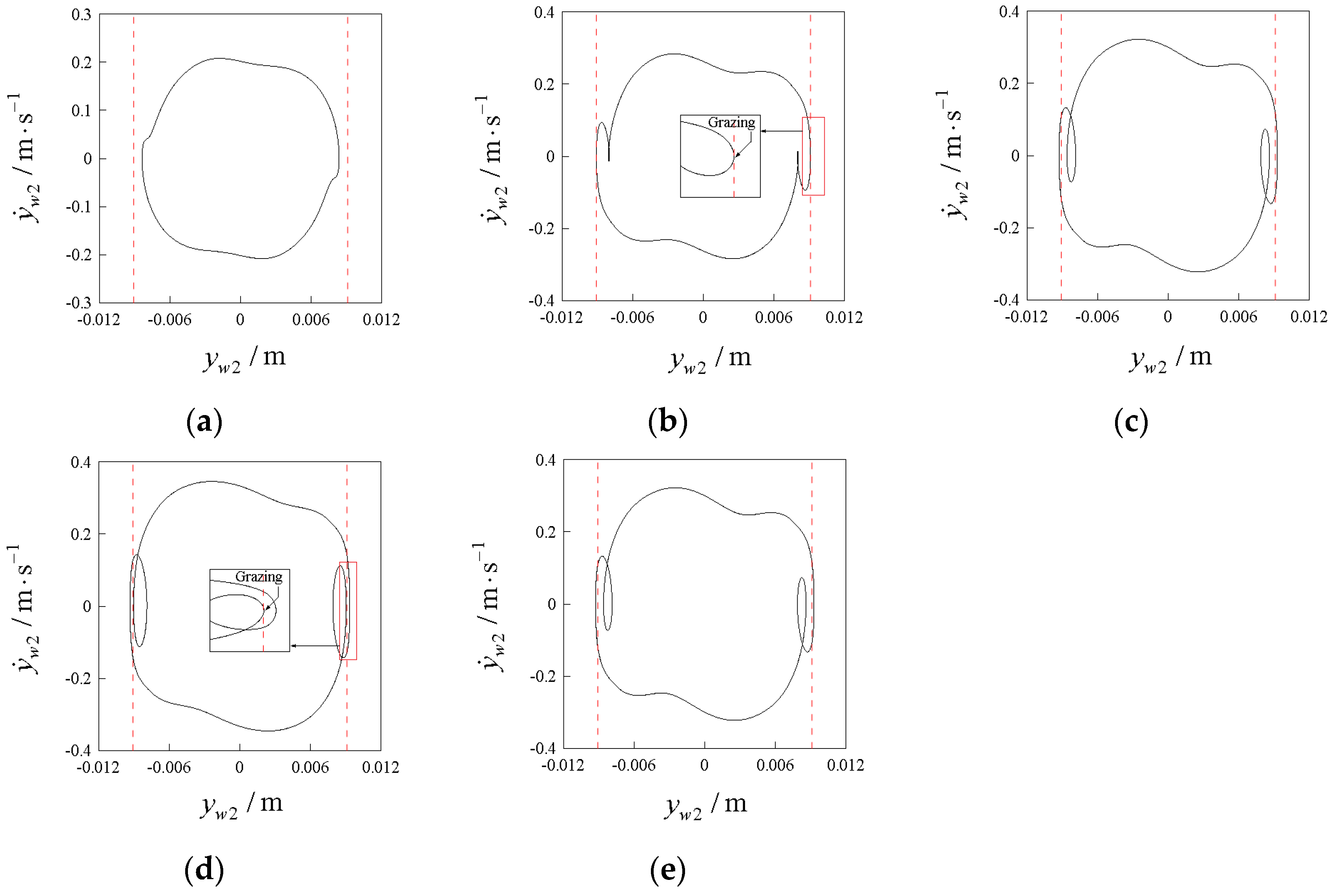

| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Mw | Mass of the wheelset | 1400 kg |
| Iwy | Spin moment of inertia of wheelset | 140 kg·m2 |
| Iwz | Yaw moment of inertia of wheelset | 915 kg·m2 |
| Mt | Mass of bogie frame | 3000 kg |
| Itx | Roll moment of inertia of bogie frame | 2084 kg·m2 |
| Itz | Yaw moment of inertia of bogie frame | 2496 kg·m2 |
| K1x | Primary longitudinal stiffness | 10 MN/m |
| K1y | Primary lateral stiffness | 5 MN/m |
| K1z | Primary vertical stiffness | 5.5 MN/m |
| C1x | Primary longitudinal damper | 0 N·s·m−1 |
| C1y | Primary lateral damper | 0 N·s·m−1 |
| C1z | Primary vertical damper | 1.6 × 104 N·s·m−1 |
| K2x | Secondary longitudinal stiffness | 0.2 MN/m |
| K2y | Secondary lateral stiffness | 0.2 MN/m |
| K2z | Secondary vertical stiffness | 0.25 MN/m |
| C2x | Secondary longitudinal damper | 0 N·s·m−1 |
| C2y | Secondary lateral damper | 3.4 × 104 N·s·m−1 |
| C2z | Secondary vertical damper | 1.93 × 105 N·s·m−1 |
| dw | Half distance of the primary suspension | 1 m |
| ds | Half distance of the secondary suspension | 1.2 m |
| lt | Half of the axle distance | 1.2 m |
| a0 | Half of wheelset contact distance | 0.7465 m |
| r0 | Centered wheel rolling radius | 0.4575 m |
| k0 | Flange contact stiffness | 146 MN/m |
| G | Resultant shear modulus | 8.2677 × 1010 Pa |
| Parameters | Value | Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
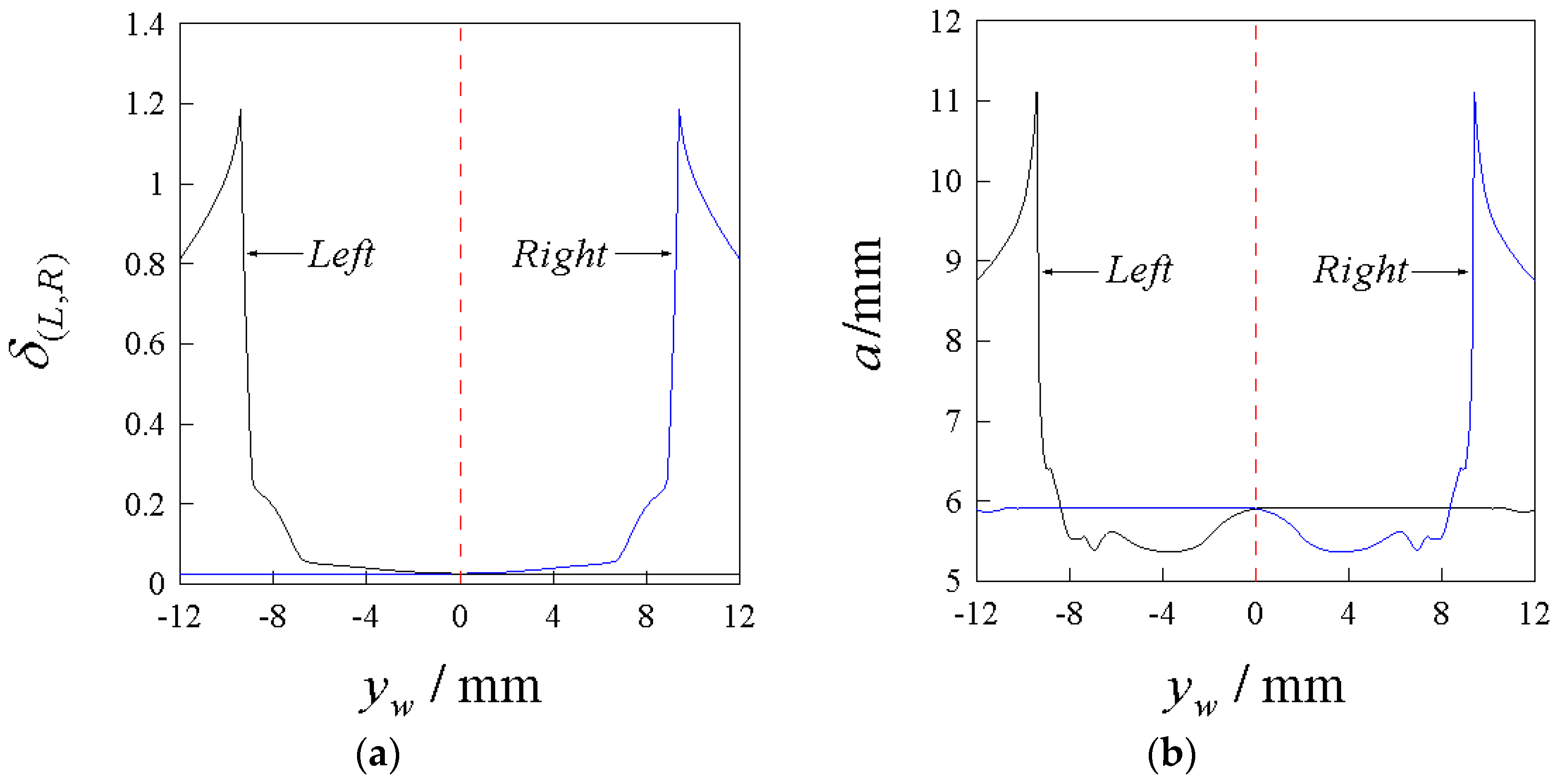
| Poisson’s ratio ν | 0.3 | wheelset lateral displacement yw (mm) | [−12, 12] |
| elastic modulus E (Pa) | 2.1 × 1011 | the flange clearance η (mm) | 9.1 |
| normal force N (N) | 55,860 |
| Symbol | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| r(L,R) | Rolling radius | m |
| δ(L,R) | Contact angle | rad |
| ϕw | Roll angle of the wheelset | rad |
| a(L,R) | Major semi-axes of the contact spot | m |
| b(L,R) | Minor semi-axes of the contact spot | m |
| C11(L,R) | Longitudinal Kalker creepage coefficient | N |
| C22(L,R) | Lateral Kalker creepage coefficient | N |
| C23(L,R) | Lateral/spin Kalker creepage coefficient | N·m |
| C33(L,R) | Spin Kalker creepage coefficient | N·m2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Zhang, L. The Two-Parameter Bifurcation and Evolution of Hunting Motion for a Bogie System. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5492. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135492
Wang S, Ma L, Zhang L. The Two-Parameter Bifurcation and Evolution of Hunting Motion for a Bogie System. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(13):5492. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135492
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shijun, Lin Ma, and Lingyun Zhang. 2024. "The Two-Parameter Bifurcation and Evolution of Hunting Motion for a Bogie System" Applied Sciences 14, no. 13: 5492. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135492
APA StyleWang, S., Ma, L., & Zhang, L. (2024). The Two-Parameter Bifurcation and Evolution of Hunting Motion for a Bogie System. Applied Sciences, 14(13), 5492. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135492






