A Virtual Reality-Based Simulation Tool for Assessing the Risk of Falls in Older Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Methods
3.1. Participants
3.2. Apparatus
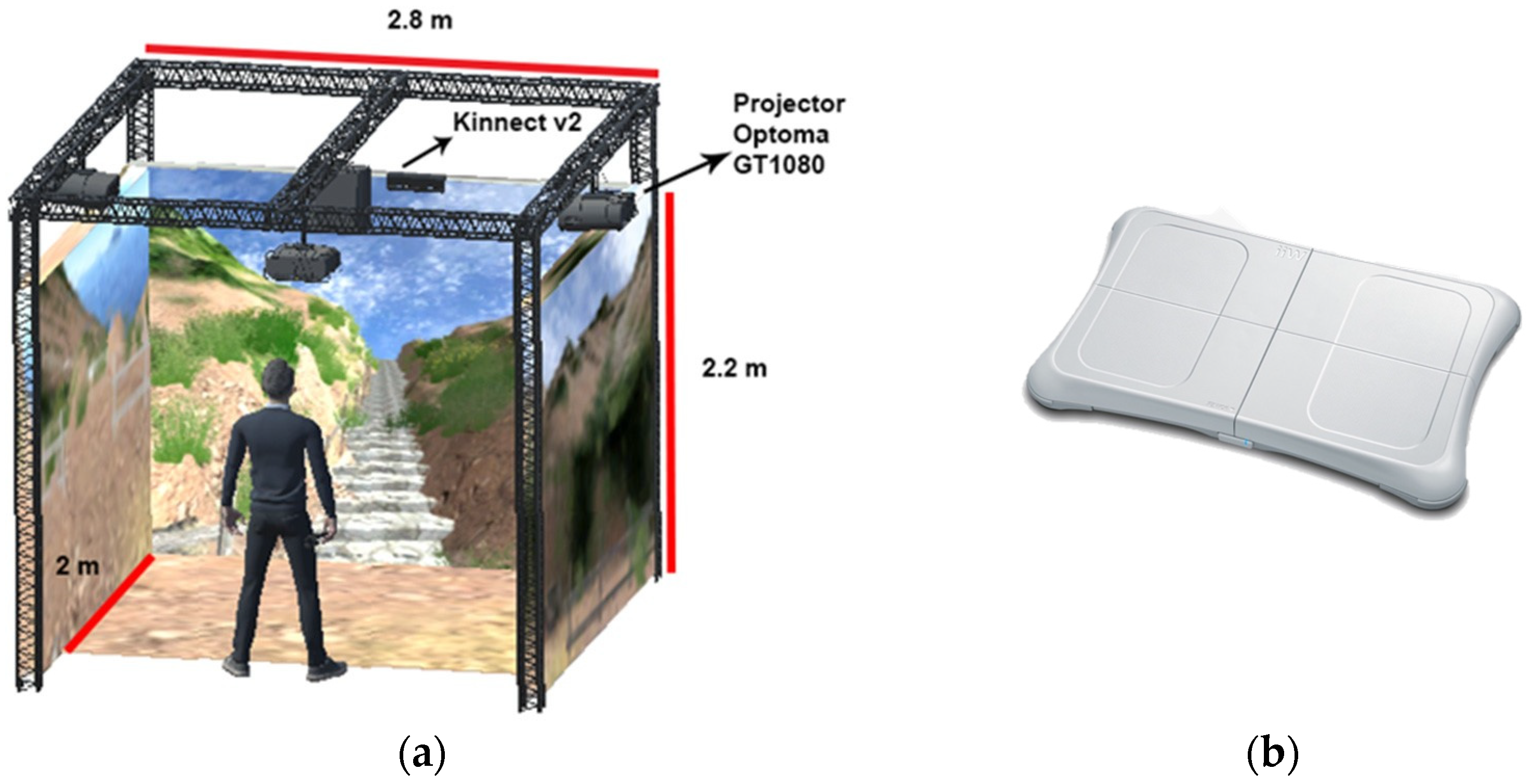
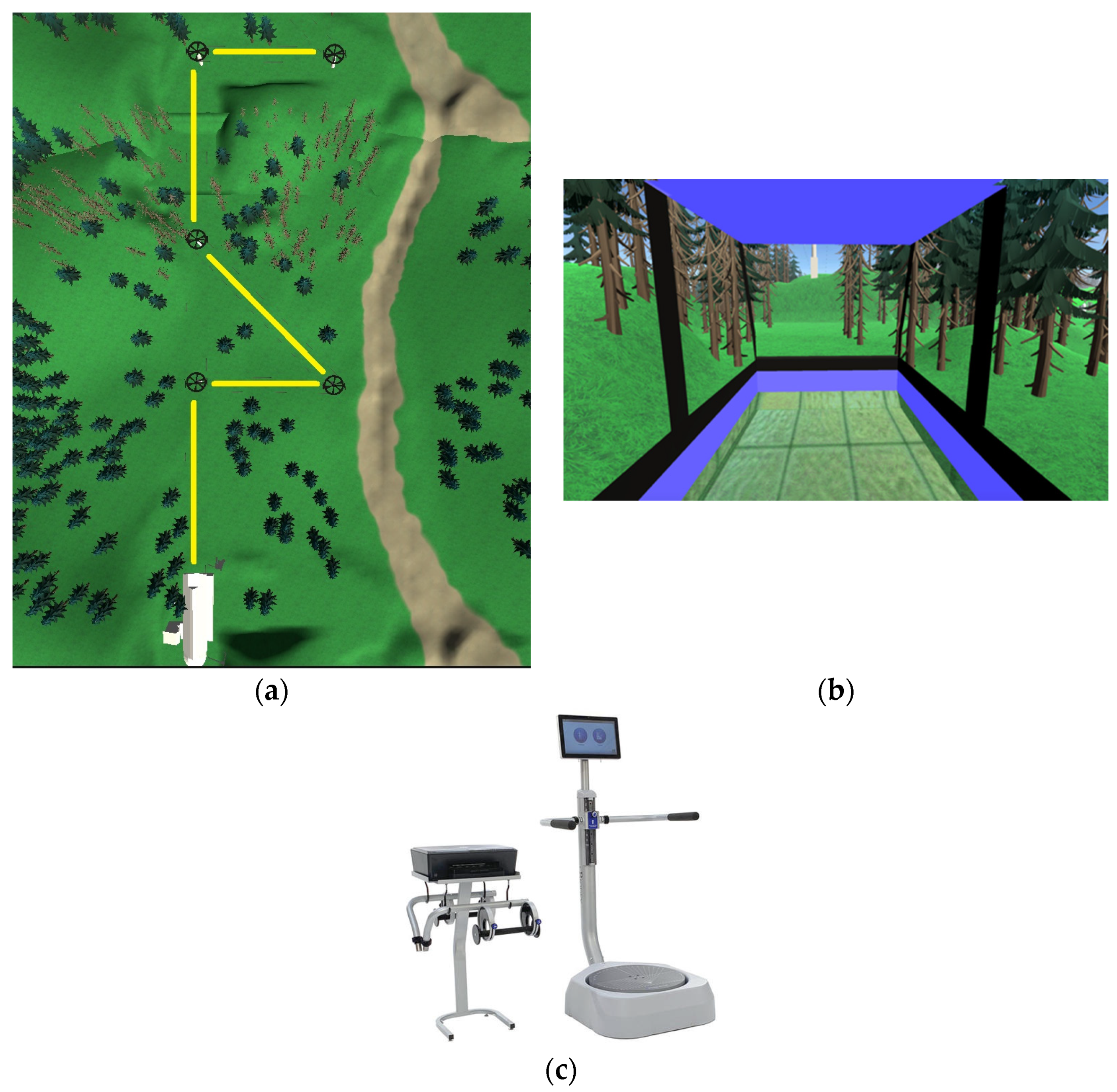
3.2.1. Hardware
3.2.2. Software
3.3. Questionnaires and Balance
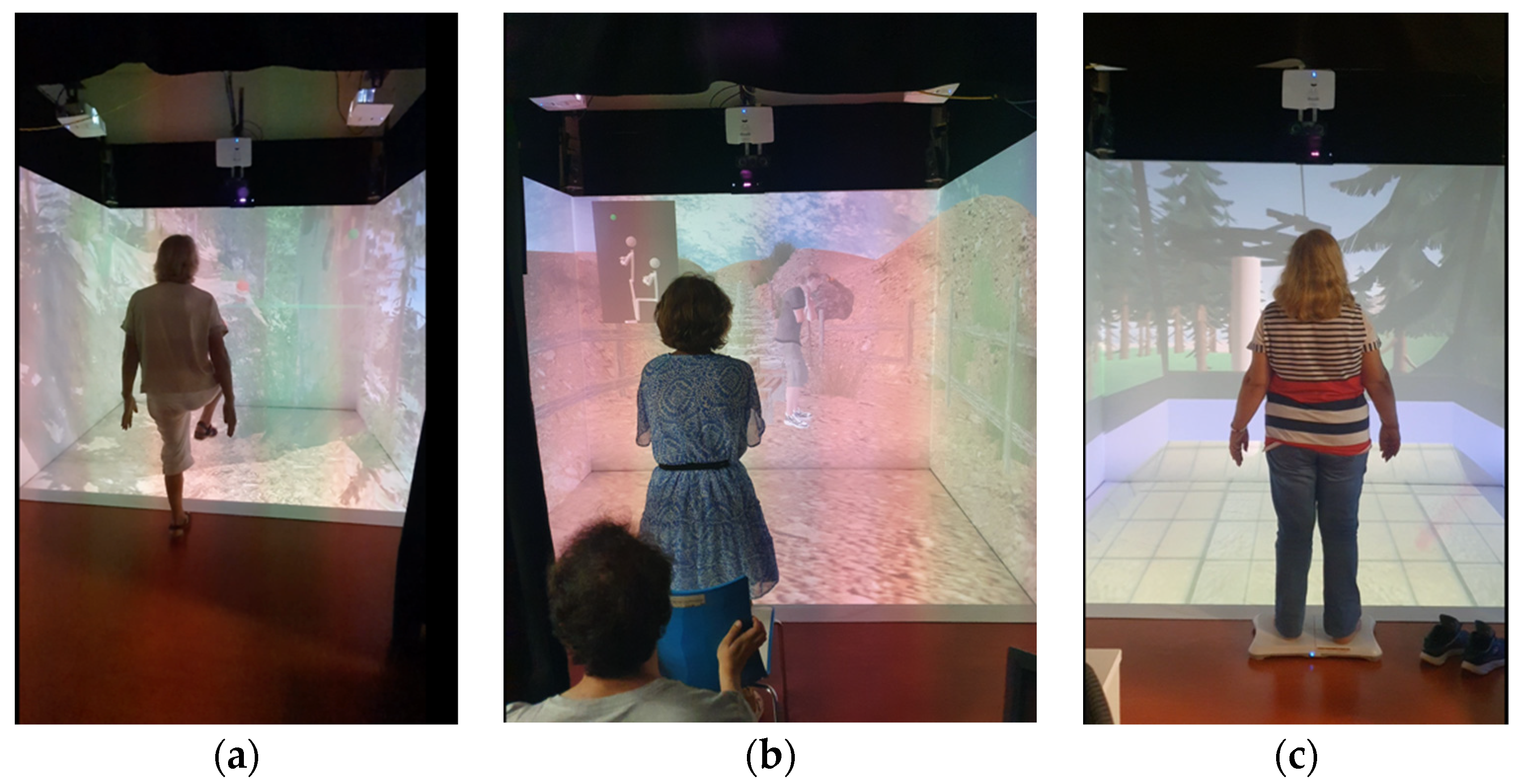
3.4. Procedure
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Report on Falls Prevention in Older Age; Ageing and life course, family and community health: WHO global report on falls prevention in older age; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, K.; Tian, M.; Andersen, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lindley, R.; Ivers, R. Incidence, Risk Factors and Economic Burden of Fall-Related Injuries in Older Chinese People: A Systematic Review. Inj. Prev. 2019, 25, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigaki, E.Y.; Ramos, L.G.; Carvalho, E.S.; Lunardi, A.C. Effectiveness of Muscle Strengthening and Description of Protocols for Preventing Falls in the Elderly: A Systematic Review. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2014, 18, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, R. Contribution of Muscle Weakness to Postural Instability in the Elderly. A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 46, 183–220. [Google Scholar]
- Mignardot, J.-B.; Deschamps, T.; Barrey, E.; Auvinet, B.; Berrut, G.; Cornu, C.; Constans, T.; De Decker, L. Gait Disturbances as Specific Predictive Markers of the First Fall Onset in Elderly People: A Two-Year Prospective Observational Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, S.W.; Gopaul, K.; Montero Odasso, M.M. The Role of Cognitive Impairment in Fall Risk among Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Age Ageing 2012, 41, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imagama, S.; Ito, Z.; Wakao, N.; Seki, T.; Hirano, K.; Muramoto, A.; Sakai, Y.; Matsuyama, Y.; Hamajima, N.; Ishiguro, N.; et al. Influence of Spinal Sagittal Alignment, Body Balance, Muscle Strength, and Physical Ability on Falling of Middle-Aged and Elderly Males. Eur. Spine J. 2013, 22, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Long, J.; Ling, W.; Huang, G.; Guo, X.; Su, L. Incidence of Fall-Related Injury among Old People in Mainland China. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2015, 61, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirguis-Blake, J.M.; Michael, Y.L.; Perdue, L.A.; Coppola, E.L.; Beil, T.L.; Thompson, J.H. Interventions to Prevent Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Systematic Review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force; U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Evidence Syntheses, formerly Systematic Evidence Reviews; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US): Rockville MD, USA, 2018.
- Shimada, H.; Suzukawa, M.; Tiedemann, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Yoshida, H.; Suzuki, T. Which Neuromuscular or Cognitive Test Is the Optimal Screening Tool to Predict Falls in Frail Community-Dwelling Older People? Gerontology 2009, 55, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woollacott, M.; Shumway-Cook, A. Attention and the Control of Posture and Gait: A Review of an Emerging Area of Research. Gait Posture 2002, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghese, J.; Buschke, H.; Viola, L.; Katz, M.; Hall, C.; Kuslansky, G.; Lipton, R. Validity of Divided Attention Tasks in Predicting Falls in Older Individuals: A Preliminary Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 1572–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchet, O.; Dubost, V.; Herrmann, F.; Rabilloud, M.; Gonthier, R.; Kressig, R.W. Relationship between Dual-Task Related Gait Changes and Intrinsic Risk Factors for Falls among Transitional Frail Older Adults. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 17, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overview|Falls in Older People: Assessing Risk and Prevention|Guidance|NICE. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg161 (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Granacher, U.; Muehlbauer, T.; Zahner, L.; Gollhofer, A.; Kressig, R.W. Comparison of Traditional and Recent Approaches in the Promotion of Balance and Strength in Older Adults. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 377–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, M.C.; Campbell, A.J.; Gardner, M.M.; Devlin, N. Preventing Injuries in Older People by Preventing Falls: A Meta-Analysis of Individual-Level Data. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loonlawong, S.; Limroongreungrat, W.; Jiamjarasrangsi, W. The Stay Independent Brochure as a Screening Evaluation for Fall Risk in an Elderly Thai Population. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beauchamp, M.K.; Kuspinar, A.; Sohel, N.; Mayhew, A.; D’Amore, C.; Griffith, L.E.; Raina, P. Mobility Screening for Fall Prediction in the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging (CLSA): Implications for Fall Prevention in the Decade of Healthy Ageing. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, T.E.; Myklebust, J.B.; Hoffmann, R.G.; Lovett, E.G.; Myklebust, B.M. Measures of Postural Steadiness: Differences between Healthy Young and Elderly Adults. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1996, 43, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Odasso, M.; Van Der Velde, N.; Martin, F.C.; Petrovic, M.; Tan, M.P.; Ryg, J.; Aguilar-Navarro, S.; Alexander, N.B.; Becker, C.; Blain, H.; et al. World Guidelines for Falls Prevention and Management for Older Adults: A Global Initiative. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Huang, S.; Feng, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Yao, D.; Ma, D. Assessment of Balance Control Subsystems by Artificial Intelligence. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forth, K.E.; Wirfel, K.L.; Adams, S.D.; Rianon, N.J.; Lieberman Aiden, E.; Madansingh, S.I. A Postural Assessment Utilizing Machine Learning Prospectively Identifies Older Adults at a High Risk of Falling. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 591517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howcroft, J.; Kofman, J.; Lemaire, E.D. Prospective Fall-Risk Prediction Models for Older Adults Based on Wearable Sensors. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Madureira, J.; Tonelo, C.; Baltazar, D.; Silva, C.; Martins, A.; Alcobia, C.; Sousa, I. Comparing Machine Learning Approaches for Fall Risk Assessment. In Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, Porto, Portugal, 21–23 February 2017; pp. 223–230. [Google Scholar]
- Savadkoohi, M.; Oladunni, T.; Thompson, L.A. Deep Neural Networks for Human’s Fall-Risk Prediction Using Force-Plate Time Series Signal. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 182, 115220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, A.; Mouthon, A.; Sivagnanaselvam, R.S.; Bresciani, J.-P. Fast and Automatic Assessment of Fall Risk by Coupling Machine Learning Algorithms with a Depth Camera to Monitor Simple Balance Tasks. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuaya-Simbro, G.; Perez-Sanpablo, A.-I.; Morales, E.-F.; Quiñones Uriostegui, I.; Nuñez-Carrera, L. Comparing Machine Learning Methods to Improve Fall Risk Detection in Elderly with Osteoporosis from Balance Data. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8697805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bargiotas, I.; Kalogeratos, A.; Limnios, M.; Vidal, P.-P.; Ricard, D.; Vayatis, N. Revealing Posturographic Profile of Patients with Parkinsonian Syndromes through a Novel Hypothesis Testing Framework Based on Machine Learning. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Hsieh, K.L.; Sosnoff, J.J. Fall Risk Prediction in Multiple Sclerosis Using Postural Sway Measures: A Machine Learning Approach. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, M.; De Leon, P.L. Falls Risk Classification of Older Adults Using Deep Neural Networks and Transfer Learning. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, F.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Wei, Y.-C.; Chou, L.-W.; Chang, K.-M. Analysis of Center of Pressure Signals by Using Decision Tree and Empirical Mode Decomposition to Predict Falls among Older Adults. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6252445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llorens, R.; Latorre, J.; Noé, E.; Keshner, E.A. Posturography Using the Wii Balance BoardTM. Gait Posture 2016, 43, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, B.L.; Schmitz, R.J. Examination of Balance Measures Produced by the Biodex Stability System. J. Athl. Train. 1998, 33, 323–327. [Google Scholar]
- Jhon, B. SUS: A “Quick and Dirty” Usability Scal. In Usability Evaluation in Industry, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-0-429-15701-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, J.C.; Valencia, W.M. Exercise and Older Adults. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 34, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo-Prieto, P.; Cancela-Carral, J.M.; Rodríguez-Fuentes, G. Feasibility and Effects of an Immersive Virtual Reality Exergame Program on Physical Functions in Institutionalized Older Adults: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Sensors 2022, 22, 6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulos, M.N.; Yang, S.P. Exergames for Health and Fitness: The Roles of GPS and Geosocial Apps. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2013, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruivo, J.A. Exergames and Cardiac Rehabilitation: A Review. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2014, 34, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, B.; Koenig, S.; Chang, C.-Y.; McConnell, E.; Suma, E.; Bolas, M.; Rizzo, A. Designing Informed Game-Based Rehabilitation Tasks Leveraging Advances in Virtual Reality. Disabil. Rehabil. 2012, 34, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro-Junior, R.S.; Vaghetti, C.A.O.; Nascimento, O.J.M.; Laks, J.; Deslandes, A.C. Exergames: Neuroplastic Hypothesis about Cognitive Improvement and Biological Effects on Physical Function of Institutionalized Older Persons. Neural Regen Res. 2016, 11, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayama, H.; Okamoto, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; Yamada, M.; Kuroda, T.; Aoyama, T. Effect of a Kinect-Based Exercise Game on Improving Executive Cognitive Performance in Community-Dwelling Elderly: Case Control Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2014, 16, e61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillot, P.; Perrot, A.; Hartley, A. Effects of Interactive Physical-Activity Video-Game Training on Physical and Cognitive Function in Older Adults. Psychol. Aging 2012, 27, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habibnezhad, M.; Shayesteh, S.; Jebelli, H.; Puckett, J.; Stentz, T. Comparison of Ironworker’s Fall Risk Assessment Systems Using an Immersive Biofeedback Simulator. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, X.; Fan, M.; Deng, L.; Jian, C.; Wei, M.; Luo, J. The Effect of Visual Stimuli on Stability and Complexity of Postural Control. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.T.; Cluff, T.; Balasubramaniam, R. Visual Reliance for Balance Control in Older Adults Persists When Visual Information Is Disrupted by Artificial Feedback Delays. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Barbosa, F.; Del Pozo-Cruz, J.; Sañudo, B.; Alfonso-Rosa, R.M. Is the Wii Balance Board a Valid and Reliable Instrument to Assess Postural Stability in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 166, 108313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clanché, F.; Personeni, G.; Renaux, A.; Muhla, F.; Bastogne, T.; Gauchard, G. Virtual Reality as Assessment Tool of the Risk of Falls in the Elderly. Int. J. Sens. Sens. Netw. 2023, 11, 06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.A. A Virtual Reality Game-Like Tool for Assessing the Risk of Falling in the Elderly. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2019, 266, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubetzky, A.V.; Hujsak, B.D.; Fu, G.; Perlin, K. An Oculus Rift Assessment of Dynamic Balance by Head Mobility in a Virtual Park Scene: A Pilot Study. Mot. Control. 2019, 23, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Tang, Q.; Xu, S.; Leng, P.; Pan, Z. Design and Evaluation of an Augmented Reality-Based Exergame System to Reduce Fall Risk in the Elderly. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.; Bermúdez, S. KAVE: Building Kinect Based CAVE Automatic Virtual Environments, Methods for Surround-Screen Projection Management, Motion Parallax and Full-Body Interaction Support. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2018, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wii Balance Board. Wikipedia 2023. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wii_Balance_Board (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Ahmad, M.; Sousa, H.; Quintal, É.; Bermúdez, I.; Badia, S. Efficacy of Augmented Reality-Based Virtual Hiking in Cardiorespiratory Endurance: A Pilot Study. In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies, Virtual Event, 11–13 February 2021; pp. 575–582. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, H.L.; Kim, J.P.; Kim, K.; Hwang, C.H.; Koo, K. Wrist Rehabilitation System Using Augmented Reality for Hemiplegic Stroke Patient Rehabilitation: A Feasibility Study. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, B.; Teng, Y.; Ren, Y.; Hu, Z. Comparative Research of AR and VR Technology Based on User Experience. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Management Science & Engineering 21th Annual Conference Proceedings, Helsinki, Finland, 17–19 August 2014; pp. 1820–1827. [Google Scholar]
- Lessiter, J.; Freeman, J.; Keogh, E.; Davidoff, J. A Cross-Media Presence Questionnaire: The ITC-Sense of Presence Inventory. Presence Teleoperators Virtual Environ. 2001, 10, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, R.K.F.; Arliani, G.G.; Almeida, G.P.L.; Venturine, A.M.; dos Santos, C.V.; Astur, D.C.; Cohen, M. The Effects of One-Half of a Soccer Match on the Postural Stability and Functional Capacity of the Lower Limbs in Young Soccer Players. Clinics 2012, 67, 1361–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauro, J.; Lewis, J.R. Quantifying User Research. In Quantifying the User Experience; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 9–18. ISBN 978-0-12-802308-2. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.A.; Bryant, A.L.; Pua, Y.; McCrory, P.; Bennell, K.; Hunt, M. Validity and Reliability of the Nintendo Wii Balance Board for Assessment of Standing Balance. Gait Posture 2010, 31, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.; Gröger, I.; Rupprecht, R.; Gaßmann, K.G. Intrasession Reliability of Force Platform Parameters in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2008, 89, 1977–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, H.; Garcia-Agundez, A.; Müller, P.N.; Tregel, T.; Miede, A.; Göbel, S. Predicting Functional Performance via Classification of Lower Extremity Strength in Older Adults with Exergame-Collected Data. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2020, 17, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.-W.; Kim, T.; Kim, J.I.; Jeong, Y.; Jang, K.-M.; Kim, J.; Do, J.-H. Development and Application of a Stability Index Estimation Algorithm Based on Machine Learning for Elderly Balance Ability Diagnosis in Daily Life. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahedian-Nasab, N.; Jaberi, A.; Shirazi, F.; Kavousipor, S. Effect of Virtual Reality Exercises on Balance and Fall in Elderly People with Fall Risk: A Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.A.; Mentiplay, B.F.; Pua, Y.-H.; Bower, K.J. Reliability and Validity of the Wii Balance Board for Assessment of Standing Balance: A Systematic Review. Gait Posture 2018, 61, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldana, S.; Marsh, A.P.; Rejeski, W.J.; Haberl, J.; Wu, P.; Rosenthal, S.; Ip, E. Assessing Balance through the Use of a Low-Cost Head-Mounted Display in Older Adults: A Pilot Study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 1363–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cable Car Speed and Trajectory Angles | F | Sig. |
|---|---|---|
| cable_car_speed5_angle_minus_90 | 4.461 | 0.050 |
| cable_car_speed7_angle90 | 7.11 | 0.016 |
| cable_car_speed7_angle_minus_90 | 5.10 | 0.037 |
| Pearson Correlation Sig. (2-Tailed) N = 19 | Stability Overall | StabilityAntPost | Stability Media Lateral | PTnZoneA | PTinQuad1 | PTinQuad2 | PTinQuad4 | Stability IndexFB | Stability IndexLR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean_angle_0 | 0.559 0.013 | 0.519 0.023 | 0.631 0.004 | −0.499 0.030 | −0.494 0.031 | 0.64 <0.01 | −0.469 0.043 | 0.520 0.023 | 0.630 0.004 |
| mean_angle_45 | 0.57 0.01 | ||||||||
| mean_angle_90 | 0.47 0.04 | ||||||||
| mean_angle_minus_45 | 0.48 0.03 | −0.46 0.04 | |||||||
| mean_angle_minus_90 | −0.517 0.023 | 0.522 0.022 | |||||||
| mean_cc_speed3 | 0.486 0.035 | −0.50 0.029 | |||||||
| mean_cc_speed5 | −0.470 0.042 | 0.566 0.011 | |||||||
| mean_cc_speed7 | −0.495 0.031 | ||||||||
| mean_cc_speed9 | 0.459 0.048 | −0.486 0.035 | 0.570 0.011 | 0.458 0.049 | |||||
| max heart rate | −0.566 0.011 |
| LOO Cross-Validation | CCS | Mean of Turns | Mean Speeds | 2MST & 30SCST | HR | Step-Wise Feature Selection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DA Model | Pseudolinear | Linear | Diagquadratic | SVM | Diagquadratic | Linear |
| Accuracy | 0.72 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.55 | 1 |
| Recall | 0.72 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.55 | 1 |
| Precision | 0.72 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.75 | 0.55 | 1 |
| F-score | 0.72 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.73 | 0.55 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, M.A.; Gouveia, É.R.; Bermúdez i Badia, S. A Virtual Reality-Based Simulation Tool for Assessing the Risk of Falls in Older Adults. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146251
Ahmad MA, Gouveia ÉR, Bermúdez i Badia S. A Virtual Reality-Based Simulation Tool for Assessing the Risk of Falls in Older Adults. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(14):6251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146251
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Muhammad Asif, Élvio Rúbio Gouveia, and Sergi Bermúdez i Badia. 2024. "A Virtual Reality-Based Simulation Tool for Assessing the Risk of Falls in Older Adults" Applied Sciences 14, no. 14: 6251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146251
APA StyleAhmad, M. A., Gouveia, É. R., & Bermúdez i Badia, S. (2024). A Virtual Reality-Based Simulation Tool for Assessing the Risk of Falls in Older Adults. Applied Sciences, 14(14), 6251. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14146251








