Materials for Clear Aligners—A Comprehensive Exploration of Characteristics and Innovations: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
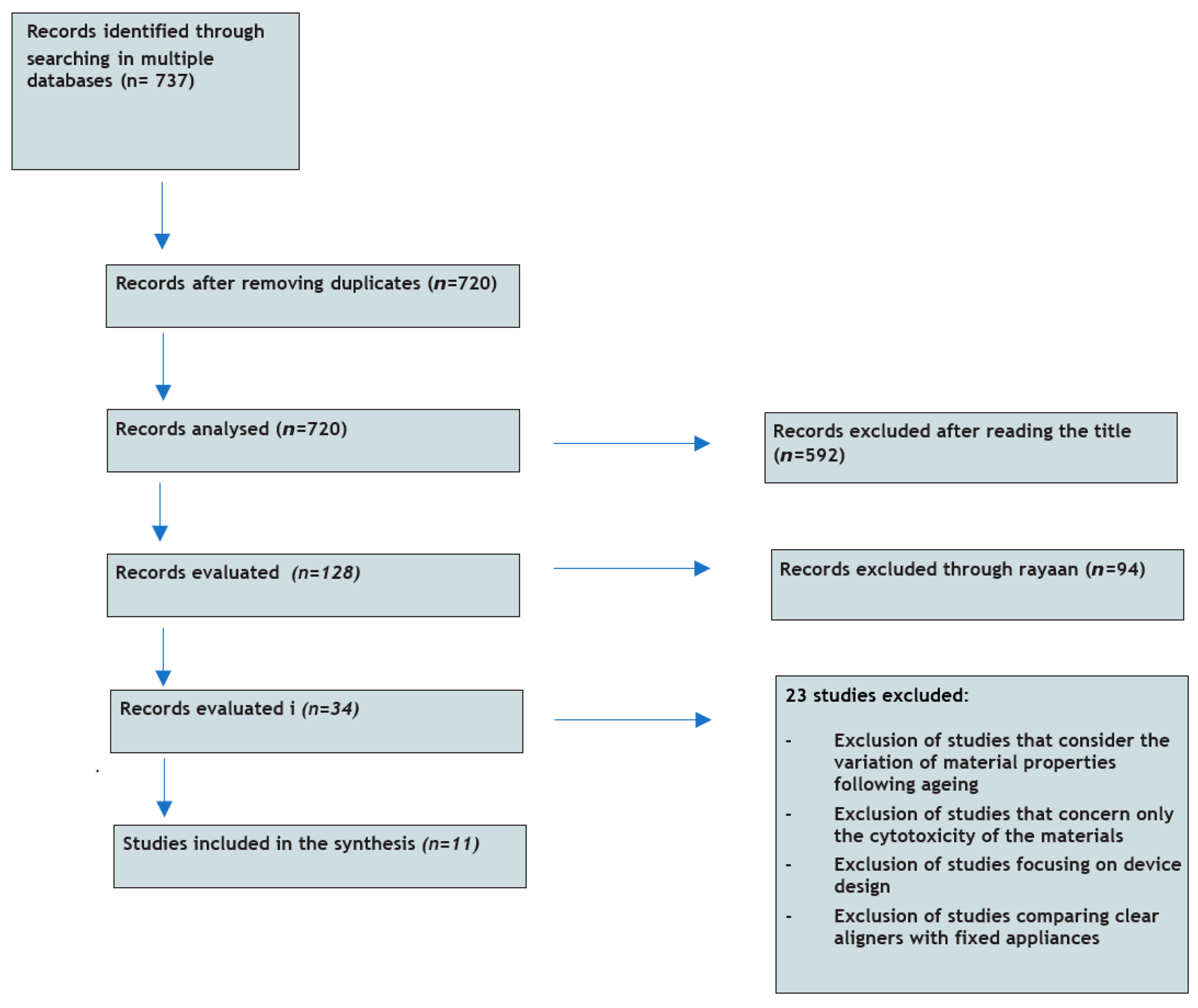
2. Materials and Methods
- Studies conducted in the last 10 years in English;
- Studies concerning only the dental field;
- Studies describing the currently used clear aligner materials and their characteristics;
- Articles for which the material of the aligner was not specified were excluded from the analysis.
- Studies linking different types and materials of clear aligners;
- Studies that consider the mechanical, thermal, physical, chemical, viscoelastic, and optical properties of the materials.
- Studies that consider the variation of material properties following aging;
- Studies concerning only the cytotoxicity of the materials;
- Studies focusing on device design;
- Studies comparing clear aligners and fixed appliances.
- Thermal, mechanical, physicochemical, and viscoelastic properties;
- Roughness and surface energy;
- Stability against intra-oral coloring agents, optical properties, and water absorption behavior;
- Structural variations (hardness and infrared spectroscopic analysis);
- Properties of absolute stress and stress decay.
3. Results
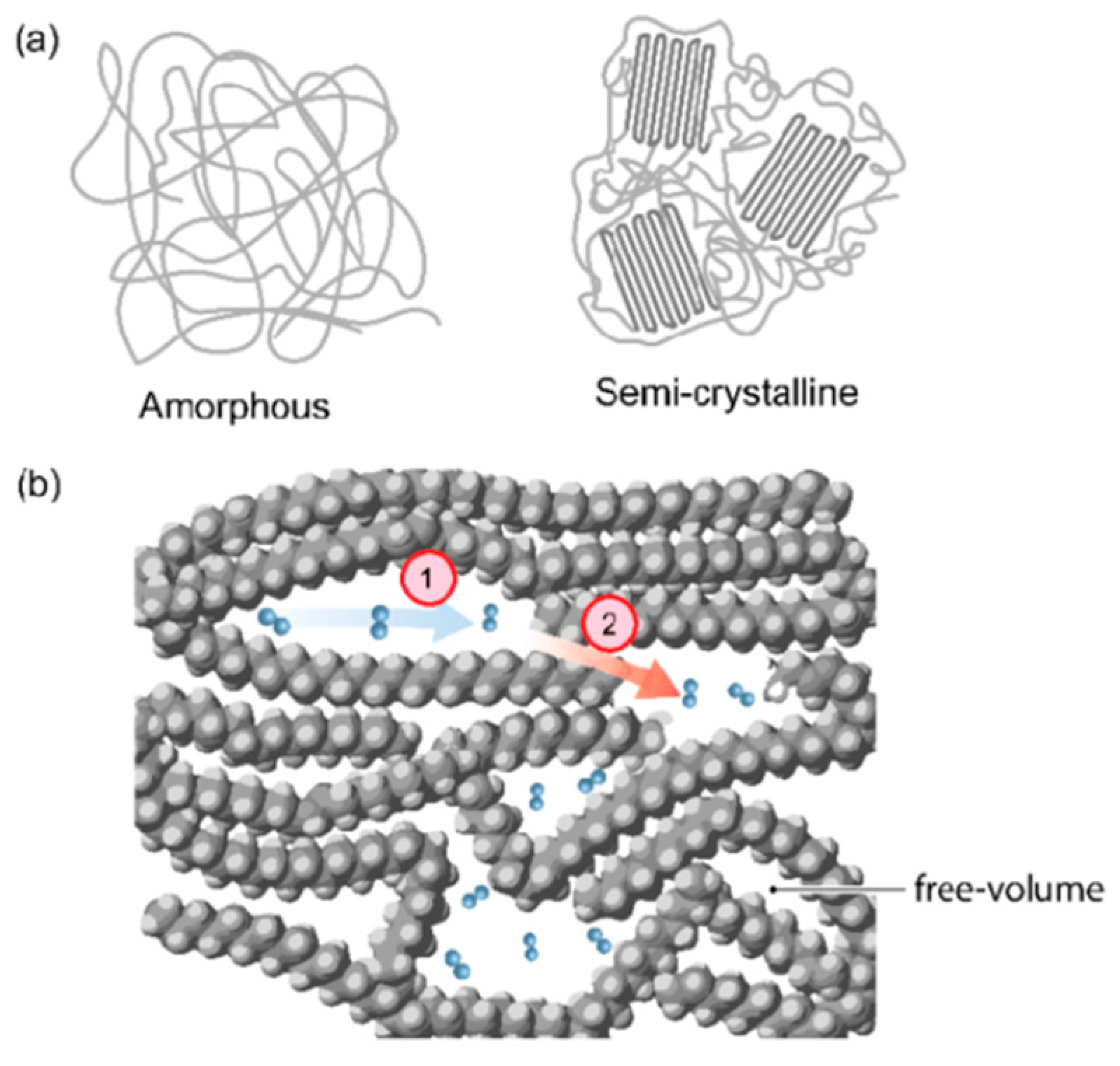
3.1. Mechanical, Physical, and Chemical Properties
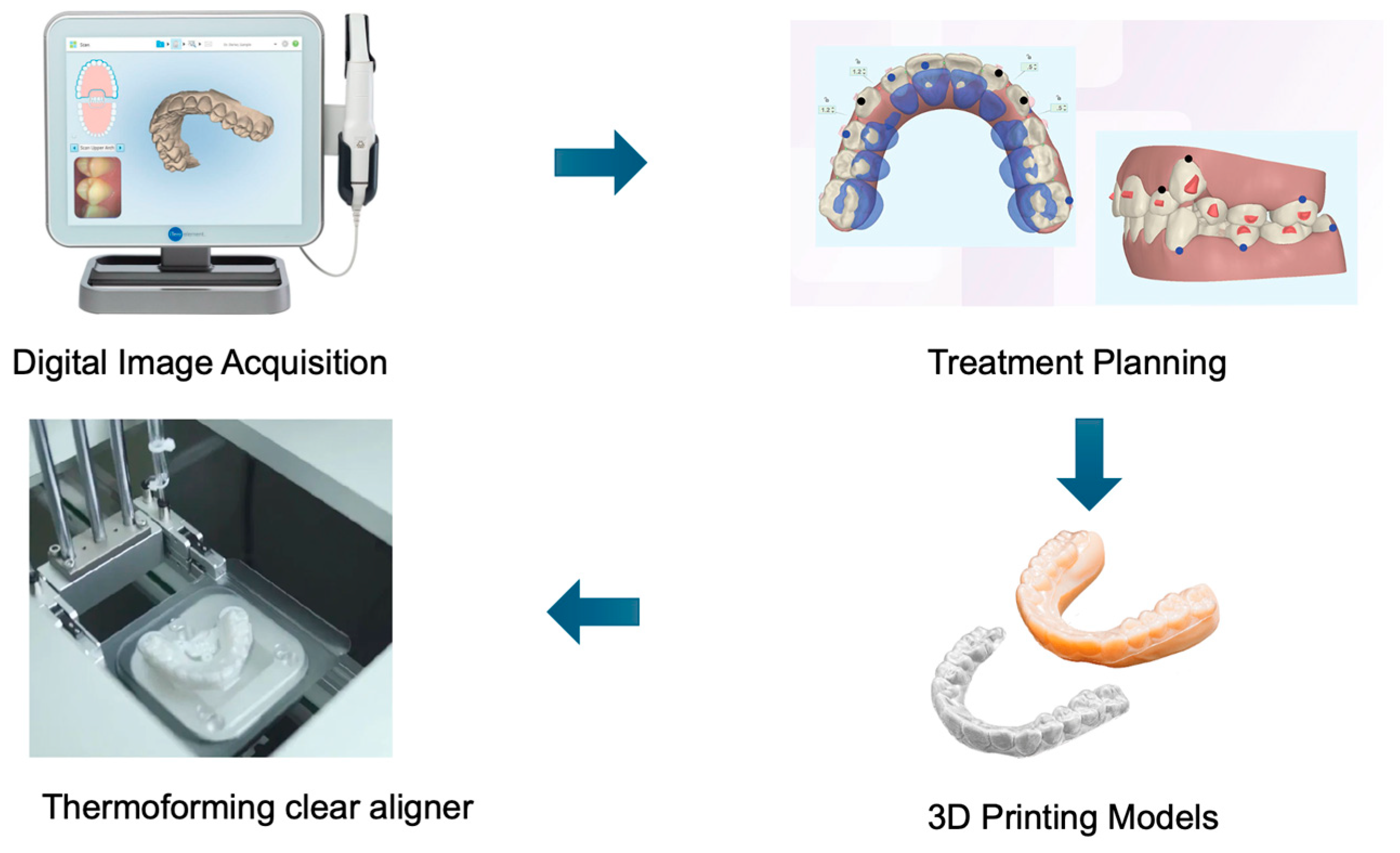
3.2. Mechanical and Physicochemical Properties after Thermoforming
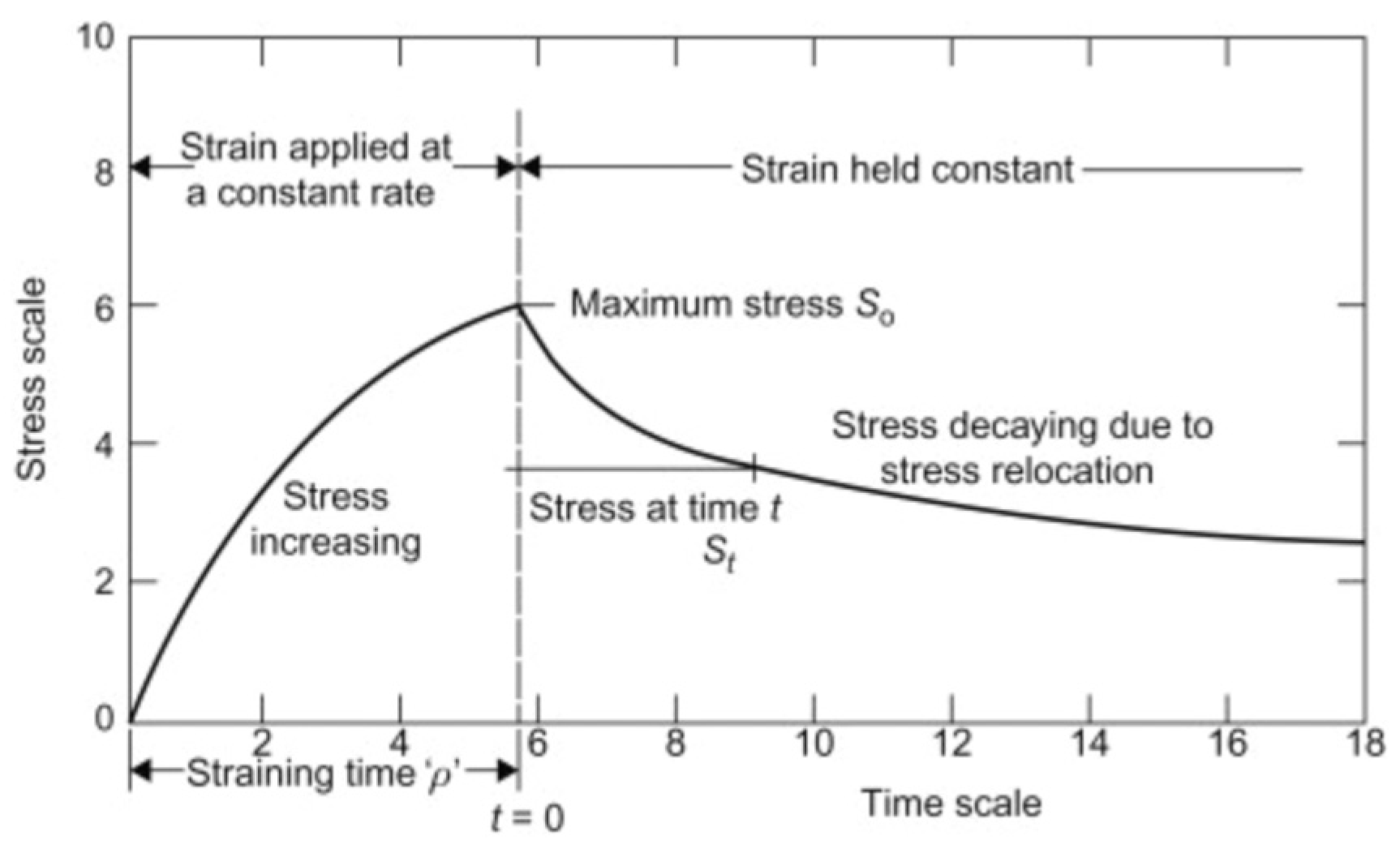
3.3. Properties of Absolute Stress and Stress Decay
3.4. Surface Roughness and Energy before and after Thermoforming
3.5. Structural Variations by Hardness and Infrared Spectroscopic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cenzato, N.; Marcolongo, L.; Sanchez, S.; Maspero, C. Qualitative Microbiological Evaluation of Dental Plaque in Patients with Fixed Appliances and Clear Aligners. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2022, 36, 647–653. [Google Scholar]
- Jindal, P.; Juneja, M.; Siena, F.L.; Bajaj, D.; Breedon, P. Mechanical and geometric properties of thermoformed and 3D printed clear dental aligners. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2019, 156, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenzato, N.; Occhipinti, C.; D’amici, E.; Savadori, P.; Baldini, B.; Maspero, C. Microbiological Analysis of Plaque and Its Composition in Three Patient Groups under Different Orthodontic Treatments. Dent. J. 2024, 12, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bichu, Y.M.; Alwafi, A.; Liu, X.; Andrews, J.; Ludwig, B.; Bichu, A.Y.; Zou, B. Advances in orthodontic clear aligner materials. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 22, 384–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, G.M.; Mapelli, A.; Maspero, C.; Santaniello, T.; Serafin, M.; Farronato, M.; Caprioglio, A. Direct 3D Printing of Clear Orthodontic Aligners: Current State and Future Possibilities. Materials 2021, 14, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, S.; Paoli, A.; Razionale, A.V.; Savignano, R. Computational design and engineering of polymeric orthodontic aligners. Int. J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2017, 33, 2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jindal, P.; Worcester, F.; Siena, F.L.; Forbes, C.; Juneja, M.; Breedon, P. Mechanical behaviour of 3D printed vs thermoformed clear dental aligner materials under non-linear compressive loading using FEM. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 112, 104045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Ryu, K.-H.; Baek, D.; Khan, T.A.; Kim, H.-J.; Shin, S.; Hyun, J.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, S.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; et al. 3D printing of polyethylene terephthalate glycol–sepiolite composites with nanoscale orientation. ACS Appl. Mater. Inferfaces 2020, 12, 23453–23463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, E.; Panayi, N.; Polychronis, G.; Papageorgiou, S.N.; Zinelis, S.; Eliades, G.; Eliades, T. In-house 3D-printed aligners: Effect of in vivo ageing on mechanical properties. Eur. J. Orthod. 2022, 44, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.-J.; Chung, C.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.-J.; Cha, J.-Y. Thermo-mechanical properties of 3D printed photocurable shape memory resin for clear aligners. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golkhani, B.; Webber, A.; Keilig, L.; Reimann, S.; Bourauel, C. Variation of the modulus of elasticity of aligner foil sheet materials due to thermoforming. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2022, 83, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, M.-H.; Porto, B.; Mohebi, S.; Zhu, L.; Hans, M. Physical and chemical properties of five different clear thermoplastic materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 139, 1097–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandropoulos, A.; Al Jabbari, Y.S.; Zinelis, S.; Eliades, T. Chemical and mechanical characteristics of contemporary thermoplastic orthodontic materials. Aust. Orthod. J. 2015, 31, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Bai, Y.; Xuejia Ding, X.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and characterization of thermoplastic materials for invisible orthodontics. Dent. Mater. J. 2011, 30, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupaix, R.B.; Boyce, M.C. Finite strain behavior of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polyethylene terephthalate-glycol (PETG). Polymer 2005, 46, 4827–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Liu, R.; Ni, Z.; Yu, Z. Efficiency, effectiveness and treatment stability of clear aligners: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2017, 20, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratto, I.; Agner Busato, M.C.; Stival Bittencourt, P.R. Thermal and mechanical characterization of thermoplastic orthodontic aligners discs after molding process. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 126, 104991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.-H.; Kwon, J.-S.; Jiang, H.B.; Cha, J.-Y.; Kim, K.-M. Effects of thermoforming on the physical and mechanical properties of thermoplastic materials for transparent orthodontic aligners. Korean J. Orthod. 2018, 48, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburrino, F.; D’Anto, V.; Bucci, R.; Alessandri-Bonetti, G.; Barone, S.; Razionale, A.V. Mechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Polymers for Aligner Manufacturing: In Vitro Study. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khijmatgar, S.; Tumedei, M.; Del Fabbro, M.; Tartaglia, G.M. Effectiveness and Efficacy of Thermoformed and 3D Printed Aligners in Correcting Malocclusion (Spacing) and Its Impact on Periodontal Oral Health and Oral Microbiome: A Double-Blinded Parallel Randomized Controlled Multicenter Clinical Trial. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Martines, E.; Mazzanti, V.; Arreghini, A.; Mollica, F.; Siciliani, G. Stress relaxation properties of four orthodontic aligner materials: A 24-hour in vitro study. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, P.; Mazzanti, V.; Mollica, F.; Pellitteri, F.; Palone, M.; Lombardo, L. Stress Relaxation Properties of Five Orthodontic Aligner Materials: A 14-Day In-Vitro Study. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.; Eliades, G.; Zinelis, S.; Eliades, T.; Bradley, T.G. Structural conformation and leaching from in vitro aged and retrieved Invisalign appliances. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2004, 126, 725–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weir, T. Clear aligners in orthodontic treatment. Aust. Dent. J. 2017, 62, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryokawa, H.; Miyazaki, Y.; Fujishima, A.; Miyazaki, T.; Maki, K. The mechanical properties of dental thermoplastic materials in a simulated intraoral environment. Orthod. Waves 2006, 65, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, F.; Zinelis, S.; Patcas, R.; Schaetzle, M.; Eliades, G.; Eliades, T. Roughness and wettability of aligner materials. J. Orthod. 2020, 47, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.; Hwang, C.-J.; Yu, H.-S.; Lee, S.-B.; Cha, J.-Y. The effect of thickness and deflection of orthodontic thermoplastic materials on its mechanical properties. Korean J. Orthod. 2010, 40, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, V.; Macera, L.; Taglieri, G.; Spera, L.; Marzo, G.; Quinzi, V. Color Stability, Chemico-Physical and Optical Features of the Most Common PETG and PU Based Orthodontic Aligners for Clear Aligner Therapy. Polymers 2021, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Lim, B.S.; Lim, Y.K. Force delivery properties of thermoplastic orthodontic materials. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2008, 133, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohda, N.; Iijima, M.; Muguruma, T.; Brantley, W.A.; Ahluwalia, K.S.; Mizoguchi, I. Effects of mechanical properties of thermoplastic materials on the initial force of thermoplastic appliances. Angle Orthod. 2013, 83, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhendi, A.; Khounganian, R.; Ali, R.; Syed, S.A.; Almudhi, A. Structural Conformation Comparison of Different Clear Aligner Systems: An In Vitro Study. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condò, R.; Mampieri, G.; Giancotti, A.; Cerroni, L.; Pasquantonio, G.; Divizia, A.; Convertino, A.; Mecheri, B.; Maiolo, L. SEM characterization and ageing analysis on two generation of invisible aligners. BMC Oral Health 2021, 21, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccon, A.; Stellini, E.; Parcianello, R.G.; Lucchi, P.; Zerman, N.; Ludovichetti, F.S. Correlation between consumption of sugared beverages and caries incidence in the pediatric patient. Minerva Dent. Oral Sci. 2023, 72, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farronato, M.; Begnoni, G.; Boodt, L.; Thevissen, P.; Willems, G.; Cadenas de Llano-Pérula, M. Are palatal rugae reliable markers for 3D superimposition and forensic human identification after palatal expansion? A systematic review. Forensic Sci. Int. 2023, 351, 111814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farronato, M.; Baselli, G.; Baldini, B.; Favia, G.; Tartaglia, G.M. 3D Cephalometric Normality Range: Auto Contractive Maps (ACM) Analysis in Selected Caucasian Skeletal Class I Age Groups. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comuzzi, L.; Tumedei, M.; De Angelis, F.; Lorusso, F.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. Influence of the dental implant macrogeometry and threads design on primary stability: An in vitro simulation on artificial bone blocks. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 2021, 24, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comuzzi, L.; Tumedei, M.; Romasco, T.; Petrini, M.; Afrashtehfar, K.I.; Inchingolo, F.; Piattelli, A.; Di Pietro, N. Insertion Torque, Removal Torque, and Resonance Frequency Analysis Values of Ultrashort, Short, and Standard Dental Implants: An In Vitro Study on Polyurethane Foam Sheets. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romasco, T.; Tumedei, M.; Inchingolo, F.; Pignatelli, P.; Montesani, L.; Iezzi, G.; Petrini, M.; Piattelli, A.; Di Pietro, N. A Narrative Review on the Effectiveness of Bone Regeneration Procedures with OsteoBiol Collagenated Porcine Grafts: The Translational Research Experience over 20 Years. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, V.; Macera, L.; Taglieri, G.; Di Giambattista, A.; Spagnoli, G.; Massaria, A.; Messori, M.; Quagliarini, E.; Chiappini, G.; Campanella, V.; et al. Thermoplastic Disks Used for Commercial Orthodontic Aligners: Complete Physicochemical and Mechanical Characterization. Materials 2020, 13, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Sun, W.T.; Liao, W.; Lu, W.X.; Li, Q.W.; Jeong, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z.H. Colour stabilities of three types of orthodontic clear aligners exposed to staining agents. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2016, 8, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimunović, L.; Čekalović Agović, S.; Marić, A.J.; Bačić, I.; Klarić, E.; Uribe, F.; Meštrović, S. Color and Chemical Stability of 3D-Printed and Thermoformed Polyurethane-Based Aligners. Polymers 2024, 16, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, A.S.; H C, K.K. A comparative study on tensile strength of various thermoplastic polymers sheets following thermoforming on a pre-treatment and post-treatment maxillary model of a patient: An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldweesh, A.H.; Al-Maflehi, N.S.; AlGhizzi, M.; AlShayea, E.; Albarakati, S.F. Comparison of mechanical properties and color stability of various vacuum-formed orthodontic retainers: An in vitro study. Saudi Dent. J. 2023, 35, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlMogbel, A. Clear Aligner Therapy: Up to date review article. J. Orthod. Sci. 2023, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koletsi, D.; Panayi, N.; Laspos, C.; Athanasiou, A.E.; Zinelis, S.; Eliades, T. In vivo aging-induced surface roughness alterations of Invisalign® and 3D-printed aligners. J. Orthod. 2023, 50, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, B.; Padmanabhan, S.; Srinivasan, S. Comparative evaluation of physical and mechanical properties of clear aligners—A systematic review. Evid. Based Dent. 2024, 25, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimunović, L.; Blagec, T.; Meštrović, S. Resistance of PETG Materials on Thermocycling and Brushing. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Authors | Year | Title | Journal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Se Yeon Lee, Hoon Kim, Hyun-Joong Kim, Chooryung J. Chung, Yoon Jeong Choi, Su-Jung Kim, Jung-Yul Cha | 2022 | Thermo-mechanical properties of 3D printed photocurable shape memory resin for clear aligners | Scientific reports |
| Fabienne Suter, Spiros Zinelis, Raffaello Patcas, Marc Schaetzle, Giorgio Eliades, Teodoro Eliades | 2020 | Roughness and wettability of aligner materials | Journal of orthodontics |
| Valeria Daniele, Ludovico Macera, Giuliana Taglieri, Loredana Spera, Giuseppe Marzo, Vincenzo Quinzi | 2021 | Color Stability, Chemico-Physical and Optical Features of the Most Common PETG and PU Based Orthodontic Aligners for Clear Aligner Therapy | Polymers |
| Bijan Golkhani, Anna Webber, Ludger Keilig, Susanne Reimann, Christoph Bourauel | 2022 | Variation of the modulus of elasticity of aligner foil sheet materials due to thermoforming | Journal of orofacial orthopedics |
| Aseel Alhendi, Rita Khounganian, Raisuddin Ali, Saeed Ali Syed, Abdullazez Almudhi | 2022 | Structural Conformation Comparison of Different Clear Aligner Systems: An In Vitro Study | Dentistry journal |
| Luca Lombardo, Elisa Martines, Valentina Mazzanti, Angela Arreghini, Francesco Mollica, Giuseppe Siciliani | 2017 | Stress relaxation properties of four orthodontic aligner materials: A 24-h in vitro study | The angle orthodontist |
| Paolo Albertini, Valentina Mazzanti, Francesco Mollica, Federica Pellitteri, Mario Palone, Luca Lombardo | 2022 | Stress Relaxation Properties of Five Orthodontic Aligner Materials: A 14-Day In-Vitro Study | Bioengineering |
| Isabella Pratto, Mauro Carlo Agner Busato, Paulo Rodrigo Stival Bittencourt | 2022 | Thermal and mechanical characterization of thermoplastic orthodontic aligners discs after molding process | Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials |
| Francesco Tamburrino, Vincenzo D’Antò, Rosaria Bucci, Giulio Alessandri-Bonetti, Sandro Barone, Armando Viviano Razionale | 2020 | Mechanical Properties of Thermoplastic Polymers for Aligner Manufacturing: In Vitro Study | Dentistry Journal |
| Alexandros Alexandropoulos, Youssef S Al Jabbari, Spiros Zinelis, Theodore Elides | 2015 | Chemical and mechanical characteristics of contemporary thermoplastic orthodontic materials | Australian Orthodontic Journal |
| Man-Hin Kwok, Betina Porto, Shadi Mohebi, Lei Zhu, Mark Hans | 2021 | Physical and chemical properties of five different clear thermoplastic materials | Journal of Applied Polymer science |
| Materials | Properties |
|---|---|
| TC-85 | High flexibility, wider elastic range, slight stress decay, shape memory properties, better adaptation post-usage, viscoelastic properties, geometric stability |
| Ca—medium, Essix-copopyester (PETG), Erkodur (PETG) | Smooth surface structure before thermoforming, very rough structure after thermoforming |
| Duran (PETG) | Increase in yield stress after thermoforming, elastic modulus increases after thermoforming, smooth surface structure before thermoforming, very rough structure after thermoforming |
| Essix ACE (PETG) | High mechanical properties, maintains high force after thermoforming, high transparency, perceptible color change after 14 days in red wine and coffee, exhibits high tensile strength and Young’s modulus |
| Zendura (PU) | Stiffest flexural modulus among tested materials, significant decrease in yield stress after thermoforming, increase in elastic modulus after thermoforming |
| SmartTrack (PU) | Higher hardness and modulus, slightly higher brittleness, lower creep resistance compared to PETG-based products |
| Essix C+ (PP-EPR) | Not soluble in any tested solvents, more crystalline characteristics, lower transparency, significant decrease in tensile strength and Young’s modulus after heat treatment |
| F22 Aligner | Single layer material, high stiffness, rapid stress decay in the first 8 h, higher absolute stress values. |
| Erkoloc-Pro | Double layer material, lower stiffness, very constant stress release, but with lower absolute stress values. |
| Durasoft | Double layer material, lower stiffness, very constant stress release, but with lower absolute stress values. |
| F22 Evoflex | Maintained high stress rates over a 15-day period, highest final stress level with a constant stress release. |
| Eon (PU) | Hardness comparable to other PU-based aligners, smooth surface but with some irregularities and impurities |
| SureSmile (PU) | Hardness comparable to other PU-based aligners, irregularities and impurities found on surface |
| Clarity (PU) | Resistant and practically invisible material, hardness comparable to other PU-based aligners, some impurities and irregularities on surface |
| Property | PETG (e.g., Duran, Essix Ace, Essix Plus, Biolon) | PU (e.g., Zendura, SmartTrack, Eon, SureSmile, Clarity) |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic Modulus | Generally higher, decreases significantly after thermoforming | Higher hardness and modulus values |
| Tensile Strength | High, but decreases after heat treatment and immersion in artificial saliva | Maintains strength, but may show slight decrease after thermoforming |
| Flexibility | Less flexible compared to PU | More elastic, allowing for predictable orthodontic movements |
| Transparency | High, can be affected by crystallinity (e.g., Essix C+ is less transparent) | High transparency, practical invisibility |
| Stress Decay | Rapid stress decay, especially in the first few hours | Rapid initial stress decay but reaches a plateau over time |
| Chemical Resistance | Good, but varies (e.g., Essix C+ has higher chemical resistance) | Generally good, with specific formulations possibly affecting resistance |
| Surface Characteristics | Smooth but can exhibit impurities after thermoforming | Smooth but may show irregularities and impurities |
| Yield Stress | Generally higher but decreases significantly after thermoforming | Slightly lower, decreases about 30% after thermoforming |
| Applications | Widely used in orthodontics for clear aligners and retainers | Used for aligners requiring more elasticity and flexibility |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cenzato, N.; Di Iasio, G.; Martìn Carreras-Presas, C.; Caprioglio, A.; Del Fabbro, M. Materials for Clear Aligners—A Comprehensive Exploration of Characteristics and Innovations: A Scoping Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156533
Cenzato N, Di Iasio G, Martìn Carreras-Presas C, Caprioglio A, Del Fabbro M. Materials for Clear Aligners—A Comprehensive Exploration of Characteristics and Innovations: A Scoping Review. Applied Sciences. 2024; 14(15):6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156533
Chicago/Turabian StyleCenzato, Niccolò, Giada Di Iasio, Carmen Martìn Carreras-Presas, Alberto Caprioglio, and Massimo Del Fabbro. 2024. "Materials for Clear Aligners—A Comprehensive Exploration of Characteristics and Innovations: A Scoping Review" Applied Sciences 14, no. 15: 6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156533
APA StyleCenzato, N., Di Iasio, G., Martìn Carreras-Presas, C., Caprioglio, A., & Del Fabbro, M. (2024). Materials for Clear Aligners—A Comprehensive Exploration of Characteristics and Innovations: A Scoping Review. Applied Sciences, 14(15), 6533. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156533









