Development of a Novel Structured Mesh-Type Pd/γ-Al2O3/Al Catalyst on Nitrobenzene Liquid-Phase Catalytic Hydrogenation Reactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
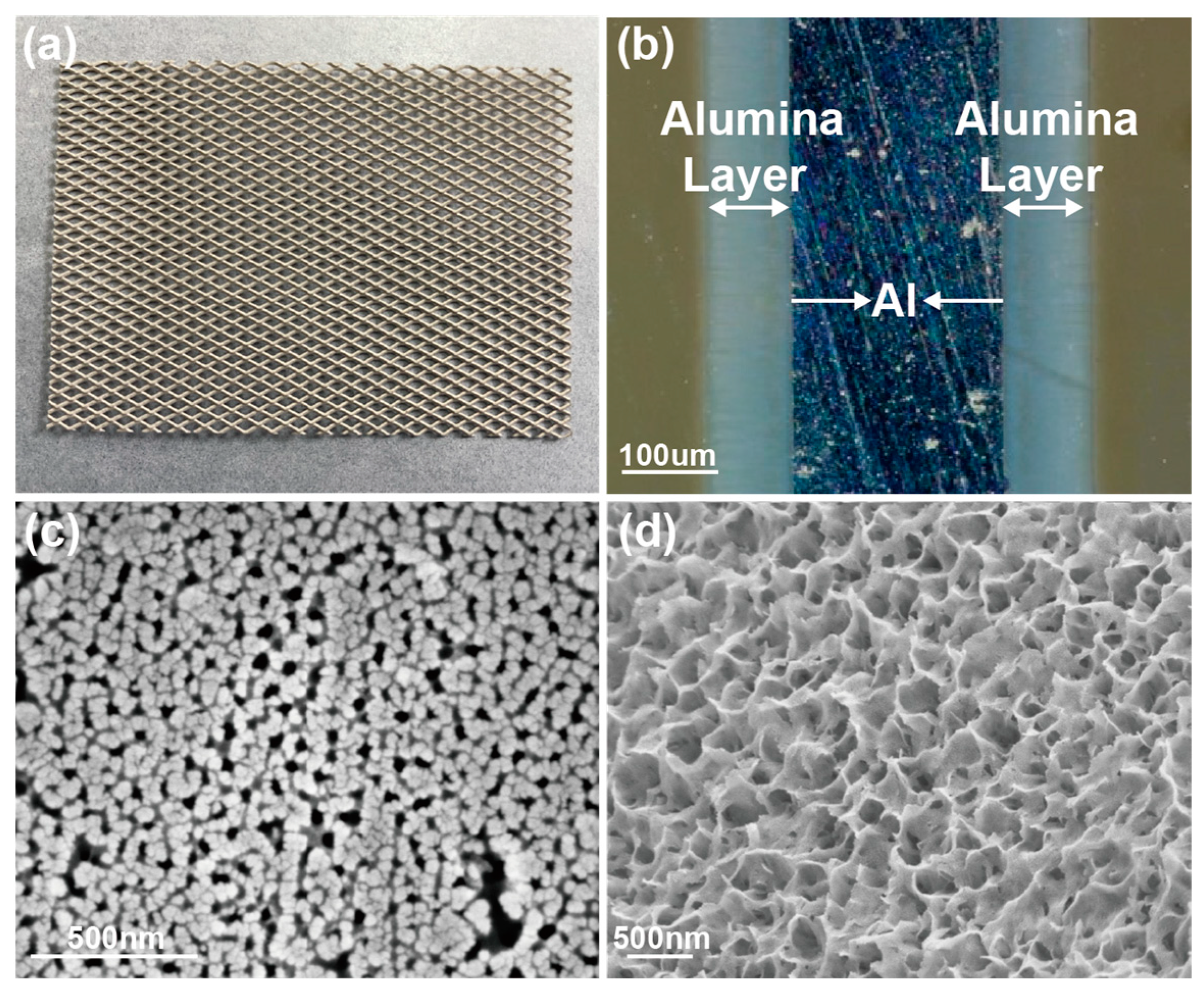
2.1. Catalyst Preparation
2.2. Acid Pore-Widening Treatment on Support
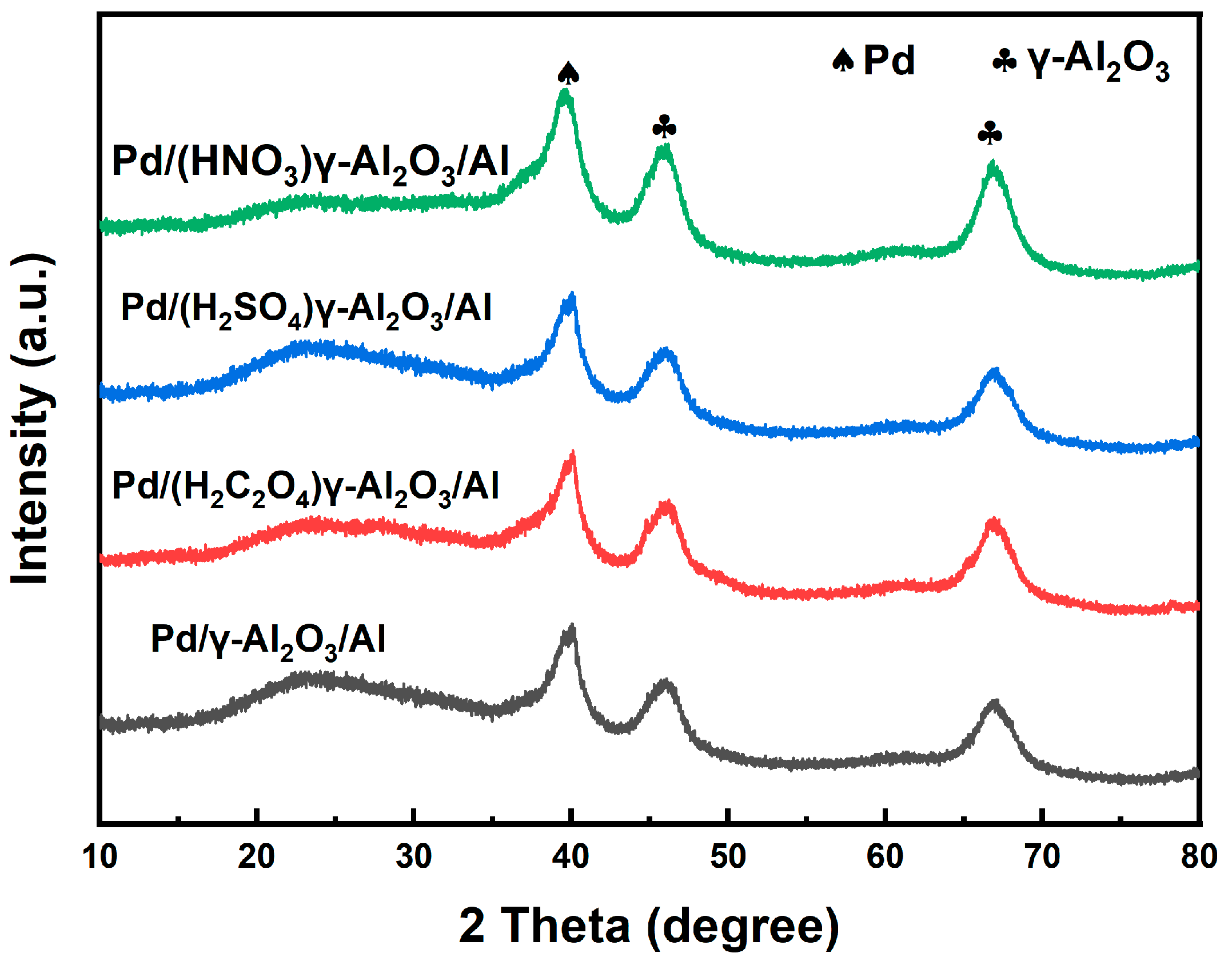
2.3. Catalyst Characterization
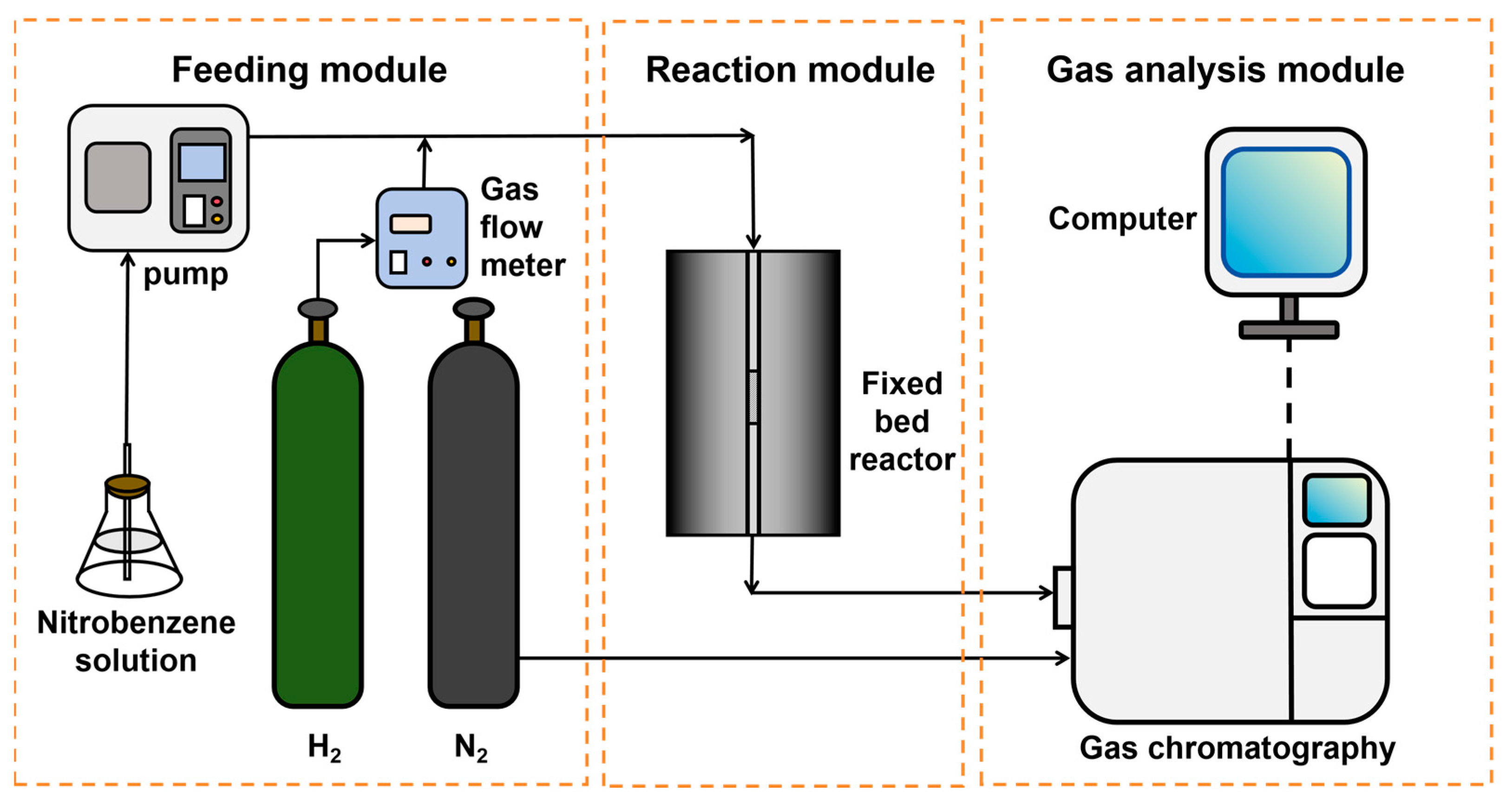
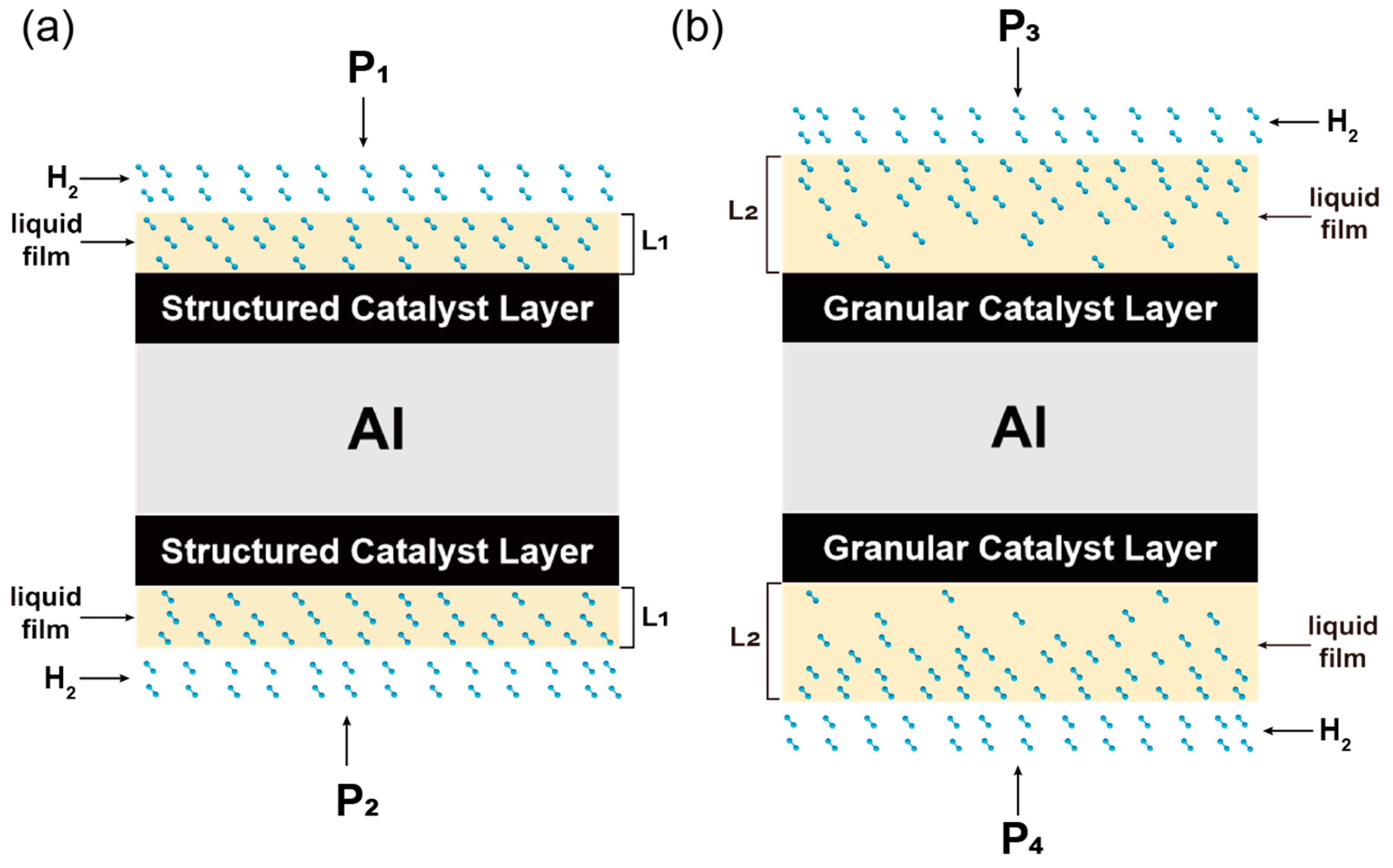
2.4. Catalyst Activity Test
3. Results
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Acid pore-widening treatments can improve the specific surface area and the pore size of the γ-Al2O3/Al supports. The HNO3/γ-Al2O3/Al support with HNO3 pore-widening treatment has the largest specific surface area, enlarging from 70 m2/g to 80 m2/g, and the largest pore size, enlarging from 3.7 nm to 4.6 nm.
- (2)
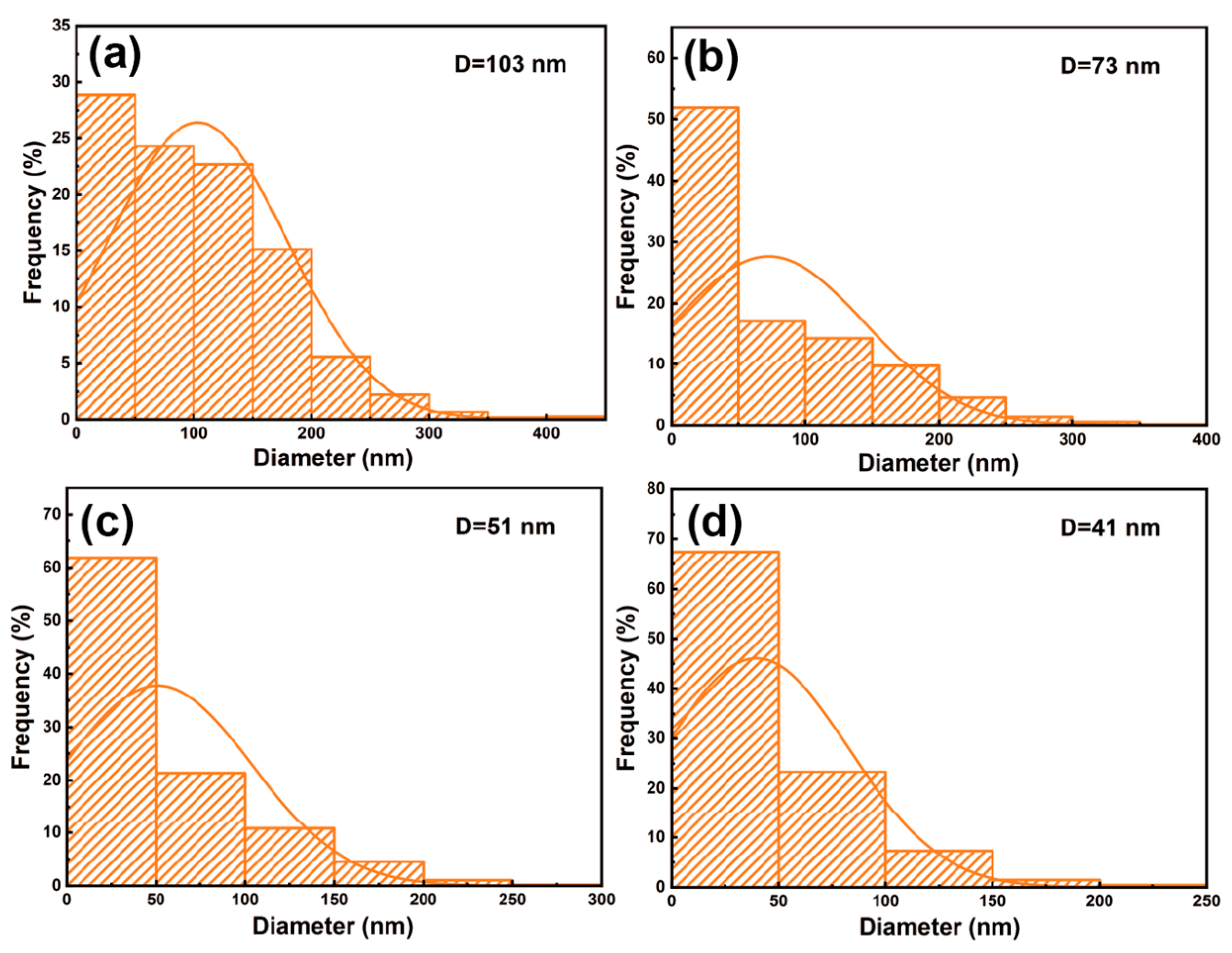
- The Pd/γ-Al2O3/Al catalysts with different acid pore-widening treatments contributes to the increased catalyst loading, more Pd0 content, and better dispersion of the metal-active particles. The Pd/(HNO3)γ-Al2O3/Al prepared by support with HNO3 pore-widening treatment has the largest active metal Pd loading, enlarging from 1.82% to 1.95%, the smallest particle size, reducing from 103 nm to 41 nm, and the largest Pd0 content, enlarging from 52.1% to 58.5%, resulting in the highest nitrobenzene conversion rate, increasing from 67.2% to 74.3%.
- (3)
- Compared to the granular catalyst, the structured mesh-type catalyst with higher porosity and more regular pore structures exerts a lower pressure drop. This facilitates diffusion of the H2 through nitrobenzene solution to the active sites of the catalyst surface. Consequently, better conversions and yields of the structured mesh-type catalyst can be obtained in the nitrobenzene liquid-phase catalytic hydrogenation reaction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, W.; Lin, R.; Shen, L.; Liang, R.; Yuan, R.; Wu, L. Highly efficient visible-light-induced photocatalytic hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to aniline in water. Rsc. Adv. 2013, 3, 10894–10899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.W.; McCullagh, A.M.; McGrath, L.; How, C.; MacLaren, D.A.; Loenders, M.; Meyer, N.; Carr, R.H.; Lennon, D. The application of alumina supported Pd catalysts for high selectivity aniline synthesis catalysis at elevated temperatures: Site-selective chemistry. Appl. Catal. A General. 2024, 670, 119541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Chadha, P. Evaluation of haematological, genotoxic, cytotoxic and ATR-FTIR alterations in blood cells of fish Channa punctatus after acute exposure of aniline. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, G.; Kummer, A.; Kozár, Z.; Varga, T. Exploration and Model-Based Analysis of Reaction Mechanisms Related to the Formation of Methylenedianiline. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 4297–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Shen, J.; Sun, X.; Han, W.; Wang, L. Reduction of nitrobenzene using nanoscale zero-valent iron confined in channels of ordered mesoporous silica. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 425, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakitin, M.Y.; Doluda, V.Y.; Tyanina, A.A.; Petrova, A.I.; Sulman, E.M.; Matveeva, V.G. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene in a Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Medium. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 11, 1113–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argesanu, C.; Bombos, D.; Matei, V.; Juganaru, T.; Bombos, M.; Vasilievici, G. Nitrobenzene Hydrogenation over Catalysts Cu based Supported on Activated Charcoal. Rev. Chim. 2014, 65, 1391–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.L.; Wang, H.F.; Qi, G. Catalytic Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene to Aniline by Ag/γ-Fe2O3. Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2016, 35, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amon, B.; Redlingshöfer, H.; Klemm, E.; Dieterich, E.; Emig, G. Kinetic investigations of the deactivation by coking of a noble metal catalyst in the catalytic hydrogenation of nitrobenzene using a catalytic wall reactor. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 1999, 38, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondeboina, M.; Enumula, S.S.; Gurram, V.R.B.; Yadagiri, J.; Burri, D.R.; Kamaraju, S.R.R. Mesoporous silica supported cobalt catalysts for gas phase hydrogenation of nitrobenzene: Role of pore structure on stable catalytic performance. N. J. Chem. 2018, 42, 15714–15725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Gao, Y.; Liu, B.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zou, Y. Nitrogen-doped carbon material NCM-T heterogeneously catalyzed liquid-phase hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to aniline. Rsc Adv. 2024, 14, 5055–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas-Lizana, F.; Gómez-Quero, S.; Keane, M.A. Ultra-selective gas phase catalytic hydrogenation of aromatic nitro compounds over Au/Al2O3. Catal. Commun. 2008, 9, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, P.S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, M.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhao, G.M.; Guo, Q.B. A solvent-free, selective liquid phase hydrogenation of nitroarenes to aniline in slurry bubble mode on porous NiMo bimetallic catalyst. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 33, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.M.; Jiang, Y.X.; Xu, Y.; Luo, X.; Xie, X.L.; Qin, Z.Z.; Ji, H.B. Ba-modified Ni-P amorphous alloy/acidified bentonite catalyst: Preparation and the catalytic hydrogenation of nitrobenzene to aniline. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2020, 131, 805–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrimpf, M.; Esteban, J.; Rösler, T.; Vorholt, A.J.; Leitner, W. Intensified reactors for gas-liquid-liquid multiphase catalysis: From chemistry to engineering. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 917–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, R.V.; Mills, P.L. Multiphase catalysis and reaction engineering for emerging pharmaceutical processes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 5337–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.S. Gas-Liquid-Solid Fluidization: Perspectives. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2004, 2, 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafete, G.A.; Habtu, N.G. Reactor configuration, operations and structural catalyst design in process intensification of catalytic reactors: A review. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2023, 184, 109290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.Y.; Wu, X.K.; Gao, J.A.; Zhao, H. Structured Cerium-Manganese Catalysts Supported on Nickel Foam for Toluene Oxidation by Electric Internal Heating. Chempluschem 2023, 89, e202300466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundra, M.; Sultan, B.B.M.; Ng, D.; Wang, Y.; Alexander, D.L.J.; Nguyen, X.; Xie, Z.; Hornung, C.H. Continuous flow semi-hydrogenation of alkynes using 3D printed catalytic static mixers. Chem. Eng. Process. -Process Intensif. 2020, 154, 108018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, O.H.; Lietor, P.F.; Iglesias Godino, F.J.; Corpas-Iglesias, F.A. A review on additive manufacturing and materials for catalytic applications: Milestones, key concepts, advances and perspectives. Mater. Des. 2021, 208, 109927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieg, B.; Doebber, J.; Kirschhoefer, F.; Pohl, M.; Franzreb, M. Advantages of Hydrogel-Based 3D-Printed Enzyme Reactors and Their Limitations for Biocatalysis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 6, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Liu, W.; Duan, X.-N.; Zhang, C.-H.; Sang, L.; Zhang, J.-S. Preparation of Highly Effective Ni Foam Monolithic Catalysts by Electrolytic Deposition for Nitrobenzene Hydrogenation in a Micropacked Bed. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 11276–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhu, X.; Chen, R.; Liao, Q.; Ye, D.; Feng, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, M. Gas-liquid-solid monolithic microreactor with Pd nanocatalyst coated on polydopamine modified nickel foam for nitrobenzene hydrogenation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1897–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yan, K.; Zheng, J.; Chen, B.H.; Wang, W. A novel modification method for nickel foam support and synthesis of a metal-supported hierarchical monolithic Ni@Pd catalyst for benzene hydrogenation. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 226, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosseau, L.R.S.; Jansen, J.T.A.; Roghair, I.; Annaland, M.V. Favorable trade-off between heat transfer and pressure drop in 3D printed baffled logpile catalyst structures. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 196, 214–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.S.; Ni, L.; Jiang, J.C.; Yu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, Z.C. Fabrication of tungstate metal foams as efficient catalysts for dimethyl sulfoxide oxidation in a microreactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 129, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, D.M.; Fan, F.Y.; Zhang, Q.H.; Zhu, Z.B. A novel monolith catalyst of plate-type anodic alumina for the hydrolysis of dimethyl ether. Catal. Commun. 2013, 34, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, B.; Zhang, L. Magnesium Modified Mesh-TYPE Cu/γ-Al2O3/Al Catalysts: Low Acid Density Catalysts for Methanol Steam Reforming. Catal. Lett. 2020, 150, 2978–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. Fast start-up structured CuFeMg/Al2O3 catalyst applied in microreactor for efficient hydrogen production in methanol steam reforming. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Ni, Y.H.; Wu, Y.Q. Development of mesh-type Fenton-like Cu/Fex/γ-Al2O3/Al catalysts and application for catalytic degradation of dyes. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 81, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Q. Monolithic Mesh-Type Fe-Pd/γ-Al2O3/Al Bifunctional Catalysts for Electro-Fenton Degradation of Rhodamine B. Mod. Res. Catal. 2021, 10, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, G.; Foltran, S.; Favier, I.; Pla, D.; Medina-González, Y.; Gómez, M. Palladium nanoparticles stabilized by novel choline-based ionic liquids in glycerol applied in hydrogenation reactions. Catal. Today 2020, 346, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Shu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Du, P.; Zhu, X. Mechanism in chlorine-enhanced Pd catalyst for H2O2 in situ synthesis in electro-Fenton system. Aiche J. 2022, 68, e17787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Roy, S. Effect of channel shape on gas/liquid catalytic reaction performance in structured catalyst/reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2004, 59, 4927–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Support | SBET (m2/g) | Vp (μL/g) | Dp (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| γ-Al2O3/Al | 70 | 97.1 | 3.7 |
| (H2C2O4)γ-Al2O3/Al | 72 | 99.9 | 3.8 |
| (H2SO4)γ-Al2O3/Al | 75 | 105.1 | 4.0 |
| (HNO3)γ-Al2O3/Al | 80 | 116.1 | 4.6 |
| Catalyst | Pd Loading (wt%) | SBET (m2/g) | Vp (μL/g) | Dp (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/γ-Al2O3/Al | 1.82 | 56 | 91.4 | 6.6 |
| Pd/(H2C2O4)γ-Al2O3/Al | 1.88 | 59 | 93.2 | 7.4 |
| Pd/(H2SO4)γ-Al2O3/Al | 1.90 | 63 | 98.5 | 7.5 |
| Pd/(HNO3)γ-Al2O3/Al | 1.95 | 69 | 108.6 | 7.8 |
| Catalyst | Pd (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Pd0 | Pd2+ | |
| Pd/γ-Al2O3/Al | 52 | 48 |
| Pd/(H2C2O4)γ-Al2O3/Al | 54 | 46 |
| Pd/(H2SO4)γ-Al2O3/Al | 56 | 44 |
| Pd/(HNO3)γ-Al2O3/Al | 59 | 41 |
| Catalyst Layer | (mm2) | (mm3) | (mm−1) | (cm3) | (cm3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd/γ-Al2O3-Al-mesh-type | 1.89 | 0.149 | 12.7 | 11.3 | 2.7 | 0.76 | 1.02 × 10−2 | 1.6 |
| Pd/γ-Al2O3-Al-granular | 2.41 | 0.149 | 13.8 | 11.3 | 7.3 | 0.35 | 3.46 × 10−3 | 140.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, H.; Shu, Q.; Xie, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Q. Development of a Novel Structured Mesh-Type Pd/γ-Al2O3/Al Catalyst on Nitrobenzene Liquid-Phase Catalytic Hydrogenation Reactions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135732
Tian H, Shu Q, Xie Z, Lu H, Zhang Q. Development of a Novel Structured Mesh-Type Pd/γ-Al2O3/Al Catalyst on Nitrobenzene Liquid-Phase Catalytic Hydrogenation Reactions. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(13):5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135732
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Haoran, Qingli Shu, Zukun Xie, Hongye Lu, and Qi Zhang. 2024. "Development of a Novel Structured Mesh-Type Pd/γ-Al2O3/Al Catalyst on Nitrobenzene Liquid-Phase Catalytic Hydrogenation Reactions" Applied Sciences 14, no. 13: 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135732
APA StyleTian, H., Shu, Q., Xie, Z., Lu, H., & Zhang, Q. (2024). Development of a Novel Structured Mesh-Type Pd/γ-Al2O3/Al Catalyst on Nitrobenzene Liquid-Phase Catalytic Hydrogenation Reactions. Applied Sciences, 14(13), 5732. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14135732





